Guide to configuring and using OpenAM features. OpenAM provides open source Authentication, Authorization, Entitlement, and Federation software.
This guide shows you how to configure, maintain, and troubleshoot OpenAM for single sign on and authorization, password reset, account lockout, cross-domain single sign on, and federation.
This guide is written for access management designers and administrators who build, deploy, and maintain OpenAM services for their organizations. This guide covers the tasks you might repeat throughout the life cycle of an OpenAM release used in your organization.
This guide starts by introducing the OpenAM administrative interfaces and tools, and by showing how to manage OpenAM services. This guide continues by showing how to configure the principle features of OpenAM. It then demonstrates how to backup, restore, monitor, tune, and troubleshoot, OpenAM services.
You do not need to be an OpenAM wizard to learn something from this guide, though a background in access management and maintaining web application software can help. You do need some background in managing services on your operating systems and in your application servers. You can nevertheless get started with this guide, and then learn more as you go along.
Most examples in the documentation are created in GNU/Linux or Mac OS X
operating environments.
If distinctions are necessary between operating environments,
examples are labeled with the operating environment name in parentheses.
To avoid repetition file system directory names are often given
only in UNIX format as in /path/to/server,
even if the text applies to C:\path\to\server as well.
Absolute path names usually begin with the placeholder
/path/to/.
This path might translate to /opt/,
C:\Program Files\, or somewhere else on your system.
Command-line, terminal sessions are formatted as follows:
$ echo $JAVA_HOME /path/to/jdk
Command output is sometimes formatted for narrower, more readable output even though formatting parameters are not shown in the command.
Program listings are formatted as follows:
class Test {
public static void main(String [] args) {
System.out.println("This is a program listing.");
}
}ForgeRock publishes comprehensive documentation online:
The ForgeRock Knowledge Base offers a large and increasing number of up-to-date, practical articles that help you deploy and manage ForgeRock software.
While many articles are visible to community members, ForgeRock customers have access to much more, including advanced information for customers using ForgeRock software in a mission-critical capacity.
ForgeRock product documentation, such as this document, aims to be technically accurate and complete with respect to the software documented. It is visible to everyone and covers all product features and examples of how to use them.
The ForgeRock.org site has links to source code for ForgeRock open source software, as well as links to the ForgeRock forums and technical blogs.
If you are a ForgeRock customer, raise a support ticket instead of using the forums. ForgeRock support professionals will get in touch to help you.
ForgeRock provides support services, professional services, training through ForgeRock University, and partner services to assist you in setting up and maintaining your deployments. For a general overview of these services, see https://www.forgerock.com.
ForgeRock has staff members around the globe who support our international customers and partners. For details, visit https://www.forgerock.com, or send an email to ForgeRock at info@forgerock.com.
This chapter provides a brief introduction to the web-based OpenAM console. It also lists and describes each command-line interface (CLI) administration tool.
After you install OpenAM, log in to the web-based console as OpenAM
administrator, amadmin with the password you set during
installation. Navigate to a URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam. In this case,
communications proceed over the HTTP protocol to a FQDN
(openam.example.com), over a standard Java EE web container
port number (8080), to a specific deployment URI (/openam).
When you log in as the OpenAM administrator, amadmin,
you have access to the complete OpenAM console. In addition, OpenAM has set a
cookie in your browser that lasts until the session expires, you logout, or
you close your browser.[1]
When you log in to the OpenAM console as a non-administrative end user, you do not have access to the administrative console. Your access is limited to self-service profile pages and user dashboard.
If you configure OpenAM to grant administrative capabilities to another user, then that user is able to access both the administration console in the realms they can administrate, and their self-service profile pages.
For more on delegated administration, see "Delegating Realm Administration Privileges".
The OpenAM web-based console is a responsive website, which means it would resize some of its features to fit the size of your screen and the layout design.
For example, the header menu would change into a dropdown menu, and those pages with many tabs would shed most of them for a dropdown menu to the left-hand side.
The script tools in the following list have .bat
versions for use on Microsoft Windows.
You can install the following OpenAM command-line tools:
- agentadmin
This tool lets you manage OpenAM policy agent installations.
Unpack this tool as part of policy agent installation.
- ampassword
This tool lets you change OpenAM Administrator passwords, and display encrypted password values.
Install this from the
SSOAdminTools-13.5.2.zip.- amverifyarchive
This tool checks log archives for tampering.
Install this from
SSOAdminTools-13.5.2.zip.- openam-distribution-configurator-13.5.2.jar
This executable
.jarfile lets you perform a silent installation of an OpenAM server with a configuration file. For example, the java -jar configurator.jar -f config.file command couples theconfigurator.jararchive with the config.file. Thesampleconfigurationfile provided with the tool is set up with the format for theconfig.file, and it must be adapted for your environment.Install this from
SSOConfiguratorTools-13.5.2.zip.- ssoadm
This tool provides a rich command-line interface for the configuration of OpenAM core services.
In a test environment, you can activate
ssoadm.jspto access the same functionality in your browser. Once active, you can use many features of the ssoadm command by navigating to thessoadm.jspURI, in a URL, such ashttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam/ssoadm.jsp.Install this from
SSOAdminTools-13.5.2.zip.To translate settings applied in OpenAM console to service attributes for use with ssoadm, log in to the OpenAM console as
amadminand access the services page, in a URL, such ashttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam/services.jsp.
The commands access the OpenAM configuration over HTTP (or HTTPS). When using the administration commands in a site configuration, the commands access the configuration through the front end load balancer.
Sometimes a command cannot access the load balancer because:
Network routing restrictions prevent the tool from accessing the load balancer.
For testing purposes, the load balancer uses a self-signed certificate for HTTPS, and the tool does not have a way of trusting the self-signed certificate.
The load balancer is temporarily unavailable.
In such cases you can work around the problem by adding an option for each node, such as the following to the java command in the tool's script.
Node 1:
-D"com.iplanet.am.naming.map.site.to.server=https://lb.example.com:443/openam=
http://server1.example.com:8080/openam"
Node 2:
-D"com.iplanet.am.naming.map.site.to.server=https://lb.example.com:443/openam=
http://server2.example.com:8080/openam"
In the above example the load balancer is on the lb
host, https://lb.example.com:443/openam is the site name,
and the OpenAM servers in the site are on server1 and
server2.
The ssoadm command will only use the latest value in the map, so if you have a mapping like:
-D"com.iplanet.am.naming.map.site.to.server=https://lb.example.com:443/openam=
http://server1.example.com:8080/openam, https://lb.example.com:443/openam=
http://server2.example.com:8080/openam"
The ssoadm command will always talk to:
http://server2.example.com:8080/openam
You can use the ssoadm.jsp page to access a large subset of the configuration capabilities of the ssoadm command. Yet, ssoadm.jsp is disabled by default to prevent potential misuse.
Log in as OpenAM administrator,
amadmin.Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced.
Add a new advanced property called
ssoadm.disabledwith the value offalse.To see if the change worked, navigate to the URL of OpenAM with the
/ssoadm.jspURI. For example, navigate tohttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam/ssoadm.jsp.
[1] Persistent cookies can remain valid when you close your browser. This section reflects OpenAM default behavior before you configure additional functionality.
An authentication service confirms the identity of a user or a client application.
This chapter describes how to configure authentication in OpenAM.
Access management is about controlling access to resources. OpenAM plays a role similar to border control at an international airport. Instead of having each and every airline company deal with access to each destination, all airlines redirects passengers to border control. Redirect control then determines who each passenger is according to passport credentials. Redirect control also checks whether the identified passenger is authorized to fly to the destination corresponding to the ticket, perhaps based on visa credentials. Then, at the departure gate, an agent enforces the authorization from border control, allowing the passenger to board the plane as long as the passenger has not gotten lost, or tried to board the wrong plane, or swapped tickets with someone else. Thus, border control handles access management at the airport.
OpenAM is most frequently used to protect web-accessible resources. Users browse to a protected web application page. An agent installed on the server with the web application redirects the user to OpenAM for access management. OpenAM determines who the user is, and whether the user has the right to access the protected page. OpenAM then redirects the user back to the protected page, with authorization credentials that can be verified by the agent. The agent allows OpenAM authorized users access the page.
Notice that OpenAM basically needs to determine two things for access management: the identity of the user, and whether the user has access rights to the protected page. Authentication is how OpenAM identifies the user. This chapter covers how to set up the authentication process. Authorization is how OpenAM determines whether a user has access to a protected resource. Authorization is covered later.
For authentication, OpenAM uses credentials from the user or client application. It then uses defined mechanisms to validate credentials and complete the authentication. The authentication methods can vary. For example, passengers travelling on international flights authenticate with passports and visas. In contrast, passengers travelling on domestic flights might authenticate with an identity card or a driver's license. Customers withdrawing cash from an ATM authenticate with a card and a PIN.
OpenAM allows you to configure authentication processes and then customize how they are applied. OpenAM uses authentication modules to handle different ways of authenticating. Basically, each authentication module handles one way of obtaining and verifying credentials. You can chain different authentication modules together. In OpenAM, this is called authentication chaining. Each authentication module can be configured to specify the continuation and failure semantics with one of the following four criteria: requisite, sufficient, required, or optional.
Authentication modules in a chain can assign a pass or fail flag to the authorization request. To successfully complete an authentication chain at least one pass flag must have been achieved, and there must be no fail flags.
Flags are assigned when completing a module as shown in the table below:
| Criteria | Fail | Pass | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Requisite |
Assigns fail flag. Exits chain. |
Assigns pass flag. Continues chain. |
Active Directory, Data Store, and LDAP authentication modules are often set as requisite because of a subsequent requirement in the chain to identify the user. For example, the Device ID (Match) authentication module needs a user's ID before it can retrieve information about the user's devices. |
Sufficient | Assigns no flag. Continues chain. | Assigns pass flag. Exits chain. |
You could set Windows Desktop SSO as sufficient, so authenticated Windows users are let through, whereas web users must traverse another authentication module, such as one requiring a username and password. One exception is that if you pass a sufficient module after having failed a required module, you will continue through the chain and will not exit at that point. Consider using a requisite module instead of a required module in this situation. |
Required |
Assigns fail flag.
Continues chain. |
Assigns pass flag. Continues chain. | You could use a required module for login with email and password, so that it can fail through to another module to handle new users who have not yet signed up. |
Optional | Assigns no flag. Continues chain. |
Assigns pass flag.
Continues chain. | You could use an optional module to assign a higher authentication level if it passes. Consider a chain with a requisite Data Store module and an optional Certificate module. Users who only passed the Data Store module could be assigned a lower authentication level than users who passed both the Data Store and Certificate modules. The users with the higher authentication level could be granted access to more highly-secured resources. |
Tip
In authentication chains with a single module, requisite and required are equivalent. For authentication chains with multiple modules, use required only when you want the authentication chain to continue evaluating modules even after the required criterion fails.
The OpenAM authentication chain editor displays the flags that could be assigned by each module in the chain, and whether execution of the chain continues downwards through the chain or exits out, as shown below:
With OpenAM, you can further set authentication levels per module, with higher levels being used typically to allow access to more restricted resources. The OpenAM SPIs also let you develop your own authentication modules, and post authentication plugins. Client applications can specify the authentication level, module, user, and authentication service to use among those you have configured. As described later in this guide, you can use realms to organize which authentication process applies for different applications or different domains, perhaps managed by different people.
OpenAM leaves the authentication process flexible so that you can adapt how it works to your situation. Although at first the number of choices can seem daunting, now that you understand the basic process, you begin to see how choosing authentication modules and arranging them in authentication chains lets you use OpenAM to protect access to a wide range of applications used in your organization.
When a user successfully authenticates, OpenAM creates a session, which allows OpenAM to manage the user's access to resources. The session is assigned an authentication level, which is calculated to be the highest authentication level of any authentication module that passed. If the user's session does not have the appropriate authentication level, then the user may need to re-authenticate again at a higher authentication level to access the requested resource.
If an authentication chain contains requisite or
required modules that were not executed due to the
presence of a passing sufficient module in front of them,
the session's authentication level is calculated to be whichever
is greater: the highest authentication level of any authentication module
that passed, or the highest authentication level of requisite or
required modules that were not executed.
You can modify OpenAM's default behavior, so that a session's authentication
level is always the highest authentication level of any
authentication module that passed, even if there are requisite or
required modules in the authentication chain that were
not executed.
To modify the default behavior, set the
org.forgerock.openam.authLevel.excludeRequiredOrRequisite
property to true under Deployment > Servers >
Server Name > Advanced and restart the
OpenAM server.
In some deployments, you need to limit how many active sessions a user can have at a given time. For example, you might want to prevent a user from using more than two devices at once. See "Configuring Session Quotas" for instructions.
OpenAM allows delegation of authentication to any third party OpenID Connect 1.0 server that implements the OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0 specification.
The OpenAM console provides wizards for configuring authentication with selected third parties: Facebook, Google, or Microsoft. An additional wizard provides the ability to configure other third party authentication providers.
The wizards create an authentication module and an authentication chain containing the correct configuration needed to authenticate with the third party. The wizard also adds configuration data to the realm's Social Authentication Implementations Service (and provisions the service if it is not already present) that enables the display of logos of configured third-party authentication providers on the OpenAM login screen, as shown below.
OpenAM provides a wizard to quickly enable authentication with any third party provider that supports the OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0 specification.
You must first register an application with the third party provider to obtain a Client ID, Client Secret, and the OpenID Discovery URL.
Once you have registered an application and obtained your credentials from the social authentication provider, follow the steps below to configure authentication with the provider:
Select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure Social Authentication, and then click the Configure Other Authentication link.
On the configure social authentication page:
Select the realm in which to enable social authentication.
Enter the OpenID Discovery URL obtained from the third party authentication provider.
Enter a name for the provider in the
Provider Namefield. OpenAM uses this as a label on the login page to identify the provider.Enter the URL of an image to be used on the login page in the
Image URLfield. OpenAM places the image on the login page, to enable authentication with the provider.Enter the Client ID obtained from the third party authentication provider.
Enter the Client Secret obtained from the third party authentication provider, and repeat it in the
Confirm Client Secretfield.Leave the default
Redirect URL, unless you are using an external server as a proxy.Click
Create.
On completion, the wizard displays a message confirming the successful creation of a new authentication module and an authentication chain for the provider, and either the creation of a new Social Authentication Implementations service named
socialAuthNService, or an update if it already existed.
You can configure the authentication module, authentication chain, and Social Authentication Implementations service that you created by using the wizard in the same way as manually created versions. For more information, see "Configuring Authentication Modules", "Configuring Authentication Chains", and "Configuring the Social Authentication Implementations Service".
You can add logos to the login page to allow users to authenticate using configured social authentication providers.
Wizards are provided to configure common social authentication providers, which also configure the Social Authentication Implementations Service to add logos to the login page. You can manually add other authentication chains that contain an OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication module.
To add a social authentication provider to the login screen, you must first configure an OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication module, and an authentication chain that contains it:
Use a wizard. See "Configuring Pre-Populated Social Authentication Providers" and "Configuring Custom Social Authentication Providers".
Configure the Social Authentication Implementations Service, and then create an authentication module and a chain. See "To Configure the Social Authentication Implementations Service", "Configuring Authentication Modules" and "Configuring Authentication Chains".
Once you have created an authentication chain containing an OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication module, follow the steps below to add a logo for the authentication provider to the login screen:
On the Realms page of the OpenAM console, click the realm containing the authentication module and authentication chain to be added to the login screen.
On the Services page for the realm:
If the
Social Authentication Implementations Serviceexists, click on it.
If the
Social Authentication Implementations Servicedoes not exist, click Add a Service, and then select Social Authentication Implementations, and then click Create.
On the Social Authentication Implementations page:
In the Display Names section, enter a Map Key, enter the text to display as ALT text on the logo in the Corresponding Map Value field, and then click Add.
Note
OpenAM uses the value in the Map Key fields throughout the configuration to tie the various implementation settings to each other. The value is case-sensitive.
In the Authentication Chains section, re-enter the Map Key used in the previous step, select the authentication chain from the Corresponding Map Value list, and then click Add.
In the Icons section, re-enter the Map Key used in the previous steps, enter the path to a logo image to be used on the login screen in the Corresponding Map Value list, and then click Add.
In the Enabled Implementations field, re-enter the Map Key used in the previous steps, and then click Add.
Tip
Removing a Map Key from the Enabled Implementations list removes the associated logo from the login screen. There is no need to delete the Display Name, Authentication Chain or Icon configuration to remove the logo from the login screen.
Click Save Changes.
An icon now appears on the OpenAM login screen, allowing users to authenticate with the third party authentication provider.
Use core authentication attributes to configure:
The list of available authentication modules
Which types of clients can authenticate with which modules
Connection pools for access to directory servers
Whether to retain objects used during authentication so they can be used at logout
Defaults for configuring authentication in a particular realm
To configure core authentication attributes in the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Authentication, and then click Core Attributes.
The core authentication attributes page is divided into seven tabs, which are explained in the following sections:
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthService
The Global tab includes attributes for the list of available modules, LDAP connection settings, authentication process options, and an option to disable the XUI and make the classic UI the default end user interface. The global attributes are defined in "Authentication Configuration" in the Reference.
- Administrator Authentication Configuration
Specifies the default authentication chain used when an administrative user, such as
amAdmin, logs in to the OpenAM console.- Organization Authentication Configuration
Specifies the default authentication chain used when a non-administrative user logs in to OpenAM.
- User Profile
Specifies whether a user profile needs to exist in the user data store, or should be created on successful authentication.
- Dynamic
Specifies that on successful authentication, OpenAM creates a user profile if one does not already exist. OpenAM then issues the SSO token. OpenAM creates the user profile in the user data store configured for the realm.
- Dynamic with User Alias
Specifies that on successful authentication, OpenAM creates a user profile that contains the
User Alias Listattribute, which defines one or more aliases for mapping a user's multiple profiles.- Ignored
Specifies that a user profile is not required for OpenAM to issue an SSO token after a successful authentication.
- Required
Specifies that on successful authentication, the user must have a user profile in the user data store configured for the realm in order for OpenAM to issue an SSO token.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-dynamic-profile-creation. Set this attribute's value to one of the following:truefor DynamiccreateAliasfor Dynamic With User Aliasignorefor Ignoredfalsefor Required
- User Profile Dynamic Creation Default Roles
Specifies the distinguished name (DN) of a role to be assigned to a new user whose profile is created when either the
trueorcreateAliasoptions are selected under the User Profile property. There are no default values. The role specified must be within the realm for which the authentication process is configured.This role can be either an OpenAM or Sun DSEE role, but it cannot be a filtered role. If you wish to automatically assign specific services to the user, you have to configure the Required Services property in the user profile.
This functionality is deprecated.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-default-role- Alias Search Attribute Name
After a user is successfully authenticated, the user's profile is retrieved. OpenAM first searches for the user based on the data store settings. If that fails to find the user, OpenAM will use the attributes listed here to look up the user profile. This setting accepts any data store specific attribute name.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-alias-attr-nameNote
If the
Alias Search Attribute Nameproperty is empty, OpenAM uses theiplanet-am-auth-user-naming-attrproperty from theiPlanetAmAuthService. Theiplanet-am-auth-user-naming-attrproperty is only configurable through the ssoadm command-line tool and not through the OpenAM console.$ ssoadm get-realm-svc-attrs \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file PATH_TO_PWDFILE \ --realm REALM \ --servicename iPlanetAMAuthService $ ssoadm set-realm-svc-attrs \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file PATH_TO_PWDFILE \ --realm REALM \ --servicename iPlanetAMAuthService \ --attributevalues iplanet-am-auth-user-naming-attr=SEARCH_ATTRIBUTE
- Login Failure Lockout Mode
Selecting this attribute enables a physical lockout. Physical lockout inactivates an LDAP attribute (defined in the Lockout Attribute Name property) in the user's profile. This attribute works in conjunction with the other account lockout and notification attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-lockout-mode- Login Failure Lockout Count
Defines the number of attempts that a user has to authenticate within the time interval defined in Login Failure Lockout Interval before being locked out.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-count- Login Failure Lockout Interval
Defines the time in minutes during which failed login attempts are counted. If one failed login attempt is followed by a second failed attempt within this defined lockout interval time, the lockout count starts, and the user is locked out if the number of attempts reaches the number defined by the Login Failure Lockout Count property. If an attempt within the defined lockout interval time proves successful before the number of attempts reaches the number defined by the Login Failure Lockout Count property, the lockout count is reset.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-duration- Email Address to Send Lockout Notification
Specify one or more email addresses to which notification is sent if a user lockout occurs.
Separate multiple addresses with spaces, and append
|locale|charsetto addresses for recipients in non-English locales.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-lockout-email-address- Warn User After N Failures
Specifies the number of authentication failures after which OpenAM displays a warning message that the user will be locked out.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-lockout-warn-user- Login Failure Lockout Duration
Defines how many minutes a user must wait after a lockout before attempting to authenticate again. Entering a value greater than 0 enables memory lockout and disables physical lockout. Memory lockout means the user's account is locked in memory for the number of minutes specified. The account is unlocked after the time period has passed.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-lockout-duration- Lockout Duration Multiplier
Defines a value with which to multiply the value of the Login Failure Lockout Duration attribute for each successive lockout. For example, if Login Failure Lockout Duration is set to 3 minutes, and the Lockout Duration Multiplier is set to 2, the user is locked out of the account for 6 minutes. After the 6 minutes has elapsed, if the user again provides the wrong credentials, the lockout duration is then 12 minutes. With the Lockout Duration Multiplier, the lockout duration is incrementally increased based on the number of times the user has been locked out.
ssoadm attribute:
sunLockoutDurationMultiplier- Lockout Attribute Name
Defines the LDAP attribute used for physical lockout. The default attribute is
inetuserstatus, although the field in the OpenAM console is empty. The Lockout Attribute Value field must also contain an appropriate value.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-lockout-attribute-name- Lockout Attribute Value
Specifies the action to take on the attribute defined in Lockout Attribute Name. The default value is
inactive, although the field in the OpenAM console is empty. The Lockout Attribute Name field must also contain an appropriate value.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-lockout-attribute-value- Invalid Attempts Data Attribute Name
Specifies the LDAP attribute used to hold the number of failed authentication attempts towards Login Failure Lockout Count.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsDataAttrName- Store Invalid Attempts in Data Store
Enables the storage of information regarding failed authentication attempts as the value of the Invalid Attempts Data Attribute Name in the user data store. Information stored includes number of invalid attempts, time of last failed attempt, lockout time and lockout duration. Storing this information in the identity repository allows it to be shared among multiple instances of OpenAM.
ssoadm attribute:
sunStoreInvalidAttemptsInDS
- Default Authentication Locale
Specifies the default language subtype to be used by the Authentication Service. The default value is
en_US.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-locale- Identity Types
Lists the type or types of identities used during a profile lookup. You can choose more than one to search on multiple types if you would like OpenAM to conduct a second lookup if the first lookup fails. Default: Agent and User
- Agent
Searches for identities under your agents.
- agentgroup
Searches for identities according to your established agent group.
- agentonly
Searches for identities only under your agents.
- Group
Searches for identities according to your established groups.
- User
Searches for identities according to your users.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMIdentityType- Pluggable User Status Event Classes
Specifies one or more Java classes used to provide a callback mechanism for user status changes during the authentication process. The Java class must implement the
com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AMAuthCallBackinterface. OpenAM supports account lockout and password changes. OpenAM supports password changes through the LDAP authentication module, and so the feature is only available for the LDAP module.A
.jarfile containing the user status event class belongs in theWEB-INF/libdirectory of the deployed OpenAM instance. If you do not build a.jarfile, add the class files underWEB-INF/classes.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMUserStatusCallbackPlugins- Default Authentication Level
Specifies the default authentication level for authentication modules.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-default-auth-level- Use Stateless Sessions
When selected, specifies that OpenAM users authenticating to this realm are assigned stateless sessions. Otherwise, OpenAM users authenticating to this realm are assigned stateful sessions.
For more information about session state, see "Configuring Session State".
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-stateless-sessions- Two Factor Authentication Mandatory
When selected, specifies that users authenticating to a chain that includes a ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module will always be required to perform authentication using a registered device before they can access OpenAM. When not selected, users can opt to forego registering a device and providing a token and still successfully authenticate.
Letting users choose not to provide a verification token while authenticating carries implications beyond the
required,optional,requisite, orsufficientflag settings on the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module in the authentication chain. For example, suppose you configured authentication as follows:The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module is in an authentication chain.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module has the
requiredflag set.Two Factor Authentication Mandatory is not selected.
Users authenticating to the chain can authenticate successfully without providing tokens from their devices. The reason for successful authentication in this case is that the
requiredsetting relates to the execution of the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module itself. Internally, the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module has the ability to forego processing a token while still returning a passing status to the authentication chain.ssoadm attribute:
forgerockTwoFactorAuthMandatory
- Module Based Authentication
Enables users to authenticate using module-based authentication. Otherwise, all attempts at authentication using the
module=module-namelogin parameter result in failure.ForgeRock recommends disabling module-based authentication in production environments.
ssoadm attribute:
sunEnableModuleBasedAuth- Persistent Cookie Encryption Certificate Alias
Specifies the keystore alias for encrypting persistent cookies.
Default:
testssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-key-alias- Zero Page Login
If enabled, allow users to authenticate using only GET request parameters without showing a login screen.
Caution
Enable this with caution as browsers can cache credentials and servers can log credentials when they are part of the URL.
OpenAM always allows HTTP POST requests for zero page login.
Default: false (disabled)
ssoadm attribute:
openam.auth.zero.page.login.enabled- Zero Page Login Referer Whitelist
List of HTTP referer URLs for which OpenAM allows zero page login. These URLs are supplied in the
RefererHTTP request header, allowing clients to specify the web page that provided the link to the requested resource.If you enable zero page login, include the URLs here for the pages from which to allow zero page login, or leave this list blank to allow zero page login from any Referer.
This setting applies for both HTTP GET and also HTTP POST requests for zero page login.
ssoadm attribute:
openam.auth.zero.page.login.referer.whitelist- Zero Page Login Allowed Without Referer?
If enabled and zero page login is enabled, allow zero page login for requests without an HTTP
Refererrequest header.Default: true (enabled)
ssoadm attribute:
openam.auth.zero.page.login.allow.null.referer- Organization Authentication Signing Secret
Specifies an HMAC shared secret for signing a RESTful authentication request. When users attempt to authenticate to the XUI, OpenAM signs a JSON Web Token (JWT) with this shared secret. The JWT contains the authentication session ID, realm, and authentication index type value, but does not contain the user's credentials.
Default: An automatically generated key
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-hmac-signing-shared-secret
- Default Success Login URL
Accepts a list of values that specifies where users are directed after successful authentication. The format of this attribute is
client-type|URLalthough the only value you can specify at this time is a URL which assumes the type HTML. The default value is/openam/console. Values that do not specify HTTP have that appended to the deployment URI.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url- Default Failure Login URL
Accepts a list of values that specifies where users are directed after authentication has failed. The format of this attribute is
client-type|URLalthough the only value you can specify at this time is a URL which assumes the type HTML. Values that do not specify HTTP have that appended to the deployment URI.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url- Authentication Post Processing Classes
Specifies one or more Java classes used to customize post authentication processes for successful or unsuccessful logins. The Java class must implement the
com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AMPostAuthProcessInterfaceOpenAM interface.A
.jarfile containing the post processing class belongs in theWEB-INF/libdirectory of the deployed OpenAM instance. If you do not build a.jarfile, add the class files underWEB-INF/classes. For deployment, add the.jarfile or classes into a custom OpenAM.warfile.For information on creating post-authentication plugins, see "Creating a Post Authentication Plugin" in the Developer's Guide.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-post-login-process-class- Generate UserID Mode
When enabled, the Membership module generates a list of alternate user identifiers if the one entered by a user during the self-registration process is not valid or already exists. The user IDs are generated by the class specified in the Pluggable User Name Generator Class property.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-username-generator-enabled- Pluggable User Name Generator Class
Specifies the name of the class used to generate alternate user identifiers when Generate UserID Mode is enabled. The default value is
com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.DefaultUserIDGenerator.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-username-generator-class- User Attribute Mapping to Session Attribute
Enables the authenticating user's identity attributes (stored in the identity repository) to be set as session properties in the user's SSO token. The value takes the format
User-Profile-Attribute|Session-Attribute-Name. If Session-Attribute-Name is not specified, the value of User-Profile-Attribute is used. All session attributes contain theam.protectedprefix to ensure that they cannot be edited by the Client SDK.For example, if you define the user profile attribute as
mailand the user's email address, available in the user session, asuser.mail, the entry for this attribute would bemail|user.mail. After a successful authentication, theSSOToken.getProperty(String)method is used to retrieve the user profile attribute set in the session. The user's email address is retrieved from the user's session using theSSOToken.getProperty("am.protected.user.mail")method call.Properties that are set in the user session using User Attribute Mapping to Session Attributes cannot be modified (for example,
SSOToken.setProperty(String, String)). This results in anSSOException. Multivalued attributes, such asmemberOf, are listed as a single session variable with a|separator.When configuring authentication for a realm that uses stateless sessions, be careful not to add so many session attributes that the session cookie size exceeds the maximum allowable cookie size. For more information about stateless session cookies, see "Session Cookies".
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMUserAttributesSessionMapping
The OpenAM console provides two places where the OpenAM administrator can configure authentication modules:
Under Configure > Authentication, you configure default properties for global authentication modules.
Under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Modules, you configure modules for your realm.
The configuration of individual modules depend on its function. The configuration of an Active Directory over LDAP user authentication module requires connection information and details about where to search for users. In contrast, the configuration of the HOTP module for OTP authentication requires data about the password length and the mail server or SMS gateway for to send the password during authentication.
OpenAM connects to Active Directory over Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). OpenAM provides separate Active Directory and LDAP modules to support the use of both Active Directory and another directory service in an authentication chain.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthADService
- Primary Active Directory Server, Secondary Active Directory Server
The default port for LDAP is 389. If you are connecting to Active Directory over SSL, the default port for LDAP/SSL is 636.
To allow users to change passwords through OpenAM, Active Directory requires that you connect over SSL.
If you want to use SSL or TLS for security, then scroll down to enable SSL/TLS Access to Active Directory Server. Make sure that OpenAM can trust the Active Directory certificate when using this option.
OpenAM first attempts to contact primary servers. If no primary server is available, then OpenAM attempts to contact secondaries.
When authenticating users from a directory server that is remote to OpenAM, set the primary server values, and optionally the secondary server values. Primary servers have priority over secondary servers.
ssoadm attributes are: primary is
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-server; secondary isiplanet-am-auth-ldap-server2.Both properties take more than one value; thus, allowing more than one primary or secondary remote server, respectively. Assuming a multi-data center environment, OpenAM determines priority within the primary and secondary remote servers, respectively, as follows:
Every LDAP server that is mapped to the current OpenAM instance has highest priority.
For example, if you are connected to
openam1.example.comandldap1.example.comis mapped to that OpenAM instance, then OpenAM usesldap1.example.com.Every LDAP server that was not specifically mapped to a given OpenAM instance has the next highest priority.
For example, if you have another LDAP server,
ldap2.example.com, that is not connected to a specific OpenAM server and ifldap1.example.comis unavailable, OpenAM connects to the next highest priority LDAP server,ldap2.example.com.LDAP servers that are mapped to different OpenAM instances have the lowest priority.
For example, if
ldap3.example.comis connected toopenam3.example.comandldap1.example.comandldap2.example.comare unavailable, thenopenam1.example.comconnects toldap3.example.com.
- DN to Start User Search
LDAP data is organized hierarchically, a bit like a file system on Windows or UNIX. More specific DNs likely result in better performance. When configuring the module for a particular part of the organization, you can perhaps start searches from a specific organizational unit, such as
OU=sales,DC=example,DC=com.If multiple entries exist with identical search attribute values, make this value specific enough to return only one entry.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-base-dn- Bind User DN, Bind User Password
If OpenAM stores attributes in Active Directory, for example to manage account lockout, or if Active Directory requires that OpenAM authenticate in order to read users' attributes, then OpenAM needs the DN and password to authenticate to Active Directory.
The default is
amldapuser. If the administrator authentication chain (default:ldapService) has been configured to include only the Active Directory module, then make sure that the password is correct before you logout. If it is incorrect, you will be locked out. If you do get locked out, you can login with the superuser DN, which by default isuid=amAdmin,ou=People,OpenAM-deploy-base, where OpenAM-deploy-base was set during OpenAM configuration.ssoadm attributes:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-bind-dnandiplanet-am-auth-ldap-bind-passwd- Attribute Used to Retrieve User Profile, Attributes Used to Search for a User to be Authenticated, User Search Filter, Search Scope
LDAP searches for user entries with attribute values matching the filter you provide. For example, if you search under
CN=Users,DC=example,DC=comwith a filter"(MAIL=bjensen@example.com)", then the directory returns the entry that hasMAIL=bjensen@example.com. In this example the attribute used to search for a user ismail. Multiple attribute values mean the user can authenticate with any one of the values. For example, if you have bothuidandmail, then Barbara Jensen can authenticate with eitherbjensenorbjensen@example.com.The User Search Filter text box provides a more complex filter. For example, if you search on
mailand add User Search Filter(objectClass=inetOrgPerson), then OpenAM uses the resulting search filter(&(mail=address) (objectClass=inetOrgPerson)), where address is the mail address provided by the user.This controls how and the level of the directory that will be searched. You can set the search to run at a high level or against a specific area:
OBJECT will search only for the entry specified as the DN to Start User Search.
ONELEVEL will search only the entries that are directly children of that object.
SUBTREE will search the entry specified and every entry under it.
ssoadm attributes:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-user-naming-attribute,iplanet-am-auth-ldap-user-search-attributes,iplanet-am-auth-ldap-search-filter, andiplanet-am-auth-ldap-search-scope- LDAP Connection Mode
If you want to initiate secure communications to data stores using SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust Active Directory certificates, either because the Active Directory certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- Return User DN to DataStore
When enabled, and OpenAM uses Active Directory as the user store, the module returns the DN rather than the User ID, so the bind for authentication can be completed without a search to retrieve the DN.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-return-user-dn- User Creation Attributes
This list lets you map (external) attribute names from Active Directory to (internal) attribute names used by OpenAM.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-ldap-user-creation-attr-list- Trust All Server Certificates
When enabled, blindly trust server certificates, including self-signed test certificates.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-ssl-trust-all- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
Specifies how often OpenAM should send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-heartbeat-interval- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Specifies the time unit corresponding to LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval.
Default: minute
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-heartbeat-timeunit- LDAP operations timeout
Defines the timeout in milliseconds that OpenAM should wait for a response from the directory server.
Default: 0 (means no timeout)
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-operation-timeout- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthADAuthLevel- LDAPS Server Protocol Version
Defines which protocol version is used to establish the secure connection to the LDAP Directory Server.
Default:
TLSv1ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-secure-protocol-versionPossible values:
TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2
The Adaptive Risk module is designed to assess risk during authentication so that OpenAM can determine whether to require the user to complete further authentication steps. After configuring the Adaptive Risk module, insert it in your authentication chain with criteria set to Sufficient as shown in the following example:
In the example authentication chain shown, OpenAM has users authenticate first using the LDAP module providing a user ID and password combination. Upon success, OpenAM calls the Adaptive Risk module. The Adaptive Risk module assesses the risk based on your configured parameters. If the Adaptive Risk module calculates a total score below the threshold you set, the module returns success, and OpenAM finishes authentication processing without requiring further credentials.
Otherwise, the Adaptive Risk module evaluates the score to be above the risk threshold, and returns failure. OpenAM then calls the HOTP module, requiring the user to authenticate with a one-time password delivered to her by email or by SMS to her mobile phone.
When you configure the Adaptive Risk module to save cookies and
profile attributes after successful authentication, OpenAM performs the
save as post-authentication processing, only after the entire authentication
chain returns success. You must set up OpenAM to save the data as part of
post-authentication processing by editing the authentication chain to add
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.adaptive.Adaptive
to the list of post-authentication plugins.
When the Adaptive Risk module relies on the client IP address,
and OpenAM lies behind a load balancer or proxy layer,
configure the load balancer or proxy to send the address
by using the X-Forwarded-For header,
and configure OpenAM to consume and forward the header as necessary.
For details, see "Handling HTTP Request Headers" in the Installation Guide.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthAdaptiveService
Tip
If you cannot find the attribute you are looking for, click on the dropdown button on the left-hand side of the tabs or use the Search box. For more information, see " OpenAM Console Responsiveness" and "OpenAM Console Search Feature".
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-auth-level- Risk Threshold
Risk threshold score. If the sum of the scores is greater than the threshold, the Adaptive Risk module returns failure.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-auth-threshold
- Failed Authentication Check
When enabled, check the user profile for authentication failures since the last successful login. This check therefore requires OpenAM to have access to the user profile, and Account Lockout to be enabled (otherwise, OpenAM does not record authentication failures).
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-failure-check- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Failed Authentication Check. Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-failure-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the score to the total score if the user passes the Failed Authentication Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-failure-invert
- IP Range Check
When enabled, check whether the client IP address is within one of the specified IP Ranges.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-range-check- IP Range
For IPv4, specifies a list of IP ranges either in CIDR-style notation (
x.x.x.x/YY) or as a range from one address to another (x.x.x.x-y.y.y.y, meaning from x.x.x.x to y.y.y.y).For IPv6, specifies a list of IP ranges either in CIDR-style notation (
X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X/YY) or as a range from one address to another (X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X-Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y, meaning from X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X to Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y:Y).ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-range-range- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the IP Range Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-range-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the IP Range Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-range-invert
- IP History Check
When enabled, check whether the client IP address matches one of the known values stored on the profile attribute you specify. This check therefore requires that OpenAM have access to the user profile.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-history-check- History size
Specifies how many IP address values to retain on the profile attribute you specify.
Default: 5
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ip-adaptive-history-count- Profile Attribute Name
Name of the user profile attribute on which to store known IP addresses. Ensure the specified attribute exists in your user data store; the
iphistoryattribute does not exist by default, and it is not created when performing OpenAM schema updates.Default:
iphistoryssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-history-attribute- Save Successful IP Address
When enabled, save new client IP addresses to the known IP address list following successful authentication.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-history-save- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the IP History Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-history-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the IP History Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-ip-history-invert
- Cookie Value Check
When enabled, check whether the client browser request has the specified cookie and optional cookie value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-check- Cookie Name
Specifies the name of the cookie for which OpenAM checks when you enable the Cookie Value Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-name- Cookie Value
Specifies the value of the cookie for which OpenAM checks. If no value is specified, OpenAM does not check the cookie value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-value- Save Cookie Value on Successful Login
When enabled, save the cookie as specified in the client's browser following successful authentication. If no Cookie Value is specified, the value is set to 1.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-save- Score
Value to add to the total score if user passes the Cookie Value Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Cookie Value Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-known-cookie-invert
- Device Registration Cookie Check
When enabled, check whether the client browser request has the specified cookie with the correct device registration identifier as the value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-device-cookie-check- Cookie Name
Specifies the name of the cookie for the Device Registration Cookie Check.
Default: Device
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-device-cookie-name- Save Device Registration on Successful Login
When enabled, save the specified cookie with a hashed device identifier value in the client's browser following successful authentication.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-device-cookie-save- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Device Registration Cookie Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-device-cookie-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Device Registration Cookie Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-device-cookie-invert
- Time since Last login Check
When enabled, check whether the client browser request has the specified cookie that holds the encrypted last login time, and check that the last login time is more recent than a maximum number of days you specify.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-check- Cookie Name
Specifies the name of the cookie holding the encrypted last login time value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-cookie-name- Max Time since Last login
Specifies a threshold age of the last login time in days. If the client's last login time is more recent than the number of days specified, then the client successfully passes the check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-value- Save time of Successful Login
When enabled, save the specified cookie with the current time encrypted as the last login value in the client's browser following successful authentication.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-save- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Time Since Last Login Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Time Since Last Login Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-time-since-last-login-invert
- Profile Risk Attribute check
When enabled, check whether the user profile contains the specified attribute and value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-risk-attribute-check- Attribute Name
Specifies the attribute to check on the user profile for the specified value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-risk-attribute-name- Attribute Value
Specifies the value to match on the profile attribute. If the attribute is multi-valued, a single match is sufficient to pass the check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-risk-attribute-value- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Profile Risk Attribute Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-risk-attribute-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Profile Risk Attribute Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-risk-attribute-invert
- Geolocation Country Code Check
When enabled, check whether the client IP address location matches a country specified in the Valid Country Codes list.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-adaptive-geo-location-check- Geolocation Database Location
Path to GeoIP data file used to convert IP addresses to country locations. The geolocation database is not packaged with OpenAM. You can download the GeoIP Country database from MaxMind. Use the binary
.mmdbfile format, rather than.csv. You can use the GeoLite Country database for testing.ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-geo-location-database- Valid Country Codes
Specifies the list of country codes to match. Use
|to separate multiple values.ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-geo-location-values.- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Geolocation Country Code Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-geo-location-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Geolocation Country Code Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-geo-location-invert
- Request Header Check
When enabled, check whether the client browser request has the specified header with the correct value.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-req-header-check- Request Header Name
Specifies the name of the request header for the Request Header Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-req-header-name- Request Header Value
Specifies the value of the request header for the Request Header Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-req-header-value- Score
Value to add to the total score if the user fails the Request Header Check.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-req-header-score- Invert Result
When selected, add the Score to the total score if the user passes the Request Header Check.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-adaptive-req-header-invert
This module lets you configure and track anonymous users, who can log in to your application or web site without login credentials. Typically, you would provide such users with very limited access, for example, an anonymous user may have access to public downloads on your site. When the user attempts to access resources that require more protection, the module can force further authentication for those resources.
You can configure the Anonymous authentication module by specifying the ssoadm service name and Anonymous Authentication realm attributes: Valid Anonymous Users, Default User Name, Case Sensitive User IDs, and Authentication Level.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthAnonymousService
- Valid Anonymous Users
Specifies the list of valid anonymous user IDs that can log in without submitting a password.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-anonymous-users-listWhen user accesses the default module instance login URL, then the module prompts the user to enter a valid anonymous user name.
The default module instance login URL is defined as follows:
protocol://hostname:port/deploy_URI/XUI/#login?module=Anonymous&org=org_name
- Default Anonymous User Name
Specifies the user ID assigned by the module if the Valid Anonymous Users list is empty. The default value is
anonymous. Note that the anonymous user must be defined in the realm.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-anonymous-default-user-name- Case Sensitive User IDs
Determines whether case matters for anonymous user IDs.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-anonymous-case-sensitive- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 (default) to any positive integer and is set for each authentication method. The higher number corresponds to a higher level of authentication. If you configured your authentication levels from a 0 to 5 scale, then an authentication level of 5 will require the highest level of authentication.
After a user has authenticated, OpenAM stores the authentication level in the session token. When the user attempts to access a protected resource, the token is presented to the application. The application uses the token's value to determine if the user has the correct authentication level required to access the resource. If the user does not have the required authentication level, the application can prompt the user to authenticate with a higher authentication level.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-anonymous-auth-level
Note
You can configure the Anonymous Authentication module using the OpenAM console by clicking Configure > Authentication > Anonymous.
X.509 digital certificates can enable secure authentication without the need for user names and passwords or other credentials. Certificate authentication can be handy to manage authentication by applications. If all certificates are signed by a recognized Certificate Authority (CA), then you might get away without additional configuration. If you need to look up public keys of OpenAM clients, this module can also look up public keys in an LDAP directory server.
When you store certificates and certificate revocation lists (CRL) in an LDAP directory service, you must configure both how to access the directory service and also how to look up the certificates and CRLs, based on the fields in the certificates that OpenAM clients present to authenticate.
Access to the LDAP server and how to search for users is similar
to LDAP module configuration as in "Hints for the LDAP Authentication Module".
The primary difference is that, unlike for LDAP configuration, OpenAM
retrieves the user identifier from a field in the certificate that the
client application presents, then uses that identifier to search for the
LDAP directory entry that holds the certificate, which should match the
certificate presented. For example, if the Subject field of a typical
certificate has a DN C=FR, O=Example Corp, CN=Barbara
Jensen, and Barbara Jensen's entry in the directory has
cn=Barbara Jensen, then you can use CN=Barbara
Jensen from the Subject DN to search for the entry with
cn=Barbara Jensen in the directory.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthCertService
- Match Certificate in LDAP
When enabled, OpenAM searches for a match for the user's certificate in the LDAP directory. If a match is found and not revoked according to a CRL or OCSP validation, then authentication succeeds.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-check-cert-in-ldap- Subject DN Attribute Used to Search LDAP for Certificates
Indicates which attribute and value in the certificate Subject DN is used to find the LDAP entry holding the certificate.
Default: CN
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-attr-check-ldap- Match Certificate to CRL
When enabled, OpenAM checks whether the certificate has been revoked according to a CRL in the LDAP directory.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-check-crl- Issuer DN Attribute Used to Search LDAP for CRLs
Indicates which attribute and value in the certificate Issuer DN is used to find the CRL in the LDAP directory.
Default: CN
If only one attribute is specified, the LDAP search filter used to find the CRL based on the Subject DN of the CA certificate is
(attr-name=attr-value-in-subject-DN).For example, if the subject DN of the issuer certificate is
C=US, CN=Some CA, serialNumber=123456, and the attribute specified isCN, then the LDAP search filter used to find the CRL is(CN=Some CA).In order to distinguish among different CRLs for the same CA issuer, specify multiple attributes separated by commas (
,) in the same order they occur in the subject DN. When multiple attribute names are provided in a comma-separated list, the LDAP search filter used is(cn=attr1=attr1-value-in-subject-DN,attr2=attr2-value-in-subject-DN,...,attrN=attrN-value-in-subject-DN).For example, if the subject DN of the issuer certificate is
C=US, CN=Some CA, serialNumber=123456, and the attributes specified areCN,serialNumber, then the LDAP search filter used to find the CRL is(cn=CN=Some CA,serialNumber=123456).ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-attr-check-crl- HTTP Parameters for CRL Update
Your certificate authority should provide the URL to use here, from which OpenAM can get CRL updates.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-param-get-crl- Match CA Certificate to CRL
When enabled, OpenAM checks the CRL against the CA certificate to ensure it has not been compromised.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMValidateCACert- Cache CRLs in memory
When enabled, CRLs will be cached.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-am-auth-cert-attr-cache-crl- Update CA CRLs from CRLDistributionPoint
When enabled, OpenAM updates CRLs from the LDAP directory store.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-am-auth-cert-update-crl- OCSP Validation
Enable this to use Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) instead of CRLs to check certificates' revocation status.
If you enable this, you also must configure OSCP for OpenAM under Configure > Server Defaults or Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Security.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-check-ocsp- LDAP Server Where Certificates are Stored
Identifies the LDAP server with certificates. Remember to specify URLs with appropriate port numbers (389 for unencrypted LDAP, 636 for LDAP over SSL). When configuring a secure connection, scroll down to enable Use SSL/TLS for LDAP Access.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-ldap-provider-url- LDAP Search Start or Base DN
Valid base DN for the LDAP search, such as
dc=example,dc=com.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-start-search-loc- LDAP Server Authentication User, LDAP Server Authentication Password
If OpenAM stores attributes in the LDAP directory, for example to manage account lockout, or if the LDAP directory requires that OpenAM authenticate in order to read users' attributes, then OpenAM needs the DN and password to authenticate to the LDAP directory.
ssoadm attributes:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-principal-user, andiplanet-am-auth-cert-principal-passwd- Use SSL/TLS for LDAP Access
If you use SSL/TLS for LDAP access, OpenAM must be able to trust the LDAP server certificate.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-use-ssl- Certificate Field Used to Access User Profile
If the user profile is in a different entry from the user certificate, then this can be different from subject DN attribute used to find the entry with the certificate. When you select other, provide an attribute name in the Other Certificate Field Used to Access User Profile text box.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-user-profile-mapper- Other Certificate Field Used to Access User Profile
This field is only used if the Certificate Field Used to Access User Profile attribute is set to other. This field allows a custom certificate field to be used as the basis of the user search.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-user-profile-mapper-other- SubjectAltNameExt Value Type to Access User Profile
Use this if you want to look up the user profile from an RFC 822 style name, or a User Principal Name as used in Active Directory.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-user-profile-mapper-ext- Trusted Remote Hosts
Defines a list of hosts trusted to send certificates to OpenAM, such as load balancers doing SSL termination.
Valid values:
none,any, andIP_ADDR, where IP_ADDR is one or more IP addresses of trusted hosts that can send client certificates to OpenAM.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-gw-cert-auth-enabled- HTTP Header Name for Client Certificates
Specifies the name of the HTTP request header containing the PEM-encoded certificate. If Trusted Remote Hosts is set to
anyor specifies the IP address of the trusted host (for example, an SSL-terminated load balancer) that can supply client certificates to OpenAM, the administrator must specify the header name in this attribute.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMHttpParamName- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-cert-auth-level
The Data Store authentication module allows a login using the Identity Repository of the realm to authenticate users. Using the Data Store module removes the requirement to write an authentication plugin module, load, and then configure the authentication module if you need to authenticate against the same data store repository. Additionally, you do not need to write a custom authentication module where flatfile authentication is needed for the corresponding repository in that realm.
Yet, the Data Store module is generic. It does not implement data store-specific capabilities, such as the password policy and password reset features provided by LDAP modules. Therefore, the Data Store module returns failure when such capabilities are invoked.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthDataStoreService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthDataStoreAuthLevel
The Device ID (Match) module provides device fingerprinting functionality for risk-based authentication. The Device ID (Match) module collects the unique characteristics of a remote user's computing device and compares them to characteristics on a saved device profile. The module computes any variances between the collected characteristics to those stored on the saved device profile and assigns penalty points for each difference.
In general, you can configure and gather the following device print items:
User agents associated with the configuration of a web browser
Installed fonts
The plugins installed for the web browser
The resolution and color depth associated with a display
The timezone or even the geolocation of a device
For example, when a user who typically authenticates to OpenAM using Firefox and then logs on using Chrome, the Device ID (Match) module notes the difference and assigns penalty points to this change in behavior. If the module detects additional differences in behavior, such as browser fonts, geolocation, and so forth, then additional points are assessed and calculated.
If the total maximum number of penalty points exceeds a pre-configured threshold value, the Device ID (Match) module fails and control is determined by how you configured your authentication chain. If you include the HOTP module in your authentication chain, and if the Device ID (Match) module fails after the maximum number of penalty points have been exceeded, then the authentication chain issues a HOTP request to the user, requiring the user to identify himself using two-factor authentication.
Important
By default, the maximum penalty points is set to 0, which you can adjust in the server-side script.
The Device ID (Match) module comes pre-configured with default client-side and server-side JavaScript code, supplying the logic necessary to fingerprint the user agent and computer. Scripting allows you to customize the code, providing more control over the device fingerprint elements that you would like to collect. While OpenAM scripting supports both the JavaScript (default) and Groovy languages, only server-side scripts can be writtern in either language. The client-side scripts must be written in the JavaScript language.
Caution
The Device ID (Match) module's default JavaScript client-side and server-side scripts are fully functional. If you change the client-side script, you must also make a corresponding change to the server-side script. For a safer option, if you want to change the behavior of the module, you can make a copy of the scripts, customize the behavior, and update the Device ID (Match) modules to use the new scripts.
The Device ID (Match) does not stand on its own within an authentication chain and requires additional modules. For example, you can have any module that identifies the user (for example, DataStore, Active Directory or others), Device ID (Match), any module that provides two-factor authentication, for example the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) or ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication modules, and Device ID (Save) within your authentication chain.
As an example, you can configure the following modules with the specified criteria:
DataStore - Requisite. The Device ID (Match) module requires user authentication information to validate the username. You can also use other modules that identify the username, such as LDAP, Active Directory, or RADIUS.
Device ID (Match) - Sufficient. The Device ID (Match) runs the client-side script, which invokes the device fingerprint collectors, captures the data, and converts it into a JSON string. It then auto-submits the data in a JSP page to the server-side scripting engine.
The server-side script calculates the penalty points based on differences between the client device and stored device profile, and or whether the client device successfully "matches" the stored profile. If a match is successful, OpenAM determines that the client's device has the required attributes for a successful authentication.
If the device does not have a match, then the module fails and falls through to the HOTP module for further processing.
HOTP - Requisite. If the user's device does not match a stored profile, OpenAM presents the user with a HMAC One-Time Password (HOTP) screen either by SMS or email, prompting the user to enter a password.
You can also use any other module that provides two-factor authentication.
After the HOTP has successfully validated the user, the Device ID (Save) module gathers additional data from the user. For specific information about the HOTP module, see "Hints for the HOTP Authentication Module".
Device ID (Save) - Required. The Device ID (Save) module provides configuration options to enable an auto-save feature on the device profile as well as set a maximum number of stored device profiles on the user entry or record. Once the maximum number of stored device profiles is reached, OpenAM deletes the old data from the user record as new ones are added. User records could thus contain both old and new device profiles.
If the auto-save feature is not enabled, OpenAM presents the user with a screen to save the new device profile.
The module also takes the device print and creates a JSON object that includes the ID, name, last selected date, selection counter, and device print. For specific information about the Device ID (Save) module, see "Hints for the Device ID (Save) Module".
Note
If a user has multiple device profiles, the profile that is the closest match to the current client details is used for the comparison result.
The Device ID (Match) module has the following properties:
- Client-Side Script Enabled
Enable Device ID (Match) to send JavaScript in an authentication page to the device to collect data about the device by a self-submitting form.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-client-script-enabled- Client-Side Script
You can see default client-side JavaScript code that you can modify if necessary. Note that if you change the client-side script, you must make a corresponding change in the server-side script to account for the specific addition or removal of an element.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-client-script- Server-side Script
You can see default server-side JavaScript code that you can modify if necessary. Note that a change in the client-side script requires a corresponding change in the server-side script to account for the specific addition or removal of an element.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-server-script- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-auth-level
Log into the OpenAM console as an administrator.
On the Realms page, click the realm from which you want to work.
Click Authentication > Modules.
To add the Device ID (Match) module, do the following substeps:
Click Add Module.
In the Module Name box, enter
Device-ID-Match.In the Type box, select
Device Id (Match), and then click Create.Click Save Changes.
To make adjustments to the default scripts, click Scripts drop-down list, and then click
Device Id (Match) - Client Side.To make corresponding changes to the server-side script, click Scripts drop-down list, and then click
Device Id (Match) - Server Side. For more information, see "Managing Scripts".
Log into the OpenAM console as an administrator.
On the Realms page, click the realm from which you want to work.
Click Authentication > Chains.
On the Authentication Chains page, do the following steps:
Click Add Chain. In the Chain Name box, enter a descriptive label for your authentication chain, and then click Create.
Click Add Module.
On the New Module dialog, select the authentication module, select the criteria, and then click Ok to save your changes. Repeat the last two steps to enter each module to your chain.
For example, you can enter the following modules and criteria:
Module Criteria DataStore REQUISITE Device-ID-Match SUFFICIENT HOTP REQUISITE Device-ID-Save REQUIRED It is assumed that you have added the Device Id (Match) and Device Id (Save) modules. If you have not added these modules, see "To Configure the Device ID (Match) Authentication Module" and "To Configure the Device ID (Save) Authentication Module".
Review your authentication chain, and then click Save Changes.
When the user logs on to the console, OpenAM determines if the user's device differs from that of the stored profile. If the differences exceed the maximum number of penalty points or a device profile has not yet been stored, OpenAM sends an "Enter OTP" page, requiring the user to enter a one-time password, which is sent to the user via email or SMS. The user also has the option to request a one-time password.
Next, because the Device ID (Save) module is present, OpenAM presents the user with a "Add to Trusted Devices?" page, asking if the user wants to add the device to the list of trusted device profiles. If the user clicks "Yes", OpenAM prompts the user to enter a descriptive name for the trusted device.
Next, OpenAM presents the user with the User Profile page, where the user can click the Dashboard link at top to access the My Applications and Authentication Devices page. Once on the Dashboard, the user can view the list of trusted devices or remove the device by clicking the Delete Device link.
The Device ID (Save) module saves a user's device profile. The module can either save the profile upon request, requiring the user to provide a name for the device and explicitly save it, or it can save the profile automatically.
Note
If a user has multiple device profiles, the profile that is the closest match to the current client details is used for the comparison result.
Within its configured authentication chain, the Device ID (Save) module also takes the device print and creates a JSON object that consists of the ID, name, last selected date, selection counter, and device print itself.
The Device ID (Save) module has the following properties:
- Automatically store new profiles
Select the checkbox to automatically store new profiles. After successful HOTP confirmation, OpenAM stores the new profile automatically.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-device-id-save-auto-store-profile- Maximum stored profile quantity
Sets the maximum number of stored profiles on the user's record.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-device-id-save-max-profiles-allowed- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-device-id-save-auth-level
Log into the OpenAM console as an administrator.
Click the realm from which you want to work.
Click Authentication > Modules.
To add the Device ID (Save) module, click Add Module.
In the Module Name box, enter
Device-ID-Save.In the Type box, select
Device Id (Save), and then click Create.To configure the Device-Id (Save) module, do the following:
Click the Automatically store new profiles checkbox. If this box is left unchecked, the user will be prompted to give consent to store new profiles.
In the Maximum stored profile quantity box, enter the max number of stored profiles. Any profile that exceeds this number will not be stored.
In the Authentication Level box, enter a number corresponding to the authentication level of the module.
Click Save Changes.
The Federation authentication module is used by a service provider to create a user session after validating single sign-on protocol messages. This authentication module is used by the SAML, SAMLv2, ID-FF, and WS-Federation protocols.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthFederationService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthFederationAuthLevel
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module provides a more secure method for users to access their accounts with the help of a device such as a mobile phone. For detailed information about two-step verification with the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module in OpenAM, see "Multi-Factor Authentication".
Note
OpenAM provides two authentication modules that support OATH:
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module, which is optimized for use with the ForgeRock Authenticator app and provides device profile encryption.
The OATH authentication module, which is a raw OATH implementation requiring more configuration for users and the OpenAM administrator.
We recommend using the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module when possible.
Also, the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH), HOTP, and OATH authentication modules all support HOTP passwords, but the way that users obtain passwords differs. See "Differences Among OpenAM Authentication Modules That Support HOTP" for more information.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthAuthenticatorOATHService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-auth-level- One-Time Password Length
Sets the length of the OTP to six digits or longer. The default value is six.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-password-length- Minimum Secret Key Length
The minimum number of hexadecimal characters allowed for the secret key.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-min-secret-key-length- OATH Algorithm to Use
Select whether to use HOTP or TOTP. You can create an authentication chain to allow for a greater variety of devices. The default value is HOTP.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-algorithm- HOTP Window Size
The window that the OTP device and the server counter can be out of sync. For example, if the window size is 100 and the server's last successful login was at counter value 2, then the server will accept an OTP from device counter 3 to 102. The default value is 100.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-hotp-window-size- Add Checksum Digit
Adds a checksum digit at the end of the HOTP password to verify the OTP was generated correctly. This is in addition to the actual password length. Set this only if your device supports it. The default value is No.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-add-checksum- Truncation Offset
Advanced feature that is device-specific. Let this value default unless you know your device uses a truncation offset. The default value is -1.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-truncation-offset- TOTP Time Step Interval
The time interval for which an OTP is valid. For example, if the time step interval is 30 seconds, a new OTP will be generated every 30 seconds, and an OTP will be valid for 30 seconds. The default value is 30 seconds.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-size-of-time-step- TOTP Time Steps
The number of time step intervals that the system and the device can be off before password resynchronization is required. For example, if the number of TOTP time steps is 2 and the TOTP time step interval is 30 seconds, the server will allow an 89 second clock skew between the client and the server—two 30 second steps plus 29 seconds for the interval in which the OTP arrived. The default value is 2.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-fr-oath-steps-in-window- Maximum Allowed Clock Drift
The maximum acceptable clock skew before authentication fails. When this value is exceeded, the user must re-register the device.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-fr-oath-maximum-clock-drift- Name of the Issuer
A value that appears as an identifier on the user's device. Common choices are a company name, a web site, or an OpenAM realm.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-fr-oath-issuer-name
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module provides a way to send push notification messages to a device such as a mobile phone, enabling multi-factor authentication. For detailed information about multi-factor authentication with the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module in OpenAM, see "Multi-Factor Authentication".
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthAuthenticatorPushService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-auth-level- Return Message Timeout (ms)
The period of time (in milliseconds) within which a push notification should be replied to.
Default:
120000ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-message-response-timeout- Login Message
Text content of the push message, which is used for the notification displayed on the registered device. The following variables can be used in the message:
{{user}}Replaced with the username value of the account registered in the ForgeRock Authenticator app, for example Demo.
{{issuer}}Replaced with the issuer value of the account registered in the ForgeRock Authenticator app, for example ForgeRock.
Default:
Login attempt from {{user}} at {{issuer}}ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-message
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration module provides a way to register a device such as a mobile phone for multi-factor authentication. For detailed information about multi-factor authentication with the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module in OpenAM, see "Managing Devices for Multi-Factor Authentication".
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthAuthenticatorPushRegistrationService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-reg-auth-level- Issuer Name
A value that appears as an identifier on the user's device. Common choices are a company name, a web site, or an OpenAM realm.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-reg-issuer- Registration Response Timeout (ms)
The period of time (in milliseconds) to wait for a response to the registration QR code. If no response is received during this time the QR code times out and the registration process fails.
Default:
120000ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-push-message-registration-response-timeout- Background Color
The background color in hex notation to display behind the issuer's logo within the ForgeRock Authenticator app.
Default:
#519387ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-hex-bgcolour- Image URL
The location of an image to download and display as the issuer's logo within the ForgeRock Authenticator app.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-img-url- App Store App URL
URL of the app to download on the App Store.
Default:
https://itunes.apple.com/app/forgerock-authenticator /id1038442926(the ForgeRock Authenticator app)ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-apple-link- Google Play URL
URL of the app to download on Google Play.
Default:
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.forgerock.authenticator(the ForgeRock Authenticator app)ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-google-link
The HOTP authentication module works with an
authentication chain with any module that stores the username
attribute.
The module uses the username from the sharedState
set by the previous module in the chain and retrieves the user's email address
or telephone number to send a one-time password to the user. The user then
enters the password on a Login page and completes the authentication process if
successful.
For example, to set up HOTP in an authentication chain, you can configure
the Data Store module (or any module that stores the user's
username) as the requisite first module,
and the HOTP module as the second requisite module.
When authentication succeeds against the Data Store module, the HOTP module
retrieves the Email Address and Telephone Number attributes from the data store
based on the username value.
For the HOTP module to use either attribute, the Email Address must contain
a valid email address, or the Telephone Number must contain a valid
SMS telephone number.
You can set the HOTP module to automatically generate a password when users begin logging into the system. You can also set up mobile phone, mobile carrier, and email attributes for tighter controls over where the messages are generated and what provider the messages go through to reach the user.
Note
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH), HOTP, and OATH authentication modules all support HOTP passwords, but the way that users obtain passwords differs. See "Differences Among OpenAM Authentication Modules That Support HOTP" for more information.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthHOTPService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPAuthLevel- SMS Gateway Implementation Class
Change this if you must customize the SMS gateway implementation. The default class sends an SMS or email, depending on the configuration.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMSGatewayImplClassName- Mail Server Host Name
Host name of the mail server supporting SMTP for electronic mail.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPHostName- Mail Server Host Port
The default outgoing mail server port is 25, 465 (when connecting over SSL).
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPHostPort- Mail Server Authentication Username
User name for OpenAM to connect to the mail server.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPUserName- Mail Server Authentication Password
Password for OpenAM to connect to the mail server.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPUserPassword- Mail Server Secure Connection
If OpenAM connects to the mail server securely, OpenAM must be able to trust the server certificate.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPSSLEnabled- One-Time Password Validity Length (in minutes)
One-time passwords are valid for five minutes after they are generated by default.
Note
You may also also need to configure the login page session timeouts in OpenAM. For more information, see How do I configure login page session timeouts in OpenAM (All versions)?
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPPasswordValidityDuration- One-Time Password Length
Set the length of the OTP to 6 or 8.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPPasswordLength- One-Time Password Delivery
Send the one-time password by SMS, by mail, or both.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPasswordDelivery- Mobile Phone Number Attribute Name
Provides the attribute name used for the text message. The default value is
telephoneNumber.ssoadm attribute:
openamTelephoneAttribute- Mobile Carrier Attribute Name
Specifies a user profile attribute that contains a mobile carrier domain for sending SMS messages.
The uncustomized OpenAM user profile does not have an attribute for the mobile carrier domain. You can:
Customize the OpenAM user profile by adding a new attribute to it. Then you can populate the new attribute with users' SMS messaging domains.
All mobile carriers and bulk SMS messaging services have associated SMS messaging domains. For example, Verizon uses
vtext.com, T-Mobile usestmomail.net, and the TextMagic service usestextmagic.com. If you plan to send text messages internationally, determine whether the messaging service requires a country code.Leave the value for Mobile Carrier Attribute Name blank, and let OpenAM default to sending SMS messages using
txt.att.netfor all users.
ssoadm attribute:
openamSMSCarrierAttribute- Email Attribute Name
Provides the attribute name used to email the OTP. The default value is
mail(email).ssoadm attribute:
openamEmailAttribute- Auto Send OTP Code
Set up the HOTP module to automatically generate an email or text message when users begin the login process.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPAutoClicking- Email From Address
Specifies the
From:address when sending a one-time password by mail.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthHOTPSMTPFromAddress- One Time Password Max Retry
Sets the number of times an OTP may be entered. Minimum is 1, maximum is 10.
Default: 3
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-oath-max-retry
HTTP basic authentication takes a user name and password from HTTP authentication and tries authentication against the backend module in OpenAM, depending on what you configure as the Backend Module Name.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthHTTPBasicService
- Backend Module Name
Specifies the module that checks the user credentials. The credentials are then supplied to either a data store or other identity repository module for authentication.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-http-basic-module-configured- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-httpbasic-auth-level
The Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) module lets OpenAM connect to a database, such as MySQL or Oracle DB to authenticate users.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthJDBCService
- Connection Type
Choose Connection pool is retrieved via JNDI to connect using the Java Naming and Directory Interface connection pool supported by the web container in which OpenAM runs. Choose Non-persistent JDBC connection to connect directly through the JDBC driver.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCConnectionType- Connection Pool JNDI Name
When using Connection pool is retrieved via JNDI, this specifies the pool. How you configure connection pooling depends on the web container where you run OpenAM. Refer to the documentation for your web container for instructions on setting up connection pooling.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCJndiName- JDBC Driver
When using a non-persistent JDBC connection, this specifies the JDBC driver provided by the database.
The
.jarcontaining the JDBC driver belongs in theWEB-INF/libdirectory of the deployed OpenAM instance, and so you should add it to a custom OpenAM.warfile that you deploy.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCDriver- JDBC URL
When using a non-persistent JDBC connection, this specifies the URL to connect to the database.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCUrl- Database Username
Specify the user name to open the database connection.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCDbuser- Database Password
Specify the password for the user opening the database connection.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCDbpassword- Password Column Name
Specify the database column name where passwords are stored.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCPasswordColumn- Prepared Statement
Specify the SQL query to return the password corresponding to the user to authenticate.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCStatement- Class to Transform Password Syntax
Specify the class that transforms the password retrieved to the same format as provided by the user.
The default class expects the password in clear text. Custom classes must implement the
JDBCPasswordSyntaxTransforminterface.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCPasswordSyntaxTransformPlugin- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthJDBCAuthLevel
Note
OpenAM provides two properties, iplanet-am-admin-console-invalid-chars and
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-invalid-chars, that store
LDAP-releated special characters that are not allowed in username searches.
When using JDBC databases, consider adding the '%' wildcard character to
the iplanet-am-admin-console-invalid-chars and
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-invalid-chars properties. By default,
the '%' character is not included in the properties.
OpenAM connects to directory servers using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). To build an easy-to-manage, high-performance, pure Java, open source directory service, try OpenDJ directory services.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthLDAPService
- Primary LDAP Server, Secondary LDAP Server
Directory servers generally use built-in data replication for high availability. Thus, a directory service likely consists of a pool of replicas to which OpenAM can connect to retrieve and update directory data. You set up primary and secondary servers in case a replica is down due to maintenance or to a problem with a particular server.
Set one or more primary and optionally, one or more secondary directory server for each OpenAM server. For the current OpenAM server, specify each directory server as a
host:portcombination. For other OpenAM servers in the deployment, you can specify each directory server asserver-name|host:port, where server-name is the FQDN portion of the OpenAM server from the list under Deployment > Servers, and host:port identifies the directory server.For example, if the server-name that is listed is
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam, and the directory server is accessible atopendj.example.com:1389, you would enteropenam.example.com|opendj.example.com:1389.When authenticating users from a directory server that is remote to OpenAM, set the primary server values, and optionally the secondary server values. Primary servers have priority over secondary servers.
ssoadm attributes are: primary is
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-server; secondary isiplanet-am-auth-ldap-server2.Both properties take more than one value; thus, allowing more than one primary or secondary remote server, respectively. Assuming a multi-data center environment, OpenAM determines priority within the primary and secondary remote servers, respectively, as follows:
Every LDAP server that is mapped to the current OpenAM instance has highest priority.
For example, if you are connected to
openam1.example.comandldap1.example.comis mapped to that OpenAM instance, then OpenAM usesldap1.example.com.Every LDAP server that was not specifically mapped to a given OpenAM instance has the next highest priority.
