Guide to developing OpenAM client applications and service providers. OpenAM provides open source Authentication, Authorization, Entitlement and Federation software.
Preface
This guide demonstrates how to handle sessions to permit single sign on and single log out in OpenAM client applications. This guide further demonstrates how to use the OpenAM APIs including both APIs for client applications, and also SPIs for authentication, policy, service management, delegation, and identity storage. Finally, this guide demonstrates how to write your own web policy agent.
1. Who Should Use this Guide
This guide is written for developers who adapt client applications to use OpenAM access management capabilities. It is also written for designers and developers extending and integrating OpenAM services for their organizations.
You do not need to be an OpenAM wizard to learn something from this guide, though a background in access management and developing web applications or developing for web and application servers can help. You can nevertheless get started with this guide, and then learn more as you go along.
2. Formatting Conventions
Most examples in the documentation are created in GNU/Linux or Mac OS X
operating environments.
If distinctions are necessary between operating environments,
examples are labeled with the operating environment name in parentheses.
To avoid repetition file system directory names are often given
only in UNIX format as in /path/to/server,
even if the text applies to C:\path\to\server as well.
Absolute path names usually begin with the placeholder
/path/to/.
This path might translate to /opt/,
C:\Program Files\, or somewhere else on your system.
Command-line, terminal sessions are formatted as follows:
$ echo $JAVA_HOME /path/to/jdk
Command output is sometimes formatted for narrower, more readable output even though formatting parameters are not shown in the command.
Program listings are formatted as follows:
class Test {
public static void main(String [] args) {
System.out.println("This is a program listing.");
}
}3. Accessing Documentation Online
ForgeRock publishes comprehensive documentation online:
The ForgeRock Knowledge Base offers a large and increasing number of up-to-date, practical articles that help you deploy and manage ForgeRock software.
While many articles are visible to community members, ForgeRock customers have access to much more, including advanced information for customers using ForgeRock software in a mission-critical capacity.
ForgeRock product documentation, such as this document, aims to be technically accurate and complete with respect to the software documented. It is visible to everyone and covers all product features and examples of how to use them.
4. Using the ForgeRock.org Site
The ForgeRock.org site has links to source code for ForgeRock open source software, as well as links to the ForgeRock forums and technical blogs.
If you are a ForgeRock customer, raise a support ticket instead of using the forums. ForgeRock support professionals will get in touch to help you.
Chapter 1. OpenAM APIs and Protocols
Although policy agents and standards support make it possible for applications to use OpenAM for access management without changing your code, some deployments require tighter integration, or direct use of supported protocols and OpenAM APIs.
OpenAM supports a range of protocols and APIs that allow you not only to define specifically how access is managed in your client applications, but also to extend OpenAM capabilities to meet even those deployment requirements not yet covered in OpenAM.
This short chapter presents an overview of the APIs and protocols that OpenAM supports.
This guide primarily covers the OpenAM client APIs and SPIs, with emphasis on the Java APIs.
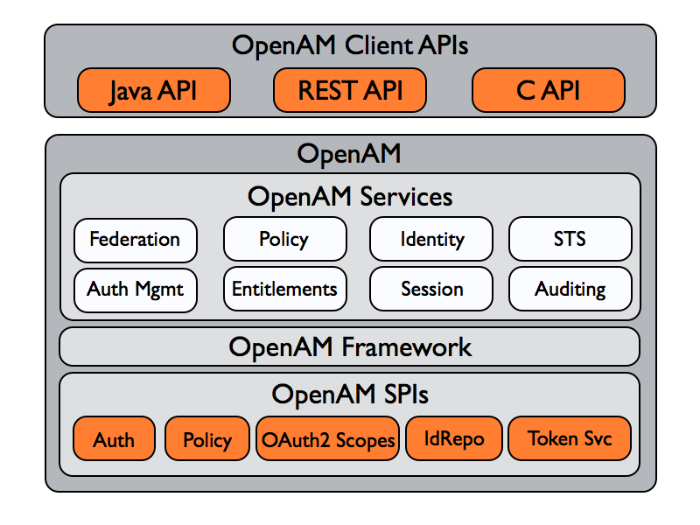
1.1. OpenAM APIs
OpenAM provides client application programming interfaces for a variety of needs.
The OpenAM Java APIs provided through the OpenAM Java SDK let your Java and Java EE applications call on OpenAM for authentication, and authorization in both OpenAM and federated environments.
Detailed reference information is provided in the OpenAM Java SDK API Specification.
The C SDK also provides APIs for native applications, such as new web server policy agents. The C SDK is delivered with OpenAM for Linux, Solaris, and Windows platforms.
OpenAM exposes a RESTful API that can return JSON or XML over HTTP, allowing you to access authentication, authorization, and identity services from your web applications using REST clients in the language of your choice.
1.2. OpenAM SPIs
OpenAM provides Java based service provider interfaces to let you extend services for the requirements of your particular deployment.
Some examples of the plugins you can write follow in the list below. This guide demonstrates how to implement such plugins.
Custom OAuth 2.0 scopes plugins define how OpenAM playing the role of authorization server handles scopes, including what token information to return regarding scopes set when authorization was granted.
Custom authentication plugins let OpenAM authenticate users against a new authentication service or an authentication service specific to your deployment
Post authentication plugins perform additional processing at the end of the authentication process, but before the subject is authenticated. Post authentication plugins can for example store information about the authentication in the user's profile, or call another system for audit logging purposes.
Policy evaluation plugins implement new policy conditions, send attributes from the user profile as part of a policy response, extend the definition of the subjects to whom the policy applies, or customize how policy management is delegated.
Identity repository plugins let OpenAM employ a new or custom user data store, other than a directory server or JDBC-accessible database.
1.3. OpenAM, IPv4, and IPv6
OpenAM provides functionality for IPv4, IPv6, and a hybrid of the two. While the majority of the interaction is done on the backend, there are a few places where the GUI requires some inputs, such as setting up policy conditions. These areas follow the same standard that applies to IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses a 32-bit integer value, with a dot-decimal system. IPv6 uses a hexadecimal system, and the eight groups of hexadecimal digits are separated by a colon.
Chapter 2. Developing Client Applications
Client applications access OpenAM services for authentication, authorization, and single sign on/single log out through the use of sessions. Client applications can also be allowed to manage authorization policies.
Client application integration with OpenAM can be coupled loosely, as in the case of an application running in a web server with an OpenAM policy agent to handle interaction with OpenAM service, more directly, as in the case where the client interacts with OpenAM over protocol, or tightly, as in the case of an application using the OpenAM Java or C API to interact with OpenAM services.
This part of the guide covers client interaction with OpenAM over supported protocols and using OpenAM APIs.
Chapter 3. Using RESTful Web Services
This chapter shows how to use the OpenAM RESTful interfaces for direct integration between web client applications and OpenAM.
3.1. About the RESTful API
Interface Stability: Evolving in the Administration Guide
OpenAM offers a RESTful API for these access and identity management operations:
Authentication (login)
Identity management (creating, reading, updating, deleting identities)
Realm management (creating, reading, updating, deleting realms)
This chapter also includes a section on Section 3.15, "REST Status Codes".
In this chapter, long URLs are wrapped to fit the printed page, as some of the output is formatted for easier reading.
3.2. Token Encoding
Valid tokens in OpenAM requires configuration either in percent encoding or in C66Encode format. C66Encode format is encouraged. It is the default token format for OpenAM, and is used in this chapter. The following is an example token that has not been encoded:
AQIC5wM2LY4SfczntBbXvEAOuECbqMY3J4NW3byH6xwgkGE=@AAJTSQACMDE=#
This token includes reserved characters such as +, /,
and = (The @, #, and * are not
reserved characters per se, but substitutions are still required). To c66encode this token,
you would substitute certain characters for others, as follows:
+ is replaced with - / is replaced with _ = is replaced with . @ is replaced with * # is repalced with * * (first instance) is replaced with @ * (subsequent instances) is replaced with #
In this case, the translated token would appear as shown here:
AQIC5wM2LY4SfczntBbXvEAOuECbqMY3J4NW3byH6xwgkGE.*AAJTSQACMDE.*
3.3. Authentication & Logout
OpenAM provides REST APIs for authentication and for logout.
Under
/json/authenticateand/json/sessions, you find the newer JSON-based APIs.See Section 3.3.1, "Authentication & Logout" below.
Under
/identity/authenticateand/identity/logout, you find the backwards-compatible, legacy API.See Section 3.3.2, "Authentication & Logout (Legacy API)" below.
3.3.1. Authentication & Logout
The simplest user name/password authentication returns a
tokenId that applications can present as a cookie
value for other operations that require authentication. In this case use
HTTP POST to prevent the web container from logging the credentials.
Pass the user name in an X-OpenAM-Username header, and
the password in an X-OpenAM-Password header.
$ curl --request POST
--header "X-OpenAM-Username: demo" --header "X-OpenAM-Password: changeit"
--header "Content-Type: application/json" --data "{}"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate
{ "tokenId": "AQIC5w...NTcy*", "successUrl": "/openam/console" }This "zero page login" mechanism works only for name/password authentication. If you include a POST body with the request, it must be an empty JSON string as shown in the example. Alternatively, you can leave the POST body empty. Otherwise, OpenAM interprets the body as a continuation of an existing authentication attempt, one that uses a supported callback mechanism.
The authentication service at /json/authenticate
supports callback mechanisms that make it possible to perform other types of
authentication in addition to simple user name/password login.
Callbacks that are not completed based on the content of the client HTTP request are returned in JSON as a response to the request. Each callback has an array of output suitable for displaying to the end user, and input which is what the client must complete and send back to OpenAM. The default is still user name/password authentication.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate
{
"authId": "...jwt-value...",
"template": "",
"stage": "DataStore1",
"callbacks": [
{
"type": "NameCallback",
"output": [
{
"name": "prompt",
"value": " User Name: "
}
],
"input": [
{
"name": "IDToken1",
"value": ""
}
]
},
{
"type": "PasswordCallback",
"output": [
{
"name": "prompt",
"value": " Password: "
}
],
"input": [
{
"name": "IDToken2",
"value": ""
}
]
}
]
}The "authId" value is a JSON Web Token (JWT) that uniquely identifies the authentication context to OpenAM, and so must also be sent back with the requests.
To respond to the callback, send back the JSON object with the missing
values filled, as in this case where the user name is demo
and the password is changeit.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "authId": "...jwt-value...", "template": "", "stage": "DataStore1",
"callbacks": [ { "type": "NameCallback", "output": [ { "name": "prompt",
"value": " User Name: " } ], "input": [ { "name": "IDToken1", "value": "demo" } ] },
{ "type": "PasswordCallback", "output": [ { "name": "prompt", "value": " Password: " } ],
"input": [ { "name": "IDToken2", "value": "changeit" } ] } ] }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate
{ "tokenId": "AQIC5wM2...U3MTE4NA..*", "successUrl": "/openam/console" }The response is a token ID holding the SSO Token value.
Alternatively, you can authenticate without requesting a session
using the noSession query string parameter.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "authId": "...jwt-value...", "template": "", "stage": "DataStore1",
"callbacks": [ { "type": "NameCallback", "output": [ { "name": "prompt",
"value": " User Name: " } ], "input": [ { "name": "IDToken1", "value": "demo" } ] },
{ "type": "PasswordCallback", "output": [ { "name": "prompt", "value": " Password: " } ],
"input": [ { "name": "IDToken2", "value": "changeit" } ] } ] }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate?noSession=true
{ "message": "Authentication Successful", "successUrl": "/openam/console" }OpenAM can be configured to return a failure URL value when
authentication fails. No failure URL is configured by default. The Default
Failure Login URL can be configured for the Core in the Administration Guide authentication
module. Alternatively, failure URLs can be configured per authentication
chain, which your client can specify using the service
parameter described below. On failure OpenAM then returns HTTP status
code 401 Unauthorized, and the JSON in the reply indicates the failure
URL.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json"
--header "X-OpenAM-Username: demo" --header "X-OpenAM-Password: badpassword"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate
{ "errorMessage": "Invalid Password!!",
"failureUrl": "http://www.example.com/401.html" }You can set the realm by using the realm query string parameter as
in ?realm=myRealm.
You can use the authIndexType and
authIndexValue query string parameters as a pair
to provide additional information about how you are authenticating.
The authIndexType can be one of the following
types.
- composite
Set the value to a composite advice string.
- level
Set the value to the authentication level.
- module
Set the value to the name of an authentication module.
- resource
Set the value to a URL protected by an OpenAM policy.
- role
Set the value to an OpenAM role.
- service
Set the value to the name of an authentication chain.
- user
Set the value to an OpenAM user ID.
OpenAM uses the following callback types depending on the authentication module in use.
ChoiceCallback
ConfirmationCallback
HttpCallback
LanguageCallback
NameCallback
PasswordCallback
RedirectCallback
TextInputCallback
TextOutputCallback
X509CertificateCallback
Authenticated users can log out with the token cookie value and an HTTP
POST to /json/sessions/?_action=logout.
$ curl
--request POST
--header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2...U3MTE4NA..*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/sessions/?_action=logout"
{"result":"Successfully logged out"}3.3.2. Authentication & Logout (Legacy API)
Interface Stability: Deprecated in the Administration Guide
Simple authentication with a user name and password returns a token.
$ curl --request POST --data "username=bjensen&password=hifalutin" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/authenticate token.id=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxvdvHOXjtC_eWSs2RB54tgvgK8SuYi7aQ.*AAJTSQACMDE.*
If you must specify parameters as when authenticating to
/UI/Login, you provide a percent encoded string of the
parameters as the value of the uri parameter. The
/UI/Login parameter deals with the realm,
module, and service parameters. Setting the
client parameter sets the user's IP address as part of the
token following successful authentication. The default for the client
parameter is the IP of the machine making the REST request.
$ curl --request POST --data "username=bjensen &password=hifalutin &uri=realm%3D%2F%26module%3DDataStore &client=192.168.1.1" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/authenticate token.id=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxvdvHOXjtC_eWSs2RB54tgvgK8SuYi7aQ.*AAJTSQACMDE.*
You log out using the token to end the user session.
$ curl --request POST --data "subjectid=AQIC5w...*AAJTSQACMDE.*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/logout
3.4. Cookie Information
You can retrieve the cookie domains that OpenAM supports by HTTP GET on
/json/serverinfo/cookieDomains.
$ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/serverinfo/cookieDomains
{"domains":[".example.com"]}You can retrieve the name of the cookie used for storing the session
token. By default it is iPlanetDirectoryPro.
$ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/getCookieNameForToken string=iPlanetDirectoryPro
You can also retrieve the name of the cookie used for storing the session token and the names of the cookies to forward with requests.
$ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/getCookieNamesToForward string=iPlanetDirectoryPro string=amlbcookie
3.5. Token Validation, Attribute Retrieval
You check whether a token is valid as follows.
$ curl --request POST --data "tokenid=AQIC5w...*AAJTSQACMDE.*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/isTokenValid boolean=true
An invalid token returns boolean=false.
$ curl --request POST --data "tokenid=INVALID" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/isTokenValid boolean=false
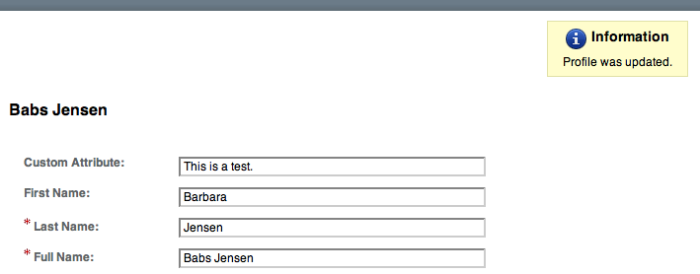
With a valid token, you can retrieve attributes about the subject. OpenAM returns a series of name, value pairs.
The newer API for retrieving user information is demonstrated in Section 3.12.2, "Reading Identities". What follows describes the legacy API.
$ curl --request POST --data "subjectid=AQIC5w...*AAJTSQACMDE.*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/attributes
userdetails.token.id=
AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.*
userdetails.attribute.name=uid
userdetails.attribute.value=bjensen
userdetails.attribute.name=mail
userdetails.attribute.value=bjensen@example.com
userdetails.attribute.name=sn
userdetails.attribute.value=Jensen
userdetails.attribute.name=userpassword
userdetails.attribute.value={SSHA}rhusOfYpkapDWEHcfT2Y7y83LMuC++F4Abqvig==
userdetails.attribute.name=cn
userdetails.attribute.value=Babs Jensen
userdetails.attribute.value=Barbara Jensen
userdetails.attribute.name=givenname
userdetails.attribute.value=Barbara
userdetails.attribute.name=dn
userdetails.attribute.value=uid=bjensen,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
userdetails.attribute.name=telephonenumber
userdetails.attribute.value=+1 408 555 1862
userdetails.attribute.name=objectclass
userdetails.attribute.value=organizationalPerson
userdetails.attribute.value=person
userdetails.attribute.value=posixAccount
userdetails.attribute.value=inetOrgPerson
userdetails.attribute.value=krbprincipalaux
userdetails.attribute.value=krbTicketPolicyAux
userdetails.attribute.value=topYou can specify attributes to limit what you retrieve.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/attributes? subjectid=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &attributenames=mail &attributenames=uid" userdetails.token.id= AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.* userdetails.attribute.name=uid userdetails.attribute.value=bjensen userdetails.attribute.name=mail userdetails.attribute.value=bjensen@example.com
When retrieving attributes, you can refresh the session thus setting
the idle time to 0, by adding the boolean parameter
refresh=true to the query string.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/attributes? subjectid=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &attributenames=cn &refresh=true" userdetails.token.id= AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.* userdetails.attribute.name=cn userdetails.attribute.value=Babs Jensen userdetails.attribute.value=Barbara Jensen
3.6. Authorization
You can call on OpenAM to decide whether to authorize access to a protected resource based on a valid token. Of course, you must percent encode the resource URI.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/authorize? uri=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%3A8080%2Fexamples%2Findex.html &subjectid=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.*" boolean=true
To indicate access denied, OpenAM returns
boolean=false.
3.6.1. Requesting Policy Decisions
OpenAM provides additional REST APIs for requesting policy decisions.
The policy decision interfaces use the following path suffixes and query string parameters.
Path suffixes for policy decision requests include the following.
ws/1/entitlement/decision: request a decision pertaining to a single resourcews/1/entitlement/decisions: request decisions pertaining to multiple resourcesws/1/entitlement/entitlement: request decisions for a specified resource URL and all resources underneath
Query string parameters for policy decision requests include the following.
subject=encoded-token, where the token is encoded using the method implemented inEncoder.java.In the examples for this section, the token ID obtained during authentication for
amadminis abbreviated asAQIC5...DU3*and the encoded token ID for the subject isMJ3QFTr4ZV2QrtlJvXlg0Q2dMRM=.action=get, oraction=post, which identifies the user agent action when requesting a decision.application=iPlanetAMWebAgentServiceresource=resource-url, or multipleresources=resource-urlparameters for multiple decisions.env=requestDnsName%3Dfqdn,env=requestIP%3Ddotted-quads,env=requestTime%3Dseconds-since-epoch, andenv=requestDnsName%3Dtime-zonewhere time-zone is from JavaTimeZone.getTimeZone().getID(). Theenvparameters thus express conditions.
Authentication for these interfaces uses cookies, so if your application is not running in a browser, first authenticate as described in Section 3.3, "Authentication & Logout".
To request a decision for a single resource, use an HTTP GET on
/ws/1/entitlement/decision as in the following example.
$ curl --request GET --cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*" "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/decision ?subject=MJ3QFTr4ZV2QrtlJvXlg0Q2dMRM=&action=GET &application=iPlanetAMWebAgentService &resource=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2Findex.html" allow
If access is denied, the result is deny.
To request decisions for multiple resources, use an HTTP GET on
/ws/1/entitlement/decisions as in the following example.
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/decisions
?subject=MJ3QFTr4ZV2QrtlJvXlg0Q2dMRM=&action=GET
&application=iPlanetAMWebAgentService
&resources=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2Findex.html
&resources=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2Ffavicon.ico"
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"results": [
{
"actionsValues": {
"POST": true,
"GET": true
},
"attributes": {},
"advices": {},
"resourceName": "http://www.example.com:80/index.html"
},
{
"actionsValues": {
"POST": true,
"GET": true
},
"attributes": {},
"advices": {},
"resourceName": "http://www.example.com:80/favicon.ico"
}
]
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}To request decisions for all resource underneath a given resource, use
an HTTP GET on /ws/1/entitlement/entitlement as in the
following example.
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/entitlement
?subject=MJ3QFTr4ZV2QrtlJvXlg0Q2dMRM=
&application=iPlanetAMWebAgentService
&resource=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2F*"
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": true,
"GET": true
},
"attributes": {},
"advices": {},
"resourceName": "http://www.example.com:80/*"
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}3.6.2. Managing Policies
OpenAM exposes a REST API through the
/ws/1/entitlement/privilege endpoint under the
deployment URI. The API lets you create, read, update, delete, and query
policies.
Authentication for these interfaces uses cookies, so if your application is not running in a browser, first authenticate as described in Section 3.3, "Authentication & Logout".
3.6.2.1. Creating Policies
You create a policy by using an HTTP POST of the JSON representation to the endpoint. You must URL encode the JSON before passing it to OpenAM.
$ cat entitlement.json
{
"name": "Example HTTP",
"eSubject": {
"state": {
"className": "com.sun.identity.policy.plugins.AuthenticatedUsers",
"exclusive": false,
"name": "All Authenticated Users",
"values": []
},
"className": "com.sun.identity.entitlement.opensso.PolicySubject"
},
"entitlement": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": true,
"GET": true
},
"applicationName": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService",
"name": "authorize",
"resourceNames": [
"http://www.example.com:80/*"
]
}
}$ curl
--request POST
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
--data-urlencode "privilege.json@entitlement.json"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege
{"statusCode":201,"body":"Created","statusMessage":"Created"}
$ cat entitlement2.json
{
"name": "Example HTTPS",
"eSubject": {
"state": {
"className": "com.sun.identity.policy.plugins.AuthenticatedUsers",
"exclusive": false,
"name": "All Authenticated Users",
"values": []
},
"className": "com.sun.identity.entitlement.opensso.PolicySubject"
},
"entitlement": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": false,
"GET": true
},
"applicationName": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService",
"name": "authorize",
"resourceNames": [
"https://www.example.com:443/*?*"
]
}
}$ curl
--request POST
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
--data-urlencode "privilege.json@entitlement2.json"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege
{"statusCode":201,"body":"Created","statusMessage":"Created"}3.6.2.2. Reading Policies
To read a policy, use an HTTP GET on the endpoint followed by the URL-encoded name of the policy.
Notice that the "state" is returned as a long string, and so is not shown here in full.
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege/Example%20HTTP
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"results": {
"name": "Example HTTP",
"eSubject": {
"state": "{\n \"className\": \"com.sun.identity.policy...}",
"className": "com.sun.identity.entitlement.opensso.PolicySubject"
},
"entitlement": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": true,
"GET": true
},
"applicationName": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService",
"name": "authorize",
"resourceNames": [
"http://www.example.com:80/*"
]
}
}
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege/Example%20HTTPS
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"results": {
"name": "Example HTTPS",
"eSubject": {
"state": "{\n \"className\": \"com.sun.identity.policy...}",
"className": "com.sun.identity.entitlement.opensso.PolicySubject"
},
"entitlement": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": false,
"GET": true
},
"applicationName": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService",
"name": "authorize",
"resourceNames": [
"https://www.example.com:443/*?*"
]
}
}
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}3.6.2.3. Updating Policies
To update a policy, use an HTTP PUT on the endpoint followed by the URL-encoded name of the policy.
$ cat update.json {
"name": "Example HTTP",
"eSubject": {
"state": {
"className": "com.sun.identity.policy.plugins.AuthenticatedUsers",
"exclusive": false,
"name": "All Authenticated Users",
"values": []
},
"className": "com.sun.identity.entitlement.opensso.PolicySubject"
},
"entitlement": {
"actionsValues": {
"POST": false,
"GET": true
},
"applicationName": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService",
"name": "authorize",
"resourceNames": [
"http://www.example.com:80/*?*"
]
}
}$ curl
--request PUT
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
--data-urlencode "privilege.json@update.json"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege/Example%20HTTP
{"statusCode":200,"body":"OK","statusMessage":"OK"}3.6.2.4. Deleting Policies
To delete a policy, use an HTTP DELETE on the endpoint followed by the URL-encoded name of the policy.
$ curl
--request DELETE
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege/Example%20HTTPS
{"statusCode":200,"body":"OK","statusMessage":"OK"}3.6.2.5. Querying Policies
To get the names of policies, use an HTTP GET on the endpoint.
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"results": [
"Example HTTPS",
"Example HTTP"
]
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}You can pass a filter query parameter to get only policies that match the filter. Make sure you URL encode the filter value.
$ curl
--request GET
--cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5...DU3*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/ws/1/entitlement/privilege
?subject=MJ3QFTr4ZV2QrtlJvXlg0Q2dMRM=&filter=name%3D*HTTP"
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"results": [
"Example HTTP"
]
},
"statusMessage": "OK"
}
3.7. OAuth 2.0 Authorization
OpenAM exposes the following REST endpoints for different OAuth 2.0 purposes.