For example, if you have another LDAP server,
ldap2.example.com, that is not connected to a specific OpenAM server and ifldap1.example.comis unavailable, OpenAM connects to the next highest priority LDAP server,ldap2.example.com.LDAP servers that are mapped to different OpenAM instances have the lowest priority.
For example, if
ldap3.example.comis connected toopenam3.example.comandldap1.example.comandldap2.example.comare unavailable, thenopenam1.example.comconnects toldap3.example.com.
If you want use SSL or StartTLS to initiate a secure connection to a data store, then scroll down to enable SSL/TLS Access to LDAP Server. Make sure that OpenAM can trust the server's certificates when using this option.
ssoadm attributes:
openam-auth-ldap-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- DN to Start User Search
LDAP data is organized hierarchically, a bit like a file system on Windows or UNIX. More specific DNs likely result in better search performance. When configuring the module for a particular part of the organization, you can perhaps start searches from a specific organizational unit, such as
ou=sales,dc=example,dc=com.If multiple entries exist with identical search attribute values, make this value specific enough to return only one entry.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-base-dn- Bind User DN, Bind User Password
If OpenAM stores attributes in the directory, for example to manage account lockout, or if the directory requires that OpenAM authenticate in order to read users' attributes, then OpenAM needs the DN and password to authenticate to the directory.
The default is
cn=Directory Manager. Make sure that password is correct before you log out. If it is incorrect, you will be locked out. If this should occur, you can login with the superuser DN, which by default isuid=amAdmin,ou=People,OpenAM-deploy-base, where OpenAM-deploy-base you set during OpenAM configuration.ssoadm attributes:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-bind-dn,iplanet-am-auth-ldap-bind-passwd- Attribute Used to Retrieve User Profile, Attributes Used to Search for a User to be Authenticated, User Search Filter, Search Scope
LDAP searches for user entries return entries with attribute values matching the filter you provide. For example, if you search under
ou=people,dc=example,dc=comwith a filter"(mail=bjensen@example.com)", then the directory returns the entry that hasmail=bjensen@example.com. In this example the attribute used to search for a user ismail. Multiple attribute values mean the user can authenticate with any one of the values. For example, if you have bothuidandmail, then Barbara Jensen can authenticate with eitherbjensenorbjensen@example.com.Should you require a more complex filter for performance, you add that to the User Search Filter text box. For example, if you search on
mailand add User Search Filter(objectClass=inetOrgPerson), then OpenAM uses the resulting search filter(&(mail=address)(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)), where address is the mail address provided by the user.Scope OBJECT means search only the entry specified as the DN to Start User Search, whereas ONELEVEL means search only the entries that are directly children of that object. SUBTREE means search the entry specified and every entry under it.
ssoadm attributes:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-user-naming-attribute,iplanet-am-auth-ldap-user-search-attributes,iplanet-am-auth-ldap-search-filter, andiplanet-am-auth-ldap-search-scope- LDAP Connection Mode
If you want use SSL or StartTLS to initiate a secure connection to a data store, OpenAM must be able to trust LDAP certificates, either because the certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- Return User DN to DataStore
When enabled, and OpenAM uses the directory service as the user store, the module returns the DN, rather than the User ID. From the DN value, OpenAM uses the RDN to search for the user profile. For example, if a returned DN value is
uid=demo,ou=people,dc=openam,dc=example,dc=org, OpenAM usesuid=demoto search the data store.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-return-user-dn- User Creation Attributes
This list lets you map (external) attribute names from the LDAP directory server to (internal) attribute names used by OpenAM.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-ldap-user-creation-attr-list- Minimum Password Length
Specify the minimum acceptable password length.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-min-password-length- LDAP Behera Password Policy Support
When enabled, support interoperability with servers that implement the Internet-Draft, Password Policy for LDAP Directories.
Support for this Internet-Draft is limited to the LDAP authentication module. Other components of OpenAM, such as the password change functionality in the
/idm/EndUserpage, do not support the Internet-Draft. In general, outside of the LDAP authentication module, OpenAM binds to the directory server as an administrator, such as Directory Manager. When OpenAM binds to the directory server as an administrator rather than as an end user, many features of the Internet-Draft password policies do not apply.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-behera-password-policy-enabled- Trust All Server Certificates
When enabled, blindly trust server certificates, including self-signed test certificates.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-ssl-trust-all- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
Specifies how often OpenAM should send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
Default: 1
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-heartbeat-interval- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Specifies the time unit corresponding to LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval.
Default: minute
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-heartbeat-timeunit- LDAP operations timeout
Defines the timeout in milliseconds that OpenAM should wait for a response from the directory server.
Default: 0 (means no timeout)
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-operation-timeout- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-ldap-auth-level- LDAPS Server Protocol Version
Defines which protocol version is used to establish the secure connection to the LDAP Directory Server.
Default:
TLSv1ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-ldap-secure-protocol-versionPossible values:
TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2
The Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) authentication module enables non-interactive authentication using a mobile subscriber ISDN associated with a terminal, such as a mobile phone. The module checks the subscriber ISDN against the value found on a user's entry in an LDAP directory service.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthMSISDNService
- Trusted Gateway IP Address
Specifies a list of IP addresses of trusted clients that can access MSISDN modules. Either restrict the clients allowed to access the MSISDN module by adding each IPv4 or IPv6 address here, or leave the list empty to allow all clients to access the module. If you specify the value
none, no clients are allowed access.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNTrustedGatewayList- MSISDN Number Search Parameter Name
Specifies a list of parameter names that identify which parameters to search in the request header or cookie header for the MSISDN number. For example, if you define x-Cookie-Param, AM_NUMBER, and COOKIE-ID, the MSISDN authentication service checks those parameters for the MSISDN number.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNParameterNameList- LDAP Server and Port
If you want to use SSL or TLS for security, then scroll down to enable SSL/TLS Access to LDAP. Make sure that OpenAM can trust the servers' certificates when using this option.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNLdapProviderUrl- LDAP Start Search DN
Specify the DN of the entry where the search for the user's MSISDN number should start.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNBaseDn- Attribute To Use To Search LDAP
Specify the name of the attribute in the user's profile that contains the MSISDN number to search for the user. The default is
sunIdentityMSISDNNumber.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNUserSearchAttribute- LDAP Server Authentication User
If OpenAM must authenticate to the directory server in order to search, then specify the bind DN. The default is
cn=amldapuser,ou=DSAME Users,dc=example,dc=com.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNPrincipalUser- LDAP Server Authentication Password
Specify the password corresponding to the bind DN.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNPrincipalPasswd- SSL/TLS for LDAP Access
If you choose to enable SSL or TLS, then make sure that OpenAM can trust the servers' certificates.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNUseSsl- MSISDN Header Search Attribute
Specify the headers to use for searching the request for the MSISDN number:
Cookie Header tells OpenAM to search the cookie.
Request Header tells OpenAM to search the request header.
Request Parameter tells OpenAM to search the request parameters.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNHeaderSearch- LDAP Attribute Used to Retrieve User Profile
Specify the LDAP attribute that is used during a search to return the user profile for MSISDN authentication service. The default is
uid.ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNUserNamingAttribute- Return User DN to DataStore
Enable this option only when the OpenAM directory is the same as the directory configured for MSISDN searches. When enabled, this option allows the authentication module to return the DN instead of the User ID. OpenAM thus does not need to perform an additional search with the user ID to find the user's entry.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNReturnUserDN- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthMSISDNAuthLevel
The Open Authentication (OATH) module provides a more secure method for users to access their accounts with the help of a device, such as their mobile phone or Yubikey. Users can log into OpenAM and update their information more securely from a one-time password (OTP) displayed on their device. The OATH module includes the OATH standard protocols (RFC 4226 and RFC 6238). The OATH module has several enhancements to the HMAC One-Time Password (HOTP) Authentication Module, but does not replace the original module for those already using HOTP prior to the 10.1.0 release. The OATH module includes HOTP authentication and Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP) authentication. Both types of authentication require an OATH compliant device that can provide the OTP.
HOTP authentication generates the OTP every time the user requests a new OTP on their device. The device tracks the number of times the user requests a new OTP, called the counter. The OTP displays for a period of time you designate in the setup, so the user may be further in the counter on their device than on their account. OpenAM will resynchronize the counter when the user finally logs in. To accommodate this, you set the number of passwords a user can generate before their device cannot be resynchronized. For example, if you set the number of HOTP Window Size to 50 and someone presses the button 30 on the user's device to generate a new OTP, the counter in OpenAM will review the OTPs until it reaches the OTP entered by the user. If someone presses the button 51 times, you will need to reset the counter to match the number on the device's counter before the user can login to OpenAM. HOTP authentication does not check earlier passwords, so if the user attempts to reset the counter on their device, they will not be able to login until you reset the counter in OpenAM to match their device. See "Deleting Registered Devices by using REST" for more information.
TOTP authentication constantly generates a new OTP based on a time interval you specify. The device tracks the last two passwords generated and the current password. The Last Login Time monitors the time when a user logs in to make sure that user is not logged in several times within the present time period. Once a user logs into OpenAM, they must wait for the time it takes TOTP to generate the next two passwords and display them. This prevents others from being able to access the users account using the OTP they entered. The user's account can be accessed again after the generation of the third new OTP is generated and displayed on their device. For this reason, the TOTP Time-Step Interval should not be so long as to lock users out, with a recommended time of 30 seconds.
An authentication chain can be created to generate an OTP from either HOTP or TOTP.
Note
OpenAM provides two authentication modules that support OATH:
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module, which is optimized for use with the ForgeRock Authenticator app and provides device profile encryption.
The OATH authentication module, which is a raw OATH implementation requiring more configuration for users and the OpenAM administrator.
We recommend using the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module when possible.
Also, the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH), HOTP, and OATH authentication modules all support HOTP passwords, but the way that users obtain passwords differs. See "Differences Among OpenAM Authentication Modules That Support HOTP" for more information.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthOATHService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-auth-level- One Time Password Length
Sets the length of the OTP to six digits or longer. The default value is six.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-password-length- Minimum Secret Key Length
The minimum number of hexadecimal characters allowed for the secret key.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-min-secret-key-length- Secret Key Attribute Name
The name of the attribute where the key will be stored in the user profile.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-secret-key-attribute- OATH Algorithm to Use
Select whether to use HOTP or TOTP. You can create an authentication chain to allow for a greater variety of devices. The default value is HOTP.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-algorithm- HOTP Window Size
The window that the OTP device and the server counter can be out of sync. For example, if the window size is 100 and the server's last successful login was at counter value 2, then the server will accept an OTP from device counter 3 to 102. The default value is 100.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-hotp-window-size- Counter Attribute Name
The name of the HOTP attribute where the counter will be stored in the user profile.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-hotp-counter-attribute- Add Checksum Digit
Adds a checksum digit at the end of the HOTP password to verify the OTP was generated correctly. This is in addition to the actual password length. Set this only if your device supports it. The default value is No.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-add-checksum- Truncation Offset
Advanced feature that is device-specific. Let this value default unless you know your device uses a truncation offset. The default value is -1.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-truncation-offset- TOTP Time Step Interval
The time interval for which an OTP is valid. For example, if the time step interval is 30 seconds, a new OTP will be generated every 30 seconds, and an OTP will be valid for 30 seconds. The default value is 30 seconds.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-size-of-time-step- TOTP Time Steps
The number of time step intervals that the system and the device can be off before password resynchronization is required. For example, if the number of TOTP time steps is 2 and the TOTP time step interval is 30 seconds, the server will allow an 89 second clock skew between the client and the server—two 30 second steps plus 29 seconds for the interval in which the OTP arrived. The default value is 2.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-steps-in-window- Last Login Time Attribute
The name of the attribute where both HOTP and TOTP authentication will store information on when a person last logged in.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oath-last-login-time-attribute-name- The Shared Secret Provider Class
The class that processes the user profile attribute where the user's secret key is stored. The name of this attribute is specified in the Secret Key Attribute Name property.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oath.plugins.DefaultSharedSecretProviderssoadm attribute:
forgerock-oath-sharedsecret-implementation-class- Clock Drift Attribute Name
The user profile attribute where the clock drift is stored. If this field is not specified, then OpenAM does not check for clock drift.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-oath-observed-clock-drift-attribute-name- Maximum Allowed Clock Drift
The maximum acceptable clock drift before authentication fails. If this value is exceeded, the user must register their device again.
The Maximum Allowed Clock Drift value should be greater than the TOTP Time Steps value.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-oath-maximum-clock-drift- One Time Password Max Retry
Sets the number of times an OTP may be entered. Minimum is 1, maximum is 10.
Default: 3
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-oath-max-retry
The OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication module lets OpenAM authenticate clients of OAuth resource servers. References in this section are to RFC 6749, The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework.
Tip
OpenAM provides a wizard for configuring common OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication providers, such as Facebook, Google, and Microsoft. For more information, see "Configuring Pre-Populated Social Authentication Providers".
If the module is configured to create an account if none exists, then you must provide valid SMTP settings. As part of account creation, the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect client authentication module sends the resource owner an email with an account activation code. To send email, OpenAM uses the SMTP settings from the configuration for the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect authentication module.
Note
The default settings are for Facebook.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthOAuthService
- Client id
OAuth
client_idas described in section 2.2 of RFC 6749.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-client-id- Client Secret
OAuth
client_secretas described in section 2.3 of RFC 6749.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-client-secret- Authentication Endpoint URL
URL to the end point handling OAuth authentication as described in section 3.1 of RFC 6749.
Default:
https://www.facebook.com/dialog/oauth.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-auth-service- Access Token Endpoint URL
URL to the end point handling access tokens as described in section 3.2 of RFC 6749.
Default:
https://graph.facebook.com/oauth/access_token.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-token-service- User Profile Service URL
User profile URL that returns profile information in JSON format.
Default:
https://graph.facebook.com/me.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-user-profile-service- Scope
According to The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework, a space-separated list of user profile attributes that the client application requires. The list depends on the permissions that the resource owner, such as the end user, grants to the client application.
Some authorization servers use non-standard separators for scopes. Facebook, for example, takes a comma-separated list.
Default:
email,read_stream(Facebook example)ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-scope- OAuth2 Access Token Profile Service Parameter name
Access token parameter name.
Default:
access_token.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-user-profile-param- Proxy URL
URL to the
/oauth2c/OAuthProxy.jspfile, part of OpenAM.Default:
@SERVER_PROTO@://@SERVER_HOST@:@SERVER_PORT@/@SERVER_URI@/oauth2c/OAuthProxy.jsp.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-sso-proxy-url- Account Provider
An account provider class.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.DefaultAccountProviderssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-account-provider- Account Mapper
Class implementing account mapping.
Default: Depends on how the module is created:
If the OAuth2 authentication module is created from the OpenAM console authentication tab of a realm, the default is:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.JsonAttributeMapper.If the OAuth2 authentication module is created from the OpenAM console Facebook authentication wizard, the default is:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.JsonAttributeMapper|*|facebook-.If the OAuth2 authentication module is created from the OpenAM console Google authentication wizard, the default is:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oidc.JwtAttributeMapper|*|Google-.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-account-mapper- Account Mapper Configuration
Map of OAuth Provider user account attributes used to find the local profile of the authenticated user, with values in the form
provider-attr=local-attr.Default:
email=mailandid=facebook-id.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-account-mapper-configuration- Attribute Mapper
Specifies the list of fully qualified class names for implementations that map attributes from the OAuth 2.0 authorization server or OpenID Connect provider to OpenAM profile attributes.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.JsonAttributeMapperProvided implementations are:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.JsonAttributeMapperorg.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oidc.JwtAttributeMapper(can only be used when using theopenidscope)Tip
You can provide string constructor parameters by appending pipe (
|) separated values.For example, the
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oidc.JwtAttributeMapperclass can take two constructor parameters: a comma-separated list of attributes and a prefix to apply to their values. Specify these as follows:org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oidc.JsonAttributeMapperssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-attribute-mapper- Attribute Mapper Configuration
Map of OAuth Provider user account attributes to local user profile attributes, with values in the form
provider-attr=local-attr.Default:
first_name=givenname,last_name=sn,name=cn,email=mail,id=facebook-id,first_name=facebook-fname,last_name=facebook-lname,email=facebook-email.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-attribute-mapper-configuration- Save attributes in the session
When enabled, add the mapped attributes to the session saved.
Valid values:
true,false.Default:
true.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-save-attributes-to-session-flag- Email attribute in OAuth2 Response
Specifies the attribute identifying email address in the response from the profile service in the OAuth provider. This setting is used to send an email address with an activation code for accounts created dynamically.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-mail-attribute- Create account if it does not exist
When enabled, if the user profile does not exist, optionally retrieve a password and activation code from the user, and then create the profile.
Valid values:
true,false.Default:
true.When the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect client is configured to create new accounts, the SMTP settings must also be valid. As part of account creation, the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect client authentication module sends the resource owner an email with an account activation code. To send the mail, OpenAM uses the SMTP settings you provide here in the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect client configuration.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-createaccount-flag- Prompt for password setting and activation code
When enabled, the user sets a password, receives an activation code by email. The user must correctly set both in order for the account to be created.
Valid values:
true,false.Default:
true.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-prompt-password-flag- Map to anonymous user
When enabled, map the OAuth authenticated user to the anonymous user you specify. No account is created, even if Create account if it does not exist is enabled.
Valid values:
true,false.Default:
false.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-map-to-anonymous-flag- Anonymous User
Specifies an anonymous user that exists in the current realm.
Default:
anonymous.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-anonymous-user- OAuth 2.0 Provider logout service
Specifies the optional URL of the OAuth Provider.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-logout-service-url- Logout options
Specifies whether not to log the user out without prompting from the OAuth Provider on logout, to log the user out without prompting, or to prompt the user regarding whether to log out from the OAuth provider.
Valid values:
prompt,logout,donotlogout.Default:
prompt.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-logout-behaviour- Mail Server Gateway implementation class
Class to interact with the mail server.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oauth2.DefaultEmailGatewayImplssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-email-gwy-impl- SMTP host
Host name of the mail server.
Default:
localhost.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-hostname- SMTP port
SMTP port number for the mail server.
Default:
25.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-port- SMTP User Name
If the mail server requires authentication to send mail, specifies the user name.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-username- SMTP User Password
If the mail server requires authentication to send mail, specifies the password.
ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-password- SMTP SSL Enabled
When enabled, connect to the mail server over SSL. OpenAM must be able to trust the SMTP server certificate.
Valid values:
true,false.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-ssl_enabled- SMTP From address
Specifies the message sender address, such as
no-reply@example.com.Default:
info@forgerock.com.ssoadm attribute:
org-forgerock-auth-oauth-smtp-email-from- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
Default: 0.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-oauth-auth-level- OpenID Connect validation configuration type
Validates the ID Token from the OpenID Connect provider, the module needs either a URL to get the public keys for the provider, or the symmetric key for an ID Token signed with a HMAC-based algorithm.
By default, the configuration type is
.well-known/openid-configuration_url. This means the module should retrieve the keys based on information in the OpenID Connect provider configuration document.You can instead configure the authentication module to validate the ID Token signature with the client secret key you provide, or to validate the ID token with the keys retrieved from the URL to the OpenID Connect provider's JSON Web Key Set.
/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration_url(Default)Retrieve the provider keys based on the information provided in the OpenID Connect Provider Configuration Document.
Specify the URL to the document as the discovery URL.
client_secretUse the client secret that you specify as the key to validate the ID Token signature according to the HMAC by using the client secret to the decrypt the hash, and then checking that the hash matches the hash of the ID token JWT.
jwk_urlRetrieve the provider's JSON web key set as the URL that you specify.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-crypto-context-type- OpenID Connect validation configuration value
Edit this field depending on the Configuration type you specified.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-crypto-context-value- Token Issuer
Required when the
openidscope is included. Value must match theissfield in the issued ID token. For example,accounts.google.com.The issuer value MUST be provided when OAuth 2.0 mix-up mitigation is enabled. For more information, see "OAuth 2.0 Mix-Up Mitigation".
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-issuer-name
Note
Old uses of DefaultAccountMapper are automatically
upgraded to the equivalent default implementations.
The following tables show endpoint URLs for OpenAM when configured as an OAuth 2.0 provider. For details, see "Managing OAuth 2.0 Authorization". The default endpoints are for Facebook as the OAuth 2.0 provider.
In addition to the endpoint URLs you can set other fields, like scope and attribute mapping, depending on the provider you use:
| OpenAM Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Authorization Endpoint URL |
Example: |
| Access Token Endpoint URL |
Example: |
| User Profile Service URL |
Example: |
[a] This OpenAM endpoint can take additional parameters. In particular, you must specify the realm if the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than the Top Level Realm (/). For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for the
realm The | |
OpenAM has added a new property to the OAuth 2.0 authentication module,
openam-auth-oauth-mix-up-mitigation-enabled. This OAuth 2.0
mix-up mitigation property controls whether the OAuth 2.0 authentication module
carries out additional verification steps when it receives the authorization
code from the authorization server. This setting should be only enabled when
the authorization server also supports OAuth 2.0 mix-up mitigation.
- OAuth 2.0 Mix-Up Mitigation Enabled
Specifies that the client must compare the issuer identifier of the authorization server upon registration with the issuer value returned in the
issresponse parameter. If they do not match, the client must abort the authorization process. The client must also confirm that the authorization server's response is intended for the client by comparing the client's client identifier to the value of theclient_idresponse parameter.For more information, see section 4 of OAuth 2.0 Mix-Up Mitigration Draft.
Note
At the time of this release, Facebook, Google, and Microsoft identity providers do not support this draft.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-oauth-mix-up-mitigation-enabledOn the OpenAM console, the field Token Issuer must be provided when the OAuth 2.0 mix-up mitigation feature is enabled. The authorization code response will contain an issuer value (
iss) that will be validated by the client. When the module is an OAuth2-only module (that is, OIDC is not used), the issuer value needs to be explicitly set in the Token Issuer field, so that the validation can succeed.Note
Consult with the authorization server's documentation on what value it uses for the issuer field.
The OpenID Connect id_token bearer module lets OpenAM rely on an OpenID Connect 1.0 provider's ID Token to authenticate an end user.
Note
This module validates an OpenID Connect ID token and matches it with a user profile. You should not use this module if you want OpenAM to act as a client in the full OpenID Connect authentication flow.
To provision OpenAM as an OpenID Connect client, you should instead configure an OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect module. OpenAM provides a wizard to configure an OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect module that will authenticate against an OpenID Connect 1.0 provider. For more information, see "Configuring Custom Social Authentication Providers".
The OpenID Connect id_token bearer module expects an OpenID Connect ID Token in an HTTP request header. It validates the ID Token, and if successful, looks up the OpenAM user profile corresponding to the end user for whom the ID Token was issued. Assuming the ID Token is valid and the profile is found, the module authenticates the OpenAM user.
You configure the OpenID Connect id_token bearer module to specify how OpenAM gets the information needed to validate the ID Token, which request header contains the ID Token, the issuer identifier for the provider who issued the ID Token, and how to map the ID Token claims to an OpenAM user profile.
Note
The default settings are for Google's provider.
ssoadm service name:
amAuthOpenIdConnect
- Account provider class
The account provider provides the means to search for and create OpenID Connect users given a set of attributes.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.mapping.DefaultAccountProviderssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-account-provider-class- OpenID Connect validation configuration type
In order to validate the ID Token from the OpenID Connect provider, the module needs either a URL to get the public keys for the provider, or the symmetric key for an ID Token signed with a HMAC-based algorithm.
By default, the configuration type is
.well-known/openid-configuration_url. This means the module should retrieve the keys based on information in the OpenID Connect Provider Configuration Document.You can instead configure the authentication module to validate the ID Token signature with the client secret key you provide, or to validate the ID token with the keys retrieved from the URL to the OpenID Connect provider's JSON Web Key Set.
.well-known/openid-configuration_url(Default)Retrieve the provider keys based on the information provided in the OpenID Connect Provider Configuration Document.
Specify the URL to the document as the discovery URL.
client_secretUse the client secret that you specify as the key to validate the ID Token signature according to the HMAC, using the client secret to the decrypt the hash and then checking that the hash matches the hash of the ID Token JWT.
jwk_urlRetrieve the provider's JSON Web Key Set at the URL that you specify.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-crypto-context-type- OpenID Connect validation configuration value
Edit this field depending on the Configuration type you specified.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-crypto-context-value- Name of header referencing the ID Token
The module looks for the ID Token in this HTTP request header.
Default:
oidc_id_tokenssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-header-name- Token Issuer
This corresponds to the expected issue identifier value in the
issof the ID Token.Default:
accounts.google.comssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-issuer-name- Mapping of jwt attributes to local LDAP attributes
This setting maps OpenID Connect ID Token claims to local user profile attributes, allowing the module to retrieve the user profile based on the ID Token.
In OpenID Connect, an ID Token is represented as a JSON Web Token (JWT). The ID Token section of the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 specification defines a number of claims included in the ID Token for all flows. Additional claims depend on the scopes requested of the OpenID Connect provider.
For each item in the map, the key is the ID Token field name and the value is the local user profile attribute name.
Default:
mail=email,uid=subssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-local-to-jwt-attribute-mappings- Audience name
The audience name for this OpenID Connect authentication module. Used to check that the ID token received is intended for this module as an audience.
Default:
examplessoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-audience-name- List of accepted authorized parties
A list of case-sensitive strings and/or URIs from which this authentication module accepts ID tokens. This list is checked against the authorized party claim of the ID token.
Default:
AuthorizedPartyExamplehttp://www.example.com/authorized/partyssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-accepted-authorized-parties- Principal Mapper class
The principal mapper matches the OpenID Connect end user with an OpenAM account. The default principal mapper uses the mapping of local attributes to ID Token attributes to find a user profile.
Default:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oidc.JwtAttributeMapperssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-openidconnect-principal-mapper-class
The Persistent Cookie module supports the configuration of cookie lifetimes
based on requests and a maximum time. Note that by default, the persistent
cookie is called session-jwt.
Important
If Secure Cookie is enabled (Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Security > Cookie), the Persistent Cookie module only works over HTTPS.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthPersistentCookieService
Before you begin, make sure a public key alias is defined in OpenAM.
The Persistent Cookie module encrypts a JSON Web Token (JWT) using a public
key from the OpenAM keystore. The keystore must be configured under Realms
> Realm Name > Authentication > Settings
> Security > Persistent Cookie Encryption Certificate Alias. If the
keystore changes and the default test key is no longer
present, the public key alias must be updated to reflect the change,
otherwise the module will fail. Similarly, in multi-instance deployments,
the keypair must be available on all OpenAM instances.
To configure the Persistent Cookie module globally in the console, navigate to Configure > Authentication, and then click Persistent Cookie. In the window that appears you should see the following attributes:
- Idle Timeout
Specify the maximum idle time between requests in hours. If that time is exceeded, the cookie is no longer valid.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-idle-time- Max Life
Specify the maximum life of the cookie in hours.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-max-life- Enforce Client IP
When enabled, enforces that the persistent cookie can only be used from the same client IP to which the cookie was issued.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-enforce-ip- Use secure cookie
When enabled, adds the "Secure" attribute to the persistent cookie.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-secure-cookie- Use HTTP only cookie
When enabled, adds the
HttpOnlyattribute to the persistent cookie.ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-http-only-cookie- HMAC Signing Key
Specify a key to use for HMAC signing of the persistent cookie. Values must be base64-encoded and at least 256 bits (32 bytes) long.
For example, to generate an HMAC signing key, run the following:
openssl rand -base64 32
or
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1|base64
Default: a random 256-bit secret key.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-persistent-cookie-hmac-key
When the Persistent Cookie module enforces the client IP address,
and OpenAM lies behind a load balancer or proxy layer,
configure the load balancer or proxy to send the address
by using the X-Forwarded-For header,
and configure OpenAM to consume and forward the header as necessary.
For details, see
"Handling HTTP Request Headers" in the Installation Guide.
The Persistent Cookie module belongs with a second module in an authentication chain. To see how this works, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Chains. Create a new chain and add modules as shown in the figure. The following example shows how a Persistent Cookie module is sufficient. If the persistent cookie does not yet exist, authentication relies on LDAP:
Select the Settings tab and locate settings for the post-authentication
processing class. Set the Class Name to
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.persistentcookie.PersistentCookieAuthModule,
as shown in the following figure:
You should now be able to authenticate automatically, as long as the cookie exists for the associated domain.
The Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) module lets OpenAM authenticate users against RADIUS servers.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthRadiusService
- Primary Radius Servers, Secondary Radius Servers
Specify the IP address or fully qualified domain name of one or more primary RADIUS server. The default is
127.0.0.1(localhost loopback), and optionally, set secondary servers.ssoadm attribute:
primary is iplanet-am-auth-radius-server1; secondary isiplanet-am-auth-radius-server2When authenticating users from a directory server that is remote to OpenAM, set the primary values, and optionally, the secondary server values. Primary servers have priority over secondary servers.
Both properties take more than one value; thus, allowing more than one primary or secondary remote server, respectively. Assuming a multi-data center environment, OpenAM determines priority within the primary and secondary remote servers, respectively, as follows:
Every RADIUS server that is mapped to the current OpenAM instance has highest priority.
Every RADIUS server that was not specifically mapped to a given OpenAM instance has the next highest priority.
RADIUS servers that are mapped to different OpenAM instances have the lowest priority.
- Shared Secret
Specify the shared secret for RADIUS authentication. The shared secret should be as secure as a well-chosen password.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-radius-secret- Port Number
Specify the RADIUS server port.
Default is 1645.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-radius-server-port- Timeout
Specify how many seconds to wait for the RADIUS server to respond. The default value is 3 seconds.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-radius-timeout- Health Check Interval
Used for failover. Specify how often OpenAM performs a health check on a previously unavailable RADIUS server by sending an invalid authentication request.
Default: 5 minutes
ssoadm attribute:
openam-auth-radius-healthcheck-interval- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-radius-auth-level
The Secure Attribute Exchange (SAE) module lets OpenAM authenticate a user who has already authenticated with an entity that can vouch for the user to OpenAM, so that OpenAM creates a session for the user. This module is useful in virtual federation, where an existing entity instructs the local OpenAM instance to use federation protocols to transfer authentication and attribute information to a partner application.
ssoadm attribute:
sunAMAuthSAEService
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm service name:
sunAMAuthSAEAuthLevel
The SAML2 authentication module lets administrators integrate SAML v2.0 single sign-on and single logout into an OpenAM authentication chain.
You use the SAML2 authentication module when deploying SAML v2.0 single sign-on in integrated mode. In addition to configuring SAML2 authentication module properties, integrated mode deployment requires that you make several changes to service provider configurations. Before attempting to configure a SAML2 authentication module instance, review "Implementing SAML v2.0 Single Sign-On in Integrated Mode" and make sure that you have made any required changes to your service provider configuration.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthSAML2Service
- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-saml2-auth-level- IdP Entity ID
The identity provider (IdP) for authentication requests to this module. Specify the name of a SAML v2.0 entity provider that is defined in the SAML2 authentication module's realm.
You can find configured entity providers in the OpenAM console under Federation. The Realm column identifies the realm in which an entity provider has been configured.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-entity-name- SP MetaAlias
Specifies the local alias for the service provider (SP).
For service providers configured in the Top Level Realm, use the format /SP Name.
For service providers configured in subrealms, use the format /Realm Name/SP Name.
You can find the local aliases for entity providers in the OpenAM console under Federation > Entity Provider Name > Services.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-meta-alias- Allow IdP to Create NameID
Specifies whether the IdP should create a new identifier for the authenticating user if none exists.
A value of
truepermits the IdP to create an identifier for the authenticating user if none exists. A value offalseindicates a request to constrain the IdP from creating an identifier.For detailed information, see the section on the
AllowCreateproperty in SAML Version 2.0 Errata 05.Default:
truessoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-allow-create- Linking Authentication Chain
Specifies an authentication chain that is invoked when a user requires authentication to the SP.
Authentication to the SP is required when the authentication module running on the SP is unable to determine the user's identity based on the assertion received from the IdP. In this case, the linking authentication chain is invoked to allow the end user to link their remote and local accounts.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-login-chain- Comparison Type
Specifies a comparison method to evaluate authentication context classes or statements. The value specified in this property overrides the value set in the SP configuration under Federation > Entity Providers > Service Provider Name > Assertion Content > Authentication Context > Comparison Type.
Valid comparison methods are
exact,minimum,maximum, orbetter.For more information about the comparison methods, see the section on the
<RequestedAuthnContext>element in Assertions and Protocols for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0.Default:
exactssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-auth-comparison- Authentication Context Class Reference
Specifies one or more URIs for authentication context classes to be included in the SAML request. Authentication context classes are unique identifiers for an authentication mechanism. The SAML v2.0 protocol supports a standard set of authentication context classes, defined in Authentication Context for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0. In addition to the standard authentication context classes, you can specify customized authentication context classes.
Any authentication context class that you specify in this field must be supported for the service provider. To determine which authentication context classes are supported, locate the list of authentication context classes that are available to the SP under Federation > Entity Providers > Service Provider Name > Assertion Content > Authentication Context, and then review the values in the Supported column.
When specifying multiple authentication context classes, use the | character to separate the classes.
Example value:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:Password|urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:TimesyncTokenssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-authn-context-class-ref- Authentication Context Declaration Reference
Specifies one or more URIs that identify authentication context declarations.
This field is optional.
When specifying multiple URIs, use the | character to separate the URIs.
For more information, see the section on the
<RequestedAuthnContext>element in Assertions and Protocols for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0.ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-authn-context-decl-ref- Request Binding
Specifies the format used to send the authentication request from the SP to the IdP.
Valid values are
HTTP-RedirectandHTTP-POST.Default:
HTTP-Redirectssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-req-binding. When using the ssoadm command, set this attribute's value tourn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirectorurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST.- Response Binding
Specifies the format used to send the response from the IdP to the SP.
A value of
HTTP-POSTindicates that the HTTP POST binding with a self-submitting form should be used in assertion processing. A value ofHTTP-Artifactindicates that the HTTP Artifact binding should be used.Default:
HTTP-Artifactssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-binding. When using the ssoadm command, set this attribute's value tourn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Artifactorurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST.- Force IdP Authentication
Specifies whether the IdP should force authentication or can reuse existing security contexts.
A value of
trueindicates that the IdP should force authentication. A value offalseindicates that the IdP can reuse existing security contexts.ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-force-authn- Passive Authentication
Specifies whether the IdP should use passive authentication or not. Passive authentication requires the IdP to only use authentication methods that do not require user interaction. For example, authenticating using an X.509 certificate.
A value of
trueindicates that the IdP should authenticate passively. A value offalseindicates that the IdP should not authenticate passively.ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-is-passive- NameID Format
Specifies a SAML name ID format to be requested in the SAML authentication request.
Default:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-name-id-format- Single Logout Enabled
Specifies whether OpenAM should attempt to log out of the user's IdP session during session logout.
When enabling SAML v2.0 single logout, you must also configure the post-authentication processing class for the authentication chain containing the SAML2 authentication module to
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.saml2.SAML2PostAuthenticationPlugin.For more information about configuring single logout when implementing SAML v2.0 federation using the SAML2 authentication module, see "Configuring Single Logout in an Integrated Mode Implementation".
Default:
falsessoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-slo-enabled- Single Logout URL
Specifies the URL to which the user is forwarded after successful IdP logout. Configure this property only if you have enabled SAML v2.0 single logout by selecting the Single Logout Enabled check box.
ssoadm attribute:
forgerock-am-auth-saml2-slo-relay
This section covers what to configure for scripted authentication modules.
A scripted authentication module runs scripts to authenticate a user. The configuration for the module can hold two scripts, one to include in the web page run on the client user-agent, another to run in OpenAM on the server side.
The client-side script is intended to retrieve data from the user-agent. This must be in a language the user-agent, such as JavaScript, even if the server-side script is written in Groovy.
The server-side script is intended to handle authentication.
Scripts are stored not as files, but instead as OpenAM configuration data. This makes it easy to update a script on one OpenAM server, and then to allow replication to copy it to other servers. You can manage the scripts through OpenAM console, where you can write them in the text boxes provided or upload them from files.
You can also upload scripts and associate them with a scripted authentication module by using the ssoadm command.
The following example shows how to upload a server-side script from a file, create a scripted authentication module, and then associate the uploaded script with the new module.
#
# Upload a server-side script from a script file, myscript.groovy.
#
ssoadm create-sub-cfg \
--realm / \
--adminid amadmin \
--password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \
--servicename ScriptingService \
--subconfigname scriptConfigurations/scriptConfiguration \
--subconfigid myScriptId \
--attributevalues \
"name=My Scripted Auth Module Script" \
"script-file=myscript.groovy" \
"context=AUTHENTICATION_SERVER_SIDE" \
"language=GROOVY"
#
# Create a scripted authentication module, myScriptedAuthModule.
#
ssoadm create-auth-instance \
--realm / \
--adminid amadmin \
--password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \
--authtype Scripted \
--name myScriptedAuthModule
#
# Associate the script with the auth module, and disable client-side scripts.
#
ssoadm update-auth-instance \
--realm / \
--adminid amadmin \
--password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \
--name myScriptedAuthModule \
--attributevalues \
"iplanet-am-auth-scripted-server-script=myScriptId" \
"iplanet-am-auth-scripted-client-script-enabled=false"If you have multiple separate sets of client-side and server-side scripts, then configure multiple modules, one for each set of scripts.
For details on writing authentication module scripts, see "Default Server-side Authentication Script" in the Developer's Guide.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthScriptedService
Use the following settings at the realm level when configuring an individual scripted authentication module, in OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Modules.
- Client-Side Script Enabled
When selected, include the specified client-side script in the login page to be executed on the user-agent prior to the server-side script.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-client-script-enabled- Client-Side Script
The ID of the script to include in the login page. This script is run on the user-agent prior to the server-side script.
This script must be written in a language the user-agent can interpret, such as JavaScript, even if the server-side script is written in Groovy.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-client-script- Server Side Script
The ID of the script to run in OpenAM after the client-side script has completed.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-server-script- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the scripted authentication module.
The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-scripted-auth-level
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Scripting, click the script type in the Instances table, and then click Engine Configuration.
Note
Only server-side script context types have engine configurations.
On the Engine Configuration page, configure the following settings for the scripting engine of the selected type:
- Server-side Script Timeout
The maximum execution time any individual script should take on the server (in seconds). OpenAM terminates scripts which take longer to run than this value.
ssoadm attribute:
serverTimeout- Core thread pool size
The initial number of threads in the thread pool from which scripts operate. OpenAM will ensure the pool contains at least this many threads.
ssoadm attribute:
coreThreads- Maximum thread pool size
The maximum number of threads in the thread pool from which scripts operate. If no free thread is available in the pool, OpenAM creates new threads in the pool for script execution up to the configured maximum.
ssoadm attribute:
maxThreads- Thread pool queue size
The number of threads to use for buffering script execution requests when the maximum thread pool size is reached.
ssoadm attribute:
queueSize- Thread idle timeout (seconds)
Length of time (in seconds) for a thread to be idle before OpenAM terminates created threads. If the current pool size contains the number of threads set in
Core thread pool size, then idle threads will not be terminated, maintaining the initial pool size.ssoadm attribute:
idleTimeout- Java class whitelist
Specifies the list of class name patterns allowed to be invoked by the script. Every class accessed by the script must match at least one of these patterns.
You can specify the class name as-is or use a regular expression.
ssoadm attribute:
whiteList- Java class blacklist
Specifies the list of class name patterns that are NOT allowed to be invoked by the script. The blacklist is applied AFTER the whitelist to exclude those classes. Access to a class specified in both the whitelist and the blacklist will be denied.
You can specify the class name to exclude as-is or use a regular expression.
ssoadm attribute:
blackList- Use system SecurityManager
If enabled, OpenAM will make a call to
System.getSecurityManager().checkPackageAccess(...)for each class that is accessed. The method throwsSecurityExceptionif the calling thread is not allowed to access the package.Note
This feature only takes effect if the security manager is enabled for the JVM.
ssoadm attribute:
useSecurityManager
The SecurID module lets OpenAM authenticate users with RSA Authentication Manager software and RSA SecurID authenticators.
Important
To use the SecurID authentication module, you must first build an OpenAM war file that includes the supporting library. For more information, see "Enabling RSA SecurID Support" in the Installation Guide.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthSecurIDService
- ACE/Server Configuration Path
Specify the directory where the SecurID ACE/Server
sdconf.recfile is located, which by default is expected under the OpenAM configuration directory, such as$HOME/openam/openam/auth/ace/data. The directory must exist before OpenAM can use SecurID authentication.ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-securid-server-config-path- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-securid-auth-level
The Windows Desktop SSO module uses Kerberos authentication. The user presents a Kerberos token to OpenAM through the Simple and Protected GSS-API Negotiation Mechanism (SPNEGO) protocol. The Windows Desktop SSO authentication module enables desktop single sign on such that a user who has already authenticated with a Kerberos Key Distribution Center can authenticate to OpenAM without having to provide the login information again. Users might need to set up Integrated Windows Authentication in Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge to benefit from single sign on when logged on to a Windows desktop.
Warning
If you are using the Windows Desktop SSO module as part of an
authentication chain and Windows Desktop SSO fails, you may no longer be
able to POST data to non-NTLM-authenticated web sites.
For information on a possible workaround, see
Microsoft knowledge base article KB251404.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthWindowsDesktopSSOService
- Service Principal
Specify the Kerberos principal for authentication in the following format.
HTTP/host.domain@dc-domain-name
Here, host and domain correspond to the host and domain names of the OpenAM instance, and dc-domain-name is the domain name of the Windows Kerberos domain controller server. The dc-domain-name can differ from the domain name for OpenAM.
You set up the account on the Windows domain controller, creating a computer account for OpenAM and associating the new account with a service provider name.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-principal-name- Keytab File Name
Specify the full path of the keytab file for the Service Principal. You generate the keytab file using the Windows ktpass utility.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-keytab-file- Kerberos Realm
Specify the Kerberos Key Distribution Center realm. For the Windows Kerberos service, this is the domain controller server domain name.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-kerberos-realm- Kerberos Server Name
Specify the fully qualified domain name of the Kerberos Key Distribution Center server, such as that of the domain controller server.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-kdc- Return Principal with Domain Name
When enabled, OpenAM automatically returns the Kerberos principal with the domain controller's domain name during authentication.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-returnRealm- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-auth-level- Trusted Kerberos realms
List of trusted Kerberos realms for user Kerberos tickets. If realms are configured, then Kerberos tickets are only accepted if the realm part of the user principal name of the user's Kerberos ticket matches a realm from the list.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-kerberos-realms-trusted- Search for the user in the realm
Validates the user against the configured data stores. If the user from the Kerberos token is not found, authentication will fail. If an authentication chain is set, the user is able to authenticate through another module. This search uses the
Alias Search Attribute Namefrom the core realm attributes. See "Core Authentication Attributes - User Profile".ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-windowsdesktopsso-lookupUserInRealm
Note
Sending a ForceAuth=true authentication request when the user
has a valid session may result in failed authentication unless the request
hits the authoritative OpenAM server.
Authentication cross-talk requires an authorization header in the request that grants the new server access to the user's authentication token.
To ensure the authorization headers are included in the cross-talk requests, perform the following steps:
Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced.
Modify the following advanced properties:
Add the
WWW-Authenticatevalue to theopenam.retained.http.headersproperty.Add the
Authorizationvalue to theopenam.retained.http.request.headersproperty.
Save your changes.
The Windows NT module lets OpenAM authenticate against a Microsoft Windows NT server.
This module requires that you install a Samba client in a
bin directory under the OpenAM configuration directory,
such as $HOME/openam/openam/bin.
ssoadm service name:
iPlanetAMAuthNTService
- Authentication Domain
Specify the Windows domain name to which users belong.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-nt-domain- Authentication Host
Specify the NetBIOS name of the Windows NT host to which to authenticate users.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-nt-host- Samba Configuration File Name
Specify the full path to the Samba configuration file.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-samba-config-file-name- Authentication Level
Sets the authentication level used to indicate the level of security associated with the module. The value can range from 0 to any positive integer.
ssoadm attribute:
iplanet-am-auth-nt-auth-level
Once you have configured authentication modules and added the modules to the list of module instances, you can configure authentication chains. Authentication chains let you handle cases where alternate modules or credentials are needed. If you need modules in the chain to share user credentials, then set options for the module.
Tip
OpenAM provides a wizard for configuring authentication providers, including Facebook, Google, and Microsoft. The wizard creates a relevant authentication chain as part of the process. For more information, see "Configuring Social Authentication".
On the Realms page of the OpenAM console, click the realm for which to create the authentication chain.
On the Realm Overview page, click Authentication in the left-hand menu, and then click Chains.
On the Authentication Chains page, click Add Chain. Enter new chain name, and then click Create.
On the New Module dialog, select the authentication module in the chain, and then assign appropriate criteria (Optional, Required, Requisite, Sufficient) as described in "About Authentication in OpenAM". You can also configure where OpenAM redirects the user upon successful and failed authentication, and plug in your post-authentication processing classes as necessary.
(Optional) If you need modules in the chain to share user credentials, consider the following available options. Enter the key and its value, and then click Plus (+). When you finish entering the options, click OK.
iplanet-am-auth-store-shared-state-enabledSet
iplanet-am-auth-store-shared-state-enabled=trueto store the credentials captured by this module in shared state. This enables subsequent modules in the chain to access the credentials captured by this module. The shared state is cleared when the user successfully authenticates, quits the chain, or logs out.Default:
trueiplanet-am-auth-shared-state-enabledSet
iplanet-am-auth-shared-state-enabled=trueto allow this module to access the credentials, such as user name and password, that have been stored in shared state by previous modules in the authentication chain.Default:
falseiplanet-am-auth-shared-state-behavior-patternSet
iplanet-am-auth-shared-state-behavior-pattern=tryFirstPassto try authenticating with the username and password stored in shared state. If authentication fails, OpenAM displays the login screen of this module for the user to re-enter their credentials.Set
iplanet-am-auth-shared-state-behavior-pattern=useFirstPassto prevent the user from entering the username and password twice during authentication. Typically, you set the property touseFirstPassfor all modules in the chain except the first module. If authentication fails, then the module fails.Default:
tryFirstPass
For example, consider a chain with two modules sharing credentials according to the following settings: The first module in the chain has the option
iplanet-am-auth-store-shared-state-enabled=true, and criteriaREQUIRED.The second module in the chain has options
iplanet-am-auth-shared-state-enabled=true,iplanet-am-auth-shared-state-behavior-pattern=useFirstPasswith criteriaREQUIRED.Click Save Changes.
The following authentication sequence would occur: The user enters their credentials for the first module and successfully authenticates. The first module shares the credentials with the second module, successfully authenticating the user without prompting again for their credentials, unless the credentials for the first module do not successfully authenticate the user to the second module.
Before you select the default chain for users, and especially for
administrators, test the authentication chain first. For example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?service=NewChain.
If you cannot log in, then go back and fix the authentication chain's
configuration before making it the default.
On the Realms page of the OpenAM console, click the realm for which to set the default authentication chain.
(Optional) If necessary, on the Authentication tab page for the realm, adjust the drop-down lists for Organization Authentication Configuration and Administrator Authentication Configuration to the appropriate authentication chains.
The Organization Authentication Configuration serves when users access
/openam/UI/Login.The Administrator Authentication Configuration serves when users access
/openam/console.You can set these independently to separate administrative login from user login. For example, you can change the default user chain, but leave the default administrator chain as is to avoid locking yourself out as administrator. By default,
amadmincan log in at/openam/UI/Login. You can change that for your deployment.Save your work.
A post-authentication plugin provides custom processing at the end of the authentication process and immediately before the subject is authenticated. Post authentication plugins are often used in conjunction with policy agents. The post-authentication plugin sets custom session properties, and then the policy agent injects the custom properties into the request header to the protected application. Other common uses of post authentication plugins include setting cookies and session variables. You can configure a post authentication plugin for individual realms or for an authentication chain.
Important
Implementing a post authentication processing plugin in the top level realm can have unexpected effects. OpenAM invokes a post authentication plugin when the plugin is configured in the top level realm, which will then run for all types of authentication during startup, including user logins and internal administrative logins. The best practice first and foremost is to configure end-users to only log into subrealms, while administrators only log into the top level realm. If you need to execute the post authentication plugin for administrative logins, make sure that the plugin can also handle internal authentications.
An alternate solution is to configure the post authentication plugin on a per authentication chain basis, which can be configured separately for user logins or administrative logins.
Configure a post authentication plugin for a realm or authentication chain as follows:
Realm. You can configure a post authentication plugin for all users in a specific realm using the OpenAM console by navigating to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > Post Authentication Processing > Authentication Post Processing Classes. Add the required post authentication class.
You can also configure the post authentication plugin for a realm using an ssoadm command, as follows:
$ ./ssoadm set-svc-attrs -s iPlanetAMAuthService -e realm-name \ -u adminID -f passwordfile \ -a iplanet-am-auth-post-login-process-class=post-auth-class
Authentication Chain. You can configure a post authentication plugin for a specific authentication chain on the OpenAM console by navigating to Realms > realm-name > Authentication > Chains > chain-name > Settings > Post Authentication Processing Class. Add the post authentication class.
Using ssoadm, run the following:
$ ./ssoadm update-auth-cfg-props -e realm-name -m auth-chain -u adminID -f passwordfile \ -a iplanet-am-auth-post-login-process-class=post-auth-class
OpenAM provides some post-authentication plugins as part of the standard product delivery.
- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.adaptive.Adaptive The adaptive authentication plugin serves to save cookies and profile attributes after successful authentication.
Add it to your authentication chains that use the adaptive authentication module configured to save cookies and profile attributes.
- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.common.JaspiAuthLoginModulePostAuthenticationPlugin The Java Authentication Service Provider Interface (JASPI) post authentication plugin initializes the underlying JASPI
ServerAuthmodule.JASPI defines a standard service provider interface (SPI) where developers can write message level authentication agents for Java EE containers on either the client side or the server side.
- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oauth2.OAuth2PostAuthnPlugin The OAuth 2.0 post-authentication plugin builds a global logout URL used by
/oauth2c/OAuthLogout.jspafter successful OAuth 2.0 client authentication. This logs the resource owner out with the OAuth 2.0 provider when logging out of OpenAM.Before using this plugin, configure the OAuth 2.0 authentication module with the correct OAuth 2.0 Provider logout service URL, and set the Logout options to Log out or Prompt. This plugin cannot succeed unless those parameters are correctly set.
Sometimes OAuth 2.0 providers change their endpoints, including their logout URLs. When using a provider like Facebook, Google, or MSN, make sure you are aware when they change their endpoint locations so that you can change your client configuration accordingly.
- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.plugins.AccountExpirePlugin The account expiration post-authentication plugin sets an account expiration date after successful authentication. OpenAM uses this to prevent expired accounts from being used to authenticate.
The default of 30 days can be changed using the advanced OpenAM server property,
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.accountExpire.days.- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.saml2.SAML2PostAuthenticationPlugin The SAML v2.0 post-authentication plugin that gets activated for single logout. Supports HTTP-Redirect for logout-sending messages only.
Set the post-authentication processing class for the authentication chain that contains the SAML v2.0 authentication module.
- Class name:
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.persistentcookie.PersistentCookieAuthModule The Persistent Cookie Authentication Module provides logic for persistent cookie authentication in OpenAM. It makes use of the JASPI
JwtSessionmodule to create and verify the persistent cookie.
If necessary, you can also write your own custom post-authentication plugin as described in "Creating a Post Authentication Plugin" in the Developer's Guide.
This section explains how to connect to OpenAM for user authentication by adding parameters to the login URL when testing your configuration.
When using the XUI, the base URL to authenticate to OpenAM points to
/XUI/#login under the deployment URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#login.
The base URL to log out is similar, for example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#logout/.
You can specify the realm that you want to log in to as follows:
| Description | Example URL |
|---|---|
| As part of the URL path |
|
| As a URL parameter |
|
As a parameter of XUI
|
|
| As the fully-qualified host name in the URL, if the realm has a DNS alias |
|
Use any of the options listed in "OpenAM Authentication Parameters" as URL parameters. The following are example URLs with parameters:
| Description | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Log in to the top level realm, requesting that OpenAM display the user interface in German. |
|
Log in to the myRealm realm, requesting that OpenAM
display the user interface in German.
|
|
Log in to the myRealm realm using the
HOTPChain authentication chain, requesting that
OpenAM display the user interface in German.
|
|
When using the classic UI, the base URL to authenticate to OpenAM points to
/UI/Login under the deployment URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login.
The base URL to log out is similar, for example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Logout.
You can specify the realm that you want to log in to as follows:
| Description | Example URL |
|---|---|
Use the &realm URL parameter to specify the
realm that you want to log in to.
|
|
| If the realm has a DNS alias, use it to reference the realm. |
|
Use any of the options listed in "OpenAM Authentication Parameters" as URL parameters. The following are example URLs with parameters:
| Description | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Log in to the top level realm, requesting that OpenAM display the user interface in German. |
|
Log in to the myRealm realm, requesting that OpenAM
display the user interface in German.
|
|
Log in to the myRealm realm using the
HOTPChain authentication chain, requesting that
OpenAM display the user interface in German.
|
|
OpenAM accepts the following parameters in the query string. With
the exception of IDToken parameters, use no more than
one occurrence of each.
- arg=newsession
Request that OpenAM end the user's current session and start a new session.
- authlevel
Request that OpenAM authenticate the user using a module with at least the specified authentication level that you have configured.
As this parameter determines authentication module selection, do not use it with
module,service, oruser.- ForceAuth
If
ForceAuth=true, request that OpenAM force the user to authenticate even if they already has a valid session. On successful authentication, OpenAM updates the session token.- goto
On successful authentication, or successful logout, request that OpenAM redirect the user to the specified location. Values must be URL-encoded.
- gotoOnFail
On authentication failure, request that OpenAM redirect the user to the specified location. Values must be URL-encoded.
- IDToken1, IDToken2, ..., IDTokenN
Pass the specified credentials as
IDTokenparameters in the URL. TheIDTokencredentials map to the fields in the login page for the authentication module, such asIDToken1as user ID andIDToken2as password for basic user name, password authentication. The order depends on the callbacks in login page for the module;IDTokenNrepresents the Nth callback of the login page.- locale
Request that OpenAM display the user interface in the specified, supported locale. Locale can also be set in the user's profile, in the HTTP header from her browser, configured in OpenAM, and so on.
- module
Request that OpenAM use the authentication module instance as configured for the realm where the user is authenticating.
As this parameter determines authentication module selection, do not use it with
authlevel,service, oruser.- realm
Request that OpenAM authenticate the user to the specified realm.
- service
Request that OpenAM authenticate the user with the specified authentication chain.
As this parameter determines authentication module selection, do not use it with
authlevel,module, oruser.- user
Request that the user, specified by their OpenAM universal ID, authenticates according to the chain specified by the User Authentication Configuration property in their user profile. You can configure this property for a user under Realms > Realm Name > Subjects > User > User Name.
In order for the User Authentication Configuration property to appear in user profiles, the
iplanet-am-user-serviceobject class must contain theiplanet-am-user-auth-configattribute in the identity repository schema. The default identity repository schemas provided with OpenAM include this object class and attribute. See "Preparing an External Identity Repository" in the Installation Guide for information about identity repository schema.As this parameter determines authentication module selection, do not use it with
authlevel,module, orservice.
This section explains multi-factor authentication in OpenAM. Multi-factor authentication requires that users provide more than one form of credential when logging in. A very common multi-factor authentication scenario is for users to be prompted to submit a user ID and password, and then to be prompted to submit a one-time password generated by an authenticator app on their mobile phone.
This section provides general information about multi-factor authentication, describes how end users authenticate using multi-factor authentication, and covers how administrators implement and support multi-factor authentication.
Multi-factor authentication is an authentication technique that requires users to provide multiple forms of identification when logging in to OpenAM. Multi-factor authentication provides a more secure method for users to access their accounts with the help of a device.
Note that the word device is used in this section to mean a piece of equipment that can display a one-time password or that supports push notifications using protocols supported by OpenAM multi-factor authentication. Devices are most commonly mobile phones with authenticator apps that support the OATH protocol or push notifications, but could also include other equipment.
The following is an example scenario of multi-factor authentication in OpenAM:
An OpenAM administrator configures an authentication chain with the Data Store and ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication modules.
An end user authenticates to OpenAM using that authentication chain.
OpenAM prompts the user to enter the user ID and password as required by the Data Store authentication module—the first factor in multi-factor authentication.
If the user ID and password were correct, OpenAM prompts the user to obtain a one-time password.
The user runs an authenticator app on a mobile phone that generates and displays a one-time password.
The user provides the one-time password to OpenAM to successfully complete authentication—the second factor in multi-factor authentication.
Administrators set up multi-factor authentication by creating authentication chains with two or more authentication modules. The initial module in the chain defines the first authentication module for multi-factor authentication. In the preceding scenario, the first authentication module is the Data Store authentication module. Subsequent modules in the chain define the additional factors required to log in, for example the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) or ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication modules.
OpenAM supports the Open AuTHentication (OATH) protocols, and also push notification for multi-factor authentication.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module supports HMAC one-time password (HOTP) and time-based one-time password (TOTP) authentication as defined in the OATH standard protocols for HOTP (RFC 4226) and TOTP (RFC 6238). Both HOTP and TOTP authentication require an OATH-compliant device that can provide the password.
HOTP authentication generates the one-time password every time the user requests a new password on their device. The device tracks the number of times the user requests a new one-time password with a counter. The one-time password displays for a period of time you designate in the setup, so the user may be further in the counter on their device than on their account.
OpenAM will resynchronize the counter when the user finally logs in. To accommodate this, you set the number of passwords a user can generate before their device cannot be resynchronized. For example, if you set the number of HOTP Window Size to 50 and someone presses the button 30 times on the user's device to generate a new password, the counter in OpenAM will review the passwords until it reaches the one-time password entered by the user. If someone presses the button 51 times, you will need to reset the counter to match the number on the device's counter before the user can login to OpenAM. HOTP authentication does not check earlier passwords, so if the user attempts to reset the counter on their device, they will not be able to login until you reset the counter in OpenAM to match their device. For more information, see "Deleting Registered Devices by using REST".
TOTP authentication constantly generates a new one-time password based on a time interval you specify. The device tracks the last several passwords generated and the current password. The TOTP Time Steps setting configures the number of passwords tracked. The Last Login Time setting monitors the time when a user logs in to make sure that user is not logged in several times within the present time period. The TOTP Time-Step Interval should not be so long as to lock users out, with a recommended time of 30 seconds.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH), OATH, and HOTP authentication modules all let you configure authentication that prompts users to enter HMAC one-time passwords. It is important that administrators understand the differences among these authentication modules:
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) and OATH authentication modules accept one-time passwords generated by the end user's device, while the HOTP authentication module generates passwords and sends them to users by e-mail or SMS.
All three of the authentication modules support HOTP passwords. The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) and OATH authentication modules also support TOTP passwords.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) and OATH authentication modules require users to register their devices, and store the device registration details in the user profile. The HOTP authentication module requires the presence of mobile phone numbers and/or e-mail addresses in user profiles.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module can encrypt stored device registration details.
Before deciding on an implementation strategy, assess your requirements against the following capabilities in OpenAM:
| Requirement | Available With the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) Authentication Module? | Available With the HOTP Authentication Module? |
|---|---|---|
| End users can authenticate using a HOTP password | Yes | Yes |
| OpenAM can generate a HOTP password and send it to end users in a text message or an e-mail | No | Yes |
| End users can register a mobile phone with OpenAM, and an authenticator app on the phone can generate a HOTP or TOTP password that OpenAM accepts as proof of authentication | Yes | No |
| End users can authenticate with a TOTP password | Yes | No |
| End users can opt out of providing a one-time password | Yes | No |
| End users can authenticate using XUI | Yes | Yes |
| End users can authenticate using the legacy UI | No | Yes |
You can use push notifications as part of the authentication process in OpenAM.
To receive push notifications when authenticating, end users must register an Android or iOS device with OpenAM. The registered device can then be used as an additional factor when authenticating to OpenAM. OpenAM can send the device a push notification, which can be accepted by the ForgeRock Authenticator app. In the app, the user can allow or deny the request that generated the push notification and return the response to OpenAM.
The following steps occur when OpenAM receives an authentication request and is configured for multi-factor authentication using push notifications:
The user must provide credentials to enable OpenAM to locate the user in the identity store and determine if they have a registered mobile device.
OpenAM prompts the user to register a mobile device if they have not done so already. Registering a device associates metadata about the device essential for enabling push notifications with the user's profile in the identity store.
For more information, see "Managing Devices for Multi-Factor Authentication".
Once the details of the registered device are obtained, OpenAM creates a push message specific to the registered device. The message has a unique ID, which OpenAM stores in anticipation of a response from the registered device.
A pending record using the same message ID is also written to the CTS store, providing redundancy should an individual server go offline during the authentication process.
OpenAM sends the push message to the registered device.
OpenAM uses cloud-based push notification services to deliver the messages to the devices. Depending on the registered device, OpenAM uses either Apple Push Notification Services (APNS) or Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) to deliver the push notification.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module begins to poll OpenAM and the CTS for an accepted response from the registered device.
The user responds to the notification on the registered device, which will open the ForgeRock Authenticator app. In the ForgeRock Authenticator app, the user approves the authentication request with either a swipe, or by using a fingerprint on supported hardware.
For more information, see "To Perform Authentication using Push Notifications".
The app returns the response to the OpenAM cluster.
OpenAM verifies the message is from the correct registered phone and has not been tampered with, and marks the pending record as accepted if valid.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module detects the accepted record and redirects the user to their profile page, completing the authentication.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module operates in passwordless mode if not preceded by a Data Store module in an authentication chain. When authenticating using such a chain, the user will be asked to enter their user ID, but not their password. A push notification is then sent to their registered device to complete the authentication by using the ForgeRock Authenticator app.
You should be aware of the following potential limitations before deciding to implement passwordless push authentication:
Unsolicited push messages could be sent to a user's registered device by anyone who knew or was able to guess their user ID.
If a malicious user attempted to authenticate by using push at the same time as a legitimate user, the legitimate user might unintentionally approve the malicious attempt. This is because push notifications only contain the username and issuer in the text, and it is not easy to determine which notification relates to which authentication attempt.
Consider using push notifications as part of a multi-factor authentication chain For an example, see "Creating Authentication Chains for Push Authentication".
This section explains the server configuration required to implement multi-factor authentication in OpenAM:
OpenAM provides a number of services that must be configured to provide multi-factor authentication with the ForgeRock Authenticator app.
The service for customizing one-time password implementation is:
- ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) Service
Specifies the attribute in which to store information about a registered device, and whether to encrypt that information.
Also specifies the attribute used to indicate if a user has opted out of one-time passwords.
For detailed information about the available properties, see "ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) Service" in the Reference.
The services required for implementing push notifications are:
- ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Service
Specifies the attribute in which to store information about a registered device, and whether to encrypt the data.
For detailed information about the available properties, see "ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Service" in the Reference.
- Push Notification Service
Configures how OpenAM sends push notifications to registered devices, including endpoints, and access credentials.
For information on provisioning the credentials required by the Push Notification Service, see How do I set up AM/OpenAM Push Notification Service credentials in the ForgeRock Knowledge Base.
For detailed information about the available properties, see "Push Notification Service" in the Reference.
To configure these services globally for an OpenAM deployment, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click the service to configure.
To configure these services for a realm, navigate to Realms > Realm Name, and then click Services. Add an instance of the service to the realm and configure settings in the service as required.
Letting users opt out of providing one-time passwords when they perform multi-factor authentication is an important implementation decision. The Two Factor Authentication Mandatory setting under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > General configures whether users can opt out.
When the Two Factor Authentication Mandatory setting is enabled, users must provide a one-time password every time they authenticate to a chain that includes a ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module. When the setting is disabled, the user can optionally skip one-time passwords.
By default, OpenAM lets users opt out of providing one-time passwords. Users authenticating with one-time passwords for the first time are prompted with a screen that lets them opt out of providing one-time passwords.
With the Two Factor Authentication Mandatory setting enabled, the user experience differs from the default behavior. OpenAM does not provide an option to skip multi-factor authentication during the initial attempt at multi-factor authentication:
When configuring an authentication chain that implements one-time passwords, you need to be aware that a user's decision to opt out affects the authentication process. When a user who has opted out of providing one-time passwords authenticates to a chain that includes a ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module, that module always passes authentication.
Consider the example authentication chain in "Creating Authentication Chains for One-Time Password Authentication". The first authentication module is a Data Store module and the second authentication module is a ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module. Both authentication modules have the Requisite flag setting.
A user who has opted out of providing one-time passwords might experience the following sequence of events when authenticating to the chain:
The Data Store authentication module prompts the user to provide a user ID and password.
The user provides a valid user ID and password.
Data Store authentication passes, and authentication proceeds to the next module in the chain—the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module determines that the user has opted out of providing one-time passwords.
ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication passes. Because it is the last authentication module in the chain, OpenAM considers authentication to have completed successfully.
Contrast the preceding sequence of events to the experience of a user who has not opted out of providing one-time passwords, or who is required to provide one-time passwords, while authenticating to the same chain:
The Data Store authentication module prompts the user to provide a user ID and password.
The user provides a valid user ID and password.
Data Store authentication passes, and authentication proceeds to the next module in the chain—the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module.
The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module determines that the user has not opted out of providing one-time passwords, and prompts the user for a one-time password.
The user obtains a one-time password from the authenticator app on their mobile phone.
If the one-time password is valid, ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication passes. Because it is the last authentication module in the chain, OpenAM considers authentication to have completed successfully. However, if the one-time password is not valid, ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication fails, and OpenAM considers authentication to have failed.
The following procedures provide steps for creating authentication chains that implement multi-factor authentication.
Push authentication uses two separate authentication modules:
A module to register a device to receive push notifications called ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration.
A module to perform the actual authentication itself, called ForgeRock Authenticator (Push).
You can insert both modules into a single chain to register devices and then authenticate with push notifications. See "To Create an Authentication Chain for Push Registration and Authentication".
The ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module can also be used for passwordless authentication using push notifications. If the module is placed at the start of a chain, it will ask the user to enter their user ID, but not their password. A push notification is then sent to their registered device to complete the authentication by using the ForgeRock Authenticator app.
For information on configuring an authentication chain for passwordless authentication, see "To Create an Authentication Chain for Push Registration and Passwordless Authentication".
For information on the potential limitations of passwordless authentication, see "Limitations When Using Passwordless Push Authentication".
The procedure assumes the following:
Users will provide user IDs and passwords as the first step of multi-factor authentication.
If the user does not have a device registered to receive push notifications, they will be asked to register a device. After successfully registering a device for push, authentication will proceed to the next step.
A push notification will be sent to the device as a second factor to complete authentication.
To create a multi-factor authentication chain that uses the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration and ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) modules, follow these steps:
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example
amadmin.Select the realm that will contain the authentication chain.
Create a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration authentication module as follows:
Select Authentication > Modules, and then click Add Module.
The New Module page appears.
Fill in fields in the Create New Module dialog box as follows:
Name: Specify a module name of your choosing, for example push-reg.
Type: Select ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration.
Click Create.
A page that lets you configure the authentication module appears.
Configure the module to meet your organization's requirements.
For more information about the authentication module's configuration settings, see "Hints for the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration Authentication Module".
Create a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module as follows:
Select Authentication > Modules, and then click Add Module.
The New Module page appears.
Fill in fields in the Create New Module dialog box as follows:
Name: Specify a module name of your choosing, for example push-authn.
Type: Select ForgeRock Authenticator (Push).
Click Create.
A page that lets you configure the authentication module appears.
Configure the module to meet your organization's requirements.
For more information about the authentication module's configuration settings, see "Hints for the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Authentication Module".
Create the authentication chain as follows:
Select Authentication > Chains, and then click Add Chain.
The Add Chain page appears.
Specify a name of your choosing, for example
myPushAuthChain, and then click Create.A page appears with the Edit Chain tab selected.
Add the Data Store authentication module to the authentication chain as follows:
Click Add a Module.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Fill in the New Module dialog box, specifying the Data Store authentication module. For this example, specify the
Requiredflag.Click OK.
The graphic showing your authentication chain now includes a Data Store authentication module.
Add the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration authentication module to the authentication chain as follows:
Click Add a Module.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Fill in the New Module dialog box, specifying the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration authentication module that you just created. For this example, specify the
Requiredflag.Click OK.
The graphic showing your authentication chain now includes a Data Store, and a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration authentication module.
Add the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module to the authentication chain as follows:
Click Add a Module.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Fill in the New Module dialog box, specifying the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module that you created. For this example, specify the
Requiredflag.Click OK.
The graphic showing your authentication chain now includes a Data Store, a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Registration, and a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module.
Click Save Changes to save the authentication chain.
Test your authentication chain as follows:
Navigate to a URL similar to the following:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=myPushAuthChainA login screen prompting you to enter your user ID and password appears.
Follow the procedure described in "To Perform Authentication using Push Notifications" to verify that you can use the ForgeRock Authenticator app to perform multi-factor authentication. If the chain is correctly configured, authentication is successful and OpenAM displays the user profile page.
The procedure assumes the following:
Users will provide only their user IDs as the first step of multi-factor authentication.
The user already has a device registered for receiving push notifications. For details of an authentication chain which can register a device for push notifications, see "To Create an Authentication Chain for Push Registration and Authentication".
A push notification will be sent to the device as a second factor, to complete authentication without the need to enter a password.
To create a multi-factor authentication chain that uses the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) module for passwordless authentication, follow these steps:
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example
amadmin.Select the realm that will contain the authentication chain.
Create a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module as follows:
Select Authentication > Modules, and then click Add Module.
The New Module page appears.
Fill in fields in the Create New Module dialog box as follows:
Name: Specify a module name of your choosing, for example push-authn.
Type: Select ForgeRock Authenticator (Push).
Click Create.
A page that lets you configure the authentication module appears.
Configure the module to meet your organization's requirements.
For more information about the authentication module's configuration settings, see "Hints for the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Authentication Module".
Create the authentication chain as follows:
Select Authentication > Chains, and then click Add Chain.
The Add Chain page appears.
Specify a name of your choosing, for example myPasswordlessAuthChain, and then click Create.
A page appears with the Edit Chain tab selected.
Add the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module to the authentication chain as follows:
Click Add a Module.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Fill in the New Module dialog box, specifying the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module that you created. For this example, specify the
Requisiteflag.Click OK.
The graphic showing your authentication chain now includes a ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module.
Click Save Changes to save the authentication chain.
Test your authentication chain as follows:
Navigate to a URL similar to the following:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=myPasswordlessAuthChainA login screen prompting you to enter your user ID appears.
Follow the procedure described in "To Perform Authentication using Push Notifications" to verify that you can use the ForgeRock Authenticator app to perform multi-factor authentication. If the chain is correctly configured, authentication is successful and OpenAM displays the user profile page, without having to enter a password.
This section covers one-time password authentication.
The procedure assumes the following:
Users will provide user IDs and passwords as the first step of multi-factor authentication.
An existing Data Store authentication module will collect and verify user IDs and passwords.
All authentication modules in the chain will use the
Requisiteflag setting. See "About Authentication in OpenAM" for details about authentication module flag settings.Users can opt out of one-time password authentication.
To create a multi-factor authentication chain that uses the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module, follow these steps:
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example
amadmin.Select the realm that will contain the authentication chain.
You can allow users to opt out of using OATH-based one-time passwords as follows:
Select Authentication > Settings > General.
Make sure that the Two Factor Authentication Mandatory is not enabled.
See "Core Authentication Attributes - General" for details about this configuration setting.
For information about how letting users skip multi-factor authentication impacts the behavior of authentication chains, see "Letting Users Opt Out of One-Time Password Authentication".
Create a ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module as follows:
Select Authentication > Modules, and then click Add Module.
The New Module page appears.
Fill in fields in the Create New Module dialog box as follows:
Name: Specify a module name of your choosing.
Type: Select ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH).
Click Create.
A page that lets you configure the authentication module appears.
Configure the ForgeRock Authenticator authentication module to meet your organization's requirements.
For more information about the authentication module's configuration settings, see "Hints for the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) Authentication Module".
Create the authentication chain as follows:
Select Authentication > Chains, and then click Add Chain.
The Add Chain page appears.
Specify a name of your choosing, for example myOathAuthChain, and then click Create.
A page appears with the Edit Chain tab selected.
Click Add a Module. Fill in fields in the New Module dialog box as follows:
Select Module: Select the existing Data Store module to use in this chain.
Select Criteria: Select a flag setting for the module in the authentication chain. For this example, specify the
Requisiteflag.See "About Authentication in OpenAM" for information about authentication module flag settings.
Click OK.
A graphic showing an authentication chain with a single Data Store module appears on the page.
Add the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module to the authentication chain as follows:
Click Add a Module.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Fill in the New Module dialog box, specifying the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module that you just created. For this example, specify the
Requisiteflag.Click OK.
The graphic showing your authentication chain now includes the Data Store and ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module.
Click Save Changes to save the authentication chain.
Test your authentication chain as follows:
Navigate to a URL similar to the following:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=myOathAuthChainA login screen prompting you to enter your user ID and password appears.
Follow the procedure described in "To Perform Authentication using a One-Time Password" to verify that you can use the ForgeRock Authenticator app to perform multi-factor authentication. If the chain is correctly configured, authentication is successful and OpenAM displays the user profile page.
Multi-factor authentication requires you to register a device, which is used as an additional factor when you log in to OpenAM.
This section covers the following topics relating to devices used for multi-factor authentication:
If you have not already done so, download and install the ForgeRock Authenticator app on your phone, so that you can perform multi-factor authentication.
The ForgeRock Authenticator app supports push authentication notifications and one-time passwords.
The app is available for both Android and iOS devices, and is free to download. Source code is also available:
- Android
Download: Google Play
Source code: https://stash.forgerock.org/projects/OPENAM/repos/forgerock-authenticator-android
- iOS
Download: App Store
Source code: https://stash.forgerock.org/projects/OPENAM/repos/forgerock-authenticator-ios
Registering a device with OpenAM by using the ForgeRock Authenticator app enables it to be used as an additional factor when logging in.
The ForgeRock Authenticator app supports registration of multiple accounts and multiple different authentication methods in each account, such as push notifications and one-time passwords.
Device registration only needs to be completed the first time an authentication method is used with an identity provider. Use of a different authentication method may require that device registration with the identity provider is repeated for that additional method.
The device needs access to the internet to register to receive push notifications. Registering for one-time password authentication does not require a connection to the internet.
When visiting a protected resource without having any registered devices for multi-factor authentication, OpenAM requires that you register a device.
To register your mobile phone with OpenAM, click Register Device. A screen with a QR code appears:
Start the ForgeRock Authenticator app on the device to register, and then click the plus icon:
The screen on the device changes to an interface similar to your camera app.
Point the camera at the QR code on the OpenAM page and the ForgeRock Authenticator app will acquire the QR code and read the data encoded within.
If you are logging in to OpenAM on the registered device and cannot scan the screen, click the button labelled On a mobile device?. The ForgeRock Authenticator app will request permission to launch. If allowed, the information required to register the device will be transferred to the ForgeRock Authenticator app directly, without the need to scan the QR code.
After registering, the app displays the registered accounts and the authentication methods they support, for example one-time passwords (a timer icon) or push notifications (a bell icon):
Your device is now registered. You will able to use it to perform multi-factor authentication.
Important
After registering a new device and successfully performing multi-factor authentication, you should obtain the recovery codes for the registered device and store them somewhere safe. See "Accessing Your Recovery Codes".
After successful first-time authentication with multi-factor authentication, you should safeguard your ability to use multi-factor authentication in case you lose your phone. OpenAM provides each device you register with a set of one-time recovery codes that you can use in cases where you cannot complete multi-factor authentication using your registered device.
After registering a new device with OpenAM, use the following steps to access your recovery codes:
Log in to OpenAM.
Select Dashboard from the top-level menu.
Locate the entry for the device type in the Authentication Devices section, click the context menu button, and then click Recovery Codes:
A list of recovery codes appears:
Keep a copy of the codes for each of your registered device types in a safe place. You will need to use one of your recovery codes to authenticate to OpenAM if you lose your phone.
See "Recovering After Replacing a Lost Device" for the procedure to authenticate to OpenAM using a recovery code instead of performing multi-factor authentication.
Unless the OpenAM administrator has made one-time password authentication mandatory, users can choose to opt out of using one-time passwords by clicking the Skip This Step button on the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) screen. [2] This button appears:
When users are prompted to register their mobile devices during their initial login from a new device.
Every time users are prompted by the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module to enter one-time passwords.
Users who decide to opt out of using one-time passwords are not prompted to enter one-time passwords when authenticating to OpenAM.
The decision to opt out of using one-time passwords in OpenAM is revocable: users who have decided to opt out of using one-time passwords can reverse their decisions, so that one-time password authentication is once again required.
End users should follow these steps to opt out or opt in to using one-time passwords:
Log in to OpenAM.
Select Dashboard from the top navigation bar.
In the Authentication Devices section of the Dashboard page, click the context menu button, and then click Settings:
Enable or disable the 2-Step Authentication option:
Click Save.
If you register a device with OpenAM and then lose it, you must authenticate to OpenAM using a recovery code, delete the lost device, and then register the new device. Follow these steps:
Log in to OpenAM. If push authentication is enabled, enter your user ID, click Log In, and then click Use Emergency Code. If one-time passwords are enabled, when prompted to enter a verification code, instead enter one of your recovery codes.
Because recovery codes are valid for a single use only, make a note to yourself not to attempt to reuse this code.
If you did not save the recovery codes for the lost device, contact your administrator to remove the registered device from your OpenAM user profile.
Select Dashboard from the top-level menu.
Locate the entry for your phone in the Authentication Devices section, click the context menu button, and then click Delete:
If you have not already done so, install the ForgeRock Authenticator app on your new phone. See "Downloading the ForgeRock Authenticator App".
Register your new device. See "Registering a Device for Multi-Factor Authentication".
Users who do not save recovery codes or who run out of recovery codes and cannot authenticate to OpenAM without a verification code require administrative support to reset their device profiles. See "Deleting Registered Devices by using REST" for more information.
If you repeatedly enter valid one-time passwords that appear to be valid passwords, but OpenAM rejects the passwords as unauthorized, it is likely that your device has become out of sync with OpenAM.
When a registered device becomes out of sync with OpenAM, you must authenticate to OpenAM using a recovery code, delete your device, and then re-register your device. You can do so by performing the steps in "To Register a New Device After Losing a Registered Device".
Users who do not save recovery codes or who run out of recovery codes and cannot authenticate to OpenAM without a verification code require administrative support to reset their device profiles. See "Deleting Registered Devices by using REST" for more information.
As described in "Recovering After Replacing a Lost Device", a user who has lost a mobile phone registered with OpenAM can register a replacement device by authenticating using a recovery code, deleting their existing device, and then re-registering a new device.
Additional support is required for users who lose mobile phones but did not save their recovery codes when they initially registered the phone, and for users who have used up all their recovery codes.
OpenAM provides a REST API to reset a device profile by deleting information about a user's registered device. Either the user or an administrator can call the REST API to reset a device profile. Device profile reset can be implemented as follows:
Administrators provide authenticated users with a self-service page that calls the REST API to let the users reset their own device profiles.
Administrators can call the REST API themselves to reset users' device profiles.
Administrators can call the REST API themselves to reset a device when the HOTP counter exceeds the HOTP threshold window and requires a reset.
Note
The reset action deletes the OATH device profile, which by default has a limit of one profile per device, and sets the
Select to Enable Skipoption to its default value ofNot Set.
For details about the REST API to reset users' device profiles, see "Resetting Device Profiles" in the Developer's Guide.
This section provides an example of how end users might authenticate with OpenAM configured for multi-factor authentication. Use the following procedures to complete multi-factor authentication using the ForgeRock Authenticator:
This example uses the authentication chain as created in "Creating Authentication Chains for One-Time Password Authentication".
Because the first module in the authentication chain is a Data Store module, OpenAM presents you with a page for entering your user ID and password. After you provide those credentials, OpenAM verifies them. If your credentials are valid, OpenAM proceeds to the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module.
On the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) screen, follow these steps to complete one-time password authentication:
On your registered device, open the ForgeRock Authenticator app, and then tap the account matching the user ID you entered earlier. The registered authentication methods for that account are displayed:
In the One-time Password section, click the refresh icon. A one-time password is displayed:
On the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) page in OpenAM, enter the one-time password that the authenticator app generated on your phone, and then click Submit:
OpenAM will display the user's profile page.
This example uses one of the authentication chains as created in "Creating Authentication Chains for Push Authentication".
OpenAM presents you with a page for entering only your user ID, or user ID and password. After you provide those credentials, OpenAM verifies them. If your credentials are valid and the account has a device registered for push notifications, OpenAM proceeds to the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module, and a push notification is sent to the registered device.
Note
The device needs access to the Internet to receive push notifications, and the OpenAM server must be able to receive responses from the device.
Follow these steps to complete authentication using push notifications:
On your registered device, you will receive a push notification from OpenAM. Depending on the state of the phone and the ForgeRock Authenticator app, respond to the notification as follows:
If the phone is locked, the notification may appear similar to the following:
Slide the notification across the screen, then unlock the phone. The ForgeRock Authenticator app will automatically open and display the push notification authentication screen.
If the phone is not locked, and the ForgeRock Authenticator app is not open, the notification may appear similar to the following:
Tap the notification. The ForgeRock Authenticator app will automatically open and display the push notification authentication screen.
If the phone is not locked, and the ForgeRock Authenticator app is open, the app will open the push notification authentication screen automatically.
On the push notification authentication screen, you can approve the request or deny it:
Slide the switch with a checkmark on horizontally to the right.
OpenAM will display the user's profile page.
If the registered device supports Touch ID, and fingerprints have been provided, you can approve the request by using a registered fingerprint.
OpenAM will display the user's profile page.
To deny the request, tap the cancel icon in the top-right of the screen, or if Touch ID is enabled, click the Cancel button.
After a timeout has passed, OpenAM will report that authentication has failed and return to the first screen in the chain.
Note
If you do not approve or deny the request on the registered device, the OpenAM Push Authentication page will timeout and the authentication will fail. The timeout can be configured in the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) authentication module settings. See "Hints for the ForgeRock Authenticator (Push) Authentication Module".
As shown in "Configuring Authentication Modules", authentication modules are configured with an authentication level. This configuration sets the level of security associated with the module, Stronger forms of authentication are assigned higher authentication levels. (Or lower authentication level numbers if the deployment defines stronger authentication with lower authentication level numbers.) Upon successful authentication, a user's session includes information about the authentication level achieved.
Authorization policies can require a particular authentication level for access to sensitive resources (or at most or at least a specified authentication level). When a user who is already authenticated in the realm tries to access a sensitive resource with a valid session that does not have the requisite authentication level, OpenAM denies access to the resource. However, OpenAM also returns advices with the authorization decision. The advices indicate the need for the required authentication level. The policy agent or policy enforcement point can then send the user back to OpenAM for session upgrade.
During session upgrade the user authenticates with a stronger authentication module. The stronger module is typically part of the same authentication chain that handled the original authentication, though not required for access to less sensitive resources. Upon successful stronger authentication, the user session is upgraded to the new authentication level and modified to include any settings related to the stronger authentication.
If unsuccessful, session upgrade leaves the user session as it was before the attempt at stronger authentication. If session upgrade failed because the login page times out, OpenAM redirects the user's browser to the success URL from the last successful authentication.
OpenAM policy agents generally handle session upgrade without additional configuration, as policy agents are built to handle OpenAM's advices. If you build your own policy enforcement point (PEP), however, take advices and session upgrade into consideration. For RESTful PEPs, see "Requesting Policy Decisions" in the Developer's Guide, and for indications on how to handle advices and session upgrade see "Authentication and Logout" in the Developer's Guide.
OpenAM's support for session upgrades requires stateful sessions. Be sure that OpenAM is configured for stateful sessions—the default configuration—before attempting to upgrade OpenAM sessions.
OpenAM supports two different approaches to account lockout, where OpenAM locks an account after repeated authentication failures. Lockout works with modules for which users can enter a password incorrectly. For example:
Memory lockout locks the user account, keeping track of the locked state only in memory, and then unlocking the account after a specified delay. Memory lockout is also released when OpenAM restarts.
Persistent (physical) lockout sets the user account status to
inactivein the user profile. For persistent lockout, OpenAM tracks failed authentication attempts by writing to the user repository.Persistent account lockout works independently of account lockout mechanisms in the underlying directory server that serves as the user data store.
You configure account lockout by editing settings for the core authentication module. For details, see "Configuring Core Authentication Attributes". Access the settings in OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > Account Lockout. The inline help explains the settings in detail. To do this:
Enable lockout by checking Login Failure Lockout Mode, setting the number of attempts, and setting the lockout interval and duration.
You can also opt to warn users after several consecutive failures, or to multiply the lockout duration on each successive lockout.
You can set up email notification upon lockout to an administrator if OpenAM is configured to send mail. (You can configure OpenAM to send mail in Configure > Server Defaults > General > Mail Server.)
For persistent lockout, OpenAM sets the value of the user's
inetuserstatusprofile attribute toinactive. You can also specify another attribute to update on lockout. You can further set a non-default attribute on which to store the number of failed authentication attempts. When you do store the number of failed attempts in the data store, other OpenAM servers accessing the user data store can also see the number.
If you need to unlock a user's account, find the user under Realms > Realm Name > Subjects > User, set the user's User Status to Active, and click Save.
OpenAM lets you limit the number of active sessions for a user by setting session quotas. You also configure session quota exhaustion actions so that when a user goes beyond the session quota, OpenAM takes the appropriate action.
OpenAM's support for session quotas requires stateful sessions. Be sure that OpenAM is configured for stateful sessions—the default configuration—before attempting to configure session quotas.
Important
To enforce session quotas across multiple servers in a site, configure session failover as described in "Setting Up OpenAM Session Failover" in the Installation Guide.
The session quota applies to all sessions opened for the same user (as represented by the user's universal identifier). To configure:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Session.
Set Enable Quota Constraints to
ON.Set Resulting behavior if session quota exhausted.
The following settings are available by default:
DENY_ACCESSDeny access, preventing the user from creating an additional session.
DESTROY_NEXT_EXPIRINGRemove the next session to expire, and create a new session for the user. The next session to expire is the session with the minimum time left until expiration.
This is the default setting.
DESTROY_OLDEST_SESSIONRemove the oldest session, and create a new session for the user.
DESTROY_OLD_SESSIONSRemove all existing sessions, and create a new session for the user.
If none of these session quota exhaustion actions fit your deployment, you can implement a custom session quota exhaustion action. For an example, see "Customizing Session Quota Exhaustion Actions" in the Developer's Guide.
Set Active User Sessions to the session quota.
The default is 5 sessions.
Save your work.
(Optional) If you have multiple servers but session failover is not configured, configure multi-server mode as described below:
If you have only a single OpenAM server, skip this step. OpenAM enforces the session quota you set for the server.
If you have multiple servers with session failover configured, then also skip this step. In this case OpenAM uses the session store to enforce session quotas globally across your deployment. In other words when the Set Active User Sessions is 5, a user can have a maximum of five active sessions.
If you have multiple OpenAM servers but session failover is not configured, configure multi-server mode for session quotas as follows:
Navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced, or Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced.
Set the
openam.session.useLocalSessionsInMultiServerModeproperty totrue.
When you set this property to
truefor your OpenAM servers, users can potentially reach the session quota for each individual server before all session quotas are exhausted. In other words, if you have four OpenAM servers and Set Active User Sessions is 5, then the user can have a maximum of 20 (5 * 4) sessions.
By default, OpenAM redirects the user to the URL specified in the
goto and gotoOnFail query string parameters
supplied to the authentication interface in the login URL.
You can increase security against possible phishing attacks through open redirect
by specifying a list of valid URL resources using the Validation Service.
OpenAM only redirects a user if the goto and
gotoOnFail URL matches any of the resources specified in
this setting.
If no setting is present, it is assumed that the goto or
gotoOnFail URL is valid.
The URL whitelisting and pattern matching follow the wildcard rules as specified in "Specifying Resource Patterns with Wildcards".
Here are some general examples of URL pattern matching:
If no port is specified,
http://www.example.comcanonicalizes tohttp://www.example.com:80andhttps://www.example.comcanonicalizes tohttp://www.example.com:443.A wildcard before "://" only matches up to "://"
For example,
http*://*.com/*matcheshttp://www.example.com/hello/worldandhttps://www.example.com/hello.A wildcard between "://" and ":" matches up to ":"
For example,
http://*:85matcheshttp://www.example.com:85.A wildcard between ":" and "/" only matches up to the first "/"
For example,
http://www.*:*/matcheshttp://www.example.com:80. In another example,http://www.example.com:*matcheshttp://ww.example.com:[any port]andhttp://www.example.com:[any port]/, but nothing more.A wildcard after "/" matches anything, depending on whether it is single-level or a wildcard appropriately.
For example,
https://www.example.com/*matcheshttps://www.example.com:443/foo/bar/baz/meIf you do not use any wildcards, OpenAM exactly matches the string, so
http://www.example.comonly matcheshttp://www.example.com, but NOThttp://www.example.com/(trailing slash).If you put the wildcard after the path, OpenAM expects a path (even if it is blank), so
http://www.example.com/*matcheshttp://www.example.com/andhttp://www.example.com/foo/bar/baz.html, but NOThttp://www.example.com.http://www.example.com:*/matcheshttp://www.example.com/, which also canonicalizes tohttp://www.example.com:80/.https://www.example.com:*/matcheshttps://www.example.com/, which also canonicalizes tohttps://www.example.com:443/.
OpenAM determines the redirection URL based on authentication success or failure.
Upon a successful authentication, OpenAM determines the redirection URL in the following order:
The URL set in the authentication chain.
In the OpenAM console, you can set the Successful Login URL parameter by navigating to realm > Authentication > Chains > chain > Settings.
The URL set in the
gotologin URL parameter. For example,http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/?realm=/#login/&goto=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.comThe URL set in the Success URL attribute in the user's profile.
In the OpenAM console, you can set the Success URL parameter by navigating to realm > Subjects > subject. Scroll down to Success URL, enter a URL in the New Value field, and then click Add.
You can also specify the client type by entering
ClientType|URLas the property value. If the client type is specified, it will have precedence over a regular URL in the user's profile.The URL set in the Default Success Login URL attribute in the Top Level realm.
You can set this property on the OpenAM console by navigating to Configure > Authentication > Core Attributes > Post Authentication Processing.
You can also specify the client type by entering
ClientType|URLas the property value. If the client type is specified, it will have precedence over a Default Success Login URL in the Top Level realm.
Upon a failed authentication, OpenAM determines the redirection URL in the following order:
The URL set in the authentication chain.
In the OpenAM console, you can set the Failed Login URL parameter by navigating to realm > Authentication > Chains > chain > Settings.
The URL set in the
gotoOnFailURL parameter. For example,http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/?realm=/#login/&gotoOnFail=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.comThe URL set in the Failure URL attribute in the user's profile.
In the OpenAM console, you can set the Failure URL parameter by navigating to realm > Subjects > subject. Scroll down to Failure URL, and enter a URL in the New Value field, and then click Add.
You can also specify the client type by entering
ClientType|URLas the property value. If the client type is specified, it will have precedence over a regular URL in the user's profile.The URL set in the Default Failure Login URL attribute in the Top Level realm.
You can set this property on the OpenAM console by navigating to Configure > Authentication > Core Attributes > Post Authentication Processing.
You can also specify the client type by entering
ClientType|URLas the property value. If the client type is specified, it will have precedence over a Default Failure Login URL in the Top Level realm.
[2] For information about making the usage of one-time passwords mandatory in OpenAM, see "Letting Users Opt Out of One-Time Password Authentication".
Authorization is determining whether to grant or to deny a user access to a resource. Policies define how to determine whether to grant or deny access. This chapter describes how to configure authorization policies in OpenAM.
Applications rely on OpenAM for access management, which breaks down into authentication, or determining who is trying to access a resource, and authorization, or determining whether to grant or deny access. This is because whether access is granted generally depends on what the policies about access are, who is trying to gain access, and perhaps some other conditions, such as whether the access itself needs to happen over a secure channel or what time of day it is.
To return to the international airport example from the discussion on authentication the policy might be that passengers with valid passports and visas presenting valid plane tickets are allowed through to the gate where the plane is waiting to take off, but only under the condition that the plane is going to leave soon. (You cannot expect to get to the gate today with a scheduled departure for three months from now.)
Define authorization policies to allow OpenAM to determine whether to grant a subject access to a resource.
A policy defines the following:
- resources
The resource definitions constrain which resources, such as web pages or access to the boarding area, the policy applies to.
- actions
The actions are verbs that describe what the policy allows users to do to the resources, such as read a web page, submit a web form, or access the boarding area.
- subject conditions
The subject conditions constrain who the policy applies to, such as all authenticated users, only administrators, or only passengers with valid tickets for planes leaving soon.
- environment conditions
The environment conditions set the circumstances under which the policy applies, such as only during work hours, only when accessing from a specific IP address, or only when the flight is scheduled to leave within the next four hours.
- response attributes
The response attributes define information that OpenAM attaches to a response following a policy decision, such as a name, email address, or frequent flyer status.
When queried about whether to let a user through to a protected resource, OpenAM decides whether to authorize access or not based on applicable policies as described below in "OpenAM Policy Decisions". OpenAM communicates its decision to the application that is using OpenAM for access management. In the common case, this is a policy agent installed on the server where the application runs. The agent then enforces the authorization decision from OpenAM.
To help with the creation of policies, OpenAM uses resource types and policy sets.
- Resource types
Resource types define a template for the resources that policies apply to, and the actions that could be performed on those resources.
For example, the
URLresource type that is included by default in OpenAM acts as a template for protecting web pages or applications. It contains resource patterns, such as*://*:*/*?*, which can be made more specific when used in the policy. The actions that the resource supports are also defined, as follows:GETPOSTPUTHEADPATCHDELETEOPTIONS
OpenAM also includes a resource type to protect REST endpoints, with patterns including
https://*:*/*?*and the CRUDPAQ actions:CREATEREADUPDATEDELETEPATCHACTIONQUERY
- Policy Sets
Policy Sets are associated with a set of resource types, and contain one or more policies based upon the template it provides.
For example, an application for Example.com's HR service
might contain resource types that constrain all policies to apply to URL
resource types under http*://example.com/hr* and
http*://example.com/hr*?*, and only the HTTP
GET and POST actions.
Configure policy sets, policies, and resource types in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Authorization.
For more information on viewing, creating, and editing policies and resource types, see "Configuring Resource Types, Policy Sets, and Policies".
OpenAM relies on policies to reach authorization decisions, such as whether to grant or to deny access to a resource. OpenAM acts as the policy decision point (PDP), whereas OpenAM policy agents act as policy enforcement points (PEP). In other words, a policy agent or other PEP takes responsibility only for enforcing a policy decision rendered by OpenAM. When you configured applications and their policies in OpenAM, you used OpenAM as a policy administration point (PAP).
Concretely speaking, when a PEP requests a policy decision from OpenAM
it specifies the target resource(s),
the policy set (default: iPlanetAMWebAgentService),
and information about the subject and the environment.
OpenAM as the PDP retrieves policies within the specified policy set
that apply to the target resource(s).
OpenAM then evaluates those policies to make a decision
based on the conditions matching those of the subject and environment.
When multiple policies apply for a particular resource,
the default logic for combining decisions is that
the first evaluation resulting in a decision to deny access
takes precedence over all other evaluations.
OpenAM only allows access if all applicable policies evaluate
to a decision to allow access.
OpenAM communicates the policy decision to the PEP. The concrete decision, applying policy for a subject under the specified conditions, is called an entitlement.
The entitlement indicates the resource(s) it applies to, the actions permitted and denied for each resource, and optionally response attributes and advice.
When OpenAM denies a request due to a failed condition, OpenAM can send advice to the PEP, and the PEP can then take remedial action. For instance, suppose a user comes to a web site having authenticated with an email address and password, which is configured as authentication level 0. Had the user authenticated using a one-time password, the user would have had authentication level 1 in their session. Yet, because they have authentication level 0, they currently cannot access the desired page, as the policy governing access requires authentication level 1. OpenAM sends advice, prompting the PEP to have the user re-authenticate using a one-time password module, gaining authentication level 1, and thus having OpenAM grant access to the protected page.
Consider the case where OpenAM protects a user profile web page. An OpenAM policy agent installed in the web server intercepts client requests to enforce policy. The policy says that only authenticated users can access the page to view and to update their profiles.
When a user browses to the profile page, the OpenAM policy agent intercepts the request. The policy agent notices that the request is to access a protected resource, but the request is coming from a user who has not yet logged in and consequently has no authorization to visit the page. The policy agent therefore redirects the user's browser to OpenAM to authenticate.
OpenAM receives the redirected user, serving a login page that collects the user's email and password. With the email and password credentials, OpenAM authenticates the user, and creates a session for the user. OpenAM then redirects the user to the policy agent, which gets the policy decision from OpenAM for the page to access, and grants access to the page.
While the user has a valid session with OpenAM, the user can go away to another page in the browser, come back to the profile page, and gain access without having to enter their email and password again.
Notice how OpenAM and the policy agent handle the access in the example. The web site developer can offer a profile page, but the web site developer never has to manage login, or handle who can access a page. As OpenAM administrator, you can change authentication and authorization independently of updates to the web site. You might need to agree with web site developers on how OpenAM identifies users so web developers can identify users by their own names when they log in. By using OpenAM and policy agents for authentication and authorization, your organization no longer needs to update web applications when you want to add external access to your Intranet for roaming users, open some of your sites to partners, only let managers access certain pages of your HR web site, or allow users already logged in to their desktops to visit protected sites without having to type their credentials again.
OpenAM has to match policies to resources to take policy decisions. For a policy to match, the resource has to match one of the resource patterns defined in the policy. The user making the request has to match a subject. Furthermore, at least one condition for each condition type has to be satisfied.
If more than one policy matches, OpenAM has to reconcile differences. When multiple policies match, the order in which OpenAM uses them to make a policy decision is not deterministic. However, a deny decision overrides an allow decision, and so by default once OpenAM reaches a deny decision it stops checking further policies. If you want OpenAM to continue checking despite the deny, navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Policy Configuration, and then enable Continue Evaluation on Deny Decision.
You can configure resource types, policy sets, and policies by using the OpenAM console, or by using the REST interface.
This section explains how to use the OpenAM console to configure resource types, policy sets, and policies to protect resources.
For information on managing resource types, policy sets, and policies by using the REST API, see "Managing Resource Types" in the Developer's Guide, "Managing Policy Sets" in the Developer's Guide, and "Managing Policies" in the Developer's Guide.
Tip
You can also configure policy sets and policies by using the ssoadm command. For more information see ssoadm(1) in the Reference.
This section describes the process of using the OpenAM console for creating resource types, which define a template for the resources that policies apply to, and the actions that could be performed on those resources.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Resource Types.
To create a new resource type, click New Resource Type.
To modify an existing resource type, click the resource type name.
To delete an existing resource type, in the row containing the resource type click the Delete button.
You can only delete resource types that are not being used by policy sets or policies. Trying to delete a resource type that is in use returns an HTTP 409 Conflict status code.
Remove the resource type from any associated policy sets or policies to be able to delete it.
Provide a name for the resource type, and optionally a description.
Do not use special characters within resource type, policy, or policy set names (for example, "my+resource+type") when using the console or REST endpoints. Using the special characters listed below causes OpenAM to return a 400 Bad Request error. The special characters are: double quotes ("), plus sign (+), comma (,), less than (<), equals (=), greater than (>), backslash (\), forward slash (/), semicolon (;), and null (\u0000).
To define resource patterns that policies using this resource type can expand upon, follow the steps below:
In the Add a new pattern box, enter a pattern with optional wildcards that the policies will use as a template.
For information on specifying patterns for matching resources, see "Specifying Resource Patterns with Wildcards".
Click the Add Pattern button to confirm the pattern.
Tip
To remove a pattern, click the Delete icon.
To define the actions that policies using this resource type can allow or deny, follow the steps below:
In the Add a new action box, enter an action related to the types of resources being described, and then click Add Action.
Select either allow or deny as the default state for the action.
To remove an action, click the Delete icon.
Continue adding the patterns and actions that your resource type requires.
Click Create Resource Type to save a new resource type or Save Changes to save modifications to an existing resource type.
This section describes how to use the OpenAM console to create policy sets, which are used as templates for policies protecting Web sites, Web applications, or other resources.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Policy Sets.
To create a new policy set, click New Policy Set.
To modify an existing policy set, in the row containing the name of the policy set click the Edit icon, and then click the Settings tab.
Enter an ID for the policy set. This is a required parameter
Enter a name for the policy set. The name is optional and is for display purposes only.
Do not use special characters within resource type, policy, or policy set names (for example, "my+resource+type") when using the console or REST endpoints. Using the special characters listed below causes OpenAM to return a 400 Bad Request error. The special characters are: double quotes ("), plus sign (+), comma (,), less than (<), equals (=), greater than (>), backslash (\), forward slash (/), semicolon (;), and null (\u0000).
In the Resource Types drop-down menu, select one or more resource types that policies in this policy set will use.
Tip
To remove a resource type from the policy set, select the label, and then press Delete or Backspace.
Click Create to save a new policy set or Save Changes to save modifications to an existing policy set.
To make use of a policy set and any policies it contains, you must configure a policy agent to use the policy set for policy decisions. For details see "To Specify the Realm and Application for Policy Decisions".
Note
Once a policy set is created, users can only change the
displayName of an existing policy set, not the ID,
without deleting the associated policies.
This section describes the process of using the OpenAM console to configure policies, which are used to protect a web site, web application, or other resource.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Policy Sets, and then click the name of the policy set in which to configure a policy:
To create a new policy, click Add a Policy.
In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the policy.
Note
Do not use special characters within resource type, policy, or policy set names (for example, "my+resource+type") when using the console or REST endpoints. Using the special characters listed below causes OpenAM to return a 400 Bad Request error. The special characters are: double quotes ("), plus sign (+), comma (,), less than (<), equals (=), greater than (>), backslash (\), forward slash (/), semicolon (;), and null (\u0000).
To define resources that the policy applies to, follow the steps below:
Select a resource type from the Resource Type drop-down list. The set of resource patterns within the selected resource type will populate the Resources drop-down list. For information on configuring resource types, see "Configuring Resource Types by Using the OpenAM Console".
Select a resource pattern from the Resources drop-down list.
(Optional) Optionally, replace the asterisks with values to define the resources that the policy applies to.
For information on specifying patterns for matching resources, see "Specifying Resource Patterns with Wildcards".
Click Add to save the resource.
The OpenAM console displays a page for your new policy. The Tab pages let you modify the policy's properties.
Tip
To remove a resource, click the Delete icon.
Repeat these steps to add all the resources to which your policy applies, and then click Create.
To configure the policy's actions, select the Actions tab and perform the following:
Select an action that the policy applies to by selecting them from the Add an Action drop-down list.
Select whether to allow or deny the action on the resources specified earlier.
Repeat these steps to add all the appropriate actions, and then click Save Changes.
Define conditions in the OpenAM console by combining logical operators with blocks of configured parameters to create a rule set that the policy uses to filter requests for resources. Use drag and drop to nest logical operators at multiple levels to create complex rule sets.
Valid drop-points in which to drop a block are displayed with a grey horizontal bar.
To define the subjects that the policy applies to, complete the following steps on the Subjects tab:
Click Add a Subject Condition, choose the type from the drop-down menu, specify any required subject values, click the checkmark to the right when done, and then drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set above.
The available subject condition types are:
- Authenticated Users
Any user that has successfully authenticated with OpenAM.
- Users & Groups
A user or group as defined in the Subjects pages of the realm the policy is created in.
Select one or more users or groups from the User Subjects or Group Subjects drop-down lists, which display the subjects and groups available within the realm.
To remove an entry, click the value, and then press Delete (Windows/GNU/Linux) or Backspace (Mac OS X).
- OpenID Connect/Jwt Claim
Validate a claim within a JSON Web Token (JWT).
Type the name of the claim to validate in the Claim Name field, for example
sub, and the required value in the Claim Value field, and then click the checkmark.Repeat the step to enter additional claims.
The claim(s) will be part of the JWT payload together with the JWT header and signature. The JWT is sent in the authorization header of the bearer token.
This condition type only supports string equality comparisons, and is case-sensitive.
- Never Match
Never match any subject. Has the effect of disabling the policy, as it will never match a subject.
If you do not set a subject condition, "Never Match" is the default. In other words, you must set a subject condition for the policy to apply.
To match regardless of the subject, configure a subject condition that is "Never Match" inside a logical
Notblock.
To add a logical operator, click the Add a Logical Operator button, choose between
All Of,Not, andAny Offrom the drop-down menu, and then drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set above.Continue combining logical operators and subject conditions. To edit an item, click the Edit button. To remove an item, click the Delete button. When complete, click Save Changes.
To configure environment conditions in the policy, complete the following steps on the Environments tab:
To add an environment condition, click the Environment Condition button, choose the type from the drop-down menu, specify any required parameters, and then drag the block into a drop-point in a logical block above.
The available environment condition types are:
- Active Session Time
Make the policy test how long the user's stateful or stateless session has been active, as specified in Max Session Time. To terminate the session if it has been active for longer than the specified time, set Terminate Sessions to
True. The user will need to re-authenticate.- Authentication by Module Chain
Make the policy test the service that was used to authenticate the user.
- Authentication by Module Instance
Make the policy test the authentication module used to authenticate, specified in Authentication Scheme. Specify a timeout for application authentication in Application Idle Timeout Scheme and the name of the application in Application Name.
- Authentication Level (greater than or equal to)
Make the policy test the minimum acceptable authentication level specified in Authentication Level.
- Authentication to a Realm
Make the policy test the realm to which the user authenticated.
- Current Session Properties
Make the policy test property values set in the user's stateful or stateless session.
Set Ignore Value Case to
Trueto make the test case-insensitive.Specify one or more pairs of session properties and values using the format
property:value. For example, specifyclientType:genericHTMLto test whether the value of theclientTypeproperty is equal togenericHTML.- Identity Membership
Make the policy apply if the UUID of the invocator is a member of at least one of the AMIdentity objects specified in AM Identity Name.
Often used to filter requests on the identity of a Web Service Client (WSC).
- IPv4 Address/DNS Name
Make the policy test the IP version 4 address that the request originated from.
The IP address is taken from the
requestIpvalue of policy decision requests. If this is not provided, the IP address stored in the SSO token is used instead.Specify a range of addresses to test against by entering four sets of up to three digits, separated by full stops (.) in both Start IP and End IP.
If only one of these values is provided, it is used as a single IP address to match.
Optionally, specify a DNS name in DNS Name to filter requests to that domain.
- IPv6 Address/DNS Name
Make the policy test the IP version 6 address that the request originated from.
The IP address is taken from the
requestIpvalue of policy decision requests. If this is not provided, the IP address stored in the SSO token is used instead.Specify a range of addresses to test against by entering eight sets of four hexadecimal characters, separated by a colon (:) in both Start IP and End IP.
If only one of these values is provided, it is used as a single IP address to match.
Optionally, specify a DNS name in DNS Name to filter requests to those coming from the specified domain.
Use an asterisk (*) in the DNS name to match multiple subdomains. For example
*.example.comapplies to requests coming fromwww.example.com,secure.example.com, or any other subdomain ofexample.com.- LDAP Filter Condition
Make the policy test whether the user's entry can be found using the LDAP search filter you specify in the directory configured for the policy service, which by default is the identity repository. Navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Policy Configuration to see the global LDAP configuration.
Alternatively, to configure these settings for a realm, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click Policy Configuration.
- OAuth2 Scope
Make the policy test whether an authorization request includes all of the specified OAuth 2.0 scopes.
Scope names must follow OAuth 2.0 scope syntax described in RFC 6749, Access Token Scope . As described in that section, separate multiple scope strings with spaces, such as
openid profile.The scope strings match regardless of order in which they occur, so
openid profileis equivalent toprofile openid.The condition is also met when additional scope strings are provided beyond those required to match the specified list. For example, if the condition specifies
openid profile, thenopenid profile emailalso matches.- Resource/Environment/IP Address
Make the policy apply to a complex condition such as whether the user is making a request from the localhost and has also authenticated with the LDAP authentication module.
Entries must take the form of an
IF...ELSEstatement. TheIFstatement can specify eitherIPto match the user's IP address, ordnsNameto match their DNS name.If the
IFstatement is true, theTHENstatement must also be true for the condition to be fulfilled. If not, relevant advice is returned in the policy evaluation request.The available parameters for the
THENstatement are as follows:-
module The module that was used to authenticate the user, for example
DataStore.-
service The service that was used to authenticate the user.
-
authlevel The minimum required authentication level.
-
role The role of the authenticated user.
-
user The name of the authenticated user.
-
redirectURL The URL the user was redirected from.
-
realm The realm that was used to authenticate the user.
The IP address can be IPv4, IPv6, or a hybrid of the two.
Example:
IF IP=[127.0.0.1] THEN role=admins.-
- Time (day, date, time, and timezone)
Make the policy test when the policy is evaluated.
The values for day, date and time must be set in pairs that comprise a start and an end.
To add a logical operator, click the Logical button, choose between
All Of,Not, andAny Offrom the drop-down menu, and then drag the block into a valid drop point in the rule set above.Continue combining logical operators and environment conditions, and when finished, click Save Changes.
(Optional) Add response attributes, retrieved from the user entry in the identity repository, into the headers of the request at policy decision time. The policy agent for the protected resources/applications or the protected resources/applications themselves retrieve the policy response attributes to customize or personalize the application. Policy response attributes come in two formats: subject attributes and static attributes.
To configure response attributes in the policy, complete the following steps on the Response attributes tab:
To add subject attributes, select them from the Subject attributes drop-down list
To remove an entry, click the value, and then press Delete (Windows/GNU/Linux) or Backspace (Mac OS X)
To add a static attribute, specify the key-value pair for each static attribute. Enter the Property Name and its corresponding Property Value in the fields, and then click the Add (+) icon.
Note
To edit an entry, click the Edit icon in the row containing the attribute, or click the row itself. To remove an entry, click the Delete icon in the row containing the attribute.
Continue adding subject and static attributes, and when finished, click Save Changes.
Resource patterns can specify an individual URL or resource name to protect. Alternatively, a resource pattern can match URLs or resource names by using wildcards.
The wildcards you can use are
*and-*-.These wildcards can be used throughout resource patterns to match URLs or resource names. For a resource pattern used to match URLs, wildcards can be employed to match the scheme, host, port, path, and query string of a resource.
When used within the path segment of a resource, the wildcard
*matches multiple path segments.For example,
http://www.example.com/*matcheshttp://www.example.com/,http://www.example.com/index.html, and alsohttp://www.example.com/company/images/logo.png.When used within the path segment of a resource, the wildcard
-*-will only match a single path segment.For example,
http://www.example.com/-*-matcheshttp://www.example.com/index.htmlbut does not matchhttp://www.example.com/company/resource.htmlorhttp://www.example.com/company/images/logo.png.
Wildcards do not match
?. You must explicitly add patterns to match URLs with query strings.When matching URLs sent from a web policy or J2EE agent, an asterisk (*) used at the end of a pattern after a
?character matches one or more characters, not zero or more characters.For example,
http://www.example.com/*?*matcheshttp://www.example.com/users?_action=create, but nothttp://www.example.com/users?.To match everything under
http://www.example.com/specify three patterns, one forhttp://www.example.com/*, one forhttp://www.example.com/*?, and one forhttp://www.example.com/*?*.When matching resources by using the
policies?_action=evaluateREST endpoint, an asterisk (*) used at the end of a pattern after a?character matches zero or more characters.For example,
http://www.example.com/*?*matcheshttp://www.example.com/users?_action=create, as well ashttp://www.example.com/users?.To match everything under
http://www.example.com/specify two patterns, one forhttp://www.example.com/*, one forhttp://www.example.com/*?*.
When defining patterns to match URLs with query strings, OpenAM sorts the query string field-value pairs alphabetically by field name when normalizing URLs before checking whether a policy matches. Therefore the query string
?subject=SPBnfm+t5PlP+ISyQhVlplE22A8=&action=getis equivalent to the query string?action=get&subject=SPBnfm+t5PlP+ISyQhVlplE22A8=.Duplicate slashes (
/) are not considered part of the resource name to match. A trailing slash is considered by OpenAM as part of the resource name.For example,
http://www.example.com//path/, andhttp://www.example.com/path//are treated in the same way.http://www.example.com/path, andhttp://www.example.com/path/are considered two distinct resources.Wildcards can be used to match protocols, host names, and port numbers.
For example,
*://*:*/*matcheshttp://www.example.com:80/index.html,https://www.example.com:443/index.html, andhttp://www.example.net:8080/index.html.When a port number is not explicitly specified, then the default port number is implied. Therefore
http://www.example.com/*is the same ashttp://www.example.com:80/*, andhttps://www.example.com/*is the same ashttps://www.example.com:443/*.Wildcards cannot be escaped.
Do not mix
*and-*-in the same pattern.By default, comparisons are not case sensitive. The delimiter, wildcards and case sensitivity are configurable. To see examples of other configurations, in the OpenAM Console, navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Policy Configuration, and scroll to Resource Comparator.
You can import and export policies to and from files.
You can use these files to backup policies, transfer policies between OpenAM instances, or store policy configuration in a version control system such as Git or Subversion.
OpenAM supports exporting policies in JSON and eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML) Version 3.0 format. The features supported by each format are summarized in the table below:
| Feature | Supported? | |
|---|---|---|
| JSON | XACML | |
| Can be imported/exported from within the OpenAM console? | No | Yes |
| Can be imported/exported on the command line, using the ssoadm command? | Yes | Yes |
| Exports policies? | Yes | Yes |
| Exports policy sets? | Yes | Partial [a] |
| Exports resource types? | Yes | Partial [a] |
| Creates an exact copy of the original policy sets, resource types, and policies upon import? | Yes | Partial [b] |
[a] Only the details of policy sets and resource types that are actually used within a policy is exported to the XACML format. The full definition is not exported. [b] Policy sets and resource types will be generated from the details in the XML, but may not match the definitions of the originals, for example the names are auto-generated. | ||
Note
OpenAM can only import XACML 3.0 files that were either created by an OpenAM instance, or that have had minor manual modifications, due to the reuse of some XACML 3.0 parameters for non-standard information.
You can import and export policies by using the policy editor in the OpenAM console, using the REST API, or with the ssoadm command.
For information on importing and exporting policies in XACML format by using the REST API, see "Importing and Exporting XACML 3.0" in the Developer's Guide.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Policy Sets, and then click Export Policy Sets.
All policy sets, and the policies within will be exported in XACML format.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Authorization > Policy Sets, and then click Import Policy Sets.
Browse to the XACML format file, select it, and then click Open.
Any policy sets, and the policies within will be imported from the selected XACML format file.
Note
Policy sets and resource types will be generated from the details in the XACML format file, but may not match the definitions of the originals, for example the names are auto-generated.
Use the ssoadm policy-export command:
$ ssoadm \ policy-export \ --realm "/" \ --servername "http://openam.example.com:8080/openam" \ --jsonfile "myPolicies.json" \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt { "RESOURCE_TYPE" : 1, "POLICY" : 1, "APPLICATION" : 1 }If exporting from a subrealm, include the top level realm ("
/") in the--realmvalue. For example--realm "/myRealm".For more information on the syntax of this command, see "ssoadm policy-export" in the Reference.
Use the ssoadm policy-import command:
$ ssoadm \ policy-import \ --realm "/myRealm" \ --servername "http://openam.example.com:8080/openam" \ --jsonfile "myPolicies.json" \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt { "POLICY" : { "CREATE_SUCCESS" : { "count" : 1 } }, "RESOURCE_TYPE" : { "CREATE_SUCCESS" : { "count" : 1 } }, "APPLICATION" : { "CREATE_SUCCESS" : { "count" : 1 } } }If importing to a subrealm, include the top level realm ("
/") in the--realmvalue. For example--realm "/myRealm".For more information on the syntax of this command, see "ssoadm policy-import" in the Reference.
Use the ssoadm list-xacml command:
$ ssoadm \ list-xacml \ --realm "/" \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <PolicySet xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:3.0:core:schema:wd-17" PolicyCombiningAlgId="urn...rule-combining-algorithm:deny-overrides" Version="2014.11.25.17.41.15.597" PolicySetId="/:2014.11.25.17.41.15.597"> <Target /> <Policy RuleCombiningAlgId="urn...rule-combining-algorithm:deny-overrides" Version="2014.11.25.17.40.08.067" PolicyId="myPolicy"> <Description /> <Target> <AnyOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:json-subject-match"> <AttributeValue DataType="urn...entitlement.conditions.subject.AuthenticatedUsers"> {} </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="urn...entitlement.conditions.subject.AuthenticatedUsers" AttributeId="urn...entitlement:json-subject" Category="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject-category:access-subject" /> </Match> </AllOf> </AnyOf> <AnyOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:resource-match:application:iPlanetAMWebAgentService"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> http://www.example.com:8000/*?* </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:resource:resource-id" Category="urn...attribute-category:resource" /> </Match> </AllOf> </AnyOf> <AnyOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...application-match"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> iPlanetAMWebAgentService </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="false" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn...application-id" Category="urn...application-category" /> </Match> </AllOf> </AnyOf> <AnyOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:action-match:application:iPlanetAMWebAgentService"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> POST </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" Category="urn...attribute-category:action" /> </Match> </AllOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:action-match:application:iPlanetAMWebAgentService"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> GET </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" Category="urn...attribute-category:action" /> </Match> </AllOf> </AnyOf> </Target> <VariableDefinition VariableId="....entitlement.applicationName"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> iPlanetAMWebAgentService </AttributeValue> </VariableDefinition> <VariableDefinition VariableId="...privilege.createdBy"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> id=amadmin,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org </AttributeValue> </VariableDefinition> <VariableDefinition VariableId="...privilege.lastModifiedBy"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> id=amadmin,ou=user,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org </AttributeValue> </VariableDefinition> <VariableDefinition VariableId="...privilege.creationDate"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#dateTime"> 2014-11-25T17:40:08.067 </AttributeValue> </VariableDefinition> <VariableDefinition VariableId="...privilege.lastModifiedDate"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#dateTime"> 2014-11-25T17:40:08.067 </AttributeValue> </VariableDefinition> <Rule Effect="Permit" RuleId="null:permit-rule"> <Description>Permit Rule</Description> <Target> <AnyOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:action-match:application:iPlanetAMWebAgentService"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> POST </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" Category="urn...attribute-category:action" /> </Match> </AllOf> <AllOf> <Match MatchId="urn...entitlement:action-match:application:iPlanetAMWebAgentService"> <AttributeValue DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> GET </AttributeValue> <AttributeDesignator MustBePresent="true" DataType="htp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string" AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" Category="urn...attribute-category:action" /> </Match> </AllOf> </AnyOf> </Target> <Condition> <Apply FunctionId="urn...entitlement:json-subject-and-condition-satisfied"> <AttributeValue DataType="urn...entitlement.conditions.subject.AuthenticatedUsers" privilegeComponent="entitlementSubject"> {} </AttributeValue> </Apply> </Condition> </Rule> </Policy> </PolicySet> Policy definitions were returned under realm, /.For more information on the syntax of this command, see "ssoadm list-xacml" in the Reference.
Use the ssoadm create-xacml command:
$ ssoadm \ create-xacml \ --realm "/" \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --xmlfile policy.xml Policies were created under realm, /.
For more information on the syntax of this command, see "ssoadm create-xacml" in the Reference.
To delegate policy management and other administrative tasks, use privileges. You set privileges in OpenAM console on the Privileges page for a realm.
For more information, see "Delegating Realm Administration Privileges".
This chapter shows how to configure OpenAM realms, which are used to group configuration and identities together. For example, you might have one realm for OpenAM administrators and agents, and another realm for users. In this two-realm setup, the OpenAM administrator can log in to the administrative realm to manage the services, but cannot authenticate as OpenAM administrator to the realm that protects web sites with HR and financial information.
OpenAM associates a realm with at least one identity repository and authentication chain. OpenAM also associates the realm with authorization applications and their policies, and with privileges for administrators. Each realm can have its own configuration for the services it provides.
When you first configure OpenAM,
OpenAM sets up the default Top Level Realm, sometimes referred to as the
/ realm or root realm. The Top Level Realm
contains OpenAM configuration data and allows authentication using the
identity repository that you choose during initial configuration.
The Top Level Realm might hold the overall configuration
for Example.com, for instance.
You create new realms to subdivide authentication and authorization, and to delegate management of subrealms. For example, your organization might require separate realms for payroll, human resources, and IT management domains and their applications.
By default a new realm inherits configuration from its parent's configuration. The default identity repository is the one you choose when you deploy and configure OpenAM. The default authentication mechanism corresponds to that identity repository as well. You can, however, constrain authentication to rely on different data stores, and set policy for agents to define authorization in the realm:
Note
OpenAM requires cookies for all configured realms when using
DNS aliases. For example, if you install OpenAM in the domain,
openam.example.net and have realms,
identity.example.org and security.example.com
then you must configure cookie domains for
.example.net, .example.org, and
.example.com.
You can set up the cookie domains for each realm using the OpenAM console
under Configuration > System > Platform > Cookie Domains, and then
add the domains as needed.
You create and configure realms through the console, starting from the Realms page. You delegate administration for a realm by setting privileges in the realm.
You can create a new realm through the OpenAM console as described below, or by using the ssoadm create-realm command:
Log in to the OpenAM console as OpenAM Administrator,
amadmin.On the Realms page, click New Realm. The New Realm dialog box appears. Use this dialog box to configure the realm.
Note
Do not use the names of OpenAM REST endpoints as the name of a realm. The OpenAM REST endpoint names that should not be used include: "users", "groups", "realms", "policies" and "applications".
If you configure the realm to be inactive, then users cannot use it to authenticate or be granted access to protected resources.
Realm/DNS aliases must follow standard FQDN conventions, such as
hr.example.comorpay.example.com.[3]Save your work after defining the configuration for the new realm.
You assign administration privileges to groups of users.
You can grant privileges through the OpenAM console, see "To Delegate Privileges using the OpenAM Console", or by using the ssoadm add-privileges command, see "ssoadm add-privileges" in the Reference.
On the Realms page, click the realm for which you want to delegate administration to view the realm configuration.
Delegating administration privileges in the top-level realm allows members of the group full administration access to the OpenAm instance. Administration privileges in any other realm allows the group to administrate only in that realm, and any child realms.
On the Privileges tab, click the name of the group to which you intend to grant access.
Select the administrative privileges to delegate for the realm:
(Optional) To grant users in the group access to the administration console for the realm, select Read and write access to all realm and policy properties.
In OpenAM 13.5.2-15, administrators can use the OpenAM administration console as follows:
Delegated administrators with the
RealmAdminprivilege can access full administration console functionality within the realms they can administer.Administrators with lesser privileges, such as the
PolicyAdminprivilege, can not access the OpenAM administration console.Both the top-level administrator (such as
amadmin) and delegated administrators in the Top Level Realm with theRealmAdminprivilege have access to full console functionality in all realms and can access OpenAM's global configuration.
(Optional) To grant users in the group access to REST endpoints, select them from the list.
For information about the available OpenAM privileges, see "OpenAM Privileges".
Save your work.
The following table describes privileges that you can assign in the OpenAM console or by using the ssoadm add-privileges command:
| Privilege as it Appears in the Console | Privilege Name to Use With the ssoadm add-privileges Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Read and write access to all realm and policy properties | RealmAdmin | Assign this privilege to administrators in order to let them modify or read any part of an OpenAM realm. Use this privilege when you do not require granularity in your delegation model. All other OpenAM privileges are included with this privilege. Administrators using the OpenAM administration console must have this privilege. |
| Read and write access to all log files | LogAdmin | Subset of the RealmAdmin privilege. |
| Read access to all log files | LogRead | Subset of the RealmAdmin privilege. |
| Write access to all log files | LogWrite | Subset of the RealmAdmin privilege. |
| Read and write access to all configured agents | AgentAdmin |
Provides access to centralized agent configuration;
subset of the RealmAdmin privilege.
|
| Read and write access to all federation metadata configurations | FederationAdmin | Subset of the RealmAdmin privilege. |
| REST calls for reading realms | RealmReadAccess | Subset of the RealmAdmin privilege. |
| Read and write access only for policy properties, including REST calls | PolicyAdmin |
Assign this privilege to policy administrators
in order to let them modify or read any part of the OpenAM
policy configuration. This privilege lets an
administrator modify or read all policy components:
policies, applications, subject types,
condition types, subject attributes, and decision combiners.
All other OpenAM privileges that affect policy components
are included with this privilege. Subset of the
RealmAdmin privilege.
|
| REST calls for policy evaluation | EntitlementRestAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading policies | PrivilegeRestReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for managing policies | PrivilegeRestAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading policy applications | ApplicationReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for modifying policy applications | ApplicationModifyAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for modifying policy resource types | ResourceTypeModifyAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading policy resource types | ResourceTypeReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading policy application types | ApplicationTypesReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading environment conditions | ConditionTypesReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading subject conditions | SubjectTypesReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading decision combiners | DecisionCombinersReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for reading subject attributes | SubjectAttributesReadAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
| REST calls for modifying session properties | SessionPropertyModifyAccess |
Subset of the RealmAdmin and
PolicyAdmin privileges.
|
You can configure a policy agent to be directed to a realm and application when requesting policy decisions, or to log users into a different realm than the policy agent's realm:
By default, policy agents request policy decisions
in the Top Level Realm (/) from the default policy set,
iPlanetAMWebAgentService.
When the realm and policy set differ for your policy agent,
you can specify the realm and policy set in the policy agent profile.
OpenAM then directs requests from the policy agent
to the specified realm and policy set,
so this is backwards compatible with existing policy agents.
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Web or Java EE Agent Type > Agent Name > OpenAM Services > Policy Client Service.
Set the Realm and Policy Set.
Note that Policy Sets are labelled as "Application" in some parts of the user interface.
For example, if the realm is
/hrand the policy set ismyHRApp:Realm:
/hrApplication:
myHRApp
Save your work.
You might choose to configure your agent in one realm, yet have your real users authenticate through another realm. In this case, you want your policy agents to redirect users to authenticate to their realm, rather than the agent realm:
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Web or Java EE Agent Type > Agent Name > OpenAM Services.
Add login and logout URLs, including the realm in the query string.
For example, if your Realm Name is
hr, and you access OpenAM athttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam:Login URL:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?realm=hrLogout URL:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Logout?realm=hr
Save your work.
When you first set up a realm, the new realm inherits the data store from the parent realm. Yet, if your administrators are in one realm and your users in another, your new child realm might retrieve users from a different data store.
An external identity repository is a user store other than the OpenAM embedded repository. Before configuring an OpenAM data store as an external identity repository, make sure that you have prepared the external identity repository for OpenAM. For more information, see "Preparing an External Identity Repository" in the Installation Guide.
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores.
Click New in the Data Stores table to create a data store profile, and to provide the information needed to connect to the data store.
In the first screen, name the data store and select the type of data store.
Most data stores are directory services, though the Database Repository lets you connect to an SQL database through JDBC.
In the second screen, provide information on how to connect to your data store, and then click Finish to save your work.
See the following sections for hints depending on the type of data store.
You must index several directory attributes as a post-configuration step if you configured the data store as follows:
You configured the data store to access an external identity repository.
You used the "Load schema when finished" option.
For more information about indexing external identity repository attributes, see "To Index External Identity Repository Attributes" in the Installation Guide.
Click the Subjects tab, and make sure the connection to your new data store is working, by searching for a known identity.
By default the Subjects list only retrieves 100 entries from the data store. Narrow your search if you do not see the identity you are looking for.
If you no longer need the connection to the inherited data store in this realm, then you can delete its entry in the Data Stores table.
Also, once you change the data store for a realm, you might opt to change the authentication module configuration to use your realm data store, rather than the inherited settings. See "Configuring Authentication Modules".
Use these hints when configuring Active Directory Data Stores:
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first:
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server.- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authidDefault:
CN=Administrator,CN=Users,base-dn- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
SECONDS- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB)
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMappingDefault:
userPassword=unicodePwd- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
group=read,create,edit,delete,realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,user=read,create,edit,delete- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
cnWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=person)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-nameDefault:
cn- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-valueDefault:
users- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any such unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings, if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
organizationalPerson,person,top,User,- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
assignedDashboard,cn,devicePrintProfiles,displayName,distinguishedName,dn,employeeNumber,givenName,iplanet-am-auth-configuration,iplanet-am-session-add-session-listener-on-all-sessions,iplanet-am-session-destroy-sessions,iplanet-am-session-get-valid-sessions,iplanet-am-session-max-caching-time,iplanet-am-session-max-idle-time,iplanet-am-session-max-session-time,iplanet-am-session-quota-limit,iplanet-am-session-service-status,iplanet-am-user-account-life,iplanet-am-user-admin-start-dn,iplanet-am-user-alias-list,iplanet-am-user-auth-config,iplanet-am-user-auth-modules,iplanet-am-user-failure-url,iplanet-am-user-federation-info-key,iplanet-am-user-federation-info,iplanet-am-user-login-status,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-force-reset,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-options,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-question-answer,iplanet-am-user-success-url,mail,name,objectclass,objectGUID,postalAddress,preferredlanguage,preferredLocale,preferredtimezone,sAMAccountName,sn,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey,sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsData,sunIdentityMSISDNNumber,sunIdentityServerDiscoEntries,sunIdentityServerPPAddressCard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameAltCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameFN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameMN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNamePT,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameSN,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsAge,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsBirthDay,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsDisplayLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsTimeZone,sunIdentityServerPPEmergencyContact,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityAltO,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityJobTitle,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityOrg,sunIdentityServerPPEncryPTKey,sunIdentityServerPPFacadegreetmesound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeGreetSound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeMugShot,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeNamePronounced,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeWebSite,sunIdentityServerPPInformalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityDOB,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityGender,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityLegalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityMaritalStatus,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPMsgContact,sunIdentityServerPPSignKey,telephoneNumber,unicodePwd,userAccountControl,userpassword,userPrincipalname- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
The LDAP user profile entries require the Common Name (
cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so that LDAP constraint violations do not occur when performing an add operation.The
cnattribute gets its value from theuidattribute, which comes from the User Name field on the console's login page. Thesnattribute gets the value of thegivenNameattribute. Attributes not mapped to another attribute and attributes mapped to themselves (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
userAccountControl- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault: 544
- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault: 546
- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=group)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-valueDefault:
users- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
Group,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
cn,distinguishedName,dn,member,name,objectCategory,objectclass,sAMAccountName,sAMAccountType- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
member- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
Specify either
SCOPE_BASEorSCOPE_ONE. Do not specifySCOPE_SUB, as it can have a severe impact on Active Directory performance.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: false
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
Use these hints when configuring Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM) Data Stores.
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration.
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first:
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server.- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authidDefault:
CN=Administrator,CN=Users,base-dn- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
second- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMappingDefault:
userPassword=unicodePwd- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
group=read,create,edit,delete,realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,user=read,create,edit,delete- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
cnWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=person)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-name- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-value- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings, if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
devicePrintProfilesContainer,forgerock-am-dashboard-service,iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service,iplanet-am-managed-person,iplanet-am-user-service,iPlanetPreferences,organizationalPerson,person,sunAMAuthAccountLockout,sunFederationManagerDataStore,sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier,sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService,top,User- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
assignedDashboard,cn,devicePrintProfiles,displayName,distinguishedName,dn,employeeNumber,givenName,iplanet-am-auth-configuration,iplanet-am-session-add-session-listener-on-all-sessions,iplanet-am-session-destroy-sessions,iplanet-am-session-get-valid-sessions,iplanet-am-session-max-caching-time,iplanet-am-session-max-idle-time,iplanet-am-session-max-session-time,iplanet-am-session-quota-limit,iplanet-am-session-service-status,iplanet-am-user-account-life,iplanet-am-user-admin-start-dn,iplanet-am-user-alias-list,iplanet-am-user-auth-config,iplanet-am-user-auth-modules,iplanet-am-user-failure-url,iplanet-am-user-federation-info-key,iplanet-am-user-federation-info,iplanet-am-user-login-status,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-force-reset,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-options,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-question-answer,iplanet-am-user-success-url,mail,name,objectclass,objectGUID,postalAddress,preferredlanguage,preferredLocale,preferredtimezone,sAMAccountName,sn,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey,sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsData,sunIdentityMSISDNNumber,sunIdentityServerDiscoEntries,sunIdentityServerPPAddressCard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameAltCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameFN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameMN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNamePT,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameSN,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsAge,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsBirthDay,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsDisplayLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsTimeZone,sunIdentityServerPPEmergencyContact,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityAltO,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityJobTitle,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityOrg,sunIdentityServerPPEncryPTKey,sunIdentityServerPPFacadegreetmesound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeGreetSound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeMugShot,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeNamePronounced,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeWebSite,sunIdentityServerPPInformalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityDOB,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityGender,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityLegalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityMaritalStatus,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPMsgContact,sunIdentityServerPPSignKey,telephoneNumber,unicodePwd,userAccountControl,userpassword,userPrincipalname- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
Attributes not mapped to another attribute (for example,
cn) and attributes mapped to themselves, (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile. The object classes for user profile LDAP entries generally require Common Name (cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so this prevents an LDAP constraint violation when performing the add operation.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
msDS-UserAccountDisabled- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault: FALSE
- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault: TRUE
- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=group)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-value- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
Group,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
cn,distinguishedName,dn,member,name,objectCategory,objectclass,sAMAccountName,sAMAccountType- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
member- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
Specify either
SCOPE_BASEorSCOPE_ONE. Do not specifySCOPE_SUB, as it can have a severe impact on Active Directory performance.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: false
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
Use these hints when configuring Generic LDAPv3 compliant data stores.
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration.
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first:
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authid- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
second- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMapping- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,user=read,create,edit,delete,group=read,create,edit,delete- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
uidWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=inetorgperson)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-name- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-value- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings, if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
inetorgperson,inetUser,organizationalPerson,person,top,- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
uid,caCertificate,authorityRevocationList,inetUserStatus,mail,sn,manager,userPassword,adminRole,objectClass,givenName,memberOf,cn,telephoneNumber,preferredlanguage,userCertificate,postalAddress,dn,employeeNumber,distinguishedName- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
Attributes not mapped to another attribute (for example,
cn) and attributes mapped to themselves (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile. The object classes for user profile LDAP entries generally require Common Name (cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so this prevents an LDAP constraint violation when performing the add operation.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
inetuserstatus- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault:
Active- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault:
Inactive- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
uid- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=groupOfUniqueNames)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-valueDefault:
groups- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
groupofuniquenames,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
ou,cn,description,dn,objectclass,uniqueMember- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
uniqueMember- Attribute Name of Group Member URL
Attribute in the dynamic group's LDAP entry whose value is a URL specifying the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberurlDefault:
memberUrl- Default Group Member's User DN
DN of member added to all newly created groups.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-dftgroupmember- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Filter
LDAP filter to apply when performing persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-filterDefault:
(objectclass=*)- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: false
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
Use these hints when configuring OpenDJ data stores.
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration.
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first:
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authid- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
second- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMapping- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,user=read,create,edit,delete,group=read,create,edit,delete- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
uidWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=inetorgperson)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-valueDefault:
people- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings, if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
devicePrintProfilesContainer,forgerock-am-dashboard-service,inetorgperson,inetuser,iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service,iplanet-am-managed-person,iplanet-am-user-service,iPlanetPreferences,organizationalperson,person,sunAMAuthAccountLockout,sunFederationManagerDataStore,sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier,sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService,top- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsBirthDay,uid,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityLegalName,manager,assignedDashboard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameSN,userPassword,iplanet-am-session-get-valid-sessions,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityJobTitle,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-question-answer,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityDOB,sunIdentityServerPPEmergencyContact,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameCN,iplanet-am-user-success-url,iplanet-am-user-admin-start-dn,iplanet-am-user-federation-info,userCertificate,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeGreetSound,sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsData,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeNamePronounced,distinguishedName,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsTimeZone,sunIdentityMSISDNNumber,iplanet-am-session-max-caching-time,sn,iplanet-am-session-quota-limit,iplanet-am-session-max-session-time,adminRole,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityAltO,objectClass,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityMaritalStatus,iplanet-am-user-login-status,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdType,devicePrintProfiles,iplanet-am-session-max-idle-time,sunIdentityServerPPFacadegreetmesound,cn,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-options,telephoneNumber,preferredlanguage,iplanet-am-user-federation-info-key,sunIdentityServerPPMsgContact,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityGender,iplanet-am-user-alias-list,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameFN,caCertificate,inetUserStatus,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameMN,sunIdentityServerPPEncryPTKey,givenName,memberOf,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdValue,preferredLocale,iplanet-am-session-service-status,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsAge,sunIdentityServerDiscoEntries,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdType,iplanet-am-user-auth-config,iplanet-am-user-failure-url,sunIdentityServerPPAddressCard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNamePT,dn,iplanet-am-session-add-session-listener-on-all-sessions,mail,authorityRevocationList,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-force-reset,inetUserHttpURL,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameAltCN,preferredtimezone,sunIdentityServerPPInformalName,sunIdentityServerPPSignKey,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityOrg,iplanet-am-session-destroy-sessions,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeMugShot,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeWebSite,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsDisplayLanguage,postalAddress,iplanet-am-auth-configuration,employeeNumber,iplanet-am-user-account-life,iplanet-am-user-auth-modules,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsLanguage- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
Attributes not mapped to another attribute (for example,
cn) and attributes mapped to themselves (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile. The object classes for user profile LDAP entries generally require Common Name (cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so this prevents an LDAP constraint violation when performing the add operation.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
inetuserstatus- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault:
Active- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault:
Inactive- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
uid- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=groupOfUniqueNames)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-valueDefault:
groups- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
groupofuniquenames,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
cn,dn,objectclass,uniqueMember- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
uniqueMember- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Filter
LDAP filter to apply when performing persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-filterDefault:
(objectclass=*)- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
The OpenDJ data store uses this setting only for persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: true
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
Use these hints when configuring Data Stores for Oracle DSEE or Sun DSEE using OpenAM schema.
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration.