Endpoints for OAuth 2.0 clients and resource servers, mostly defined in RFC 6749, The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework, with an additional
tokeninfoendpoint useful to resource servers.An endpoint for OAuth 2.0 token administration. This is specific to OpenAM.
An endpoint for OAuth 2.0 client administration. This is specific to OpenAM.
When accessing the APIs, browser-based REST clients can rely on OpenAM to handle the session as usual. First authenticate with OpenAM. Then perform the operations in the browser session.
Clients not running in a browser can authenticate as described in
Section 3.3, "Authentication & Logout", whereby OpenAM returns a
token.id value. Clients pass the
token.id value in a header named after the
authentication cookie, by default iplanetDirectoryPro.
3.7.1. OAuth 2.0 Client & Resource Server Endpoints
As described in the Administration Guide chapter on Managing OAuth 2.0 Authorization in the Administration Guide, OpenAM exposes REST endpoints for making calls to OpenAM acting as an authorization server.
In addition to the standard authorization and token endpoints described in RFC 6749, OpenAM also exposes a token information endpoint for resource servers to get information about access tokens so they can determine how to respond to requests for protected resources. OpenAM as authorization server exposes the following endpoints for clients and resource servers.
/oauth2/authorizeAuthorization endpoint defined in RFC 6749, used to obtain an authorization grant from the resource owner
Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize/oauth2/access_tokenToken endpoint defined in RFC 6749, used to obtain an access token from the authorization server
Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token/oauth2/tokeninfoEndpoint not defined in RFC 6749, used to validate tokens, and to retrieve information such as scopes
Given an access token, a resource server can perform an HTTP GET on
/oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=token-idto retrieve a JSON object indicatingtoken_type,expires_in,scope, and theaccess_tokenID.Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo
The /oauth2/authorize, and
/oauth2/access_token endpoints function as described
in RFC 6749.
The /oauth2/authorize endpoint is protected by the
policy created during OAuth 2.0 authorization server configuration, which
grants all authenticated users access.
The /oauth2/tokeninfo endpoint takes an HTTP GET
on /oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=token-id, and returns information about the
token.
Resource servers — or any party having the token ID — can get token information through this endpoint without authenticating. This means any application or user can validate the token without having to be registered with OpenAM.
The following example shows OpenAM issuing an access token, and then returning token information.
$ curl
--request POST
--user "myClientID:password"
--data "grant_type=password&username=demo&password=changeit&scope=cn%20mail"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token
{
"expires_in": 599,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"refresh_token": "f6dcf133-f00b-4943-a8d4-ee939fc1bf29",
"access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9"
}
$ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo
?access_token=f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9
{
"mail": "demo@example.com",
"scope": [
"mail",
"cn"
],
"cn": "demo",
"realm": "/",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 577,
"access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9"
}The resource server making decisions about whether the token is valid
can thus use the /oauth2/tokeninfo endpoint to retrieve
expiration information about the token. Depending on the scopes
implementation, the JSON response about the token can also contain scope
information. As described in the Administration Guide,
the default scopes implementation in OpenAM considers scopes to be names of
attributes in the resource owner's user profile. Notice that the JSON
response contains the values for those attributes from the user's profile,
as in the preceding example, with scopes set to mail and
cn.
Both the /oauth2/authorize and
/oauth2/access_token endpoints can take additional
parameters. In particular you must specify the realm using the
realm=realm-name parameter if
the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than /
(Top-Level Realm). For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured
for the /customers realm, then use
/oauth2/authorize?realm=/customers and
/oauth2/access_token?realm=/customers.
The /oauth2/authorize endpoint can also take
module and service parameters. Use
either as described in Authenticating
To OpenAM in the Administration Guide, where module specifies the
authentication module instance to use or service
specifies the authentication chain to use when authenticating the resource
owner.
3.7.2. OAuth 2.0 Token Administration Endpoint
The OpenAM-specific OAuth 2.0 token administration endpoint lets administrators read, list, and delete OAuth 2.0 tokens. OAuth 2.0 clients can also manage their own tokens.
OpenAM exposes the token administration endpoint at
/frrest/oauth2/token, such as
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/token.
Note
This endpoint location is likely to change in the future.
To get a token, perform an HTTP GET on
/frrest/oauth2/token/token-id,
as in the following example.
$ curl
--request POST
--user "myClientID:password"
--data "grant_type=password&username=demo&password=changeit&scope=cn%20mail"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token
{
"expires_in": 599,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"refresh_token": "f838e7d4-7e84-4743-af7c-9a9c42c2969e",
"access_token": "9c6a48fc-44b1-4a0c-b4f0-672fba468b0f"
}
$ curl
--header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcxs...EwNDU2NjE0*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/token/9c6a48fc...fba468b0f
{
"scope": [
"mail",
"cn"
],
"type": [
"access_token"
],
"username": [
"demo"
],
"realm": [
"/"
],
"id": [
"9c6a48fc-44b1-4a0c-b4f0-672fba468b0f"
],
"parent": [
"f838e7d4-7e84-4743-af7c-9a9c42c2969e"
],
"expiry_time": [
"1355741494888"
],
"client_id": [
"myClientID"
]
}To list tokens, perform an HTTP GET on
/frrest/oauth2/token/?_query_id=conditions,
where conditions is a comma-separated list of
field=value
conditions. The fields are taken from the fields
returned in the token object through this endpoint.
"expiry_time"Token expiration time in milliseconds since 00:00:00 UTC, January 1, 1970.
"type"Either
"access_token"or"refresh_token"."username"OAuth 2.0 client to whom the token was issued.
"realm"The realm for which the token was issued.
"id"Unique ID of the token.
The following example shows a search for current access tokens that
were issued to myClientID.
$ curl
--header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcxs...EwNDU2NjE0*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/token/?_queryID
=username%3DmyClientID%2Ctype%3Daccess_token
{
"result": [
{
"scope": [
"mail",
"cn"
],
"id": [
"1b836369-4fcf-4fb2-b819-ee4b1314d4f1"
],
"type": [
"access_token"
],
"username": [
"myClientID"
],
"realm": [
"/"
],
"expiry_time": [
"1355741986154"
]
},
{
"scope": [
"mail",
"cn"
],
"type": [
"access_token"
],
"username": [
"myClientID"
],
"realm": [
"/"
],
"id": [
"5f1763fc-37ae-4698-9e84-d301d49e1f7e"
],
"expiry_time": [
"1355741982091"
]
}
],
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}To delete a token, perform an HTTP DELETE on
/frrest/oauth2/token/token-id,
as in the following example.
$ curl
--request POST
--data "grant_type=client_credentials&username=demo&password=changeit
&client_id=myClientID&client_secret=password&scope=cn%20mail"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token
{
"expires_in": 599,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"access_token": "867aaab2-61d7-4b78-9b80-4f9098034540"
}
$ curl
--request DELETE
--header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcxs...EwNDU2NjE0*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/token/867aaab2..098034540
{
"success": "true"
}3.7.3. OAuth 2.0 Client Administration Endpoint
The OAuth 2.0 administration endpoint lets OpenAM administrators and agent administrators create (that is, register) and delete OAuth 2.0 clients.
OpenAM exposes this endpoint at /frrest/oauth2/client,
such as
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/client.
Note
This endpoint location is likely to change in the future.
To create an OAuth 2.0 client, perform an HTTP POST to
/frrest/oauth2/client/?_action=create
with a JSON object fully specifying the client, as in the following
example.
$ curl --request POST --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM...3MTYxOA..*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"client_id":["testClient"],
"realm":["/"]
"userpassword":["secret12"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clientType":["Confidential"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.redirectionURIs":
["www.client.com","www.example.com"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.scopes":["cn","sn"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.defaultScopes":["cn"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.name":["My Test Client"],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.description":["OAuth 2.0 Client"]
}'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/client/?_action=create
{"success":"true"}When creating an OAuth 2.0 client, use the following fields in your JSON object.
"client_id"(Required) This field takes an array containing the client identifier as defined in RFC 6749.
"realm"(Required) This field takes an array containing the OpenAM realm in which to create the client as defined in RFC 6749.
"userpassword"(Required) This field takes an array containing the client secret as defined in RFC 6749.
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clientType"(Required) This field takes an array containing the client type, either
"Confidential"or"Public"as defined in RFC 6749."com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.redirectionURIs"(Optional for confidential clients) This field takes an array of client redirection endpoints as defined in RFC 6749.
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.scopes"(Optional) This field takes an array of scopes as defined in RFC 6749. The default scopes implementation takes scopes to be names of attributes in the resource owner profile.
Specify localized scopes in
scope|locale|localized descriptionformat."com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.defaultScopes"(Optional) This field takes an array of default scopes set automatically when tokens are issued.
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.name"(Optional) This field takes an array containing the client name to display to the resource owner when the resource owner must authorize client access to protected resources.
Specify localized names in
locale|localized nameformat."com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.description"(Optional) This field takes an array containing the description to display to the resource owner when the resource owner must authorize client access to protected resources.
Specify localized descriptions in
locale|localized descriptionformat.
To delete an OAuth 2.0 client, perform an HTTP DELETE on
/frrest/oauth2/client/client-id,
as in the following example.
$ curl --request DELETE
--header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM...3MTYxOA..*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/frrest/oauth2/client/testClient
{"success":"true"}3.8. OpenID Connect 1.0
OpenID Connect 1.0 extends OAuth 2.0 so the client can verify claims about the identity of the end user, get profile information about the end user, and log the user out at the end of the OpenAM session.
OpenAM exposes the following REST endpoints for OpenID Connect 1.0 purposes.
Endpoints for discovering information.
An endpoint for registering client applications.
Endpoints for client authorization.
Endpoints for session management.
3.8.1. Discovering OpenID Connect 1.0 Configuration
OpenAM exposes endpoints for discovering information about the provider configuration, and about the provider for a given end user.
/.well-known/openid-configurationallows clients to retrieve OpenID Provider configuration by HTTP GET as specified by OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0./.well-known/webfingerallows clients to retrieve the provider URL for an end user by HTTP GET as specified by OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0.
For examples, see Configuring OpenAM For OpenID Connect Discovery in the Administration Guide.
3.8.2. Registering OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients
OpenAM allows both static and dynamic registration of OpenID Connect
client applications. For dynamic registration according to the OpenID Connect
Dynamic Client Registration 1.0 specification, the endpoint is
/oauth2/connect/register. See To Register a
Client Dynamically in the Administration Guide for details.
3.8.3. Performing OpenID Connect 1.0 Client Authorization
Registered clients can request authorization through OpenAM.
OpenID Connect 1.0 supports both a Basic Client Profile using the OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant, and an Implicit Client Profile using the OAuth 2.0 implicit grant. These client profiles rely on the OAuth 2.0 endpoints for authorization. Those endpoints are described in Section 3.7.1, "OAuth 2.0 Client & Resource Server Endpoints".
In addition, authorized clients can access end user information through
the OpenID Connect 1.0 specific endpoint
/oauth2/userinfo.
For examples, see Client Examples in the Administration Guide.
3.8.4. Managing OpenID Connect 1.0 Sessions
Registered clients can use OpenID Connect Session Management 1.0 to handle end user logout actions.
/oauth2/connect/checkSessionallows clients to retrieve session status notifications./oauth2/connect/endSessionallows clients to terminate end user sessions.
For an example, see Managing User Sessions in the Administration Guide.
3.9. User Self-Registration
The OpenAM REST API for users provides an action for self-registration.
The feature works by sending an email to the user in response to RESTful HTTP POST requesting registration with an email address. When the user clicks the link received by mail, an application intercepts the HTTP GET, transforms the query string values into an HTTP POST to confirm the operation. OpenAM responds to the application with a JSON object that the application can further use to request creation of the user account to complete the transaction.
An example follows, showing the steps in more detail.
Configure the Email Service and REST Security.
In particular, you must configure the Email Service to send mail to users who self-register, and you must enable self-registration in the REST Security service.
You can configure these globally in OpenAM Console at Configuration > Global > Email Service for notifications and Configuration > Global > REST Security to allow self-registration.
Alternatively, you can configure them for an individual realm under Access Control > Realm Name > Services.
Perform an HTTP POST on
/json/users?_action=registerwith the new user's mail.Notice that authentication is not required.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"email":"newuser@example.com"}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=register {}On success, the response is an empty JSON object
{}as shown in the example.The user receives an email message that includes a URL as in the following example.
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/confirmation/register?confirmationId=P23PK5kyAgNdqeNJpAvq1ebcpcg=&email=newuser@example.com&tokenId=+8rWf5O8KG0rfz3Pa+WwDLkH9Ac=
Intercept the HTTP GET request to this URL when the user clicks the link.
Your application must use the confirmation link to construct an HTTP POST to
/json/users?_action=confirmfrom the query string parameters as shown in the following example.$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"email":"newuser@example.com", "tokenId":"+8rWf5O8KG0rfz3Pa+WwDLkH9Ac=", "confirmationId":"P23PK5kyAgNdqeNJpAvq1ebcpcg="}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=confirm { "email": "newuser@example.com", "tokenId": "+8rWf5O8KG0rfz3Pa+WwDLkH9Ac=", "confirmationId": "P23PK5kyAgNdqeNJpAvq1ebcpcg=" }The response is a further confirmation that the account can be created.
Using the confirmation, your application must make an authenticated HTTP POST to
/json/users?_action=anonymousCreateto create the user as shown in the following example.$ curl --request POST --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM...3MTYxOA..*" --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"email":"newuser@example.com", "tokenId":"+8rWf5O8KG0rfz3Pa+WwDLkH9Ac=", "confirmationId":"P23PK5kyAgNdqeNJpAvq1ebcpcg=", "name":"newuser","userpassword":"password"}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=anonymousCreate { "username": "mark", "realm": "/", "uid": [ "newuser" ], "mail": [ "newuser@example.com" ], "sn": [ "newuser" ], "userPassword": [ "{SSHA}dAiONYMxqFiNilXeLXUQoDpHlePYtiJcjYw8Dw==" ], "cn": [ "newuser" ], "inetUserStatus": [ "Active" ], "dn": [ "uid=newuser,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" ], "objectClass": [ "devicePrintProfilesContainer", "person", "sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService", "inetorgperson", "sunFederationManagerDataStore", "iPlanetPreferences", "iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service", "organizationalperson", "sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier", "inetuser", "forgerock-am-dashboard-service", "iplanet-am-managed-person", "iplanet-am-user-service", "sunAMAuthAccountLockout", "top" ], "universalid": [ "id=newuser,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" ] }
At this point the user is registered, active, and can authenticate with OpenAM.
3.10. Resetting Forgotten Passwords
The OpenAM REST API for users provides an action for handling forgotten passwords as long as the user has a valid email address in their profile.
The option is disabled by default. You can enable it in the OpenAM Console globally via Configuration > Global > REST Security.
Alternatively, you can enable it for an individual realm under Access Control > Realm Name > Services > Add > REST Security.
An example follows, showing the steps in more detail.
Configure the Email Service.
In particular, you must configure the Email Service to send mail allowing the user to reset the forgotten password.
You can configure the service globally in the OpenAM Console via Configuration > Global > Email Service.
Alternatively, you can configure it for an individual realm under Access Control > Realm Name > Services.
Perform an HTTP POST on
/json/users?_action=forgotPasswordwith the user's ID.Notice that authentication is not required.
curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"username":"demo"}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=forgotPassword {}On success, the response is an empty JSON object
{}as shown in the example.OpenAM looks up the email address in the user profile, and sends an email message that includes a URL as in the following example.
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/confirmation/forgotPassword?confirmationId=jrUZ3E7CK4UQJM5jnDHGNKH1UaQ=&tokenId=M8cVqWqbKtCtpd/UqEAr0x25fxA=&username=demo
Intercept the HTTP GET request to this URL when the user clicks the link.
Your application must use the confirmation link to construct an HTTP POST to
/json/users?_action=forgotPasswordResetfrom the query string parameters as shown in the following example.Your POST includes the new password as the value of the "userpassword" field in the JSON payload.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"username":"demo", "userpassword":"password", "tokenId":"M8cVqWqbKtCtpd/UqEAr0x25fxA=", "confirmationId":"jrUZ3E7CK4UQJM5jnDHGNKH1UaQ="}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=forgotPasswordReset { "name": "demo", "realm": "/", "uid": [ "demo" ], "mail": [ "demo@example.com" ], "sn": [ "demo" ], "userPassword": [ "{SSHA}zgeBu4yOAy1i9QAgnldMCzW8LWX36ViVj9leig==" ], "cn": [ "demo" ], "inetUserStatus": [ "Active" ], "objectClass": [ "devicePrintProfilesContainer", "person", "sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService", "inetorgperson", "sunFederationManagerDataStore", "iPlanetPreferences", "iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service", "organizationalperson", "sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier", "inetuser", "forgerock-am-dashboard-service", "iplanet-am-managed-person", "iplanet-am-user-service", "sunAMAuthAccountLockout", "top" ], "universalid": [ "id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" ] }On success, the response is the JSON representation of the user profile with the new password hashed according to the password storage scheme for the identity repository.
At this point the user can authenticate with the new password.
3.11. Logging
You can send OpenAM messages to log, specifying the message content and the log file in which to write your message.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/log? appid=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcwyCZkk-1JXzx6q1EzgagabHfBjMidb5jI.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &subjectid=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxuxIP0VnP2lVjs7ypEM6VDx6srk56CN1Q.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &logname=rest.access &message=Hello%20World"
Logging takes a valid appid token for the subject
with access to log the message, and also a subjectid token
for the user whom the message concerns. If the tokens are valid and the
access rights correct, your message ends up in the log specified.
$ cat openam/openam/log/rest.access #Version: 1.0 #Fields: time Data LoginID ContextID IPAddr LogLevel Domain LoggedBy MessageID ModuleName NameID HostName "2011-09-14 16:38:17" /home/mark/openam/openam/log/ "cn=dsameuser,ou=DSAME Users,o=openam" aa307b2dcb721d4201 "Not Available" INFO o=openam "cn=dsameuser,ou=DSAME Users,o=openam" LOG-1 rest.access "Not Available"192.168.56.2 "2011-09-14 16:38:17" "Hello World" id=bjensen,ou=user,o=openam 8a4025a2b3af291d01 "Not Available" INFO o=openam id=amadmin,ou=user,o=openam "Not Available" rest.access "Not Available" 192.168.56.2
3.12. Identity Management
This section shows how to create, read, update, delete, and list identities using the RESTful APIs.
Important
OpenAM has two REST APIs for managing identities.
Under the
/json/agents,/json/groups, and/json/users, you find the newer JSON-based APIs. The newer APIs follow the ForgeRock common REST pattern creating, reading, updating, deleting, and querying resources.Examples in this section do not repeat the authentication shown in Section 3.3, "Authentication & Logout". For browser-based clients, you can rely on OpenAM cookies rather than construct the header in your application. Managing agent profiles, groups, realms, and users with these APIs of course require authorization. The examples shown in this section were performed with the token ID gained after authenticating as OpenAM administrator.
Although the examples here show user management, you can use
/json/agents,/json/groups,/json/realmsin similar fashion. See Section 3.13, "Realm Management" for examples related to realms.The following sections cover this JSON-based API.
Under the
/identityendpoint, you find the backwards-compatible, legacy API.The following sections cover this backwards-compatible API.
3.12.1. Creating Identities
OpenAM lets administrators create a user profile by making
an HTTP POST of the JSON representation of the profile to
/json/subrealm/users/?_action=create.
To add a user to the Top Level Realm, you do not need to specify the realm.
The following example shows an administrator creating a new user. The
only required fields are username and
userpassword. If no other name is provided, the entry
you make for username defaults to both the user id and the
user's last name.
$ curl --request POST --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "username": "bjensen", "userpassword": "secret12",
"mail": "bjensen@example.com" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/?_action=create
{
"username": "bjensen",
"realm": "/",
"uid": [
"bjensen"
],
"mail": [
"bjensen@example.com"
],
"sn": [
"bjensen"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SSHA}0pXpKLPRKCGY7g3YqZygJmKMW6IC2BLJimmlwg=="
],
"cn": [
"bjensen"
],
"inetuserstatus": [
"Active"
],
"dn": [
"uid=bjensen,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"objectclass": [
"person",
"sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService",
"sunFederationManagerDataStore",
"inetorgperson",
"iPlanetPreferences",
"iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service",
"organizationalperson",
"sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier",
"inetuser",
"iplanet-am-managed-person",
"sunAMAuthAccountLockout",
"iplanet-am-user-service",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=bjensen,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}Alternatively, administrators can create user profiles with specific
user IDs by doing an HTTP PUT of the JSON representation of the changes to
/json/users/user-id, as
shown in the following example.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "If-None-Match: *"
--data '{ "username": "janedoe" userpassword": "secret12", "mail": "janedoe@example.com" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/janedoe
{
"username": "janedoe",
"realm": "/",
"uid": [
"janedoe"
],
"mail": [
"janedoe@example.com"
],
"sn": [
"janedoe"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SSHA}e4DJoxvYVW/nsp62XJf29ZADE16YQgrxK+XuKA=="
],
"cn": [
"janedoe"
],
"inetuserstatus": [
"Active"
],
"dn": [
"uid=janedoe,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"objectclass": [
"devicePrintProfilesContainer",
"person",
"sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService",
"inetorgperson",
"sunFederationManagerDataStore",
"iPlanetPreferences",
"iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service",
"organizationalperson",
"sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier",
"inetuser",
"forgerock-am-dashboard-service",
"iplanet-am-managed-person",
"iplanet-am-user-service",
"sunAMAuthAccountLockout",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=janedoe,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}As shown in the examples, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on successful creation. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
The same HTTP POST and PUT mechanisms also work for other objects such as policy agent profiles and groups.
$ curl --request POST --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"name":"myWebAgent","realm":"/",
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.default":["www.example.com"],
"sunidentityserverdevicekeyvalue":["agentRootURL=http://www.example.com:80/"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.remote.logfile":["amAgent_www_example_com_80.log"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.repository.location":["centralized"],
"agenttype":["WebAgent"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url":
["[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/cdcservlet"],
"com.sun.identity.client.notification.url":
["http://www.example.com:80/UpdateAgentCacheServlet?shortcircuit=false"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.agenturi.prefix":
["http://www.example.com:80/amagent"],
"userpassword":["password"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url":
["[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Login"],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url":
["[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Logout"],
"sunidentityserverdevicestatus":["Active"]}'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/agents/?_action=create
{
"name": "myWebAgent",
"realm": "/",
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cookie.domain": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.get.client.host.name": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.fetch.mode": [
"NONE"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.ip": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.check.enable": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cleanup.interval": [
"30"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.url.attributes.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.ignore.preferred.naming.url": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.client.ip.header": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.session.attribute.mapping": [
"[]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.audit.accesstype": [
"LOG_NONE"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.proxy.override.host.port": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.load.balancer.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.encode.url.special.chars.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.convert.mbyte.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.domino.check.name.database": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.owa.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.override.port": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.clock.skew": [
"0"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.sso.only": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.owa.enable.session.timeout.url": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.domino.ltpa.config.name": [
"LtpaToken"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.default": [
"www.example.com"
],
"sunIdentityServerDeviceKeyValue": [
"agentRootURL=http://www.example.com:80/"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.domino.ltpa.cookie.name": [
"LtpaToken"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.password.header": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.attribute.mapping": [
"[]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.userid.param.type": [
"session"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.url.comparison.case.ignore": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.cookie.maxage": [
"300"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.remote.logfile": [
"amAgent_www_example_com_80.log"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.domino.ltpa.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.url": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.notification.enable": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.cookie.prefix": [
"HTTP_"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.cookie.reset": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.polling.interval": [
"60"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.attribute.multi.value.separator": [
"|"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.debug.file.rotate": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.debug.level": [
"Error"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.local.log.rotate": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.repository.location": [
"centralized"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.client.ip.validation.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.override.protocol": [
"false"
],
"AgentType": [
"WebAgent"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.redirect.url": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.ignore.path.info": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.override.notification.url": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.session.attribute.fetch.mode": [
"NONE"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.cache.polling.interval": [
"3"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url": [
"[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/cdcservlet"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.name": [
"iPlanetDirectoryPro"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.mapping": [
"[]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.filter.priority": [
"HIGH"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.auth.type": [],
"com.sun.identity.client.notification.url": [
"http://www.example.com:80/UpdateAgentCacheServlet?shortcircuit=false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.secure": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.ignore.path.info.for.not.enforced.list": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.remote.log.interval": [
"5"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.url.invert": [
"false"
],
"universalid": [
"id=myWebAgent,ou=agent,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.replaypasswd.key": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.owa.enable.change.protocol": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.userid.param": [
"UserToken"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SHA-1}W6ph5Mm5Pz8GgiULbPgzG37mj9g="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.attribute.fetch.mode": [
"NONE"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.freeformproperties": [
"sunidentityserverdevicestatus=Active",
"sunidentityserverdevicekeyvalue=agentRootURL=http://www.example.com:80/",
"realm=/",
"name=myWebAgent"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.log.disposition": [
"REMOTE"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.agenturi.prefix": [
"http://www.example.com:80/amagent"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.override.host": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.local.log.size": [
"52428800"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.access.denied.url": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.debug.file.size": [
"10000000"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.change.notification.enable": [
"true"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.anonymous.user.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.domino.ltpa.org.name": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.agent.logout.url": [
"[0]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.poll.primary.server": [
"5"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.mapping": [
"[]="
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.auth.connection.timeout": [
"2"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.client.hostname.header": [],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.iis.logonuser": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.ignore.server.check": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.fetch.from.root.resource": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url": [
"[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Login"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.redirect.param": [
"goto"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url": [
"[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Logout"
],
"sunIdentityServerDeviceStatus": [
"Active"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.sso.cache.polling.interval": [
"3"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.anonymous.user.id": [
"anonymous"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.encode.cookie.special.chars.enable": [
"false"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.locale": [
"en_US"
],
"com.sun.identity.agents.config.postcache.entry.lifetime": [
"10"
]
}$ curl --request POST --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"name":"newGroup","realm":"/",
"uniquemember":["uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"]}'
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups?_action=create"
{
"name": "newGroup",
"realm": "/",
"uniqueMember": [
"uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"cn": [
"newGroup"
],
"objectclass": [
"groupofuniquenames",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=newGroup,ou=group,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}
$ curl --request PUT --header "If-None-Match: *"
--header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"name":"anotherGroup","realm":"/",
"uniquemember":["uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"]}'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups/anotherGroup
{
"name": "anotherGroup",
"realm": "/",
"uniqueMember": [
"uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"cn": [
"anotherGroup"
],
"objectclass": [
"groupofuniquenames",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=anotherGroup,ou=group,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}3.12.2. Reading Identities
OpenAM lets users and administrators read profiles by requesting an HTTP
GET on /json/subrealm/users/user-id.