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first:
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server.- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authidDefault:
cn=dsameuser,ou=DSAME Users,base-dn- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
second- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMapping- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
filteredrole=read,create,edit,delete,group=read,create,edit,delete,realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,role=read,create,edit,delete,user=read,create,edit,delete,service- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
uidWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=inetorgperson)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-valueDefault:
people- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings, if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
devicePrintProfilesContainer,forgerock-am-dashboard-service,inetadmin,inetorgperson,inetuser,iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service,iplanet-am-managed-person,iplanet-am-user-service,iPlanetPreferences,organizationalperson,person,sunAMAuthAccountLockout,sunFederationManagerDataStore,sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier,sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService,top- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsBirthDay,uid,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityLegalName,manager,assignedDashboard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameSN,userPassword,iplanet-am-session-get-valid-sessions,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityJobTitle,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-question-answer,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityDOB,sunIdentityServerPPEmergencyContact,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameCN,iplanet-am-user-success-url,iplanet-am-user-admin-start-dn,iplanet-am-user-federation-info,userCertificate,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeGreetSound,sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsData,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeNamePronounced,distinguishedName,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsTimeZone,sunIdentityMSISDNNumber,iplanet-am-session-max-caching-time,sn,iplanet-am-session-quota-limit,iplanet-am-session-max-session-time,adminRole,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityAltO,objectClass,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityMaritalStatus,iplanet-am-user-login-status,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdType,devicePrintProfiles,iplanet-am-session-max-idle-time,sunIdentityServerPPFacadegreetmesound,cn,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-options,telephoneNumber,preferredlanguage,iplanet-am-user-federation-info-key,sunIdentityServerPPMsgContact,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityGender,iplanet-am-user-alias-list,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameFN,caCertificate,inetUserStatus,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameMN,sunIdentityServerPPEncryPTKey,givenName,memberOf,iplanet-am-static-group-dn,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdValue,preferredLocale,iplanet-am-session-service-status,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsAge,sunIdentityServerDiscoEntries,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdType,iplanet-am-user-auth-config,iplanet-am-user-failure-url,sunIdentityServerPPAddressCard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNamePT,dn,iplanet-am-session-add-session-listener-on-all-sessions,mail,authorityRevocationList,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-force-reset,inetUserHttpURL,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameAltCN,preferredtimezone,sunIdentityServerPPInformalName,sunIdentityServerPPSignKey,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityOrg,iplanet-am-session-destroy-sessions,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeMugShot,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeWebSite,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsDisplayLanguage,postalAddress,iplanet-am-auth-configuration,employeeNumber,iplanet-am-user-auth-modules,iplanet-am-user-account-life,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsLanguage- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
Attributes not mapped to another attribute (for example,
cn) and attributes mapped to themselves (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile. The object classes for user profile LDAP entries generally require Common Name (cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so this prevents an LDAP constraint violation when performing the add operation.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
inetuserstatus- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault:
Active- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault:
Inactive- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
uid- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=groupOfUniqueNames)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-valueDefault:
groups- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
groupofuniquenames,iplanet-am-managed-group,iplanet-am-managed-static-group,groupofurls,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
cn,iplanet-am-group-subscribable,dn,objectclass,uniqueMember- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
uniqueMember- Attribute Name of Group Member URL
Attribute in the dynamic group's LDAP entry whose values are LDAP URLs specifying members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberurlDefault:
memberUrl- LDAP Roles Search Attribute
When searching for a role by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-roles-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Roles Search Filter
When searching for roles, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-roles-search-filterDefault:
(&(objectclass=ldapsubentry)(objectclass=nsmanagedroledefinition))- LDAP Roles Object Class
Role profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-role-objectclassDefault:
ldapsubentry,nsmanagedroledefinition,nsroledefinition,nssimpleroledefinition,top- LDAP Filter Roles Search Attribute
When searching for a filtered role by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-filterroles-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Filter Roles Search Filter
When searching for filtered roles, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-filterroles-search-filterDefault:
(&(objectclass=ldapsubentry)(objectclass=nsfilteredroledefinition))- LDAP Filter Roles Object Class
Filtered role profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-filterrole-objectclassDefault:
ldapsubentry,nscomplexroledefinition,nsfilteredroledefinition,nsroledefinition- LDAP Filter Roles Attributes
Filtered role profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-filterrole-attributesDefault:
nsRoleFilter- Attribute Name for Filtered Role Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the filtered roles to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-nsroleDefault:
nsrole- Attribute Name of Role Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the roles to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-nsrolednDefault:
nsRoleDN- Attribute Name of Filtered Role Filter
LDAP attribute whose values are the filters for filtered roles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-nsrolefilterDefault:
nsRoleFilter- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Filter
LDAP filter to apply when performing persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-filterDefault:
(objectclass=*)- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: true
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
Use these hints when configuring Tivoli Directory Server data stores.
ssoadm service name:
sunIdentityRepositoryService
- Name
Name for the data store configuration.
- Load schema when finished
Add appropriate LDAP schema to the directory server when saving the configuration. The LDAP Bind DN user must have access to perform this operation.
This attribute is not available for use with the ssoadm command.
Default: false
- LDAP Server
host:portto contact the directory server, with optional|server_ID|site_IDfor deployments with multiple servers and sites.OpenAM uses the optional settings to determine which directory server to contact first. OpenAM tries to contact directory servers in the following priority order, with highest priority first.
The first directory server in the list whose server_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the list whose site_ID matches the current OpenAM server.
The first directory server in the remaining list.
If the directory server is not available, OpenAM proceeds to the next directory server in the list.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-ldap-serverDefault:
host:portof the initial directory server configured for this OpenAM server- LDAP Bind DN
Bind DN for connecting to the directory server. Some OpenAM capabilities require write access to directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authid- LDAP Bind Password
Bind password for connecting to the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-authpw- LDAP Organization DN
The base DN under which to find user and group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-organization_nameDefault:
base-dn- LDAP SSL/TLS Enabled
Whether to use LDAPS or StartTLS to connect to the directory server. If you enable SSL or StartTLS, OpenAM must be able to trust server certificates, either because the server certificates were signed by a CA whose certificate is already included in the trust store used by the container where OpenAM runs, or because you imported the certificates into the trust store.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection-modePossible values:
LDAP,LDAPS, andStartTLS- LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size
Maximum number of connections to the directory server. Make sure the directory service can cope with the maximum number of client connections across all servers.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-connection_pool_max_sizeDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval
How often to send a heartbeat request to the directory server to ensure that the connection does not remain idle. Some network administrators configure firewalls and load balancers to drop connections that are idle for too long. You can turn this off by setting the value to 0 or to a negative number. To set the units for the interval, use LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-intervalDefault: 10
- LDAP Connection Heartbeat Time Unit
Time unit for the LDAP Connection Heartbeat Interval setting.
ssoadm attribute:
openam-idrepo-ldapv3-heartbeat-timeunitDefault:
second- Maximum Results Returned from Search
A cap for the number of search results to request. For example, when using the Subjects tab to view profiles, even if you set Configuration > Console > Administration > Maximum Results Returned from Search to a larger number, OpenAM does not exceed this setting. Rather than raise this number, consider narrowing your search to match fewer directory entries.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-max-resultDefault: 1000
- Search Timeout
Maximum time to wait for search results in seconds. Does not apply to persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-time-limitDefault: 10
- LDAPv3 Plugin Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-search-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- LDAPv3 Repository Plugin Class Name
OpenAM identity repository implementation.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoClassDefault:
org.forgerock.openam.idrepo.ldap.DJLDAPv3Repo- Attribute Name Mapping
Map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoAttributeMapping- LDAPv3 Plugin Supported Types and Operations
Map of OpenAM operations that can be performed in the specified OpenAM contexts.
ssoadm attribute:
sunIdRepoSupportedOperationsDefault:
group=read,create,edit,delete,realm=read,create,edit,delete,service,user=read,create,edit,delete,service- LDAP Users Search Attribute
When searching for a user by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-attributeDefault:
cnWarning
Do not modify the value of the search attribute in user profiles. Modifying this attribute value can result in incorrectly cached identity data. For example, if you configure the search attribute to
mail, it could prevent users from being able to update their email addresses in their user profiles.- LDAP Users Search Filter
When searching for users, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-users-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=inetorgperson)- LDAP People Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP People Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains user profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-people-container-value- LDAP User Object Class
User profiles have these LDAP object classes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
For example, with default settings if you request that OpenAM execute a search that asks for the
mailAlternateAddressattribute, OpenAM does the search, but does not requestmailAlternateAddress. In the same way, OpenAM does perform an update operation with a request to set the value of an unlisted attribute likemailAlternateAddress, but it drops the unlisted attribute from the update request.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-objectclassDefault:
devicePrintProfilesContainer,forgerock-am-dashboard-service,inetorgperson,inetuser,iplanet-am-auth-configuration-service,iplanet-am-managed-person,iplanet-am-user-service,iPlanetPreferences,organizationalperson,person,sunAMAuthAccountLockout,sunFederationManagerDataStore,sunFMSAML2NameIdentifier,sunIdentityServerLibertyPPService,top- LDAP User Attributes
User profiles have these LDAP attributes.
OpenAM handles only those attributes listed in this setting. OpenAM discards any unlisted attributes from requests and the request proceeds without the attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-user-attributesDefault:
adminRole,assignedDashboard,authorityRevocationList,caCertificate,cn,devicePrintProfiles,distinguishedName,dn,employeeNumber,givenName,inetUserHttpURL,inetUserStatus,iplanet-am-auth-configuration,iplanet-am-session-add-session-listener-on-all-sessions,iplanet-am-session-destroy-sessions,iplanet-am-session-get-valid-sessions,iplanet-am-session-max-caching-time,iplanet-am-session-max-idle-time,iplanet-am-session-max-session-time,iplanet-am-session-quota-limit,iplanet-am-session-service-status,iplanet-am-user-account-life,iplanet-am-user-admin-start-dn,iplanet-am-user-alias-list,iplanet-am-user-auth-config,iplanet-am-user-auth-modules,iplanet-am-user-failure-url,iplanet-am-user-federation-info-key,iplanet-am-user-federation-info,iplanet-am-user-login-status,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-force-reset,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-options,iplanet-am-user-password-reset-question-answer,iplanet-am-user-success-url,mail,manager,memberOf,objectClass,postalAddress,preferredlanguage,preferredLocale,preferredtimezone,sn,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info,sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey,sunAMAuthInvalidAttemptsData,sunIdentityMSISDNNumber,sunIdentityServerDiscoEntries,sunIdentityServerPPAddressCard,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameAltCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameCN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameFN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameMN,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNamePT,sunIdentityServerPPCommonNameSN,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsAge,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsBirthDay,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsDisplayLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsLanguage,sunIdentityServerPPDemographicsTimeZone,sunIdentityServerPPEmergencyContact,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityAltO,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityJobTitle,sunIdentityServerPPEmploymentIdentityOrg,sunIdentityServerPPEncryPTKey,sunIdentityServerPPFacadegreetmesound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeGreetSound,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeMugShot,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeNamePronounced,sunIdentityServerPPFacadeWebSite,sunIdentityServerPPInformalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityAltIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityDOB,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityGender,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityLegalName,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityMaritalStatus,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdType,sunIdentityServerPPLegalIdentityVATIdValue,sunIdentityServerPPMsgContact,sunIdentityServerPPSignKey,telephoneNumber,uid,userCertificate,userPassword- Create User Attribute Mapping
When creating a user profile, apply this map of OpenAM profile attribute names to directory server attribute names.
Attributes not mapped to another attribute (for example,
cn) and attributes mapped to themselves (for example,cn=cn) take the value of the username unless the attribute values are provided when creating the profile. The object classes for user profile LDAP entries generally require Common Name (cn) and Surname (sn) attributes, so this prevents an LDAP constraint violation when performing the add operation.ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-createuser-attr-mappingDefault:
cn,sn- Attribute Name of User Status
Attribute to check/set user status.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-isactiveDefault:
inetuserstatus- User Status Active Value
Active users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-activeDefault:
Active- User Status Inactive Value
Inactive users have the user status attribute set to this value.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-inactiveDefault:
Inactive- Authentication Naming Attribute
RDN attribute for building the bind DN when given a username and password to authenticate a user against the directory server.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-auth-naming-attrDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Attribute
When searching for a group by name, match values against this attribute.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-attributeDefault:
cn- LDAP Groups Search Filter
When searching for groups, apply this LDAP search filter as well.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-groups-search-filterDefault:
(objectclass=groupOfNames)- LDAP Groups Container Naming Attribute
RDN attribute of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-nameDefault:
ou- LDAP Groups Container Value
RDN attribute value of the LDAP base DN which contains group profiles.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-container-value- LDAP Groups Object Class
Group profiles have these LDAP object classes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-objectclassDefault:
groupofnames,top- LDAP Groups Attributes
Group profiles have these LDAP attributes.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-group-attributesDefault:
cn,description,dn,member,objectclass,ou- Attribute Name for Group Membership
LDAP attribute in the member's LDAP entry whose values are the groups to which a member belongs.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-memberof- Attribute Name of Unique Member
Attribute in the group's LDAP entry whose values are the members of the group.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-uniquememberDefault:
member- Default Group Member's User DN
DN of member added to all newly created groups.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-dftgroupmember- Persistent Search Base DN
Base DN for LDAP-persistent searches used to receive notification of changes in directory server data.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearchbaseDefault:
base-dn- Persistent Search Filter
LDAP filter to apply when performing persistent searches.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-filterDefault:
(objectclass=*)- Persistent Search Scope
LDAP searches can apply to a single entry (SCOPE_BASE), entries directly below the search DN (SCOPE_ONE), or all entries below the search DN (SEARCH_SUB).
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-config-psearch-scopeDefault:
SCOPE_SUB- The Delay Time Between Retries
How long to wait after receiving an error result that indicates OpenAM should try the LDAP operation again.
ssoadm attribute:
com.iplanet.am.ldap.connection.delay.between.retriesDefault: 1000 milliseconds
- DN Cache Enabled
Whether to enable the DN cache, which is used to cache DN lookups that can happen in bursts during authentication. As the cache can become stale when a user is moved or renamed, enable DN caching when the directory service allows move/rename operations (Mod DN), and when OpenAM uses persistent searches to obtain notification of such updates.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-enabledDefault: true
- DN Cache Size
Maximum number of DNs cached when caching is enabled.
ssoadm attribute:
sun-idrepo-ldapv3-dncache-sizeDefault: 1500 items
You install policy agents in web servers and web application containers to enforce access policies OpenAM applies to protected web sites and web applications. Policy agents depend on OpenAM for all authentication and authorization decisions. Their primary responsibility consists of enforcing what OpenAM decides in a way that is unobtrusive to the user. In organizations with many servers, you might well install many policy agents.
Policy agents can have local configurations where they are installed. Typically, you store all policy agent configuration information in the OpenAM configuration store, defining policy agent profiles for each, and then you let the policy agents access their profiles through OpenAM. In this way, you manage all agent configuration changes centrally. This chapter describes how to set up policy agent profiles in OpenAM for centralized configuration.
OpenAM supports both OpenIG and also a variety of policy agents. OpenIG and the policy agents can both enforce policy, redirecting users to authenticate when necessary, and controlling access to protected resources. OpenIG runs as a self-contained reverse proxy located between the users and the protected applications. Policy agents are installed into the servers where applications run, intercepting requests in that context.
Use OpenIG to protect access to applications not suited for a policy agent. Not all web servers and Java EE applications have policy agents. Not all operating systems work with policy agents.
Policy agents have the advantage of sitting within your existing server infrastructure. Once you have agents installed into the servers with web applications or sites to protect, then you can manage their configurations centrally from OpenAM.
For organizations with both servers on which you can install policy agents and also applications that you must protect without touching the server, you can use policy agents on the former and OpenIG for the latter.
You can configure a number of different types of agents.
Each agent type requires an agent profile in OpenAM. The agent profile contains essential configuration for agent operation, such as a password to authenticate the agent, and the URL the agent resides at. For agents that support it, the agent profile can store all agent configuration centrally, rather than locally on the agent server.
Web and J2EE policy agents are the most common, requiring the least integration effort. The available agent types are:
- Web
You install web agents in web servers to protect web sites.
- J2EE
You install J2EE agents in web application containers to protect web applications.
- 2.2 Agents
Version 2.2 web and Java EE policy agents hold their configuration locally, connecting to OpenAM with a username/password combination. This agent type is provided for backwards compatibility.
- OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client
Register OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect clients using this type of profile.
- Agent Authenticator
The agent authenticator can read agent profiles by connecting to OpenAM with a user name, password combination, but unlike the agent profile administrator, cannot change agent configuration.
- SOAP STS Agent
Secure requests from a SOAP STS deployment to OpenAM using this type of agent profile.
This section concerns creating agent profiles, and creating groups that let agents inherit settings when you have many agents with nearly the same profile settings.
To create a new Web or Java EE policy agent profile, you need to create a name and password for the agent. You also need the URLs to OpenAM and the application to protect:
Login to OpenAM Console as an administrative user.
On the Realms menu of the OpenAM console, select the realm in which the agent profile is to be managed.
Click the Agents link, click the tab page for the kind of agent profile you want to create, and then click the New button in the Agent table.
In the Name field, enter a name for the agent profile.
In the Password and Re-Enter Password fields, enter a password for the new agent profile.
Click
LocalorCentralized(Default) to determine where the agent properties are stored. If you selectLocal, the properties are stored on the server on which the agent is running. If you selectCentralized, the properties are stored on the OpenAM server.In the Server URL field, enter the URL to OpenAM. For example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam.In the Agent URL field, enter the primary URL of the web or application server protected by the policy agent. Note for web agents, an example URL would look like:
http://www.example.com:80. For Java EE policy agents, an example URL must include theagentappcontext:http://www.example.com:8080/agentapp.Click Create. After creating the agent profile, you can click the link to the new profile to adjust and export the configuration.
Agent profile groups let you set up multiple agents to inherit settings from the group. To create a new agent profile group, you need a name and the URL to the OpenAM server in which you store the profile:
Login to OpenAM Console as an administrative user.
On the Realms menu of the OpenAM console, Select the realm in which you manage agents.
Click the Agents link, click the tab page for the kind of agent group you want to create, and then in the Group table, click New.
After creating the group profile, you can click the link to the new group profile to fine-tune or export the configuration.
Inherit group settings by selecting your agent profile, and then selecting the group name in the Group drop-down list near the top of the profile page.
You can then adjust inheritance by clicking Inheritance Settings on the agent profile page.
You can create a policy agent profile in OpenAM using the ssoadm command-line tool. You do so by specifying the agent properties either as a list of attributes, or by using an agent properties file as shown below. Export an existing policy agent configuration before you start to see what properties you want to set when creating the agent profile.
The following procedure demonstrates creating a policy agent profile using the ssoadm command:
Make sure the ssoadm command is installed. See "To Set Up Administration Tools" in the Installation Guide.
Determine the list of properties to set in the agent profile.
The following properties file shows a minimal configuration for a policy agent profile:
$ cat myAgent.properties com.iplanet.am.server.port=8443 com.sun.identity.agents.config.agenturi.prefix=http://www.example.com:80/amagent com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url[0]= \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/cdcservlet com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.default=www.example.com com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url[0]= \ http://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Login com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url[0]= \ http://openam.example.com:8443/openam/UI/Logout com.sun.identity.agents.config.remote.logfile=amAgent_www_example_com_80.log com.sun.identity.agents.config.repository.location=centralized com.sun.identity.client.notification.url= \ http://www.example.com:80/UpdateAgentCacheServlet?shortcircuit=false sunIdentityServerDeviceKeyValue[0]=agentRootURL=http://www.example.com:80/ sunIdentityServerDeviceStatus=Active userpassword=passwordCreate a password file, for example
$HOME/.pwd.txt. The file should only contain the password string, on a single line.The password file must be read-only for the user who creates the policy agent profile, and must not be accessible to other users:
$ chmod 400 $HOME/.pwd.txt
Create the profile in OpenAM:
$ ssoadm create-agent \ --realm / \ --agentname myAgent \ --agenttype J2EEAgent \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file $HOME/.pwd.txt \ --datafile myAgent.properties Agent configuration was created.
At this point you can view the profile in OpenAM Console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents to make sure the configuration is what you expect.
If you want to create policy agent profiles when installing policy agents, then you need the credentials of an OpenAM user who can read and write agent profiles.
You can use the OpenAM administrator account when creating policy agent profiles. If you delegate policy agent installation, then you might not want to share OpenAM administrator credentials with everyone who installs policy agents.
Follow these steps to create agent administrator users for a realm:
In OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Subjects.
Under Group click New... and create a group for agent administrators.
Switch to the Privileges tab for the realm, and click the name of the group you created.
Select Read and write access to all configured agents, and then Save your work.
Return to the Subjects tab, and under User create as many agent administrator users as needed.
For each agent administrator user, edit the user profile.
Under the Group tab of the user profile, add the user to agent profile administrator group, and then Save your work.
Provide each system administrator who installs policy agents with their agent administrator credentials.
When installing the policy agent with the
--custom-installoption, the system administrator can choose the option to create the profile during installation, and then provide the agent administrator user name and the path to a read-only file containing the agent administrator password. For silent installs, you can add the--acceptLicenseoption to auto-accept the software license agreement.
When you create a web policy agent profile and install the agent, you can choose to store the agent configuration centrally and configure the agent through OpenAM console. Alternatively, you can choose to store the agent configuration locally and configure the agent by changing values in the properties file. For information on the properties used in a centralized configuration, and the corresponding properties for use in a local configuration file where applicable, see Configuring Web Policy Agent Properties in the OpenAM Web Policy Agent User's Guide.
When you create a Java EE policy agent profile and install the agent, you can choose to store the agent configuration centrally and configure the agent through OpenAM console. Alternatively, you can store the agent configuration locally and configure the agent by changing values in the properties file. This section covers centralized configuration, indicating the corresponding properties for use in a local configuration file where applicable. [4]
Tip
To show the agent properties in configuration file format that correspond to what you see in the console, click Export Configuration after editing agent properties.
After changing properties specified as Hot swap: no, you must
restart the application server or web server, or the agent's container.
This section covers global Java EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > Global.
- Group
For assigning the agent to a previously configured Java EE agent group in order to inherit selected properties from the group.
- Password
Agent password used when creating the password file and when installing the agent.
- Status
Status of the agent configuration.
- Agent Notification URL
URL used by agent to register notification listeners.
Property:
com.sun.identity.client.notification.urlHot swap: no
- Location of Agent Configuration Repository
Indicates agent's configuration located either on agent's host or centrally on OpenAM server.
If you change this to a local configuration, you can no longer manage the policy agent configuration through OpenAM console.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.repository.location- Configuration Reload Interval
Interval in seconds to fetch agent configuration from OpenAM. Used if notifications are disabled. Default: 0
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.load.interval- Agent Configuration Change Notification
Enable agent to receive notification messages from OpenAM server for configuration changes.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.change.notification.enable- Agent Root URL for CDSSO
The agent root URL for CDSSO. The valid value is in the format
protocol://hostname:port/where protocol represents the protocol used, such ashttporhttps, hostname represents the host name of the system where the agent resides, and port represents the port number on which the agent is installed. The slash following the port number is required.If your agent system also has virtual host names, add URLs with the virtual host names to this list as well. OpenAM checks that
gotoURLs match one of the agent root URLs for CDSSO.
- Agent Filter Mode
Specifies how the agent filters requests to protected web applications. The global value functions as a default, and applies for protected applications that do not have their own filter settings. Valid settings include the following.
ALLEnforce both the Java EE policy defined for the web container where the protected application runs, and also OpenAM policies.
When setting the filter mode to
ALL, set the Map Key, but do not set any Corresponding Map Value.J2EE_POLICYEnforce only the J2EE policy defined for the web container where the protected application runs.
NONEDo not enforce policies to protect resources. In other words, turn off access management. Not for use in production.
SSO_ONLYEnforce only authentication, not policies.
URL_POLICYEnforce only URL resource-based policies defined in OpenAM.
When setting the filter mode to
URL_POLICY, set the Map Key to the application name and the Corresponding Map Value toURL_POLICY.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.filter.modeHot swap: no
- HTTP Session Binding
When enabled, the agent invalidates the HTTP session upon login failure, when the user has no SSO session, or when the principal user name does not match the SSO user name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.httpsession.binding- Login Attempt Limit
When set to a value other than zero, this defines the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed during a single browser session, after which the agent blocks requests from the user.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.attempt.limit- Custom Response Header
Specifies the custom headers the agent sets for the client. The key is the header name. The value is the header value.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.headerFor example,
com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.header[Cache-Control]=no-cache.- Redirect Attempt Limit
When set to a value other than zero, this defines the maximum number of redirects allowed for a single browser session, after which the agent blocks the request.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.redirect.attempt.limit- Agent Debug Level
Default is
Error. Increase toMessagefor fine-grained detail.Property:
com.iplanet.services.debug.level
- User Mapping Mode
Specifies the mechanism used to determine the user ID.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.user.mapping.mode- User Attribute Name
Specifies the data store attribute that contains the user ID.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.user.attribute.name- User Principal Flag
When enabled, OpenAM uses both the principal user name and also the user ID for authentication.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.user.principal- User Token Name
Specifies the session property name for the authenticated user's ID. Default:
UserToken.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.user.token
- Audit Access Types
Types of messages to log based on user URL access attempts.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.audit.accesstypeValid values for the configuration file property include
LOG_NONE,LOG_ALLOW,LOG_DENY, andLOG_BOTH.- Audit Log Location
Specifies where audit messages are logged. By default, audit messages are logged remotely.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.log.dispositionValid values for the configuration file property include
REMOTE,LOCAL, andALL.- Remote Log File Name
Name of file stored on OpenAM server that contains agent audit messages if log location is remote or all.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.remote.logfileHot swap: no
- Rotate Local Audit Log
When enabled, audit log files are rotated when reaching the specified size.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.local.log.rotate- Local Audit Log Rotation Size
When beyond this size limit in bytes, the agent rotates the local audit log file if rotation is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.local.log.sizeDefault: 50 MB
- FQDN Check
Enables checking of FQDN default value and FQDN map values.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.check.enable- FQDN Default
FQDN users should use to access resources.
This property ensures that when users access protected resources on the web server without specifying the FQDN, the agent can redirect the users to URLs containing the correct FQDN.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.default- FQDN Virtual Host Map
Enables virtual hosts, partial hostname and IP address to access protected resources. Maps invalid or virtual name keys to valid FQDN values so the agent can properly redirect users and the agents receive cookies belonging to the domain.
To map
myservertomyserver.mydomain.example, entermyserverin the Map Key field, and entermyserver.mydomain.examplein the Corresponding Map Value field. This corresponds tocom.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.mapping[myserver]= myserver.mydomain.example.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.mapping
This section covers application J2EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > Application.
- Login Form URI
Specifies the list of absolute URIs corresponding to a protected application's
web.xmlform-login-pageelement, such as/myApp/jsp/login.jsp.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.form- Login Error URI
Specifies the list of absolute URIs corresponding to a protected application's
web.xmlform-error-pageelement, such as/myApp/jsp/error.jsp.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.error.uri- Use Internal Login
When enabled, the agent uses the internal default content file for the login.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.use.internal- Login Content File Name
Full path name to the file containing custom login content when Use Internal Login is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.content.file
- Application Logout Handler
Specifies how logout handlers map to specific applications. The key is the web application name. The value is the logout handler class.
To set a global logout handler for applications without other logout handlers defined, leave the key empty and set the value to the global logout handler class name,
GlobalApplicationLogoutHandler.To set a logout handler for a specific application, set the key to the name of the application, and the value to the logout handler class name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.application.handler- Application Logout URI
Specifies request URIs that indicate logout events. The key is the web application name. The value is the application logout URI.
To set a global logout URI for applications without other logout URIs defined, leave the key empty and set the value to the global logout URI,
/logout.jsp.To set a logout URI for a specific application, set the key to the name of the application, and the value to the application logout page.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.uri- Logout Request Parameter
Specifies parameters in the HTTP request that indicate logout events. The key is the web application name. The value is the logout request parameter.
To set a global logout request parameter for applications without other logout request parameters defined, leave the key empty and set the value to the global logout request parameter,
logoutparam.To set a logout request parameter for a specific application, set the key to the name of the application, and the value to the application logout request parameter, such as
logoutparam.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.request.param- Logout Introspect Enabled
When enabled, the agent checks the HTTP request body to locate the Logout Request Parameter you set.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.introspect.enabled- Logout Entry URI
Specifies the URIs to return after successful logout and subsequent authentication. The key is the web application name. The value is the URI to return.
To set a global logout entry URI for applications without other logout entry URIs defined, leave the key empty and set the value to the global logout entry URI,
/welcome.html.To set a logout entry URI for a specific application, set the key to the name of the application, and the value to the application logout entry URI, such as
/myApp/welcome.html.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.entry.uri
- Resource Access Denied URI
Specifies the URIs of custom pages to return when access is denied. The key is the web application name. The value is the custom URI.
To set a global custom access denied URI for applications without other custom access denied URIs defined, leave the key empty and set the value to the global custom access denied URI,
/sample/accessdenied.html.To set a custom access denied URI for a specific application, set the key to the name of the application, and the value to the application access denied URI, such as
/myApp/accessdenied.html.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.access.denied.uri
- Not Enforced URIs
List of URIs for which no authentication is required, and the agent does not protect access. You can use wildcards to define a pattern for a URI.
The
*wildcard matches all characters except question mark (?), cannot be escaped, and spans multiple levels in a URI. Multiple forward slashes do not match a single forward slash, so*matchesmult/iple/dirs, yetmult/*/dirsdoes not matchmult/dirs.The
-*-wildcard matches all characters except forward slash (/) or question mark (?), and cannot be escaped. As it does not match/,-*-does not span multiple levels in a URI.OpenAM does not let you mix
*and-*-in the same URI.Examples include
/logout.html,/images/*,/css/-*-, and/*.jsp?locale=*.Trailing forward slashes are not recognized as part of a resource name. Therefore
/images//and/imagesare equivalent.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.uri- Invert Not Enforced URIs
Only enforce not enforced list of URIs. In other words, enforce policy only for those URIs and patterns specified in the list.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.uri.invert- Not Enforced URIs Cache Enabled
When enabled, the agent caches evaluation of the not enforced URI list.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.uri.cache.enable- Not Enforced URIs Cache Size
When caching is enabled, this limits the number of not enforced URIs cached.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.uri.cache.sizeDefault: 1000
- Refresh Session Idle Time
When enabled, the agent resets the stateful session idle time when granting access to a not enforced URI, prolonging the time before the user must authenticate again. This setting has no effect on users with stateless sessions.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.refresh.session.idletime
- Not Enforced Client IP List
No authentication and authorization are required for the requests coming from these client IP addresses.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.ipNote
Loopback addresses are not considered valid IPs on the Not Enforced IP list. If specified, the policy agent ignores the loopback address.
- Not Enforced IP Invert List
Only enforce the not enforced list of IP addresses. In other words, enforce policy only for those client addresses and patterns specified in the list.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.ip.invert- Not Enforced IP Cache Flag
When enabled, the agent caches evaluation of the not enforced IP list.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.ip.cache.enable- Not Enforced IP Cache Size
When caching is enabled, this limits the number of not enforced addresses cached.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.notenforced.ip.cache.sizeDefault: 1000
- Profile Attribute Fetch Mode
When set to
HTTP_COOKIEorHTTP_HEADER, profile attributes are introduced into the cookie or the headers, respectively. When set toREQUEST_ATTRIBUTE, profile attributes are part of the HTTP request.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.fetch.mode- Profile Attribute Mapping
Maps the profile attributes to HTTP headers for the currently authenticated user. Map Keys are attribute names, and Map Values are HTTP header names. The user profile can be stored in LDAP or any other arbitrary data store.
To populate the value of profile attribute CN under
CUSTOM-Common-Name: enter CN in the Map Key field, and enterCUSTOM-Common-Namein the Corresponding Map Value field. This corresponds tocom.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.mapping[cn]=CUSTOM-Common-Name.In most cases, in a destination application where an HTTP header name shows up as a request header, it is prefixed by
HTTP_, lower case letters become upper case, and hyphens (-) become underscores (_). For example,common-namebecomesHTTP_COMMON_NAME.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.profile.attribute.mapping
- Response Attribute Fetch Mode
When set to
HTTP_COOKIEorHTTP_HEADER, response attributes are introduced into the cookie or the headers, respectively. When set toREQUEST_ATTRIBUTE, response attributes are part of the HTTP request.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.attribute.fetch.mode- Response Attribute Mapping
Maps the policy response attributes to HTTP headers for the currently authenticated user. The response attribute is the attribute in the policy response to be fetched.
To populate the value of response attribute
uidunderCUSTOM-User-Name: enteruidin the Map Key field, and enterCUSTOM-User-Namein the Corresponding Map Value field. This corresponds tocom.sun.identity.agents.config.response.attribute.mapping[uid]=Custom-User-Name.In most cases, in a destination application where an HTTP header name shows up as a request header, it is prefixed by
HTTP_, lower case letters become upper case, and hyphens (-) become underscores (_). For example,response-attr-onebecomesHTTP_RESPONSE_ATTR_ONE.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.response.attribute.mapping
- Cookie Separator Character
Specifies the separator for multiple values of the same attribute when it is set as a cookie. Default:
|(also known as the vertical bar character).Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.attribute.cookie.separator- Fetch Attribute Date Format
Specifies the
java.text.SimpleDateFormatof date attribute values used when an attribute is set in an HTTP header. Default:EEE, d MMM yyyy hh:mm:ss z.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.attribute.date.format- Attribute Cookie Encode
When enabled, attribute values are URL-encoded before being set as a cookie.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.attribute.cookie.encode
- Session Attribute Fetch Mode
When set to
HTTP_COOKIEorHTTP_HEADER, session attributes are introduced into the cookie or the headers, respectively. When set toREQUEST_ATTRIBUTE, session attributes are part of the HTTP request.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.session.attribute.fetch.mode- Session Attribute Mapping
Maps session attributes to HTTP headers for the currently authenticated user. The session attribute is the attribute in the session to be fetched.
To populate the value of session attribute
UserTokenunderCUSTOM-userid: enterUserTokenin the Map Key field, and enterCUSTOM-useridin the Corresponding Map Value field. This corresponds tocom.sun.identity.agents.config.session.attribute.mapping[UserToken]=CUSTOM-userid.In most cases, in a destination application where an HTTP header name shows up as a request header, it is prefixed by
HTTP_, lower case letters become upper case, and hyphens (-) become underscores (_). For example,success-urlbecomesHTTP_SUCCESS_URL.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.session.attribute.mapping
Privileged attributes are used when the agent is running in
ALL or J2EE_POLICY filter mode.
Privileged attributes contain the list of declarative Java EE roles that the
user can have:
- Default Privileged Attribute
Specifies that every authenticated user with a valid OpenAM session will have the
AUTHENTICATED_USERSrole.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.default.privileged.attribute- Privileged Attribute Type
Specifies the group and role memberships that will be turned into roles for each user.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.privileged.attribute.type- Privileged Attributes To Lower Case
Specifies how privileged attribute types should be converted to lower case.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.privileged.attribute.tolowercase- Privileged Session Attribute
Specifies the list of session property names when an authenticated user's roles are store within a session property.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.privileged.session.attribute- Enable Privileged Attribute Mapping
When enabled, lets you use Privileged Attribute Mapping.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.privileged.attribute.mapping.enable- Privileged Attribute Mapping
OpenAM allows original attribute values to be mapped to other values. For example, you can map UUIDs to principal names in roles specified in a web application's deployment descriptor. To map the UUID
id=employee,ou=group,o=openamto the principal nameam_employee_rolein the deployment descriptor, set the key toid=employee,ou=group,o=openam, and the value toam_employee_role.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.privileged.attribute.mapping
- Custom Authentication Handler
Specifies custom authentication handler classes for users authenticated with the application server. The key is the web application name and the value is the authentication handler class name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.auth.handler- Custom Logout Handler
Specifies custom logout handler classes to log users out of the application server. The key is the web application name and the value is the logout handler class name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.handler- Custom Verification Handler
Specifies custom verification classes to validate user credentials with the local user repository. The key is the web application name and the value is the validation handler class name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.verification.handler
This section covers SSO J2EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > SSO.
- Cookie Name
Name of the SSO Token cookie used between the OpenAM server and the agent. Default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro.Property:
com.iplanet.am.cookie.nameHot swap: no
- SSO Cache Enable
When enabled, the agent exposes SSO Cache through the agent SDK APIs.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.amsso.cache.enable
- Cross-Domain SSO
Enables CDSSO.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.enable- CDSSO Redirect URI
Specifies a URI the agent uses to process CDSSO requests.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.redirect.uri- CDSSO Servlet URL
List of URLs of the available CDSSO controllers that the agent can use for CDSSO processing. For example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url- CDSSO Clock Skew
When set to a value other than zero, specifies the clock skew in seconds that the agent accepts when determining the validity of the CDSSO authentication response assertion.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.clock.skew- CDSSO Trusted ID Provider
Specifies the list of OpenAM servers or identity providers the agent trusts when evaluating CDC Liberty Responses.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.trusted.id.provider- CDSSO Secure Enable
When enabled, the agent marks the SSO Token cookie as secure, thus the cookie is only transmitted over secure connections.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.secure.enable- CDSSO Domain List
List of domains, such as
.example.com, in which cookies have to be set in CDSSO.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.domain
- Cookie Reset
When enabled, agent resets cookies in the response before redirecting to authentication.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset.enable- Cookie Reset Name List
List of cookies to reset if Cookie Reset is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset.name- Cookie Reset Domain Map
Specifies how names from the Cookie Reset Name List correspond to cookie domain values when the cookie is reset.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset.domain- Cookie Reset Path Map
Specifies how names from the Cookie Reset Name List correspond to cookie paths when the cookie is reset.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.reset.path
This section covers OpenAM services J2EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > OpenAM Services.
- OpenAM Login URL
OpenAM login page URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login, to which the agent redirects incoming users without sufficient credentials so that they can authenticate. If CDSSO is enabled, this property is not used, instead the CDCServlet URL will be used.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url- OpenAM Conditional Login URL (Not yet in OpenAM console)
To conditionally redirect users based on the incoming request URL, set this property.
This takes the incoming request domain to match, a vertical bar (
|), and then a comma-separated list of URLs to which to redirect incoming users.If the domain before the vertical bar matches an incoming request URL, then the policy agent uses the list of URLs to determine how to redirect the user-agent. If the global property FQDN Check (
com.sun.identity.agents.config.fqdn.check.enable) is enabled for the policy agent, then the policy agent iterates through the list until it finds an appropriate redirect URL that matches the FQDN check. Otherwise, the policy agent redirects the user-agent to the first URL in the list.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.login.urlExamples:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.login.url[0]= login.example.com|http://openam1.example.com/openam/UI/Login, http://openam2.example.com/openam/UI/Login,com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.login.url[1]= signin.example.com|http://openam3.example.com/openam/UI/Login, http://openam4.example.com/openam/UI/LoginIf CDSSO is enabled for the policy agent, then this property takes CDSSO Servlet URLs for its values (
com.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url), rather than OpenAM login URLs.CDSSO examples:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.login.url[0]= login.example.com|http://openam1.example.com/openam/cdcservlet, http://openam2.example.com/openam/cdcservlet,com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.login.url[1]= signin.example.com|http://openam3.example.com/openam/cdcservlet, http://openam4.example.com/openam/cdcservlet- Login URL Prioritized
When enabled, OpenAM uses the priority defined in the OpenAM Login URL list as the priority for Login and CDSSO URLs when handling failover.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url.prioritized- Login URL Probe
When enabled, OpenAM checks the availability of OpenAM Login URLs before redirecting to them.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url.probe.enabled- Login URL Probe Timeout
Timeout period in milliseconds for OpenAM to determine whether to failover between Login URLs when Login URL Probe is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.url.probe.timeoutDefault: 2000
- OpenAM Logout URL
OpenAM logout page URLs, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Logout. The user is logged out of the OpenAM session when accessing these URLs.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url- OpenAM Conditional Logout URL (Not yet in OpenAM console)
The values take the incoming request URL to match and a comma-separated list of URLs to which to redirect users logging out.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.logout.urlExample:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.conditional.logout.url[0]= logout.example.com|http://openam1.example.com/openam/UI/Logout, http://openam2.example.com/openam/UI/Logout- Logout URL Prioritized
When enabled, OpenAM uses the priority defined in the OpenAM Logout URL list as the priority for Logout URLs when handling failover.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url.prioritized- Logout URL Probe
When enabled, OpenAM checks the availability of OpenAM Logout URLs before redirecting to them.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url.probe.enabled- Logout URL Probe Timeout
Timeout period in milliseconds for OpenAM to determine whether to failover between Logout URLs when Logout URL Probe is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.url.probe.timeoutDefault: 2000
- OpenAM Authentication Service Protocol
Specifies the protocol used by the OpenAM authentication service.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.server.protocolHot swap: no
- OpenAM Authentication Service Host Name
Specifies the OpenAM authentication service host name.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.server.hostHot swap: no
- OpenAM Authentication Service Port
Specifies the OpenAM authentication service port number.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.server.portHot swap: no
- Realm
Realm where OpenAM starts policy evaluation for this policy agent.
Default: Top Level Realm (/)
Edit this property when OpenAM should start policy evaluation in a realm other than the Top Level Realm,
/, when handling policy decision requests from this policy agent.This property is recognized by OpenAM, not the policy agent.
Property:
org.forgerock.openam.agents.config.policy.evaluation.realmHot swap: yes
- Application
The name of the policy set where OpenAM looks for policies to evaluate for this policy agent.
Default:
iPlanetAMWebAgentServiceEdit this property when OpenAM should look for policies that belong to a policy set other than
iPlanetAMWebAgentServicewhen handling policy decision requests from this policy agent.This property is recognized by OpenAM, not the policy agent.
Property:
org.forgerock.openam.agents.config.policy.evaluation.applicationHot swap: yes
- Enable Policy Notifications
When enabled, OpenAM sends notification about changes to policy.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.notification.enabledHot swap: no
- Policy Client Polling Interval
Specifies the time in minutes after which the policy cache is refreshed.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.polling.intervalDefault: 3
Hot swap: no
- Policy Client Cache Mode
Set to cache mode subtree when only a small number of policy rules are defined. For large numbers of policy rules, set to self.
Property:
com.sun.identity.policy.client.cacheModeDefault: self
Hot swap: no
- Policy Client Boolean Action Values
Specifies the values, such as
allowanddeny, that are associated with boolean policy decisions. The string is presented below in multiple lines for readability purposes.Default:
iPlanetAMWebAgentService|GET|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|POST|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|PUT|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|DELETE|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|HEAD|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|OPTIONS|allow|deny: iPlanetAMWebAgentService|PATCH|allow|denyProperty:
com.sun.identity.policy.client.booleanActionValuesHot swap: no
- Policy Client Resource Comparators
Specifies the comparators used for service names in policy.
Default:
serviceType=iPlanetAMWebAgentService| class=com.sun.identity.policy.plugins.HttpURLResourceName|wildcard=*| delimiter=/|caseSensitive=falseProperty:
com.sun.identity.policy.client.resourceComparatorsHot swap: no
- Policy Client Clock Skew
Time in seconds used to adjust time difference between agent system and OpenAM. Clock skew in seconds = AgentTime - OpenAMServerTime.
Default: 10
Property:
com.sun.identity.policy.client.clockSkewHot swap: no
- URL Policy Env GET Parameters
Specifies the list of HTTP GET request parameters whose names and values the agents set in the environment map for URL policy evaluation by the OpenAM server.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.env.get.param- URL Policy Env POST Parameters
Specifies the list of HTTP POST request parameters whose names and values the agents set in the environment map for URL policy evaluation by the OpenAM server.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.env.post.param- URL Policy Env jsession Parameters
Specifies the list of HTTP session attributes whose names and values the agents set in the environment map for URL policy evaluation by the OpenAM server.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.env.jsession.param- Use HTTP-Redirect for composite advice
When enabled, the remote policy client is configured to use HTTP-Redirect instead of HTTP-POST for composite advice.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.policy.advice.use.redirect
- Enable Notification of User Data Caches
When enabled, receive notification from OpenAM to update user management data caches.
Property:
com.sun.identity.idm.remote.notification.enabledHot swap: no
- User Data Cache Polling Time
If notifications are not enabled and set to a value other than zero, specifies the time in minutes after which the agent polls to update cached user management data.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.sdk.remote.pollingTimeDefault: 1
Hot swap: no
- Enable Notification of Service Data Caches
When enabled, receive notification from OpenAM to update service configuration data caches.
Property:
com.sun.identity.sm.notification.enabledHot swap: no
- Service Data Cache Time
If notifications are not enabled and set to a value other than zero, specifies the time in minutes after which the agent polls to update cached service configuration data.
Property:
com.sun.identity.sm.cacheTimeDefault: 1
Hot swap: no
- Enable Client Polling
When enabled, the session client polls to update the session cache rather than relying on notifications from OpenAM.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.session.client.polling.enableHot swap: no
- Client Polling Period
Specifies the time in seconds after which the session client requests an update from OpenAM for cached session information.
Property:
com.iplanet.am.session.client.polling.periodDefault: 180
Hot swap: no
This section covers miscellaneous J2EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > Miscellaneous.
- Locale Language
The default language for the agent.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.locale.languageHot swap: no
- Locale Country
The default country for the agent.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.locale.countryHot swap: no
- Port Check Enable
When enabled, activate port checking, correcting requests on the wrong port.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.port.check.enable- Port Check File
Specifies the name of the file containing the content to handle requests on the wrong port when port checking is enabled.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.port.check.file- Port Check Setting
Specifies which ports correspond to which protocols. The agent uses the map when handling requests with invalid port numbers during port checking.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.port.check.setting
- Bypass Principal List
Specifies a list of principals the agent bypasses for authentication and search purposes, such as
guestortestuser.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.bypass.principal
- Encryption Provider
Specifies the agent's encryption provider class.
Default:
com.iplanet.services.util.JCEEncryptionProperty:
com.iplanet.security.encryptorHot swap: no
- Ignore Path Info in Request URL
When enabled, strip the path information from the request URL while doing the Not Enforced List check, and URL policy evaluation. This is designed to prevent a user from accessing a URI by appending the matching pattern in the policy or not enforced list.
For example, if the not enforced list includes
/*.gif, then stripping path info from the request URL prevents access tohttp://host/index.htmlby usinghttp://host/index.html?hack.gif.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.ignore.path.info
- Goto Parameter Name
Property used only when CDSSO is enabled. Only change the default value,
gotowhen the login URL has a landing page specified, such ascom.sun.identity.agents.config.cdsso.cdcservlet.url = http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet?goto= http://www.example.com/landing.jsp. The agent uses this parameter to append the original request URL to this cdcservlet URL. The landing page consumes this parameter to redirect to the original URL.As an example, if you set this value to
goto2, then the complete URL sent for authentication ishttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet?goto= http://www.example.com/landing.jsp?goto2=http://www.example.com/original.jsp.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.redirect.param- Legacy User Agent Support Enable
When enabled, provide support for legacy browsers.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.legacy.support.enable- Legacy User Agent List
List of header values that identify legacy browsers. Entries can use the wildcard character,
*.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.legacy.user.agent- Legacy User Agent Redirect URI
Specifies a URI the agent uses to redirect legacy user agent requests.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.legacy.redirect.uri
This section covers advanced J2EE agent properties. After creating the agent profile, you access these properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > Advanced.
If the agent is behind a proxy or load balancer, then the agent can get client IP and host name values from the proxy or load balancer. For proxies and load balancers that support providing the client IP and host name in HTTP headers, you can use the following properties.
When multiple proxies or load balancers sit in the request path,
the header values can include a comma-separated list of values with the
first value representing the client, as in
client,next-proxy,first-proxy.
- Client IP Address Header
HTTP header name that holds the IP address of the client.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.client.ip.header- Client Hostname Header
HTTP header name that holds the hostname of the client.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.client.hostname.header
- Web Service Enable
Enable web service processing.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.enable- Web Service End Points
Specifies a list of web application end points that represent web services.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.endpoint- Web Service Process GET Enable
When enabled, the agent processes HTTP GET requests for web service endpoints.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.process.get.enable- Web Service Authenticator
Specifies a class implementing
com.sun.identity.agents.filter.IWebServiceAuthenticator, used to authenticate web service requests.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.authenticator- Web Service Response Processor
Specifies a class implementing
com.sun.identity.agents.filter.IWebServiceResponseProcessor, used to process web service responses.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.responseprocessor- Web Service Internal Error Content File
Specifies a file the agent uses to generate an internal error fault for the client application.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.internalerror.content- Web Service Authorization Error Content File
Specifies a file the agent uses to generate an authorization error fault for the client application.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.webservice.autherror.content
- Alternative Agent Host Name
Specifies the host name of the agent protected server to show to client browsers, rather than the actual host name.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.agent.host- Alternative Agent Port Name
Specifies the port number of the agent protected server to show to client browsers, rather than the actual port number.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.agent.port- Alternative Agent Protocol
Specifies the protocol used to contact the agent from the browser client browsers, rather than the actual protocol used by the server. Either
httporhttps.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.agent.protocol
- WebAuthentication Available
When enabled, allow programmatic authentication with the JBoss container using the WebAuthentication feature. This feature works only with certain versions of JBoss when the
J2EE_POLICYorALLfilter mode is in use.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.jboss.webauth.availableNote
This setting is not necessary for the JBoss v7 agent.
- Possible XSS code elements
Specifies strings that, when found in the request, cause the agent to redirect the client to an error page.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.xss.code.elements- XSS detection redirect URI
Maps applications to URIs of customized pages to which to redirect clients upon detection of XSS code elements.
For example, to redirect clients of MyApp to
/myapp/error.html, enter MyApp as the Map Key and/myapp/error.htmlas the Corresponding Map Value.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.xss.redirect.uri
- POST Data Preservation enabled
Enables HTTP POST data preservation, storing POST data before redirecting the browser to the login screen, and then autosubmitting the same POST after successful authentication to the original URL.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.enable- Missing PDP entry URI
Specifies a list of application-specific URIs if the referenced Post Data Preservation entry cannot be found in the local cache because it has exceeded its POST entry TTL. Either the agent redirects to a URI in this list, or it shows an HTTP 403 Forbidden error.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.cache.noentry.url- PDP entry TTL
POST data storage lifetime in milliseconds. Default: 300000.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.cache.entry.ttl- PDP Stickysession mode
Specifies whether to create a cookie, or to append a query string to the URL to assist with sticky load balancing.
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.stickysession.mode- PDP Stickysession key-value
Specifies the key-value pair for stickysession mode. For example, a setting of
lb=myservereither sets anlbcookie withmyservervalue, or addslb=myserverto the URL query string.Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.postdata.preserve.stickysession.value
- TCP Connection Timeout
Sets the TCP connection timeout for outbound HTTP connections created by the Java EE policy agent. Set the property in the
OpenSSOAgentBootstrap.propertiesfile.Property:
org.forgerock.openam.url.connectTimeout
- Custom Properties
Additional properties to augment the set of properties supported by agent. Such properties take the following forms.
customproperty=custom-value1customlist[0]=customlist-value-0customlist[1]=customlist-value-1custommap[key1]=custommap-value-1custommap[key2]=custommap-value-2
Property:
com.sun.identity.agents.config.freeformproperties
This section covers version 2.2 policy agent properties. Version 2.2 agents store their configurations locally with a username-password combination used to connect to OpenAM.
Warning
ForgeRock no longer supports 2.2 policy agents. Documentation exists only for legacy systems. Do not use 2.2 policy agents for new deployments.
After creating the agent profile, you access agent properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > 2.2 Agents > Agent Name. Properties include:
- Password
Specifies the password the agent uses to connect to OpenAM.
- Status
Specifies whether the agent profile is active, and so can be used.
- Description
Specifies a short description for the agent.
- Agent Key Value(s)
Additional key-value pairs that OpenAM uses to receive agent requests concerning credential assertions.
OpenAM currently supports one property,
agentRootURL=protocol://host:port/where the key is case-sensitive.
To register an OAuth 2.0 client with OpenAM as the OAuth 2.0 authorization server, or register an OpenID Connect 1.0 client through OpenAM console, then create an OAuth 2.0 Client agent profile. After creating the agent profile, you can further configure the properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > Client Name.
The following configuration fields are for OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0:
- Group
Set this field if you have configured an OAuth 2.0 Client agent group.
- Status
Specify whether the client profile is active for use or inactive.
- Client password
Specify the client password as described by RFC 6749 in the section, Client Password.
- Client type
Specify the client type.
Confidential clients can maintain the confidentiality of their credentials, such as a web application running on a server where its credentials are protected. Public clients run the risk of exposing their passwords to a host or user agent, such as a JavaScript client running in a browser.
- Redirection URIs
Specify client redirection endpoint URIs as described by RFC 6749 in the section, Redirection Endpoint. OpenAM's OAuth 2.0 authorization service redirects the resource owner's user-agent back to this endpoint during the authorization code grant process. If your client has more than one redirection URI, then it must specify the redirection URI to use in the authorization request. The redirection URI must NOT contain a fragment (#).
Redirection URIs are required for OpenID Connect 1.0 clients.
- Scopes
Specify scopes that are to be presented to the resource owner when the resource owner is asked to authorize client access to protected resources.
Scopes can be entered as simple strings, such as
read,email,profile, oropenid, or as a pipe-separated string in the format:scope|locale|localized description. For example,read|en|Permission to view email messages.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleand pipe is omitted, the localized description is displayed to all users having undefined locales. If the localized description is omitted, nothing is displayed to all users. For example, a scope ofread|would allow the client to use thereadscope but would not display it to the user when requested.- Claim(s)
Specify one or more claim name translations that will override those specified for the authentication session. Claims are values that are presented to the user to inform them what data is being made available to the client.
Claims can be in entered as simple strings, such as
name,email,profile, orsub, or as a pipe-separated string in the format:scope|locale|localized description. For example,name|en|Full name of user.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleand pipe is omitted, the localized description is displayed to all users having undefined locales. If the localized description is omitted, nothing is displayed to all users. For example, a claim ofname|would allow the client to use thenameclaim but would not display it to the user when requested.If a value is not given, the value is computed from the OAuth2 provider.
- Display name
Specify a client name to display to the resource owner when the resource owner is asked to authorize client access to protected resources. Valid formats include
nameorlocale|localized name.The Display name can be entered as a single string or as a pipe-separated string for locale and localized name, for example,
en|My Example Company.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleis omitted, the name is displayed to all users having undefined locales.- Display description
Specify a client description to display to the resource owner when the resource owner is asked to authorize client access to protected resources. Valid formats include
descriptionorlocale|localized description.The Display description can be entered as a single string or as a pipe-separated string for locale and localized name, for example,
en|The company intranet is requesting the following access permission.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleis omitted, the name is displayed to all users having undefined locales.- Default Scope(s)
Specify scopes in
scopeorscope|locale|localized descriptionformat. These scopes are set automatically when tokens are issued.Default scopes can be in entered as simple strings, such as
read,email,profile, oropenid, or as a pipe-separated string in the format:scope|locale|localized description. For example,read|en|Permission to view email messages.Locale strings have the format: language_country_variant. For example,
en,en_GB, oren_US_WIN. If thelocaleand pipe is omitted, the localized description is displayed to all users having undefined locales. If the localized description is omitted, nothing is displayed to all users. For example, a scope ofread|would allow the client to use thereadscope but would not display it to the user when requested.- Response Types
Specify the response type that the client uses. The response type value specifies the flow that determine how the ID token and access token are returned to the client. For more information, see OAuth 2.0 Multiple Response Type Encoding Practices.
By default, the following response types are available:
code. Specifies that the client application requests an authorization code grant.token. Specifies that the client application requests an implicit grant type and requests a token from the API.id_token. Specifies that the client application requests an ID token.code token. Specifies that the client application requests an access token, access token type, and an authorization code.token id_token. Specifies that the client application requests an access token, access token type, and an ID token.code id_token. Specifies that the client application requests an authorization code and an ID token.code token id_token. Specifies that the client application requests an authorization code, access token, access token type, and an ID token.
- Contacts
Specify the email addresses of users who administer the client.
- Token Endpoint Authentication Method
Specify the authentication method the token endpoint should use as specified in section 9 of the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 incorporating errata set 1.
client_secret_basic. Clients authenticate with OpenAM (as an authorization server) using the HTTP Basic authentication scheme after receiving aclient_secretvalue.client_secret_post. Clients authenticate with OpenAM (as an authorization server) by including the client credentials in the request body after receiving aclient_secretvalue.private_key_jwt. Clients sign a JSON web token (JWT) with a registered public key.
- Json Web Key URI
Specify the URI that contains the client's public keys in JSON web key format.
- Json Web Key
Raw JSON web key value containing the client's public keys.
- Sector Identifier URI
Specify the host component of this URI, which is used in the computation of pairwise subject identifiers.
- Subject Type
Specify the subject identifier type, which is a locally unique identifier that will be consumed by the client. Select one of two options:
public. Provides the same
sub(subject) value to all clients.pairwise. Provides a different
sub(subject) value to each client.
- ID Token Signing Algorithm
Specify the signing algorithm that the ID token must be signed with.
- Enable ID Token Encryption
Enable ID token encryption using the specified ID token encryption algorithm.
- ID Token Encryption Algorithm
Specify the algorithm that the ID token must be encrypted with.
Default value:
RSA1_5(RSAES-PKCS1-V1_5).- ID Token Encryption Method
Specify the method that the ID token must be encrypted with.
Default value:
A128CBC-HS256.- Client ID Token Public Encryption Key
Specify the Base64-encoded public key for encrypting ID tokens.
- Post Logout Redirect URIs
Specify the URI to which to redirect the user-agent after the client logout process.
- Access Token
Specify the
registration_access_tokenvalue that you provide when registering the client, and then subsequently when reading or updating the client profile.- Client Session URI
Specify the relying party (client) URI to which the OpenID Connect Provider sends session changed notification messages using the HTML 5
postMessageAPI.- Client Name
Specify a human-readable name for the client.
- Client JWT Bearer Public Key Certificate
Specify the public key certificate of the client's key pair that is used to sign JWTs issued by the client and used for client authentication or to request access tokens.
This is the base64-encoded X509 certificate containing the public key in PEM format, as in the following example.
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDETCCAfmgAwIBAgIEQKeM1DANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADA5MRswGQYDVQQKExJv cGVuYW0uZXhhbXBsZS5jb20xGjAYBgNVBAMTEWp3dC1iZWFyZXItY2xpZW50MB4X DTE2MDgyMjIzMjIzMFoXDTI2MDgyMDIzMjIzMFowOTEbMBkGA1UEChMSb3BlbmFt LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tMRowGAYDVQQDExFqd3QtYmVhcmVyLWNsaWVudDCCASIwDQYJ KoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAOGbrYP1phjab8GpHKJ93EvPi209RyTs g/iaSetgaOeVIepEqKjIpj91v69a2VlrJCeaUDCcCF/JiCBGuyfA8AngtP85bZcY MLNdRVmkA3G/wVdE9buzMFWUcl5teVS8Xcgut9mXCjd7GEcCkfLbMU8B1s5nm2dE +a8Y1+QXJ1hA4MpI+SdlyRTYkfrn8L3dyJOuFtsedAnv9AbNx2y3Qi315OUykoRo ewS7gokWeZsjf0sJuJrtN7drjx8Tx7w0QCxKB0XFRqJpMoRWAWQwgrTpoBEHGbWp eeMko50fLcflI8ZUpmN8afJDW72c7ppk80pe/7K//tY/tg22Or/f1IUCAwEAAaMh MB8wHQYDVR0OBBYEFMUXBJzh5UFlDJc/lbd8mnbdzu56MA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA A4IBAQCpiDgSaNaEYuEKeI2edkiaVDx2wX+XE7pP0AfImNPfQkKpPNmlMQY9fY+l Uy/eS5bTt7983NzqvySpaxJHqaWpW8udZ3kBbfFBiON44uk7st+Kf3PDSQp4oCdi qB8KTqTFaX1B368jIMCpbYkRZSPQEXoZfHRv1omRD3YT2dmhOoIIj/JM7XTtS03I dZeyQgiUOKIkn2DJN6qB7wcH1pql7tFtRBnnOYinAJuC3FcSGSTzWeCKQn29yb39 4ab5bHMDpS+F34qqjHBKmIj9TrL9EC5AOh8746i9orat1OEwtLsFh2r1Ia8Nz6a8 U/tcxzZSu9pNnCEC7Pi0oZ++6Fo/ -----END CERTIFICATE-----You can generate a key pair and export the certificate by using the Java keytool command.
$ keytool \ -genkeypair \ -keysize 2048 \ -alias self-signed \ -keyalg rsa \ -dname "CN=jwt-bearer-client,O=openam.example.com" \ -keystore keystore.jceks \ -storetype JCEKS \ -keypass changeit \ -storepass changeit \ -validity 3650 \ -v Generating 2,048 bit RSA key pair and self-signed certificate (SHA256withRSA) with a validity of 3,650 days for: CN=jwt-bearer-client, O=openam.example.com [Storing keystore.jceks] $ keytool \ -list \ -alias self-signed \ -rfc \ -keystore keystore.jceks \ -storepass JCEKS \ -keypass changeit \ -storepass changeit Alias name: self-signed Creation date: Oct 27, 2014 Entry type: PrivateKeyEntry Certificate chain length: 1 Certificate[1]: -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDETCCAfmgAwIBAgIEQKeM1DANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADA5MRswGQYDVQQKExJv cGVuYW0uZXhhbXBsZS5jb20xGjAYBgNVBAMTEWp3dC1iZWFyZXItY2xpZW50MB4X DTE2MDgyMjIzMjIzMFoXDTI2MDgyMDIzMjIzMFowOTEbMBkGA1UEChMSb3BlbmFt LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tMRowGAYDVQQDExFqd3QtYmVhcmVyLWNsaWVudDCCASIwDQYJ KoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAOGbrYP1phjab8GpHKJ93EvPi209RyTs g/iaSetgaOeVIepEqKjIpj91v69a2VlrJCeaUDCcCF/JiCBGuyfA8AngtP85bZcY MLNdRVmkA3G/wVdE9buzMFWUcl5teVS8Xcgut9mXCjd7GEcCkfLbMU8B1s5nm2dE +a8Y1+QXJ1hA4MpI+SdlyRTYkfrn8L3dyJOuFtsedAnv9AbNx2y3Qi315OUykoRo ewS7gokWeZsjf0sJuJrtN7drjx8Tx7w0QCxKB0XFRqJpMoRWAWQwgrTpoBEHGbWp eeMko50fLcflI8ZUpmN8afJDW72c7ppk80pe/7K//tY/tg22Or/f1IUCAwEAAaMh MB8wHQYDVR0OBBYEFMUXBJzh5UFlDJc/lbd8mnbdzu56MA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA A4IBAQCpiDgSaNaEYuEKeI2edkiaVDx2wX+XE7pP0AfImNPfQkKpPNmlMQY9fY+l Uy/eS5bTt7983NzqvySpaxJHqaWpW8udZ3kBbfFBiON44uk7st+Kf3PDSQp4oCdi qB8KTqTFaX1B368jIMCpbYkRZSPQEXoZfHRv1omRD3YT2dmhOoIIj/JM7XTtS03I dZeyQgiUOKIkn2DJN6qB7wcH1pql7tFtRBnnOYinAJuC3FcSGSTzWeCKQn29yb39 4ab5bHMDpS+F34qqjHBKmIj9TrL9EC5AOh8746i9orat1OEwtLsFh2r1Ia8Nz6a8 U/tcxzZSu9pNnCEC7Pi0oZ++6Fo/ -----END CERTIFICATE------ Default Max Age
Specify the maximum time in seconds that a user can be authenticated. If the user last authenticated earlier than this value, then the user must be authenticated again. If specified, the request parameter
max_ageoverrides this setting.Minimum value: 1.
Default: 600
- Default Max Age Enabled
Enable the default max age feature.
- Public key selector
Select the public key for this client, which comes from either the
JWKs_URI, manual JWKs, or X.509 field.- Authorization Code Lifetime (seconds)
Specify the time in seconds for an authorization code to be valid. If this field is set to zero, the authorization code lifetime of the OAuth2 provider is used.
Default: 6000
- Refresh Token Lifetime (seconds)
Specify the time in seconds for a refresh token to be valid. If this field is set to zero, the refresh token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider is used. If the field is set to
-1, the token will never expire.Default: 6000
- Access Token Lifetime (seconds)
Specify the time in seconds for an access token to be valid. If this field is set to zero, the access token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider is used.
Default: 6000
- OpenID Connect JWT Token Lifetime (seconds)
Specify the time in seconds for a JWT to be valid. If this field is set to zero, the JWT token lifetime of the OAuth2 provider is used.
Default: 6000
- Implied Consent
Enable the implied consent feature. When enabled, the resource owner will not be asked for consent during authorization flows. The OAuth2 Provider must also be configured to allow clients to skip consent.
- JWKs URI content cache timeout in ms
Specify the maximum amount of time, in milliseconds, that the content of the JWKS URI can be cached before being refreshed. This avoids fetching the JWKS URI content for every token encryption.
Default:
3600000- JWKs URI content cache miss cache time
Specify the minimum amount of time, in milliseconds, that the content of the JWKS URI is cached. This avoids fetching the JWKS URI content for every token signature verification, for example if the key ID (
kid) is not in the JWKS content already cached.Default:
60000- User info signed response algorithm
Specify the JSON Web Signature (JWS) algorithm for signing UserInfo Responses. If specified, the response will be JSON Web Token (JWT) serialized, and signed using JWS.
The default, if omitted, is for the UserInfo Response to return the claims as a UTF-8-encoded JSON object using the
application/jsoncontent type.- User info encrypted response algorithm
Specify the JSON Web Encryption (JWE) algorithm for encrypting UserInfo Responses.
If both signing and encryption are requested, the response will be signed then encrypted, with the result being a nested JWT.
The default, if omitted, is that no encryption is performed.
- User info encrypted response encryption algorithm
Specify the JWE encryption method for encrypting UserInfo Responses. If specified, you must also specify an encryption algorithm in the User info encrypted response algorithm property.
OpenAM supports the following encryption methods:
A128GCM,A192GCM, andA256GCM- AES in Galois Counter Mode (GCM) authenticated encryption mode.A128CBC-HS256,A192CBC-HS384, andA256CBC-HS512- AES encryption in CBC mode, with HMAC-SHA-2 for integrity.
Default:
A128CBC-HS256- User info response format
Specify the output format from the UserInfo endpoint.
The supported output formats are as follows:
User info JSON response format.
User info encrypted JWT response format.
User info signed JWT response format.
User info signed then encrypted response format.
For more information on the output format of the UserInfo Response, see Successful UserInfo Response in the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 incorporating errata set 1 specification.
Default: User info JSON response format.
- Token Endpoint Authentication Signing Algorithm
Specify the JWS algorithm that must be used for signing JWTs used to authenticate the client at the Token Endpoint.
JWTs that are not signed with the selected algorithm in token requests from the client using the
private_key_jwtorclient_secret_jwtauthentication methods will be rejected.Default:
RS256
An agent authenticator has read-only access to multiple agent profiles defined in the same realm, typically allowing an agent to read web service agent profiles.
After creating the agent profile, you access agent properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Agent Authenticator > Agent Name.
- Password
Specifies the password the agent uses to connect to OpenAM.
- Status
Specifies whether the agent profile is active, and so can be used.
- Agent Profiles allowed to Read
Specifies which agent profiles in the realm the agent authenticator can read.
- Agent Root URL for CDSSO
Specifies the list of agent root URLs for CDSSO. The valid value is in the format
protocol://hostname:port/where protocol represents the protocol used, such ashttporhttps, hostname represents the host name of the system where the agent resides, and port represents the port number on which the agent is installed. The slash following the port number is required.If your agent system also has virtual host names, add URLs with the virtual host names to this list as well. OpenAM checks that
gotoURLs match one of the agent root URLs for CDSSO.
A SOAP STS deployment accesses OpenAM using a SOAP STS agent.
After creating the agent profile, you access agent properties in the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > SOAP STS Agent > Agent Name.
- Group
Assigns the agent to a previously configured SOAP STS agent group in order to inherit selected properties from the group.
- Password
Specifies the password the SOAP STS deployment uses when accessing OpenAM.
- Poll Interval
Specifies how often the SOAP STS deployment should poll OpenAM for configuration changes to SOAP STS instances in the deployment.
[4] The configuration file syntax is that of a standard Java properties file. See java.util.Properties.load() for a description of the format. The value of a property specified multiple times is not defined.
OpenAM supports a comprehensive Audit Logging Service that captures key auditing events, critical for system security, troubleshooting, and regulatory compliance.
Audit logs gather operational information about events occurring within an OpenAM deployment to track processes and security data, such as authentication mechanisms, system access, user and administrator activity, error messages, and configuration changes.
This chapter describes the new, common REST-based Audit Logging Service available in OpenAM 13.5.2-15. OpenAM 13.5.2-15 also supports a legacy Logging Service, based on a Java SDK and available in OpenAM versions prior to OpenAM 13.5.2-15. The legacy Logging Service will be deprecated in a future release of OpenAM.
The Audit Logging Service uses a structured message format that adheres to a consistent and documented log structure common across the ForgeRock stack, including OpenAM, OpenIDM, OpenDJ, and OpenIG.
Important
By default, OpenDJ 3.0 does not have audit logging enabled; thus, administrators must manually enable audit logging in the directory server. For more information, see To Enable LDAP CSV Access Logs in the OpenDJ Administration Guide.
OpenAM writes log messages generated from audit events triggered by its instances, policy agents, the ssoadm tool, and connected ForgeRock stack implementations.
OpenAM's Audit Logging Service provides a versatile and rich feature set as follows:
Global and Realm-Based Log Configuration. You can configure audit logging globally, which ensures that all realms inherit your global log settings. You can also configure audit logging by realm, which allows you to set different log settings for each realm.
Audit Event Handlers. The Audit Logging Service supports a variety of audit event handlers that allow you to write logs to different types of data stores. See "Configuring Audit Event Handlers" for a list of event handlers available in OpenAM 13.5.2-15.
Audit Event Buffering. By default, OpenAM writes each log message separately as they are generated. OpenAM supports message buffering, a type of batch processing, that stores log messages in memory and flushes the buffer after a preconfigured time interval or after a certain number of log messages reaches the configured threshold value.
Tamper-Evident Logging. You can digitally sign your audit logs to ensure no unauthorized tampering of your logs has taken place. To configure this feature, you must deploy a preconfigured logger certificate and store it at
/path/to/openam/openam/Logger.jks.Log Rotation and Retention Policies. OpenAM rotates JSON and CSV audit logs when it reaches a specified maximum size. You can also configure a time-based rotation policy, which disables the max-size rotation policy and implements log rotation based on a preconfigured time sequence. You also have the option to disable log rotation and use an external log rotation tool. preconfigured time sequence. OpenAM also provides the option to disable log rotation completely for these file types. OpenAM does not support external log rotation for JSON and CSV audit logs.
For Syslog, JDBC, ElasticSearch, JMS, and Splunk handlers, OpenAM does not control log rotation and retention as they are handled by each respective service.
Blacklisting Sensitive Fields. The Audit Logging Service supports blacklisting, a type of filtering to hide sensitive values or fields, such as HTTP headers, query parameters, cookies, or the entire field value.
Reverse DNS Lookup. The Audit Logging Service supports a reverse DNS lookup feature for network troubleshooting purposes. Reverse DNS lookup is disabled by default as it enacts a performance hit in operation throughput.
OpenAM integrates log messages based on four different audit topics. A topic is a category of audit log event that has an associated one-to-one mapping to a schema type. Topics can be broadly categorized as access details, system activity, authentication operations, and configuration changes. The following table shows the basic event topics and associated audit log files, whose filenames are fixed:
| Event Topic | File Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access | access.csv |
Captures who, what, when, and output for every access request. |
| Activity | activity.csv |
Captures state changes to objects that have been created, updated, or deleted by end users (that is, non-administrators). For this release, only session changes are captured in the logs. Future releases may also record changes to user trusted devices, UMA policies, OAuth 2.0 tokens and others. |
| Authentication |
authentication.csv
|
Captures when and how a subject is authenticated and related events. |
| Configuration | config.csv |
Captures configuration changes to the product with a timestamp and
by whom. Note that the |
By default, OpenAM logs to a comma-separated value (CSV) audit event handler
and stores CSV log files under
/path/to/openam/openam/log.
To modify the global audit logging configuration, navigate to Configure > Global Services > Audit Logging and change the default configuration as needed.
To override the global audit logging configuration for a realm, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services, add the Audit Logging service to the realm, and configure the service as needed.
OpenAM supports the following types of audit event handlers:
| Audit Event Handler Type | Publishes to | How to Configure |
|---|---|---|
| CSV | CSV files | "Configuring CSV Audit Event Handlers" |
| Syslog | The syslog daemon | "Configuring Syslog Audit Event Handlers" |
| JDBC | A relational database | "Implementing JDBC Audit Event Handlers" |
| Elasticsearch | An Elasticsearch store | "Implementing Elasticsearch Audit Event Handlers" |
| JMS | JMS topics | "Configuring JMS Audit Event Handlers" |
This section provides procedures for configuring each type of audit handler.
OpenAM's default audit event handler is the comma-separated values (CSV) handler, which is already configured for the global Audit Logging Service. The global configuration is used to control audit logging in realms that do not have the Audit Logging Service added to them.
The following procedure describes how to configure a CSV audit event handler:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
In the Event Handler Instances table, click Global CSV Handler.
Under General Handler Configuration, verify that the Enabled box is checked.
Select the topics for your audit logs. For a description of each topic, see "Audit Log Topics".
In the Log Directory field, override the default location of your logs if necessary. The default location is:
%BASE_DIR%/%SERVER_URI%/log/.Warning
It is very important that a different log directory be configured for each instance of the CSV audit event handler. If two instances are writing to the same file, it can interfere with log rotation and tamper-evident logs.
For File Rotation, configure how files are rotated once they reach a specified file size or time interval. Enter the following parameters:
For Rotation Enabled, keep the Enabled box check-marked. If disabled, OpenAM ignores log rotation and appends to the same file.
For Maximum File Size, enter the maximum size of an audit file before rotation.
Default: 100000000 bytes.
OPTIONAL. For File Rotation Prefix, enter an arbitrary string that will be prefixed to every audit log to identify it. This parameter is used when time-based or size-based rotation is enabled.
For File Rotation Suffix, enter a timestamp suffix based on the Java SimpleDateFormat that will be added to every audit log. This parameter is used when time-based or size-based log rotation is enabled.
Default:
-MM.dd.yy-kk.mm.For Rotation Interval, enter a time interval to trigger audit log file rotation in seconds. A negative or zero value disables this feature.
Default: -1
Note
Any combination of the three rotation policies (maximum file size, periodic duration, and duration since midnight) can be implemented including none at all.
For Rotation Times, enter a time duration after midnight to trigger file rotation, in seconds. For example, you can provide a value of
3600to trigger rotation at 1:00 AM.Note
Negative durations are not supported.
For File Retention, determine how long log files should be retained in your system. Configure the following file retention parameters:
For Maximum Number of Historical Files, enter a number for allowed backup audit files.
Default:
-1, which indicates an unlimited number of files and disables the pruning of old history files.For Maximum Disk Space, enter the maximum amount of disk space that the total number of audit files can store. A negative or zero value indicates that this policy is disabled.
Default:
-1, which indicates an unlimited amount of disk space.For Minimum Free Space Required, enter the minimum amount of disk space required to store audit files. A negative or zero value indicates that this policy is disabled.
Default:
-1, which indicates no minimum amount of disk space is required.
For Buffering, configure if log events should be buffered in memory before they are written to the CSV file:
For Buffering Enabled, click the Enabled box to start audit event buffering.
The default buffer size is 5000 bytes.
When buffering is enabled, all audit events are put into an in-memory buffer (one per handled topic), so that the original thread that generated the event can fulfill the requested operation, rather than wait for I/O to complete. A dedicated thread (one per handled topic) constantly pulls events from the buffer in batches and writes them to the CSV file. If the buffer becomes empty, the dedicated thread goes to sleep until a new item gets added.
For Flush Each Event Immediately, click Enabled to write all buffered events before flushing.
When the dedicated thread accesses the buffer, it copies the contents to an array to reduce contention, and then iterates through the array to write to the CSV file. The bytes written to the file can be buffered again in Java classes and the underlying operating system.
When Flush Each Event Immediately is enabled, OpenAM flushes the bytes after each event is written. If the feature is disabled (default), the Java classes and underlying operation system determine when to flush the bytes.
For Tamper Evident Configuration, set up the feature to detect any tampering of the audit logs.
When tamper evident logging is enabled, OpenAM generates an HMAC digest for each audit log event and inserts it into each audit log entry. The digest detects any addition or modification to an entry.
OpenAM also supports another level of tamper evident security by periodically adding a signature entry to a new line in each CSV file. The entry signs the preceding block of events, so that verification can establish if any of these blocks have been added, removed, or edited by some user.
Click Is Enabled to turn on the tamper evident feature for CSV logs.
In the Certificate Store Location field, enter the location of the keystore. You must manually create the keystore and place it in this location. You can use a simple script to create your Java keystore: create-keystore.sh.
Default:
%BASE_DIR%/%SERVER_URI%/Logger.jksIn the Certificate Store Password field, enter the certificate password.
In the Certificate Store Password (confirm), re-enter the certificate password.
In the Signature Interval field, enter a value in seconds for OpenAM to generate and add a new signature to the audit log entry.
Default:
900(seconds)
In the Audit Event Handler Factory field, keep the default class name for the audit event handler.
Click Add to save your changes.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save.
OpenAM can publish audit events to a syslog server, which is based on a widely-used logging protocol. You can configure your syslog settings on the OpenAM console.
The following procedure describes how to configure a Syslog audit event handler:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
In the Event Handler Instances section, click New.
On the Select Audit Event Handler page, click Syslog, and then click Next.
On the Add Audit Event Handler page, enter a name for your event handler. For example,
Syslog Audit Event Handler.Under General Handler Configuration, verify that the Enabled box is checked.
Select the topics for your audit logs. For a description of each topic, see "Audit Log Topics".
In the Server hostname field, enter the hostname or IP address of the receiving syslog server.
In the Server port field, enter the port of the receiving syslog server.
Select the Transport protocol for your configuration:
TCPorUDP.In the Connection timeout field, enter the number of seconds to connect to the syslog server. If the server has not responded in the specified time, a connection timeout occurs.
Select the syslog facility.
A syslog message includes a PRI field that is calculated from the facility and severity values. All topics set the severity to
INFORMATIONALbut allow you to choose the facility:Facility Description AUTH Security or authorization messages AUTHPRIV Security or authorization messages CLOCKD Clock daemon CRON Scheduling daemon DAEMON System daemons FTP FTP daemon KERN Kernel messages LOCAL0 Local use 0 (local0) LOCAL1 Local use 1 (local1) LOCAL2 Local use 2 (local2) LOCAL3 Local use 3 (local3) LOCAL4 Local use 4 (local4) LOCAL5 Local use 5 (local5) LOCAL6 Local use 6 (local6) LOCAL7 Local use 7 (local7) LOGALERT Log alert LOGAUDT Log audit LPR Line printer subsystem MAIL Mail system NEWS Network news subsystem NTP Network time protocol SYSLOG Internal messages generated by syslogd USER User-level messages UUCP Unix-to-unix-copy (UUCP) subsystem In the Audit Event Handler Factory field, keep the default class name for the audit event handler.
For Buffering Enabled, click the Enabled box to start audit event buffering.
When buffering is enabled, all audit events that get generated are formatted as syslog messsages and put into a queue. A dedicated thread constantly pulls events from the queue in batches and transmits them to the syslog server. If the queue becomes empty, the dedicated thread goes to sleep until a new item gets added. The default queue size is 5000.
Click Add to save your settings.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save.
OpenAM supports audit logging to relational databases using the JDBC audit event handler. You can configure OpenAM to write to Oracle, MySQL, or other databases.
Before configuring the JDBC audit event handler, you must perform several steps to allow OpenAM to log to the database:
Create tables in the relational database in which you will write the audit logs. The SQL for Oracle and MySQL table creation is in the
audit.sqlfile under/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/template/sql/db-type.If you are using a different relational database, tailor the Oracle or MySQL
audit.sqlfile to conform to your database's SQL syntax.JDBC audit logging requires a database user with read and write privileges for the audit tables. Do one of the following:
Identify an existing database user and grant that user privileges for the audit tables.
Create a new database user with read and write privileges for the audit tables.
Obtain the JDBC driver from your database vendor. Place the JDBC driver
.zipor.jarfile in the container'sWEB-INF/libclasspath. For example, place the JDBC driver in/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/libif you use Apache Tomcat.
The following procedure describes how to configure a JDBC audit event handler. Perform the following steps after you have created audit log tables in your database and installed the JDBC driver in the OpenAM web container:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
In the Event Handler Instances section, click New.
On the Select Audit Event Handler page, click JDBC, and then click Next.
On the Add Audit Event Handler page, enter a name for your event handler. For example,
JDBC Audit Event Handler.Under General Handler Configuration, verify that the Enabled box is checked.
Select the topics for your audit logs. For a description of each topic, see "Audit Log Topics".
For Database Type, click one of the following:
Oracle
MySQL
Other
For JDBC Database URL, enter the URL for your database server. For example,
jdbc:oracle:thin@//host.example.com:1521/ORCL.In the Database Driver Name field, enter the classname of the driver to connect to the datbase. For example,
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriverorcom.mysql.jdbc.Driver.In the Database Username field, enter the username to authenticate to the database server.
This user must have read and write privileges for the audit tables.
In the Database User Password field, enter the password used to authenticate to the database server. Then, re-enter the password in the Database User Password (confirm) field.
In the Connection Timeout (seconds) field, enter the maximum wait time before failing the connection.
Default: 30 (seconds)
In the Maximum Connection Idle Timeout (seconds) field, enter the maximum idle time in seconds before the connection is closed.
Default: 600 (seconds)
In the Maximum Connection Time (seconds) field, enter the maximum time in seconds for a connection to stay open.
Default: 1800 (seconds)
In the Minimum Idle Connections field, enter tne minimum number of idle connections allowed in the connection pool.
In the Maximum Connections field, enter the maximum number of connections in the connection pools.
In the Factory Class Name, enter the fully qualified class name of your custom JDBC audit event handler.
Click Add to save your changes.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save.
OpenAM supports audit logging to Elasticsearch 5.0. When you store OpenAM's audit logs in an Elasticsearch data store, you can use Kibana to perform data discovery and visualization on your logs.
You can experiment with an Elasticsearch audit handler without enabling any Elasticsearch security features. However, for a more secure deployment, ForgeRock recommends that you use Elasticsearch Shield to require authentication to Elasticshield. Depending on your network topology, you might also want to configure SSL for Elasticsearch Shield.
Before configuring the Elasticsearch audit event handler, you must configure an Elasticsearch index with OpenAM's audit schema:
Perform the following steps to prepare an Elasticsearch instance for storing OpenAM audit events.
Note
These steps apply to Elasticsearch 5.0 only. Breaking changes in Elasticsearch 6.0 make it incompatible with the schemas provided in this version of OpenAM.
For more information, see Breaking Changes in 6.0 in the Elasticsearch Reference Docs.
Review the JSON file containing OpenAM's audit schema. You can find the JSON file for the audit schema at the path
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/template/elasticsearch/audit.json.Copy the
audit.jsonfile to the system where you will create the Elasticsearch index for OpenAM auditing.In this example, you create an Elasticsearch index by executing an Elasticsearch REST API call using the curl command. Copy the
audit.jsonfile to a location that is accessible to the curl command you will run in the next step.Create an Elasticsearch index for OpenAM auditing as follows:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --data @audit.json \ http://elasticsearch.example.com:9200/my_openam_audit_index
In this example, note the following:
elasticsearch.example.comis the name of the host on which Elasticsearch runs.9200is the port number that you use to access Elasticsearch's REST API.my_openam_audit_indexis the name of the Elasticsearch index that you want to create.
Tip
For more information on connecting to Elasticsearch, see Talking to Elasticsearch in the Elasticsearch documentation.
The following procedure describes how to configure an Elasticsearch audit event handler. Perform the following steps after you have created an Elasticsearch index for OpenAM audit logging:
If your Elasticsearch deployment uses Elasticsearch Shield configured for SSL, import the CA certificate used to sign Elasticsearch node certificates into the Java keystore on the host that runs OpenAM. For example:
$ keytool \ -import \ -trustcacerts \ -alias elasticsearch \ -file /path/to/cacert.pem \ -keystore $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/cacerts
If you are running an OpenAM site, import the CA certificate on all the servers in your site.
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
In the Event Handler Instances section, click New.
On the Select Audit Event Handler page, click Elasticsearch, and then click Next.
On the Add Audit Event Handler page, enter a name for your event handler. For example,
Elasticsearch Event Handler.Under General Handler Configuration:
Verify that the Enabled box is checked.
Select the topics for your audit logs. For a description of each topic, see "Audit Log Topics".
Under Elasticsearch Configuration:
In the Server Hostname field, enter the hostname or IP address of the Elasticsearch server to which OpenAM should connect when writing audit logs.
In the Server Port field, enter the port number to access Elasticsearch's REST API. The default port number is 9200.
If SSL is enabled in your Elasticsearch deployment, click the Enabled check box for SSL Enabled.
In the Elasticsearch Index field, specify the name of the index to be used for OpenAM audit logging. The index you specify in this field must be identical to the index you created in "To Prepare for Elasticsearch Audit Logging".
If you have configured Elasticsearch Shield for user authentication, specify the name and password of an Elasticsearch user in the Username and Password fields under Authentication.
If you are not using Elasticsearch Shield for user authentication, you can leave these fields blank.
Under Buffering, configure whether log events should be buffered in memory before they are written to the Elasticsearch data store:
For Buffering enabled, click the Enabled box to start audit event buffering.
When buffering is enabled, all audit events are put into an in-memory buffer (one per handled topic), so that the original thread that generated the event can fulfill the requested operation, rather than wait for I/O to complete. A dedicated thread (one per handled topic) constantly pulls events from the buffer in batches and writes them to Elasticsearch. If the buffer becomes empty, the dedicated thread goes to sleep until a new item gets added.
For Batch Size, specify the number of audit events that OpenAM pulls from the audit buffer when writing a batch of events to Elasticsearch. The default is 500 audit events.
For Queue Capacity, specify the maximum number of audit events that OpenAM can queue in this audit handler's buffer. The default is 10000 audit events.
If the number of events to queue exceeds the queue capacity, OpenAM raises an exception and the excess audit events are dropped, and therefore not written to Elasticsearch.
For Write interval, specify how often OpenAM should write buffered events to Elasticsearch. The default interval is 250 milliseconds.
In the Factory Class Name field under Audit Event Handler Factory, keep the default class name for the audit event handler.
Click Add to add the Elasticsearch audit logging event handler to the Audit Logging Service.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save to save your changes to the Audit Logging Service.
If you have configured the audit logging event handler correctly, OpenAM starts logging to Elasticsearch immediately after you have saved your changes to the Audit Logging Service.
OpenAM supports audit logging to a JMS message broker. JMS is a Java API for sending messages between clients using a publish and subscribe model as follows:
OpenAM audit logging to JMS requires that the JMS message broker supports using JNDI to locate a JMS connection factory. See your JMS message broker documentation to verify that you can make connections to your broker by using JNDI before attempting to implement an OpenAM JMS audit handler.
OpenAM acts as a JMS publisher client, publishing JMS messages containing audit events to a JMS topic. [5]
A JMS subscriber client, which is not part of the OpenAM software and must be developed and deployed separately from OpenAM, subscribes to the JMS topic to which OpenAM publishes audit events. The client then receives the audit events over JMS and processes them as desired.
Before configuring the JMS audit event handler, you must perform several steps to allow OpenAM to publish audit events as a JMS client:
Obtain JNDI connection properties that OpenAM requires to connect to your JMS message broker. The specific connection properties vary depending on the broker. See your JMS message broker documentation for details.
For example, connecting to an Apache ActiveMQ message broker requires the following properties:
Property Name Example Value java.naming.factory.initialorg.apache.activemq.jndi.ActiveMQInitialContextFactoryjava.naming.provider.urltcp://localhost:61616topic.auditauditObtain the JNDI lookup name of the JMS connection factory for your JMS message broker.
For example, for Apache ActiveMQ, the JNDI lookup name is
ConnectionFactory.Obtain the JMS client
.jarfile from your JMS message broker vendor. Add the.jarfile to OpenAM's classpath by placing it in theWEB-INF/libdirectory.For example, place the JMS client
.jarfile in/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/libif you use Apache Tomcat.
The following procedure describes how to configure a JMS audit event handler.
If your JMS message broker requires an SSL connection, you might need to perform additional, broker-dependent configuration tasks. For example, you might need to import a broker certificate into OpenAM's keystore, or provide additional JNDI context properties.
See your JMS message broker's documentation for specific requirements for making SSL connections to your broker, and implement them as needed in addition to the steps in the following procedure.
Perform the following steps after you have installed the JMS client
.jar file in the OpenAM web container:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
In the Event Handler Instances section, click New.
On the Select Audit Event Handler page, click JMS, and then click Next.
On the Add Audit Event Handler page, enter a name for your event handler. For example,
JMS Event Handler.Under General Handler Configuration:
Verify that the Enabled box is checked.
Select the OpenAM event handler topics[5] for your audit logs. For a description of OpenAM event handler topics, see "Audit Log Topics".
Under JMS Configuration:
In the Delivery Mode field, specify the JMS delivery mode.
With persistent delivery, the JMS provider ensures that messages are not lost in transit in case of a provider failure by logging messages to storage when they are sent. Therefore, persistent delivery mode guarantees JMS message delivery, while non-persistent mode provides better performance.
The default delivery mode is non-persistent delivery. Therefore, if your deployment requires delivery of every audit event to JMS subscriber clients, be sure to set the default configuration to
PERSISTENT.For Session Mode, use the default setting,
AUTO, unless your JMS broker implementation requires otherwise. See your broker documentation for more information.Specify properties that OpenAM will use to connect to your JMS message broker as key-value pairs in the JNDI Context Properties field. The format for properties is
[myPropertyName]=myPropertyValue. For example,[java.naming.provider.url]=tcp://localhost:61616.Specify the name of the JMS topic to which OpenAM will publish messages containing audit events.
Subscriber clients that process OpenAM audit events must subscribe to this topic.
Specify the JNDI lookup name of the JMS connection factory in the JMS Connection Factory Name field.
Under Batch Events, configure whether log events should be batched before they are published to the JMS message broker:
For Batch enabled, click the Enabled box to start batch publishing of audit events. Audit events will be queued and published to the JMS message broker in batches.
If batch publishing is not enabled, OpenAM publishes audit events to the JMS message broker individually.
For Capacity, specify the maximum capacity of the publishing queue. Execution is blocked if the queue size reaches capacity.
For Max Batched, specify the maximum number of events to be delivered when OpenAM publishes the events to the JMS message broker.
For Thread Count, specify the number of worker threads OpenAM should use to process the batch queue.
Specify the batching timeout configuration as follows:
For Insert Timeout, specify the amount of time, in seconds, for queued events to be transmitted to the JMS message broker.
For Polling Timeout, specify the amount of time, in seconds, that worker threads wait for new audit events before becoming idle.
For Shutdown Timeout, specify the amount of time, in seconds, that worker threads wait for new audit events before shutting down.
In the Factory Class Name field under Audit Event Handler Factory, keep the default class name for the audit event handler.
Click Add to add the JMS audit logging event handler to the Audit Logging Service.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save to save your changes to the Audit Logging Service.
If you have configured the audit logging event handler correctly, OpenAM starts logging to JMS immediately after you have saved your changes to the Audit Logging Service.
You can easily enable the Audit Logging service on the OpenAM Admin console, either globally or on a per-realm basis.
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Audit Logging.
Make sure you have configured your audit event handler. See "Configuring Audit Event Handlers".
In the Realm Attributes section, click Enabled to turn on Audit Logging.
For Resolve host name, click Enabled if you want to perform DNS host lookups, which populates the record's host name field in the logs. Note that enabling DNS host lookups may result in an overall performance hit due to the hostname searches.
For Field exclusion policies, enter any fields or values to exclude from your audit events in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The purpose of this feature is to allow customers to perform two kinds of filtering: 1) Filter fields from the event. For example, customers with more basic auditing requirements may not be interested in capturing HTTP headers, query parameters, and cookies in the access logs; 2) Filter specific values from within fields that store key-value pairs as JSON. For example, the HTTP headers, query parameters and cookies.
On the Audit Logging page, click Save.
You can configure the audit logging server on a per realm basis, which allows you to set up different log locations for your realms and different types of handlers for each realm.
If no specific realm is configured, audit logging will be governed by the global settings.
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, and select the realm from which you want to work.
Click Services > Add a Service, select Audit Logging, and then click Create.
Make sure you have configured your audit event handler. See "Configuring Audit Event Handlers".
On the Configuration tab, select the Audit logging checkbox to turn on audit logging.
For Field exclusion policies, enter any fields or values to exclude from your audit events in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The purpose of this feature is to allow customers to perform two kinds of filtering: 1) Filter fields from the event. For example, customers with more basic auditing requirements may not be interested in capturing HTTP headers, query parameters, and cookies in the access logs; 2) Filter specific values from within fields that store key-value pairs as JSON. For example, the HTTP headers, query parameters and cookies.
Click Save Changes.
OpenAM supports the propagation of the transaction ID across the ForgeRock
platform, such as from OpenDJ or OpenIDM to OpenAM,
using the HTTP header X-ForgeRock-TransactionId.
The X-ForgeRock-TransactionId header is automatically
set in all outgoing HTTP calls from one ForgeRock product to another.
Customers can also set this header themselves from their own applications
or scripts calling into the ForgeRock platform.
You can set a new property org.forgerock.http.TrustTransactionHeader
to true, which will trust any incoming
X-ForgeRock-TransactionId headers.
By default, the org.forgerock.http.TrustTransactionHeader
is set to false, so that a malicious actor cannot
flood the system with requests using the same transaction ID header to hide
their tracks.
Log in to the OpenAM console.
Navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced.
In the Add a Name field, enter
org.forgerock.http.TrustTransactionHeader, and entertruein the corresponding Add a Value field.Click Save Changes.
Your OpenAM instance will now accept incoming
X-ForgeRock-Transactionidheaders, which can then be tracked in the audit logs.
To configure OpenAM logging properties, log in to the OpenAM console as OpenAM administrator, and navigate to Configure > Global Services > System, and then click Logging.
For more information on the available settings, see "Logging" in the Reference reference.
By default, OpenAM audit logs are written to files in the
configuration directory for the instance, such as
$HOME/openam/log/.
OpenAM sends messages to different log files, each named after the
service logging the message, with two different types log files per service:
.access
and.error. Thus, the
current log files for the authentication service are named
amAuthentication.access
and
amAuthentication.error.
For details, see "Log Files and Messages" in the Reference.
OpenAM supports sending audit log messages to a syslog server for collation.
You can enable syslog audit logging by using the OpenAM console,
or the ssoadm command.
Log in to the OpenAM console as OpenAM administrator.
Navigate to Configure > Global Services > System, and then click Logging.
Set the Logging Type option to
Syslog.Complete the following settings as appropriate for your syslog server:
Syslog server hostSyslog server portSyslog server protocolSyslog facilitySyslog connection timeout
For information on these settings, see "Logging" in the Reference.
Save your work.
Create a text file, for example,
MySyslogServerSettings.txtcontaining the settings used when audit logging to a syslog server, as shown below:iplanet-am-logging-syslog-port=514 iplanet-am-logging-syslog-protocol=UDP iplanet-am-logging-type=Syslog iplanet-am-logging-syslog-connection-timeout=30 iplanet-am-logging-syslog-host=localhost iplanet-am-logging-syslog-facility=local5Use the following SSOADM command to configure audit logging to a syslog server:
$ ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --servicename iPlanetAMLoggingService \ --schematype Global \ --datafile MySyslogServerSettings.txt Schema attribute defaults were set.
By default, OpenAM Policy Agents log to local files in their configuration directories for debugging. The exact location depends on where you installed the agent.
By default, OpenAM policy agents send log messages remotely to OpenAM when you log auditing information about URL access attempts. To configure audit logging for a centrally managed policy agent, login to the OpenAM console as administrator, and browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Agent Type > Agent Name > Global, and then scroll down to the Audit section.
[5] Note that OpenAM and JMS use the term topic differently. An OpenAM audit topic is a category of audit log event that has an associated one-to-one mapping to a schema type. A JMS topic is a distribution mechanism for publishing messages delivered to multiple subscribers.
When building applications that run on mobile devices, you can use the same OpenAM service that you also use for access management in your web, cloud, and other applications. OpenAM has features that make it particularly well-suited to the mobile world, too.
On many mobile devices, users want to avoid repeatedly entering credentials, such as an email address or user name and a password. They do not want new credentials to manage for every application they try. They do not want to share their credentials across applications. Instead, users want single sign-on with few identity providers. They want to authorize access for applications rather than share their credentials.
OpenAM supports modern web standards including "Managing OAuth 2.0 Authorization", "Managing OpenID Connect 1.0 Authorization", and GSMA Mobile Connect. After registering an application with OpenAM as an OAuth/OpenID Connect client, the application can then redirect a user to OpenAM to authenticate and to authorize access to resources that the user owns, such as profile data. The application gets an access token that can be used to gain authorized access without requiring the user to share credentials. OpenID Connect extends OAuth, standardizing how client applications discover and register with identity providers, and also defining how applications can manage user sessions and handle logout when they no longer want to authorize access.
An OAuth 2.0 client application can thus simplify the user experience on the phone to authorizing access.
In addition to serving as an identity provider, OpenAM can also function as an OAuth 2.0 client, protecting access to resources within your control based on authorization granted by an identity provider who users already know and use, such as Facebook, Google, MSN, and so forth. OpenAM's built in authorization policy management makes it straightforward to integrate this capability into your applications.
The OAuth and OpenID Connect standards specify REST interfaces, making them essentially programming language-independent and accessible for web applications and mobile applications alike.
Mobile Connect is an application of OpenID Connect that enables authentication to work through a mobile phone, regardless of the service provided or the device consuming the service. Mobile Connect therefore allows Mobile Network Operators to act as an identity provider for their customers. OpenAM fits well in Mobile Connect deployments as it can play both the role of OpenID Provider and also of Authenticator, with many authentication modules built in as described in "Protecting Access for Mobile Users". For details on using OpenAM in a Mobile Connect installation, see "Using OpenAM with Mobile Connect".
OpenAM also supports Open Authentication architecture with the OATH module mentioned in the next section.
You must give users access to your organization's resources while they are on the go. At the same time, you must manage risk. OpenAM supports risk-based adaptive authentication, device fingerprints, one-time passwords, and other multi-factor authentication capabilities that help you do both. As OpenAM handles authentication through plugin modules that you can chain, your OpenAM service can meet a variety of requirements.
The Adaptive Risk authentication module lets you add risk assessment to any authentication chain, dynamically requiring stronger authentication when circumstances require it (new location, ancient last login time, new device, new IP address, specific application, and so forth). For more information about the Adaptive Risk module, see "Hints for the Adaptive Risk Authentication Module".
You can add the Device ID (Match) authentication module to an authentication chain to fingerprint users' devices for additional risk assessment, making it easier to handle sign-on when users authenticate from their own devices. For more information about the Device ID (Match) module, see "Hints for the Device ID (Match) Authentication Module".
OpenAM also lets you decide exactly what stronger authentication means in your situation. You can, for example, add multi-factor authentication involving mobile devices using one-time passwords:
Users can generate one-time passwords with ForgeRock's authenticator mobile app. See "Multi-Factor Authentication" for more information.
OpenAM can generate one-time passwords and then send them to mobile phones using a text message or e-mail. See "Hints for the HOTP Authentication Module" for more information.
In addition to capabilities supporting new applications, OpenAM integrates well with existing systems needed by users on the move. Whether users are authenticating from a mobile device through a gateway using an MSISDN, starting single sign-on by logging on to a laptop, or connecting to a VPN with certificate-based authentication, OpenAM has an authentication module for that.
Representational State Transfer (REST) is a architectural style designed in parallel with HTTP. REST simplifies integration and deployment while enabling layered, web-scale services. REST APIs in OpenAM implement REST in a way that reuses common HTTP verbs and decouples APIs from the programming languages that developers use to interact with them. OpenAM exposes REST APIs for many capabilities, such as those in the following list:
Authentication (including a callback mechanism so applications can work with all OpenAM authentication modules)
Logout
Managing groups
Managing policy agent profiles
Managing realms
Managing user profiles
OAuth 2.0 authorization
OpenAM native authorization
OpenID Connect 1.0 authorization
Resetting forgotten passwords
Token validation
User self-registration
As "Using the REST API" in the Developer's Guide provide language-independent access, they make it easier to build cross-device applications. Developers can use the same APIs to access OpenAM both from web applications and also from native mobile applications.
Furthermore, OpenAM REST APIs are built on an underlying common REST framework designed to provide common access to resource providers. The common REST framework standardizes how resource providers serve standard requests (create, read, update, delete, query, patch), and also how resource providers offer extended operations in a managed way (using actions). Applications built to interact with OpenAM REST APIs increasingly can interoperate with other products in the ForgeRock stack, such as OpenIDM for identity management and OpenDJ for highly available data.
Source code for the sample mobile applications is available in sample repositories in the ForgeRock commons project. Get local clones of one or more of the following repositories so that you can try these sample applications on your system:
For example, if you have a Mac running OS X 10.8 or later with Xcode installed, try the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 iOS Sample App.
OpenAM provides user self-service features that enable your customers to self-register to your web site, securely reset forgotten passwords, and retrieve their usernames. OpenAM's user self-service capabilities greatly reduces help desk costs and offers a rich online experience that strengthens customer loyalty.
Note
The Password Reset service, located on the OpenAM console at Configure > Global Services, is deprecated for OpenAM 13.5.2-15 and will no longer be supported in a future OpenAM release.
OpenAM's User Self-Service feature supports automated account registration for new users, forgotten password reset, and forgotten username retrieval for your existing customer base. The User Self-Service features include the following capabilities:
User self-registration. Allows non-authenticated users to register to your site on their own. You can add additional security features like email verification, knowledge-based authentication (KBA) security questions, Google reCAPTCHA, and custom plugins to add to your user self-registration process.
Knowledge-based authentication security questions. Supports the capability to present security questions during the registration process. When enabled, the user is prompted to enter answers to pre-configured or custom security questions. Then, during the forgotten password or forgotten username process, the user is presented with the security questions and must answer them correctly to continue the process.
Forgotten password reset. Allows registered users already in your system to reset their passwords. The default password policy is set in the underlying directory server and requires a minimum password length of eight characters by default. If security questions are enabled, users must also correctly answer their pre-configured security questions before resetting their passwords.
Forgotten username support. Allows users to retrieve their forgotten usernames. If security questions are enabled, users must also correctly answer their pre-configured security questions before retrieving their usernames.
Google reCAPTCHA plugin. Supports the ability to add a Google reCAPTCHA plugin to the registration page. This plug-in protects against any software bots that may be used against your site.
Configurable plugins. Supports the ability to add plugins to customize the user services process flow. You can develop your custom code and drop the
.jarfile into your container.Customizable confirmation emails. Supports the ability to customize or localize confirmation email in plain text or HTML.
Password policy configuration. Supports password policy configuration, which is enforced by the underlying OpenDJ directory server and manually aligned with frontend UI templates. The default password policy requires a password with a minimum length of eight characters.
Self registration user attribute whitelist. Supports attribute whitelisting, which allows you to specify which attributes can be set by the user during account creation.
User Self-Service features support various user flows depending on how you configure your security options, which include email verification, security questions, Google reCAPTCHA, and any custom plugins that you create.
The following diagram shows the basic user self-registration flow without the optional features:
The following diagrams show the possible flows for user self-registration flow with the optional features:
Forgotten username retrieval and forgotten password reset support various user flows depending on how you configure your security options. If you enabled security questions and the user entered responses to each question during self-registration, the security questions are presented to the user in random order.
The following diagram shows the possible flows for forgotten username:
The following diagram shows the possible flows for forgotten password reset:
You can configure the user self-service features to use email address verification, which sends an email containing a link for user self-registration and forgotten password reset via OpenAM's email service. You can also send the forgotten username to the user by email if configured.
Tip
For information on the RESTful API for the user self-service features, see "RESTful User Self-Service" in the Developer's Guide.
Follow the steps in the sections below:
OpenAM's user self service feature requires two key aliases: one secret key alias for signing and one key pair alias for encryption. OpenAM is pre-configured with a JCEKS keystore with three key aliases that you can use for testing purposes. For more information about keystores and key aliases in OpenAM, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".
Unlike a JKS keystore that supports asymmetric keys, the JCEKS keystore supports both asymmetric keys for encryption and symmetric keys for signing. In an OpenAM site with multiple OpenAM servers deployed behind a load balancer, the JCEKS keystore allows one server to decrypt and validate a JSON Web Token (JWT) from the other server.
The key aliases must exist in the JCEKS keystore before the user self service feature can be configured, since they need to be specified at configuration time.
To provide user self-service features, you must configure suitable key aliases.Perform the following steps to populate the values of the Encryption Key Pair Alias and the Signing Secret Key Alias properties:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator, for example,
amadmin.Navigate to Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
Populate the values of the Encryption Key Pair Alias and the Signing Secret Key Alias properties with the names of the key pair aliases in your JCEKS keystore. For example, if you are using the demo keys in the default
keystore.jceksfile, set the properties as follows:Encryption Key Pair Alias to
selfserviceenctest.Signing Secret Key Alias to
selfservicesigntest.
Save your changes.
The user self-service feature lets you send confirmation emails via OpenAM's SMTP Email Service to users who are registering at your site or resetting forgotten passwords. If you choose to send confirmation emails, you can configure the Email Service globally.
By default, OpenAM expects the SMTP service to listen on
localhost:465. You can change this setting.
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator.
On the Realms page, click the realm in which you will install the Email Service, and then click Services.
Click Services, and then click Add a Service.
On the Choose a Service drop-down list, select Email Service, and then enter the following:
Enter the Mail Server Hostname. If you are using the Google SMTP server, you must also configure the Google Mail settings to enable access for less secure applications.
Enter the Mail Server Authentication Username. The default is
amadmin. If you are testing on a Google account, you can enter a known Gmail address.Enter the Mail Server Authentication Password property value.
Enter the Email From Address. The default is
no-reply@example.com.Click Create.
The user self-service feature supports the Google reCAPTCHA plugin, which can be placed on the Register Your Account, Reset Your Password, and Retrieve Your Username pages. The Google reCAPTCHA plugin protects your user self-service implementation from software bots.
Note
Google reCAPTCHA is the only supported plugin for user self-service. Any other Captcha service will require a custom plugin.
Register your web site at a Captcha provider, such as Google reCAPTCHA, to get your site and secret key.
When you register your site for Google reCAPTCHA, you only need to obtain the site and secret key, which you enter in the user self-service configuration page in the OpenAM console. You do not have to do anything with client-side integration and server-side integration. The Google reCAPTCHA plugin appears automatically on the Register Your Account, Reset Your Password, and Retrieve Your Username pages after you configure it in the OpenAM console.
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrator.
Click Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
In the Google Recaptcha Site Key field, enter the site key that you obtained from the Google reCAPTCHA site.
In the Google Recaptcha Secret Key field, enter the secret key that you obtained from the Google reCAPTCHA site.
In the Google Recaptcha Verification URL field, keep the default.
Knowledge-based authentication (KBA) is an authentication mechanism in which the user must correctly answer a number of pre-configured security questions that are set during the initial registration setup. If successful, the user is granted the privilege to carry out an action, such as registering an account, resetting a password, or retrieving a username. The security questions are presented in a random order to the user during the user self-registration, forgotten password reset, and forgotten username processes.
OpenAM provides a default set of security questions and easily allows OpenAM administrators and users to add their own custom questions.
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator.
Click Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
On the User Self Service page, scroll to the Security Questions section. Enter your own security question in the New Value field, and then click Add. The syntax is:
OrderNum|ISO-3166-2 Country Code|Security Question. For example,5|en|What is your dog's name?. Make sure that order numbers are unique.Warning
You should never remove any security questions as a user may have reference to a given question.
In the Minimum Answers to Define field, enter the number of security questions that will be presented to the user during the registration process.
In the Minimum Answers to Verify field, enter the number of security questions that must be answered during the Forgotten Password and Forgotten Username services.
Click Finish to save your changes.
OpenAM provides a self-registration feature that allows users to create an account to your web site. Although you can configure user self registration without any additional security mechanisms, such as email verification or KBA security questions, we recommend configuring the email verification service with user self registration at a minimum.
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator.
Configure the email service presented in "Configuring the Email Service".
Click Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
On the User Self Service page, click Enabled next to User Registration.
For Captcha, click Enabled to turn on the Google reCAPTCHA plugin. Make sure you configured the plugin as presented in "Configuring the Google reCAPTCHA Plugin".
For Email Verification, clear the Enabled box if you want to turn off the email verification service. We recommend that you keep it selected.
For Security Questions, click Enabled to display security questions to the user during the self registration, after which the user must enter their answers to the questions. During the forgotten password or forgotten username services, the user will be presented with the security questions to be able to reset their passwords or retrieve their usernames if Security Questions is enabled.
In the Token LifeTime field, enter an appropriate number of seconds for the token lifetime. If the token lifetime expires before the user self-registers, then the user will need to restart the registration process over again.
Default: 900 seconds.
To customize the Self Registration outgoing email, run the following steps:
In the Outgoing Email Subject field, enter the Subject line of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The subject line format is
lang|subject-text, wherelangis the ISO-639 language code, such asenfor English,frfor French, and others. For example, the subject line values could be:en|Registration Emailandfr|Inscription E-mail.In the Outgoing Email Body field, enter the text of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The email body text format is
lang|email-text, wherelangis the ISO-639 language code. Note that email body text must be all on one line and can contain any HTML tags within the body of the text.For example, the email body text could be:
en|Thank you for registration to our site! Click <a href="%link%">here</a> to register to the site.
In the Valid Creation Attributes field, enter the user attributes the user can set during the user self-registration. The attributes are based on the OpenAM identity repository.
For Destination After Successful Registration, select one of the following:
User is automatically logged in and sent to the appropriate page within the system.
User is sent to a success page without being logged in. In this case, OpenAM displays a "You have successfully registered" page. The user can then click the Login link to log in to OpenAM. This is the default selection.
User is sent to the login page to authenticate.
Under Advanced Configuration, configure the User Registration Confirmation Email URL for your deployment. The default is:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#register/.Click Finish to apply your changes.
The forgotten password feature allows existing users to reset their passwords when they cannot remember them.
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator.
Click Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
On the User Self Service page, click Enabled next to Forgotten Passwords.
For Captcha, click Enabled to turn on the Google reCAPTCHA plugin. Make sure you configured the plugin as presented in "Configuring the Google reCAPTCHA Plugin".
For Email Verification, clear the Enabled box if you want to turn off the email verification service. We recommend that you keep it selected.
For Security Questions, click Enabled to display security questions to the user during the forgotten password reset process. The user must correctly answer the security questions to be able to reset passwords.
In the Forgotten Password Token LifeTime field, enter an appropriate number of seconds for the token lifetime. If the token lifetime expires before the user resets their password, then the user will need to restart the forgotten password process over again.
Default: 900 seconds.
To customize the Forgotten Password outgoing email, run the following steps:
In the Outgoing Email Subject field, enter the subject line of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The subject line format is
lang|subject-text, wherelangis the ISO-639 language code, such asenfor English,frfor French, and others. For example, the subject line value could be:en|Forgotten Password Email.In the Outgoing Email Body field, enter the text of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The email body text format is
lang|email-text, wherelangis the ISO-639 language code. Note that email body text must be all on one line and can contain any HTML tags within the body of the text.For example, the email body text could be:
en|Thank you for request! Click <a href="%link%">here</a> to reset your password.
Under Advanced Configuration, change the default Forgotten Password Confirmation Email URL for your deployment. The default is:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#passwordReset/.
The forgotten username feature allows existing users to retrieve their usernames when they cannot remember them.
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator.
Click Configure > Global Services > User Self Service.
On the User Self Service page, click Enabled next to Forgotten Username.
For Captcha, click Enabled to turn on the Google reCAPTCHA plugin. Make sure you configured the plugin as presented in "Configuring the Google reCAPTCHA Plugin".
For Security Questions, click Enabled to display security questions to the user during the forgotten username process. The users must correctly answer the security questions to be able to retrieve their usernames.
For Email Username, click Enabled if you want the user to receive the retrieved username by email.
For Show Username, click Enabled if you want the user to see their retrieved username on the browser.
In the Forgotten Username Token LifeTime field, enter an appropriate number of seconds for the token lifetime. If the token lifetime expires before the user retrieves their username, then the user will need to restart the forgotten username process.
Default: 900 seconds.
To customize the Forgotten Username outgoing email, run the following steps:
In the Outgoing Email Subject field, enter the subject line of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The subject Line format is
lang|subject-text, wherelangis the ISO 639 language code, such asenfor English,frfor French, and others. For example, the subject line value could be:en|Forgotten username email.In the Outgoing Email Body field, enter the text of your email in the New Value field, and then click Add.
The email body text format is
lang|email-text, wherelangis the ISO 639 language code. Note that email body text must be all on one line and can contain any HTML tags within the body of the text.For example, the email body text could be:
en|Thank you for your inquiry! Your username is %username%.
Once the user has self-registered to your system, the user can change their password and security questions at any time on the user profile page. The user profile page provides tabs to carry out these functions.
OpenAM supports two types of sessions: stateful and stateless.
This chapter describes the differences between stateful and stateless sessions, and shows you how to configure OpenAM for either type of session.
When a user successfully authenticates, OpenAM creates a session to manage the user's access to resources. OpenAM uses information stored in the session to determine if a user's login is still valid, or if a user needs to reauthenticate.
OpenAM sessions are "stateful" or "stateless," and are described in detail in the following sections.
Stateful sessions are sessions that reside in the OpenAM server's memory
and, if session failover is enabled, are also persisted in the Core Token
Service's token store. OpenAM sends clients a reference to the session in
OpenAM memory but it does not contain any of the session state information.
The session reference is also known as an SSO token.
For browser clients, OpenAM sets a cookie in the browser that contains
the session reference. For REST clients, OpenAM returns the session
reference in response to calls to the authentication
endpoint.
Stateful sessions are malleable. The OpenAM server can modify various aspects of users' sessions during the sessions' lifetime.
Stateless sessions are sessions in which state information is encoded in OpenAM and sent to clients, but the information from the sessions is not retained in OpenAM's memory. For browser-based clients, OpenAM sets a cookie in the browser that contains the session state. When the browser transmits the cookie back to OpenAM, OpenAM decodes the session state from the cookie.
Stateless sessions are immutable. This means that when OpenAM sets a cookie for a stateless session in a user's browser, it never updates the cookie until the user has logged out of OpenAM, or until the user's session has expired.
Session statefulness and statelessness are configured at the realm level. OpenAM realms use stateful sessions by default. Sessions for all users authenticating to a given realm are either stateful or stateless, depending on the individual realm's configuration. OpenAM can be deployed with some realms using stateless sessions and so forth using stateful sessions.
There is, however, one exception to the per-realm session state
configuration. When the top-level administrator (by default,
the amadmin user) authenticates to OpenAM, the session is
always stateful, even if the Top Level Realm is configured for stateless
sessions.
During authentication, OpenAM maintains the authenticating user's session in its memory regardless of whether you have configured the realm to which the user is authenticating for stateful or stateless sessions.
After authentication has completed, OpenAM deletes in-memory sessions for users authenticating to realms configured for stateless sessions. Sessions for users authenticating to realms configured for stateful sessions remain in OpenAM's memory heap.
You can store custom information in both stateful and stateless sessions with post authentication plugins. For more information about post authentication plugins, see "Creating a Post Authentication Plugin" in the Developer's Guide.
OpenAM writes a cookie in the authenticated user's browser for both stateful
and stateless sessions. By default, the cookie's name is
iPlanetDirectoryPro. For stateful sessions, the size of
this cookie's value is relatively small—approximately 100 bytes—and
contains a reference to the stateful session on the OpenAM server and
several other pieces of information. For stateless sessions, the
iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie is considerably
larger—approximately 2000 bytes or more—and contains
all the information that would be held in the OpenAM server's memory if the
session were stateful.
Stateless session cookies are comprised of two parts. The first part of the cookie is identical to the cookie for stateful sessions, which ensures the compatibility of the cookies regardless of the session type. The second part is a base 64-encoded JSON Web Token (JWT), and it contains session information, as illustrated in the figure below.
The preceding diagram illustrates the difference between stateful and
stateless session cookie values. Note that the diagram is not to scale.
The iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie for a stateless session is
more than ten times larger than for a stateful session.
The size of the stateless session cookie increases when you customize OpenAM to store additional attributes in users' sessions. You are responsible for ensuring that the size of the cookie does not exceed the maximum cookie size allowed by your end users' browsers.
When using stateless session cookies, you should configure OpenAM to
sign and encrypt the JWT inserted in
the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie.
Configuring stateless session cookies for JWT signing and encryption is discussed in "Configuring Stateless Session Cookie Security".
OpenAM sets the iPlanetDirectoryPro
cookie in the user's browser as proof of previous authentication
whenever single sign-on is desired. OpenAM verifies that the cookie is
authentic by validating a signature configured in the Session Service.
OpenAM thwarts attackers who might attempt to tamper with the contents
of the cookie or its signature, or who might attempt to sign the cookie
with an incorrect signature.
Knowledgeable users can easily decode base 64-encoded JWTs. Because an OpenAM session contains information that might be considered sensitive, encrypting the JWT that contains the session protects its contents by ensuring opaqueness.
Encrypting the JWT prevents man-in-the-middle attacks that could log the state of every OpenAM session. Encryption also ensures that end users are unable to access the information in their OpenAM session.
OpenAM uses the Core Token Service differently for stateful and stateless sessions.
For stateful sessions, OpenAM uses the Core Token Service's token store to save user sessions when session failover is enabled. In the event of the failure of an OpenAM server, one or more backup servers can retrieve the sessions from the Core Token Service's token store to reestablish users login sessions during session failover.
With stateless sessions, OpenAM does not store user sessions in the Core
Token Service's token store. Instead, OpenAM stores sessions in the
iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie on the user's browser. If an
OpenAM server fails, another server handling the user's request simply reads
the stateless session from the iPlanetDirectoryPro
cookie. Session failover need not be enabled for the other server to be
able to read the session.
Session blacklisting is an optional feature that maintains a list of logged out stateless sessions in the Core Token Service's token store. The next section describes session logout, including session blacklisting for stateless sessions.
OpenAM manages active sessions, allowing single sign-on when authenticated users attempt to access system resources in OpenAM's control.
OpenAM ensures that user sessions are terminated when a configured timeout is reached, or when OpenAM users perform actions that cause session termination. Session termination effectively logs the user out of all systems protected by OpenAM.
With stateful sessions, OpenAM terminates sessions in four situations:
When a user explicitly logs out
When an administrator monitoring sessions explicitly terminates a session
When a session exceeds the maximum time-to-live
When a user is idle for longer than the maximum session idle time
Under these circumstances, OpenAM responds by removing stateful sessions from the memory heap of the OpenAM server on which the session resides, and from the Core Token Service's token store (if session failover is enabled). With the user's stateful session no longer in memory, OpenAM forces the user to reauthenticate on subsequent attempts to access resources protected by OpenAM.
When a user explicitly logs out of OpenAM, OpenAM also attempts to
invalidate the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie in users'
browsers by sending a Set-Cookie header with an invalid
session ID and a cookie expiration time that is in the past. In the case of
administrator session termination and session timeout, OpenAM cannot
invalidate the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie until the next
time the user accesses OpenAM.
Session termination differs for stateless sessions. Since stateless
sessions are not maintained in OpenAM's memory, administrators cannot
monitor or terminate stateless sessions. Because OpenAM does not modify
the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie for stateless sessions
after authentication, the session idle time is not maintained in the cookie.
Therefore, OpenAM does not automatically terminate stateless sessions
that have exceeded the idle timeout.
As with stateful sessions, OpenAM attempts to invalidate the
iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie from a user's browser when the
user logs out. When the maximum session time is exceeded, OpenAM also
attempts to invalidate the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie
in the user's browser the next time the user accesses OpenAM.
It is important to understand that OpenAM cannot guarantee cookie
invalidation. For example, the HTTP response containing the
Set-Cookie header might be lost. This is not an issue for
stateful sessions, because a logged out stateful session no longer exists in
OpenAM memory, and a user who attempts to reaccess OpenAM after previously
logging out will be forced to reauthenticate.
However, the lack of a guarantee of cookie invalidation is an issue for
deployments with stateless sessions. It could be possible for a
logged out user to have an iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie.
OpenAM could not determine that the user previously logged out. Therefore,
OpenAM supports a feature that takes additional action when users log out of
stateless sessions. OpenAM can maintain a list of logged out stateless
sessions in a session blacklist in the Core Token Service's token store.
Whenever users attempt to access OpenAM with stateless sessions, OpenAM
checks the session blacklist to validate that the user has not, in fact,
logged out.
For more information about session blacklist options, see "Configuring Session Blacklisting".
With stateful sessions, OpenAM ties users' sessions to specific servers. Servers can be added to OpenAM sites, but as servers are added, the overall workload balances gradually, assuming a short session lifetime. If an OpenAM server fails, sessions are retrieved from the Core Token Service's token store, and performance can take some time to recover. Crosstalk, an expensive operation, is incurred whenever a user arrives at an OpenAM server that is not the user's home server. Adding servers to OpenAM sites does not improve performance in a horizontally scalable manner; as more servers are added to a site, coordination among the servers becomes more complex.
Stateless sessions provide the following advantages:
- Elasticity and horizontal scalability
With stateless sessions, you can add and remove OpenAM servers to a site and the session load should balance horizontally. Elasticity is important for cloud deployments with very large numbers of users when there are significant differences between peak and normal system loads.
Stateful sessions provide the following advantages:
- Faster performance with equivalent hosts
Stateless sessions must send a larger cookie to the OpenAM server, and the JWT in the stateless session cookie must be decrypted. The decryption operation can significantly impact OpenAM server performance, reducing the number of session validations per second per host.
Because using stateless sessions provides horizontal scalability, overall performance on hosts using stateless sessions can be easily improved by adding more hosts to the OpenAM deployment.
- Full feature support
Stateful sessions support all OpenAM features. Stateless sessions do not. For information about restrictions on OpenAM usage with stateless sessions, see "Limitations When Using Stateless Sessions".
- Session information is not resident in browser cookies
With stateful sessions, all the information about the session resides on the OpenAM server. With stateless sessions, session information is held in browser cookies. This information could be very long-lived.
The following table contrasts the impact of using stateful and stateless sessions in an OpenAM deployment:
| Deployment Area | Stateful Session Deployment | Stateless Session Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Higher RAM consumption | Higher CPU consumption |
| Logical Hosts | Smaller number of hosts | Variable or large number of hosts |
| Session Monitoring | Available | Not available |
| Session Location | In OpenAM server memory heap | In a cookie in the user's browser |
| Session Failover | Requires session stickiness to be configured in the load balancer | Does not require session stickiness |
| Core Token Service Usage | Supports session failover | Supports session blacklisting for logged out sessions |
| Core Token Service Demand | Heavier | Lighter |
| Session Security | Sessions are not accessible to users because they reside in memory on the OpenAM server. | Sessions should be signed and encrypted. |
| Policy Agents | Sessions cached in the Policy Agent can receive change notification. | Sessions cached in the Policy Agent cannot receive change notification. |
Session blacklisting uses the Core Token Service's token store during the logout process. For more information about deploying the Core Token Service, see "Configuring the Core Token Service" in the Installation Guide.
Also, ensure the trust store used by OpenAM has the necessary certificates installed:
A certificate is required for encrypting JWTs containing stateless sessions.
If you are using RS256 signing, then a certificate is required to sign JWTs. (HMAC signing uses a shared secret.)
The same certificates must be stored on all servers participating in an OpenAM site.
To configure stateless sessions for a realm, follow these steps:
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > General.
Select the "Use Stateless Sessions" check box.
Click Save.
To verify that OpenAM creates a stateless session when non-administrative users authenticate to the realm, follow these steps:
Authenticate to the OpenAM console as the top-level administrator (by default, the
amadminuser). Note that theamadminuser's session will be stateful, because OpenAM sessions for the top-level administrator are always stateful.Select the Sessions tab.
Verify that a session is present for the
amadminuser.In your browser, examine the OpenAM cookie, named
iPlanetDirectoryProby default. Copy and paste the cookie's value into a text file and note its size.Start up a private browser session that will not have access to the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie for theamadminuser:On Chrome, open an incognito window.
On Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge, start InPrivate browsing.
On Firefox, open a new private window.
On Safari, open a new private window.
Authenticate to OpenAM as a non-administrative user in the realm for which you enabled stateless sessions. Be sure not to authenticate as the
amadminuser this time.In your browser, examine the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie. Copy and paste the cookie's value into a second text file and note its size. The size of the stateless session cookie's value should be considerably larger than the size of the stateful session cookie's value for theamadminuser. If the cookie is not larger, you have not enabled stateless sessions correctly.Return to the original browser window in which the OpenAM console appears.
Refresh the window containing the Sessions tab.
Verify that a session still appears for the
amadminuser, but that no session appears for the non-administrative user in the realm with stateless sessions enabled.
When using stateless sessions, you should sign and encrypt JWTs in
the iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie.
Prior to configuring stateless session cookie security, ensure that you have deployed certificates as needed. For more information about managing certificates for OpenAM, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".
To ensure security of stateless session cookie JWTs, configure a JWT signature and encrypt the entire JWT. The sections that follow provide detailed steps for configuring stateless session cookie security.
For more information about stateless session cookie security, see "Stateless Session Cookie Security".
Important
When deploying multiple OpenAM servers in an OpenAM site, every server must have the same security configuration. Shared secrets and security keys must be identical. If you modify shared secrets or keys, you must make the modifications to all the servers on the site.
Configure a JWT signature to prevent malicious tampering of stateless session cookies.
Perform the following steps to configure the JWT signature:
Navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Session, and then locate the Stateless Sessions section.
Specify the Signing Algorithm Type. The default value is
HS256.If you specified an HMAC signing algorithm, change the value in the Signing HMAC Shared Secret field if you do not want to use the generated default value.
If you specified the RS256 signing algorithm, specify a value in the Signing RSA Certificate Alias field to use for signing the JWT signature.
Click Save.
For detailed information about Session Service configuration attributes, see the entries for "Session" in the Reference.
Configure JWT encryption to prevent man-in-the-middle attackers from accessing users' session details, and to prevent end users from examining the content in the JWT.
Perform the following steps to encrypt the JWT:
Navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Session, and then scroll to the Stateless Sessions section.
Specify the Encryption Algorithm Type as a value other than NONE.
Specify a value in the Encryption RSA Certificate Alias to use for encrypting the JWT signature.
Click Save.
Ensure that the JWT signature configuration is identical on every OpenAM server in your OpenAM site.
For detailed information about Session Service configuration attributes, see the entries for "Session" in the Reference.
OpenAM supports Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithms (ECDSA) as an alternative to RSA cryptography (RS256) or HMAC with SHA (HS256, HS384, HS512) signatures (see the JSON Web Algorithms specification, RFC 7518). The elliptic curve algorithms provide smaller key lengths for the same level of security that RSA provides (256-bit elliptic curve key vs 2048-bits RSA). The smaller key lengths result in faster signature and key generation times, and faster data transmission over TLS. One disadvantage for ECDSA is that signature verification can be significantly slower on the JVM.
OpenAM supports the following elliptic curve signature algorithms:
ES256. Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) using SHA-256 hashes and the NIST standard P-256 elliptic curve. For more information on the NIST curves, see Digital Signature Standard (DSS).
ES384. ECDSA using SHA-384 hashes and NIST standard P-384 curve.
ES512. ECDSA using SHA-512 hashes and NIST standard P-521 curve.
Generate the public and private keys to use with the ECDSA algorithms using the standard curves parameters. You can use keytool to generate these key pairs. The following examples use a JCEKS keystore to store the keys:
To generate an ES256-compatible keypair (picks the P-256 NIST curve):
keytool -genkeypair -keystore mykeystore.jceks -alias ecdsa-test-cert -storepass xxx \ -keypass yyy -dname 'CN=...' -storetype JCEKS -keyalg ec -keysize 256 \ -validity 365To generate an ES384-compatible keypair (picks the P-384 NIST curve):
keytool -genkeypair -keystore mykeystore.jceks -alias ecdsa-test-cert -storepass xxx \ -keypass yyy -dname 'CN=...' -storetype JCEKS -keyalg ec -keysize 384 \ -validity 365To generate an ES512-compatible keypair (picks the P-521 NIST curve):
keytool -genkeypair -keystore mykeystore.jceks -alias ecdsa-test-cert -storepass xxx \ -keypass yyy -dname 'CN=...' -storetype JCEKS -keyalg ec -keysize 521 \ -validity 365Note
For ES512, the
-keysizeis521, not512.
Configure the ECDSA on OpenAM:
On the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click Session.
For the Signing Algorithm Type, select the ECDSA algorithm that matches the alias in your keystore. For example, select
ES256if you generated a ES256-compatible keypair.In the Signing RSA/ECDSA Certificate Alias field, enter the certificate alias that points to the ECDSA keypair.
Save your changes.
Session blacklisting ensures that users who have logged out of stateless sessions cannot achieve single sign-on without reauthenticating to OpenAM.
Perform the following steps to configure session blacklisting:
Make sure that you deployed the Core Token Service during OpenAM installation. The session blacklist is stored in the Core Token Service's token store.
Navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Session, and then locate the Stateless Sessions section.
Select the Enable Session Blacklisting option to enable session blacklisting for stateless sessions. When you configure one or more OpenAM realms for stateless sessions, you should enable session blacklisting in order to track session logouts across multiple OpenAM servers.
Configure the Session Blacklist Cache Size property.
OpenAM maintains a cache of logged out stateless sessions. The cache size should be around the number of logouts expected in the maximum session time. Change the default value of 10,000 when the expected number of logouts during the maximum session time is an order of magnitude greater than 10,000. An underconfigured session blacklist cache causes OpenAM to read blacklist entries from the Core Token Service store instead of obtaining them from cache, which results in a small performance degradation.
Configure the Blacklist Poll Interval property.
OpenAM polls the Core Token Service for changes to logged out sessions if session blacklisting is enabled. By default, the polling interval is 60 seconds. The longer the polling interval, the more time a malicious user has to connect to other OpenAM servers in a cluster and make use of a stolen session cookie. Shortening the polling interval improves the security for logged out sessions, but might incur a minimal decrease in overall OpenAM performance due to increased network activity.
Configure the Blacklist Purge Delay property.
When session blacklisting is enabled, OpenAM tracks each logged out session for the maximum session time plus the blacklist purge delay. For example, if a session has a maximum time of 120 minutes and the blacklist purge delay is one minute, then OpenAM tracks the session for 121 minutes. Increase the blacklist purge delay if you expect system clock skews in a cluster of OpenAM servers to be greater than one minute. There is no need to increase the blacklist purge delay for servers running a clock synchronization protocol, such as Network Time Protocol.
Click Save.
For detailed information about Session Service configuration attributes, see the entries for "Session" in the Reference.
The following OpenAM features are not supported in realms that use stateless sessions:
This chapter describes the configuration of Single Sign-On (SSO) services for multiple resources on one domain. To understand how SSO works, you need to understand some key elements of the HTTP cookie, as described in RFC 6525, HTTP State Management Mechanism.
With SSO, a user can access multiple independent services from a single session.
Within an HTTP cookie, you can store a single custom
name=value pair, such as
sessionid=value.
Other custom names within a cookie are as follows:
- Domain
Normally set to the full URL that was used to access the configurator. To work with multiple subdomains, the
Domainshould be set to a URL likeDomain=server.example.net. This is also known as the cookie domain, as defined in "Configuration Reference" in the Reference.- Path
The directory in the URL to which the cookie applies. If the
Path=/openam, the cookie applies to the/openamsubdirectory of the FQDN, and lower level directories, includingopenam/UIandopenam/UI/Login.- Secure
If the
Securename is included, the cookie can be transferred only over HTTPS. When a request is made over HTTP, the cookie is not made available to the application.- HttpOnly
When the
HttpOnlyname is included, that cookie will not be accessible through JavaScript. According to RFC 6265, the noted flag "instructs the user agent to omit the cookie when providing access to cookies via 'non-HTTP' APIs (for example, a web browser API that exposes cookies to scripts)."- Expires
The lifetime of a cookie can be limited, with an
Expiresname configured with a time, based on UTC (GMT).
Note
Be careful. Do not take a shortcut with a top-level domain. Web browser
clients today are designed to ignore cookies set to top-level domains including
com, net, and co.uk.
In addition, a cookie with a value like Domain=
app1.example.net will not work for similar subdomains, such as
app2.example.net.
OpenAM uses cookies to track user sessions. The diagram shown next illustrates how OpenAM assigns and tracks cookies.
In the diagram:
The domain shown in the description is
example.net.The protected resource application can be found on
app.example.net.The OpenAM server is located on
sso.example.net.
A client points their browser to a protected resource application. An agent on the application checks the client browser cookies for the presence of a session. If a session cookie exists and is valid, the agent requests validation (see arrow 8).
If no valid session cookie exists, the agent redirects the client to OpenAM for authentication (AuthN). The client is then sent to OpenAM for AuthN. If the client submits valid credentials, the AuthN service creates a session cookie for the configured domain. The contents of the session cookie varies, depending on the configuration of the realm to which the user authenticates:
If the realm is configured for stateful sessions, an SSO token is embedded in the cookie.
If the realm is configured for stateless sessions, the session itself is embedded in the cookie.
OpenAM issues an HTTP redirect to send the client browser back to the protected resource.
The agent then verifies the validity of the session with the OpenAM session service, before granting access.
In general, problems with SSO relate to some sort of mismatch of domain
names. For example, a cookie that is configured on a third-level domain, such
as sso.example.net will not work with an application on a
similar domain, such as app.example.net. Even if the Session
ID is valid, the application will not receive the SSO Token. The request is
then redirected to OpenAM. The client gets what appears as a SSO Token in the
diagram, which is actually a valid SSO tracking cookie that redirects immediately,
and the cycle continues. Other issues that may lead to similar problems are shown here:
When a cookie domain does not match a domain for the protected application.
Assume the application is configured on a domain named
example.org. That application will not receive an SSO Token configured on theexample.netdomain.When a third-level domain is used for the SSO Token.
If an SSO Token is configured on
sso.example.net, an application onapp.example.netdoes not receive the corresponding cookie. In this case, the solution is to configure the SSO Token onexample.net.When the
Secureflag is used with a regular HTTP application.If you need encrypted communications for an application protected by OpenAM, use the
Secureflag and make sure the application is accessible over HTTPS.When the path listed in the cookie does not match the path for the application.
Perhaps the cookie is configured with a
/helloworldpath; that will not match an application that might be configured with a/hellomarspath. In that case, the application will not receive the cookie.When an inappropriate name is used for the cookie domain
As noted earlier, client browsers are configured to ignore first-level domains, such as
comandnetas well as functional equivalents, such asco.ukandco.jp.When working with different browsers
The
name=valuepairs described earlier may not apply to all browsers. The requirements for an HTTP cookie sent to an IE browser may differ from the requirements for other standard browsers, such as Firefox and Chrome. Based on anecdotal reports, IE does not recognize domain names that start with a number. In addition, IE reportedly refuses cookies that include the underscore (_) character in the FQDN.When a stateless session cookie exceeds the maximum size permitted by the browser
As described in "Session Cookies", the default size of the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie is approximately 2,000 bytes. When you customize OpenAM sessions by adding attributes, the cookie size grows. Browsers allow cookie sizes between 4,000 and 5,200 bytes, depending on the browser. OpenAM single sign-on does not function correctly when the cookie size exceeds the maximum size allowed by the browser.
Now that you have read about the SSO process, you should be able to set it up on a server configured with OpenAM and a web service protected by an OpenAM agent. The following procedure assumes that you know how to configure OpenAM, the Apache Web server, and associated OpenAM Apache agent.
Install OpenAM as described in the Installation Guide. This procedure uses a Server URL of
http://openam.example.net:8080/openam.Install the appropriate policy agent, as described in the OpenAM Web Policy Agent User's Guide or the OpenAM Java EE Policy Agent User's Guide. This procedure uses an agent URL of
http://app.example.net:80, and an agent name ofwebagent1.Make sure that both URLs are configured with IP addresses, as described in "Installing OpenAM Core Services" in the Installation Guide.
Return to the OpenAM server on
http://openam.example.net:8080/openam. Log in as the administrative user, normallyamadmin. To activate and configure the agent, follow the procedure described in the OpenAM Web Policy Agent User's Guide or the OpenAM Java EE Policy Agent User's Guide.Now you can configure SSO Only mode. In the OpenAM console, click Realms > Realm Name > Agents >
webagent1. Scroll down to SSO Only Mode and activate the Enabled box.Save your changes.
Make sure you have configured the SSO domain, in this case,
example.net. Navigate to Configure > Global Services > System, and then click Platform. Make sureexample.net(or your chosen domain) is selected as a cookie domain.Save your changes.
Restart the web server. The agent should be active. You should now be able to log out of the OpenAM server.
Verify the agent URL, in this case,
http://app.example.net. The OpenAM web agent should now redirect requests to the OpenAM server.
If you want to configure OpenAM and an application on two different cookie
domains, such as example.org and example.net,
you will need to set up Cross-Domain SSO (CDSSO). For more information, see the
chapter on "Configuring Cross-Domain Single Sign-On".
This chapter shows you how to configure cross-domain single sign-on (CDSSO). When you have multiple domains in a single organization, CDSSO lets your OpenAM servers in one domain work with policy agents from other domains.
Cross-domain single sign-on provides a safe mechanism for managing access across multiple, different domains that you control. CDSSO lets OpenAM authenticate users redirected by policy agents in other DNS domains.
CDSSO is an OpenAM-specific capability. For single sign-on across multiple organizations or when integrating with other access management software, use OpenAM's federation capabilities.
CDSSO requires stateful OpenAM sessions. Be sure that OpenAM is configured for stateful sessions—the default configuration—before attempting to use CDSSO.
Single sign-on depends on cookies to store session information. Yet for security reasons, browsers do not let a web site in one domain to get access to a cookie from another domain. With CDSSO, the policy agents work around this by negotiating with OpenAM to allow access.
The Java EE policy agent allows CDSSO by using a mechanism to write the SSO token from OpenAM authentication to a cookie with the domain the host where the agent runs. The following sequence diagram illustrates this mechanism.
Whereas the Java EE policy agent has an endpoint specifically to handle the cookie domain translation, the web policy agent handles the request directly as shown in the following sequence diagram.