This allows users and administrators to verify user data, status, and directory.
If users or administrators see missing or incorrect information, they can write
down the correct information and add it using Section 3.12.3, "Updating Identities".
To read a profile on the Top Level Realm, you do not need to specify the realm.
Users can review the data associated with their accounts and administrators
can read other user's profiles. The following example shows an administrator
accessing user data. Users can view their information by changing
username=amadmin to user-id.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo
{
"username": "demo",
"realm": "/",
"uid": [
"demo"
],
"sn": [
"demo"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SSHA}S14oR2gusLWtiDkAS4twj63slXNNaMKpwrOWdw=="
],
"cn": [
"demo"
],
"inetuserstatus": [
"Active"
],
"dn": [
"uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"objectclass": [
"person",
"sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService",
"sunFederationManagerDataStore",
"inetorgperson",
"iPlanetPreferences",
"iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service",
"organizationalperson",
"sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier",
"inetuser",
"iplanet-am-managed-person",
"sunAMAuthAccountLockout",
"iplanet-am-user-service",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}Use the _fields query string parameter to restrict
the list of attributes returned. This parameter takes a comma-separated list
of JSON object fields to include in the result.
$ curl --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo?_fields=name,uid
{"name":"demo","uid":["demo"]}As shown in the examples, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
Using HTTP GET to read also works for other objects such as agent profiles and groups.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/agents/myClientID
{
"name": "myClientID",
"realm": "/",
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.accessToken": [],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clientSessionURI": [],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.subjectType": [
"Pairwise"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.defaultScopes": [
"[1]=profile",
"[0]=openid"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clientType": [
"Confidential"
],
"universalid": [
"id=myClientID,ou=agent,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SHA-1}W6ph5Mm5Pz8GgiULbPgzG37mj9g="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.name": [
"[0]="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.redirectionURIs": [
"[1]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openid/cb-implicit.html",
"[0]=https://openam.example.com:8443/openid/cb-basic.html"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.scopes": [
"[1]=profile",
"[0]=openid"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.idTokenSignedResponseAlg": [
"HmacSHA256"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.postLogoutRedirectURI": [],
"sunIdentityServerDeviceStatus": [
"Active"
],
"AgentType": [
"OAuth2Client"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.description": [
"[0]="
]
}The _prettyPrint query string parameter can make
the resulting JSON easier to read when you are viewing the resulting JSON
directly.
$ curl --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups/myGroup?_prettyPrint=true"
{
"name" : "myGroup",
"realm" : "/",
"uniquemember" : [ "uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" ],
"cn" : [ "myGroup" ],
"objectclass" : [ "groupofuniquenames", "top" ],
"universalid" : [ "id=myGroup,ou=group,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" ]
}3.12.3. Updating Identities
OpenAM lets users update their own profiles, and lets administrators
update other users' profiles. To update an identity do an HTTP PUT of the JSON
representation of the changes to /json/subrealm/users/user-id.
To update a profile on the Top Level Realm, you do not need to specify the realm.
The following example shows how users can update their own profiles.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5...Y3MTAx*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "mail": "demo@example.com" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo
{
"username": "demo",
"realm": "/",
"uid": [
"demo"
],
"mail": [
"demo@example.com"
],
"sn": [
"demo"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SSHA}S14oR2gusLWtiDkAS4twj63slXNNaMKpwrOWdw=="
],
"cn": [
"demo"
],
"inetuserstatus": [
"Active"
],
"dn": [
"uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"objectclass": [
"person",
"sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService",
"sunFederationManagerDataStore",
"inetorgperson",
"iPlanetPreferences",
"iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service",
"organizationalperson",
"sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier",
"inetuser",
"iplanet-am-managed-person",
"sunAMAuthAccountLockout",
"iplanet-am-user-service",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}As shown in the example, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
You can use HTTP PUT to update other objects as well, such as policy agent profiles groups.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5...Y3MTAx*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"name":"masterClient","realm":"/","accesstoken":[],
"clientsessionuri":[],"subjecttype":["Pairwise"],
"defaultscopes":["[0]=openid"],"clienttype":["Confidential"],
"universalid":["id=masterClient,ou=agent,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"],
"userpassword":"changeit","name":["[0]="],"redirectionuris":["[0]="],
"idtokensignedresponsealg":["HmacSHA512"],"scopes":["[0]=openid"],
"postlogoutredirecturi":[],"sunidentityserverdevicestatus":["Active"],
"agenttype":["OAuth2Client"],"description":["[0]="]}'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/agents/masterClient
{
"name": "masterClient",
"realm": "/",
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.accesstoken": [],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clientsessionuri": [],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.subjecttype": [
"Pairwise"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.defaultscopes": [
"[0]="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.clienttype": [
"Confidential"
],
"universalid": [
"id=masterClient,ou=agent,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"userpassword": [
"{SHA-1}W6ph5Mm5Pz8GgiULbPgzG37mj9g="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.name": [
"[0]="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.redirectionuris": [
"[0]="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.idtokensignedresponsealg": [
"HmacSHA256"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.scopes": [
"[0]="
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.postlogoutredirecturi": [],
"sunidentityserverdevicestatus": [
"Active"
],
"agenttype": [
"OAuth2Client"
],
"com.forgerock.openam.oauth2provider.description": [
"[0]="
]
}Notice in the following example that updates myGroup
the object class value is not included in the JSON sent to OpenAM.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5...Y3MTAx*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"name":"myGroup","realm":"/",
"uniquemember":["uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"],
"cn":["myGroup"],"description":["Updated the group"]}'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups/myGroup
{
"name": "myGroup",
"realm": "/",
"uniqueMember": [
"uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"cn": [
"myGroup"
],
"dn": [
"cn=myGroup,ou=groups,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
],
"objectclass": [
"groupofuniquenames",
"top"
],
"universalid": [
"id=myGroup,ou=group,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org"
]
}
3.12.4. Deleting Identities
OpenAM lets administrators delete a user profile by making an HTTP DELETE
call to /json/subrealm/users/user-id.
To delete a user from the Top Level Realm, you do not need to specify the realm.
The following example removes a user from the top level realm. Only administrators should delete users. The user id is the only field required to delete a user.
$ curl --request DELETE --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/bjensen
{"success":"true"}On success, OpenAM returns a JSON object indicating success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
You can use this same logic for other resources such as performing an HTTP DELETE of an agent profile or of a group.
$ curl --request DELETE --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/agents/myOAuth2ClientAgent
{"success":"true"}$ curl --request DELETE --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups/myGroup
{"success":"true"}3.12.5. Listing Identities
OpenAM lets administrators list identities by making an HTTP GET
call to /json/subrealm/users/?_queryId=*. To query the Top Level Realm, you do not need
to specify the realm.
$ curl --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_queryID=*"
{
"result" : [ "amAdmin", "demo", "anonymous" ],
"resultCount" : 3,
"pagedResultsCookie" : null,
"remainingPagedResults" : -1
}This also works for other types of objects, such as agent profiles and groups.
$ curl --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/agents?_queryID=*"
{
"result" : [ "wsp", "wsc", "agentAuth", "SecurityTokenService" ],
"resultCount" : 4,
"pagedResultsCookie" : null,
"remainingPagedResults" : -1
}$ curl --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/groups?_queryID=*"
{
"result" : [ "myOtherGroup", "myGroup" ],
"resultCount" : 2,
"pagedResultsCookie" : null,
"remainingPagedResults" : -1
}As the result lists include all objects, this capability to list identity names is mainly useful in testing.
As shown in the examples, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the resource list if successful. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
3.12.6. Creating Identities (Legacy API)
Interface Stability: Deprecated in the Administration Guide
OpenAM lets you create user profiles, and also create web and J2EE policy agent profiles. When you create an entry, you must provide the following parameters.
- admin
Valid token for the user with permissions to add the identity
- identity_name
A unique name for the identity to create
- identity_attribute_names
LDAP attribute names for attributes to create
- identity_attribute_values_name
LDAP attribute values for the identity to create. For example,
identity_attribute_names=sn&identity_attribute_values_sn=Jensen.- identity_realm
The realm in which to create the identity
- identity_type
Either
userorAgentOnly
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/create? admin=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxSYA8eG-vrNHb_W7nG8XkfAGyRyuaebDY.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &identity_name=testuser &identity_attribute_names=cn &identity_attribute_values_cn=Test%20User &identity_attribute_names=sn &identity_attribute_values_sn=User &identity_attribute_names=userpassword &identity_attribute_values_userpassword=secret12 &identity_realm=%2F &identity_type=user"
3.12.7. Reading & Searching for Identities (Legacy API)
Interface Stability: Deprecated in the Administration Guide
Reading is similar to attribute retrieval, as described in Section 3.5, "Token Validation, Attribute Retrieval", but obtained using the token of a user with permissions to perform the search, as shown in the following example.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/read?
admin=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxSYA8eG-vrNHb_W7nG8XkfAGyRyuaebDY.*AAJTSQACMDE.*
&name=testuser
&attributes_names=realm
&attributes_values_realm=%2F"
identitydetails.name=testuser
identitydetails.type=user
identitydetails.realm=o=openam
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=uid
identitydetails.attribute.value=testuser
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=sn
identitydetails.attribute.value=User
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=userpassword
identitydetails.attribute.value={SSHA}AzpT+N1sjrQhL1wfX2ETWh/Aqbd+lH9LOlhDqg==
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=cn
identitydetails.attribute.value=Test User
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=inetuserstatus
identitydetails.attribute.value=Active
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=dn
identitydetails.attribute.value=uid=testuser,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=objectclass
identitydetails.attribute.value=person
identitydetails.attribute.value=sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService
identitydetails.attribute.value=inetorgperson
identitydetails.attribute.value=sunFederationManagerDataStore
identitydetails.attribute.value=iPlanetPreferences
identitydetails.attribute.value=iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service
identitydetails.attribute.value=organizationalperson
identitydetails.attribute.value=sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier
identitydetails.attribute.value=inetuser
identitydetails.attribute.value=iplanet-am-managed-person
identitydetails.attribute.value=iplanet-am-user-service
identitydetails.attribute.value=sunAMAuthAccountLockout
identitydetails.attribute.value=top
identitydetails.attribute=
identitydetails.attribute.name=universalid
identitydetails.attribute.value=id=testuser,ou=user,o=openamYou can search for user IDs by providing the following parameters.
- admin
Valid token for the user with access to perform the search
- attributes_names
LDAP attribute names for attributes to search
- attributes_values_name
LDAP attribute values for the identity to search. For example,
attribute_names=sn&attribute_values_sn=Jensen.- filter
Additional LDAP filter component to limit the search results returned
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/search? admin=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxSYA8eG-vrNHb_W7nG8XkfAGyRyuaebDY.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &attributes_names=sn &attributes_values_sn=Jensen &attributes_names=mail &attributes_values_mail=bjensen* &attributes_names=realm &attributes_values_realm=%2F" string=bjensen
3.12.8. Updating Identities (Legacy API)
Interface Stability: Deprecated in the Administration Guide
You can update an identity with the same parameters used to create identities, provided the token corresponds to a user with access to update the identity.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/update? admin=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxSYA8eG-vrNHb_W7nG8XkfAGyRyuaebDY.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &identity_name=testuser &identity_attribute_names=mail &identity_attribute_values_mail=testuser%40example.com &identity_realm=%2F &identity_type=user"
3.12.9. Deleting Identities (Legacy API)
Interface Stability: Deprecated in the Administration Guide
You can also delete an identity.
$ curl "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/identity/delete? admin=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxSYA8eG-vrNHb_W7nG8XkfAGyRyuaebDY.*AAJTSQACMDE.* &identity_name=testuser &identity_realm=%2F &identity_type=user"
3.13. Realm Management
This section shows how to create, read, update, and delete realms using the RESTful APIs.
Under the
/json/realmsendpoint, you find the newer JSON-based API.The following sections cover this JSON-based API.
3.13.1. Default Parameters for Realms
Realms have a number of fields entered with the default loading. The following table provides information on what the default realm settings are, and these settings can be updated, added, or deleted when updating a realm.
| Realm Parameter | Default | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| realm | None - the only required field to add a realm | The name of the realm Example: |
| sunOrganizationStatus | None | The status of the realm
|
| sunOrganizationAliases | None | Any applicable aliases associated with the realm. Be aware that an alias can only be used once. Entering an alias used by another realm will remove the alias from that realm and you will lose configuration. Example: |
| serviceNames | sunAMAuthHOTPService
iPlanetAMAuthConfiguration
sunAMAuthFederationService
sunIdentityRepositoryService
iPlanetAMPolicyConfigService
iPlanetAMAuthService
iPlanetAMAuthLDAPService
sunAMAuthDataStoreService
sunAMAuthSAEService
sunAMDelegationService
sunAMAuthWSSAuthModuleService
iPlanetAMAuthOATHService
| Services needed for the realm, including authentication modules |
3.13.2. Creating Realms
OpenAM lets administrators create a realm by making
an HTTP POST of the JSON representation of the profile to
/json/realms/?_action=create.
You can create realms using an HTTP POST of the JSON representation
of the profile to /json/realms/?_action=create, as shown in
the following example. The only required field is realm,
but the realm will not be active if the status is not set.
$ curl --request POST --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "realm": "testRealm" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/?_action=create
{"realmCreated":"/testRealm"}You can also set the sunOrganizationAliases parameter,
but it can only be assigned to one realm (usually the top level realm). Before
setting this parameter, make sure it is not already assigned elsewhere. If you
replace remove it from another realm, you will lose your configuration.
Alternatively, administrators can create realms by the specific realm
name using the HTTP PUT of the JSON representation of the changes to
/json/realms/realm-id, as
shown in the following example.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "sunOrganizationStatus": "Active" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/testRealm
{As shown in the examples, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on successful creation. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
3.13.3. Reading Realms
OpenAM lets administrators read realms by requesting an HTTP GET on
/json/realms/realm-id. This
allows administrators to review all active realm services for the realm,
like policy configuration and modules. If users or administrators see missing
information (such as Active status) or incorrect information, they can write
down the correct information and add it using Section 3.13.4, "Updating Realms"
The following example shows an administrator receiving information about
the testRealm.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/testRealm
{
"serviceNames":[
"sunAMAuthHOTPService",
"iPlanetAMAuthConfiguration",
"sunAMAuthFederationService",
"sunIdentityRepositoryService",
"iPlanetAMPolicyConfigService",
"iPlanetAMAuthService",
"iPlanetAMAuthLDAPService",
"sunAMAuthDataStoreService",
"sunAMAuthSAEService",
"sunAMDelegationService",
"sunAMAuthWSSAuthModuleService",
"iPlanetAMAuthOATHService"
]
}As shown in the example, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
3.13.4. Updating Realms
OpenAM lets administrators update realms. To update a realm, do an HTTP PUT
of the JSON representation of the changes to
/json/realms/realm-id.
The following example shows how to update a realm.
$ curl --request PUT --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5...Y3MTAx*"
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{ "sunOrganizationStatus": "Active" }'
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/testRealmAs shown in the example, OpenAM returns the JSON representation of the profile on success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
3.13.5. Deleting Realms
OpenAM lets administrators delete a realm by making an HTTP DELETE call to
/json/realms/realm-id.
The following example deletes a realm. The top level realm cannot be deleted. Only administrators should delete realms. The name of the realm is the only field required to delete the realm.
Make sure that you do not have any information you need within a realm before deleting it. Once a realm is deleted, the only way to restore it is to return to a backed up deployment of OpenAM.
$ curl --request DELETE --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*"
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/testRealm
{"success":"true"}On success, OpenAM returns a JSON object indicating success. On failure, OpenAM returns a JSON representation of the error including the HTTP status code.
3.14. Displaying Dashboard Applications
OpenAm lets administrators configure online applications to display applications on user Dashboards. You can used exposed REST API to display information about the online applications.
/dashboard/assignedThis endpoint retrieves the list of applications assigned to the authenticated user.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/dashboard/assigned { "google": { "dashboardIcon": [ "Google.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://www.google.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] } }/dashboard/availableThis endpoint retrieves the list of applications available in the authenticated user's realm. The example is based on two of the default Dashboard applications: Google and Salesforce.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/dashboard/available { "google": { "dashboardIcon": [ "Google.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://www.google.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] } "salesforce": { "dashboardIcon": [ "salesforce.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "Salesforce" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://salesforce.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "Salesforce" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] } }/dashboard/definedThis endpoint retrieves the list of all applications available defined for the OpenAM Dashboard service. The example is based on the three default Dashboard applications: Google, Salesforce, and Zendesk.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...2NzEz*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/dashboard/defined { "google": { "dashboardIcon": [ "Google.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://www.google.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "idm magic 34" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "Google" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] }, "salesforce": { "dashboardIcon": [ "salesforce.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "SalesForce" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://www.salesforce.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "idm magic 12" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "Salesforce" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] }, "zendesk": { "dashboardIcon": [ "ZenDesk.gif" ], "dashboardName": [ "ZenDesk" ], "dashboardLogin": [ "http://www.ZenDesk.com" ], "ICFIdentifier": [ "idm magic 56" ], "dashboardDisplayName": [ "ZenDesk" ], "dashboardClassName": [ "SAML2ApplicationClass" ] } }
If your application runs in a user-agent such as a browser, you can rely on OpenAM to handle authentication.
3.15. REST Status Codes
OpenAM REST APIs respond to successful requests with HTTP status codes in the 2xx range. OpenAM REST APIs respond to error conditions with HTTP status codes in the 4xx and 5xx range. Status codes used are described in the following list.
- 200 OK
The request was successful and a resource returned, depending on the request. For example, a successful HTTP GET on
/users/myUserreturns a user profile and status code 200, whereas a successful HTTP DELETE returns{"success","true"}and status code 200.- 201 Created
The request succeeded and the resource was created.
- 400 Bad Request
The request was malformed as in the following example, which is sending bad data in the payload for the action.
$ curl --request POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"bad":"data"}' https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users?_action=forgotPassword {"code":400,"reason":"Bad Request","message":"Username not provided"}- 401 Unauthorized
The request requires user authentication as in the following example, which is missing an SSO Token value.
$ curl --request POST https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/sessions?_action=logout { "code": 401, "reason": "Unauthorized", "message": "Access denied" }- 403 Forbidden
Access was forbidden during an operation on a resource as in the following example, which has a regular user trying to read the OpenAM administrator profile.
$ curl --request POST --header "X-OpenAM-Username: demo" --header "X-OpenAM-Password: changeit" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate { "tokenId": "AQIC5w...YyMA..*" } $ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...YyMA..*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/amadmin { "code": 403, "reason": "Forbidden", "message": "Permission to perform the read operation denied to id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org" }- 404 Not Found
The specified resource could not be found as in the following example, which is attempting to read a nonexistent user's profile.
$ curl --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...NTcy*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/missing {"code":404,"reason":"Not Found","message":"Resource cannot be found."}- 405 Method Not Allowed
The HTTP method is not allowed for the requested resource.
- 409 Conflict
The request would have resulted in a conflict with the current state of the resource.
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
The request is in a format not supported by the requested resource for the requested method as in the following example, which is attempting to pass basic authentication credentials as form-encoded data rather than query string parameters.
$ curl --request POST --data "username=demo&password=changeit" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/authenticate ... HTTP Status 415 ... The server refused this request because the request entity is in a format not supported by the requested resource for the requested method ...
- 500 Internal Server Error
The server encountered an unexpected condition which prevented it from fulfilling the request.
- 501 Not Implemented
The resource does not support the functionality required to fulfill the request as in the following example, which is attempting to delete an entry as a delete action instead of using an HTTP DELETE request.
curl --request POST --header "iplanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5w...NTcy*" https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo?_action=delete { "code": 501, "reason": "Not Implemented", "message": "Actions are not supported for resource instances" }- 503 Service Unavailable
The requested resource was temporarily unavailable.
Chapter 4. Using the OpenAM Java SDK
This chapter introduces OpenAM Java SDK. OpenAM Java SDK is delivered
with the full version of OpenAM,
OpenAM-11.0.0.zip.
4.1. Installing OpenAM Client SDK Samples
The full OpenAM download,
OpenAM-11.0.0.zip, contains the Java Client
SDK library, ClientSDK-11.0.0.jar, as well as
samples for use on the command line in
ExampleClientSDK-CLI-11.0.0.zip, and samples in a
web application, ExampleClientSDK-WAR-11.0.0.war.
The OpenAM Java
SDK API Specification provides a reference to the public
APIs.
The sample web application deploys in your container to show you the client SDK samples in action.
Deploy the .war in your Java web application container such as Apache Tomcat or JBoss.
$ cp ExampleClientSDK-WAR-11.0.0.war /path/to/tomcat/webapps/client.war
Browse to the location where you deployed the client, and configure the application to access OpenAM using the application user name,
UrlAccessAgent, and password configured when you set up OpenAM.Use the following hints to complete the configuration.
- Server Protocol
Protocol to access OpenAM (
httporhttps)- Server Host
Fully qualified domain name for OpenAM, such as
openam.example.com- Server Port
OpenAM port number such as 8080 or 8443
- Server Deployment URI
URI entry point to OpenAM such as
/openam- Debug directory
Where to write the debug messages for the client samples
- Application user name
An user agent configured to access OpenAM, such as
UrlAccessAgentset up when OpenAM was installed- Application user password
The user agent password
The sample client writes configuration information under
$HOME/OpenAMClient/, where $HOME is that of the user running the web application container.Verify that you have properly configured the sample web application.
In another browser tab page of the same browser instance, login to OpenAM as the OpenAM Administrator,
amadmin.This signs you into OpenAM, storing the cookie in your browser.
On the Samples tab page, click the link under Single Sign On Token Verification Servlet.
If the sample web application is properly configured, you should see something like the following text in your browser.
SSOToken host name: 127.0.0.1 SSOToken Principal name: id=amadmin,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org Authentication type used: DataStore IPAddress of the host: 127.0.0.1 SSO Token validation test succeeded The token id is AQIC5...CMDEAAlNLABQtODY0Mjc5MDUwNDQzOTA2MzYxNg..* ... User Attributes: {... givenName=[amAdmin], ...roles=[Top-level Admin Role], ...}
Follow these steps to set up the command-line examples.
Unpack the sample applications and related libraries.
$ mkdir sdk && cd sdk $ unzip ~/Downloads/ExampleClientSDK-CLI-11.0.0.zip
Configure the samples to access OpenAM.
$ sh scripts/setup.sh Debug directory (make sure this directory exists): /Users/me/openam/openam/debug Application user (e.g. URLAccessAgent) password: secret12 Protocol of the server: http Host name of the server: openam.example.com Port of the server: 8080 Server's deployment URI: openam Naming URL (hit enter to accept default value, http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/namingservice): $
Verify that you have properly configured the samples.
$ sh scripts/Login.sh Realm (e.g. /): / Login module name (e.g. DataStore or LDAP): DataStore Login locale (e.g. en_US or fr_FR): fr_FR DataStore: Obtained login context Nom d'utilisateur :demo Mot de passe :changeit Login succeeded. Logged Out!!
4.2. About the OpenAM Java SDK
After installing the Java SDK command line samples, you see the following content.
lib/: SDK and other librariesresources/: properties configuration files for the SDK and samplesscripts/: scripts to run the samplessource/: sample code
After deploying the Java SDK web application archive, you find the following content where the .war file was unpacked.
META-INF/: build informationWEB-INF/: sample classes and librariesconsole/: images for sample UIindex.html: sample home pagekeystore.jks: OpenAM test certificate, alias:test, key store password:changeitpolicy/: Policy Evaluator Client Sample pagesaml2/: Secure Attribute Exchange examplesample.css: sample stylessm/: Service Configuration sampleum/: User Profile sample
When writing a client using the OpenAM Java SDK, make sure you register hooks to make sure the application can be shut down gracefully. How you register for shutdown depends on the type of application.
For Java EE applications, make sure the OpenAM client SDK shuts down successfully by including the following context listener in your application's
web.xmlfile.<listener> <listener-class> com.sun.identity.common.ShutdownServletContextListener </listener-class> </listener>
For standalone applications, set the following JVM property.
-Dopenam.runtime.shutdown.hook.enabled=true
Chapter 5. Authenticating Using OpenAM Java SDK
This chapter looks at authentication with the OpenAM Java SDK and at the
sample client, Login.java, which demonstrates
authenticating to OpenAM from a client application, provided a realm, user
name, and password. This is the sample you ran to test installation of the
command-line SDK samples. The class shown in this chapter is
com.sun.identity.samples.authentication.Login.
With OpenAM, your client application performs the following steps to handle authentication.
Sets up an
AuthContext, based on the realm in which the user authenticates.Starts the login process by calling the
AuthContextlogin()method.Handling authentication callbacks to retrieve credentials from the user who is authenticating.
Your application loops through the authentication callbacks by using the
AuthContextgetRequirements()andhasMoreRequirements()methods. Each time it finishes populating a callback with the credentials retrieved, your application callssubmitRequirements()to send the credentials to OpenAM's Authentication Service.After handling all authentication callbacks, your application calls the
AuthContextgetStatus()method.On login success, OpenAM sets up an
SSOTokenthat holds information about the authentication, and also about the user's environment and session.When the user logs out, your application can end the session by calling the
AuthContextlogout()method.
The AuthContext class is provided by the
com.sun.identity.authentication package, part of the
OpenAM client API. Callback classes are provided by the
javax.security.auth.callback package, which provides
callbacks for choices, confirmations, locales, names, passwords, text input,
and text output.
See the OpenAM Public API JavaDoc for reference.
As the sample client gets the realm (called organization in the sample),
locale, and authentication module to set up the authentication context,
there is not need for a language callback to get the local afterwards. The
Login.java example does, however, show simple ways of
handling callbacks for the command-line context. The implementation of
the sample client follows.
package com.sun.identity.samples.authentication;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.security.auth.callback.Callback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.ChoiceCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.NameCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.PasswordCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.TextInputCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.TextOutputCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.UnsupportedCallbackException;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.AuthContext;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AuthLoginException;
import com.sun.identity.shared.debug.Debug;
public class Login {
private String loginIndexName;
private String orgName;
private String locale;
private Login(String loginIndexName, String orgName) {
this.loginIndexName = loginIndexName;
this.orgName = orgName;
}
private Login(String loginIndexName, String orgName, String locale) {
this.loginIndexName = loginIndexName;
this.orgName = orgName;
this.locale = locale;
}
protected AuthContext getAuthContext()
throws AuthLoginException {
AuthContext lc = new AuthContext(orgName);
AuthContext.IndexType indexType = AuthContext.IndexType.MODULE_INSTANCE;
if (locale == null || locale.length() == 0) {
lc.login(indexType, loginIndexName);
} else {
lc.login(indexType, loginIndexName, locale);
}
debugMessage(loginIndexName + ": Obtained login context");
return lc;
}
private void addLoginCallbackMessage(Callback[] callbacks)
throws UnsupportedCallbackException {
int i = 0;
try {
for (i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) {
if (callbacks[i] instanceof TextOutputCallback) {
handleTextOutputCallback((TextOutputCallback)callbacks[i]);
} else if (callbacks[i] instanceof NameCallback) {
handleNameCallback((NameCallback)callbacks[i]);
} else if (callbacks[i] instanceof PasswordCallback) {
handlePasswordCallback((PasswordCallback)callbacks[i]);
} else if (callbacks[i] instanceof TextInputCallback) {
handleTextInputCallback((TextInputCallback)callbacks[i]);
} else if (callbacks[i] instanceof ChoiceCallback) {
handleChoiceCallback((ChoiceCallback)callbacks[i]);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new UnsupportedCallbackException(callbacks[i],e.getMessage());
}
}
private void handleTextOutputCallback(TextOutputCallback toc) {
debugMessage("Got TextOutputCallback");
// display the message according to the specified type
switch (toc.getMessageType()) {
case TextOutputCallback.INFORMATION:
debugMessage(toc.getMessage());
break;
case TextOutputCallback.ERROR:
debugMessage("ERROR: " + toc.getMessage());
break;
case TextOutputCallback.WARNING:
debugMessage("WARNING: " + toc.getMessage());
break;
default:
debugMessage("Unsupported message type: " +
toc.getMessageType());
}
}
private void handleNameCallback(NameCallback nc)
throws IOException {
// prompt the user for a username
System.out.print(nc.getPrompt());
System.out.flush();
nc.setName((new BufferedReader
(new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine());
}
private void handleTextInputCallback(TextInputCallback tic)
throws IOException {
// prompt for text input
System.out.print(tic.getPrompt());
System.out.flush();
tic.setText((new BufferedReader
(new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine());
}
private void handlePasswordCallback(PasswordCallback pc)
throws IOException {
// prompt the user for sensitive information
System.out.print(pc.getPrompt());
System.out.flush();
String passwd = (new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))).
readLine();
pc.setPassword(passwd.toCharArray());
}
private void handleChoiceCallback(ChoiceCallback cc)
throws IOException {
// ignore the provided defaultValue
System.out.print(cc.getPrompt());
String[] strChoices = cc.getChoices();
for (int j = 0; j < strChoices.length; j++) {
System.out.print("choice[" + j + "] : " + strChoices[j]);
}
System.out.flush();
cc.setSelectedIndex(Integer.parseInt((new BufferedReader
(new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine()));
}
protected boolean login(AuthContext lc)
throws UnsupportedCallbackException {
boolean succeed = false;
Callback[] callbacks = null;
// get information requested from module
while (lc.hasMoreRequirements()) {
callbacks = lc.getRequirements();
if (callbacks != null) {
addLoginCallbackMessage(callbacks);
lc.submitRequirements(callbacks);
}
}
if (lc.getStatus() == AuthContext.Status.SUCCESS) {
System.out.println("Login succeeded.");
succeed = true;
} else if (lc.getStatus() == AuthContext.Status.FAILED) {
System.out.println("Login failed.");
} else {
System.out.println("Unknown status: " + lc.getStatus());
}
return succeed;
}
protected void logout(AuthContext lc)
throws AuthLoginException {
lc.logout();
System.out.println("Logged Out!!");
}
static void debugMessage(String msg) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.print("Realm (e.g. /): ");
String orgName = (new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine();
System.out.print("Login module name (e.g. DataStore or LDAP): ");
String moduleName = (new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine();
System.out.print("Login locale (e.g. en_US or fr_FR): ");
String locale = (new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine();
Login login = new Login(moduleName, orgName, locale);
AuthContext lc = login.getAuthContext();
if (login.login(lc)) {
login.logout(lc);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (AuthLoginException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedCallbackException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(0);
}
}Chapter 6. Handling Single Sign-On Using OpenAM Java SDK
This chapter looks at handling session tokens with the OpenAM Java SDK.
The class shown in this chapter is
com.sun.identity.samples.sso.SSOTokenSample.
When a user authenticates successfully, OpenAM sets up a single sign-on
(SSO) session for the user. The session is associated with an SSO token that
holds information about the authentication, and also about the user's
environment and session. OpenAM deletes the session when the authentication
context logout() method is called, or when a session timeout
is reached. At that point the SSO token is no longer valid.
When your application has an AuthContext after
successful authentication, you can retrieve the SSO token from the context.
You also can get the token as shown in the sample client by passing an SSO
token ID from OpenAM to an SSOTokenManager.
If your application needs to be notified of changes, you can register
an SSOTokenListener on the token by using the token's
addSSOTokenListener() method. OpenAM then calls your
SSOTokenListener ssoTokenChanged()
method when the session times out, is disposed of, or has a property that
changes.
The sample client takes an SSO token ID to get the token from OpenAM, and then displays some information from the SSO token. The implementation of the sample client follows.
package com.sun.identity.samples.sso;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOException;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOToken;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOTokenID;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOTokenManager;
public class SSOTokenSample {
private SSOTokenManager manager;
private SSOToken token;
private SSOTokenSample(String tokenID)
throws SSOException
{
if (validateToken(tokenID)) {
setGetProperties(token);
}
}
private boolean validateToken(String tokenID)
throws SSOException
{
boolean validated = false;
manager = SSOTokenManager.getInstance();
token = manager.createSSOToken(tokenID);
// isValid method returns true for valid token.
if (manager.isValidToken(token)) {
// let us get all the values from the token
String host = token.getHostName();
java.security.Principal principal = token.getPrincipal();
String authType = token.getAuthType();
int level = token.getAuthLevel();
InetAddress ipAddress = token.getIPAddress();
long maxTime = token.getMaxSessionTime();
long idleTime = token.getIdleTime();
long maxIdleTime = token.getMaxIdleTime();
System.out.println("SSOToken host name: " + host);
System.out.println("SSOToken Principal name: " +
principal.getName());
System.out.println("Authentication type used: " + authType);
System.out.println("IPAddress of the host: " +
ipAddress.getHostAddress());
validated = true;
}
return validated;
}
private void setGetProperties(SSOToken token)
throws SSOException
{
/*
* Validate the token again, with another method
* if token is invalid, this method throws an exception
*/
manager.validateToken(token);
System.out.println("SSO Token validation test Succeeded.");
// Get the SSOTokenID associated with the token and print it.
SSOTokenID id = token.getTokenID();
String tokenId = id.toString();
System.out.println("Token ID: " + tokenId);
// Set and get properties in the token.
token.setProperty("TimeZone", "PST");
token.setProperty("County", "SantaClara");
String tZone = token.getProperty("TimeZone");
String county = token.getProperty("County");
System.out.println("Property: TimeZone: " + tZone);
System.out.println("Property: County: " + county);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.print("Enter SSOToken ID: ");
String ssoTokenID = (new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in))).readLine();
new SSOTokenSample(ssoTokenID.trim());
} catch (SSOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(0);
}
}Before you run the script that calls the sample, authenticate to OpenAM
in order to have OpenAM generate the SSO token ID. To see the SSO token ID,
use the RESTful authenticate command as shown in the
following example, or alternatively run the
SSOTokenSampleServlet web-based sample.
$ curl --request POST --data "username=demo&password=changeit" http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/identity/authenticate token.id=AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcyy10grl...AlNLABQtNjI4OTkyNTUxNTc4MDQ3NzEzOQ..* $ sh scripts/SSOTokenSample.sh Enter SSOToken ID: AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcyy10grl...AlNLABQtNjI4OTkyNTUxNTc4MDQ3NzEzOQ..* SSOToken host name: 172.16.203.239 SSOToken Principal name: id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org Authentication type used: DataStore IPAddress of the host: 172.16.203.239 SSO Token validation test Succeeded. Token ID: AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcyy10grl...AlNLABQtNjI4OTkyNTUxNTc4MDQ3NzEzOQ..* Property: TimeZone: PST Property: County: SantaClara
Notice both the properties populated by OpenAM, and also the two
properties, TimeZone and County, that
are set by the sample client.
6.1. Receiving Notifications
If your application implements a listener for change notification, such
as a SessionListener to handle notification when a session
is invalidated, then you must configure the following settings in the
AMConfig.properties configuration file for your
application.
- com.iplanet.am.notification.url
Set this parameter to
http://host:port/context/notificationservice.- com.iplanet.am.sdk.caching.enabled
Set this parameter to
true.- com.iplanet.am.serverMode
Set this parameter to
false.- com.sun.identity.client.notification.url
Set this parameter to
http://host:port/context/notificationservice.- com.sun.identity.idm.cache.enabled
Set this parameter to
true.- com.sun.identity.idm.remote.notification.enabled
Set this parameter to
true.- com.sun.identity.sm.cache.enabled
Set this parameter to
true.- com.sun.identity.sm.enableDataStoreNotification
Set this parameter to
true.
The above configuration to access the notification service also applies
for other types of listeners, such as ServiceListener, and
IdEventListener implementations. See the OpenAM Java SDK API
Specification for details on the available listener
interfaces.
Chapter 7. Requesting Policy Decisions Using OpenAM Java SDK
This chapter shows how to request policy decision by using OpenAM Java
SDK. The chapter focuses on the sample client,
source/samples/policy/PolicyEvaluationSample.java, which
demonstrates making a request to OpenAM for a policy decision about access to
a web resource.
OpenAM centralizes policy administration, policy evaluation, and policy decision making so that your applications do not have to do so. In many deployments, OpenAM policy agents and the Open Identity gateway can handle policy enforcement independently from your application code.
If your application does need to request a policy decision from OpenAM,
then your application can retrieve a PolicyEvaluator from
a client-side PolicyEvaluatorFactory, and then call the
PolicyEvaluator getPolicyDecision()
method. For boolean decisions such as allow or deny, your application can also
call the isAllowed() method.
To make a policy decision, OpenAM needs an SSOToken,
the resource to access, the action the user wants to perform on the resource
such as HTTP GET or POST, and a
Map of environment settings you can use to specify
conditions and attributes in the session or can pass back as an empty
Map if your policy does not include conditions and
response attributes.
The PolicyEvaluationSample class takes as its
configuration the user credentials, service name, resource, and action that
you provide in a Java properties file. It then authenticates the user to get
an SSOToken using the TokenUtils.java
helper methods. At that point it has sufficient information to request a
policy decision.
The implementation of the sample client follows.
package samples.policy;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOToken;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOTokenManager;
import com.sun.identity.policy.PolicyDecision;
import com.sun.identity.policy.client.PolicyEvaluator;
import com.sun.identity.policy.client.PolicyEvaluatorFactory;
import samples.policy.TokenUtils;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.MissingResourceException;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.Set;
public class PolicyEvaluationSample {
public PolicyEvaluationSample() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PolicyEvaluationSample clientSample = new PolicyEvaluationSample();
clientSample.runSample(args);
System.exit(0);
}
public void runSample(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length == 0 || args.length > 1) {
System.out.println("Missing argument:"
+ "properties file name not specified");
} else {
System.out.println("Using properties file:" + args[0]);
Properties sampleProperties = getProperties(args[0]);
SSOToken ssoToken = getSSOToken(
(String)sampleProperties.get("user.name"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("user.password")
);
getPolicyDecision(
ssoToken,
(String)sampleProperties.get("service.name"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("resource.name"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("action.name")
);
}
}
private SSOToken getSSOToken(
String userName, String password) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Entering getSSOToken():"
+ "userName=" + userName + ","
+ "password=" + password);
SSOToken ssoToken = TokenUtils.getSessionToken("/",
userName, password);
System.out.println("TokenID:" + ssoToken.getTokenID().toString());
System.out.println("returning from getSSOToken()");
return ssoToken;
}
private void getPolicyDecision(
SSOToken ssoToken,
String serviceName,
String resourceName,
String actionName)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("Entering getPolicyDecision():"
+ "resourceName=" + resourceName + ","
+ "serviceName=" + serviceName + ","
+ "actionName=" + actionName);
PolicyEvaluator pe = PolicyEvaluatorFactory.getInstance().
getPolicyEvaluator(serviceName);
Map env = new HashMap();
Set attrSet = new HashSet();
Set actions = new HashSet();
actions.add(actionName);
PolicyDecision pd = pe.getPolicyDecision(ssoToken, resourceName,
actions, env);
System.out.println("policyDecision:" + pd.toXML());
System.out.println("returning from getPolicyDecision()");
}
private Properties getProperties(String file)
throws MissingResourceException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle(file);
Enumeration e = bundle.getKeys();
System.out.println("sample properties:");
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) e.nextElement();
String value = bundle.getString(key);
properties.put(key, value);
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
}
return properties;
}
}Before you run the script that calls the sample, edit the properties
file, resources/policyEvaluationSample.properties, to
indicate the user credentials, resource to access, and HTTP method to
use. You can use a resource that might not exist for the purposes of this
example, but you will need to set up a policy for that resource to get
meaningful results.
user.name=demo user.password=changeit service.name=iPlanetAMWebAgentService resource.name=http://www.example.com:80/banner.html action.name=GET
Also, set up a policy in OpenAM that corresponds to the resource in
question. You can set up the policy in OpenAM console under Access Control
> Realm Name > Policies. Concerning the
Realm Name, notice that unless you change the code,
the sample uses the top-level realm, / to authenticate the
user.
With the properties configured and policy in place, get the decision
from OpenAM using the script,
scripts/run-policy-evaluation-sample.sh.
$ sh scripts/run-policy-evaluation-sample.sh Using properties file:policyEvaluationSample sample properties: user.password:changeit service.name:iPlanetAMWebAgentService user.name:demo resource.name:http://www.example.com:80/banner.html action.name:GET ------------------------------------------------------------------------------: Entering getSSOToken():userName=demo,password=changeit TokenID:AQIC5wM2LY4Sfcx3aQGFRKu5-r1a-Vfyjb...5ODM4NDY0MzE0ODYzODQ1* returning from getSSOToken() Entering getPolicyDecision():resourceName=http://www.example.com:80/banner.html, serviceName=iPlanetAMWebAgentService,actionName=GET policyDecision:<PolicyDecision> <ResponseAttributes> </ResponseAttributes> <ActionDecision timeToLive="9223372036854775807"> <AttributeValuePair> <Attribute name="GET"/> <Value>allow</Value> </AttributeValuePair> <Advices> </Advices> </ActionDecision> </PolicyDecision> returning from getPolicyDecision()
As you see, the policy decision response is formatted here as an XML document.[1] Notice here the line showing that OpenAM has allowed access to the resource.
<Value>allow</Value>
[1] The PolicyDecision element is
defined in
openam/WEB-INF/remoteInterface.dtd
where openam is the location where the OpenAM web
application is deployed.
Chapter 8. Requesting a XACML Policy Decision Using OpenAM Java SDK
This chapter shows how to request a XACML policy decision with OpenAM
Java SDK, using the sample client,
source/samples/xacml/XACMLClientSample.java.
The sample client relies on an OpenAM server acting as a policy decision point
and another OpenAM server acting as a policy enforcement point.
The sample client uses the XACML ContextFactory to
create the XACML request. It then uses the
XACMLRequestProcessor to get a decision as XACML
Response from OpenAM. Most of the work in the sample
is done setting up the request.
The implementation of the XACMLClientSample class
follows.
package samples.xacml;
import com.sun.identity.saml2.common.SAML2Exception;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.client.XACMLRequestProcessor;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.common.XACMLConstants;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.common.XACMLException;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.ContextFactory;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Action;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Attribute;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Environment;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Request;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Resource;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Response;
import com.sun.identity.xacml.context.Subject;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.MissingResourceException;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class XACMLClientSample {
public XACMLClientSample() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XACMLClientSample clientSample = new XACMLClientSample();
clientSample.runSample(args);
System.exit(0);
}
public void runSample(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length == 0 || args.length > 1) {
System.out.println("Missing argument:"
+ "properties file name not specified");
} else {
System.out.println("Using properties file:" + args[0]);
Properties sampleProperties = getProperties(args[0]);
testProcessRequest(
(String)sampleProperties.get("pdp.entityId"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("pep.entityId"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("subject.id"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("subject.id.datatype"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("subject.category"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("resource.id"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("resource.id.datatype"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("resource.servicename"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("resource.servicename.datatype"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("action.id"),
(String)sampleProperties.get("action.id.datatype")
);
}
}
private void testProcessRequest(
String pdpEntityId, String pepEntityId,
String subjectId, String subjectIdType,
String subjectCategory,
String resourceId, String resourceIdType,
String serviceName, String serviceNameType,
String actionId, String actionIdType)
throws XACMLException, SAML2Exception,
URISyntaxException, Exception {
Request xacmlRequest = createSampleXacmlRequest(
subjectId, subjectIdType,
subjectCategory,
resourceId, resourceIdType,
serviceName, serviceNameType,
actionId, actionIdType);
System.out.println("\ntestProcessRequest():xacmlRequest:\n"
+ xacmlRequest.toXMLString(true, true));
Response xacmlResponse = XACMLRequestProcessor.getInstance()
.processRequest(xacmlRequest, pdpEntityId, pepEntityId);
System.out.println("testProcessRequest():xacmlResponse:\n"
+ xacmlResponse.toXMLString(true, true));
}
private Request createSampleXacmlRequest(
String subjectId, String subjectIdType,
String subjectCategory,
String resourceId, String resourceIdType,
String serviceName, String serviceNameType,
String actionId, String actionIdType)
throws XACMLException, URISyntaxException {
Request request = ContextFactory.getInstance().createRequest();
//Subject
Subject subject = ContextFactory.getInstance().createSubject();
subject.setSubjectCategory(new URI(subjectCategory));
//set subject id
Attribute attribute = ContextFactory.getInstance().createAttribute();
attribute.setAttributeId(new URI(XACMLConstants.SUBJECT_ID));
attribute.setDataType(new URI(subjectIdType));
List valueList = new ArrayList();
valueList.add(subjectId);
attribute.setAttributeStringValues(valueList);
List attributeList = new ArrayList();
attributeList.add(attribute);
subject.setAttributes(attributeList);
//set Subject in Request
List subjectList = new ArrayList();
subjectList.add(subject);
request.setSubjects(subjectList);
//Resource
Resource resource = ContextFactory.getInstance().createResource();
//set resource id
attribute = ContextFactory.getInstance().createAttribute();
attribute.setAttributeId(new URI(XACMLConstants.RESOURCE_ID));
attribute.setDataType( new URI(resourceIdType));
valueList = new ArrayList();
valueList.add(resourceId);
attribute.setAttributeStringValues(valueList);
attributeList = new ArrayList();
attributeList.add(attribute);
//set serviceName
attribute = ContextFactory.getInstance().createAttribute();
attribute.setAttributeId(new URI(XACMLConstants.TARGET_SERVICE));
attribute.setDataType(new URI(serviceNameType));
valueList = new ArrayList();
valueList.add(serviceName);
attribute.setAttributeStringValues(valueList);
attributeList.add(attribute);
resource.setAttributes(attributeList);
//set Resource in Request
List resourceList = new ArrayList();
resourceList.add(resource);
request.setResources(resourceList);
//Action
Action action = ContextFactory.getInstance().createAction();
attribute = ContextFactory.getInstance().createAttribute();
attribute.setAttributeId(new URI(XACMLConstants.ACTION_ID));
attribute.setDataType(new URI(actionIdType));
//set actionId
valueList = new ArrayList();
valueList.add(actionId);
attribute.setAttributeStringValues(valueList);
attributeList = new ArrayList();
attributeList.add(attribute);
action.setAttributes(attributeList);
//set Action in Request
request.setAction(action);
//Environment, our PDP does not use environment now
Environment environment = ContextFactory.getInstance()
.createEnvironment();
request.setEnvironment(environment);
return request;
}
private Properties getProperties(String file)
throws MissingResourceException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle(file);
Enumeration e = bundle.getKeys();
System.out.println("sample properties:");
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) e.nextElement();
String value = bundle.getString(key);
properties.put(key, value);
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
}
return properties;
}
}Before running the sample client, you must set up the configuration as
described in the comments at the outset of the
scripts/run-xacml-client-sample.sh script.
Edit
resources/xacmlClientSample.propertiesandresources/policyEvaluationSample.propertiesto set up the configuration for the sample client.The relevant settings from
resources/xacmlClientSample.propertiesare the following.pdp.entityId=xacmlPdpEntity pep.entityId=xacmlPepEntity subject.id=id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org subject.id.datatype=urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:data-type:x500Name subject.category=urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject-category:access-subject resource.id=http://www.example.com:80/banner.html resource.id.datatype=http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string resource.servicename=iPlanetAMWebAgentService resource.servicename.datatype=http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string action.id=GET action.id.datatype=http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string
The relevant settings from
resources/policyEvaluationSample.propertiesare the following.user.name=demo user.password=changeit service.name=iPlanetAMWebAgentService resource.name=http://www.example.com:80/banner.html action.name=GET
The client accesses an OpenAM server acting as the policy enforcement point, configured in a circle of trust with the OpenAM server acting as the policy decision point. When you set up the sample clients, you pointed them to an OpenAM server. For this example, configure that server to function as a policy enforcement point and also as a policy decision point.