This chapter includes the following procedures:
The federation mechanism associated with SAML v2.0 can be used as an alternative to CDSSO for both Web and Java EE policy agents. While using SAML v2.0 adds complexity, it supports attribute mapping, which may be useful when the two domains are associated with data stores that use different attribute names. For details, see "Using Policy Agents With Standalone Mode".
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > SSO.
Scroll down and enable Cross Domain SSO.
Check that the CDSSO Redirect URI is set.
Depending on where you deployed your Java EE agent application, the default is something like
/agentapp/sunwCDSSORedirectURI.Set the list of URLs for CDSSO Servlet URL to the Cross Domain Controller Servlet URLs of the servers the agent accesses, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.If the agent accesses OpenAM through a load balancer, use the load balancer URLs, such as
http://load-balancer.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.Leave the CDSSO Clock Skew set to 0.
Make sure instead that the clocks on the servers where you run OpenAM and policy agents are synchronized.
Set the list of URLs for CDSSO Trusted ID Provider to the Cross Domain Controller Servlet URLs of the OpenAM servers the agent accesses, such
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.This list should include one CDC Servlet URL for every OpenAM server the agent might access. You do not need to include site or load balancer URLs.
(Optional) To protect the SSO token from network snooping, you can select CDSSO Secure Enable to mark the SSO token cookie as secure.
If you select this, then the SSO token cookie can only be sent over a secure connection (HTTPS).
Add the domains involved in CDSSO in the CDSSO Domain List.
If necessary, update the Agent Root URL for CDSSO list on the Global tab page.
If the policy agent is on a server with virtual host names, add the virtual host URLs to the list.
If the policy agent is behind a load balancer, add the load balancer URL to the list.
Save your work.
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Web > Agent Name > SSO.
Enable Cross Domain SSO.
Set the list of URLs for CDSSO Servlet URL to the Cross Domain Controller Servlet URLs of the servers the agent accesses, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.If the agent accesses OpenAM through a load balancer, use the load balancer URLs, such as
http://load-balancer.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet.Add the domains involved in CDSSO in the Cookies Domain List.
If necessary, update the Agent Root URL for CDSSO list on the Global tab page.
If the policy agent is on a server with virtual host names, add the virtual host URLs to the list.
If the policy agent is behind a load balancer, add the load balancer URL to the list.
Save your work.
The default self-submitting form page that OpenAM presents to users contains hidden fields, but is otherwise blank. If you want to show users that the operation is in progress, then customize the necessary JSP.
Edit a copy of the file
config/federation/default/cdclogin.jspto add a clue that SSO is in progress, such as an image.You can find this file where you deployed OpenAM, such as
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/config/federation/default/cdclogin.jsp.When you add an image or other presentation element, make sure that you retain the form and JavaScript as is.
Unpack OpenAM-13.5.2.war, and replace the file with your modified version.
Also include any images you reference in the page.
Pack up your custom version of OpenAM, and then deploy it in your web container.
When a client makes an access request to some protected resource in a cross
domain single sign-on deployment, the policy agent
redirects the client to the Cross Domain Controller Servlet (CDCServlet) URL.
The CDCServlet determines that the client needs to be authenticated and proxies
the request through to an authentication interface, which typically is at /UI/Login:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login
If your application requires access to a specific URL, you can use the
loginURI parameter to do so.
For example, you can access the previous authentication UI URL as follows:
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet?loginURI=/UI/Login
If you have another authentication UI deployed at
/openam/customLoginURI, you can access this URL at:http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/cdcservlet?loginURI=/customLoginURI
In this case, you must also add the custom login URI to the whitelist that is specified by using the
org.forgerock.openam.cdc.validLoginURIsproperty.In the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced.
Set the value of the
org.forgerock.openam.cdc.validLoginURIsproperty to/UI/Login,/customLoginURI.Save your work.
For more information about this property, see "Advanced" in the Reference.
When cookies are set for an entire domain, such as
.example.com, an attacker who steals a cookie can use it
from any host in the domain, such as untrusted.example.com.
Cookie hijacking protection restricts cookies to the fully-qualified domain
name (FQDN) of the host where they are issued, such as
openam-server.example.com and
server-with-agent.example.com, using CDSSO to handle
authentication and authorization.
For CDSSO with cookie hijacking protection, when a client successfully authenticates OpenAM issues the master SSO token cookie for its FQDN. OpenAM issues restricted token cookies for the other FQDNs where the policy agents reside. The client ends up with cookies having different session identifiers for different FQDNs, and the OpenAM server stores the correlation between the master SSO token and restricted tokens, such that the client only has one master session internally in OpenAM.
To protect against cookie hijacking, you restrict the OpenAM server domain to the server where OpenAM runs. This sets the domain of the SSO token cookie to the host running the OpenAM server that issued the token. You also enable use of a unique SSO token cookie. For your Java EE policy agents, you enable use of the unique SSO token cookie in the agent configuration.
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Configuration > Global Services > System, and then select Platform.
Remove all domains from the Cookies Domains list.
Save your work.
Navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced.
Change the value of the
com.sun.identity.enableUniqueSSOTokenCookieproperty totrue, from the defaultfalse.Make sure that the property
com.sun.identity.authentication.uniqueCookieNameis set to the name of the cookie that will hold the URL to the OpenAM server that authenticated the user.The default name is
sunIdentityServerAuthNServer.Save your work.
Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced, and add the property
com.sun.identity.authentication.uniqueCookieDomain, setting the value to the FQDN of the current OpenAM server, such asopenam.example.com.Save your work.
(Optional) For each Java EE policy agent, navigate to Realms >Realm Name > Agents > J2EE > Agent Name > Advanced > Custom Properties, and add the
com.sun.identity.enableUniqueSSOTokenCookie=trueproperty to the list.Save your work.
Restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for the configuration changes to take effect.
This chapter addresses how to set up and manage SAML v2.0 for single sign-on (SSO) and single logout (SLO) across resources belonging to organizations participating in a circle of trust.
SAML v2.0 SSO is part of federated access management. Federation lets access management cross organizational boundaries. Federation helps organizations share identities and services without giving away their identity information, or the services they provide.
To bridge heterogeneous systems, federation requires interoperability, and thus depends on standards for orchestrating interaction and exchanging information between providers. OpenAM federation relies on standards, such as Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) v2.0. SAML v2.0 describes the messages, how they are relayed, how they are exchanged, and common use cases.
To achieve SAML v2.0 SSO, OpenAM separates identity providers from service providers, lets you include them in a circle of trust and configure how the providers in the circle of trust interact:
An identity provider stores and serves identity profiles, and handles authentication.
A service provider offers services that access protected resources and handles authorization.
A circle of trust groups at least one identity provider and at least one service provider who agree to share authentication information with assertions about authenticated users that let service providers make authorization decisions.
Providers in a circle of trust share metadata, configuration information that federation partners require to access each others' services.
SAML v2.0 SSO maps attributes from accounts at the identity provider to attributes on accounts at the service provider. The identity provider makes assertions to the service provider, for example, to attest that a user has authenticated with the identity provider. The service provider then consumes assertions from the identity provider to make authorization decisions, for example to let an authenticated user complete a purchase that gets charged to the user's account at the identity provider.
In federation deployments where not all providers support SAML v2.0, OpenAM can act as a multi-protocol hub, translating for providers who rely on other and older standards, such as SAML v1.x, Liberty Alliance Project frameworks, and WS-Federation (for integration with Active Directory Federation Services, for example).
Before you set up SAML v2.0 SSO in OpenAM, you must:
Know which providers will participate in circles of trust.
Know how OpenAM installations act as identity providers or service providers.
Determine whether your session state configuration limits your usage of certain SAML v2.0 profiles. For more information, see "SAML v2.0 and Session State".
Agree with other providers on a synchronized time service.
Define how to map shared user attributes in identity information exchanged with other participants in a circle of trust. Local user profile attribute names should map to user profile attribute names at other providers.
For example, if you exchange user identifiers with your partners, and you call it
uid, whereas another partner calls ituserid, then you map youruidto your partner'suserid.Import the keys used to sign assertions into the keystore in your OpenAM configuration directory. You can use the Java keytool command.
For more information about OpenAM keystores, including location and different types of keystores available and how to change the default keys, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".
Setting up and managing SAML v2.0 for SSO and SLO comprises three processes:
Configuring identity providers, service providers, and circles of trust.
OpenAM provides wizards that let you configure SAML v2.0 identity providers, service providers, and circles of trust, which define the relationships among providers. You can also configure providers and circles of trust using the OpenAM console and the ssoadm command.
See "Configuring Identity Providers, Service Providers, and Circles of Trust" for procedures to configure identity providers, service providers, and circles of trust.
Preparing your applications to initiate SSO and SLO.
After configuring the providers and circles of trust, you can implement OpenAM's support for SSO and SLO in your applications.
See "Implementing SAML v2.0 Single Sign-On and Single Logout" for procedures to implement SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO in OpenAM.
Managing federated accounts.
After you have implemented SAML v2.0 single sign-on, there are several tasks you might perform when using federated account linking.
See "Managing Federated Accounts" for procedures to manage federated accounts.
This section covers configuration tasks you perform before you can implement SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO.
During setup, you must share metadata for providers that you host with other providers in the circle of trust. You must also configure remote providers, connecting to other providers by importing their metadata. In OpenAM terms, a hosted provider is one served by the current OpenAM server; a remote provider is one hosted elsewhere.
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
| Task | See Section(s) |
|---|---|
|
(Required) Creating identity and service providers. |
"Creating a Hosted Identity Provider" "Creating a Hosted Service Provider" |
|
(Optional) Creating a fedlet for an OpenAM service provider. A fedlet is an example web application that acts as a lightweight SAML v2.0 service provider. | "Using the Fedlet" |
|
(Optional) Deploying an identity provider discovery service. When your circle of trust includes multiple identity providers, then service providers must discover which identity provider corresponds to a request. You can deploy the identity provider discovery service for this purpose as a separate web application. | "Deploying the Identity Provider Discovery Service" |
|
(Optional) Modifying identity provider, service provider, and circle of trust configurations. You might need to modify these configurations after you have created them using the wizards. |
"Modifying an Identity Provider's Configuration" |
| (Optional) Configuring providers for failover. | "Configuring Providers for Failover" |
| (Optional) Configuring Google Apps and Salesforce CRM as service providers. |
The following procedure provides steps for creating a hosted identity provider by using the Create Hosted Identity Provider wizard:
Under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers, click Create Hosted Identity Provider.
Unless you already have metadata for the provider, accept the Name for this identity provider in the field provided, or provide your own unique identifier.
The default name is the URL to the current server which hosts the identity provider.
Select the Signing Key alias you imported into the OpenAM keystore as part of your preparation for SAML v2.0 configuration.
Either add the provider to the circle of trust you already created, or select the Add to new option and provide a New Circle of Trust name.
For the attributes you share, map service provider attribute names (Name in Assertion), to user profile names from your identity repository (Local Attribute Name).
Use this approach to set up a mapping with all SPs in the circle of trust that do not have their own specific mappings configured.
The default mapping implementation has additional features beyond simply retrieving string attributes from the user profile.
Add an attribute that takes a static value by enclosing the profile attribute name in double quotes (
").For example, you can add a static SAML attribute called
partnerIDwith a value ofstaticPartnerIDValueby addingpartnerIDas the Name in Assertion with"staticPartnerIDValue"as the Local Attribute Name.Base64 encode binary attributes when adding them to the SAML attributes by adding
;binaryto the end of the attribute name, as in the following example:objectGUID=objectGUID;binary
This maps the local binary attribute
objectGUIDto a SAML attribute calledobjectGUIDthat is Base64 encoded.Use
NameFormatURIformat as shown in the following example:urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|objectGUID=objectGUID;binary
Click Configure to save your configuration.
Export the XML-based metadata from your provider to share with other providers in your circle of trust.
$ curl \ --output metadata.xml \ "http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/exportmetadata.jsp?entityid=\ http://www.idp.example:8080/openam&realm=/realm-name"
When you have configured your provider in the Top Level Realm, you can omit the query string from the URL.
Alternatively, provide the URL to other providers so they can load the metadata.
The following procedure provides steps for creating a hosted service provider by using the Create Hosted Service Provider wizard:
Under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers, click Create Hosted Service Provider.
Unless you already have metadata for the provider, accept the Name for this service provider in the field provided, or provide your own unique identifier.
The default name is the URL to the current server which hosts the service provider.
Either add the provider to the circle of trust you already created, or select the Add to new option and provide a New Circle of Trust name.
(Optional) If this SP requires more a different attribute mapping configuration than the default IdP attribute mapping, set the mapping in the Attribute Mapping section. Map identity provider attribute names in the Name in Assertion column to user profile names from your identity repository in the Local Attribute Name column.
Click Configure to save your configuration.
Export the XML-based metadata from your provider to share with other providers in your circle of trust:
$ curl \ --output metadata.xml \ "http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/exportmetadata.jsp?entityid=\ http://www.sp.example:8080/openam&realm=/realm-name"
When you have configured your provider in the Top Level Realm, you can omit the query string from the URL.
Alternatively, provide the URL to other providers so they can load the metadata.
The following procedure provides steps for configuring a remote identity provider by using the Register Remote Identity Provider wizard:
Obtain the identity provider metadata or the URL where you can obtain it.
Under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers, click Configure Remote Identity Provider.
Provide the identity provider metadata or link to obtain metadata.
The remote identity provider's metadata might contain more than one
KeyDescriptorelements. If it does, the hosted OpenAM service provider will validate assertions from the identity provider against certificates with key descriptors with an appropriateuseattribute. Incoming assertions that cannot be validated against any of the certificates will be rejected by the hosted service provider.Either add the provider to the circle of trust you already created, or select Add to new and provide a New Circle of Trust name.
Click Configure to save your configuration.
The following procedure provides steps for configuring a remote service provider by using the Register Remote Service Provider wizard:
Obtain the service provider metadata, or the URL where you can obtain it.
Under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers, click Configure Remote Service Provider.
Provide the service provider metadata or link to obtain metadata.
The remote service provider's metadata might contain more than one
KeyDescriptorelement. In this case, the hosted identity provider should consider any incoming SAML requests from the service provider to be valid as long as it can be validated with any of the certificates.(Optional) If the identity provider has not already mapped the attributes you share, map identity provider attribute names (Name in Assertion) to user profile names from your identity repository (Local Attribute Name).
Use this approach to set up a mapping that is specific to this SP. Note that a remote SP-specific attribute mapping overrides the attribute mapping configuration specified in the hosted IdP configuration.
The default mapping implementation has additional features beyond simply retrieving string attributes from the user profile.
Add an attribute that takes a static value by enclosing the profile attribute name in double quotes (
").For example, you can add a static SAML attribute called
partnerIDwith a value ofstaticPartnerIDValueby addingpartnerIDas the Name in Assertion with"staticPartnerIDValue"as the Local Attribute Name.Base64 encode binary attributes when adding them to the SAML attributes by adding
;binaryto the end of the attribute name, as in the following example:objectGUID=objectGUID;binary
This maps the local binary attribute
objectGUIDto a SAML attribute calledobjectGUIDthat is Base64 encoded.Use
NameFormatURIformat as shown in the following example:urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|objectGUID=objectGUID;binary
Either add the provider to the circle of trust you already created, or select Add to new and provide a New Circle of Trust name.
Click Configure to save your configuration.
When your organization acts as the identity provider and you want to enable service providers to federate their services with yours, you can generate configuration files for a Fedlet. A Fedlet is a small Java web application that can act as a service provider for a specific identity provider without requiring that you install all of OpenAM.
After receiving the configuration files for the Fedlet, the service provider administrator installs them, and then obtains the Fedlet web application from the OpenAM distribution and installs it in the application web container.
Fedlets support SAML v2.0 features, as shown in the following table:
| SAML v2.0 Feature | Java Fedlet |
|---|---|
| IdP and SP-initiated Single Sign-On (HTTP Artifact) | Supported |
| IdP and SP-initiated Single Sign-On (HTTP POST) | Supported |
| IdP and SP-initiated Single Logout (HTTP POST) | Supported |
| IdP and SP-initiated Single Logout (HTTP Redirect) | Supported |
| Sign Requests and Responses | Supported |
| Encrypt Assertion, Attribute, and NameID Elements | Supported |
| Export SP Metadata | Supported |
| Attribute Queries | Supported |
| XACML Requests | Supported |
| Multiple IdPs | Supported |
| External IdP Discovery Service | Supported |
| Bundled IdP Reader Service for Discovery | Supported |
For more information on installing and using Fedlets, see "Building SAML v2.0 Service Providers With Fedlets" in the Developer's Guide.
When your circle of trust includes multiple identity providers, then service providers must discover which identity provider corresponds to a request. You can deploy the identity provider discovery service for this purpose as a separate web application.
Browsers only send cookies for the originating domain. Therefore,
when a browser accesses the service provider in the www.sp.example
domain, the service provider has no way of knowing whether the user has
perhaps already authenticated at www.this-idp.example or at
www.that-idp.example. The providers therefore host an identity
provider discovery service in a common domain, such as
www.disco.example, and use that service to discover where
the user logged in. The identity provider discovery service essentially
writes and reads cookies from the common domain. The providers configure
their circle of trust to use the identity provider discovery service
as part of SAML v2.0 federation.
Deploying the identity provider discovery service involves the following stages:
Deploy the
.warinto your web application container.Configure the discovery service.
Add the identity provider discovery service endpoints for writing cookies to and reading cookies from the common domain to the circle of trust configurations for the providers.
Share metadata between identity providers and the service provider.
How you deploy the discovery service .war file depends
on your web application container. The procedure in this section shows how
to deploy on Apache Tomcat.
Copy the
IDPDiscovery-13.5.2.warfile to thewebapps/directory.$ cp ~/Downloads/openam/IDPDiscovery-13.5.2.war \ /path/to/tomcat/webapps/disco.war
Access the configuration screen through your browser.
In this example, Apache Tomcat listens for HTTP requests on
www.disco.example:8080, and Tomcat has unpacked the application under/disco, so the URL ishttp://www.disco.example:8080/disco, which redirects toConfigurator.jsp.
Configure the identity provider discovery service.
Hints for discovery service configuration parameters follow.
- Debug Directory
The discovery service logs to flat files in this directory.
- Debug Level
Default is
error. Other options includeerror,warning,message, andoff.Set this to
messagein order to see the service working when you run your initial tests.- Cookie Type
Set to PERSISTENT if you have configured OpenAM to use persistent cookies, meaning single sign-on cookies that can continue to be valid after the browser is closed.
- Cookie Domain
The cookie domain is the common cookie domain used in your circle of trust for identity provider discovery, in this case
.disco.example.- Secure Cookie
Set this to true if clients should only return cookies when a secure connection is used.
- Encode Cookie
Leave this true unless your OpenAM installation requires that you do not encode cookies. Normally, cookies are encoded such that cookies remain valid in HTTP.
- HTTP-Only Cookie
Set to true to use HTTPOnly cookies if needed to help prevent third-party programs and scripts from accessing the cookies.
Restrict permissions to the discovery service configuration file in
$HOME/libIDPDiscoveryConfig.properties, where $HOME corresponds to the user who runs the web container where you deployed the service.
Each provider has a circle of trust including itself. You configure each of these circles of trust to use the identity provider discovery service as described in the following steps:
On the service provider console, login as OpenAM Administrator.
On the service provider console, under Federation > Circle of Trust > Circle of Trust Name, add SAML2 Writer and Reader Service URLs for the identity provider discovery service endpoints, and Save your work.
In this example, the writer URL is
http://www.disco.example:8080/disco/saml2writer, and the reader URL ishttp://www.disco.example:8080/disco/saml2reader.On each identity provider console, login as OpenAM Administrator.
On the identity provider console, under Federation > Circle of Trust Configuration > Circle of Trust Name, also add SAML2 Writer and Reader Service URLs for the identity provider discovery service endpoints, and Save your work.
Once you have set up an identity provider, you can configure it through the OpenAM console under Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Assertion Content tab page:
- Request/Response Signing
Specifies what parts of messages the identity provider requires the service provider to sign digitally.
- Encryption
When selected, the service provider must encrypt NameID elements.
- Certificate Aliases
Specifies aliases for certificates in the OpenAM keystore that are used to handle digital signatures, and to handle encrypted messages.
Specify a Key Pass if the private key password is different from the keystore password, which is stored encrypted in the
.keypassfile for the server. For instructions on working with key pairs, also see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".You can specify lists of aliases for signing and encryption:
If you specify multiple aliases in the Signing property, OpenAM uses the first key alias from the list to sign SAML assertions.
If you specify multiple aliases in the Encryption property, OpenAM will attempt to decrypt incoming protocol messages with all matching certificates in the list until decryption is successful.
When a certificate is about to expire, add a new alias to either field to enable OpenAM to maintain the trust relationship between entities for a longer period of time. Make sure that the remote providers also update their copy of the OpenAM provider's metadata to ensure the key rollover process is seamless.
- NameID Format List
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on. If no name identifier is specified when initiating single sign-on, then the identity provider uses the first one that is supported by both providers.
- NameID Value Map
Maps name identifier formats to user profile attributes. The
persistentandtransientname identifiers need not be mapped.NameID mapping supports Base64-encoded binary values by adding a
;binaryflag to the mapping. With this flag set, OpenAM Base64-encodes the profile attribute when adding it to the assertion. The mapping may resemble the following:urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent=objectGUID;binary- Disable NameID Persistence
Disables the storage of the NameID values in the user data store for all NameIDs issued by the IdP instance as long as the NameID format is anything but the persistent NameID format:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent. That is, you can disable the storage of NameID values with persistent NameID-Format if and only if there is a NameID value mapping set up for the NameID-Format.Note
By preventing the storage of the NameID values, the
ManageNameIDand theNameIDMappingSAML profiles will no longer work when using any persistent NameID formats. Existing account links that have been established and stored are not removed when disabling NameID persistence.Attribute:
idpDisableNameIDPersistenceDefault value:
false
- Mapper
Specifies a class that implements the
IDPAuthnContextMapperinterface and sets up the authentication context.Attribute:
idpAuthnContextMapperDefault value:
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultIDPAuthnContextMapper- Authentication Context Class Ref Mapping
Specifies the mapping between a SAML v2.0 authentication context class reference and the OpenAM authentication scheme.
Attribute:
idpAuthncontextClassrefMappingDefault value:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport|0||default- Supported Contexts
Specifies the supported authentication contexts, where the Key and Value can specify a corresponding OpenAM authentication method, and the Level corresponds to an authentication module authentication level.
- Not-Before Time Skew
Grace period in seconds for the
NotBeforetime in assertions.- Effective Time
Validity in seconds of an assertion.
- Enabled, User Name, Password
When enabled, authenticate with the specified user name and password at SOAP end points.
- Enabled
When enabled, cache assertions.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Assertion Processing tab page:
- Attribute Mapper
Specifies a class that implements the attribute mapping.
The default implementation attempts to retrieve the mapped attribute values from the user profile first. If the attribute values are not present in the user's profile, then it attempts to retrieve them from the user's session.
Default:
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultIDPAttributeMapper- Attribute Map
Maps SAML attributes to user profile attributes.
The user profile attributes used here must both be allowed in user profiles, and also be specified for the identity repository. See "Customizing Profile Attributes" in the Developer's Guide, for instructions on allowing additional attributes in user profiles.
To specify the list of profile attributes for an LDAP identity repository, login to OpenAM console as administrator and browse to Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores, and click the data store name to open the configuration page. Scroll down to User Configuration, and edit the LDAP User Attributes list, and then click Save to keep your work.
The default IdP mapping implementation allows you to add static values in addition to values taken from the user profile. You add a static value by enclosing the profile attribute name in double quotes (
"), as in the following examples.To add a static SAML attribute called
nameIDwith a value ofstaticNameIDValuewith a name format ofurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri, add the following mapping.urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|nameID="staticNameIDValue"
- Account Mapper
Specifies a class that implements
AccountMapperto map remote users to local user profiles.
- Auth URL
URL where users are redirected to authenticate.
- Reverse Proxy URL
When a reverse proxy is used for SAML endpoints, it is specified here.
- External Application Logout URL
URL to which to send an HTTP POST including all cookies when receiving a logout request. To add a user session property as a POST parameter, include it in the URL query string as a
appsessionpropertyparameter.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Services tab page:
- MetaAlias
Used to locate the provider's entity identifier, specified as
[/realm-name]*/provider-name, where provider-name cannot contain slash characters (/). For example:/myRealm/mySubrealm/idp.
- Artifact Resolution Service
Specifies the end point to handle artifact resolution. The Index is a unique number identifier for the end point.
- Single Logout Service
Specifies the end points to handle single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
Specifies the end points to handle name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Single SignOn Service
Specifies the end points to handle single sign-on.
- URL
Specifies the end point to handle name identifier mapping.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Advanced tab page:
- IDP URL
Specifies the end point to handle Secure Attribute Exchange requests.
- Application Security Configuration
Specifies how to handle encryption for Secure Attribute Exchange operations.
- IDP Session Mapper
Specifies the class that finds a valid session from an HTTP servlet request to an identity provider with a SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy profile.
- Enabled
When enabled, the identity provider sends a SOAP logout request over the back channel to all service providers when a session times out. A session may time out when the maximum idle time or maximum session time is reached, for example.
- IDP Finder Implementation Class
Specifies a class that finds the preferred identity provider to handle a proxied authentication request.
- IDP Finder JSP
Specifies a JSP that presents the list of identity providers to the user.
- Enable Proxy IDP Finder For All SPs
When enabled, apply the finder for all remote service providers.
- Relay State URL List
List of URLs permitted for the
RelayStateparameter. OpenAM validates the redirection URL in theRelayStateparameter against this list. If theRelayStateparameter's value is in the list, OpenAM allows redirection to theRelayStateURL. If it is not in the list, a browser error occurs.Use the pattern matching rules described in "Configuring Valid goto URL Resources" to specify URLs in the list.
If you do not specify any URLs in this property, OpenAM does not validate the
RelayStateparameter.
- IDP Adapter Class
Specifies a class to invoke immediately before sending a SAML v2.0 response.
Once you have set up a service provider, you can configure it through the OpenAM console under Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Assertion Content tab page:
- Request/Response Signing
Specifies what parts of messages the service provider requires the identity provider to sign digitally.
- Encryption
The identity provider must encrypt selected elements.
- Certificate Aliases
Specifies aliases for certificates in the OpenAM keystore that are used to handle digital signatures, and to handle encrypted messages.
You can specify lists of aliases for signing and encryption:
If you specify multiple aliases in the Signing property, OpenAM uses the first key alias from the list to sign SAML assertions.
If you configure multiple aliases in the Encryption property, OpenAM will use all private keys associated with the aliases until decryption is successful.
When a certificate is about to expire, add a new alias to either field to enable OpenAM to maintain the trust relationship between entities for a longer period of time. Make sure that the remote providers also update their copy of the OpenAM provider's metadata to ensure the key rollover process is seamless.
- NameID Format List
Specifies the supported name identifiers for users that are shared between providers for single sign-on. If no name identifier is specified when initiating single sign-on, then the service provider uses the first one in the list supported by the identity provider.
- Disable Federation Persistence
Disables the storage of NameIDs in the user data store even if the
NameIDformat isurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentin the received assertion and the account mapper has identified the local user.Note
When local authentication is utilized for account linking purposes, disabling federation persistence requires end users to authenticate locally for each SAML-based login.
Attribute:
spDoNotWriteFederationInfoDefault value:
false
- Mapper
Specifies a class that implements the
SPAuthnContextMapperinterface and sets up the authentication context.- Default Authentication Context
Specifies the authentication context used if no authentication context specified in the request.
- Supported Contexts
Specifies the supported authentication contexts. The Level corresponds to an authentication module authentication level.
- Comparison Type
How the authentication context in the assertion response must compare to the supported contexts.
- Assertion Time Skew
Grace period in seconds for the
NotBeforetime in assertions.
- Enabled, User Name, Password
When enabled, authenticate with the specified user name and password at SOAP end points.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Assertion Processing tab page:
- Attribute Mapper
Specifies a class that implements the attribute mapping.
- Attribute Map
Maps SAML attributes to user profile attributes.
- Enabled
When enabled, automatically federate user's accounts at different providers based on the specified SAML attribute.
- Attribute
Specifies the SAML attribute to match accounts at different providers.
- Account Mapper
Specifies a class that implements
AccountMapperto map remote users to local user profiles.- Use Name ID as User ID
When selected, fall back to using the name identifier from the assertion to find the user.
- Encoding
Specifies the message encoding format for artifacts.
- Transient User
Specifies the user profile to map all identity provider users when sending transient name identifiers.
- Local Authentication URL
Specifies the local login URL.
- Intermediate URL
Specifies a URL to which the user is redirected after authentication but before the original URL requested.
- External Application Logout URL
Specifies the URL to which to send an HTTP POST including all cookies when receiving a logout request. To add a user session property as a POST parameter, include it in the URL query string as a
appsessionpropertyparameter.
- Default Relay State URL
Specifies the URL to which to redirect users after the request has been handled. Used if not specified in the response.
- Adapter
Specifies a class that implements the
FederationSPAdapterinterface and performs application specific processing during the federation process.- Adapter Environment
Specifies environment variables passed to the adapter class.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Services tab page:
- MetaAlias
Used to locate the hosted provider's entity identifier, specified as
[/realm-name]*/provider-name, where provider-name can not contain slash characters (/). For example:/myRealm/mySubrealm/sp.
- Single Logout Service
Specifies the end points to handle single logout, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Manage NameID Service
Specifies the end points to handle name identifiers, depending on the SAML binding selected.
- Assertion Consumer Service
Specifies the end points to consume assertions, with Index corresponding to the index of the URL in the standard metadata.
Use the following hints to adjust settings on the Advanced tab page:
- SP URL
Specifies the end point to handle Secure Attribute Exchange requests.
- SP Logout URL
Specifies the end point of the service provider that can handle global logout requests.
- Application Security Configuration
Specifies how to handle encryption for Secure Attribute Exchange operations.
- Request IDP List Finder Implementation
Specifies a class that returns a list of preferred identity providers trusted by the SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy profile.
- Request IDP List Get Complete
Specifies a URI reference used to retrieve the complete identity provider list if the
IDPListelement is not complete.- Request IDP List
Specifies a list of identity providers for the SAML Enhanced Client or Proxy to contact, used by the default implementation of the IDP Finder.
- IDP Proxy
When enabled, allow proxied authentication for this service provider.
- Introduction
When enabled, use introductions to find the proxy identity provider.
- Proxy Count
Specifies the maximum number of proxy identity providers.
- IDP Proxy List
Specifies a list of URIs identifying preferred proxy identity providers.
- Enabled
When enabled, the service provider sends a SOAP logout request over the back channel to all identity providers when a session times out. A session may time out when the maximum idle time or maximum session time is reached, for example.
- Relay State URL List
List of URLs permitted for the
RelayStateparameter. OpenAM validates the redirection URL in theRelayStateparameter against this list. If theRelayStateparameter's value is in the list, OpenAM allows redirection to theRelayStateURL. If it is not in the list, a browser error occurs.Use the pattern matching rules described in "Configuring Valid goto URL Resources" to specify URLs in the list.
If you do not specify any URLs in this property, OpenAM does not validate the
RelayStateparameter.
Once you have set up a circle of trust, you can configure it through the OpenAM console under Federation > Circle of Trust > Circle of Trust Name.
- Name
String to refer to the circle of trust.
- Description
Short description of the circle of trust.
- IDFF Writer Service URL
Liberty Identity Federation Framework service that writes identity provider entity identifiers to Common Domain cookies after successful authentication, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
http://www.disco.example:8080/openam/idffwriter.- IDFF Reader Service URL
Liberty Identity Federation Framework service that reads identity provider entity identifiers from Common Domain cookies, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
http://www.disco.example:8080/openam/transfer.- SAML2 Writer Service URL
SAML v2.0 service that writes identity provider entity identifiers to Common Domain cookies after successful authentication, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
http://www.disco.example:8080/openam/saml2writer.- SAML2 Reader Service URL
SAML v2.0 service that reads identity provider entity identifiers from Common Domain cookies, used in identity provider discovery. Example:
http://www.disco.example:8080/openam/saml2reader.- Status
Whether this circle of trust is operational.
- Realm
Name of the realm participating in this circle of trust.
- Entity Providers
Known hosted and remote identity and service providers participating in this circle of trust.
OpenAM servers can function in a site configuration behind a load balancer. In addition to configuring the OpenAM site as described in "Setting Up OpenAM Session Failover" in the Installation Guide, update provider metadata to reference the load balancer rather than the server as follows:
Before configuring the provider, follow the instructions in the Installation Guide mentioned above, and make sure that failover works through the load balancer for normal OpenAM sessions.
Configure the provider on one of the servers using the load balancer URL as the entity ID.
Export the metadata and extended metadata for the provider. You can export metadata either by using the ssoadm command, or by using the
ssoadm.jsppage in the OpenAM console. For more information about using thessoadm.jsppage, see "OpenAM ssoadm.jsp".With the ssoadm command, you can export the metadata as shown in the following example for an Identity Provider, where the entity ID is
http://lb.example.com:80/openam.$ ssoadm \ export-entity \ --entityid "http://lb.example.com:80/openam" \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --meta-data-file idp.xml \ --extended-data-file idp-extended.xml
Edit both the metadata and the extended metadata, changing all URLs in both files to use the load balancer URL.
Delete the provider configuration in OpenAM console.
Import the edited provider configuration in OpenAM console.
Enable SAML v2.0 failover in OpenAM console.
Navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click SAMLv2 Service Configuration.
Select Enabled next to Enable SAMLv2 failover, and then click Save.
At this point failover is operational for the provider you configured.
OpenAM can serve as the identity provider when you use Google Apps as a service provider, allowing users to have single sign-on with their Google Apps account.
In order to use this service, you must have a Google Apps account for
at least one of your domains, such as example.com.
If you have not yet done so, set up OpenAM as described in "To Create a Hosted Identity Provider". As part of the IdP configuration, you specify a signing key alias. In a subsequent step, you will provision Google Apps with this certificate's public key.
For details about changing the signing certificate, see "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ".
Under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard, click Configure Google Apps.
On the first Configure Google Apps for Single Sign-On page, add your domain name(s), such as
example.comto the list, and then click Create.On the second Configure Google Apps for Single Sign-On page, save the OpenAM verification certificate to a text file, such as
OpenAM.pem.Follow the instructions under To Enable Access to the Google Apps API before clicking Finish.
Access the Google Apps administration page for the first of your domains in a new browser tab or window.
Login as Google Apps administrator.
Select Enable Single Sign-On.
Copy the URLs from the OpenAM page into the Google Apps setup screen.
Upload the certificate file you saved, such as
OpenAM.pemas the Google Apps Verification Certificate.Select Use a domain specific issuer.
Save changes in Google Apps setup.
Repeat the steps above for each domain you have configured.
Click Finish to complete the process.
OpenAM can serve as the identity provider when you use Salesforce CRM as a service provider, allowing users to have single sign-on with their Salesforce CRM account.
In order to use this service, you must have Salesforce CRM accounts for your organization or enable Salesforce just-in-time provisioning, which uses content from the SAML assertion created by OpenAM to create regular and portal users in Salesforce the first time they attempt to log in. To enable Salesforce just-in-time provisioning, see "To Enable Salesforce CRM Just-in-Time Provisioning".
If you have not yet done so, set up OpenAM as described in "To Create a Hosted Identity Provider", using a signing certificate that is needed by Salesforce CRM.
For details about changing the signing certificate, see "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ".
If you do not have an account with administrator credentials on Salesforce CRM, create one. See the Salesforce documentation for information about how to create an account with administrator credentials.
In a new browser tab or window, log in to Salesforce CRM with your administrator credentials.
If your users go directly to Salesforce to access services, then their single sign-on is SP-initiated from the Salesforce side. Salesforce provides a My Domain feature to facilitate SP-initiated single sign-on for desktop and device users.
Configure SP-initiated single sign-on in Salesforce as follows:
Select Setup Home > Settings > Company Settings > My Domain.
Select the domain name, and then register the domain.
Wait until the domain is ready for testing to proceed.
After the domain has been created, log out of Salesforce.
Log back in to Salesforce using the domain alias.
Select Setup Home > Settings > Company Settings > My Domain.
Click Deploy to Users.
In the OpenAM console, under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard, click Configure Salesforce CRM.
Click Configure Salesforce CRM a second time to start the Configure Salesforce CRM wizard.
The Configure Salesforce CRM for Single Sign-On page appears.
Specify values in the Configure Salesforce CRM for Single Sign-On page as follows:
Specify the Salesforce service provider entity in the "Salesforce Service Provider entityID" field. For example,
https://openam.my.salesforce.com.The entity ID is used as the persistent
EntityDescriptormetadata element so that users can have multiple service provider instances. It also appears in the Entity Providers list in the Circle of Trust Configuration.Configure an attribute mapping to associate a Salesforce CRM attribute with the corresponding OpenAM user profile attribute. For example, you might map the Salesforce CRM
IDPEmailattribute to the OpenAMmailattribute.The Configure Salesforce CRM wizard requires you to enter at least one attribute mapping.
Click Add to insert the
IDPEmailtomailmapping to the Remote to Local Attribute Mapping Table.If desired, configure additional attribute mappings.
Click Create.
The following message appears:
Metadata now configured successfully. Click OK to retrieve the parameters for configuring the Service Provider.Click OK.
A second Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page appears.
Follow the instructions on the second Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page:
Specify single sign-on settings for Salesforce as follows:
In Salesforce CRM, navigate to Setup Home > Settings > Identity > Single Sign-On Settings.
Click Edit.
Select the SAML Enabled option.
Create a new SAML single sign-on configuration as follows:
For Issuer, copy the issuer name from the Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page in the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard.
Set the Name and API Name fields to values of your choosing.
Copy or download the OpenAM verification certificate from the Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page in the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard. Save the verification certificate to a plain text file.
For Identity Provider Certificate, use the Browse button to locate and upload the file containing the OpenAM verification certificate.
For SAML Identity Type, select the "Assertion contains the Federation ID from the User object" option.
For SAML Identity Location, select the "Identity is in an Attribute" option.
Specify the Identity Provider Login URL as the URL for the OpenAM IdP. For example,
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/SSOPOST/metaalias/idp.If you require a specific logout page, enter it in the Identity Provider Logout URL field.
If you have a page to which you would like users redirected when encountering errors, enter the URL of your error page in the Custom Error URL field.
Copy the attribute name, such as
IDPEmail, from the Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page in the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard to the Attribute Name field.Select the Entity ID corresponding to the "My Domain" that you set up.
Click Save.
The Salesforce Login URL appears.
Perform the final steps required by the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard:
Copy and paste the Salesforce Login URL to the Salesforce CRM Single Sign-On Configuration page in the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard.
Click Finish to conclude operation of the OpenAM Configure Salesforce CRM wizard.
Return to the Single Sign-On Settings page in Salesforce.
Click Download Metadata to download the Salesforce CRM SP metadata. You will import the metadata into OpenAM in a subsequent step.
Configure attribute mapping and name ID format for the OpenAM identity provider:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers > Identity Provider Name > Assertion Processing.
Review the values in the Attribute Map field, which should be the same values that you configured when you ran the Configure Salesforce CRM wizard. In this example, the values should be
IDPEmail=mail.If required, modify the values in the Attribute Map field, and then click Save.
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers > Identity Provider Name > Assertion Content > NameID Format.
Salesforce requires SAML assertions that specify an
unspecifiedname ID format. In this step, configure the OpenAM-hosted IdP to support this requirement.If a value for an
unspecifiedname ID format is already present in the NameID Value Map List, remove it from the list.Add the value
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified=attributeto the NameID Value Map List. Forattribute, specify the attribute that you copied in Step 9.b.x. For example,urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified=mail.Click Save.
Add users to Salesforce CRM:
In Salesforce CRM, navigate to Setup Home > Administration > Users > Users.
Click Users.
Add users as necessary, making sure the attribute chosen as the Federation ID matches the local attribute you mapped to the remote attribute in OpenAM.
Click Finish.
Configure OpenAM as the authentication provider for your Salesforce domain:
In Salesforce CRM, navigate to Setup Home > Settings > Company Settings > My Domain.
Click Edit in the Authentication Configuration section.
The Authentication Configuration page appears, listing the available identity providers.
Select the new Authentication Service.
Click Save.
Reconfigure the remote service provider definition for Salesforce in OpenAM by deleting the service provider definition created by the Configure Salesforce CRM wizard and then importing service provider metadata that you previously exported from Salesforce CRM:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers.
Select the checkbox next to the entity provider definition for the Salesforce CRM service provider, which should be listed as an SP provider with a Remote location.
Click Delete to remove the entity provider configuration.
Click Import Entity.
The Import Entity Provider page appears.
Specify options on the Import Entity Provider page as follows:
Update the Realm Name if desired.
Click File as the location of the metadata file.
Use the Upload button to navigate to the location of the metadata file that you obtained from Salesforce in a previous step.
Add the new remote service provider definition for Salesforce CRM to the federation circle of trust in OpenAM:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Circle of Trust > Circle of Trust Name.
Move the Salesforce CRM remote service provider from the Available column to the Selected column.
Click Save.
Configuring Salesforce CRM as a remote service provider is now complete. Users navigating to the Salesforce domain should be redirected to OpenAM for authentication. Upon successful authentication, they should be logged in to Salesforce.
With just-in-time provisioning enabled, Salesforce CRM automatically creates regular and portal users when new users access Salesforce by authenticating to OpenAM.
Add mappings to the OpenAM identity provider configuration required by Salesforce just-in-time provisioning:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers > Identity Provider Name > Assertion Processing.
Add the following entries to the Attribute Map property:
User.Email=mailUser.ProfileID="Standard User"User.LastName=snUser.Username=mail
Click Save.
Enable user provisioning in Salesforce CRM:
Log in to your Salesforce domain.
In Salesforce CRM, navigate to Setup Home > Settings > Identity > Single Sign-On Settings.
Click Edit.
Set options in the Just-in-time User Provisioning section as follows:
Select the User Provisioning Enabled check box.
For User Provisioning Type, select Standard.
Click Save.
Configuring just-in-time provisioning in Salesforce CRM is now complete. When new users access Salesforce by authenticating to OpenAM, Salesforce automatically creates regular and portal users.
OpenAM provides two options for implementing SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO:
Integrated mode, in which you include a SAML2 authentication module in an OpenAM authentication chain on a service provider (SP), thereby integrating SAML v2.0 authentication into the normal OpenAM authentication process. The authentication module handles the SAML v2.0 protocol details for you.
Because the authentication chain that includes the SAML2 authentication module resides on the SP, integrated mode supports SP-initiated SSO only. You cannot trigger IdP-initiated SSO from an integrated mode implementation.
Integrated mode supports both IdP-initiated and SP-initiated SLO.
See "Implementing SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO in Integrated Mode" for procedures to implement SSO and SLO using integrated mode.
Standalone mode, in which you invoke JSPs to initiate SSO and SLO. When implementing standalone mode, you do not configure an OpenAM authentication chain.
See "Implementing SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO in Standalone Mode" for procedures to implement SSO and SLO using standalone mode.
Integrated mode was introduced in OpenAM 13. All SAML v2.0 deployments prior to OpenAM 13 are standalone mode implementations.
When configuring OpenAM to support SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO, you choose between integrated mode and standalone mode. See "Deciding Between Integrated Mode and Standalone Mode" for details about whether to choose integrated or standalone mode for your deployment.
You can achieve SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO by using integrated mode, in which you configure a SAML2 authentication module and integrate it into an authentication chain. Or, you can use standalone mode, in which you invoke JSPs to initiate SSO and SLO.
The following table provides information to help you decide whether to implement integrated mode or standalone mode for your OpenAM SAML v2.0 deployment:
| Deployment Task or Requirement | Implementation Mode |
|---|---|
| You are migrating an existing OpenAM SAML v2.0 deployment from OpenAM 12 (or earlier) to OpenAM 13.5.2-15. Note that all OpenAM SAML v2.0 deployments prior to OpenAM 13 are standalone mode deployments. |
Do not modify your deployment to integrated mode unless you want to change your authentication scenario to have SAML v2.0 authentication integrated into an OpenAM authentication chain. |
| You want to deploy SAML v2.0 SSO and SLO using the easiest technique. | Use integrated mode. |
| You want to integrate SAML v2.0 authentication into an authentication chain, letting you configure an added layer of login security by using additional authentication modules. | Use integrated mode. |
| You want to trigger SAML v2.0 IdP-initiated SSO. | Use standalone mode. |
| You want to use the SAML v2.0 Enhanced Client or Proxy (ECP) SSO profile. | Use standalone mode. |
This section covers the following topics:
The following sequence diagram outlines the flow of SAML v2.0 authentication and persistent federation in an integrated mode implementation:
The following describes the sequence of actions in the diagram:
An unauthenticated user initiates authentication to an OpenAM SAML v2.0 service provider. The login URL references an authentication chain that includes a SAML2 authentication module. For example,
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=mySAMLChain.If there are any authentication modules that precede the SAML2 module in the authentication chain, OpenAM executes them.
SAML2 authentication module processing begins.
The authentication module requests an assertion from the identity provider. The SAML2 module's configuration determines the details of the request.
If the user is currently unauthenticated on the identity provider, the following three steps occur:
The identity provider requests credentials from the user.
The user provides their credentials.
Authentication succeeds (assuming the user provided valid credentials).
Processing continues as follows:
The identity provider responds to the service provider with a SAML assertion.
If the SAML assertion contains a persistent name ID, OpenAM searches the user datastore, attempting to locate a user with the same name ID.
The flow varies here.
The following event occurs if the name ID for the user is not found in the datastore, if dynamic profile creation is configured in the Core Authentication Service, and if auto-federation is enabled on the service provider:
OpenAM adds an entry for the user to the user datastore. Even if a linking authentication chain has been configured, it is not invoked. The user is not prompted to authenticate to the service provider.
The following two events occur if the name ID for the user is not found in the datastore, if a linking authentication chain has been configured in the SAML2 authentication module, if dynamic profile creation is not configured in the Core Authentication Service, and if auto-federation is not enabled on the service provider:
The SAML2 authentication module invokes the linking authentication chain, requiring the user to authenticate to the service provider.
After successfully completing the linking authentication chain, OpenAM writes the persistent name ID obtained in the SAML assertion sent by the identity provider into the user's profile.
At this point, SAML2 authentication module processing ends. The remaining events comprise completion of the primary authentication chain:
If there are any authentication modules remaining in the chain, OpenAM executes them.
Authentication is complete.
This section describes a SAML v2.0 implementation scenario that provides an example of how you might use integrated mode to satisfy complex authentication requirements.
The example scenario has the following requirements:
Users must authenticate with an identity provider using SAML v2.0.
Users' identities are federated on the identity and service providers.
Users without federated identities must perform two-step verification at the service provider before their identities can be federated.
Device fingerprinting for risk-based authentication must be performed for all authenticated users.
Implementation of the example scenario requires the following authentication chains and authentication modules:
A primary authentication chain, which implements SAML v2.0 single sign-on and device fingerprinting.
This chain includes three authentication modules, ordered as follows:
A SAML2 authentication module with the
Requiredflag.A Device ID (Match) authentication module with the
Sufficientflag.A Device ID (Save) authentication module with the
Requiredflag.
A linking authentication chain, which identifies the user by user ID and password and requires two-step verification.
This chain includes two authentication modules, ordered as follows:
A Data Store authentication module with the
Requiredflag.A ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication module with the
Requiredflag.
This section describes the sequence of events that occurs the first time a user successfully attempts to authenticate to the OpenAM service provider by using the primary authentication chain.
Accessing the service provider.
A user authenticates to the OpenAM server acting as a SAML v2.0 service
provider, specifying the primary authentication chain in the login URL.
For example,
http://www.sp.com:28080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=mySAMLChain.
Authentication at the identity provider. OpenAM redirects the user to the identity provider. The user authenticates successfully at the identity provider. The identity provider returns a SAML assertion with a persistent name ID to OpenAM.
Service provider attempts to access a federated identity. OpenAM attempts to locate the name ID in its user store. Because this is the first time the user has attempted to authenticate to the OpenAM service provider, the name ID has not yet been associated with any OpenAM user. The search for the name ID fails.
Invocation of the linking chain. Therefore, OpenAM invokes the linking authentication chain. The Data Store authentication module executes first, requiring the user to provide a user ID and password. The ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module executes next, requiring the user to provide a one-time password from an authenticator app on the user's mobile device.
Identity federation. OpenAM then writes the name ID into the user's profile in the OpenAM user store. This completes the SAML2 authentication module's processing.
Device fingerprinting (save). Next in sequence is the Device ID (Match) authentication module. Because this is the first time that the user has authenticated to OpenAM, this device profile has not been saved to OpenAM yet and the Device ID (Match) authentication module fails. As a result, control passes to the Device ID (Save) module, which saves the device profile.
This section describes the sequence of events that occurs during subsequent successful authentication attempts after the user's identities on the identity and service providers have been federated.
Accessing the service provider.
A user authenticates to the OpenAM server acting as a SAML v2.0 service
provider specifying the primary authentication chain in the login URL.
For example,
http://www.sp.com:28080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=mySAMLChain.
Authentication at the identity provider. OpenAM redirects the user to the identity provider, and the user authenticates successfully at the identity provider. The identity provider returns a SAML asserting with a persistent name ID to OpenAM.
Service provider attempts to access a federated identity. OpenAM attempts to locate the name ID in its user store. The search for the name ID succeeds. Therefore, OpenAM does not invokes the linking authentication chain.
Device fingerprinting (match). The Device ID (Match) authentication module then executes. Because the user previously authenticated to OpenAM from this device profile, the Device ID (Match) authentication module succeeds, and authentication is complete.
The following list is an overview of the activities you perform when implementing SAML v2.0 SSO in integrated mode:
Preparing entity providers and a circle of trust.
Changing several endpoints in the service provider configuration.
Configuring a SAML2 authentication module and include it in an authentication chain.
Deciding if and how you want to federate identities during authentication. In integrated mode, you can either create user entries dynamically, or you can configure a linking authentication chain that authenticates users at the service provider after successful authentication at the identity provider, and then federates the identity.
The following procedure provides step-by-step instructions for performing these activities:
If you have not already done so, prepare for SAML v2.0 implementation by performing the tasks listed in "Preparing for Configuring SAML v2.0 on OpenAM".
Log in to the OpenAM console on the service provider as a top-level administrative user, such as
amadmin.Create a hosted service provider by following the steps in "To Create a Hosted Service Provider".
Configure a remote identity provider by following the steps in "To Configure a Remote Identity Provider". When you specify the circle of trust for the IdP, use the Add to Existing option and specify the circle of trust that you created when you created the hosted service provider.
If you want to use dynamic profile creation with auto-federation to federate identities, configure the required options:
To configure dynamic profile creation under Configure > Authentication > Core Attributes.
To configure auto-federation under Federation > Entity Providers > Service Provider Name > Assertion Processing > Auto Federation.
Change the Assertion Consumer Service locations in the service provider configuration. The default locations support standalone mode. Therefore, you must change the locations when implementing integrated mode.
Change the locations as follows:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers > Service Provider Name > Services > Assertion Consumer Service.
Change the location of the HTTP-Artifact consumer service to use
AuthConsumerrather thanConsumer. For example, if the location ishttp://www.sp.com:28080/openam/Consumer/metaAlias/sp, change it tohttp://www.sp.com:28080/openam/AuthConsumer/metaAlias/sp.Similarly, change the location for the HTTP-POST consumer service to use
AuthConsumerrather thanConsumer.Note that you do not need to change the location for the PAOS service because integrated mode does not support the PAOS binding.
Click Save to save the changes to the endpoints.
If the OpenAM server configured as the service provider runs as part of an OpenAM site, enable SAML v2.0 failover. In the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Global Services, click SAML v2 Service Configuration, check the Enable SAMLv2 failover checkbox, and then save your changes.
Create a SAML2 authentication module:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Modules.
Specify a name for the module, and specify the module type as SAML2.
Click Create.
Configure the SAML2 authentication module options. See "Hints for the SAML2 Authentication Module" for detailed information about the configuration options.
If you want to use a linking authentication chain to authenticate users at the service provider and then federate users' identities on the identity and service providers, be sure to specify the name of this chain in the Linking Authentication Chain field.
Save your changes.
Create an authentication chain that includes the SAML2 authentication module that you created in the previous step.
If you specified a linking authentication chain in the SAML2 module configuration, create the linking chain. A linking chain is an authentication chain that authenticates the user on the service provider, enabling OpenAM to persistently federate a user on the identity and service providers.
Test your configuration. First, clear your browser's cache and cookies. Then, attempt to log in to OpenAM using a login URL that references the authentication chain that includes the SAML2 module. For example,
http://www.sp.com:28080/openam/XUI/#login/&service=mySAMLChain.OpenAM should redirect you to the identity provider for authentication. Authenticate to the identity provider.
If you configured a linking authentication chain, OpenAM should prompt you to authenticate to that chain next. When authentication is complete, try logging out of the service provider, then navigate to the same login URL that you used earlier. Because you are still logged in at the identity provider, you should not be prompted to reauthenticate to the identity provider. And because your identity at the service provider is now federated with your identity at the identity provider, you should not be prompted to reauthenticate at the service provider either.
Use the following two options to control single logout in integrated mode:
The post-authentication processing class for the authentication chain that includes the SAML2 authentication module. You configure post-authentication processing classes under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Chains > Chain Name > Settings
The Single Logout Enabled option in the SAML2 authentication module configuration.
Configure these options as follows:
| Requirement | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Single logout occurs when a user initiates logout at the identity provider or at the service provider. |
Set the post-authentication processing class for the
authentication chain that contains the SAML2 authentication module to
Set the Single Logout Enabled option to |
| Single logout occurs only when the user initiates logout at the identity provider. |
Set the post-authentication processing class for the
authentication chain that contains the SAML2 authentication module to
Set the Single Logout Enabled option to |
| Single logout occurs only when the user initiates logout at the service provider. | Not available. |
| Single logout never occurs. |
Do not set the post-authentication processing class for the
authentication chain that contains the SAML2 authentication module to
|
This section describes how to implement SSO and SLO using standalone mode.
Standalone mode requires that a Federation authentication module instance is present in the realm in which you define your circle of trust, identity providers, and service providers.
Not only must the module be of type Federation, its
name must be Federation as well.
OpenAM creates a Federation authentication module when you create a new
realm, so the required module is already available unless you explicitly
deleted it. If you deleted the Federation authentication module and need to
restore it to a realm, just create an authentication module named
Federation of module type Federation. No additional
configuration is needed.
Do not add the Federation authentication module to an authentication chain. The module is used for internal purposes.
With standalone mode, OpenAM SAML v2.0 Federation provides JSPs that let you direct users to do single sign-on (SSO) and single logout (SLO) across providers in a circle of trust. OpenAM has two JSPs for SSO and two JSPs for SLO, allowing you to initiate both processes either from the identity provider side, or from the service provider side.
SSO lets users sign in once and remain authenticated as they access services in the circle of trust.
SLO attempts to log out all session participants:
For hosted IdPs, SLO attempts to log out of all SPs with which the session established SAML federation.
For hosted SPs, SLO attempts to log out of the IdP that was source of the assertion for the user's session.
The JSP pages are found under the context root where you deployed
OpenAM, in saml2/jsp/.
spSSOInit.jspUsed to initiate SSO from the service provider side, so call this on the service provider not the identity provider. This is also mapped to the endpoint
spssoinitunder the context root.Examples:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp,http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/spssoinitidpSSOInit.jspUsed to initiate SSO from the identity provider side, so call this on the identity provider not the service provider. This is also mapped to the endpoint
idpssoinitunder the context root.Examples:
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpSSOInit.jsp,http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/idpssoinitspSingleLogoutInit.jspUsed to initiate SLO from the service provider side, so call this on the service provider not the identity provider.
Example:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSingleLogoutInit.jsp,http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/SPSloInitidpSingleLogoutInit.jspUsed to initiate SLO from the identity provider side, so call this on the identity provider not the service provider.
Example:
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpSingleLogoutInit.jsp,http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/IDPSloInit
When you invoke these JSPs, there are several parameters to specify. Which parameters you can use depends on the JSP. When setting parameters in the JSPs, make sure the parameter values are correctly URL-encoded.
metaAlias(Required) Use this parameter to specify the local alias for the provider, such as
metaAlias=/myRealm/idp. This parameter takes the format/realm-name/provider-nameas described in MetaAlias. You do not repeat the slash for the Top Level Realm, for examplemetaAlias=/idp.spEntityID(Required) Use this parameter to indicate the remote service provider. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example, specify
spEntityID=http://www.sp.example:8080/openamasspEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam.affiliationID(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML affiliation identifier.
binding(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. For example, specify
binding=HTTP-POSTto use HTTP POST binding with a self-submitting form. In addition tobinding=HTTP-POST, you can also usebinding=HTTP-Artifact.NameIDFormat(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML Name Identifier format identifier, such as
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent, orurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient.RelayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.RelayStateAlias(Optional) Use this parameter to specify the parameter to use as the
RelayState. For example, if your query string hastarget=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.com&RelayStateAlias=target, this is like settingRelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.com.
idpEntityID(Required) Use this parameter to indicate the remote identity provider. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example, specify
idpEntityID=http://www.idp.example:8080/openamasidpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam.metaAlias(Required) Use this parameter to specify the local alias for the provider, such as
metaAlias=/myRealm/sp. This parameter takes the format/realm-name/provider-nameas described in MetaAlias. You do not repeat the slash for the Top Level Realm,metaAlias=/sp.affiliationID(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML affiliation identifier.
AllowCreate(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate whether the identity provider can create a new identifier for the principal if none exists (
true) or not (false).AssertionConsumerServiceIndex(Optional) Use this parameter to specify an integer that indicates the location to which the Response message should be returned to the requester.
AuthComparison(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a comparison method to evaluate the requested context classes or statements. OpenAM accepts the following values:
better. Specifies that the authentication context statement in the assertion must be better (stronger) than any of the other provided authentication contexts.
exact. Specifies that the authentication context statement in the assertion must exactly match at least one of the provided authentication contexts.
maximum. Specifies that the authentication context statement in the assertion must not be stronger than any of the other provided authentication contexts.
minimum. Specifies that the authentication context statement in the assertion must be at least as strong as one of the provided authentication contexts.
AuthnContextClassRef(Optional) Use this parameter to specify authentication context class references. Separate multiple values with pipe characters (
|). When hosted Idp and SP entities are saved in the console, any custom authentication contexts are also saved as long as they are included in the extended metadata. You can load custom authentication contexts in the extended metadata using the ssoadm command.AuthnContextDeclRef(Optional) Use this parameter to specify authentication context declaration references. Separate multiple values with pipe characters (
|).AuthLevel(Optional) Use this parameter to specify the authentication level of the authentication context that OpenAM should use to authenticate the user.
binding(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. For example, specify
binding=HTTP-POSTto use HTTP POST binding with a self-submitting form. In addition tobinding=HTTP-POST, you can also usebinding=HTTP-Artifact.Destination(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URI Reference indicating the address to which the request is sent.
ForceAuthn(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate whether the identity provider should force authentication (
true) or can reuse existing security contexts (false).isPassive(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate whether the identity provider should authenticate passively (
true) or not (false).NameIDFormat(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML Name Identifier format identifier, such as
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent, orurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient.RelayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.RelayStateAlias(Optional) Use this parameter to specify the parameter to use as the
RelayState. For example, if your query string hastarget=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.com&RelayStateAlias=target, this is like settingRelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.com.reqBinding(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the authentication request. Valid values in include
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect(default) andurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST.sunamcompositeadvice(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URL-encoded XML blob that specifies the authentication level advice. For example, the following XML indicates a requested authentication level of 1. Notice the required
:before the 1:<Advice> <AttributeValuePair> <Attribute name="AuthLevelConditionAdvice"/> <Value>/:1</Value> </AttributeValuePair> </Advice>
binding(Required) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. The full, long name format is required for this parameter to work.
The value must be one of the following:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect(default)urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POSTurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP
Consent(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URI that is a SAML Consent Identifier.
Destination(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URI Reference indicating the address to which the request is sent.
Extension(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a list of Extensions as string objects.
goto(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete.
RelayStatetakes precedence over this parameter.logoutAll(Optional) Use this parameter to specify that the identity provider should send single logout requests to service providers without indicating a session index.
RelayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.
binding(Required) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. The full, long name format is required for this parameter to work. For example, specify
binding=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POSTto use HTTP POST binding with a self-submitting form rather than the default HTTP redirect binding. In addition, you can usebinding=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Artifact.idpEntityID(Required for Fedlets) Use this parameter to indicate the remote identity provider. If the
bindingis not set, then OpenAM uses this parameter to find the default binding. Make sure you URL encode the value. For example, specifyidpEntityID=http://www.idp.example:8080/openamasidpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam.NameIDValue(Required for Fedlets) Use this parameter to indicate the SAML Name Identifier for the user.
SessionIndex(Required for Fedlets) Use this parameter to indicate the
sessionIndexof the user session to terminate.Consent(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URI that is a SAML Consent Identifier.
Destination(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a URI Reference indicating the address to which the request is sent.
Extension(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a list of Extensions as string objects.
goto(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete.
RelayStatetakes precedence over this parameter.RelayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.spEntityID(Optional, for Fedlets) Use this parameter to indicate the Fedlet entity ID. When missing, OpenAM uses the first entity ID in the metadata.
The following URL takes the user from the service provider side to authenticate at the identity provider and then come back to the end user profile page at the service provider after successful SSO. Lines are folded to show you the query string parameters:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp?metaAlias=/sp
&idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam%2Fidm%2FEndUser
The following URL initiates SLO from the service provider side,
leaving the user at http://forgerock.com:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSingleLogoutInit.jsp?
&idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comDuring SSO login, OpenAM presents users with a self-submitting form when access has been validated. This page is otherwise blank. If you want to present users with something to indicate that the operation is in progress, then customize the necessary templates.
Modify the templates to add a clue that SSO is in progress, such as an image.
Edit the source of the OpenAM Java Server Page,
saml2/jsp/autosubmitaccessrights.jsp, under the file system directory where the OpenAM .war has been unpacked.When you add an image or other presentation element, make sure that you retain the form and Java code as is.
Unpack OpenAM-13.5.2.war, and add your modified template files under
WEB-INF/classes/where you unpacked the .war.Also include any images you reference in the page.
Pack up your custom version of OpenAM, and then deploy it in your web container.
You can use policy agents in a SAML v2.0 Federation deployment.
The following procedure applies when OpenAM is configured as an IdP in one domain, and a policy agent protects resources on behalf of a second OpenAM server configured as an SP on a second domain:
Install the policy agent.
The basic process for installing policy agents is available in the Web Policy Agent User's Guide and the Java EE Policy Agent User's Guide.
Replace the given OpenAM Login URL and OpenAM Logout URLs with SAML v2.0 URLs described in "JSP Pages for SSO and SLO".
The following steps explain how to do this for web policy agents:
If you have configured the Web policy agents to store their properties centralized on an OpenAM server, navigate to the URL for the OpenAM console. Select Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Web > Agent Name > OpenAM Services.
For the Web Agent, under the OpenAM Services tab, in the Agent Logout URL section, set up a list of application logout URLs. In the Logout Redirect URL text box, enter an appropriate URL to redirect the user after logout.
Alternatively, if the Web policy agents are set up to store properties on local systems, find the
OpenSSOAgentConfiguration.propertiesfile in the/path/to/agent/config/directory.You can specify OpenAM Login and Logout URLs with the
com.sun.identity.agents.config.login.urlandcom.sun.identity.agents.config.logout.urlattributes, respectively.
The SAML v2.0 Enhanced Client or Proxy (ECP) profile is intended for use when accessing services over devices like simple phones, medical devices, and set-top boxes that lack the capabilities needed to use the more widely used SAML v2.0 Web Browser SSO profile.
The ECP knows which identity provider to contact for the user, and is able to use the reverse SOAP (PAOS) SAML v2.0 binding for the authentication request and response. The PAOS binding uses HTTP and SOAP headers to pass information about processing SOAP requests and responses, starting with a PAOS HTTP header that the ECP sends in its initial request to the server. The PAOS messages continue with a SOAP authentication request in the server's HTTP response to the ECP's request for a resource, followed by a SOAP response in an HTTP request from the ECP.
An enhanced client, such as a browser with a plugin or an extension, can handle these communications on its own. An enhanced proxy is an HTTP server, such as a WAP gateway that can support the ECP profile on behalf of client applications.
OpenAM supports the SAML v2.0 ECP profile on the server side for identity providers and service providers. You must build the ECP.
By default, an OpenAM identity provider uses the
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.DefaultIDPECPSessionMapper
class to find a user session for requests to the IdP from the ECP. The
default session mapper uses OpenAM cookies as it would for any other client
application. If for some reason you must change the mapping after writing
and installing your own session mapper, you can change the class under
Federation > Entity Providers > IdP Name
> IDP > Advanced > ECP Configuration.
By default, an OpenAM service provider uses the
com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins.ECPIDPFinder class to
return identity providers from the list under Federation > Entity
Providers > SP Name > SP > Advanced
> ECP Configuration > Request IDP List. You must populate the list
with identity provider entity IDs.
The endpoint for the ECP to contact on the OpenAM service provider is
/SPECP as in
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/SPECP. The ECP
provides two query string parameters to identify the service provider and
to specify the URL of the resource to access.
metaAliasThis specifies the service provider, by default
metaAlias=/realm-name/sp, as described in MetaAlias.RelayStateThis specifies the resource the client aims to access, such as
RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.org%2Findex.html. Make sure this parameter is correctly URL-encoded.
For example, the URL to access the service provider and finally
the resource at http://forgerock.org/index.html
could be
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/SPECP?metaAlias=/sp&RelayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.org%2Findex.html.
Identity providers and service providers must be able to communicate about users. Yet, in some cases the identity provider can choose to communicate a minimum of information about an authenticated user, with no user account maintained on the service provider side. In other cases, the identity provider and service provider can choose to link user accounts in a persistent way, in a more permanent way, or even in automatic fashion by using some shared value in the user's profiles, such as an email address or by dynamically creating accounts on the service provider when necessary. OpenAM supports all these alternatives.
OpenAM allows you to link accounts using transient name identifiers, where the identity provider shares a temporary identifier with the service provider for the duration of the user session. Nothing is written to the user profile.
Transient identifiers are useful where the service is anonymous, and all users have similar access on the service provider side.
To use transient name identifiers, specify the name ID format
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient when
initiating single sign-on.
The examples below work in an environment where the identity provider
is www.idp.example and the service provider is
www.sp.example. Both providers have deployed OpenAM on port
8080 under deployment URI /openam.
To initiate single sign-on from the service provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp?
idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&metaAlias=/sp
&NameIDFormat=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transientFor a complete list of query parameters, see spSSOInit.jsp Parameters.
To initiate single sign-on from the identity provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown:
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpSSOInit.jsp?
spEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&metaAlias=/idp
&NameIDFormat=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transientFor a complete list of query parameters, see idpSSOInit.jsp Parameters.
The accounts are only linked for the duration of the session. Once the user logs out, for example, the accounts are no longer linked.
OpenAM lets you use persistent pseudonym identifiers to federate user identities, linking accounts on the identity provider and service provider with a SAML persistent identifier.
Persistent identifiers are useful for establishing links between otherwise unrelated accounts.
The examples below work in an environment where the identity provider
is www.idp.example and the service provider is
www.sp.example. Both providers have deployed OpenAM on port
8080 under deployment URI /openam.
To initiate single sign-on from the service provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp?
idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&metaAlias=/sp
&NameIDFormat=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentFor a complete list of query parameters, see spSSOInit.jsp Parameters.
To initiate single sign-on from the identity provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown:
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpSSOInit.jsp?
spEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam
&metaAlias=/idp
&NameIDFormat=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentFor a complete list of query parameters, see idpSSOInit.jsp Parameters.
On successful login, the accounts are persistently linked, with persistent identifiers stored in the user's accounts on the identity provider and the service provider.
Both integrated and standalone SAML v2.0 implementations allow you to persistently link accounts:
In integrated mode deployments, you specify the value
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentin the nameIDFormat field of the SAML2 authentication module.In standalone mode, when you initiate single sign-on with either the
spSSOInit.jsporidpSSOInit.jspJSP page, you specify theNameIDFormat=urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistentparameter.
This section covers the following topics:
OpenAM implements the SAML v2.0 Name Identifier Management profile, allowing you to change a persistent identifier that has been set to federate accounts, and also to terminate federation for an account.
When user accounts are stored in an LDAP directory server, name
identifier information is stored on the
sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info and
sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey attributes of a user's
entry.
[6]
You can retrieve the name identifier value on the IdP side
by checking the value of sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey.
For example, if the user's entry in the directory shows
sun-fm-saml2-nameid-infokey:
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam|http://www.sp.example:8080/openam|
XyfFEsr6Vixbnt0BSqIglLFMGjR2,
then the name identifier on the IdP side is
XyfFEsr6Vixbnt0BSqIglLFMGjR2.
You can use this identifier to initiate a change request from the service provider as in the following example.
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spMNIRequestInit.jsp? idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam &metaAlias=/sp &requestType=NewID &IDPProvidedID=XyfFEsr6Vixbnt0BSqIglLFMGjR2
If desired, you can substitute openam/SPMniInit
for openam/saml2/jsp/spMNIRequestInit.jsp
You can also initiate the change request from the identity provider as in the following example.