In OpenAM console, browse to Configuration > Global > SAMLv2 SOAP Binding, and configure a new request handler with Key
/xacmlPdpEntityand Classcom.sun.identity.xacml.plugins.XACMLAuthzDecisionQueryHandler.Set up the circle of trust, and then create and import the metadata for the policy enforcement point and the policy decision point. In the following simplified example, both the policy enforcement point and policy decision point are hosted on the same OpenAM server. You could also set up the policy enforcement point and policy decision point on separate servers, as long as the circles of trust on both servers each include both the policy enforcement point and the policy decision point. You can set up the trust relationship between the two entities either by using the ssoadm command as shown below, or by using the
ssoadm.jsppage, which you can activate as described in OpenAM ssoadm.jsp in the Administration Guide.$ ssoadm create-cot --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --cot cot Circle of trust, cot was created. $ ssoadm create-metadata-templ --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --entityid xacmlPepEntity --xacmlpep /xacmlPepEntity --meta-data-file xacmlPep.xml --extended-data-file xacmlPep-extended.xml Hosted entity configuration was written to xacmlPep-extended.xml. Hosted entity descriptor was written to xacmlPep.xml. $ ssoadm import-entity --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --cot cot --meta-data-file xacmlPep.xml --extended-data-file xacmlPep-extended.xml Import file, xacmlPep.xml. Import file, xacmlPep-extended.xml. $ ssoadm create-metadata-templ --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --entityid xacmlPdpEntity --xacmlpep /xacmlPdpEntity --meta-data-file xacmlPdp.xml --extended-data-file xacmlPdp-extended.xml Hosted entity configuration was written to xacmlPdp-extended.xml. Hosted entity descriptor was written to xacmlPdp.xml. $ ssoadm import-entity --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --cot cot --meta-data-file xacmlPdp.xml --extended-data-file xacmlPdp-extended.xml Import file, xacmlPdp.xml. Import file, xacmlPdp-extended.xml.
Create a policy that allows authenticated users to perform an HTTP
GETon the sampleresource.idURL you configured, such ashttp://www.example.com:80/banner.html.See Configuring Policies in the Administration Guide for details.
After you have configured OpenAM and the properties files, run the sample client script, and observe the XACML request and response.
$ sh scripts/run-xacml-client-sample.sh Using properties file:xacmlClientSample sample properties: subject.id.datatype:urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:data-type:x500Name pdp.entityId:xacmlPdpEntity resource.servicename.datatype:http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string resource.id:http://www.example.com:80/banner.html resource.servicename:iPlanetAMWebAgentService action.id.datatype:http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string resource.id.datatype:http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string action.id:GET subject.category:urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject-category:access-subject pep.entityId:xacmlPepEntity subject.id:id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org testProcessRequest():xacmlRequest: <xacml-context:Request xmlns:xacml-context="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:context:schema:os" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:context:schema:os http://docs.oasis-open.org/xacml/access_control-xacml-2.0-context-schema-os.xsd"> <Subject SubjectCategory= "urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject-category:access-subject"> <Attribute AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id" DataType="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:data-type:x500Name" > <AttributeValue >id=demo,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org</AttributeValue> </Attribute> </Subject> <xacml-context:Resource> <Attribute AttributeId="ResourceId" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" > <AttributeValue>http://www.example.com:80/banner.html</AttributeValue> </Attribute> <Attribute AttributeId="urn:sun:names:xacml:2.0:resource:target-service" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" > <AttributeValue>iPlanetAMWebAgentService</AttributeValue> </Attribute> </xacml-context:Resource> <xacml-context:Action> <Attribute AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" > <AttributeValue>GET</AttributeValue> </Attribute> </xacml-context:Action> <xacml-context:Environment></xacml-context:Environment> </xacml-context:Request> testProcessRequest():xacmlResponse: <xacml-context:Response xmlns:xacml-context="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:context:schema:os" > <xacml-context:Result ResourceId="http://www.example.com:80/banner.html"> <xacml-context:Decision>Permit</xacml-context:Decision> <xacml-context:Status> <xacml-context:StatusCode Value="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:status:ok"> </xacml-context:StatusCode> <xacml-context:StatusMessage>ok</xacml-context:StatusMessage> <xacml-context:StatusDetail xmlns:xacml-context="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:context:schema:cd:04"> <xacml-context:StatusDetail/></xacml-context:StatusDetail> </xacml-context:Status> </xacml-context:Result> </xacml-context:Response>
Chapter 9. Using Fedlets in Java Web Applications
This chapter introduces OpenAM Fedlets, and shows how to use the Fedlet as part of your Java web application.
9.1. Creating & Installing a Java Fedlet
An OpenAM Fedlet is a small web application that can do federation in your service provider application with OpenAM acting as the identity provider. The Fedlet does not require an entire OpenAM installation alongside your application, but instead can redirect to OpenAM for single sign on, and to retrieve SAML assertions.
The process for creating and installing a Java Fedlet is divided into several procedures.
The OpenAM administrator running the identity provider server creates
a Fedlet.zip file for your service provider application,
and then sends you the .zip.
Before creating the Fedlet, create a Hosted Identity Provider if you have not already done so, using the test certificate for the signing key.
The single sign-on and single logout features that the Java Fedlet demonstrates do work with the Hosted Identity Provider you create starting from the Common Tasks page. The Java Fedlet Attribute Query and XACML Query tests require additional configuration, however.
See Procedure 9.3, "To Try the Fedlet Attribute Query" and Procedure 9.4, "To Try the Fedlet XACML Query" for details.
On the Common Tasks page of the OpenAM console, click Create Fedlet.
Note that the Circle of Trust includes your hosted identity provider, and that Identity Provider is set to your to hosted identity provider.
Name the Fedlet, and also set the Destination URL.
You can use the deployment URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/fedletas both the name and the destination URL.Click create to generate the Fedlet.zip file, such as
$HOME/openam/myfedlets/httpopenamexamplecom8080fedlet/Fedlet.zip.Provide the Fedlet to the service provider, or install it yourself to demonstrate the Fedlet's features.
Fedlet.zip includes the
fedlet.war archive corresponding to the identity
provider, and a README file.
The
fedlet.wararchive contains both the Fedlet as a demo web application, and also the files you use to include the Fedlet in your service provider application.The README file describes how to use the Fedlet.
Perform the following steps to try single sign-on and single logout tests. For the attribute query and XACML query tests, additional configuration is required.
Deploy the Fedlet in your web container.
$ unzip Fedlet.zip $ mv fedlet.war /path/to/tomcat/webapps
Browse to the Fedlet URL, and then click the links to set up the configuration directory in
$HOME/fedlet, where $HOME corresponds to the user running the web application container.Try one or more examples from the Fedlet home page to validate Fedlet setup.
After setting up OpenAM with the default subjects, you can login on the identity provider with user name
demoand passwordchangeit.
To try the Fedlet Attribute Query test, the Identity Provider
must be configured with the Attribute Authority (AttrAuth)
type and should sign responses. The Fedlet must be configured to deal with
signed responses. Furthermore, map the attributes to request in both the
Identity Provider and the Fedlet configurations.
Add the Attribute Authority type to the hosted Identity Provider.
On OpenAM where the Identity Provider is hosted, log in to OpenAM console as
amadmin.Under Federation > Entity Providers, select the Identity Provider, and then click New..., even though you plan to change the configuration rather than create a new provider.
Select the protocol of the provider: SAMLv2.
In the Create SAMLv2 Entity Provider page, do the following.
Set the Realm.
Set the Entity Identifier to the same entity identifier you selected in the previous screen.
In the Attribute Authority section, set the Meta Alias for example to
/attra, and set the Signing certificate alias and Encryption certificate alias values totest(to use the test certificate).Click Create to save your changes.
Disregard any error messages stating that the entity already exists.
AttrAuthnow appears in the list of Types for your Identity Provider.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, click the Identity Provider link to open the provider's configuration.
Make sure attributes for the query are mapped on the Identity Provider.
Under IDP > Attribute Mapper, add the following values to the Attribute Map if they are not yet present.
cn=cnsn=snuid=uid
Note
Make sure to use thread-safe code if you implement the AttributeAuthorityMapper. You can use the attributes on the HttpRequest instead of synchronizing them. The default AttributeAuthorityMapper uses an attribute on the HttpServletRequest to pass information to the AttributeQueryUtil.
Click Save to save your changes.
Create the Fedlet as described in Procedure 9.1, "To Create a Fedlet", making sure you map the attributes.
cn=cnsn=snuid=uid
This step creates a Fedlet with updated Identity Provider metadata. If you already created a Fedlet, either use a different name, or delete the existing Fedlet.
Deploy the new Fedlet .war as described in Procedure 9.2, "To Install the Fedlet as a Demo Application".
Edit the new Fedlet configuration to request signing and encryption, and replace the existing configuration in OpenAM with the edited configuration.
Copy the test key store from OpenAM, and prepare password files.
$ scp user@openam:/home/user/openam/openam/keystore.jks ~/fedlet/
The Fedlet uses password files when accessing the keystore. These password files contain encoded passwords, where the encoding is specific to the Fedlet.
To encode the password, use
fedletEncode.jsp.fedletEncode.jspis in the deployed Fedlet, for examplehttp://openam.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletEncode.jsp. The only password to encode for OpenAM's test keystore ischangeit, because the key store and private key passwords are both the same.Use the encoded value to create the password files as in the following example.
$ echo AQIC5BHNSjLwT303GqndmHbyYvzP9Tz7OAnK > ~/fedlet/.storepass $ echo AQIC5BHNSjLwT303GqndmHbyYvzP9Tz7OAnK > ~/fedlet/.keypass
Edit
~/fedlet/sp.xmlto use the test certificate for the attribute query.Change the following:
<RoleDescriptor xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:query="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:metadata:ext:query" xsi:type="query:AttributeQueryDescriptorType" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> </RoleDescriptor>To:
<RoleDescriptor xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:query="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:metadata:ext:query" xsi:type="query:AttributeQueryDescriptorType" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> <KeyDescriptor use="signing"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <KeyDescriptor use="encryption"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> <EncryptionMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc"> <xenc:KeySize xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#" >128</xenc:KeySize> </EncryptionMethod> </KeyDescriptor> </RoleDescriptor>Edit
~/fedlet/sp-extended.xmlto use the test certificate for the attribute query.Change the following, assuming your Circle of Trust is called
cot:<AttributeQueryConfig metaAlias="/attrQuery"> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantNameIDEncrypted"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>cot</Value> </Attribute> </AttributeQueryConfig>To:
<AttributeQueryConfig metaAlias="/attrQuery"> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantNameIDEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>cot</Value> </Attribute> </AttributeQueryConfig>In OpenAM Console, under Federation > Entity Providers, delete the existing configuration for your new Fedlet.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, click Import Entity... and import your updated Fedlet configuration.
This ensures OpenAM has the correct service provider configuration for your new Fedlet.
Restart the Fedlet or the container where it is deployed.
Try the Attribute Query test.
Access the Fedlet.
Try SSO with user name
demo, passwordchangeit.Click Fedlet Attribute Query, set the attributes in the Attribute Query page to match the mapped attributes, and then click Submit.
Check that you see the attribute values in the response.
To try the Fedlet XACML Query test, the Identity Provider
must have a policy configured, must be configured with the Policy Decision
Point (XACML PDP) type, and must have a SAMLv2 SOAP Binding
PDP handler configured.
Configure a policy on the hosted Identity Provider.
OpenAM uses the policy to make the decision whether to permit or deny access to a resource. For the purpose of the demonstration, configure a simple policy that allows all authenticated users HTTP GET access on
http://www.example.com/.Log in to OpenAM console as
amadmin.Under Access Control > realm-name > Policies, click New Policy...
Set Name: Test policy.
Click Rules > New... and set the following.
Service Type:
URL Policy AgentName:
http://www.example.com/Resource Name:
http://www.example.com/Actions: allow
GET
Then click Finish.
Click Subjects > New... and set the following.
Type:
Authenticated UsersName:
All authenticated users
Then click Finish.
Click OK to save the new Test policy.
Add the Policy Decision Point type to the Identity Provider.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, select the Identity Provider, and then click New..., even though you plan to change the configuration rather than create a new provider.
Select the protocol of the provider: SAMLv2.
In the Create SAMLv2 Entity Provider page, do the following.
Set the Realm.
Set the Entity Identifier to the entity identifier for the hosted Identity Provider.
In the XACML Policy Decision Point section, set the Meta Alias for example to
/pdp.Click Create to save your changes.
Disregard any error messages stating that the entity already exists.
XACML PDPnow appears in the list of Types for your identity provider.
Add the PDP handler for the SAMLv2 SOAP Binding.
Under Configuration > Global > SAMLv2 SOAP Binding, click New...
Set the new key to match the meta alias you used when adding the XACML PDP type to the Identity Provider configuration, for example
/pdp.Key:
/pdpClass:
com.sun.identity.xacml.plugins.XACMLAuthzDecisionQueryHandler
Click OK. (Your changes are not saved, yet.)
Click Save to actually save the new Key:Class pair.
Create the Fedlet as described in Procedure 9.1, "To Create a Fedlet".
This step creates a Fedlet with updated identity provider metadata. If you already created a Fedlet, either use a different name, or delete the existing Fedlet.
Deploy the new Fedlet .war as described in Procedure 9.2, "To Install the Fedlet as a Demo Application".
Try the XACML Query test.
Access the Fedlet.
Try SSO with user name
demo, passwordchangeit.Click XACML Attribute Query, set the Resource URL in the XACML Query page to
http://www.example.com/, and then click Submit.Check that you see the permit decision in the response.
9.2. Signing & Encryption For a Fedlet
By default when you create the Java Fedlet, signing and encryption are not configured. You can however set up OpenAM and the fedlet to sign and to verify XML signatures and to encrypt and to decrypt data such as SAML assertions. If you have tried the Attribute Query demonstration, then you have already configured the Fedlet to request signing and encryption using the test keys from the identity provider.
Enable signing and encryption for the Java Fedlet involves the following high level stages.
Before you create the Fedlet, configure the IDP to sign and encrypt data. See Federation > Entity Providers > IDP Name > Signing and Encryption in the OpenAM console.
For evaluation, you can use the
testcertificate delivered with OpenAM.Initially deploy and configure the Fedlet, but do not use the Fedlet until you finish.
On the Fedlet side set up a JKS keystore used for signing and encryption. For evaluation, you can use copy the
keystore.jksfile delivered with OpenAM. You can find the file under the configuration directory for OpenAM, such as$HOME/openam/openam/for a server instance with base URIopenam. The built-in keystore includes thetestcertificate.You must also set up
.storepassand.keypassfiles using thefedletEncode.jsppage, such ashttp://openam.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletEncode.jsp, to encode passwords on the Fedlet side. The passwords for the test key store and private key are bothchangeit.Configure the Fedlet to perform signing and encryption by ensuring the Fedlet has access to the key store, and by updating the SP metadata for the Fedlet.
Import the updated SP metadata into the IDP to replace the default Fedlet configuration.
Restart the Fedlet or container in which the Fedlet runs for the changes you made on the Fedlet side to take effect.
The FederationConfig.properties file specifies
the paths to the JKS keystore holding the signing or encryption keys for
the Fedlet, the keystore password file, and the private key password
file.
After setting up your keystore and password files as described above, edit the properties file in the configuration directory, such as
$HOME/fedlet/FederationConfig.properties, to point to the keystore and password files.Export the certificate to use for signing and encryption purposes.
$ keytool -export -rfc -keystore keystore.jks -alias test Enter keystore password: -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q==
Edit the standard metadata file for the Fedlet, such as
$HOME/fedlet/sp.xml, to include the certificate in KeyDescriptor elements, that are children of the SPSSODescriptor element.<EntityDescriptor xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata" entityID="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet"> <SPSSODescriptor AuthnRequestsSigned="true" WantAssertionsSigned="true" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> <KeyDescriptor use="signing"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <KeyDescriptor use="encryption"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> <EncryptionMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc"> <xenc:KeySize xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#"> 128 </xenc:KeySize> </EncryptionMethod> </KeyDescriptor> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletSloRedirect" ResponseLocation="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletSloRedirect" /> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST" Location="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletSloPOST" ResponseLocation="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletSloPOST" /> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP" Location="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletSloSoap" /> <NameIDFormat> urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient </NameIDFormat> <AssertionConsumerService index="0" isDefault="true" Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST" Location="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletapplication" /> <AssertionConsumerService index="1" Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Artifact" Location="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/fedletapplication" /> </SPSSODescriptor> <RoleDescriptor xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:query="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:metadata:ext:query" xsi:type="query:AttributeQueryDescriptorType" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> </RoleDescriptor> <XACMLAuthzDecisionQueryDescriptor WantAssertionsSigned="false" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol" /> </EntityDescriptor>Edit the extended metadata file for the Fedlet, such as
$HOME/fedlet/sp-extended.xml, to set the certificate alias names to the alias for the Fedlet certificate, and thewant*Signedandwant*Encryptedvalues totrue.If you reformat the file, take care not to add white space around string values in elements.
<EntityConfig xmlns="urn:sun:fm:SAML:2.0:entityconfig" xmlns:fm="urn:sun:fm:SAML:2.0:entityconfig" hosted="1" entityID="http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet"> <SPSSOConfig metaAlias="/sp"> <Attribute name="description"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthOn"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthUser"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthPassword"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="autofedEnabled"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="autofedAttribute"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="transientUser"> <Value>anonymous</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAdapter"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAdapterEnv"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="fedletAdapter"> <Value>com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultFedletAdapter</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="fedletAdapterEnv"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAccountMapper"> <Value>com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultLibrarySPAccountMapper</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="useNameIDAsSPUserID"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAttributeMapper"> <Value>com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultSPAttributeMapper</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAuthncontextMapper"> <Value>com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultSPAuthnContextMapper</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAuthncontextClassrefMapping"> <Value >urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport|0|default</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spAuthncontextComparisonType"> <Value>exact</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="attributeMap"> <Value>*=*</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="saml2AuthModuleName"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="localAuthURL"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="intermediateUrl"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="defaultRelayState"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="appLogoutUrl"> <Value>http://www.example.com:8080/fedlet/logout</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="assertionTimeSkew"> <Value>300</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantAttributeEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantAssertionEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantNameIDEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantPOSTResponseSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantArtifactResponseSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantLogoutRequestSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantLogoutResponseSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantMNIRequestSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantMNIResponseSigned"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="responseArtifactMessageEncoding"> <Value>URI</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>fedlet-cot</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="saeAppSecretList"> </Attribute> <Attribute name="saeSPUrl"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="saeSPLogoutUrl"> </Attribute> <Attribute name="ECPRequestIDPListFinderImpl"> <Value>com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.ECPIDPFinder</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="ECPRequestIDPList"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="ECPRequestIDPListGetComplete"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="enableIDPProxy"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="idpProxyList"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="idpProxyCount"> <Value>0</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="useIntroductionForIDPProxy"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="spSessionSyncEnabled"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="relayStateUrlList"> </Attribute> </SPSSOConfig> <AttributeQueryConfig metaAlias="/attrQuery"> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantNameIDEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>fedlet-cot</Value> </Attribute> </AttributeQueryConfig> <XACMLAuthzDecisionQueryConfig metaAlias="/pep"> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthOn"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthUser"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="basicAuthPassword"> <Value></Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantXACMLAuthzDecisionResponseSigned"> <Value>false</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantAssertionEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>fedlet-cot</Value> </Attribute> </XACMLAuthzDecisionQueryConfig> </EntityConfig>
In OpenAM console delete the original SP entity configuration for the Fedlet, and then import the updated metadata for the new configuration into OpenAM on the IDP side.
Restart the Fedlet or the container in which it runs in order for the Fedlet to pick up the changes to the configuration properties and the metadata.
9.3. Customizing a Java Fedlet
You can customize the Java Fedlet to perform many of the SAML 2.0 service provider operations. The Java Fedlet has the SAML 2.0 capabilities identified in the table in the Administration Guide, Fedlet Support for SAML 2.0 Features in the Administration Guide.
The Fedlet includes the following files that you use when building your own service provider application based on the demo web application, including a set of JavaServer Pages (JSP) examples.
conf/Configuration files copied to
$HOME/fedletwhen you first deploy and configure the Fedlet. When deploying your application, you can move these to an alternate location passed to the Java virtual machine for the web application container at startup. For example, if you store the configuration under/export/fedlet/, then you could pass the following property to the JVM.-Dcom.sun.identity.fedlet.home=/export/fedlet/conf
You do not need to include these files in your application.
fedletAttrQuery.jsp,fedletAttrResp.jspSample SAML attribute query and response handlers.
fedletEncode.jspUtility JSP to encode a password, such as the password used to protect a Java keystore
fedletSampleApp.jsp,index.jspDemo application. You can remove these before deployment to replace them with your application.
fedletXACMLQuery.jsp,fedletXACMLResp.jspSample SAML XACML query and response handlers.
logout.jspUtility page to perform single log out
saml2/jsp/JSPs to initiate single sign on and single logout, and to handle errors, and also a JSP for obtaining Fedlet metadata,
saml2/jsp/exportmetadata.jspWEB-INF/classes/Localized Java properties files for strings used in the Fedlet user interface
WEB-INF/lib/Fedlet libraries required by your application
WEB-INF/web.xmlFedlet web application configuration, showing how JSPs map to URLs used in the Fedlet. Add mappings for your application before deployment.
In the
web.xmlmappings, your application must be mapped to/fedletapplication, as this is the assertion consumer URL set in the Fedlet metadata.<servlet> <servlet-name>yourApp</servlet-name> <jsp-file>/fedletSampleApp.jsp</jsp-file> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>yourApp</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/fedletapplication</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Follow these steps for a very simple demonstration of how to customize the Fedlet.
Backup
fedletSampleApp.jsp.$ cd /path/to/tomcat/webapps/fedlet/ $ cp fedletSampleApp.jsp fedletSampleApp.jsp.orig
Edit
fedletSampleApp.jspto reduce it to a single redirection tomyapp.jsp. An implementation of the <html> element of the file follows below.<html> <head> <title>Fedlet Sample Application</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1" /> </head> <body> <% // BEGIN : following code is a must for Fedlet (SP) side application Map map; try { // invoke the Fedlet processing logic. this will do all the // necessary processing conforming to SAMLv2 specifications, // such as XML signature validation, Audience and Recipient // validation etc. map = SPACSUtils.processResponseForFedlet(request, response); response.sendRedirect("myapp.jsp"); } catch (SAML2Exception sme) { SAMLUtils.sendError(request, response, response.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "failedToProcessSSOResponse", sme.getMessage()); return; } catch (IOException ioe) { SAMLUtils.sendError(request, response, response.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "failedToProcessSSOResponse", ioe.getMessage()); return; } catch (SessionException se) { SAMLUtils.sendError(request, response, response.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "failedToProcessSSOResponse", se.getMessage()); return; } catch (ServletException se) { SAMLUtils.sendError(request, response, response.SC_BAD_REQUEST, "failedToProcessSSOResponse", se.getMessage()); return; } // END : code is a must for Fedlet (SP) side application %> </body> </html>Add a
myapp.jsppage to the Fedlet, such as the following.<html> <head> <title>My Application</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html" /> </head> <body> <h1>My Application</h1> <p>After you change the <code>fedletSampleApp.jsp</code>, all it does is redirect to this home page after successful login.</p> </body> </html>
Browse to the Fedlet URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/fedlet/, and try one of the login methods.After login you are redirected to
myapp.jsp.
9.3.1. Performing Single Sign-On
The Java Fedlet includes a JSP file,
saml2/jsp/fedletSSOInit.jsp, that you can call to
initiate single sign-on from the Fedlet (SP) side. The Fedlet home page,
index.jsp, calls this page when the user does
Fedlet-initiated single sign-on.
When calling this JSP, the parameters to use are those also used by
saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp in OpenAM. Those parameters are
described in the Administration Guide section,
spSSOInit.jsp Parameters in the Administration Guide.
For IDP-initiated single sign-on, call the appropriate page on the
Identity Provider. OpenAM's page is described in the
Administration Guide section,
idpSSOInit.jsp Parameters in the Administration Guide.
After single sign-on, the user-agent is directed by default to the
assertion consumer URI set in the Fedlet metadata, which by default is
/fedletapplication. Also by default that URI points to
the JSP, fedletSampleApp.jsp
9.3.2. Performing Single Logout
The Java Fedlet includes a JSP file,
saml2/jsp/spSingleLogoutInit.jsp, that you can call to
initiate single logout from the Fedlet (SP) side. The Fedlet assertion
consumer page, fedletSampleApp.jsp, calls this when
the user does Fedlet-initiated single logout.
When calling this JSP, the parameters to use are those also used by
saml2/jsp/spSingleLogoutInit.jsp in OpenAM. Those
parameters are described in the Administration Guide
section, spSingleLogoutInit.jsp Parameters in the Administration Guide.
For IDP-initiated single logout, call the appropriate page on the
Identity Provider. OpenAM's page is described in the
Administration Guide section,
idpSingleLogoutInit.jsp Parameters in the Administration Guide.
Set the RelayState parameter when initiating logout
to redirect the user-agent appropriately when the process is complete.
9.3.3. Performing Attribute Queries
As seen in the procedure, Procedure 9.3, "To Try the Fedlet Attribute Query", an attribute query allows the Fedlet to get profile information about a subject from the Attribute Authority. The Fedlet must be configured to deal with responses from the Attribute Authority, including configuration for signing and encryption. Also, an Identity Provider and Attribute Authority is likely to share only those attributes that the Fedlet absolutely requires to provide service, such as, for example, a name to customize a page. The attributes must then be mapped in the Attribute Authority and Fedlet metadata.
The Java Fedlet includes a JSP file,
fedletAttrQuery.jsp, which is used in the procedure
described above to prepare an attribute query using the transient subject
identifier obtained during single sign-on. The
fedletAttrQuery.jsp also supports using the Subject
name from an X.509 identity certificate.
Another JSP file, fedletAttrResp.jsp, sends the
query to the Attribute Authority using
com.sun.identity.saml2.profile.AttributeQueryUtil.html.getAttributesForFedlet(),
and if successful processes the result, which is a
java.util.Map of the attribute types and their
values.
9.3.4. Performing XACML Queries
As seen in the procedure, Procedure 9.4, "To Try the Fedlet XACML Query", a XACML query allows the Fedlet to request a policy decision from a XACML PDP. You can configure OpenAM to respond to such queries as described in that procedure.
The Java Fedlet includes a JSP file,
fedletXACMLQuery.jsp, which is used in the procedure
described above to prepare a XACML query, identifying a resource URL and a
type of HTTP operation to perform, and specifying the subject identifier
obtained during single sign-on.
Another JSP file, fedletXACMLResp.jsp, sends the
query to the XACML PDP using
com.sun.identity.saml2.profile.XACMLQueryUtil.getPolicyDecisionForFedlet(),
and if successful processes the result, which is a
java.lang.String representing the decision, such as
Permit if the decision is to allow access, or
Deny if the decision is to deny access.
Chapter 10. Using Fedlets in .NET Applications
This chapter explains how to use the Fedlet in your .NET application. You must configure the OpenAM .NET Fedlet to work with the identity provider.
Before you try the .NET Fedlet with OpenAM, create a hosted identity
provider in a Circle of Trust to which you plan to add the Fedlet. You can
perform these steps using the Create Hosted Identity Provider wizard on the
Common Tasks page of the OpenAM console. The .NET Fedlet demo requires a
signing key for the Identity Provider. For evaluation, use the
test certificate installed with OpenAM.
Before configuring the .NET Fedlet, prepare Microsoft IIS 7 with ASP.NET v4. Import and configure access on Windows to any certificates and private keys the .NET Fedlet needs. Also prepare Windows to allow the .NET Fedlet to log messages to Windows Event Log.
This chapter covers the following topics.
Microsoft Internet Information Server must be installed with ASP.NET v4 in order to support the .NET Fedlet application. The following steps describe how to set up IIS on Windows Server 2008 R2 to support the .NET Fedlet.
Logon to the Windows server as Administrator.
In Server Manager, add the IIS 7 role to install IIS 7.
When adding the IIS 7 role, the wizard presents you with additional installation options. Under Application Development, select ASP.NET.
Under Roles > Web Server (IIS) > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager > server-name > Application Pools, change .NET Framework Version for your application pools to v4.0.
OpenAM ships with a test key pair unpacked during deployment into a Java Key Store under OpenAM's configuration directory. You can import this key pair on Windows, so that the .NET Fedlet demo can use the certificate and private key to perform signing, encryption, and logging in Windows Event Log. The following steps describe how to get the key pair imported and available to the .NET Fedlet on Windows Server 2008 R2.
See Windows documentation for instructions on using your own key pair when you plan to deploy the .NET Fedlet in production.
Move the key pair from the Java Key Store to a PKCS#12 key store.
You can use the Java keytool command to perform this step on the system where OpenAM is installed if you do not have the command installed on the Windows system.
$ keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore.jks -destkeystore keystore.p12 -srcstoretype JKS -deststoretype PKCS12 -srcstorepass changeit -deststorepass changeit -srcalias test -destalias test -srckeypass changeit -destkeypass changeit -noprompt
If necessary, copy the resulting
keystore.p12file to the Windows system.Open Microsoft Management Console.
Select Start > Run, then enter
mmc.In the console, add the Certificates snap-in for the Local Computer store.
Select Certificates > Personal > More Actions > All Tasks > Import...
In the Certificate Import Wizard select the
keystore.p12file to import the keys. The password ischangeit.Also select Mark this key as exportable.
Accept other defaults until you click Finish.
In Certificates > Personal > Certificates > test > More Actions > Properties, make sure the Friendly name is test.
Certificates > Personal > Certificates > test > More Actions > All Tasks > Manage Private Keys, add access for Everyone (or at least the IIS 7 account, IUSR).
After importing the key pair for the .NET Fedlet, edit the registry to add the key that allows the .NET Fedlet to write to the Windows Event Log, and create an Event Log Custom View for the .NET Fedlet.
Edit the Windows registry.
Open the Windows registry editor.
Select Start > Run, then enter
regedit.Browse to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Application.Add a new key named
Fedlet.Right-click Application > New > Key.
Close the Windows registry editor.
Add the Event Log Custom View.
Select Start > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer.
Select Action > Create Custom View...
Select all Event level options.
Select By source, and then in the drop-down menu, select Fedlet.
Click OK to finish creating the custom view.
When the .NET Fedlet logs messages, you can read them under Event Viewer (Local) > Custom Views > Fedlet.
Follow these steps to configure and install the .NET Fedlet demo application. These instructions are sufficient to test single sign-on and single logout. If you want to try the attribute query test, see the procedure, Procedure 10.5, "To Try the .NET Fedlet Attribute Query".
Download the .NET Fedlet (
Fedlet-aspnet.zip) from the OpenAM nightly builds page. Contact info@forgerock.com if you need .NET Fedlet support.Next, unpack the contents of the .zip file into a working directory.
bin\This folder contains the
Fedlet.dlllibrary, that you copy to your application'sbin\folder.conf\This folder contains the templates you edit to prepare your Fedlet configuration, including the identity provider and Fedlet (SP) metadata for federation. The completed configuration files belong in your application's
App_Data\folder.readme.txtThis file describes how to set up and configure .NET Fedlets.
SampleApp\This folder contains the demo application.
(Optional) To ensure the .NET Fedlet can write messages to Windows Event Log, edit
SampleApp\Web.config, to make sure that the certificate alias reflects the key pair installed in the Windows Local Computer Store and available to the IIS 7 application pool user.Default settings set the log level to write informational messages, and use the test key pair shipped with OpenAM.
<appSettings> <add key="fedletLogLevel" value="info" /> <add key="fedletMutualAuthCertAlias" value="test" /> </appSettings>The key pair specified by the
fedletMutualAuthCertAliasis used for SSL Mutual Certificate authentication when the certificate based authentication is required by and configured for the web container where the Identity Provider is deployed.Edit the template files in the
SampleApp\App_Data\folder based on where you deploy the Fedlet demo application, and on how your identity provider is configured.Edit
fedlet.cotto setcot-nameto the name of the Circle of Trust, and to setsun-fm-trusted-providersto include the entity ID of the identity provider, and the entity ID of the Fedlet service provider.Edit
sp.xmlandsp-extended.xmlto configure the entity IDs, URLs, and Circle of Trust names to correspond to your sample application.
Example files for a .NET Fedlet deployed at
http://openam.example.com/fedletand an Identity Provider in OpenAM deployed athttp://openam.example.com:8080/openamare available on the OpenAM Community Site. The Circle of Trust name in the examples iscot, and both entities use the test key pair.Export the identity provider metadata from OpenAM, and copy the resulting
idp.xmlandidp-extended.xmlmetadata to the FedletSampleApp\App_Data\folder.$ ssoadm create-metadata-templ --entityid "http://openam.example.com:8080/openam" --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --identityprovider /idp --meta-data-file idp.xml --extended-data-file idp-extended.xml --idpscertalias test Hosted entity configuration was written to idp-extended.xml. Hosted entity descriptor was written to idp.xml.
You can also perform this step using
ssoadm.jspif it is enabled.Register the Fedlet with OpenAM as a remote service provider using the
sp.xmlandsp-extended.xmlmetadata.$ ssoadm import-entity --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --cot fedlet-cot --meta-data-file sp.xml --extended-data-file sp-extended.xml Import file, sp.xml. Import file, sp-extended.xml.
You can also perform this step in OpenAM console by selecting Federation > Entity Providers > Import Entity...
Deploy the .NET Fedlet demo application in IIS.
Add read and execute permissions for
Everyoneto theSampleAppfolder.Add the .NET Fedlet as an application.
Select IIS console > server-name > Sites > Default Web Site > View Applications > Add Applications.
In the window to add the application, Alias is the deployment URI to the .NET Fedlet, so
fedletfor/fedlet. Physical path is the file system path to theSampleAppfolder.Restart IIS.
Try the demo application links to run .NET Fedlet initiated single sign-on.
At first try the .NET Fedlet as Administrator using Internet Explorer on the Windows system where you installed the Fedlet. This allows you to see more explicit error messages should any such messages appear.
Access the .NET Fedlet.
Try SSO with user name
demo, passwordchangeit.If you instead get HTTP 500.19 error status, ASP.NET did not register correctly. Register ASP.NET v4 manually as Administrator.
PS C:\> C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\aspnet_regiis.exe -i Start installing ASP.NET (4.0.30319). .... Finished installing ASP.NET (4.0.30319).
To try the .NET Fedlet Attribute Query test, the Identity Provider
must be configured with the Attribute Authority (AttrAuth)
type and should sign responses. The Fedlet must be configured to deal with
signed and encrypted responses. Furthermore, map the attributes to request
in both the Identity Provider and the Fedlet configurations.
Add the Attribute Authority type to the hosted Identity Provider.
On OpenAM where the Identity Provider is hosted, log in to OpenAM console as
amadmin.Under Federation > Entity Providers, select the Identity Provider, and then click New..., even though you plan to change the configuration rather than create a new provider.
Select the protocol of the provider: SAMLv2.
In the Create SAMLv2 Entity Provider page, do the following.
Set the Realm.
Set the Entity Identifier to the same entity identifier you selected in the previous screen.
In the Attribute Authority section, set the Meta Alias for example to
/attra, and set the Signing certificate alias and Encryption certificate alias values totest(to use the test certificate).Click Create to save your changes.
Disregard any error messages stating that the entity already exists.
AttrAuthnow appears in the list of Types for your Identity Provider.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, click the Identity Provider link to open the provider's configuration.
Make sure attributes for the query are mapped on the Identity Provider.
Under IDP > Attribute Mapper, add the following values to the Attribute Map if they are not yet present.
cn=cnsn=snuid=uid
Click Save to save your changes.
As described in the procedure, Procedure 10.4, "To Install the .NET Fedlet as a Demo Application", export the Identity Provider metadata from OpenAM, and copy the resulting
idp.xmlandidp-extended.xmlmetadata to the .NET FedletSampleApp\App_Data\folder.Update the .NET Fedlet configuration and metadata.
(Optional) To ensure the .NET Fedlet can write messages to Windows Event Log, edit
SampleApp\Web.config, to make sure that the certificate alias reflects the key pair installed in the Windows Local Computer Store and available to the IIS 7 application pool user.Default settings set the log level to write informational messages, and use the test key pair shipped with OpenAM.
<appSettings> <add key="fedletLogLevel" value="info" /> <add key="fedletMutualAuthCertAlias" value="test" /> </appSettings>The key pair specified by the
fedletMutualAuthCertAliasis used for SSL Mutual Certificate authentication when the certificate based authentication is required by and configured for the web container where the Identity Provider is deployed.Edit the .NET Fedlet metadata files in
SampleApp\App_Data,fedlet.cot,sp.xml, andsp-extended.xmlto replace the following if you have not already done so.Replace
FEDLET_COTwith the name of the Circle of Trust.Replace
FEDLET_ENTITY_IDwith the entity identifier such ashttp://openam.example.com/fedlet.Replace
FEDLET_DEPLOY_URIwith the URL to the .NET Fedlet, generally theh same as the entity identifier.Replace
IDP_ENTITY_IDwith the entity identifier of the Identity Provider such ashttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam.
Set up signing and encryption in
sp.xmlfor the .NET Fedlet.The Attribute Authority encrypts the response with the Fedlet's public key, and the Fedlet decrypts the response with its private key. You can set up both signing and encryption by adding a <KeyDescriptor> as the first element in the <SSODescriptor>, as in the following example.
<KeyDescriptor use="signing"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <KeyDescriptor use="encryption"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> <EncryptionMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc"> <xenc:KeySize xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#" >128</xenc:KeySize> </EncryptionMethod> </KeyDescriptor>For the Attribute Query feature, add a <RoleDescriptor> to the <EntityDescriptor> after the <SSODescriptor>. The <RoleDescriptor> describes the certificates that are used for signing and encryption.
<RoleDescriptor xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:query="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:metadata:ext:query" xsi:type="query:AttributeQueryDescriptorType" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> <KeyDescriptor use="signing"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <KeyDescriptor use="encryption"> <ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <ds:X509Data> <ds:X509Certificate> MIICQDCCAakCBEeNB0swDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNh bGlmb3JuaWExFDASBgNVBAcTC1NhbnRhIENsYXJhMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNTdW4xEDAOBgNVBAsTB09w ZW5TU08xDTALBgNVBAMTBHRlc3QwHhcNMDgwMTE1MTkxOTM5WhcNMTgwMTEyMTkxOTM5WjBnMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECBMKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEUMBIGA1UEBxMLU2FudGEgQ2xhcmExDDAK BgNVBAoTA1N1bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHT3BlblNTTzENMAsGA1UEAxMEdGVzdDCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0B AQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEArSQc/U75GB2AtKhbGS5piiLkmJzqEsp64rDxbMJ+xDrye0EN/q1U5Of+ RkDsaN/igkAvV1cuXEgTL6RlafFPcUX7QxDhZBhsYF9pbwtMzi4A4su9hnxIhURebGEmxKW9qJNY Js0Vo5+IgjxuEWnjnnVgHTs1+mq5QYTA7E6ZyL8CAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQB3Pw/U QzPKTPTYi9upbFXlrAKMwtFf2OW4yvGWWvlcwcNSZJmTJ8ARvVYOMEVNbsT4OFcfu2/PeYoAdiDA cGy/F2Zuj8XJJpuQRSE6PtQqBuDEHjjmOQJ0rV/r8mO1ZCtHRhpZ5zYRjhRC9eCbjx9VrFax0JDC /FfwWigmrW0Y0Q== </ds:X509Certificate> </ds:X509Data> </ds:KeyInfo> <EncryptionMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes128-cbc"> <xenc:KeySize xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#" >128</xenc:KeySize> </EncryptionMethod> </KeyDescriptor> </RoleDescriptor>Edit
sp-extended.xmlfor your configuration.Set the signing and encryption certificate aliases.
<Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute>
Update the attribute map in to coincide with the mapped attributes on the Identity Provider.
<Attribute name="attributeMap"> <Value>cn=cn</Value> <Value>sn=sn</Value> <Value>uid=uid</Value> </Attribute>
Add a logout URL.
<Attribute name="appLogoutUrl"> <Value>http://openam.example.com/fedlet/logout.aspx</Value> </Attribute>
Add an <AttributeQueryConfig> to the <EntityDescriptor> that references the certificate aliases.
<AttributeQueryConfig metaAlias="/attrQuery"> <Attribute name="signingCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="encryptionCertAlias"> <Value>test</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="wantNameIDEncrypted"> <Value>true</Value> </Attribute> <Attribute name="cotlist"> <Value>cot</Value> </Attribute> </AttributeQueryConfig>Check your work by comparing and contrasting your configuration with the sample configuration files on the OpenAM Community Site.
In OpenAM console where the hosted Identity Provider is configured, under Federation > Entity Providers delete the .NET Fedlet configuration if it exists.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, click Import Entity..., and then import the .NET Fedlet configuration using your
sp.xmlandsp-extended.xmlmetadata files.
Deploy the .NET Fedlet as described in the deploy step of the procedure, Procedure 10.4, "To Install the .NET Fedlet as a Demo Application", making sure you restart IIS.
Try the .NET Fedlet Attribute Query test.
At first try the .NET Fedlet as Administrator using Internet Explorer on the Windows system where you installed the Fedlet. This allows you to see more explicit error messages should any such messages appear.
Access the .NET Fedlet.
Try SSO with user name
demo, passwordchangeit.If you instead get HTTP 500.19 error status, ASP.NET did not register correctly. Register ASP.NET v4 manually as Administrator.
PS C:\> C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\aspnet_regiis.exe -i Start installing ASP.NET (4.0.30319). .... Finished installing ASP.NET (4.0.30319).
At the bottom of the web page, et the attributes in the Attribute Query page to match the mapped attributes, and then click Send.
Check that you see the attribute values in the response page.
(Optional) Adapt the SSL/TLS protocol version used by the .NET Fedlet client to the needs of your deployment. The default setting for .NET v4 is to use either SSLv3 or TLSv1 depending on what the remote peer supports.
For IIS 6 on Windows Server 2003, see the Windows Server documentation on TLS/SSL Tools and Settings.
For IIS 7.5 on Windows Server 2008 R2, also consider the explanation in an online article, Enable TLS 1.2 Ciphers in IIS 7.5, Server 2008 R2.
For reference, Microsoft Developer Network has an article describing Cipher Suites in Schannel.
Chapter 11. Using Secure Attribute Exchange
Most deployments can rely on OpenAM to handle authentication and provide identity assertions. Not only does OpenAM support a wide variety of authentication scenarios out of the box, but OpenAM also makes it possible to add custom authentication modules. Furthermore OpenIG lets you integrate legacy systems into your access management deployment.
In a deployment where you need OpenAM to act as a SAML 2.0 gateway to a legacy application that serves as an identity provider, you can use OpenAM Secure Attribute Exchange (SAE). On the identity provider side, SAE lets OpenAM retrieve the information needed to create assertions from an external authentication service, bypassing OpenAM authentication and trusting the external service as the authoritative source of authentication. On the service provider side, SAE lets OpenAM securely provide attributes to an application that makes its own policy decision based on the attributes rather than rely on OpenAM for the policy decision.
When you use SAE on the identity provider side, an external application
acts as the authoritative source of authentication. After a user authenticates
successfully, the application lets OpenAM know to create a session by sending
a secure HTTP GET or POST to OpenAM that asserts the identity of the user.
OpenAM processes the assertion to create a session for the user. If the user
is already authenticated and comes back to access the application, the
application sends a secure HTTP POST to OpenAM to assert both the user's
identity and also any necessary attributes related to the user. OpenAM
processes the assertion to create the session for the user and populate the
attributes in the user's session. When the user logs out, the external
authentication application can initiate single logout from the identity
provider OpenAM server by sending the sun.cmd=logout
attribute to OpenAM using SAE.
On the service provider side OpenAM communicates using SAML 2.0 with OpenAM on the identity provider side. OpenAM can use SAE to transmit attributes to an application through a secure HTTP POST.
SAE relies either on shared keys and symmetric encryption, or on public and private keys and asymmetric encryption to protect attributes communicated between OpenAM and external applications.
OpenAM ships with sample JSPs that demonstrate secure attribute exchange. In order to try the sample, you must set up an OpenAM circle of trust to include an identity provider and a service provider, install the SDK sample web application on each provider and then configure the providers appropriately as described in this chapter to secure communications with the sample SAE applications on both the identity provider and service provider sides.
11.1. Installing the Samples
Set up an OpenAM server as an identity provider, and another as a
service provider, connecting the two in a circle of trust called
samplesaml2cot. Configure both the hosted providers and
also the remote providers as described in Setting Up SAML
2.0 SSO in the Administration Guide. This chapter assumes you set up the hosted
identity provider at http://idp.example.com:8080/openam
and the hosted service provider at
http://sp.example.com:8080/openam. Use Common Tasks >
Test Federation Connectivity in OpenAM console to make sure Federation is
working before you add secure attribute exchange applications that rely
on functioning SAML 2.0 communications between the providers.
Set up the sample web application as described in Installing OpenAM
Client SDK Samples, both on the identity provider side
and also on the service provider side. The SAE samples are found under
/saml2/sae where you installed the samples.
saeIDPApp.jsp is the identity provider side external
application. saeSPApp.jsp is the service provider side
external application.
11.2. Preparing to Secure SAE Communications
In order for SAE to be secure, you must both set up a trust relationship between the application on the identity provider side and the OpenAM server acting as identity provider, and also set up a trust relationship between the application on the service provider side and the OpenAM server acting as the service provider. These trust relationships can be based on a shared secret and symmetric encryption, or on public and private key pairs and asymmetric encryption. The trust relationships on either side are independent. In other words you can for example use a shared secret on the identity provider side and certificates on the service provider side if you chose.
When using symmetric encryption, you must define a shared secret
string used both for the application and the provider. The sample uses
secret12 as the shared secret. To simplify
configuration, the sample uses the same shared secret, and thus
symmetric encryption, for both trust relationships.
When using symmetric encryption, you must also use the encoded
version of your shared secret. To get the encoded version of a shared
secret string, use the encode.jsp page on the
provider, as in
http://idp.example.com:8080/openam/encode.jsp and
http://sp.example.com:8080/openam/encode.jsp. An
encoded version of secret12 looks something like
AQICEcFhDWmb6sVmMuCJuVh43306HVacDte9.
When using asymmetric encryption, you must obtain a public-private key pair for the application, and store the keys in a key store on the application side. Also store the public key from OpenAM which is acting as the provider in the application's key store. Make note of the certificate aliases for your application's private key, and for OpenAM's public key. Also note the path to the key store for your application, the key store password, and the private key password.
11.3. Securing the Identity Provider Side
This configuration uses the default sample settings with a shared
secret of secret12, without encryption of the
attributes.
Login as
amadminto the OpenAM server console where you set up the hosted identity provider (IDP).As the sample includes a
branchattribute not found in user profiles by default, under Access Control > Realm Name > Authentication > All Core Settings..., set User Profile to Ignored, and then Save your work.Under Federation > Entity Providers, click the name for the Hosted IDP in order to access the IDP configuration.
Under Assertion Processing > Attribute Mapper, add both
mail=mailandbranch=branchto the attribute map, and then Save your work.Under Advanced > SAE Configuration, make sure the IDP URL reflects an endpoint on the IDP such as
http://idp.example.com:8080/openam/idpsaehandler/metaAlias/idp, and then Save your work.Also under Advanced > SAE Configuration > Application Security Configuration, add the URL value for the kind of encryption you are using, and then Save your work.
When using the defaults, the value is something like
url=http://idp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeIDPApp.jsp|type=symmetric|secret=encoded-secret, where the OpenAM SDK sample web application is deployed on the IDP side with context root/samplesand the encoded-secret is something likeAQICEcFhDWmb6sVmMuCJuVh43306HVacDte9.If you use a different mechanism to secure the communications between the SAE application and the provider, read the online help in the console to see how to construct your URL value.
Under Federation > Entity Providers, click the name for the Remote SP in order to access the SP configuration on the IDP side.
Under Assertion Processing > Attribute Mapper, add both
mail=mailandbranch=branchto the attribute map, and then Save your work.Under Advanced > SAE Configuration, make sure the SP URL reflects an endpoint on the SP such as
http://sp.example.com:8080/openam/spsaehandler/metaAlias/sp, and then Save your work.Also under Advanced > SAE Configuration, add the URL to the sample SAE application as the SP Logout URL such as
http://sp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeSPApp.jsp, and then Save your work.
11.4. Securing the Service Provider Side
This configuration uses the default sample setting of symmetric
encryption, with a shared secret of secret12.
Login as amadmin to the OpenAM server console where
you set up the hosted service provider (SP).
As the sample includes a
branchattribute not found in user profiles by default, under Access Control > Realm Name > Authentication > All Core Settings..., set User Profile to Ignored, and then Save your work.Under Federation > Entity Providers, click the name for the Hosted SP in order to access the SP configuration.
Under Assertion Processing > Attribute Mapper, add both
mail=mailandbranch=branchto the attribute map, and then Save your work.Also under Assertion Processing > Attribute Mapper > Auto Federation, select Enabled, set the Attribute to
mail, and then Save your work.Under Advanced > SAE Configuration, make sure the SP URL reflects an endpoint on the SP such as
http://sp.example.com:8080/openam/spsaehandler/metaAlias/sp, and then Save your work.Furthermore, under Advanced > SAE Configuration, add the URL to the sample SAE application as the SP Logout URL such as
http://sp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeSPApp.jsp, and then Save your work.Also under Advanced > SAE Configuration > Application Security Configuration, add the URL value for the kind of encryption you are using, and then Save your work.
When using the defaults, the value is something like
url=http://sp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeSPApp.jsp|type=symmetric|secret=encoded-secret, where the OpenAM SDK sample web application is deployed on the IDP side with context root/samplesand the encoded-secret is something likeAQICkX24RbZboAVgr2FG1kWoqRv1zM2a6KEH.If you use a different mechanism to secure the communications between the SAE application and the provider, read the online help in the console to see how to construct your URL value.
11.5. Trying It Out
After completing the setup described above, navigate to the IDP side
SAE application, for example at
http://idp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeIDPApp.jsp.
Make sure you set at least the "SP App URL" and "SAE URL on IDP end" to fit your configuration. For example if you used the settings above then use the following values.
- SP App URL
http://sp.example.com:8080/samples/saml2/sae/saeSPApp.jsp- SAE URL on IDP end
http://idp.example.com:8080/openam/idpsaehandler/metaAlias/idp
Check the settings, and then click Generate URL to open the Secure Attributes Exchange IDP APP SAMPLE page.
Click the ssourl link in the page to start the
exchange.