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpMNIRequestInit.jsp? spEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam &metaAlias=/idp &requestType=NewID &IDPProvidedID=XyfFEsr6Vixbnt0BSqIglLFMGjR2
If desired, you can substitute openam/IDPMniInit
for openam/saml2/jsp/idpMNIRequestInit.jsp
You can retrieve the name identifier value on the SP side
by checking the value of sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info.
For example, if the user's entry in the directory shows
sun-fm-saml2-nameid-info:
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam|
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam|
ATo9TSA9Y2Ln7DDrAdO3HFfH5jKD|
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam|
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent|
9B1OPy3m0ejv3fZYhlqxXmiGD24c|
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam|
SPRole|
false,
then the name identifier on the SP side is
9B1OPy3m0ejv3fZYhlqxXmiGD24c.
The JSP parameters are listed below. When setting parameters in the JSPs, make sure the parameter values are correctly URL-encoded.
spEntityID(Required) Use this parameter to indicate the remote service provider. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example, specify
spEntityID=http://www.sp.example:8080/openamasspEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam.metaAlias(Required) Use this parameter to specify the local alias for the provider, such as
metaAlias=/myRealm/idp. This parameter takes the format/realm-name/provider-nameas described in MetaAlias. You do not repeat the slash for the Top Level Realm, for examplemetaAlias=/idp.requestType(Required) Type of manage name ID request, either
NewIDto change the ID, orTerminateto remove the information that links the accounts on the identity provider and service provider.SPProvidedID(Required if
requestType=NewID) Name identifier in use as described above.affiliationID(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML affiliation identifier.
binding(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. The full, long name format is required for this parameter to work.
The value must be one of the following:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POSTurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirecturn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP
relayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
relayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.
idpEntityID(Required) Use this parameter to indicate the remote identity provider. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example, specify
idpEntityID=http://www.idp.example:8080/openamasidpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam.metaAlias(Required) Use this parameter to specify the local alias for the provider, such as
metaAlias=/myRealm/sp. This parameter takes the format/realm-name/provider-nameas described in MetaAlias. You do not repeat the slash for the Top Level Realm,metaAlias=/sp.requestType(Required) Type of manage name ID request, either
NewIDto change the ID, orTerminateto remove the information that links the accounts on the identity provider and service provider.IDPProvidedID(Required if
requestType=NewID) Name identifier in use as described above.affiliationID(Optional) Use this parameter to specify a SAML affiliation identifier.
binding(Optional) Use this parameter to indicate what binding to use for the operation. The full, long name format is required for this parameter to work.
The value must be one of the following:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POSTurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirecturn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP
relayState(Optional) Use this parameter to specify where to redirect the user when the process is complete. Make sure you URL-encode the value. For example,
relayState=http%3A%2F%2Fforgerock.comtakes the user tohttp://forgerock.com.
You can terminate federation as described in "Terminating Federation of Persistently Linked Accounts".
OpenAM lets you terminate account federation, where the accounts have been linked with a persistent identifier as described in "Using Persistent Federation Identifiers".
The examples below work in an environment where the identity provider
is www.idp.example and the service provider is
www.sp.example. Both providers have deployed OpenAM on port
8080 under deployment URI /openam.
To initiate the process of terminating account federation from the service provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown.
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spMNIRequestInit.jsp? idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam &metaAlias=/sp &requestType=Terminate
To initiate the process of terminating account federation from the identity provider, access the following URL with at least the query parameters shown.
http://www.idp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/idpMNIRequestInit.jsp? spEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam &metaAlias=/idp &requestType=Terminate
OpenAM lets you configure the service provider to link an account based on an attribute value from the identity provider. When you know the user accounts on both the identity provider and the service provider share a common attribute value, such as an email address or other unique user identifier, you can use this method to link accounts without user interaction. See "To Map Accounts Based on an Attribute Value".
OpenAM also lets you map users on the identity provider temporarily to a single anonymous user account on the service provider, in order to exchange attributes about the user without a user-specific account on the service provider. This approach can be useful when the service provider either needs no user-specific account to provide a service, or when you do not want to retain a user profile on the service provider but instead you make authorization decisions based on attribute values from the identity provider. See "To Map Remote Accounts to a Single-Service Provider Account".
OpenAM further allows you to use attributes from the identity provider to create accounts dynamically on the service provider. When using this method, you should inform the user and obtain consent to create the account if necessary. See "To Map Accounts With Dynamic Service Provider Account Creation".
The following steps demonstrate how to map accounts based on an attribute value that is the same in both accounts.
Perform the following steps on the hosted identity provider(s), and again on the hosted service provider(s):
Log in to the OpenAM console as administrator.
Browse to Federation > Hosted Provider Name > Assertion Processing.
If the attribute to use when linking accounts is not yet included in the attribute map, add the attribute mapping, and then save your work.
On the hosted service provider, under Auto Federation, select Enabled and enter the local attribute name in the Attribute field, and then save your work.
The following steps demonstrate how to auto-federate using a single anonymous user account on the service provider.
Perform the following steps on the hosted identity provider(s), and again on the hosted service provider(s):
Log in to the OpenAM console as administrator.
Browse to Federation > Hosted Provider Name > Assertion Processing.
If you want to get attributes from the identity provider and the attributes are not yet in the attribute map, add the attribute mappings, and then save your work.
On the hosted service provider, under Transient User, set the single account to which to map all users, such as
anonymous, and then save your work.After completing configuration on the providers, use transient identifiers to federate as described in "Using Transient Federation Identifiers".
The following steps demonstrate how to map accounts with dynamic creation of missing accounts on the service provider side:
Set up a mapping based on an attribute value as described in "To Map Accounts Based on an Attribute Value". The attributes you map from the identity provider are those that the service provider sets on the dynamically created accounts.
On the service provider console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > User Profile. For the User Profile field, select Dynamic or Dynamic with User Alias, which are described in "Configuring Core Authentication Attributes", and then save your work.
To test your work, create a user on the identity provider, log out of the console, and initiate SSO by logging in as the user you created.
To initiate SSO, browse to one of the OpenAM SAML v2.0 JSPs with the appropriate query parameters. The following is an example URL for service provider initiated SSO.
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/saml2/jsp/spSSOInit.jsp? idpEntityID=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.idp.example%3A8080%2Fopenam &metaAlias=/sp
On success, check
http://www.sp.example:8080/openam/idm/EndUserto see the new user account.
If you manage both the identity provider and service provider, you can link accounts out-of-band, in bulk. You make permanent connections for a list of identity provider and service provider by using the ssoadm bulk federation commands.
Before you can run the bulk federation commands, first establish the relationship between accounts, set up the providers as described in "Configuring Identity Providers, Service Providers, and Circles of Trust", and install the ssoadm command as described in "To Set Up Administration Tools" in the Installation Guide.
To understand the relationships between accounts, consider an example
where the identity provider is at idp.example.org and the
service provider is at sp.example.com. A demo user
account has the Universal ID,
id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=org, on the identity
provider. That maps to the Universal ID,
id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=com, on the service
provider.
The ssoadm command then needs a file that maps
local user IDs to remote user IDs, one per line, separated by the vertical
bar character |. Each line of the file appears as
follows:
local-user-ID|remote-user-ID
In the example, starting on the service provider side, the line for the demo user reads as follows.
id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=com|id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=org
All the user accounts mapped in your file must exist at the identity provider and the service provider when you run the commands to link them.
Link the accounts using the ssoadm bulk federation commands:
Prepare the data with the ssoadm do-bulk-federation command.
The following example starts on the service provider side:
$ cat /tmp/user-map.txt id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=com|id=demo,ou=user,dc=example,dc=org $ ssoadm \ do-bulk-federation \ --metaalias /sp \ --remoteentityid http://idp.example.org:8080/openam \ --useridmapping /tmp/user-map.txt \ --nameidmapping /tmp/name-map.txt \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --spec saml2 Bulk Federation for this host was completed. To complete the federation, name Id mapping file should be loaded to remote provider.
Copy the name ID mapping output file to the other provider:
$ scp /tmp/name-map.txt openam@idp.example.org:/tmp/name-map.txt openam@idp.example.org's password: name-map.txt 100% 177 0.2KB/s 00:00
Import the name ID mapping file with the ssoadm import-bulk-fed-data command.
The following example is performed on the identity provider side:
$ ssoadm \ import-bulk-fed-data \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --metaalias /idp \ --bulk-data-file /tmp/name-map.txt Bulk Federation for this host was completed.
At this point the accounts are linked.
In a SAML v2.0 federation where accounts are durably linked, authentication is required only on the identity provider side.
Authentication is also required, however, on the service provider side when the OpenAM account mapper on the service provider is not able to map the user identified in the SAML assertion from the identity provider to a local user account.
This can happen, for example, the first time accounts are linked as described in "Using Persistent Federation Identifiers", after which the persistent identifier establishes the mapping.
This also happens when transient identifiers are used to map accounts. When accounts are linked as described in "Using Transient Federation Identifiers", then the service provider must locally authenticate the user for every SAML assertion received. This is because the identifier used to link the accounts is transient; it does not provide a durable means to link the accounts.
ForgeRock recommends that you configure OpenAM to use stateful sessions when deploying OpenAM as a SAML v2.0 IdP or SP.
The following SAML v2.0 profiles are not supported when you configure OpenAM to use stateless sessions:
Single logout
Single sign-on with the HTTP POST binding
The other SAML v2.0 single sign-on profiles are not guaranteed to work with stateless sessions.
For more information about stateful and stateless sessions, see "Configuring Session State".
[6] To configure these attribute types, in the OpenAM console navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click SAMLv2 Service Configuration.
This chapter covers OpenAM support for the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework. The chapter begins by showing where OpenAM fits into the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework, and then shows how to configure the functionality.
RFC 6749, The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework, provides a standard way for resource owners to grant client applications access to the owners' web-based resources. The canonical example involves a user (resource owner) granting access to a printing service (client) to print photos that the user has stored on a photo-sharing server.
The section describes how OpenAM supports the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework in terms of the roles that OpenAM plays.[7] The following sequence diagram indicates the primary roles OpenAM can play in the OAuth 2.0 protocol flow.
OpenAM can function as an OAuth 2.0 authorization server. In this role, OpenAM authenticates resource owners and obtains their authorization in order to return access tokens to clients.
When using OpenAM as authorization server, you can register clients in OpenAM console alongside policy agent profiles under the OAuth 2.0 Client tab. OpenAM supports both confidential and public clients.
OpenAM supports the four main grants for obtaining authorization described in RFC 6749: the authorization code grant, the implicit grant, the resource owner password credentials grant, and the client credentials grant. See RFC 6749 for details on the authorization grant process, and for details on how clients should make authorization requests and handle authorization responses. OpenAM also supports the SAML v2.0 Bearer Assertion Profiles for OAuth 2.0, described in the Internet-Draft.
The authorization code grant starts with the client, such as a web-based service, redirecting the resource owner's user-agent to the OpenAM authorization service. After authenticating the resource owner and obtaining the resource owner's authorization, OpenAM redirects the resource owner's user-agent back to the client with an authorization code that the client uses to request the access token. The following sequence diagram outlines a successful process from initial client redirection through to the client accessing the protected resource.
The implicit grant is designed for clients implemented to run inside the resource-owner user agent. Instead of providing an authorization code that the client must use to retrieve an access token, OpenAM returns the access token directly in the fragment portion of the redirect URI. The following sequence diagram outlines the successful process.
The resource owner password credentials grant lets the client use the resource owner's user name and password to get an access token directly. Although this grant might seem to conflict with an original OAuth goal of not having to share resource owner credentials with the client, it can makes sense in a secure context where other authorization grant types are not available, such as a client that is part of a device operating system using the resource owner credentials once and thereafter using refresh tokens to continue accessing resources. The following sequence diagram shows the successful process.
The client credentials grant uses client credentials as an authorization grant. This grant makes sense when the client is also the resource owner, for example. The following sequence diagram shows the successful process.
The OAuth 2.0 Device Flow is designed for client devices that have limited user interfaces, such as a set-top box, streaming radio, or a server process running on a headless operating system.
Rather than logging in by using the client device itself, you can authorize the client to access protected resources on your behalf by logging in with a different user agent, such as an Internet browser on a PC or smartphone, and entering a code displayed on the client device.
The sequence diagram below demonstrates the OAuth 2.0 Devlice Flow:
The steps in the diagram are described below:
The client device requests a device code from OpenAM by using a REST call.
OpenAM returns a device code, a user code, a URL for entering the user code, and an interval, in seconds.
The client device provides instructions to the user to enter the user code. The client may choose an appropriate method to convey the instructions, for example text instructions on screen, or a QR code.
The client device begins to continuously poll OpenAM to see if authorization has been completed.
If the user has not yet completed the authorization, OpenAM returns an HTTP 403 status code, with an
authorization_pendingmessage.The user follows the instructions from the client device to enter the user code by using a separate device.
If the user code is valid OpenAM will ask the user to authenticate.
Upon authentication the user can authorize the client device. The OpenAM consent page also displays the requested scopes, and their values:
Upon authorization, OpenAM responds to the client device's polling with an HTTP 200 status, and an access token, giving the client device access to the requested resources.
For more information, see "Using Endpoints for OAuth 2.0 Device Flow" in the Developer's Guide.
The Internet-Draft, JSON Web Token (JWT) Profile for OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication and Authorization Grants describes a means to use a JWT for client authentication or to use a JWT to request an access token. When clients are also resource owners, the profile allows clients to issue JWTs to obtain access tokens rather than use the resource owner password credentials grant.
OpenAM implements both features of the profile. Both involve HTTP POST requests to the access token endpoint.
When the client bearing the JWT uses it for authentication,
then in the POST data the client sets
client_assertion_type to
urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer
and client_assertion to the JWT string.
The HTTP POST to OpenAM looks something like the following, where the assertion value is the JWT:
POST /openam/oauth2/access_token HTTP/1.1
Host: openam.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=authorization_code&
code=362ad374-735c-4f69-aa8e-bf384f8602de&
client_assertion_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3A
client-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer&
client_assertion=eyAiYWxnIjogIlJTMjU2IiB9.eyAic3ViIjogImp3...In the above profile, OpenAM must be able to validate the JWT, which must include the following claims:
"iss" (issuer) whose value identifies the JWT issuer.
"sub" (subject) whose value identifies the principal who is the subject of the JWT.
For client authentication, the "sub" value must be the same as the value of the "client_id".
"aud" (audience) whose value identifies the authorization server that is the intended audience of the JWT.
When the JWT is used for authentication, this is the OpenAM access token endpoint.
"exp" (expiration) whose value specifies the time of expiration.
Also for validation, the issuer must digitally sign the JWT or apply a keyed message digest. When the issuer is also the client, the client can sign the JWT by using a private key, and include the public key in its profile registered with OpenAM.
A sample Java-based client is available online.
The Internet-Draft, SAML v2.0 Bearer Assertion Profiles for OAuth 2.0, describes a means to use SAML v2.0 assertions to request access tokens and to authenticate OAuth 2.0 clients.
At present OpenAM implements the profile to request access tokens.
In both profiles, the issuer must sign the assertion. The client communicates the assertion over a channel protected with transport layer security by performing an HTTP POST to the OpenAM's access token endpoint. OpenAM as OAuth 2.0 authorization server uses the issuer ID to validate the signature on the assertion.
In the profile to request an access token, the OAuth 2.0 client bears a SAML v2.0 assertion that was issued to the resource owner on successful authentication. A valid assertion in this case is equivalent to an authorization grant by the resource owner to the client. OAuth 2.0 clients must make it clear to the resource owner that by authenticating to the identity provider who issues the assertion, they are granting the client permission to access the protected resources.
The HTTP POST to OpenAM to request an access token looks something like this:
POST /openam/oauth2/access_token HTTP/1.1
Host: openam.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Asaml2-bearer&
assertion=PHNhbWxwOl...[base64url encoded assertion]...ZT4&
client_id=[ID registered with OpenAM]If OpenAM is already a SAML v2.0 service provider, you can configure OpenAM as OAuth 2.0 authorization server as well, and set an adapter class name in the service provider configuration that lets OpenAM POST the assertion from the service provider to the authorization server. See "Configuring OpenAM as a SAML Service Provider and OAuth2 Authorization Server" for details.
In addition to the standard authorization and token endpoints described in RFC 6749, OpenAM also exposes a token information endpoint for resource servers to get information about access tokens so they can determine how to respond to requests for protected resources, and an introspection endpoint to retrieve metadata about a token, such as approved scopes and the context in which the token was issued. OpenAM as authorization server exposes the following endpoints for clients and resource servers.
/oauth2/authorizeAuthorization endpoint defined in RFC 6749, used to obtain an authorization grant from the resource owner.
The
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint is protected by the policy you created after OAuth 2.0 authorization server configuration, which grants all authenticated users access.The following is an example URL for obtaining consent:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/realms/root/authorize\ ?client_id=myClient\ &response_type=code\ &scope=profile\ &redirect_uri=https://www.example.comAfter logging in, the URL above presents the OAuth 2.0 consent screen, similar to the following:
If creating your own consent page, you can create a POST request to the endpoint with the following additional parameters:
decisionWhether the resource owner consents to the requested access, or denies consent.
Valid values are
allowordeny.save_consentUpdates the resource owner's profile to avoid having to prompt the resource owner to grant authorization when the client issues subsequent authorization requests.
To save consent, set the
save_consentproperty toon.You must provide the Saved Consent Attribute Name property with a profile attribute in which to store the resource owner's consent decision.
For more information on setting this property in the OAuth2 Provider service, see "OAuth2 Provider" in the Reference.
csrfDuplicates the contents of the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie, which contains the SSO token of the resource owner giving consent.Duplicating the cookie value helps prevent against Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks.
Example:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \ --Cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5w...*" \ --data "redirect_uri=http://www.example.net" \ --data "scope=profile" \ --data "response_type=code" \ --data "client_id=myClient" \ --data "csrf=AQIC5w...*" \ --data "decision=allow" \ --data "save_consent=on" \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=myClient"\ "&realm=/&scope=profile&redirect_uri=http://www.example.net"
You must specify the realm if the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than the top-level realm. For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for the
/customersrealm, then use/oauth2/customers/authorize.The
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint can take additional parameters, such as:moduleandservice. Use either as described in "Authenticating To OpenAM", wheremodulespecifies the authentication module instance to use orservicespecifies the authentication chain to use when authenticating the resource owner.response_mode=form_post. Use this parameter to return a self-submitting form that contains the code instead of redirecting to the redirect URL with the code as a string parameter. For more information, see the OAuth 2.0 Form Post Response Mode spec.code_challenge. Use this parameter when Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) support is enabled in the OAuth2 Provider service. To configure it, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services > OAuth2 Provider > Advanced and enable the Code Verifier Parameter Required property. For more information about the PKCE support, see Proof Key for Code Exchange by OAuth Public Clients - RFC 7636.
/oauth2/access_tokenToken endpoint defined in RFC 6749, used to obtain an access token from the authorization server.
Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_tokenThe
/oauth2/access_tokenendpoint can take an additional parameter,auth_chain=authentication-chain, which allows client to specify the authentication chain to use for Password Grant Type.The following example shows how a client can specify the authentication chain,
myAuthChain:$ curl \ --request POST \ --user "myClientID:password" \ --data "grant_type=password&username=amadmin&password=cangetinam&scope=profile&auth_chain=myAuthChain" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token
The
/oauth2/access_tokenendpoint can take additional parameters. In particular, you must specify the realm if the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than the top-level realm.For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for the
/customersrealm, then use/oauth2/customers/access_token./oauth2/deviceDevice flow endpoint as defined by the Internet-Draft OAuth 2.0 Device Flow, used by a client device to obtain a device code or an access token.
Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/device/codeFor more information, see "Using Endpoints for OAuth 2.0 Device Flow" in the Developer's Guide.
/oauth2/token/revokeWhen a user logs out of an application, the application revokes any OAuth 2.0 tokens (access and refresh tokens) that are associated with the user. The client can also revoke a token without the need of an
SSOTokenby sending a request to the/oauth2/token/revokeendpoint as follows:$ curl \ --request POST \ --data "token=d06ab31e-9cdb-403e-855f-bd77652add84" \ --data "client_id=MyClientID" \ --data "client_secret=password" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/token/revoke
If you are revoking an access token, then that token will be revoked. If you are revoking a refresh token, then both the refresh token and any other associated access tokens will also be revoked. Associated access tokens means that any other tokens that have come out of the same authorization grant will also be revoked. For cases where a client has multiple access tokens for a single user that were obtained via different authorization grants, then the client will have to make multiple calls to the
/oauth2/token/revokeendpoint to invalidate each token./oauth2/tokeninfoEndpoint not defined in RFC 6749, used to validate tokens, and to retrieve information, such as scopes.
The
/oauth2/tokeninfoendpoint takes an HTTP GET on/oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=token-id, and returns information about the token.Resource servers — or any party having the token ID — can get token information through this endpoint without authenticating. This means any application or user can validate the token without having to be registered with OpenAM.
Given an access token, a resource server can perform an HTTP GET on
/oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=token-idto retrieve a JSON object indicatingtoken_type,expires_in,scope, and theaccess_tokenID.Example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/tokeninfoThe following example shows OpenAM issuing an access token, and then returning token information:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --user "myClientID:password" \ --data "grant_type=password&username=demo&password=changeit&scope=cn%20mail" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token { "expires_in": 599, "token_type": "Bearer", "refresh_token": "f6dcf133-f00b-4943-a8d4-ee939fc1bf29", "access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9" } $ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo\ ?access_token=f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9 { "mail": "demo@example.com", "grant_type":"password", "scope": [ "mail", "cn" ], "cn": "demo", "realm": "/", "cnf": { "jwk": { "alg": "RS512", "e": "AQAB", "n": "k7qLlj...G2oucQ", "kty": "RSA", "use": "sig", "kid": "myJWK" } } "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 577, "client_id": "MyClientID", "access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9" }Note
Running a GET method to the
/oauth2/tokeninfoendpoint as shown in the previous example writes the token ID to the access log. To not expose the token ID in the logs, send the OAuth 2.0 access token as part of the authorization bearer header:$ curl \ --request GET \ --header "Authorization Bearer aec6b050-b0a4-4ece-a86f-bd131decbb9c" \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo"
The resource server making decisions about whether the token is valid can thus use the
/oauth2/tokeninfoendpoint to retrieve expiration information about the token. Depending on the scopes implementation, the JSON response about the token can also contain scope information. As described in "Using Your Own Client and Resource Server", the default scopes implementation in OpenAM considers scopes to be names of attributes in the resource owner's user profile. Notice that the JSON response contains the values for those attributes from the user's profile, as in the preceding example, with scopes set tomailandcn./oauth2/introspectEndpoint defined in draft-ietf-oauth-introspection-04, used to retrieve metadata about a token, such as approved scopes and the context in which the token was issued.
Given an access token, a client can perform an HTTP POST on
/oauth2/introspect?token=access_tokento retrieve a JSON object indicating the following:activeIs the token active.
scopeA space-separated list of the scopes associated with the token.
client_idClient identifier of the client that requested the token.
user_idThe user who authorized the token.
token_typeThe type of token.
expWhen the token expires, in seconds since January 1 1970 UTC.
subSubject of the token.
issIssuer of the token.
The
/oauth2/introspectendpoint requires authentication, and supports basic authorization (a base64-encoded string ofclient_id:client_secret),client_idandclient_secretpassed as header values, or a JWT bearer token.The following example demonstrates the
/oauth2/introspectendpoint with basic authorization:$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Authorization: Basic ZGVtbzpjaGFuZ2VpdA==" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/introspect \ ?token=f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9 { "active": true, "scope": "mail cn", "client_id": "myOAuth2Client", "user_id": "demo", "token_type": "Bearer", "exp": 1419356238, "sub": "https://resources.example.com/", "iss": "https://openam.example.com/" }Note
Running a POST method to the
/oauth2/introspectendpoint as shown in the previous example writes the token ID to the access log. To hide the token ID in the logs, send the OAuth 2.0 access token as part of the POST body:$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Authorization Basic ZGVtbzpjaGFuZ2VpdA==" \ --data "token=f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9" \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/introspect"
For examples, and information about OAuth 2.0 token administration and client administration endpoints that are specific to OpenAM, see "OAuth 2.0" in the Developer's Guide.
OpenAM can function as an OAuth 2.0 client for installations where the web resources are protected by OpenAM. To configure OpenAM as an OAuth 2.0 client, you set up an OpenAM OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module instance, and then integrate the authentication module into your authentication chains as necessary.
When OpenAM functions as an OAuth 2.0 client, OpenAM provides an OpenAM SSO session after successfully authenticating the resource owner and obtaining authorization. This means the client can then access resources protected by policy agents. In this respect the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 client is just like any other authentication module, one that relies on an OAuth 2.0 authorization server to authenticate the resource owner and obtain authorization. The following sequence diagram shows how the client gains access to protected resources in the scenario where OpenAM functions as both authorization server and client for example.
As the OAuth 2.0 client functionality is implemented as an OpenAM authentication module, you do not need to deploy your own resource server implementation when using OpenAM as an OAuth 2.0 client. Instead, use policy agents or OpenIG to protect resources.
To configure OpenAM as an OAuth 2.0 client, see the section "Hints for the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Authentication Module".
OpenAM returns bearer tokens as described in RFC 6750, The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage. Notice in the following example JSON response to an access token request that OpenAM returns a refresh token with the access token. The client can use the refresh token to get a new access token as described in RFC 6749:
{
"expires_in": 599,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"refresh_token": "f6dcf133-f00b-4943-a8d4-ee939fc1bf29",
"access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9"
}In addition to implementing your client, the resource server must also
implement the logic for handling access tokens. The resource server can use
the /oauth2/tokeninfo endpoint to determine whether the
access token is still valid, and to retrieve the scopes associated with the
access token.
The default OpenAM implementation of OAuth 2.0 scopes assumes that the space-separated (%20 when URL-encoded) list of scopes in an access token request correspond to names of attributes in the resource owner's profile.
To take a concrete example, consider an access token request where
scope=mail%20cn and where the resource owner is the
default OpenAM demo user. (The demo user has no email address by default, but
you can add one, such as demo@example.com to the demo
user's profile.) When the resource server performs an HTTP GET on the token
information endpoint, /oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=token-id, OpenAM populates the
mail and cn scopes with the email
address (demo@example.com) and common name
(demo) from the demo user's profile. The result is
something like the following token information response:
{
"mail": "demo@example.com",
"scope": [
"mail",
"cn"
],
"cn": "demo",
"realm": "/",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 577,
"client_id": "MyClientID",
"access_token": "f9063e26-3a29-41ec-86de-1d0d68aa85e9"
}OpenAM is designed to allow you to plug in your own scopes implementation if the default implementation does not do what your deployment requires. See "Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling" in the Developer's Guide for an example.
You configure the OAuth 2.0 authorization service for a particular realm from the Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard page of the OpenAM console.
Follow the steps in this procedure to set up the service with the Configure OAuth Provider wizard:
When you create the service with the Configure OAuth Provider wizard, the wizard also creates a standard policy in the Top Level Realm (/) to protect the authorization endpoint. In this configuration, OpenAM serves the resources to protect, and no separate application is involved. OpenAM therefore acts both as the policy decision point and also as the policy enforcement point that protects the OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint.
There is no requirement to use the wizard
or to create the policy in the Top Level Realm.
However, if you create the OAuth 2.0 authorization service without the wizard,
then you must set up the policy independently as well.
The policy must appear in a policy set of type
iPlanetAMWebAgentService,
which is the default in the OpenAM policy editor.
When configuring the policy allow all authenticated users
to perform HTTP GET and POST requests on the authorization endpoint.
The authorization endpoint is described
in "OAuth 2.0 Client and Resource Server Endpoints" in the Developer's Guide.
For details on creating policies, see "Defining Authorization Policies".
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider > Configure OAuth 2.0.
On the Configure OAuth 2.0 page, select the Realm for the authorization service.
(Optional) If necessary, adjust the lifetimes for authorization codes (a lifetime of 10 minutes or less is recommended in RFC 6749), access tokens, and refresh tokens.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens unless you do not want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when returning an access token.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens if you want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when refreshing an access token.
(Optional) If you want to use the default scope implementation, whereby scopes are taken to be resource owner profile attribute names, then keep the default setting.
If you have a custom scope validator implementation, put it on the OpenAM classpath, and provide the class name as Scope Implementation Class. For an example, see "Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling" in the Developer's Guide.
Click Create to complete the process.
To access the authorization server configuration in OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click OAuth2 Provider.
As mentioned at the outset of this procedure, the wizard sets up a policy in the Top Level Realm to protect the authorization endpoint. The policy appears in the
iPlanetAMWebAgentServicepolicy set. Its name isOAuth2ProviderPolicy.(Optional) If your provider has a custom response type plugin, put it on the OpenAM classpath, and then add the custom response types and the plugin class names to the list of Response Type Plugins.
(Optional) If you use an external identity repository where resource owners log in not with their user ID, but instead with their mail address or some other profile attribute, then complete this step.
The following steps describe how to configure OpenAM authentication so OAuth 2.0 resource owners can log in using their email address, stored on the LDAP profile attribute,
mail. Adapt the names if you use a different LDAP profile attribute, such ascn:When configuring the data store for the LDAP identity repository, make sure that you select Load schema when saved, and that you set the Authentication Naming Attribute to
mail. You can find the data store configuration under Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores.Add the
mailprofile attribute name to the list of attributes that can be used for authentication.To make the change, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services, click OAuth2 Provider, add the profile attributes to the list titled User Profile Attribute(s) the Resource Owner is Authenticated On, and then click Save Changes.
Create an LDAP authentication module to use with the external directory:
In OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Modules, create a module to access the LDAP identity repository, such as
LDAPAuthUsingMail.In the Attribute Used to Retrieve User Profile field, set the attribute to
mail.In the Attributes Used to Search for a User to be Authenticated list, remove the default
uidattribute and add themailattribute.Click Save.
Create an authentication chain to include the module, such as
authUsingMail.When creating the authentication chain, choose the
LDAPAuthUsingMailmodule in the Instance drop-down list, and set the criteria to REQUIRED.Click Save.
Set Organization Authentication Configuration to use the new chain,
authUsingMail, and then click Save.At this point OAuth 2.0 resource owners can authenticate using their email address rather than their user ID.
Add a multi-valued string syntax profile attribute to your identity repository. OpenAM stores resource owners' consent to authorize client access in this profile attribute. On subsequent requests from the same client for the same scopes, the resource owner no longer sees the authorization page.
You are not likely to find a standard profile attribute for this. For evaluation purposes only, you might try an unused existing profile attribute, such as
description.When moving to production, however, use a dedicated, multi-valued, string syntax profile attribute that clearly is not used for other purposes. For example, you might call the attribute
oAuth2SavedConsent.Adding a profile attribute involves updating the identity repository to support use of the attribute, updating the AMUser Service for the attribute, and optionally allowing users to edit the attribute. The process is described in "Customizing Profile Attributes" in the Developer's Guide, which demonstrates adding a custom attribute when using OpenDJ directory services to store user profiles.
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services, click OAuth2 Provider, and then specify the name of the attribute created in the previous step in the Saved Consent Attribute Name field.
Click Save Changes.
To further adjust the authorization server configuration after you create it, in the OpenAM console navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click OAuth2 Provider.
To adjust global defaults, in the OpenAM console navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click OAuth2 Provider.
You register an OAuth 2.0 client with the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 authorization service by creating and configuring an OAuth 2.0 Client agent profile.
At minimum you must have the client identifier and client password in order to register your OAuth 2.0 client.
Use either of these two facilities:
In the OpenAM console, access the client registration endpoint at
/oauth2/registerClient.jsp.The full URL depends on where you deployed OpenAM. For example,
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/registerClient.jsp.The Register a Client page lets you quickly create and configure an OAuth 2.0 client in a simple web page without inline help.
In the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > Agent, click New, then provide the client identifier and client password, and finally click Create to create the profile.
This page requires that you perform additional configuration separately.
After initially registering or creating a client agent profile as necessary.
In the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > Agent > Client Name to open the Edit Client Name page.
Adjust the configuration as needed using the inline help for hints, and also the documentation section "Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients".
Examine the client type option. An important decision to make at this point is whether your client is a confidential client or a public client. This depends on whether your client can keep its credentials confidential, or whether its credentials can be exposed to the resource owner or other parties. If your client is a web-based application running on a server, such as the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 client, then you can keep its credentials confidential. If your client is a user-agent based client, such as a JavaScript client running in a browser, or a native application installed on a device used by the resource owner, then yours is a public client.
When finished, save your work.
OpenAM exposes a RESTful API that lets administrators read, list, and delete OAuth 2.0 tokens. OAuth 2.0 clients can also manage their own tokens. For details, see "OAuth 2.0 Token Administration Endpoint" in the Developer's Guide.
This section takes a high-level look at how to set up OpenAM both as an OAuth 2.0 authorization server and also as an OAuth 2.0 client in order to protect resources on a resource server by using an OpenAM policy agent.
The example in this section uses three servers,
http://authz.example.com:8080/openam as the
OAuth 2.0 authorization server,
http://client.example.com:8080/openam as the
OAuth 2.0 client, which also handles policy,
http://www.example.com:8080/ as the
OAuth 2.0 resource server protected with an OpenAM policy agent
where the resources to protect are deployed in Apache Tomcat.
The two OpenAM servers communicate using OAuth 2.0.
The policy agent on the resource server communicates with OpenAM
as policy agents normally do, using OpenAM specific requests.
The resource server in this example does not need to support OAuth 2.0.
The high-level configuration steps are as follows:
On the OpenAM server that you will configure to act as an OAuth 2.0 client, configure a policy agent profile, and the policy used to protect the resources.
On the web server or application container that will act as an OAuth 2.0 resource server, install and configure the OpenAM policy agent.
Make sure that you can access the resources when you log in through an authentication module that you know to be working, such as the default DataStore authentication module.
In this example, you would try to access
http://www.example.com:8080/examples/. The policy agent should redirect you to the OpenAM login page. After you log in successfully as a user with access rights to the resource, OpenAM should redirect you back tohttp://www.example.com:8080/examples/, and the policy agent should allow access.Fix any problems you have in accessing the resources before you try to set up access through the OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module.
Configure one OpenAM server as an OAuth 2.0 authorization service, which is described in "Configuring the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Service".
Configure the other OpenAM server with the policy agent profile and policy as an OAuth 2.0 client, by setting up an OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module according to the section "Hints for the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Authentication Module".
On the authorization server, register the OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module as an OAuth 2.0 client, which is described in "Registering OAuth 2.0 Clients With the Authorization Service".
Log out and access the protected resources to see the process in action.
This example pulls everything together (except security considerations), using OpenAM servers both as the OAuth 2.0 authorization server, and also as the OAuth 2.0 client, with an OpenAM policy agent on the resource server requesting policy decisions from OpenAM as OAuth 2.0 client. In this way, any server protected by a policy agent that is connected to an OpenAM OAuth 2.0 client can act as an OAuth 2.0 resource server:
On the OpenAM server that will be configured as an OAuth 2.0 client, set up an OpenAM policy agent and policy in the Top Level Realm,
/, to protect resources.See the Web Policy Agent User's Guide or the Java EE Policy Agent User's Guide for instructions on installing a policy agent. This example relies on the Apache Tomcat Java EE policy agent, configured to protect resources in Apache Tomcat (Tomcat) at
http://www.example.com:8080/.The policies for this example protect the Tomcat examples under
http://www.example.com:8080/examples/, allowing GET and POST operations by all authenticated users. For more information, see "Defining Authorization Policies".After setting up the policy agent and the policy, you can make sure everything is working by attempting to access a protected resource, in this case,
http://www.example.com:8080/examples/. The policy agent should redirect you to OpenAM to authenticate with the default authentication module, where you can login as userdemopasswordchangeit. After successful authentication, OpenAM redirects your browser back to the protected resource and the policy agent lets you get the protected resource, in this case, the Tomcat examples top page.On the OpenAM server to be configured as an OAuth 2.0 authorization server, configure OpenAM's OAuth 2.0 authorization service as described in "Configuring the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Service".
The authorization endpoint to protect in this example is at
http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/authorize.On the OpenAM server to be configured as an OAuth 2.0 client, configure an OpenAM OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module instance for the Top Level Realm:
Under Realms > Top Level Realm > Authentication > Modules, click Add Module. Name the module
OAuth2, and select the OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect type, then click Create. The OAuth 2.0 client configuration page appears. This page offers numerous options. The key settings for this example are the following:- Client Id
This is the client identifier used to register your client with OpenAM's authorization server, and then used when your client must authenticate to OpenAM.
Set this to
myClientIDfor this example.- Client Secret
This is the client password used to register your client with OpenAM's authorization server, and then used when your client must authenticate to OpenAM.
Set this to
passwordfor this example. Make sure you use strong passwords when you actually deploy OAuth 2.0.- Authentication Endpoint URL
In this example,
http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/authorize.This OpenAM endpoint can take additional parameters. In particular, you must specify the realm if the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than for the Top Level Realm.
For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for the realm
/customers, then use the following URL:http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/authorize?realm=/customers.The
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint can also takemoduleandserviceparameters. Use either as described in "Authenticating To OpenAM", wheremodulespecifies the authentication module instance to use orservicespecifies the authentication chain to use when authenticating the resource owner.- Access Token Endpoint URL
In this example,
http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token.This OpenAM endpoint can take additional parameters. In particular, you must specify the realm if the OpenAM OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for a subrealm rather than the Top Level Realm (/).
For example, if the OAuth 2.0 provider is configured for the realm
/customers, then use the following URL:http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token?realm=/customers.- User Profile Service URL
In this example,
http://authz.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo.- Scope
In this example,
cn.The demo user has common name
demoby default, so by setting this tocn|Read your user name, OpenAM can get the value of the attribute without the need to create additional subjects, or to update existing subjects. The description,Read your user name, is shown to the resource owner in the consent page.- OAuth2 Access Token Profile Service Parameter name
Identifies the parameter that contains the access token value, which in this example is
access_token.- Proxy URL
The client redirect URL, which in this example is
http://client.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2c/OAuthProxy.jsp.- Account Mapper
In this example,
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oauth2.DefaultAccountMapper.- Account Mapper Configuration
In this example,
cn=cn.- Attribute Mapper
In this example,
org.forgerock.openam.authentication.modules.oauth2.DefaultAttributeMapper.- Attribute Mapper Configuration
In this example,
cn=cn.- Create account if it does not exist
In this example, disable this functionality.
OpenAM can create local accounts based on the account information returned by the authorization server.
On the OpenAM server configured to act as an OAuth 2.0 authorization server, register the OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect authentication module as an OAuth 2.0 confidential client, which is described in "Registering OAuth 2.0 Clients With the Authorization Service".
Under Realms > Top Level Realm > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > Agents >
myClientID, adjust the following settings:- Client type
In this example,
confidential. OpenAM protects its credentials as an OAuth 2.0 client.- Redirection URIs
In this example,
http://client.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2c/OAuthProxy.jsp.- Scopes
In this example,
cn.
Before you try it out, on the OpenAM server configured to act as an OAuth 2.0 client, you must make the following additional change to the configuration.
Your OpenAM OAuth 2.0 client authentication module is not part of the default chain, and therefore OpenAM does not call it unless you specifically request the OAuth 2.0 client authentication module.
To cause the policy agent to request your OAuth 2.0 client authentication module explicitly, browse in OpenAM console to your policy agent profile configuration, in this case Realms > Top Level Realm > Agents > J2EE > Agents > Agent Name > OpenAM Services > OpenAM Login URL, and add
http://client.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Login?module=OAuth2, moving it to the top of the list.Save your work.
This ensures that the policy agent directs the resource owner to OpenAM with the instruction to authenticate using the
OAuth2authentication module.Try it out.
First make sure you are logged out of OpenAM, for example by browsing to the logout URL, in this case
http://client.example.com:8080/openam/UI/Logout.Next attempt to access the protected resource, in this case
http://www.example.com:8080/examples/.If everything is set up properly, the policy agent redirects your browser to the login page of OpenAM with
module=OAuth2among other query string parameters. After you authenticate, for example as userdemo, passwordchangeit, OpenAM presents you with an authorization decision page.When you click Allow, the authorization service creates an SSO session, and redirects the client back to the resource, thus allowing the client to access the protected resource. If you configured an attribute on which to store the saved consent decision, and you choose to save the consent decision for this authorization, then OpenAM can use that saved decision to avoid prompting you for authorization next time the client accesses the resource, but only ensure that you have authenticated and have a valid session.
As described in "SAML v2.0 Bearer Assertion Profiles", OpenAM as OAuth 2.0 authorization server can handle the profile where a SAML v2.0 assertion borne by the client functions as an authorization grant to get an access token. This lets a client get an access token when a resource owner completes SAML v2.0 Web Single Sign-On.
You can configure OpenAM as both SAML v2.0 service provider and OAuth 2.0 authorization server, using a built-in adapter class to POST assertions returned to the service provider to the access token endpoint of the authorization server. This allows clients to send a resource owner to the identity provider for SAML v2.0 web SSO, get an assertion at the service provider, and retrieve an access token from the authorization server. In other words, once this scenario is configured, the client must only direct the resource owner to start web SSO as described in "JSP Pages for SSO and SLO", and then retrieve the access token on success or handle the error condition on failure.
For this scenario to work, the following conditions must be met:
The client must make the resource owner understand that by authenticating to the SAML v2.0 identity provider the resource owner grants the client access to the protected resources. OpenAM does not present the resource owner with an authorization decision.
The SAML v2.0 identity provider issuing the assertion must sign the assertion, and must correctly handle the name ID for the subject.
OpenAM as relying party must request that assertions are signed, must verify the signatures on assertions, must correctly handle name IDs from the issuer, and must use the built-in
org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.saml2.core.OAuth2Saml2GrantSPAdapteradapter class in the service provider configuration to POST assertions to the OAuth 2.0 authorization service.The OAuth 2.0 authorization service and SAML v2.0 service provider must be configured together on the same OpenAM server.
An OAuth 2.0 client configuration on OpenAM with the same name as the service provider entity ID must be set up on OpenAM.
The OAuth 2.0 client initiating the process must be able to consume the access token and to handle errors if necessary.
Default scopes must be set up in the OAuth 2.0 client profile.
Follow these steps. The test configuration hints in this procedure let you prepare configuration to test with the demo user created in OpenAM by default.
Make sure the SAML v2.0 identity provider signs assertions and that name IDs are correctly configured to map resource owner accounts.
When configuring OpenAM as a hosted identity provider follow these steps:
Make sure the Signing Key is properly configured on setup.
For a test configuration, select the
testcertificate shown in the Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers > Create Identity Provider wizard.Make sure name IDs are properly configured.
For a test configuration, in the OpenAM console under Federation > Entity Providers > IdP Name > NameID Value Map, add
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified=cnand then Save your work.
For more detail on configuring OpenAM as a SAML v2.0 identity provider, see "Modifying an Identity Provider's Configuration".
Configure OpenAM as service provider.
Set up a hosted service provider in OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers > Create Hosted Service Provider, keeping track of the name, such as
https://www.sp.example:8443/openam, and selecting Use default attribute mapping from Identity Provider.For details on configuring OpenAM as a SAML v2.0 service provider, see "Modifying a Service Provider's Configuration".
Under Federation > Entity Providers > SP Name > Assertion Content > Request/Response Signing, check Assertions Signed.
For a test configuration, in Federation > Entity Providers > SP Name > Assertion Content > NameID Format List, remove all but
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified, and then Save your work.In Federation > Entity Providers > SP Name > Assertion Processing > Adapter, add
org.forgerock.openam.oauth2.saml2.core.OAuth2Saml2GrantSPAdapter, and then Save your work.This is the adapter class that POSTs the SAML v2.0 assertion to the OAuth 2.0 access token endpoint.
Use the wizard under Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure SAMLv2 Providers > Configure Remote Identity Provider to import the identity provider metadata.
Make sure the identity provider imports the metadata for your service provider.
If your service provider is at
https://www.sp.example:8443/openam, then the metadata can be accessed athttps://www.sp.example:8443/openam/saml2/jsp/exportmetadata.jsp.On the service provider OpenAM server, set up the OAuth 2.0 authorization server as described in "Configuring the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Service".
For a test configuration, set the realm to
/, and accept the defaults.On the service provider and authorization server OpenAM server, set up an OAuth 2.0 client profile with the same name as the service provider under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > New. For example, if the service provider name is
https://www.sp.example:8443/openam, then make that the name of the OAuth 2.0 client profile.On the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client page, click the service provider name, for example, https://www.sp.example:8443/openam. On the Edit page, scroll down to the Scope(s) section, enter your default scopes (for example,
cn,mail) in the New Value field, and then click Add.You can make additional changes to the client profile if necessary. See "Registering OAuth 2.0 Clients With the Authorization Service" for details.
Click Save to apply your settings.
Test your configuration.
Log out of all OpenAM servers.
Initiate SAML v2.0 Web SSO.
For example, if your identity provider is at
https://www.idp.example:8443/openamwith meta alias/idpand your service provider is athttps://www.sp.example:8443/openam, then browse to the following URL (without line breaks or spaces):http://www.idp.example:8443/openam/saml2/jsp/idpSSOInit.jsp ?metaAlias=/idp&spEntityID=http://www.sp.example:8443/openamFor other configurations, see "JSP Pages for SSO and SLO".
Log in to the identity provider.
For OpenAM, login with user name
demoand passwordchangeit.Log in to the service provider.
For OpenAM, login with user name
demoand passwordchangeit.See the resulting access token on successful login.
The result looks something like this, all on one line:
{ "expires_in": 59, "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "f0f731e0-6013-47e3-9c07-da598157a85f" }
Users of OAuth 2.0 clients can now manage their authorized applications
on their user page in the OpenAM console.
For example, the user logs in to the OpenAM console as demo,
and then clicks the Dashboard link on the Profile page.
In the Authorized Apps section, the users can view their OAuth 2.0 tokens or
remove them by clicking the Revoke Access button, effectively removing their
consent to the application.
Companies that have internal applications that use OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect 1.0 can allows clients to skip consent and make consent confirmation optional so as not to disrupt their online experience.
Start the OpenAM console. Under Realms, select the realm that you are working with.
First, create or update your OAuth2 provider:
Select Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider, then select Configure OpenID Connect, then click Create.
Click Services > OAuth2 Provider.
Enable Allow clients to skip consent.
Click Save Changes.
Next, create or update an OpenID Connect client. Click Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client.
Under Agent, click New, enter a name and password for the agent, and then click Create.
Click the agent you just created.
Click the Enabled checkbox for Implied consent.
Click Save.
When both settings are set on the OAuth2 provider and OAuth 2.0 Client (agent) settings, OpenAM will treat the requests as if the client has already saved its consent and will suppress any user consent pages to the client.
OpenAM supports stateless access and refresh tokens
for OAuth 2.0. Stateless access and refresh tokens allow clients to directly
validate the tokens without storing session information in server memory.
The stateless token is a JWT, which is stored in the
iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie if accessed through a web browser
or in the tokenid response header if accessed over REST.
The stateless access token allows any OpenAM instance in the issuing cluster to validate an OAuth 2.0 token without the need for cross-server communication.
Open the OpenAM console.
Under Realms, select the realm that you are working with.
Click Services, and then select OAuth2 Provider.
For Use Stateless Access & Refresh Tokens, slide the toggle button to the right to enable the feature.
Optional. For Issue Refresh Tokens, slide the toggle button to the right to enable the feature.
For Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens, slide the toggle button to the right to enable the feature.
OpenAM provides a blacklisting feature that prevents stateless OAuth v2.0 tokens from being reused if the authorization code has been replayed or tokens have been revoked by either the client or resource owner.
On the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Global Services > Global > OAuth2 Provider.
Under Global Attributes, enter the number of blacklisted tokens in the Token Blacklisting Cache Size field.
Token Blacklisting Cache Size determines the number of blacklisted tokens to cache in memory to speed up blacklist checks. You can enter a number based on the estimated number of token revocations that a client will issue (for example, when the user gives up access or an administrator revokes a client's access).
Default: 10000
In the Blacklist Poll Interval field, enter the interval in seconds for OpenAM to check for token blacklist changes from the CTS data store.
The longer the polling interval, the more time a malicious user has to connect to other OpenAM servers in a cluster and make use of a stolen OAuth v2.0 access and refresh token. Shortening the polling interval improves the security for revoked tokens but might incur a minimal decrease in overall OpenAM performance due to increased network activity.
Default: 60 seconds
In the Blacklist Purge Delay field, enter the length of time in minutes that blacklist tokens can exist before being purged beyond their expiration time.
When stateless blacklisting is enabled, OpenAM tracks OAuth v2.0 access and refresh tokens over the configured lifetime of those tokens plus the blacklist purge delay. For example, if the access token lifetime is set to 6000 seconds and the blacklist purge delay is one minute, the OpenAM tracks the access token for 101 minutes. You can increase the blacklist purge delay if you expect system clock skews in an OpenAM server cluster to be greater than one minute. There is no need to increase the blacklist purge delay for servers running a clock synchronization protocol, such as Network Time Protocol.
Default: 1 minute
Click Save to apply your changes.
OpenAM supports digital signature algorithms that secure the integrity of its JSON payload, which is outlined in the JSON Web Algorithm specification (RFC 7518).
OpenAM supports signing algorithms listed in JSON Web Algorithms (JWA): "alg" (Algorithm) Header Parameter Values for JWS:
| • HS256 - HMAC with SHA-256 |
| • HS384 - HMAC with SHA-384 |
| • HS512 - HMAC with SHA-512 |
| • RS256 - RSA using SHA-256 |
| • ES256 - ECDSA with SHA-256 and NIST standard P-256 elliptic curve |
| • ES384 - ECDSA with SHA-384 and NIST standard P-384 elliptic curve |
| • ES512 - ECDSA with SHA-512 and NIST standard P-521 elliptic curve |
If you intend to use an ECDSA signing algorithm, you must generate a public/private key pair for use with ECDSA. To generate the public and private key pair, see step 1 in "Configuring Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithms".
Start the OpenAM console. Under Realms, select the realm that you are working with.
First, create or update your OAuth2 provider:
Select Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider, then select Configure OpenID Connect, then click Create.
Click Services > OAuth2 Provider.
On the OAuth2 Token Signing Algorithm drop-down list, select the signing algorithm to use for your digital signatures.
Take one of the following actions depending on the token signing algorithm:
If you are using an HMAC signing algorithm, enter the Base64-encoded key used by HS256, HS384 and HS512 in the Token Signing HMAC Shared Secret field.
If you are using RS256, enter the public/private key pair used by RS256 in the Token Signing RSA public/private key pair field. The public/private key pair will be retrieved from the keystore referenced by the property
com.sun.identity.saml.xmlsig.keystore.If you are using an ECDSA signing algorithm, enter the list of public/private key pairs used for the elliptic curve algorithms (ES256/ES384/ES512) In the Token Signing ECDSA public/private key pair alias field. For example,
ES256|es256test. Each of the public/private key pairs will be retrieved from the keystore referenced by the propertycom.sun.identity.saml.xmlsig.keystore.Click Save Changes.
Next, update the OpenID Connect client:
Under Agent, click New, enter a Name and Password for the agent, and then click Create.
In the ID Token Signing Algorithm field, enter the signing algorithm that the ID token for this client must be signed with. Default:
RS256.• HS256 (HMAC with SHA-256) • HS384 (HMAC with SHA-384) • HS512 (HMAC with SHA-512) • RS256 (RSA using SHA-256) • ES256 (ECDSA with SHA-256 and NIST standard P-256 elliptic curve) • ES384 (ECDSA with SHA-384 and NIST standard P-384 elliptic curve) • ES512 (ECDSA with SHA-512 and NIST standard P-521 elliptic curve) Click Save.
OpenAM exposes the public keys used to digitally sign OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 access and refresh tokens at a JWK (JSON Web Key) URI endpoint, which is exposed from all realms for an OAuth2 provider. The following steps show how to access the public keys:
To find the JWK URI, perform an HTTP GET at
/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration.curl http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration { "id_token_encryption_alg_values_supported":[ "RSA1_5" ], "response_types_supported":[ "token id_token", "code token", "code token id_token", "token", "code id_token", "code", "id_token" ], "registration_endpoint":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/connect/register", "token_endpoint":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token", "end_session_endpoint":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/connect/endSession", "scopes_supported":[ "phone", "address", "email", "openid", "profile" ], "acr_values_supported":[ ], "version":"3.0", "userinfo_endpoint":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/userinfo", "token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported":[ "client_secret_post", "private_key_jwt", "client_secret_basic" ], "subject_types_supported":[ "public" ], "issuer":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2", "id_token_encryption_enc_values_supported":[ "A256CBC-HS512", "A128CBC-HS256" ], "claims_parameter_supported":true, "jwks_uri":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/connect/jwk_uri", "id_token_signing_alg_values_supported":[ "ES384", "ES256", "ES512", "HS256", "HS512", "RS256", "HS384" ], "check_session_iframe":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/connect/ checkSession", "claims_supported":[ "zoneinfo", "phone_number", "address", "email", "locale", "name", "family_name", "given_name", "profile" ], "authorization_endpoint":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/authorize" }Perform an HTTP GET at the JWKS URI to get the public signing key:
$ curl http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/connect/jwk_uri { "keys": [ { "kty":"RSA", "kid":"SylLC6Njt1KGQktD9Mt+0zceQSU=", "use":"sig", "alg":"RS256", "n":"AK0kHP1O-RgdgLSoWxkuaYoi5Jic6hLKeuKw8WzCfsQ68ntBDf6tVOTn_kZA7Gjf4oJ AL1dXLlxIEy-kZWnxT3FF-0MQ4WQYbGBfaW8LTM4uAOLLvYZ8SIVEXmxhJsSlvaiTWCbNFaOf iII8bhFp4551YB07NfpquUGEwOxOmci_", "e":"AQAB" } ] }
OAuth 2.0 messages involve credentials and access tokens that allow the bearer to retrieve protected resources. Therefore, do not let an attacker capture requests or responses. Protect the messages going across the network.
RFC 6749 includes a number of Security Considerations, and also requires Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect sensitive messages. Make sure you read the section covering Security Considerations, and that you can implement them in your deployment.
Also, especially when deploying a mix of other clients and resource servers, take into account the points covered in the Internet-Draft, OAuth 2.0 Threat Model and Security Considerations, before putting your service into production.
This chapter covers OpenAM support for OpenID Connect 1.0. OpenID Connect 1.0 is an authentication layer built on OAuth 2.0. OpenID Connect 1.0 is a specific implementation of OAuth 2.0 where the identity provider that runs the authorization server also holds the protected resource that the third-party application aims to access. This resource is the UserInfo, information about the authenticated end user expressed in a standard format. In this way, OpenID Connect 1.0 allows relying parties both to verify the identity of the end user and also to obtain user information using REST. This contrasts with OAuth 2.0, which only defines the authorization mechanism.
The names used in OpenID Connect 1.0 differ from those used in OAuth 2.0. In OpenID Connect 1.0, the key entities are the following:
The end user (OAuth 2.0 resource owner) whose user information the application needs to access.
The end user wants to use an application through existing identity provider account without signing up to and creating credentials for yet another web service.
The Relying Party (RP) (OAuth 2.0 client) needs access to the end user's protected user information.
For example, an online mail application needs to know which end user is accessing the application in order to present the correct inbox.
As another example, an online shopping site needs to know which end user is accessing the site in order to present the right offerings, account, and shopping cart.
The OpenID Provider (OP) (OAuth 2.0 authorization server and also resource server) that holds the user information and grants access.
OpenAM can play this role in an OpenID Connect deployment.
The OP effectively has the end user's consent to providing the RP with access to some of its user information. As OpenID Connect 1.0 defines unique identification for an account (subject identifier + issuer identifier), the RP can use this as a key to its own user profile.
In the case of the online mail application, this key could be used to access the mailboxes and related account information. In the case of the online shopping site, this key could be used to access the offerings, account, shopping cart and so forth. The key makes it possible to serve users as if they had local accounts.
In OpenID Connect, the relying party can verify claims about the identity of the end user, and log the user out at the end of a session. OpenID Connect also makes it possible to discover the OpenID Provider for an end user, and to register relying party client applications dynamically. OpenID connect services are built on OAuth 2.0, JSON Web Token (JWT), WebFinger and Well-Known URIs.
In its role as OpenID Provider, OpenAM lets OpenID Connect relying parties (clients) discover its capabilities, handles both dynamic and static registration of OpenID Connect relying parties, responds to relying party requests with authorization codes, access tokens, and user information according to the Authorization Code and Implicit flows of OpenID Connect, and manages sessions.
This section describes how OpenAM fits into the OpenID Connect picture in terms of the roles that it plays in the authorization code and implicit flows, provider discovery, client registration, and session management.
The OpenID Connect Authorization Code Flow specifies how the relying party interacts with the OpenID Provider, in this case OpenAM, based on use of the OAuth 2.0 authorization grant. The following sequence diagram shows successful processing from the authorization request, through grant of the authorization code, access token, and ID token, and optional use of the access token to get information about the end user.
In addition to what OAuth 2.0 specifies, OpenID Connect uses an ID token so the relying party can validate claims about the end user. It also defines how to get user information, such as profile, email, address, and phone details from the UserInfo endpoint with a valid access token.
The OpenID Connect Implicit Flow specifies how the relying party interacts with the OpenID Provider, in this case OpenAM, based on use of the OAuth 2.0 implicit grant. The following sequence diagram shows successful processing from the authorization request, through grant of the access and ID tokens, and optional use of the access token to get information about the end user.
As for the Authorization Code Flow, the Implicit Flow specifies an ID token so that the relying party can validate claims about the end user. It also defines how to get user information, such as profile, email, address, and phone details from the UserInfo endpoint with a valid access token.
OpenID Connect defines how a relying party can discover the OpenID Provider and corresponding OpenID Connect configuration for an end user. The discovery mechanism relies on WebFinger to get the information based on the end user's identifier. The server returns the information in JSON Resource Descriptor (JRD) format.
OpenID Connect relying parties register OAuth 2.0 client profiles with OpenAM. Relying parties can register with OpenAM as a provider both statically, as for other OAuth 2.0 clients, and also dynamically, as specified by OpenID Connect Discovery. To allow dynamic registration, you register an initial OAuth 2.0 client that other relying parties can use to get access tokens for registration.
You can also enable OpenID Connect relying parties to register dynamically
without having to provide an access token.
For details, see the documentation on the advanced server property,
org.forgerock.openam.openidconnect.allow.open.dynamic.registration,
in "Advanced" in the Reference.
Take care to limit or throttle dynamic registration
if you enable this capability on production systems.
OpenID Connect lets the relying party track whether the end user is logged in at the provider, and also initiate end user logout at the provider. The specification has the relying party monitor session state using an invisible iframe and communicate status using the HTML 5 postMessage API.
You can configure OpenAM's OAuth 2.0 provider service to double as an OpenID Connect provider service.
Follow the steps in this procedure to set up the OAuth2 provider service with OpenID Connect defaults by using the Configure OAuth Provider wizard:
When you create the service with the Configure OAuth Provider wizard, the wizard also creates a standard policy in the Top Level Realm (/) to protect the authorization endpoint. In this configuration, OpenAM serves the resources to protect, and no separate application is involved. OpenAM therefore acts both as the policy decision point and policy enforcement point that protects the OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint used by OpenID Connect.
There is no requirement to use the wizard
or to create the policy in the Top Level Realm.
However, if you create the OAuth 2.0 provider service without the wizard,
then you must set up the policy independently, if required.
The policy must appear in a policy set of type
iPlanetAMWebAgentService.
When configuring the policy allow all authenticated users
to perform HTTP GET and POST requests on the authorization endpoint.
The authorization endpoint is described
in "OAuth 2.0 Client and Resource Server Endpoints" in the Developer's Guide.
For details on creating policies, see "Defining Authorization Policies".
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider > Configure OpenID Connect.
On the Configure OAuth2/OpenID Connect Service page, select the Realm for the provider service.
(Optional) If necessary, adjust the lifetimes for authorization codes, access tokens, and refresh tokens.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens unless you do not want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when returning an access token.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens if you want the authorization service to supply a new refresh token when refreshing an access token.
(Optional) If you have a custom scope validator implementation, put it on the OpenAM classpath, for example
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/, and specify the class name in the Scope Implementation Class field. For an example, see "Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling" in the Developer's Guide.Click Create to save your changes.
OpenAM creates an OAuth2 provider service, with OpenID Connect default parameter values, and a policy to protect the OAuth2 authorization endpoints.
Warning
If an OAuth2 provider service already exists, it will be overwritten with the new OpenID Connect parameter values.
To access the provider service configuration in the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click OAuth2 Provider.
For OpenID Connect providers you may want to configure the following settings:
The optional Remote JSON Web Key URL field allows you to set a URL to a JSON Web Key set with the public key(s) for the provider.
If this setting is not configured, then OpenAM provides a local URL to access the public key of the private key used to sign ID tokens.
The Subject Types supported map allows you to support pairwise subject types as described in the OpenID Connect core specification section concerning Subject Identifier Types.
The ID Token Signing Algorithms supported list allows you to change the list of algorithms used to sign ID Tokens.
The Supported Claims list allows you to restrict the claims supported by OpenAM's userinfo endpoint.
For more information, see "Understanding OpenID Connect Scopes and Claims".
The Alias of ID Token Signing Key alias allows you to set the key pair alias for the key used to sign ID Tokens when using a signing algorithm that involves asymmetric keys.
For instructions on changing the key pair, see "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ".
The Allow Open Dynamic Client Registration checkbox enables relying parties to register without using an access token.
The Generate Registration Access Tokens checkbox has OpenAM generate Registration Access Tokens for dynamic client registration when Allow Open Dynamic Client Registration is enabled. This allows the client to view and update its registration.
Click Save to complete the process.
If your provider is part of a GSMA Mobile Connect deployment, see "Configuring OpenAM as an OP for Mobile Connect".
This section explains how scopes and claims can be used when OpenAM is acting as an OpenID Connect provider.
When OpenAM is configured as an OAuth 2.0 provider, a scope is
considered to be a concept, rather than directly relating to a piece
of data in the user profile. For example, Facebook has an OAuth 2.0 scope
named read_stream. OpenAM returns whether the
scope is allowed or not, with no associated data.
When OpenAM is configured as an OpenID Connect provider, scopes can relate to data in a user profile by making use of one or more claims. Each claim maps directly to an attribute in the user profile.
For example, OpenAM supports a scope named profile
when configured as an OpenID Connect provider, which by default is made up
of the following claims:
| Claim | User profile attribute |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The mappings between scopes, claims, and user profile attributes are controlled by the OIDC Claims Script specified in the OAuth 2.0 provider. For more information, see "Using the Default Scripts" in the Developer's Guide.
As each claim represents a piece of information from the user profile, OpenAM displays the actual data the relying party is given if the user clicks Allow:
You can configure OpenAM to support requests for individual
claims as query parameters, as described in section 5.5 of the
OpenID Connect specification, by enabling the
claims_parameter_supported option.
In section 5.6 of the specification, OpenAM supports Normal Claims. The optional Aggregated Claims and Distributed Claims representations are not supported by OpenAM.
For more information, see "OAuth2 Provider" in the Reference.
In order to allow relying parties to discover the OpenID Connect Provider for an end user, OpenAM supports OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0. In addition to discovering the OpenID Provider for an end user, the relying party can also request the OpenID Provider configuration.
OpenAM as OpenID Connect provider exposes two endpoints for discovery:
/oauth2/.well-known/webfinger |
/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration |
A relying party needs to be able to discover the OpenID Connect provider for
an end user.
In this case you should consider redirecting requests to URIs at the server root,
such as http://www.example.com/.well-known/webfinger
and http://www.example.com/.well-known/openid-configuration,
to these Well-Known URIs in OpenAM's space.
Discovery relies on WebFinger, a protocol to discover information about people and other
entities using standard HTTP methods. WebFinger uses Well-Known URIs,
which defines the path prefix /.well-known/ for the
URLs defined by OpenID Connect Discovery.
Unless you deploy OpenAM in the root context of a container listening on port 80 on the primary host for your domain, relying parties need to find the right host:port/deployment-uri combination to locate the well-known endpoints. Therefore you must manage the redirection to OpenAM. If you are using WebFinger for something else than OpenID Connect Discovery, then you probably also need proxy logic to route the requests.
OpenID Connect Discovery requires an OAuth 2.0 provider service to be configured
within OpenAM. The service must have openid as a supported scope in
order to use the /oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration endpoint. For
information on configuring an OAuth 2.0 provider service for OpenID Connect in OpenAM, see
"Configuring OpenAM As OpenID Connect Provider".
To retrieve the OpenID Connect provider for an end user, the relying party needs the following:
hostThe server where the relying party can access the WebFinger service.
Notice that this is a host name rather than a URL to the endpoint, which is why you might need to redirect relying parties appropriately as described above.
resourceIdentifies the end user that is the subject of the request.
The relying party must percent-encode the resource value when using it in the query string of the request, so when using the
acctURI scheme and the resource isacct:user@example.com, then the value to use isacct%3Auser%40example.com.relURI identifying the type of service whose location is requested.
In this case
http://openid.net/specs/connect/1.0/issuer, which ishttp%3A%2F%2Fopenid.net%2Fspecs%2Fconnect%2F1.0%2Fissuer.
If you have not set up the redirection to the root of the domain yet, you can test the endpoint for the demo user account with the following curl:
$ curl \
"https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/.well-known/webfinger\
?resource=acct%3Ademo%40example.com\
&rel=http%3A%2F%2Fopenid.net%2Fspecs%2Fconnect%2F1.0%2Fissuer"
{
"subject": "acct:demo@example.com",
"links": [
{
"rel": "http://openid.net/specs/connect/1.0/issuer",
"href": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam"
}
]
}The example shows that the OpenID Connect provider for the OpenAM demo user is indeed the OpenAM server.
The relying party can also discover the OpenID Connect provider configuration. If you have not set up the redirection to the root of the domain yet, you can test this making the following curl call:
$ curl https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration
{
"response_types_supported": [
"token id_token",
"code token",
"code token id_token",
"token",
"code id_token",
"code",
"id_token"
],
"registration_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/register",
"token_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token",
"end_session_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/endSession",
"version": "3.0",
"userinfo_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/userinfo",
"subject_types_supported": [
"public"
],
"issuer": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam",
"jwks_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/jwk_uri?realm=/",
"id_token_signing_alg_values_supported": [
"HS256",
"HS512",
"RS256",
"HS384"
],
"check_session_iframe": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/checkSession",
"claims_supported": [
"phone",
"email",
"address",
"openid",
"profile"
],
"authorization_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize"
}
When the OpenID Connect provider is configured in a subrealm,
then relying parties can get the configuration
by passing the realm as a query string parameter, as in
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/.well-known/openid-configuration?realm=realm-name.
In many deployments, OpenAM determines the base URL of a provider using the incoming HTTP request. However, there are often cases when the base URL of a provider cannot be determined from the incoming request alone, especially if the provider is behind some proxying application. For example, if an OpenAM instance is part of a site where the external connection is over SSL but the request to the OpenAM instance is over plain HTTP, then OpenAM would have difficulty in reconstructing the base URL of the provider.
In these cases, OpenAM supports a provider service that allows a realm to have a configured option for obtaining the base URL including protocol for components that need to return a URL to the client.
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrative user, such as
amAdmin, and then navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services.Click Add a Service, select Base URL Source, and then click Create.
For Base URL Source, select one of the following options:
Option Description Extension class Click the Extension class to return a base URL from a provided
HttpServletRequestobject. In the Extension class name field, enterorg.forgerock.openam.services.baseurl.BaseURLProvider.Fixed value Click Fixed value to enter a specific base URL value. In the Fixed value base URL field, enter the base URL.
Forwarded header Click Forwarded header to retrieve the base URL from the
Forwardedheader field in the HTTP request. The Forwarded HTTP header field is standardized and specified in RFC 7239.Host/protocol from incoming request (default) Click Host/protocol from incoming request to get the hostname, server name, and port from the HTTP request.
X-Forwarded-* headers Click X-Forwarded-* headers to use non-standard header fields, such as
X-Forwarded-For,X-Forwarded-By, andX-Forwarded-Proto.In the Context path, enter the context path for the base URL. If provided, the base URL includes the deployment context path appended to the calculated URL. For example,
/openam.Click Finish to save your configuration.
OpenID Connect relying parties can register with OpenAM both statically through OpenAM console for example, and also dynamically using OpenID Connect 1.0 Dynamic Registration.
Registering a relying party by using the OpenAM console consists of first creating an OAuth 2.0 Client agent profile, and then editing the profile for the settings pertinent to OpenID Connect 1.0.
In the OpenAM console under Realms > Realm Name > Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client > Agent, click New..., then provide the client identifier and client password, and finally click Create to create the profile.
To edit the profile to match the relying party configuration, follow the hints in "Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients" .
In order to read and edit the relying party profile dynamically later without using OpenAM console, be sure to set an access token in the Access Token field.
For dynamic registration you need the relying party profile data, and an access token to write the configuration to OpenAM by HTTP POST. To obtain the access token, register an initial client statically after creating the provider, as described in "To Register a Relying Party With OpenAM Console". Relying parties can then use that client to obtain the access token needed to perform dynamic registration.
Tip
As described in "OpenID Connect Relying Party Registration",
you can allow relying parties to register without having an access token
by setting the advanced server property,
org.forgerock.openam.openidconnect.allow.open.dynamic.registration,
to true.