The resulting web page shows the attributes exchanged, including the mail and branch values used. The text of that page is something like the following.
SAE SP APP SAMPLE Secure Attrs : mail testuser@foo.com sun.idpentityid http://idp.example.com:8080/openam sun.spentityid http://sp.example.com:8080/openam branch mainbranch sun.authlevel 0
Chapter 12. Using the OpenAM C API
This chapter introduces OpenAM C SDK. OpenAM C SDK is available for selected platforms on the OpenAM nightly builds page. Contact info@forgerock.com if you need OpenAM C SDK support.
To prepare to install OpenAM C SDK, first download the version for your platform and unpack the archive as in the following example.
# mkdir -p /path/to/openam-client # cd /path/to/openam-client $ unzip ~/Downloads/common_3_0_Linux_64bit.zip
All C SDK deliveries are .zip files, and the filenames are self-explanatory.
The SunOS in some of the .zip files refer to the Solaris
OS.
common_3_0_Linux.zipcommon_3_0_Linux_64bit.zipcommon_3_0_windows.zipcommon_3_0_windows_64bit.zipcommon_3_0_SunOS_x86.zipcommon_3_0_SunOS_64bit.zipcommon_3_0_SunOS_sparc.zipcommon_3_0_SunOS_sparc_64bit.zip
Once unpacked, you have several directories that include the SDK, and also sample client applications.
bin/The crypt_util or cryptit.exe command for encrypting passwords
config/Configuration data for the SDK
include/Header files for the SDK
lib/SDK and other required libraries
samples/Sample code
Review the
samples/README.TXTfile to complete any specific instructions required for your platform. The two commands shown here confirm that the specified system is a 64-bit Linux OS. Make sure it matches the C SDK package that you have downloaded.$ uname -s Linux $ uname -m x86_64
Set up
OpenSSOAgentBootstrap.propertiesandOpenSSOAgentConfiguration.propertiesas appropriate for your environment.Base your work on the template files in the
config/directory. You can find the Password Encryption Key in the OpenAM console under Configuration > Servers and Sites > Server Name > Security.Try one of the samples you built to test your build.
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=../lib ./am_auth_test -f ../config/OpenSSOAgentBootstrap.properties -u demo -p changeit -o / Login 1 Succeeded! SSOToken = AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxZfk4EzC9Y46P9cXG9ogwf2ixnYOeZ0K0.*AAJTSQACMDE.* Organization = / Module Instance Name [0] = SAE Module Instance Name [1] = LDAP Module Instance Name [2] = WSSAuthModule Module Instance Name [3] = Federation Module Instance Name [4] = HOTP Module Instance Name [5] = DataStore Logout 1 Succeeded!
Chapter 13. Extending OpenAM
OpenAM services solve a wide range of access and federation management problems out of the box. Yet, OpenAM also exposes APIs and SPIs that enable you extend OpenAM services when built-in functionality does not fit your deployment.
This part of the guide covers OpenAM mechanisms for plugging in additional functionality not available out of the box.
Chapter 14. Customizing Profile Attributes
You can extend user profiles by adding custom attributes. This chapter demonstrates how to add a custom attribute to a user profile when storing user profiles in the embedded LDAP directory.
Adding a custom attribute involves both updating the
iPlanetAMUserService, and also updating the identity
repository schema to hold the new attribute. Furthermore, to allow users
to update the attribute in their own profiles, you must also update the
OpenAM policy configuration stored in the configuration directory.
This chapter includes the following procedures.
Follow the steps below to create a custom attribute in OpenAM.
Create a backup copy of the configuration file for the
iPlanetAmUserService.$ cd $HOME $ cp openam/config/xml/amUser.xml openam/config/xml/amUser.xml.orig
Edit the file to add your attribute as one of the list of
<User>attributes.<AttributeSchema name="customAttribute" type="single" syntax="string" any="display" i18nKey="Custom Attribute"> </AttributeSchema>Here, the name refers to the attribute type name used in LDAP. The
i18nKeyholds either the reference, or in this case the content, of the text that appears in the user interface.Delete
iPlanetAMUserService, and then create it from your updated configuration file.$ cd /path/to/tools/openam/bin/ $ ssoadm delete-svc --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMUserService Service was deleted. $ ssoadm create-svc --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --xmlfile $HOME/openam/config/xml/amUser.xml Service was added.
Follow the steps below to update the identity repository LDAP schema for the custom attribute, and then update OpenAM to use the custom attribute and object class.
If you are adding an existing attribute that is already allowed on user profile entries, you can skip this procedure.
Tip
If you are using OpenDJ as the identity repository, you can update the schema through OpenDJ Control Panel > Schema > Manage Schema, as described in the OpenDJ documentation.
Prepare the attribute type object class definitions in LDIF format.
$ cat custom-attr.ldif dn: cn=schema changetype: modify add: attributeTypes attributeTypes: ( temp-custom-attr-oid NAME 'customAttribute' EQUALITY case IgnoreMatch ORDERING caseIgnoreOrderingMatch SUBSTR caseIgnoreSubstrings Match SYNTAX 1.3.6.1.4.1.1466.115.121.1.15 USAGE userApplications ) - add: objectClasses objectClasses: ( temp-custom-oc-oid NAME 'customObjectclass' SUP top AUX ILIARY MAY customAttribute )
Add the schema definitions to the directory.
$ /path/to/OpenDJ/bin/ldapmodify --port 1389 --hostname openam.example.com --bindDN "cn=Directory Manager" --bindPassword password --filename custom-attr.ldif Processing MODIFY request for cn=schema MODIFY operation successful for DN cn=schema
In OpenAM console, browse to Access Control > Realm Name > Data Stores > Data Store Name.
Add the object class, here
customObjectclass, to the LDAP User Object Class list.Add the attribute type, here
customAttribute, to the LDAP User Attributes list.Save your work.
Follow these steps to make the new attribute editable by users. The steps imply use of the embedded configuration directory. If you use a different directory server to store the configuration, then adapt them for your tools.
Login to the control panel for the embedded configuration directory.
$ ./openam/opends/bin/control-panel &
Connect using bind DN
cn=Directory Managerand the the password foramadmin.Select Manage Entries to open the LDAP browser.
Search with
LDAP Filter:set toou=SelfWriteAttributes, and then expand the tree views to see the two entries found.In the entry under
iPlanetAMPolicyService, edit thesunKeyValueattribute to add your custom attribute to the list of self-writable attributes, as in<Value>customAttribute</Value>.In the entry under
sunEntitlementIndexes, edit thesunKeyValueattribute to add your custom attribute to the list of self-writable attributes, as in replacing the last\nin the list with,\n \"customAttribute\"\n.Restart OpenAM or the web container where it runs. The following example applies to Tomcat.
$ /path/to/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh $ /path/to/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
Login to OpenAM console as a user to check that a user can save a value for your new, custom attribute.
Chapter 15. Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling
RFC 6749, The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework, describes access token scopes as a set of case-sensitive strings defined by the authorization server. Clients can request scopes, and resource owners can authorize them.
The default scopes implementation in OpenAM treats scopes as profile
attributes for the resource owner. When a resource server or other entity uses
the access token to get token information from OpenAM, OpenAM populates the
scopes with profile attribute values. For example, if one of the scopes
is mail, OpenAM sets mail to the
resource owner's email address in the token information returned.
You can change this behavior by writing your own scopes plugin. This chapter shows how to write a custom OAuth 2.0 scopes plugin for use in an OAuth 2.0 provider (authorization server) configuration.
15.1. Designing an OAuth 2.0 Scopes Plugin
A scopes plugin implements the
org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.provider.Scope interface. The
Scope interface has four methods that your plugin
overrides.
public Set<String> scopeToPresentOnAuthorizationPage(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes);
public Set<String> scopeRequestedForAccessToken(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes);
public Set<String> scopeRequestedForRefreshToken(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> allScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes);
public Map<String, Object> evaluateScope(AccessToken token);The first three methods return the scopes to display when the resource
owner makes the authorization decision, or when an access token or refresh
token is granted, respectively. The fourth method,
evaluateScope can be used to set values for scopes
returned when token information is requested.
The following example plugin sets whether read and
write permissions were granted.
package org.forgerock.openam.examples;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.model.AccessToken;
import org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.provider.Scope;
/**
* Custom scope providers implement the
* {@link org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.provider.Scope} interface.
*
* This custom scope implementation follows the OpenAM default scope
* implementation for all methods except {@link #evaluateScope}.
*
* The {@code evaluateScope} method is called when a client accesses
* the {@code /tokeninfo} endpoint to retrieve token information.
*
* In this example, the method populates scope values returned in the
* JSON with the token information.
*/
public class CustomScope implements Scope {
@Override
public Set<String> scopeToPresentOnAuthorizationPage(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes) {
if (requestedScope == null) {
return defaultScopes;
}
Set<String> scopes = new HashSet<String>(availableScopes);
scopes.retainAll(requestedScope);
return scopes;
}
@Override
public Set<String> scopeRequestedForAccessToken(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes) {
if (requestedScope == null){
return defaultScopes;
}
Set<String> scopes = new HashSet<String>(availableScopes);
scopes.retainAll(requestedScope);
return scopes;
}
@Override
public Set<String> scopeRequestedForRefreshToken(
Set<String> requestedScope,
Set<String> availableScopes,
Set<String> allScopes,
Set<String> defaultScopes) {
if (requestedScope == null){
return defaultScopes;
}
Set<String> scopes = new HashSet<String>(availableScopes);
scopes.retainAll(requestedScope);
return scopes;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> evaluateScope(AccessToken token) {
Set<String> scopes = token.getScope();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
String[] permissions = {"read", "write"};
for (String scope : permissions) {
if (scopes.contains(scope)) {
map.put(scope, true);
} else {
map.put(scope, false);
}
}
return map;
}
}15.2. Building an OAuth 2.0 Scopes Plugin
As the plugin imports at least
org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.model.AccessToken
and org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.provider.Scope, add
openam-oauth2-common-11.0.0.jar to
the classpath.
After compiling, put it in a .jar file that you can deploy with OpenAM.
$ mkdir classes $ javac -d classes -cp /path/to/.../openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-oauth2-common-11.0.0.jar CustomScope.java $ cd classes/ $ jar cf ../CustomScope.jar
15.3. Configuring OpenAM to Use the Plugin
After building your plugin jar file, add the file under
WEB-INF/lib/ where you deployed OpenAM.
Restart OpenAM.
In OpenAM console, you can either configure a specific OAuth 2.0 provider to use your plugin, or configure your plugin as the default for new OAuth 2.0 providers. To configure a specific OAuth 2.0 provider to use your plugin, add the class name of your scopes plugin under Access Control > Realm Name > Services > OAuth2 Provider Name > Scope Implementation Class. To configure your plugin as the default for new providers, add the class name of your scopes plugin under Configuration > Global > OAuth2 Provider > Scope Implementation Class.
15.4. Trying the Example Plugin
If you build the example plugin shown above in
Section 15.1, "Designing an OAuth 2.0 Scopes Plugin", and then create an OAuth 2.0
client that takes scopes read and write,
you can configure OpenAM to use the plugin, and then try it as shown in the
following example.
$ curl
-d "grant_type=client_credentials&username=demo&password=changeit
&client_id=myClientID&client_secret=password&scope=read"
http://oauth2.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token
{
"expires_in": 599,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"access_token": "84122d5e-0462-4d81-93c3-7bc58bd416b3"
}
$ curl http://oauth2.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo
?access_token=84122d5e-0462-4d81-93c3-7bc58bd416b3
{
"write": false,
"read": true,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 539,
"access_token": "84122d5e-0462-4d81-93c3-7bc58bd416b3"
}Chapter 16. Customizing Authentication Modules
This chapter shows how to customize authentication with a sample custom authentication module. For deployments with particular requirements not met by existing OpenAM authentication modules, determine whether you can adapt one of the built-in or extension modules for your needs. If not, build the functionality into a custom authentication module.
16.1. About the Sample Authentication Module
The sample authentication module prompts for a user name and password to authenticate the user, and handles error conditions. The sample shows how you integrate an authentication module into OpenAM such that you can configure the module through OpenAM console, and also localize the user interface.
The sample authentication module source is available online. Get a local clone so that you can try the sample on your system. In the sources you find the following files.
pom.xmlApache Maven project file for the module
This file specifies how to build the sample authentication module, and also specifies its dependencies on OpenAM components and on the Java Servlet API.
src/main/java/org/forgerock/openam/examples/SampleAuth.javaCore class for the sample authentication module
This class is called by OpenAM to initialize the module and to process authentication. See Section 16.4, "The Sample Authentication Logic" for details.
src/main/java/org/forgerock/openam/examples/SampleAuthPrincipal.javaClass implementing
java.security.Principalinterface that defines how to map credentials to identitiesThis class is used to process authentication. See Section 16.5, "The Sample Auth Principal" for details.
src/main/resources/amAuthSampleAuth.propertiesProperties file mapping UI strings to property values
This file makes it easier to localize the UI. See Section 16.2, "Sample Auth Properties" for details.
src/main/resources/amAuthSampleAuth.xmlConfiguration file for the sample authentication service
This file is used when registering the authentication module with OpenAM. See Section 16.6, "The Sample Auth Service Configuration" for details.
src/main/resources/config/auth/default/SampleAuth.xmlCallback file for OpenAM classic UI authentication pages
The sample authentication module does not include localized versions of this file. See Section 16.3, "Sample Auth Callbacks" for details.
16.2. Sample Auth Properties
OpenAM uses a Java properties file per locale to retrieve the appropriate, localized strings for the authentication module.
The following is the Sample Authentication Module properties file,
amAuthSampleAuth.properties.
sampleauth-service-description=Sample Authentication Module a500=Authentication Level a501=Service Specific Attribute sampleauth-ui-login-header=Login sampleauth-ui-username-prompt=User Name: sampleauth-ui-password-prompt=Password: sampleauth-error-1=Error 1 occurred during the authentication sampleauth-error-2=Error 2 occurred during the authentication
16.3. Sample Auth Callbacks
OpenAM callbacks XML files are used to build the classic UI to prompt
the user for identity information needed to process the authentication.
The document type for a callback XML file is described in
WEB-INF/Auth_Module_Properties.dtd where OpenAM is
deployed.
The following is the SampleAuth.xml callbacks
file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE ModuleProperties PUBLIC
"=//iPlanet//Authentication Module Properties XML Interface 1.0 DTD//EN"
"jar://com/sun/identity/authentication/Auth_Module_Properties.dtd">
<ModuleProperties moduleName="SampleAuth" version="1.0" >
<Callbacks length="0" order="1" timeout="600" header="#NOT SHOWN#" />
<Callbacks length="2" order="2" timeout="600" header="#TO BE SUBSTITUTED#">
<NameCallback isRequired="true">
<Prompt>#USERNAME#</Prompt>
</NameCallback>
<PasswordCallback echoPassword="false" >
<Prompt>#PASSWORD#</Prompt>
</PasswordCallback>
</Callbacks>
<Callbacks length="1" order="3" timeout="600" header="#TO BE SUBSTITUTED#"
error="true" >
<NameCallback>
<Prompt>#THE DUMMY WILL NEVER BE SHOWN#</Prompt>
</NameCallback>
</Callbacks>
</ModuleProperties>This file specifies three states.
The initial state (order="1") is used dynamically to replace the dummy strings shown between hashes (for example,
#USERNAME#) by thesubstituteUIStrings()method inSampleAuth.java.The next state (order="2") handles prompting the user for authentication information.
The last state (order="3") has the attribute
error="true". If the authentication module state machine reaches this order then the authentication has failed. TheNameCallbackis not used and not displayed to user. OpenAM requires that the callbacks array have at least one element. Otherwise OpenAM does not permit header substitution.
16.4. The Sample Authentication Logic
An OpenAM authentication module must extend the
com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AMLoginModule abstract
class, and must implement the methods shown below.
See the OpenAM Java SDK API Specification for reference.
// OpenAM calls the init() method once when the module is created. public void init(Subject subject, Map sharedState, Map options) // OpenAM calls the process() method when the user submits authentication // information. The process() method determines what happens next: // success, failure, or the next state specified by the order // attribute in the callbacks XML file. public int process(Callback[] callbacks, int state) throws LoginException // OpenAM expects the getPrincipal() method to return an implementation of // the java.security.Principal interface. public Principal getPrincipal()
OpenAM does not reuse authentication module instances. This means that you can store information specific to the authentication process in the instance.
The implementation, SampleAuth.java, is shown
below.
/**
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS HEADER.
*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2013 ForgeRock AS. All Rights Reserved
*
* The contents of this file are subject to the terms
* of the Common Development and Distribution License
* (the License). You may not use this file except in
* compliance with the License.
*
* You can obtain a copy of the License at
* http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
* See the License for the specific language governing
* permission and limitations under the License.
*
* When distributing Covered Code, include this CDDL
* Header Notice in each file and include the License file
* at http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
* If applicable, add the following below the CDDL Header,
* with the fields enclosed by brackets [] replaced by
* your own identifying information:
* "Portions Copyrighted [year] [name of copyright owner]"
*
*/
package org.forgerock.openam.examples;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.security.auth.Subject;
import javax.security.auth.callback.Callback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.NameCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.PasswordCallback;
import javax.security.auth.login.LoginException;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AMLoginModule;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AuthLoginException;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.InvalidPasswordException;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.util.ISAuthConstants;
import com.sun.identity.shared.datastruct.CollectionHelper;
import com.sun.identity.shared.debug.Debug;
public class SampleAuth extends AMLoginModule
{
// Name for the debug-log
private final static String DEBUG_NAME = "SampleAuth";
// Name of the resource bundle
private final static String amAuthSampleAuth = "amAuthSampleAuth";
// User names for authentication logic
private final static String USERNAME = "demo";
private final static String ERROR_1_NAME = "test1";
private final static String ERROR_2_NAME = "test2";
// Orders defined in the callbacks file
private final static int STATE_BEGIN = 1;
private final static int STATE_AUTH = 2;
private final static int STATE_ERROR = 3;
private final static Debug debug = Debug.getInstance(DEBUG_NAME);
private Map options;
private ResourceBundle bundle;
public SampleAuth()
{
super();
}
@Override
// This method stores service attributes and localized properties
// for later use.
public void init(Subject subject, Map sharedState, Map options)
{
if (debug.messageEnabled())
{
debug.message("SampleAuth::init");
}
this.options = options;
bundle = amCache.getResBundle(amAuthSampleAuth, getLoginLocale());
}
@Override
public int process(Callback[] callbacks, int state) throws LoginException
{
if (debug.messageEnabled())
{
debug.message("SampleAuth::process state: " + state);
}
switch (state)
{
case STATE_BEGIN:
// No time wasted here - simply modify the UI and
// proceed to next state
substituteUIStrings();
return STATE_AUTH;
case STATE_AUTH:
// Get data from callbacks. Refer to callbacks XML file.
NameCallback nc = (NameCallback) callbacks[0];
PasswordCallback pc = (PasswordCallback) callbacks[1];
String username = nc.getName();
String password = new String(pc.getPassword());
// First errorstring is stored in "sampleauth-error-1" property.
if (username.equals(ERROR_1_NAME))
{
setErrorText("sampleauth-error-1");
return STATE_ERROR;
}
// Second errorstring is stored in "sampleauth-error-2" property.
if (username.equals(ERROR_2_NAME))
{
setErrorText("sampleauth-error-2");
return STATE_ERROR;
}
if (username.equals(USERNAME) && password.equals("changeit"))
{
return ISAuthConstants.LOGIN_SUCCEED;
}
throw new InvalidPasswordException("password is wrong", USERNAME);
case STATE_ERROR:
return STATE_ERROR;
default:
throw new AuthLoginException("invalid state");
}
}
@Override
public Principal getPrincipal()
{
return new SampleAuthPrincipal(USERNAME);
}
private void setErrorText(String err) throws AuthLoginException
{
// Receive correct string from properties and substitute the
// header in callbacks order 3.
substituteHeader(STATE_ERROR, bundle.getString(err));
}
private void substituteUIStrings() throws AuthLoginException
{
// Get service specific attribute configured in OpenAM
String ssa = CollectionHelper.getMapAttr(options,
"sampleauth-service-specific-attribute");
// Get property from bundle
String new_hdr = ssa + " "
+ bundle.getString("sampleauth-ui-login-header");
substituteHeader(STATE_AUTH, new_hdr);
Callback[] cbs_phone = getCallback(STATE_AUTH);
replaceCallback(STATE_AUTH, 0, new NameCallback(bundle
.getString("sampleauth-ui-username-prompt")));
replaceCallback(STATE_AUTH, 1, new PasswordCallback(bundle
.getString("sampleauth-ui-password-prompt"), false));
}
}
16.5. The Sample Auth Principal
The implementation, SampleAuthPrincipal.java, is
shown below.
/**
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS HEADER.
*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2013 ForgeRock AS. All Rights Reserved
*
* The contents of this file are subject to the terms
* of the Common Development and Distribution License
* (the License). You may not use this file except in
* compliance with the License.
*
* You can obtain a copy of the License at
* http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
* See the License for the specific language governing
* permission and limitations under the License.
*
* When distributing Covered Code, include this CDDL
* Header Notice in each file and include the License file
* at http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
* If applicable, add the following below the CDDL Header,
* with the fields enclosed by brackets [] replaced by
* your own identifying information:
* "Portions Copyrighted [year] [name of copyright owner]"
*
*/
package org.forgerock.openam.examples;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.security.Principal;
public class SampleAuthPrincipal implements Principal, Serializable
{
private final String name;
private final static String CLASSNAME = "SampleAuthPrincipal";
private final static String COLON = " : ";
public SampleAuthPrincipal(String name)
{
if (name == null)
{
throw new NullPointerException("illegal null input");
}
this.name = name;
}
/**
* Return the LDAP username for this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
*
* @return the LDAP username for this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>
*/
@Override
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
/**
* Return a string representation of this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
*
* @return a string representation of this
* <code>TestAuthModulePrincipal</code>.
*/
@Override
public String toString()
{
return new StringBuilder().append(CLASSNAME).append(COLON)
.append(name).toString();
}
/**
* Compares the specified Object with this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>
* for equality. Returns true if the given object is also a
* <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code> and the two SampleAuthPrincipal have
* the same username.
*
* @param o Object to be compared for equality with this
* <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
* @return true if the specified Object is equal equal to this
* <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == null)
{
return false;
}
if (this == o)
{
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof SampleAuthPrincipal))
{
return false;
}
SampleAuthPrincipal that = (SampleAuthPrincipal) o;
if (this.getName().equals(that.getName()))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Return a hash code for this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
*
* @return a hash code for this <code> SampleAuthPrincipal </code>.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
return name.hashCode();
}
}
16.6. The Sample Auth Service Configuration
OpenAM requires that all authentication modules be configured by means
of an OpenAM service. At minimum, the service must include an authentication
level attribute. Your module can access these configuration attributes in
the options parameter passed to the
init() method.
Some observations about the service configuration file follow in the list below.
The document type for a service configuration file is described in
WEB-INF/sms.dtdwhere OpenAM is deployed.The service name is taken from the module name:
iPlanetAMAuthmodule-nameService. In this case, the service name isiPlanetAMAuthSampleAuthService.The service must have a localized description, retrieved from a properties file.
The
i18nFileNameattribute in the service configuration holds the default (non-localized) base name of the Java properties file. Thei18nKeyattributes indicate properties keys to string values in the Java properties file.The authentication level attribute name is taken from the module name:
iplanet-am-auth-module-name-auth-level, where the module-name is all lower case. Here, the authentication level attribute is namediplanet-am-auth-sampleauth-auth-level.The Sample Auth service configuration includes an example
sampleauth-service-specific-attribute, which can be configured through OpenAM console.
The service configuration file,
amAuthSampleAuth.xml, is shown below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS HEADER.
Copyright (c) 2011 ForgeRock AS. All Rights Reserved
The contents of this file are subject to the terms
of the Common Development and Distribution License
(the License). You may not use this file except in
compliance with the License.
You can obtain a copy of the License at
http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
See the License for the specific language governing
permission and limitations under the License.
When distributing Covered Code, include this CDDL
Header Notice in each file and include the License file
at http://forgerock.org/license/CDDLv1.0.html
If applicable, add the following below the CDDL Header,
with the fields enclosed by brackets [] replaced by
your own identifying information:
"Portions Copyrighted [year] [name of copyright owner]"
-->
<!DOCTYPE ServicesConfiguration
PUBLIC "=//iPlanet//Service Management Services (SMS) 1.0 DTD//EN"
"jar://com/sun/identity/sm/sms.dtd">
<ServicesConfiguration>
<Service name="iPlanetAMAuthSampleAuthService" version="1.0">
<Schema
serviceHierarchy="/DSAMEConfig/authentication/iPlanetAMAuthSampleAuthService"
i18nFileName="amAuthSampleAuth" revisionNumber="10"
i18nKey="sampleauth-service-description">
<Organization>
<AttributeSchema name="iplanet-am-auth-sampleauth-auth-level"
type="single" syntax="number_range" rangeStart="0" rangeEnd="2147483647"
i18nKey="a500">
<DefaultValues>
<Value>1</Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
<AttributeSchema name="sampleauth-service-specific-attribute"
type="single" syntax="string" validator="no" i18nKey="a501">
<DefaultValues>
<Value></Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
<SubSchema name="serverconfig" inheritance="multiple">
<AttributeSchema name="iplanet-am-auth-sampleauth-auth-level"
type="single" syntax="number_range" rangeStart="0" rangeEnd="2147483647"
i18nKey="a500">
<DefaultValues>
<Value>1</Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
<AttributeSchema name="sampleauth-service-specific-attribute"
type="single" syntax="string" validator="no" i18nKey="a501">
<DefaultValues>
<Value></Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
</SubSchema>
</Organization>
</Schema>
</Service>
</ServicesConfiguration>16.7. Building & Installing the Sample Auth Module
Build the module with Apache Maven, and install the module in OpenAM.
16.7.1. Building the Module
Build the module using Apache Maven.
$ cd /path/to/openam-auth-sample $ mvn install [INFO] Scanning for projects... [INFO] [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Building openam-auth-sample 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ... [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-jar-plugin:2.3.1:jar (default-jar) @ openam-auth-sample --- [INFO] Building jar: ...target/openam-auth-sample-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar ... [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 3.651s [INFO] Finished at: Thu Oct 03 11:19:07 CEST 2013 [INFO] Final Memory: 20M/226M [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
After you successfully build the module, you find the .jar in
the target/ directory of the project.
16.7.2. Installing the Module
Installing the sample authentication module consists of copying the
.jar to OpenAM's WEB-INF/lib/ directory, registering
the module with OpenAM, and then restarting OpenAM or the web application
container where it runs.
Copy the sample authentication module .jar file to
WEB-INF/lib/where OpenAM is deployed.$ cp target/openam-auth-sample*.jar /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/
Register the module with OpenAM using the ssoadm command.
$ ssoadm create-svc --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --xmlfile amAuthSampleAuth.xml Service was added. $ ssoadm register-auth-module --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --authmodule org.forgerock.openam.examples.SampleAuth Authentication module was registered.
See the ssoadm reference in the Reference a full list of Authentication Service Management subcommands.
Restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs.
For example if you deployed OpenAM in Apache Tomcat, then you shut down Tomcat and start it again.
$ /path/to/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh $ /path/to/tomcat/bin/startup.sh $ tail -1 /path/to/tomcat/logs/catalina.out INFO: Server startup in 14736 ms
16.8. Configuring & Testing the Sample Auth Module
Authentication modules are registered as services with OpenAM globally, and then set up for use in a particular realm. In this example, you set up the sample authentication module for use in the realm / (Top Level Realm).
Login to OpenAM Console as OpenAM administrator,
amadmin, and browse to Access Control
> / (Top Level Realm) > Authentication > Module Instances.
Then click New, and create an instance of the Sample Authentication Module.
Name the module Sample.
After creating the module, click the name in the Module Instances list, and configure as appropriate.
Now that the module is configured, logout of OpenAM console.
Finally, try the module by specifying the Sample
module using a query string parameter. Browse to the login URL such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?module=Sample,
and then authenticate with user name demo and password
changeit.
After authentication you are redirected to the end user page for
the demo user. You can logout of OpenAM console, and then try the
authentication as users test1 or test2
to see what the error handling looks like to the user.
Chapter 17. Customizing Session Quota Exhaustion Actions
This chapter demonstrates how to develop a custom session quota exhaustion action. You only need a custom session quota exhaustion action if the built-in actions, described in the Administration Guide procedure To Configure Session Quotas & Exhaustion Actions in the Administration Guide, are not flexible enough for your deployment.
17.1. Creating & Installing a Custom Session Quota Exhaustion Action
You build custom session quota exhaustion actions into a .jar that you then plug in to OpenAM. You must also add your new action to the Session service configuration, and restart OpenAM in order to be able to configure it for your use.
Your custom session quota exhaustion action implements the
com.iplanet.dpro.session.service.QuotaExhaustionAction
interface, overriding the action method. The
action method performs the action when the session quota
is met, and returns true only if the request for a new
session should not be granted.
The following example simply removes the first session it finds as the session quota exhaustion action.
package org.forgerock.openam.examples.quotaexhaustionaction;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.Session;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.SessionException;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.SessionID;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.service.InternalSession;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.service.QuotaExhaustionAction;
import com.iplanet.dpro.session.service.SessionService;
import com.sun.identity.shared.debug.Debug;
import java.util.Map;
public class SampleQuotaExhaustionAction implements QuotaExhaustionAction {
private static Debug debug = SessionService.sessionDebug;
/**
* Check if the session quota for a given user has been exhausted and
* if so perform the necessary actions. This implementation randomly
* destroys the first session it finds.
*
* @param is The InternalSession to be activated.
* @param existingSessions All existing sessions that belong to the same
* uuid (Map:sid->expiration_time).
* @return true If the session activation request should be rejected,
* otherwise false.
*/
@Override
public boolean action(InternalSession is, Map<String, Long> existingSessions) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Long> entry : existingSessions.entrySet()) {
try {
// Get an actual Session instance based on the session ID.
Session session = Session.getSession(new SessionID(entry.getKey()));
//we use the session to destroy itself.
session.destroySession(session);
// Only destroy the first session.
break;
} catch (SessionException se) {
if (debug.messageEnabled()) {
debug.message("Failed to destroy existing session.", se);
}
// In this case, deny the session activation request.
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}When you have prepared the class file, compile it into a .jar. The following example shows compilation against the libraries with OpenAM deployed in Apache Tomcat.
$ mkdir classes $ javac -d classes -cp /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar: /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-shared-11.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar: /path/to/tomcat/lib/servlet-api.jar org/forgerock/openam/examples/quotaexhaustionaction/SampleQuotaExhaustionAction.java $ cd classes $ jar cvf ../my-quota-exhaustion-action.jar * $ cd ..
Add the .jar into WEB-INF/lib/ where OpenAM is
deployed.
$ cp my-quota-exhaustion-action.jar /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/
Using the ssoadm command, update the Session service configuration.
$ ssoadm set-attr-choicevals --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMSessionService --schematype Global --attributename iplanet-am-session-constraint-handler --add --choicevalues myKey= org.forgerock.openam.examples.quotaexhaustionaction.SampleQuotaExhaustionAction Choice Values were set.
Add the following line to
WEB-INF/classes/amSession.properties where OpenAM
is deployed.
myKey=Randomly Destroy Session
Restart OpenAM or the underlying container.
You can now use the new session quota exhaustion action in the OpenAM console under Configuration > Global > Session > Resulting behavior if session quota exhausted.
Before moving to your test and production environments, be sure to
add your .jar and updates to amSession.properties into
a custom .war that you can then deploy. You must still update the Session
service configuration in order to use your custom session quota exhaustion
action.
17.2. Listing Session Quota Exhaustion Actions
List session quota exhaustion actions with the ssoadm command.
$ ssoadm get-attr-choicevals --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMSessionService --schematype Global --attributename iplanet-am-session-constraint-handler I18n Key Choice Value ------------------------- ---...----------------------------------------- choiceDestroyOldSession org...session.service.DestroyOldestAction choiceDenyAccess org...session.service.DenyAccessAction choiceDestroyNextExpiring org...session.service.DestroyNextExpiringAction choiceDestroyAll org...session.service.DestroyAllAction myKey org...examples...SampleQuotaExhaustionAction
17.3. Removing a Session Quota Exhaustion Action
Remove a session quota exhaustion action with the ssoadm command.
$ ssoadm remove-attr-choicevals --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMSessionService --schematype Global --attributename iplanet-am-session-constraint-handler --choicevalues org.forgerock.openam.examples.quotaexhaustionaction.SampleQuotaExhaustionAction Choice Values were removed.
Chapter 18. Creating a Post Authentication Plugin
Post authentication plugins (PAP) let you include custom processing at the end of the authentication process, immediately before the subject is authenticated. Common uses of post authentication plugins include setting cookies and session variables. Post authentication plugins are often used in conjunction with policy agents. The post authentication plugin sets custom session properties, and then the policy agent injects the custom properties into the request header to the protected application.
This chapter explains how to create a post authentication plugin.
18.1. Designing Your Post Authentication Plugin
Your post authentication plugin class implements the
AMPostAuthProcessInterface interface, and in particular
the following three methods.
public void onLoginSuccess( Map requestParamsMap, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, SSOToken token ) throws AuthenticationException public void onLoginFailure( Map requestParamsMap, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response ) throws AuthenticationException public void onLogout( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, SSOToken token ) throws AuthenticationException
OpenAM calls the onLoginSuccess() and
onLoginFailure() methods immediately before informing the
user of login success or failure, respectively. OpenAM calls the
onLogout() method only when the user actively logs out,
not when a user's session times out.
See the OpenAM Java SDK API Specification for reference.
These methods can perform whatever processing you require. Yet, know that OpenAM calls your methods synchronously as part of the authentication process. Therefore, if your methods take a long time to complete, you will keep users waiting. Minimize the processing done in your post authentication methods.
18.2. Building Your Sample Post Authentication Plugin
The following example post authentication plugin sets a session property during successful login, writing to its debug log if the operation fails.
package com.forgerock.openam.examples;
import java.util.Map;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOException;
import com.iplanet.sso.SSOToken;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AMPostAuthProcessInterface;
import com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AuthenticationException;
import com.sun.identity.shared.debug.Debug;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class SamplePAP implements AMPostAuthProcessInterface
{
private final static String PROP_NAME = "MyProperty";
private final static String PROP_VALUE = "MyValue";
private final static String DEBUG_FILE = "SamplePAP";
protected Debug debug = Debug.getInstance(DEBUG_FILE);
public void onLoginSuccess(
Map requestParamsMap,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
SSOToken token
) throws AuthenticationException
{
try {
token.setProperty(PROP_NAME, PROP_VALUE);
} catch (SSOException ssoe) {
debug.error("Unable to set property");
}
}
public void onLoginFailure(
Map requestParamsMap,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response
) throws AuthenticationException
{
; // Not used
}
public void onLogout(
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
SSOToken token
) throws AuthenticationException
{
; // Not used
}
}A post authentication plugin code relies on three .jar files, two of which are deployed with OpenAM, and the third which is provided by your web application container.
openam-core-11.0.0.jarWhen you deploy OpenAM, the file is
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0.jar.openam-shared-11.0.0.jarWhen you deploy OpenAM, the file is
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/openam-shared-11.0.0.jar.servlet-api.jarThis .jar provides the Java EE Servlet API.
If you use Apache Tomcat as your web application container, the file is
/path/to/tomcat/lib/servlet-api.jar.
Put the sample plugin in
src/com/forgerock/openam/examples/SamplePAP.java,
and compile the class.
$ cd src $ mkdir ../classes $ javac -d ../classes -classpath /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0.jar: /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-shared-11.0.0.jar: /path/to/tomcat/lib/servlet-api.jar com/forgerock/openam/examples/SamplePAP.java
Copy the classes to the WEB-INF/classes directory
where you deployed OpenAM.
$ cp -r ../classes/* /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/classes/
Restart OpenAM or your web container to ensure the post authentication plugin class is loaded.
$ /etc/init.d/tomcat stop $ /etc/init.d/tomcat start $ tail -1 /path/to/tomcat/logs/catalina.out INFO: Server startup in 32070 ms
18.3. Configuring Your Post Authentication Plugin
You can configure the post authentication plugin for a realm, for a service (authentication chain), or for a role. Where you configure the plugin depends on the scope to which the plugin should apply. Configuring the plugin at the realm level as shown here, for example, ensures that OpenAM calls your plugin for all authentications to the realm.
In the OpenAM console, browse to Access Control > Realm
Name > Authentication > All Core Settings... In the
Authentication Post Processing Classes list, add the sample plugin class,
com.forgerock.openam.examples.SamplePAP, and then click
Save.
Alternatively, you can configure sample plugin for the realm by using the ssoadm command.
$ ssoadm set-svc-attrs --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMAuthService --realm /realm --attributevalues iplanet-am-auth-post-login-process-class= com.forgerock.openam.examples.SamplePAP iPlanetAMAuthService under /realm was modified.
18.4. Testing Your Post Authentication Plugin
To test the sample post authentication plugin, login successfully to
OpenAM in the scope where the plugin is configured. For example, if you
configured your plugin for the realm, /realm, specify the
realm in the login URL.
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?realm=realm
Although as a user you do not notice anywhere in the user interface that OpenAM calls your plugin, a policy agent or custom client code could retrieve the session property your plugin added to the user session.
Chapter 19. Customizing Policy Evaluation
OpenAM policies let you restrict access to resources based both on identity and group membership, and also on a range of conditions including session age, authentication chain or module used, authentication level, realm, session properties, IP address and DNS name, user profile content, resource environment, date, day, time of day, and time zone. Yet, some deployments require further distinctions for policy evaluation. This chapter explains how to customize policy evaluation for deployments with particular requirements not met by built-in OpenAM functionality.
OpenAM comes with sample plugins that demonstrate how to customize policy evaluation. This chapter shows how to compile the samples, and how to configure OpenAM to use one of the plugins.
19.1. About the Sample Plugins
The OpenAM policy framework lets you build plugins to extend subjects,
conditions, and response providers for policies, and also extend referrals
for policy delegation. You can find Java code for sample
policy evaluation plugins in the OpenAM project source code. Download the sample Java class
files into a suitable location, such as
~/Downloads/com/sun/identity/samples/policy/.
SampleCondition.javaExtends the
Conditioninterface. Shows an implementation of a condition to base the policy decision on the length of the user name.SampleReferral.javaExtends the
Referralinterface. Shows an implementation of a policy referral for delegation.SampleResponseProvider.javaExtends the
ResponseProviderinterface. Shows an implementation of a response provider to send an attribute from the user profile with the response.SampleSubject.javaExtends the
Subjectinterface. Shows an implementation that defines the users to whom the policy applies, in this case all authenticated users.
Before including the plugins in OpenAM, you compile the four files, and package the classes into a .jar for deployment.
The sample policy evaluation code relies on two .jar files deployed with OpenAM.
openam-core-11.0.0.jarWhen you deploy OpenAM, the file is
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0.jar.openam-shared-11.0.0.jarWhen you deploy OpenAM, the file is
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/openam-shared-11.0.0.jar.
$ cd /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/ $ mkdir classes $ javac -d classes -classpath /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0.jar: /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-shared-11.0.0.jar ~/Downloads/com/sun/identity/samples/policy/Sample*.java $ cd classes/ $ jar cf ../policy-plugins.jar .
The .jar belongs under
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/.
$ cp ../policy-plugins.jar /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib
Alternatively, you can add individual classes under
war-file-name/WEB-INF/classes/.
19.2. Configuring A Sample Policy Plugin
This section shows how to configure the sample custom policy condition
that you built. Configuration involves defining the strings that describe
the policy condition, and plugging the policy condition into the
iPlanetAMPolicyService, and then restarting OpenAM
to be able to add the condition to your policies.
You need to update two files where the strings describing your plugin are included as properties values.
In war-file-name/WEB-INF/classes/amPolicy.properties
add this property:
samplecondition-policy-name=Sample Condition
In war-file-name/WEB-INF/classes/amPolicyConfig.properties
add this property:
x100=Sample Condition
Add the schema that describes your plugin to OpenAM.
$ ssoadm add-plugin-schema --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMPolicyService --interfacename Condition --pluginname SampleCondition --i18nname amPolicy --i18nkey samplecondition-policy-name --classname com.sun.identity.samples.policy.SampleCondition Plug-in schema, Condition was added to service, iPlanetAMPolicyService.
Set the choice values of the schema to include your plugin with other policy conditions in the policy service.
$ ssoadm set-attr-choicevals --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMPolicyConfigService --schematype Organization --attributename iplanet-am-policy-selected-conditions --add --choicevalues "x100=SampleCondition" Choice Values were set.
Set the plugin policy condition as one of the default attibutes of the policy service.
$ ssoadm add-attr-defs --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename iPlanetAMPolicyConfigService --schematype Organization --attributevalues "iplanet-am-policy-selected-conditions=SampleCondition" Schema attribute defaults were added.
After completing configuration, restart OpenAM or the web application container.
$ /etc/init.d/tomcat stop Password: Using CATALINA_BASE: /path/to/tomcat Using CATALINA_HOME: /path/to/tomcat Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /path/to/tomcat/temp Using JRE_HOME: /path/to/jdk/jre Using CLASSPATH: /path/to/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar: /path/to/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar $ /etc/init.d/tomcat start Password: Using CATALINA_BASE: /path/to/tomcat Using CATALINA_HOME: /path/to/tomcat Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /path/to/tomcat/temp Using JRE_HOME: /path/to/jdk/jre Using CLASSPATH: /path/to/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar: /path/to/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
In OpenAM console, browse to Access Control > Realm Name > Policies > Policy Name > Conditions > New... Notice in the list of conditions that you can now apply your Sample Condition.
Chapter 20. Customizing Identity Data Storage
OpenAM maps user and group identities into a realm using data stores. An OpenAM data store relies on a Java identity repository (IdRepo) plugin to implement interaction with the identity repository where the users and groups are stored.
20.1. About the Identity Repository Plugin
This chapter describes how to create a custom identity repository plugin. OpenAM includes built-in support for LDAP and JDBC identity repositories. For most deployments, you therefore do not need to create your own custom identity repository plugin. Only create custom identity repository plugins for deployments with particular requirements not met by built-in OpenAM functionality.
Tip
Before creating your own identity repository plugin, start by reading
the OpenAM source code for the FilesRepo or
DatabaseRepo plugins under
com.sun.identity.idm.plugins.
20.1.1. IdRepo Inheritance
Your identity repository plugin class must extend the
com.sun.identity.idm.IdRepo abstract class, and must
include a constructor method that takes no arguments.
20.1.2. IdRepo Lifecycle
When OpenAM instantiates your IdRepo plugin, it calls the
initialize() method.
public void initialize(Map configParams)
The configParams are service configuration
parameters for the realm where the IdRepo plugin is configured. The
configParams normally serve to set up communication with
the underlying identity data store. OpenAM calls the
initialize() method once, and considers the identity
repository ready for use.
If you encounter errors or exceptions during initialization, catch and store them in your plugin for use later when OpenAM calls other plugin methods.
After initialization, OpenAM calls the addListener()
and removeListener() methods to register listeners that
inform OpenAM client code of changes to identities managed by your
IdRepo.
public int addListener(SSOToken token, IdRepoListener listener) public void removeListener()
You must handle listener registration in your IdRepo plugin, and also
return events to OpenAM through the IdRepoListener.
When stopping, OpenAM calls your IdRepo plugin
shutdown() method.
public void shutdown()
You are not required to implement shutdown() unless
your IdRepo plugin has shut down work of its own to do, such as close
connections to the underlying identity data store.
20.1.3. IdRepo Plugin Capabilities
Your IdRepo plugin provides OpenAM with a generic means to manage subjects—including users and groups but also special types such as roles, realms, and agents— and to create, read, update, delete, and search subjects. In order for OpenAM to determine your plugin's capabilities, it calls the methods described in this section.
public Set getSupportedTypes()
The getSupportedTypes() method returns a set of
IdType objects, such as IdType.USER
and IdType.GROUP. You can either hard-code the supported
types into your plugin, or make them configurable through the IdRepo
service.
public Set getSupportedOperations(IdType type)
The getSupportedOperations() method returns a set
of IdOperation objects, such as
IdOperation.CREATE and
IdOperation.EDIT. You can also either hard-code these, or
make them configurable.
public boolean supportsAuthentication()
The supportsAuthentication() method returns true if
your plugin supports the authenticate() method.
20.2. Identity Repository Plugin Implementation
Your IdRepo plugin implements operational methods depending on what you support. These methods perform the operations in your data store.
- Create
OpenAM calls
create()to provision a new identity in the repository, wherenameis the new identity's name, andattrMapholds the attributes names and values.public String create(SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Map attrMap) throws IdRepoException, SSOException
- Read
OpenAM calls the following methods to retrieve subjects in the identity repository, and to check account activity. If your data store does not support binary attributes, return an empty
MapforgetBinaryAttributes().public boolean isExists( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public boolean isActive( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public Map getAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public Map getAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Set attrNames ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public Map getBinaryAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Set attrNames ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public RepoSearchResults search( SSOToken token, IdType type, String pattern, Map avPairs, boolean recursive, int maxResults, int maxTime, Set returnAttrs ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public RepoSearchResults search( SSOToken token, IdType type, String pattern, int maxTime, int maxResults, Set returnAttrs, boolean returnAllAttrs, int filterOp, Map avPairs, boolean recursive ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException
- Edit
OpenAM calls the following methods to update a subject in the identity repository.
public void setAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Map attributes, boolean isAdd ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public void setBinaryAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Map attributes, boolean isAdd ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public void removeAttributes( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Set attrNames ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public void modifyMemberShip( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, Set members, IdType membersType, int operation ) throws IdRepoException, SSOException public void setActiveStatus( SSOToken token, IdType type, String name, boolean active )
- Authenticate
OpenAM calls
authenticate()with the credentials from theDataStoreauthentication module.public boolean authenticate(Callback[] credentials) throws IdRepoException, AuthLoginException
- Delete
The
delete()method removes the subject from the identity repository. Thenamespecifies the subject.public void delete(SSOToken token, IdType type, String name) throws IdRepoException, SSOException
- Service
The
IdOperation.SERVICEoperation is rarely used in recent OpenAM deployments.
20.3. Identity Repository Plugin Deployment
Your IdRepo plugin must link to openam-core-11.0.0.jar,
which when you deploy OpenAM is
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/openam-core-11.0.0.jar.
You can either package your plugin as a .jar, and then add it to
war-file-name/WEB-INF/lib/,
or add the classes under
war-file-name/WEB-INF/classes/.
To register your plugin with OpenAM, you add a
SubSchema to the
sunIdentityRepositoryService using the
ssoadm command. First, you create the
SubSchema document having the following structure.
<SubSchema i18nKey="x4000" inheritance="multiple" maintainPriority="no"
name="CustomRepo" supportsApplicableOrganization="no" validate="yes">
<AttributeSchema cosQualifier="default" isSearchable="no"
name="RequiredValueValidator" syntax="string"
type="validator" >
<DefaultValues>
<Value>com.sun.identity.sm.RequiredValueValidator</Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
<AttributeSchema any="required" cosQualifier="default"
i18nKey="x4001" isSearchable="no"
name="sunIdRepoClass" syntax="string"
type="single" validator="RequiredValueValidator" >
<DefaultValues>
<Value>org.test.CustomRepo</Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
<AttributeSchema cosQualifier="default" i18nKey="x4002" isSearchable="no"
name="sunIdRepoAttributeMapping" syntax="string" type="list">
<DefaultValues>
<Value></Value>
</DefaultValues>
</AttributeSchema>
</SubSchema>Also include the AttributeSchema required to
configure your IdRepo plugin.
Notice the i18nKey attributes on
SubSchema elements. The i18nKey
attribute values correspond to properties in the
amIdRepoService.properties file, stored under
war-file-name/WEB-INF/classes/.
OpenAM console displays the label for the configuration user interface that
it retrieves from the value of the i18nKey property in the
amIdRepoService.properties file.
Register your plugin using the ssoadm command after copy the files into place.
$ ssoadm add-sub-schema --adminid amadmin --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt --servicename sunIdentityRepositoryService --schematype Organization --filename customIdRepo.xml --subschemaname CustomRepo
Login to OpenAM console as administrator, then then Browse to Access Control > Realm Name > Data Stores. In the Data Stores table, click New... to create a Data Store corresponding to your custom IdRepo plugin. In the first screen of the wizard, name the Data Store and select the type corresponding to your plugin. In the second screen of the wizard, add the configuration for your plugin.
After creating the Data Store, create a new subject in the realm to check that your plugin works as expected. You can do this under Access Control > Realm Name > Subjects.
If your plugin supports authentication, then users should now be able
to authenticate using the DataStore module for the
realm.
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?realm=test&module=DataStore
Index
A
- Authentication
- Custom module, Customizing Authentication Modules
- Java API, Authenticating Using OpenAM Java SDK
- Post authentication plugins, Creating a Post Authentication Plugin
- REST API, Authentication & Logout
D
- Dashboard services, Displaying Dashboard Applications
F
- Fedlets
I
- Installing
- C SDK, Using the OpenAM C API
- Java SDK samples, Installing OpenAM Client SDK Samples
O
- OAuth 2.0, Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling
- REST API, OAuth 2.0 Authorization
- OpenID Connect 1.0
- REST API, OpenID Connect 1.0
P
- Password reset, Resetting Forgotten Passwords
- Policy
- Java API, Requesting Policy Decisions Using OpenAM Java SDK
- Plugins, Customizing Policy Evaluation
- REST API, Authorization
R
- Realm data
- REST access, Realm Management
- REST API, Using RESTful Web Services
S
- Secure Attribute Exchange (SAE), Using Secure Attribute Exchange
- Self-registration, User Self-Registration
- Session tokens
- Java API, Handling Single Sign-On Using OpenAM Java SDK
- REST API, Authentication & Logout
U
- User data
- Custom profile attributes, Customizing Profile Attributes
- Custom repository, Customizing Identity Data Storage
- REST access, Token Validation, Attribute Retrieval, Identity Management