When using that setting in production systems,
take care to limit or throttle dynamic registration.
On successful registration, OpenAM responds with information including an access token to allow the relying party subsequently to read and edit its profile:
Register an initial OAuth 2.0 client statically with a client ID, such as
masterClientand client secret likepassword.Obtain an access token using the client you registered.
For example, if you created the client as described in the previous step, and OpenAM administrator
amadminhas passwordpassword, you can use the OAuth 2.0 resource owner password grant as in the following example:$ curl \ --request POST \ --user "masterClient:password" \ --data "grant_type=password&username=amadmin&password=password" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token { "expires_in": 59, "token_type": "Bearer", "refresh_token": "26938cd0-6870-4e31-ade9-df31afc37ee1", "access_token": "515d6551-4512-4279-98b6-c0ef3f03a722" }HTTP POST the relying party registration profile to the
/oauth2/connect/registerendpoint, using bearer token authorization with the access token you obtained from OpenAM.Ensure that you provide a
client_namewhen registering the client. Without theclient_namevalue the auto-generatedclient_idwill be used on consent screens. The client ID is a UUID string and may not be desirable on end-user facing pages.For an example written in JavaScript, see the registration page in the OpenID Connect examples. Successful registration shows a response that includes the client ID and client secret. Lines are folded in the following example:
{ "issued_at": 1392364349, "expires_at": 0, "client_secret": "7f446ca9-3f1f-48fb-bf8c-150b9e643f29", "client_name": "Example.com OpenID Connect Client", "redirect_uris": [ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openid/cb-basic.html", "https://openam.example.com:8443/openid/cb-implicit.html" ], "registration_access_token": "515d6551-4512-4279-98b6-c0ef3f03a722", "client_id": "6e4abd50-3f03-41dc-b807-c6705c3e45d7", "registration_client_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/register ?client_id=6e4abd50-3f03-41dc-b807-c6705c3e45d7" }
OpenID Connect Session Management 1.0 allows the relying party to manage OpenID Connect sessions, making it possible to know when the end user should be logged out.
As described in the OpenID Connect Session Management 1.0 specification,
OpenAM's OpenID Provider exposes both a check_session_iframe URL
that allows the relying party to receive notifications when the end user's session
state changes at the provider, and also an end_session_endpoint URL to
which to redirect an end user for logout.
When registering your relying party that uses session management, you set the OAuth 2.0 client agent profile properties Post Logout Redirect URI and Client Session URI, described in "Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients". The Post Logout Redirect URI is used to redirect the end user user-agent after logout. The Client Session URI is the relying party URI where OpenAM sends notifications when the end user's session state changes.
OpenID Connect Authorization Code Flow and Implicit Flow define how clients interact with the provider to obtain end user authorization and profile information. Although you can run the simple example relying parties that are mentioned in this section without setting up Transport Layer Security, do not deploy relying parties in production without securing the transport.
Code for the relying party examples shown here is
available online.
Clone the example project to deploy it in the same web container as OpenAM.
Edit the configuration at the outset of the .js files in the project,
register a corresponding profile for the example relying party
as described in "Registering OpenID Connect Relying Parties",
and browse the deployment URL to see the initial page.
OpenID Connect Authorization Code Flow is designed for web-based relying parties that use the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code grant type. This grant type makes it possible for the relying party to get the access code by using the authorization code directly, without passing through the end user's browser. To protect its client secret (password), part of the relying party must run on a server.
In the example, the Basic Client Profile Start Page describes the prerequisite configuration, which must be part of the relying party profile that is stored in the OpenAM realm where you set up the OpenID Provider. In OpenAM console, check that the OAuth 2.0 client profile matches the settings described.
Log out of OpenAM,
and click the link at the bottom of the page to request authorization.
The link sends an HTTP GET request
asking for openid profile scopes
to the OpenID Provider authorization URI.
If everything is configured correctly,
OpenAM's OpenID Provider has you authenticate as an end user,
such as the demo user
with username demo and password changeit,
and grant (Allow) the relying party access to your profile.
If you successfully authenticate and allow the example relying party access to your profile, OpenAM returns an authorization code to the example relying party. The example relying party then uses the authorization code to request an access token and an ID token. It shows the response to that request. It also validates the ID token signature using the default (HS256) algorithm, and decodes the ID token to validate its content and show it in the output. Finally, it uses the access token to request information about the end user who authenticated, and displays the result.
Notice that in addition to the standard payload,
the ID token indicates the end user's OpenAM realm,
in this case "realm": "/".
OpenID Connect Implicit Flow is designed for relying parties that use the OAuth 2.0 Implicit grant type. This grant type is designed for relying parties implemented in a browser. Rather than protect a client secret, the client profile must register a protected redirect URI in advance with the OpenID Provider.
In the example, the Implicit Client Profile Start Page describes the prerequisite configuration, which must be part of the relying party profile that is stored in the OpenAM realm where you set up the OpenID Provider. In OpenAM console, check that the OAuth 2.0 client profile matches the settings described. If you have already configured the agent profile for the Authorization Code Flow example, then you still need to add the redirect URI for the Implicit Flow.
Log out of OpenAM,
and click the link at the bottom of the page to request authorization.
The link sends an HTTP GET request asking
for id_token token response types
and openid profile scopes
to the OpenID Provider authorization URI.
If everything is configured correctly,
OpenAM's OpenID Provider has you authenticate as an end user,
such as the demo user
with username demo and password changeit,
and grant (Allow) the relying party access to your profile.
If you successfully authenticate
and allow the example relying party access to your profile,
OpenAM returns the access token and ID token
directly in the fragment (after #) of the redirect URI.
The relying party does not get an authorization code.
The relying party shows the response to the request.
It also validates the ID token signature using the default (HS256) algorithm,
and decodes the ID token to validate its content and show it in the output.
Finally, the relying party uses the access token
to request information about the end user who authenticated,
and displays the result.
As for the Authorization Code Flow example, the ID Token indicates the end user's OpenAM realm and OpenAM token ID in addition to the standard information.
GSMA Mobile Connect is an application of OpenID Connect (OIDC). Mobile Connect builds on OIDC to facilitate use of mobile phones as authentication devices independently of the service provided and independently of the device used to consume the service. Mobile Connect thus offers a standard way for Mobile Network Operators to act as general-purpose identity providers, providing a range of levels of assurance and profile data to Mobile Connect-compliant Service Providers.
This section includes an overview, as well as the following:
In a Mobile Connect deployment, OpenAM can play the OpenID Provider role, implementing the Mobile Connect Profile as part of the Service Provider - Identity Gateway interface.
OpenAM can also play the Authenticator role as part of the Identity Gateway - Authenticators interface. In this role, OpenAM serves to authenticate users at the appropriate Level of Assurance (LoA). In Mobile Connect, LoAs represent the authentication level achieved. A Service Provider can request LoAs without regard to the implementation, and the Identity Gateway includes a claim in the ID Token that indicates the LoA achieved.
In OpenAM, Mobile Connect LoAs map to an authentication mechanism.
Service Providers acting as OpenID Relying Parties (RP) request an LoA
by using the acr_values field in an OIDC authentication request.
In OIDC, acr_values specifies Authentication Context Class Reference values.
The RP sets acr_values as part of the OIDC Authentication Request.
OpenAM returns the corresponding acr claim in the Authentication Response
as the value of the ID Token acr field.
OpenAM as OP supports LoAs 1 (low - little or no confidence), 2 (medium - some confidence, as in single-factor authentication), and 3 (high - high confidence, as in multi-factor authentication), though out of the box it does not include support for 4, which involves digital signatures.
As Mobile Connect OP, OpenAM supports mandatory request parameters, and a number of optional request parameters:
| Request Parameter | Support | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Supported |
OAuth 2.0 grant type to use.
Set this to |
|
|
Supported |
Set this to the client identifier. |
|
|
Supported |
Space delimited OAuth 2.0 scope values.
Required:
Optional: |
|
|
Supported |
OAuth 2.0 URI where the authorization request callback should go.
Must match the |
state
|
Supported |
Value to maintain state between the request and the callback. Required for Mobile Connect. |
nonce
|
Supported |
String value to associate the client session with the ID Token. Optional in OIDC, but required for Mobile Connect. |
display
|
Supported |
String value to specify the user interface display. |
login_hint
|
Supported |
String value indicating the the ID to use for login.
When provided as part of the OIDC Authentication Request,
the |
acr_values
|
Supported |
Authentication Context class Reference values used to communicate acceptable LoAs.
When the OIDC relying party on the server provider
supplies |
dtbs
|
Not supported |
Data To Be Signed At present OpenAM does not support LoA 4. |
As Mobile Connect OP, OpenAM responds to a successful authorization request
with a response containing all the required fields,
and also the optional expires_in field.
OpenAM supports the mandatory ID Token properties,
though the relying party is expected to use the expires_in value,
rather than specifying max_age as a request parameter:
| Request Parameter | Support | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Supported |
Issuer identifier |
|
|
Supported |
Subject identifier By default OpenAM returns the identifier from the user profile. |
|
|
Supported |
Audience, an array including the |
|
|
Supported |
Expiration time in seconds since the epoch. |
|
|
Supported |
Issued at time in seconds since the epoch. |
nonce
|
Supported |
The nonce supplied in the request. |
|
|
Supported. |
Base64url-encoding of the SHA-256 hash of the "access_token" value. |
|
|
Supported |
Authentication Context class Reference for the LoA achieved.
For example, if the request specifies
|
|
|
Supported |
Authentication Methods Reference to indicate the authentication method. OpenAM maps these to authentication modules.
Suggested values include the following:
|
|
|
Supported |
Authorized party identifier, which is the |
In addition to the standard OIDC user information returned with userinfo,
OpenAM as OP for Mobile Connect returns the updated_at property,
representing the time last updated as seconds since the epoch.
You configure OpenAM as an OpenID Connect provider for Mobile Connect by changing the OAuth2 Provider configuration.
Follow the steps in this procedure to set up the OAuth2 provider service with Mobile Connect defaults by using the Configure OAuth Provider wizard.
When you create the OAuth2 provider service with the Configure OAuth Provider wizard, the wizard also creates a standard policy in the Top Level Realm (/) to protect the authorization endpoint. In this configuration, OpenAM serves the resources to protect, and no separate application is involved. OpenAM therefore acts both as the policy decision point and policy enforcement point that protects the OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint used by OpenID Connect.
There is no requirement to use the wizard
or to create the policy in the Top Level Realm.
However, if you create the OAuth 2.0 provider service without the wizard,
then you must set up the policy independently as well.
The policy must appear in a policy set of type
iPlanetAMWebAgentService.
When configuring the policy allow all authenticated users
to perform HTTP GET and POST requests on the authorization endpoint.
The authorization endpoint is described
in "OAuth 2.0 Client and Resource Server Endpoints" in the Developer's Guide.
For details on creating policies, see "Defining Authorization Policies".
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider > Configure Mobile Connect.
On the Configure Mobile Connect page, select the Realm for the provider service.
(Optional) If necessary, adjust the lifetimes for authorization codes, access tokens, and refresh tokens.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens unless you do not want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when returning an access token.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens if you want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when refreshing an access token.
(Optional) If you have a custom scope validator implementation, put it on the OpenAM classpath, for example
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/, and specify the class name in the Scope Implementation Class field. For an example, see "Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling" in the Developer's Guide.Click Create to save your changes.
OpenAM creates an OAuth2 provider service with Mobile Connect default parameter values, as well as a policy to protect the OAuth2 authorization endpoints.
Warning
If an OAuth2 provider service already exists, it will be overwritten with the new Mobile Connect parameter values.
To access the provider service configuration in the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click OAuth2 Provider.
For Mobile Connect providers you may want to configure the following settings:
For the OpenID Connect acr_values to Auth Chain Mapping, configure the mapping between
acr_valuesin the authorization request and OpenAM authentication chains.For example, if the relying party request includes
acr_values=loa-3 loa-2and the map includes[loa-2]=ldapService, and[loa-3]=msisdnAndHotpChain, then the authentication chain for the request ismsisdnPlusHotpChain.The ssoadm attribute is
forgerock-oauth2-provider-loa-mapping.For the OpenID Connect default acr claim, set the "acr" claim value to return in the ID Token when falling back to the default authentication chain.
The ssoadm attribute is
forgerock-oauth2-provider-default-acr.For the OpenID Connect id_token amr values to Auth Module mappings, set the "amr" values to return in the ID Token after successfully authenticating with specified authentication modules.
For example, you could set
[UID_PWD]=LDAPto return"amr": [ "UID_PWD" ]in the ID Token after authenticating with the LDAP module.The ssoadm attribute is
forgerock-oauth2-provider-amr-mappings.Configure the identity Data Store attributes used to return
updated_atvalues in the ID Token.For Mobile Connect clients, the user info endpoint returns
updated_atvalues in the ID Token. If the user profile has never been updatedupdated_atreflects creation time.The
updated_atvalues are read from the profile attributes you specify. When using OpenDJ directory server as an identity Data Store, the value is read from themodifyTimestampattribute, or thecreateTimestampattribute for a profile that has never been modified.The ssoadm attribute for Modified Timestamp attribute name is
forgerock-oauth2-provider-modified-attribute-name.The ssoadm attribute is for Created Timestamp attribute name is
forgerock-oauth2-provider-created-attribute-name.In addition, you must also add these attributes to the list of LDAP User Attributes for the data store. Otherwise, the attributes are not returned when OpenAM reads the user profile. To edit the list in OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores > Data Store Name > LDAP User Attributes.
Click Save to complete the process.
A simple, non-secure GSMA Mobile Connect relying party example is available online.
OpenAM supports stateless access and refresh tokens for OpenID Connect 1.0 (OIDC). Stateless tokens allow clients to directly validate the tokens without storing session information in an external CTS data store. This feature also allows any OpenAM instance in the issuing cluster to validate an OIDC tokens without cross-talk.
Open the OpenAM console.
Under Realms, select the realm that you are working with.
Click Services, and then select OAuth2 Provider.
Enable Use Stateless Access & Refresh Tokens.
Enable Issue Refresh Tokens.
Enable Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens.
Generate some OIDC tokens using the REST API. Notice how each token is larger than a non-stateless example:
curl --request POST --user "MyClient:password" \ --data "grant_type=password&username=demo&password=changeit&scope=cn%20openid%20profile"\ http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token { "scope":"cn openid profile", "expires_in":5998, "token_type":"Bearer", "refresh_token":"eyAidHlwIjogIkpXVCIsICJhbGciOiAiSFMyNTYiIH0.eyAidG9rZW5OYW1l IjogInJlZnJlc2hfdG9rZW4iLCAic3ViIjogImRlbW8iLCAic2NvcGUiOiBbICJjbiIsICJvcGV uaWQiLCAicHJvZmlsZSIgXSwgImF1dGhHcmFudElkIjogIjU2Y2VhYzM2LTZjNTItNGQ2NS05MT hiLTY4ZmY3MThiOTAzMyIsICJuYmYiOiAxNDY1NDE4OTc5LCAiaXNzIjogImh0dHA6Ly9vcGVuY W0uZXhhbXBsZS5jb206ODA4MC9vcGVuYW0vb2F1dGgyIiwgImV4cGlyZXNfaW4iOiA2MDAwMDAw LCAiaWF0IjogMTQ2NTQxODk3OSwgImV4cCI6IDE0NjU0MjQ5NzksICJhdWRpdFRyYWNraW5nSWQ iOiAiZGU4NjM4ZDUtMzhjNC00N2E1LWE5ODMtZDBjNDMzMTQyYTRhIiwgInJlYWxtIjogIi8iLC AiYXVkIjogIk15Q2xpZW50IiwgImp0aSI6ICJlNjY0YjgwZS03ZmY0LTRjMGEtOGVlZC01ZTViM 2QwNGU4YWEiLCAidG9rZW5fdHlwZSI6ICJCZWFyZXIiIH0.VhXDFhI7K7BhouirMNgWQbeQvtrJ 9IZg4MUH4bAOO3M", "id_token":"eyAidHlwIjogIkpXVCIsICJhbGciOiAiUlMyNTYiLCAia2lkIjogIlN5bExDNk5qd DFLR1FrdEQ5TXQrMHpjZVFTVT0iIH0.eyAidG9rZW5OYW1lIjogImlkX3Rva2VuIiwgImF6cCI6 ICJNeUNsaWVudCIsICJzdWIiOiAiZGVtbyIsICJhdF9oYXNoIjogIkNIb0VDUzF1V3VRUS1RM1F rMUdMdnciLCAiaXNzIjogImh0dHA6Ly9vcGVuYW0uZXhhbXBsZS5jb206ODA4MC9vcGVuYW0vb2 F1dGgyIiwgIm9yZy5mb3JnZXJvY2sub3BlbmlkY29ubmVjdC5vcHMiOiAiNzE5MzVjNDUtOTk4Z S00NzBjLWFjMDQtMGMzNTM0NGRmYzNmIiwgImlhdCI6IDE0NjU0MTg5NzksICJhdXRoX3RpbWUi OiAxNDY1NDE4OTc5LCAiZXhwIjogMTQ2NTQyNDk3OSwgInRva2VuVHlwZSI6ICJKV1RUb2tlbiI sICJyZWFsbSI6ICIvIiwgIm5hbWUiOiAiZGVtbyIsICJhdWQiOiAiTXlDbGllbnQiLCAiZmFtaW x5X25hbWUiOiAiZGVtbyIgfQ.RpWyfifklukI_YmNASbexM-tLUw4-RGlDouo8vAe5BTQbYdjAC HPDfngq0iFFVUVnJHhCIlJeo7GBn459lNR7boefgkaglTz2Q9wYo7TGX-B7ioV0qMnkYsZniTvx X2qQc5le_BJnp_2BJOfzzK83WnW93d9A4JGEAKCrfojrXI", "access_token":"eyAidHlwIjogIkpXVCIsICJhbGciOiAiSFMyNTYiIH0.eyAidG9rZW5OYW1lI jogImFjY2Vzc190b2tlbiIsICJzdWIiOiAiZGVtbyIsICJzY29wZSI6IFsgImNuIiwgIm9wZW5p ZCIsICJwcm9maWxlIiBdLCAiYXV0aEdyYW50SWQiOiAiNTZjZWFjMzYtNmM1Mi00ZDY1LTkxOGI tNjhmZjcxOGI5MDMzIiwgIm5iZiI6IDE0NjU0MTg5NzksICJpc3MiOiAiaHR0cDovL29wZW5hbS 5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTo4MDgwL29wZW5hbS9vYXV0aDIiLCAiZXhwaXJlc19pbiI6IDYwMDAwMDAsI CJpYXQiOiAxNDY1NDE4OTc5LCAiZXhwIjogMTQ2NTQyNDk3OSwgImF1ZGl0VHJhY2tpbmdJZCI6 ICI2ZTI2MzA4ZC05YzY2LTRkNjQtODE2Zi1iZTdmYTcyMDc2MTgiLCAicmVhbG0iOiAiLyIsICJ hdWQiOiAiTXlDbGllbnQiLCAianRpIjogImY4MDEwZjE2LWZiYTQtNDg1ZS04NGM1LWM2OGU2Mj k2ZjIxYyIsICJ0b2tlbl90eXBlIjogIkJlYXJlciIgfQ.JOAG50dLwfB6lKQr4fdKB1zRdKZyfY 5bRRof61knJDs" }Decode the stateless access token to view its contents:
curl http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/tokeninfo?access_token=eyAid...1knJDs { "tokenName":"access_token", "sub":"demo", "scope":["cn","openid","profile"], "iss":"http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2", "nbf":1465418979, "authGrantId":"56ceac36-6c52-4d65-918b-68ff718b9033", "expires_in":6000000, "iat":1465418979, "exp":1465424979, "auditTrackingId":"6e26308d-9c66-4d64-816f-be7fa7207618", "cn":"demo", "realm":"/", "aud":"MyClient", "openid":"", "jti":"f8010f16-fba4-485e-84c5-c68e6296f21c", "token_type":"Bearer", "access_token":"eyAid...1knJDss", "profile":"" }
OpenAM provides security mechanisms to ensure that OpenID Connect 1.0 ID tokens are properly protected against malicious attackers: TLS, digital signatures, and token encryption.
While designing a security mechanism, you can also take into account the points developed in the section on Security Considerations in the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 incorporating errata set 1 specification.
All OpenID Connect 1.0 require the protection of network messages with Transport Layer Security (TLS). For information about protecting traffic the web container in which OpenAM runs, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".
OpenAM supports digital signatures for OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 tokens. To configure the signatures, see "Configuring Digital Signatures".
OpenAM supports the ability to encrypt OpenID Connect 1.0 ID tokens, which are JSON Web Tokens (JWT). OpenAM uses RSAES-PKCS1-v1_5, which is an encryption and decryption scheme in version 1.5 of PKCS #1, as the encryption algorithm for the ID token.
The supported encryption methods are A256CBC-HS512, which specifies the AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_512 authenticated encryption algorithm (512-bit key), and A128CBC-HS256, which specifies the AES_128_CBC_HMAC_SHA_256 authenticated encryption algorithm (256-bit key).
Start the OpenAM console, and select the realm that you are working with.
Click Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider > Configure OpenID Connect, and then click Create.
Click Agents > OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client.
Under Agent, click New, configure the Name and Password fields for the agent, and then click Create.
On the OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect Client page, click the agent you just created, and add the
openidscope.Select the Enabled checkbox for Enable ID Token Encryption.
Run Java code to generate an encoded public client encryption key. An example snippet is presented below:
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024); StringWriter writer = new StringWriter(); PEMWriter pemWriter = new PEMWriter(writer); pemWriter.writeObject(keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair().getPublic()); pemWriter.flush(); return writer.toString();Copy and paste the encoded public client key generated in the previous step into the Client ID Token Public Encryption Key field. This encoded public key will be used for encrypting ID tokens.
Run through the authorization OpenID Connect code flow to generate the encrypted ID token. For more information, see "OpenID Connect Authorization Code Flow".
This chapter introduces User-Managed Access (UMA) 1.0, and the part OpenAM plays in the UMA workflow. UMA 1.0 is a profile of OAuth 2.0.
UMA defines a workflow for allowing resource owners to manage access to their protected resources by creating authorization policies on a centralized authorization server, such as OpenAM.
The actions that form the UMA workflow are as follows:
- 1. Manage
The resource owner manages their resources on the resource server.
- 2. Protect
The resource owner links their resource server and chosen authorization server, for example an OpenAM instance.
The authorization server provides a protection API so that the resource server can register sets of resources. Use of the protection API requires a protection API token (PAT) - an OAuth 2.0 token with a specific scope.
For more information, see "Managing UMA Resource Sets".
- 3. Control
The resource owner controls who has access to their registered resources by creating policies on the authorization server.
For more information, see "Managing UMA Policies".
- 4. Authorize
The client, acting on behalf of the requesting party, uses the authorization server's authorization API to acquire a requesting party token (RPT). The requesting party or client may need further interaction with the authorization server at this point, for example to supply identity claims. Use of the authorization API requires an authorization API token (AAT) - an OAuth 2.0 token with a specific scope.
For more information, see "Accessing UMA-Protected Resources".
- 5. Access
The client presents the RPT to the resource server, which verifies its validity with the authorization server and, if both valid and containing sufficient permissions, returns the protected resource to the requesting party.
For more information, see "Accessing UMA-Protected Resources".
This section explains how to use the UMA features the OpenAM provides for end users.
The functionality covered is described in the following procedures:
To apply labels to a resource:
Log in to OpenAM as a user. The profile page is displayed.
Navigate to Shares > Resources > My Resources, and then click the name of the resource to add labels to.
On the resource details page, click Edit Labels.
In the edit box that appears, you can:
Enter the label you want to add to the resource, and then press Enter.
If you enter a label containing forward slash (/) characters, a hierarchy of each component of the label is created. The resource only appears in the last component of the hierarchy.
For example, the screenshot below shows the result of the label:
2015/October/Bristol:Click an existing label, and then press Delete or Backspace to delete the label from the resource.
When you have finished editing labels you can:
Click the checkmark button to save any changes made.
Click the X button to cancel any changes made.
Mark resources as favorites to have them appear on the Starred page.
Log in to OpenAM as a user. The profile page is displayed.
Navigate to Shares > Resources > My Resources, and then click the name of the resource to add to the list of favorites.
On the resource details page, click the star icon, as shown below:
To view the list of favorite resources, click Starred.
This section explains how to setup OpenAM as an authorization server in the User-Managed Access (UMA) workflow.
To enable OpenAM to act as an authorization server in the UMA workflow, you must create an UMA Provider service.
In the OpenAM console, select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure OAuth Provider > Configure User Managed Access.
On the Configure UMA page, select the Realm for the provider service.
(Optional) If necessary, adjust the lifetimes for authorization codes, access tokens, and refresh tokens.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens unless you do not want the authorization service to supply a refresh token when returning an access token.
(Optional) Select Issue Refresh Tokens on Refreshing Access Tokens if you want the authorization service to supply a new refresh token when refreshing an access token.
(Optional) If you have a custom scope validator implementation, put it on the OpenAM classpath, for example
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/, and specify the class name in the Scope Implementation Class field. For an example, see "Customizing OAuth 2.0 Scope Handling" in the Developer's Guide.Click Create to save your changes. OpenAM creates the following:
An UMA provider service.
An OAuth2 provider service that supports OpenID Connect.
A policy to protect the OAuth2 authorization endpoints.
Warning
If an UMA provider service already exists, it will be overwritten with the new UMA parameter values.
To access the provider service configuration in the OpenAM console, browse to Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click UMA Provider.
For information about the available attributes, see "UMA Provider" in the Reference.
To complete the configuration, click Save Changes.
OpenAM stores information about registered resource sets, and also audit information generated when users manage access to their protected resources. OpenAM provides a default store, or you can configure external stores to maintain this information.
Tip
If you cannot find the attribute you are looking for, click on the dropdown button on the left-hand side of the tabs or use the Search box. For more information, see " OpenAM Console Responsiveness" and "OpenAM Console Search Feature".
Resource Sets Store properties are inherited from the defaults. For more information about inherited properties, see "Configuring Servers" in the Reference
Log in to the OpenAM console as an OpenAM administrator, for example
amadmin.Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > UMA > Resource Sets Store.
Unlock the Store Mode property and choose External Token Store.
Unlock the Root Suffix property and enter the base DN of the store. For example
dc=uma-rs,dc=example,dc=com.Save your work.
Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > UMA > External Resource Sets Store Configuration.
Enter the properties for the store. For information about the available settings, see "UMA" in the Reference.
Save your work.
UMA Audit Store properties are inherited from the defaults. For more information about inherited properties, see "Configuring Servers" in the Reference
Log in to the OpenAM console as an OpenAM administrator, for example
amadmin.Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > UMA > UMA Audit Store.
Unlock the Store Mode property and choose External Token Store.
Unlock the Root Suffix property and enter the base DN of the store. For example
dc=uma-rs,dc=example,dc=com.Save your work.
Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > UMA > External UMA Audit Store Configuration.
Enter the properties for the store. For information about the available settings, see "UMA" in the Reference.
Save your work.
OpenAM exposes an endpoint for discovering information about UMA Provider configuration.
To use the endpoint, you must first create both an OAuth 2.0 Provider service, and an UMA Provider service in OpenAM. For more information on creating these services, see "Configuring the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Service" and "Configuring the UMA Provider Service".
A resource server or client can perform an HTTP GET on
/uma/{realm}/.well-known/uma-configuration
to retrieve a JSON object indicating the UMA Provider configuration for
realm if specified, or the Top Level Realm
if not.
Tip
Resource servers and clients need to be able to discover the
UMA provider for a resource owner. You should consider
redirecting requests to URIs at the server root, such as
http://www.example.com/.well-known/uma-configuration,
to the well-known URIs in OpenAM's space:
http://www.example.com/openam/uma/.well-known/uma-configuration.
Note
OpenAM supports a provider service that allows a realm to have a configured
option for obtaining the base URL (including protocol) for components that
need to return a URL to the client. This service is used to provide the
URL base that is used in the .well-known endpoints used in
OpenID Connect 1.0 and UMA.
For more information, see "Configuring the Base URL Source Service".
The following is an example of a GET request to the UMA configuration discovery endpoint for the Top Level Realm:
$ curl \
--request GET \
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/uma/.well-known/uma-configuration
{
"version": "1.0",
"issuer": "openam.example.com",
"pat_profiles_supported": [
"bearer"
],
"aat_profiles_supported": [
"bearer"
],
"rpt_profiles_supported": [
"bearer"
],
"pat_grant_types_supported": [
"authorization_code"
],
"aat_grant_types_supported": [
"authorization_code"
],
"token_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/access_token",
"authorization_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize",
"introspection_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/introspect",
"resource_set_registration_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set",
"permission_registration_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/uma/permission_request",
"rpt_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/uma/authz_request",
"dynamic_client_endpoint": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/connect/register"
}The JSON object returned includes the following configuration information:
versionThe supported UMA core protocol version.
issuerThe URI of the issuing authorization server.
pat_profiles_supportedThe supported OAuth token types used for issuing Protection API Tokens (PATs).
aat_profiles_supportedThe supported OAuth token types used for issuing Authorization API Tokens (AATs).
rpt_profiles_supportedThe supported Requesting Party Token (RPT) profiles.
pat_grant_types_supportedThe supported OAuth grant types used for issuing PATs.
aat_grant_types_supportedThe supported OAuth grant types used for issuing AATs.
token_endpointThe URI to request a PAT or AAT.
authorization_endpointThe URI to request authorization for issuing a PAT or AAT.
introspection_endpointThe URI to introspect an RPT.
For more information, see "OAuth 2.0 Client and Resource Server Endpoints" in the Developer's Guide.
resource_set_registration_endpointThe URI for a resource server to register a resource set.
For more information, see "Managing UMA Resource Sets".
permission_registration_endpointThe URI for a resource server to register a requested permission.
For more information, see "To Register an UMA Permission Request".
rpt_endpointThe URI for the client to request authorization data.
For more information, see "To Acquire a Requesting Party Token".
dynamic_client_endpointThe URI for registering a dynamic client.
UMA resource servers register resource sets with the resource owner's chosen authorization server. Registered resources can then be protected, and are available for user-created policies.
OpenAM supports optional system labels when registering resource sets to help resource owners organize their resources. For information on labelling resources, see "Managing UMA Labels".
OpenAM provides two REST endpoints for managing resource sets, as described in the sections below:
OpenAM provides the /oauth2/resource_set REST
endpoint, as described in the OAuth 2.0 Resource Set Registration
specification, to allow UMA resource servers to register and manage
resource sets.
The endpoint requires a Protection API Token (PAT),
which is an OAuth 2.0 access token with a scope of uma_protection.
A resource server must acquire a PAT in order to use the resource
set endpoint. For more information, see "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
After acquiring a PAT, use the /oauth2/resource_set REST
endpoint for the following operations:
You must have first "Registering OAuth 2.0 Clients With the Authorization Service"
with a name, such as UMA-Resource-Server and a
client password, such as password. Ensure that
uma_protection is in the list of available scopes in the
client, and a redirection URI is configured:
Direct the resource owner to the authorization server to obtain a PAT token. The URL should specify the client name registered above, the redirect URI, and request the
uma_protectionscope, as shown in the example below:https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize?client_id=UMA-Resource-Server&redirect_uri=http://openam.example.com:8080&response_type=code&scope=uma_protectionThis example uses the OAuth 2.0 code grant, however the UMA resource server can use any of the OAuth 2.0 grants to obtain the access token.
After logging in, the consent screen asks the resource owner to allow or deny the requested scopes.
If the resource owner allows access, they are sent to the configured redirection URL, which will have a
codequery string parameter added, which is used to request the PAT.Create a POST request to the
/oauth2/access_tokenendpoint, with the client credentials registered earlier, a grant type ofauthorization_code, a redirect URL, and the value of thecodequery string parameter returned in the previous step, as shown below:$ curl \ --request POST \ --data 'client_id=UMA-Resource-Server' \ --data 'client_secret=password' \ --data 'grant_type=authorization_code' \ --data 'code=c1bb2b94-038b-4ab2-beb1-a1ee14790c6b' \ --data 'redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Fopenam.example.com%3A8080' \ http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token { "scope": "uma_protection read", "expires_in": 599, "token_type": "Bearer", "refresh_token": "f9873041-885a-4522-836c-9fa71aaad3e4", "access_token": "983e1d96-20a7-437c-8432-cfde52076714" }The value returned in
access_tokenis the PAT bearer token, used in the following procedures.
To register a resource set, the resource server must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT bearer token, you can access the
/oauth2/resource_set endpoint to register resources,
as shown in the following steps.
Create a POST request to the resource_set endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in an Authorization header.
The following example uses a PAT bearer token to register a photo album resource set and a pair of system labels:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ --data \ '{ "name" : "Photo Album", "icon_uri" : "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "scopes" : [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ], "labels" : [ "3D", "VIP" ], "type" : "http://www.example.com/rsets/photoalbum" }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/ { "_id": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "user_access_policy_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/#uma/share/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0/" }The resource owner can then visit the user access policy URI in order to manage access to the resource set.
To list registered resource sets, you must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT token, you can access the
/oauth2/resource_set endpoint to list resource sets,
as shown below:
Create a GET request to the resource_set endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in an Authorization header.
The following example uses a PAT bearer token to list the registered resource sets:
$ curl \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set [ "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "3a2fe6d5-67c8-4a5a-83fb-09734f1dd5b10", "8ed24623-fcb5-46b8-9a64-18ee1b9b7d5d0" ]On success, an array of the registered resource set IDs is returned. Use the ID to identify a resource set in the following procedures:
To read a resource set, you must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT token, you can access the
/oauth2/resource_set endpoint to read resources,
as shown below:
Create a GET request to the resource_set endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in an Authorization header.
Note
You must provide the ID of the resource set to read, specified at the end of the request, as follows:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/resource_set_ID.The following example uses a PAT bearer token and a resource set ID to read a specific resource set:
$ curl \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 { "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ], "_id": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "name": "Photo Album", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "type": "http://www.example.com/rsets/photoalbum", "user_access_policy_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/#uma/share/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, as well as a header containing the current ETag value, for example:
W/"123401234". Use this ETag value when updating a resource set. See "To Update an UMA Resource Set".Tip
Add the
-ioption to curl commands to show the returned headers. For example:$ curl -i \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-4512-4279-98b6-c0ef3f03a722" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2\ /resource_set/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 HTTP/1.1 200 OK ETag: W/"123401234" Date: Tue, 10 Feb 2015 11:57:35 GMT Accept-Ranges: bytes Server: Restlet-Framework/2.1.7 Vary: Accept-Charset, Accept-Encoding, Accept-Language, Accept Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked { "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ], "_id": "myPhotoAlbum001", "name": "Photo Album", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "type": "http://www.example.com/rsets/photoalbum", "user_access_policy_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/#uma /share/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }If the resource set ID does not exist, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "error": "not_found", "error_description": "Resource set corresponding to id: 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 not found" }
To update a resource set, you must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT token, you can access the
/oauth2/resource_set endpoint to update resources,
as shown below:
Create a PUT request to the resource_set endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in a header named
Authorization, and any new or changed parameters.The only difference between creating a resource set and updating one is the presence of an
If-Matchheader when updating. This should contain the value of the ETag header returned when creating, updating, or reading a resource set.Note
You must provide the ID of the resource set to update, specified at the end of the request, as follows:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/resource_set_ID.The following example uses a PAT bearer token, a resource set ID and an If-Match header to update a specific resource set:
$ curl \ --request PUT \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ --header "If-Match: "123401234"" \ --data \ '{ "name" : "Photo Album 2.0", "icon_uri" : "http://www.example.com/icons/camera.png", "scopes" : [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/edit", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ], "type" : "http://www.example.com/rsets/photoalbum" }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 { "_id": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "user_access_policy_uri": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/#uma/share/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, with the resource set ID, and a user access policy URI that the resource owner can visit in order to manage access to the resource set.
If the resource set ID is not found, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "error": "not_found", "error_description": "ResourceSet corresponding to id: 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 not found" }If the
If-Matchheader is missing, or does not match the current version of the resource set, an HTTP 412 Precondition Failed status code is returned, as follows:{ "error": "precondition_failed" }
To delete a resource set, you must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT token, you can access the
/oauth2/resource_set endpoint to delete resources,
as shown below:
Create a DELETE request to the resource_set endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in a header named
Authorization.Add an
If-Matchheader containing the value of the ETag header returned when creating, updating, or reading a resource set.Note
You must provide the ID of the resource set to read, specified at the end of the request, as follows:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/resource_set_ID.The following example uses a PAT bearer token, a resource set ID and an If-Match header to delete a specific resource set:
$ curl \ --request DELETE \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ --header "If-Match: "123401234"" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/resource_set/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 {}On success, an HTTP 204 No Content status code is returned, as well as an empty response body.
If the resource set ID does not exist, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "error": "not_found", "error_description": "Resource set corresponding to id: 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 not found" }If the
If-Matchheader is missing, or does not match the current version of the resource set, an HTTP 412 Precondition Failed status code is returned, as follows:{ "error": "precondition_failed" }
OpenAM provides the
/json/users/username/oauth2/resources/sets
REST endpoint for managing resource sets belonging to a user.
Specify the
username in the
URL, and provide the SSO token of that user in the
iPlanetDirectoryPro header, as shown below.
To query resource sets for a user, create a GET request including
_queryFilter=resourceOwnerId eq "username"in the query string. The query string should be URL-encoded, as shown below:$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/sets?_queryFilter=resourceOwnerId+eq+%22demo%22 { "result": [ { "scopes": [ "View Photos", "Edit Photos" ], "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47", "resourceServer": "UMA-Resource-Server", "labels": [], "name": "My Nature Photos", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "resourceOwnerId": "demo", "type": "Photo Album" } ], "resultCount": 1, "pagedResultsCookie": null, "totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE", "totalPagedResults": -1, "remainingPagedResults": 0 }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, as well as a JSON representation of the resource sets assigned to the specified user.
To read a specific resource set for a user, create a GET request including the ID of the resource set in the URL, as shown below:
$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/sets/46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47 { "scopes": [ "View Photos", "Edit Photos" ], "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47", "resourceServer": "UMA-Resource-Server", "labels": [], "name": "My Nature Photos", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "resourceOwnerId": "demo", "type": "Photo Album" }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, as well as a JSON representation of the specified resource set.
To update the user labels assigned to a resource set for a user, create a PUT request including the ID of the resource set in the URL, the full JSON representation of the resource set, and the additional user label IDs in the
labelsarray in the body of the JSON data, as shown below:$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ --data \ '{ "scopes": [ "View Photos", "Edit Photos" ], "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47", "resourceServer": "UMA-Resource-Server", "labels": ["257ee30a-b989-4fe6-9e70-a87a050f6a4a4"], "name": "My Nature Photos", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "resourceOwnerId": "demo", "type": "Photo Album" }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/sets/46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47 { "scopes": [ "View Photos", "Edit Photos" ], "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d47", "resourceServer": "UMA-Resource-Server", "labels": [ "257ee30a-b989-4fe6-9e70-a87a050f6a4a4" ], "name": "My Nature Photos", "icon_uri": "http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png", "resourceOwnerId": "demo", "type": "Photo Album" }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, as well as a JSON representation of the updated resource set.
Note
Only the
labelsfield can be updated by using PUT. All other fields are read-only but must still be included in the JSON body of the request.
Apply labels to resources to help organize and locate them more easily. Resources can have multiple labels applied to them, and labels can apply to multiple resources.
Resources support three types of label:
- User Labels
Managed by the resource owner after the resource set has been registered to them.
Can be created and deleted. Deleting a label does not delete the resources to which it was applied.
Support nested hierarchies. Separate levels of the hierarchy with forward slashes (/) when creating a label. For example
Top Level/Second Level/My Label.Are only visible to the user who created them.
You can manage user labels by using the OpenAM console, or by using a REST interface. For more information, see "UMA Labels Endpoint for Users" and "To Apply User Labels to a Resource".
- System Labels
Created by the resource server when registering a resource set.
Cannot be deleted.
Do not support a hierarchy of levels.
Are only visible to the owner of the resource.
Note
Each resource set is automatically assigned a system label containing the name of the resource server that registered it, as well as a system label allowing users to add the resource to a list of favorites.
For information on creating system labels, see "To Register an UMA Resource Set".
- Favourite Labels
Each user can assign the builtin star label to a resource to mark it as a favorite.
For more information, see "To Mark a Resource as a Favorite".
OpenAM provides the
/json/users/username/oauth2/resources/labels
REST endpoint to allow users to manage user labels.
Specify the
username in the
URL, and provide the SSO token of that user in the
iPlanetDirectoryPro header.
Use the /json/users/username/oauth2/resources/labels REST endpoint for the following
operations:
To create a new user label, create a POST request with the name of the new user label and the type,
USER, as shown below:$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ --data \ '{ "name" : "New Resource Set Label", "type" : "USER" ] }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/labels?_action=create { "_id": "db2161c0-167e-4195-a832-92b2f578c96e3", "name": "New Resource Set Label", "type": "USER" }On success, an HTTP 201 Created status code is returned, as well as the unique identifier of the new user label in the
_idproperty in the JSON-formatted body. Note that the user label is not yet associated with a resource set. To apply the new label to a resource set, see "To Manage Resource Sets for a User by using REST".
To query the labels belonging to a user, create a GET request including
_queryFilter=truein the query string, as shown below:$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/labels?_queryFilter=true { "result": [ { "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d44", "name": "2015/October/Bristol", "type": "USER" }, { "_id": "60b785c2-9510-40f5-85e3-9837ac272f1b1", "name": "Top Level/Second Level/My Label", "type": "USER" }, { "_id": "ed5fad66-c873-4b80-93bb-92656eb06deb0", "name": "starred", "type": "STAR" }, { "_id": "db2161c0-167e-4195-a832-92b2f578c96e3", "name": "New Resource Set Label", "type": "USER" } ], "resultCount": 4, "pagedResultsCookie": null, "totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE", "totalPagedResults": -1, "remainingPagedResults": -1 }
To delete a user label belonging to a user, create a DELETE request including the ID of the user label to delete in the URL, as shown below:
$ curl \ --request DELETE \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/json/users/demo/oauth2/resources/labels/46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d44 { "_id": "46a3392f-1d2f-4643-953f-d51ecdf141d44", "name": "2015/October/Bristol", "type": "USER" }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, as well as a JSON representation of the user label that was removed.
UMA authorization servers must manage the resource owner's authorization policies, so that registered resource sets can be protected.
OpenAM provides the
/json/users/{user}/uma/policies/ REST
endpoint for creating and managing user-managed authorization policies.
Managing UMA policies requires that a resource set is registered to the user in the URL. For information on registering resource sets, see "Managing UMA Resource Sets".
Once a resource set is registered to the user, use the
/json/users/{user}/uma/policies/
REST endpoint for the following operations:
To create a policy, the resource owner must be logged in to the authorization server and have an SSO token issued to them, and must also know the "To Register an UMA Resource Set" to be protected. This information is used when creating policies.
Note
Only the resource owner can create a policy to protect
a resource set. Administrator users such as amadmin cannot
create policies on behalf of a resource owner.
Create a POST request to the policies endpoint, including the SSO token in a header based on the configured session cookie name (default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro), and the resource set ID as the value ofpolicyIdin the body.Note
The SSO token must have been issued to the user specified in the URL. In this example, the user is
demo.The following example uses an SSO token to create a policy to share a resource set belonging to user demo with two subjects, with different scopes for each:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ --data \ '{ "policyId": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "permissions": [ { "subject": "user.1", "scopes": ["http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view"] }, { "subject": "user.2", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ] } ] }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo/uma/policies?_action=create {}On success, an HTTP 201 Created status code is returned, with an empty JSON body as the response.
If the permissions are not correct, an HTTP 400 Bad Request status code is returned, for example:
{ "code": 400, "reason": "Bad Request", "message": "Invalid UMA policy permission. Missing required attribute, 'subject'." }
To read a policy, the resource owner or an administrator user must be logged in to the authorization server and have an SSO token issued to them. The "To Create an UMA Policy" to read must also be known.
Tip
The ID used for a policy is always identical to the ID of the resource set it protects.
Create a GET request to the policies endpoint, including the SSO token in a header based on the configured session cookie name (default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro), and the resource set ID as part of the URL.Note
The SSO token must have been issued to the user specified in the URL, or to an administrative user such as
amadmin. In this example, the user isdemo.The following example uses an SSO token to read a specific policy with ID
43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0belonging to user demo:$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo\ /uma/policies/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 { "policyId": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "name": "Photo Album", "permissions": [ { "subject": "user.1", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view" ] }, { "subject": "user.2", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ] } ] }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, with a JSON body representing the policy.
If the policy ID does not exist, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "code": 404, "reason": "Not Found", "message": "UMA Policy not found, 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }
To update a policy, the resource owner or an administrator user must be logged in to the authorization server and have an SSO token issued to them. The "To Create an UMA Policy" to read must also be known.
Tip
The ID used for a policy is always identical to the ID of the resource set it protects.
Create a PUT request to the policies endpoint, including the SSO token in a header based on the configured session cookie name (default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro), and the resource set ID as both the value ofpolicyIdin the body and also as part of the URL.Note
The SSO token must have been issued to the user specified in the URL. In this example, the user is
demo.The following example uses an SSO token to update a policy with ID
43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0belonging to user demo with a new scope for one of the subjects:$ curl \ --request PUT \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ --data \ '{ "policyId": "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "permissions": [ { "subject": "user.1", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ] }, { "subject": "user.2", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ] } ] }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo\ /uma/policies/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 {}On success, an HTTP 204 Empty status code is returned, with an empty JSON body as the response.
If the policy ID does not exist, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "code": 404, "reason": "Not Found", "message": "UMA Policy not found, 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }If the permissions are not correct, an HTTP 400 Bad Request status code is returned, for example:
{ "code": 400, "reason": "Bad Request", "message": "Invalid UMA policy permission. Missing required attribute, 'subject'." }If the policy ID in the URL does not match the policy ID used in the sent JSON body, an HTTP 400 Bad Request status code is returned, for example:
{ "code": 400, "reason": "Bad Request", "message": "Policy ID does not match policy ID in the body." }
To delete a policy, the resource owner or an administrator user must be logged in to the authorization server and have an SSO token issued to them. The "To Create an UMA Policy" to read must also be known.
Tip
The ID used for a policy is always identical to the ID of the resource set it protects.
Create a DELETE request to the policies endpoint, including the SSO token in a header based on the configured session cookie name (default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro), and the resource set ID as part of the URL.Note
The SSO token must have been issued to the user specified in the URL. In this example, the user is
demo.The following example uses an SSO token to delete a policy with ID
43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0belonging to user demo:$ curl \ --request DELETE \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo\ /uma/policies/43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0 {}On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, with an empty JSON body as the response.
If the policy ID does not exist, an HTTP 404 Not Found status code is returned, as follows:
{ "code": 404, "reason": "Not Found", "message": "UMA Policy not found, 43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0" }
To query policies, the resource owner or an administrator user must be logged in to the authorization server and have an SSO token issued to them. The "To Create an UMA Policy" to read must also be known.
Create a GET request to the policies endpoint, including the SSO token in a header based on the configured session cookie name (default:
iPlanetDirectoryPro).Note
The SSO token must have been issued to the user specified in the URL, or to an administrative user such as
amadmin.In this example, the user is
demo.Use the following query string parameters to affect the returned results:
_sortKeys=[+-]field[,field...]Sort the results returned, where field represents a field in the JSON policy objects returned.
For UMA policies, only the
policyIdandnamefields can be sorted.Optionally use the
+prefix to sort in ascending order (the default), or-to sort in descending order._pageSize=integerLimit the number of results returned.
_pagedResultsOffset=integerStart the returned results from the specified index.
_queryFilterThe _queryFilter parameter can take
trueto match every policy,falseto match no policies, or a filter of the following form to match field values:field operator valuewhere field represents the field name, operator is the operator code, value is the value to match, and the entire filter is URL-encoded. Only the equals (eq) operator is supported by the/uma/policiesendpoint.The field value can take the following values:
resourceServer- the resource server that created the resource set.permissions/subject- the list of subjects that are assigned scopes in the policy.
Filters can be composed of multiple expressions by a using boolean operator
AND, and by using parentheses,(expression), to group expressions.Note
You must URL-encode the filter expression in
_queryFilter=filter. So, for example, the following filter:resourceServer eq "UMA-Resource-Server" AND permissions/subject eq "user.1"When URL-encoded becomes:
resourceServer+eq+%22UMA-Resource-Server%22+AND+permissions%2Fsubject+eq+%22user.1%22
The following example uses an SSO token to query the policies belonging to user demo, which have a subject
user.1in the permissions:$ curl \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2LY4S...Q4MTE4NTA2*" \ --get \ --data-urlencode '_sortKeys=policyId,name' \ --data-urlencode '_pageSize=1' \ --data-urlencode '_pagedResultsOffset=0' \ --data-urlencode \ '_queryFilter=permissions/subject eq "user.1"' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/users/demo/uma/policies { "result": [ { "policyId": "52645907-e20b-4351-8e0c-523ebe0d44710", "name": "Photo Album", "permissions": [ { "subject": "user.1", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view" ] }, { "subject": "user.2", "scopes": [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view" ] } ] } ], "resultCount": 1, "pagedResultsCookie": null, "remainingPagedResults": 0 }On success, an HTTP 200 OK status code is returned, with a JSON body representing the policies that match the query.
If the query is not formatted correctly, for example, an incorrect field is used in the
_queryFilter, an HTTP 500 Server Error is returned, as follows:{ "code": 500, "reason": "Internal Server Error", "message": "'/badField' not queryable" }
To access an UMA-protected resource, a client must provide the resource server with a Requesting Party Token (RPT) obtained from OpenAM, which is acting as the authorization server.
In order to obtain access to an UMA-protected resource, the following actions take place:
A requesting party, using a client application, requests access to an UMA-protected resource (labeled 1 in the diagram above).
The resource server registers a permission request with OpenAM on behalf of the client (2), which contains the ID of the resource set to access, and the requested scopes. A permission ticket is returned (3), which the resource server provides to the client (4).
For more information about registering permission requests, see "To Register an UMA Permission Request".
The client uses the permission ticket, and an Authorization API Token (AAT) to acquire an RPT from OpenAM (5).
For more information about acquiring an RPT, see "To Acquire a Requesting Party Token".
OpenAM makes a policy decision using the requested scopes, the scopes permitted in the registered resource set, and the user-created policy, and if successful returns an RPT (6).
The client presents the RPT to the resource server (7) which must verify the token is valid using the OpenAM introspection endpoint (8).
For more information about the introspection endpoint, see "OAuth 2.0 Client and Resource Server Endpoints" in the Developer's Guide.
If the RPT is confirmed to be valid, and non-expired (9) the resource server can return the protected resource to the requesting party (10).
OpenAM provides the /uma/permission_request REST
endpoint for a resource server to register an access request on
behalf of a client.
To register a permission request, the resource server must first acquire a PAT token, as described in "To Acquire a Protection API Token".
Once you have the PAT bearer token, you can access the
/uma/permission_request endpoint to register a
permission request, as shown below:
Create a POST request to the permission_request endpoint, including the PAT bearer token in a header named
Authorization:$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 515d6551-6512-5279-98b6-c0ef3f03a723" \ --data \ '{ "resource_set_id" : "43225628-4c5b-4206-b7cc-5164da81decd0", "scopes" : [ "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view", "http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/all" ] }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/uma/permission_request { "ticket": "dc630c21-7d55-45bf-958d-24d624441138" }On success, an HTTP 201 Created status code is returned, as well as a
ticketproperty in the JSON-formatted body, which can be used by the client to acquire a requesting party token. For more information, see "To Acquire a Requesting Party Token".If the resource set does not allow the requested scopes, an error is returned, as follows:
{ "error_description": "Requested scopes are not in allowed scopes for resource set.", "error": "invalid_scope" }
You must have first "Registering OAuth 2.0 Clients With the Authorization Service"
with a name, such as UMA-Client and a
client password, such as password. Ensure that
uma_authorization is in the list of available scopes in
the client, and a redirection URI is configured:
Direct the requesting party to the authorization server to obtain an AAT token. The URL should specify the client name registered above, the redirect URI, and request the
uma_authorizationscope, as shown in the example below:https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/authorize?client_id=UMA-Client&redirect_uri=http://openam.example.com:8080&response_type=code&scope=uma_authorizationThis example uses the OAuth 2.0 code grant, however the UMA client can use any of the OAuth 2.0 grants to obtain the access token.
After logging in, the consent screen asks the requesting party to allow or deny the requested scopes.
If the requesting party allows access, they are sent to the configured redirection URL, which will have a
codequery string parameter added, which is used to request the AAT.Create a POST request to the
/oauth2/access_tokenendpoint, with the client credentials registered earlier, a grant type ofauthorization_code, a redirect URL, and the value of thecodequery string parameter returned in the previous step, as shown below:$ curl \ --request POST \ --data 'client_id=UMA-Client' \ --data 'client_secret=password' \ --data 'grant_type=authorization_code' \ --data 'code=2b911969-5b8e-4d07-bf34-612917a37c9d' \ --data 'redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Fopenam.example.com%3A8080' \ http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/oauth2/access_token { "scope": "uma_authorization print", "expires_in": 599, "token_type": "Bearer", "refresh_token": "e77fac0e-0dc6-40c3-a600-3309451bd6ee", "access_token": "d47c2278-460b-41e8-bf98-a8a1206e2c58" }The value returned in
access_tokenis the AAT bearer token, used in the following procedures.
OpenAM provides the /uma/authz_request REST
endpoint for acquiring a Requesting Party Token (RPT).
The endpoint is protected - access requires a Authorization API Token
(AAT) - an OAuth 2.0 token with a scope of uma_authorization.
A client must acquire an AAT in order to use the authorization
request endpoint. For more information, see "To Acquire an Authorization API Token".
Once the client has an AAT bearer token, it can access the
/uma/authz_request endpoint to acquire an RPT,
as shown below:
Create a POST request to the authz_request endpoint, including the AAT bearer token in a header named
Authorization, and the permission token in the JSON body of the request, as follows:$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "Authorization: Bearer 3b08e99c-b09d-4a65-9780-ea0c9e1f0f52" \ --data \ '{ "ticket": "dc630c21-7d55-45bf-958d-24d624441138" }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/uma/authz_request { "rpt": "162d6137-68a4-4e8e-950d-edd834589eb73" }On success, an HTTP 201 Created status code is returned, as well as the
rptproperty in the JSON-formatted body.If the resource owner has not shared the resource with the requesting party, an HTTP 403 Forbidden is returned. If OpenAM is configured to email the resource owner upon pending request creation as described in "UMA Provider" in the Reference, the JSON body returned includes a message that the resource owner will be notified to allow or deny access to the resource, as shown below:
{ "error": "request_submitted", "error_description": "The client is not authorised to access the requested resource set. A request has been submitted to the resource owner requesting access to the resource" }For more information, see "Managing Pending UMA Permission Requests"
OpenAM supports an UMA workflow in which a user can request access to a resource that has not been explicitly shared with them. The resource owner receives a notification of the request and can choose to allow or deny access.
Manage pending requests for access to resources by using the steps below:
Login to OpenAM as the resource owner, and then navigate to Shares > Requests.
The Requests page is displayed:
Review the pending request, and take one of the following actions:
Click Allow to approve the request.
Tip
You can remove permissions from the request by clicking the permission, and then press either Delete or Backspace. Select the permission from the drop-down list to return it to the permissions granted to the resource owner.
The required UMA policy will be created, and optionally the requesting party will be notified that they can now access the resource.
The requesting party can view a list of resources to which they have access by navigating to Shares > Resources > Shared with me.
Click Deny to prevent the requesting party from accessing the resource. The pending request is removed, and the requesting party will not be notified.
After allowing or denying access to a resource, an entry is created in the History page.
To view a list of actions that have occurred, navigate to Shares > History.
This chapter describes OpenAM's support for the SAML v1.x framework for exchanging security data.
SAML v1.x is an XML- and SOAP-based framework that allows online trusted partners to exchange security information. In particular, SAML v1.x defines mechanisms for browser based web single sign-on (SSO) across independent organizations that work together to permit SSO for access to resources.
Important
Although not strictly compatible with SAML v1.x, SAML v2.0 extends SAML v1.x to several additional use cases and also clarifies how partners share metadata with each other. Unless you are integrating with an existing SAML v1.x deployment consider using SAML v2.0, or an alternative, such as OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect 1.0, instead.
See the following chapters for more information: "Managing SAML v2.0 Federation", "Managing OAuth 2.0 Authorization", and "Managing OpenID Connect 1.0 Authorization".
OpenAM's support for SAML 1.x requires stateful sessions. Be sure that OpenAM is configured for stateful sessions—the default configuration—before attempting to use SAML 1.x functionality in OpenAM.
SAML v1.x was defined in response to several technical problems:
Web SSO solutions often use SSO session cookies. Browsers do not return cookies across domains. For instance, browsers do not return cookies set by servers in the example.com domain to servers in the example.net domain. SAML v1.x works around this limitation of HTTP cookies.
Before SAML v1.x was defined, there were already proprietary SSO solutions, but the solutions did not interoperate well across domains.
SAML v1.x specifies a standard, cross-domain, interoperable SSO mechanism that works together with proprietary SSO services in a particular domain.
Before SAML v1.x was defined, there was not an easy way to communicate security attributes across organization boundaries.
SAML v1.x simplifies the communication of security attributes between different organizations.
In SAML v1.x, business partners can play two roles. The asserting party, also known as the SAML authority and whose domain is the Source site, authenticates users and asserts information about them. The relying party, whose domain is known as the Destination site, consumes assertions and uses information from the assertion to decide whether to allows access to resources.
In the Web Browser SSO Profiles for SAML v1.x, the user generally starts by authenticating with the asserting party and then selecting a relying party link to browse. Alternatively, the "Destination-Site-First" scenario can start with the user browsing to the relying party's site and being redirected to the asserting party's site to authenticate.
The SAML v1.x Inter-site Transfer Service is a service that redirects the authenticated user from the asserting party's site to the appropriate service on the relying party's site. The Inter-site Transfer Service also handles artifact and redirect generation. How this service transfers the user to the relying party's site depends on how the asserting party and the relying party exchange messages.
The asserting party and relying party can exchange messages either by reference, where the asserting party sends an artifact (a base64-encoded reference to the assertion) as a query string parameter value, or by value, where the asserting party directs the user's browser to HTTP POST the assertion to the relying party.
When the asserting party and relying party use artifacts, the Inter-site Transfer Service redirects the user's browser to the relying party's Artifact Receiver Service with the artifact as the value of a query string parameter. The relying party retrieves the artifact from the query string, and then sends a SAML Request to the Responder Service at the asserting party. The asserting party replies with a SAML Response containing one or more assertions.
See section 4.1.1 of the SAML v1.1 technical overview for more detail.
When the assertion is sent using the Browser/POST Profile, the Inter-site Transfer Service responds to the user's browser with an auto-submitting form containing the SAML response. The browser then submits the SAML response as form data by HTTP POST to the relying party's Assertion Consumer Service. The relying party's Assertion Consumer Service then processes the assertion.
See section 4.2.1 of the SAML v1.1 technical overview for more detail.
The Assertion Consumer Service at the relying party validates the digital signature on the SAML response, and redirects the browser to the target URL of the resource that the user is attempting to access. The server providing that resource uses the relying party's authorization decision capabilities to establish whether the user can access the resource. If so, the resource is returned to the user's browser. If the relying party is using OpenAM, for example, then the relying party sets an OpenAM SSO token based on the SAML response, and this token is used to track the user's session for authorization.
Organizations working together to achieve SAML v1.x web SSO are called trusted partners in this context. Trusted partners agree on which services they provide, which web SSO profiles they implement, and how information is exchanged in the assertions, including profile attribute values. Once the trusted partners have reached agreement on how they interact, you can collect information about your partners' configurations and configure OpenAM to match your organization's part of the agreement.
Before you can configure OpenAM to allow web SSO with trusted partners, you must first gather information about the agreement itself, as well as information for your site and for your partners sites.
This section lists the data that you must collect:
SAML protocol version to use (1.1 or 1.0; default: 1.1)
Assertion version to use (1.1 or 1.0; default: 1.1)
Which trusted partners play which roles (asserting party, relying party)
Domain names of partner sites (for example,
example.com,example.net)Whether assertions are exchanged by SAML artifact or by HTTP POST
If assertions are exchanged by artifact, also gather this information:
SAML artifact parameter name (default:
SAMLart)Artifact timeout
URL to the relying party endpoint that receives the artifact (for example,
https://rp.example.com/openam/SAMLAwareServlet)Relying party hosts that consume artifacts (by IP addresses, DNS names, or certificate aliases)
URL to the asserting party endpoint that responds to SAML requests (for example,
https://ap.example.net/openam/SAMLSOAPReceiver)Authentication credentials to connect to the asserting party endpoint, if any (for example, the username and password for HTTP Basic authentication)
Asserting party signing certificate alias
If assertions are exchanged by HTTP POST, also gather this information:
URL to the relying party endpoint that consumes the form data in the POST assertion (for example,
https://rp.example.com/openam/SAMLPOSTProfileServlet)Asserting party host:port issuing assertions
Asserting party signing certificate alias
Whether the relying party sends SOAP query requests to the asserting party, for example, to get authorization decisions
If the relying party queries the asserting party, also gather this information:
Relying party hosts that consume artifacts (by IP addresses, DNS names, or certificate aliases)
How to get SSO information, and to map partner actions to authorization decisions
Asserting party host:port issuing assertions
Asserting party signing certificate alias
Target specifier parameter name (default:
TARGET)Assertion timeout
Whether to digitally sign assertions, requests, responses
Partners' public key certificates used for HTTPS
Partners' public key certificates used for message signing (unless included on the
KeyInfoelement of signed messages)Partners' Site IDs (base64-encoded ID, for example,
XARFfsIAXeLX8BEWNIJg9Q8r0PE=)What NameID formats are used to exchange names (for example,
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress)How attributes map from an assertion to an OpenAM profile (for example,
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress|EmailAddress=mail)
For more information about your own public key certificates, see "Preparing To Secure SAML v1.x Communications".
For your own Site ID, see the following procedure.
Trusted partners should ask you for a Site ID. OpenAM generates a SAML v1.x Site ID value at configuration time. This Site ID value corresponds to the server. To find this in OpenAM console, see Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration > Local Site Properties > Site Identifiers, and then click your server URL.
If you have multiple servers in an OpenAM site set up behind a load balancer, you can generate a Site ID, and then use it for all the servers in your site.
Generate a Site ID for your site, using the primary site URL.
This example is for an asserting party where the site load balancer host is
ap.example.net. The command is bundled with OpenAM server, shown with lines folded to fit on the printed page:$ cd /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/ $ java \ -cp forgerock-util-20.0.0.jar:openam-shared-13.5.2.jar:\ openam-federation-library-13.5.2.jar com.sun.identity.saml.common.SAMLSiteID \ https://ap.example.net/openam 9BAg4UmVS6IbjccsSj9gAFYGO9Y=
SAML communications are secured using Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Communications should be protected over the network by HTTPS, and relying parties requesting assertions should use SSL or TLS mutual authentication to identify each other, meaning they should be able to trust each others' certificates. Furthermore, when an asserting party works through the user's browser to post an assertion to the relying party, then the asserting party must digitally sign the SAML response.
A certificate can be trusted when the signer's certificate is trusted, or when the certificate itself is trusted. Trusted partners must either use public key certificates signed by a well-known Certificate Authority (CA), or share their self-signed or private CA signing certificates.
See the chapter "Managing Certificates and Keystores" for instructions on handling your own key pairs.
For specific instructions on changing signing keys, see the procedure "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ".
If necessary, share signing certificates with trusted partners.
Import public key certificates shared by trusted partners into your OpenAM keystore.
After you have gathered configuration information and prepared to secure SAML v1.x communications you can configure SAML v1.x for your site.
Tip
When you enter SAML v1.x configuration data,
OpenAM console escapes these special characters by default:
& < > " ' /.
If you have already escaped these characters
in the data that you plan to enter in the OpenAM console,
set the value of the
com.sun.identity.saml.escapeattributevalue property
to false
under Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced,
and then restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs
to prevent OpenAM console from escaping the characters for you.
Using the configuration information you have gathered complete the following steps:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, amadmin, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click Local Site Properties.
If the target specifier query string parameter is something other than the standard default TARGET, set it in the Target Specifier field.
If instead of the default server Site Identifier, you use a Site Identifier for the OpenAM Site, click New in the Site Identifiers table, and then add the information for the OpenAM Site, including the Site ID that you generated.
Target URLs let you configure URLs for which HTTP POST is always used.
When the TARGET specified matches a URL in the Target URLs list, then the asserting party sends the response to the relying party by HTTP POST of an auto-submitting form returned to the browser.
If necessary, set the Default Protocol Version.
In the Assertion section, change the values if necessary.
Remove Assertion: Yes means that assertions are deleted from memory after they are used, rather than deleted only when they expire.
In the Artifact section, change the values if necessary.
In the Signing section, for an asserting party using the HTTP POST profile, check at least Sign SAML Assertion.
By default OpenAM signs messages using the certificate with alias test.
Check other options as required by your trusted partners.
In the Attribute Query section, if relying parties issue attribute queries, then set the default list of profile attributes to return.
In the NameID Format section, map SAML NameID formats to local OpenAM user profile attributes.
This allows OpenAM to map a remote user to a local user profile.
In the Attribute Map section, if the parties exchange attributes, then map the SAML attributes requested by relying parties to local OpenAM user profile attributes.
Save your work.
Using the configuration information you have gathered complete the following steps.
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, amadmin, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click Local Site Properties.
If the target specifier query string parameter is something other than the standard default TARGET, set it in the Target Specifier field.
If instead of the default server Site Identifier, you use a Site Identifier for the OpenAM Site, click New in the Site Identifiers table, and then add the information for the OpenAM Site, including the Site ID that you generated.
Ignore the Target URLs table for a relying party.
If necessary, set the Default Protocol Version.
In the Assertion section, change the values if necessary.
In the Artifact section, change the values if necessary.
Ignore the Signing section for relying parties, unless trusted partners require that your site signs SAML requests.
By default OpenAM signs messages using the certificate with alias
test.Ignore the Attribute Query section for relying parties.
In the NameID Format section, map SAML NameID formats to local OpenAM user profile attributes.
This allows OpenAM to map a remote user to a local user profile when not all the partners are using OpenAM user IDs.
In the Attribute Map section, if the parties exchange attributes, then map the SAML attributes requested by relying parties to local OpenAM user profile attributes.
Save your work.
After you have gathered configuration information and if necessary imported public key certificates from trusted partners you can configure SAML v1.x information for the partners:
OpenAM console refers to the relying party as the Destination, because the relying party's site is the destination site:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, amadmin, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click New in the Trusted Partners table.
Under Destination, select the SAML profiles used with the relying party.
In the Common Settings section, set at least a name for the partner configuration, enter the partner's Site ID as the Source ID, and specify the fully qualified domain, optionally with the port number, of the relying party in the Target field. The value in the target field is matched to TARGET parameter values, so it should correspond to the real domain (and optionally port number) in the URLs of resources to access at the relying party's site.
Optionally set a custom site attribute mapper, a custom name identifier mapper, and the SAML Version to use with the partner.
You must also set one or more values in the host list for the partner to identify all hosts from the partner site that can send requests. OpenAM rejects SAML requests from hosts not specified in this list.
In the Destination section, if the SAML Artifact profile is used with the relying party, set the SAML URL to the relying party's endpoint that receives the artifact and contacts your asserting party.
If the SAML POST profile is used with the relying party, set the Post URL to the relying party's endpoint that consumes the assertion in the HTTP POST form data and redirects the user's browser to the target at the relying party's site.
If the relying party makes SAML SOAP query requests, optionally set custom attribute or action mappers.
If the relying party signs requests, then either requests include the certificate for the signing key in the KeyInfo element, or OpenAM must find the signing certificate elsewhere. If the relying party provides the signing certificate separately, import the signing certificate into OpenAM's default keystore file, and set the alias for the signing certificate here in the configuration. For more information about OpenAM's default keystore, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".
Set the issuer to a host:port combination corresponding to the relying party server issuing the requests.
Save your work.
OpenAM console refers to the asserting party as the Source, because the asserting party's site is the source site:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, amadmin, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click New in the Trusted Partners table.
Under Source, select the SAML profiles used with the asserting party.
In the Common Settings section, set at least a name for the partner configuration and enter the partner's Site ID as the Source ID.
Optionally set a custom account mapper. By default OpenAM maps accounts based on the NameID format configuration for your site.
If the asserting party signs assertions (or other messages) and you have imported the signing certificate into OpenAM's keystore (also used as a trust store), then enter the signing certificate alias. If instead the asserting party includes the signing certificate in the KeyInfo element of signed messages, then you can leave the alias blank.
In the Source section, if the SAML Artifact profile is used with the asserting party, set the SOAP URL to the asserting party endpoint that responds to requests such as
https://ap.example.net/openam/SAMLSOAPReceiver.If the asserting party requires authentication to the SOAP URL, then configure the settings appropriately.
If the SOAP URL is accessed over HTTP, choose None or Basic. If the SOAP URL is accessed over HTTPS, choose SSL/TLS or SSL/TLS with Basic.
Basic means HTTP Basic authentication (with username and password). For HTTP Basic authentication, the authentication at this level is performed by the application server container, not OpenAM. Therefore if the asserting party runs OpenAM and wants to enforce HTTP Basic authentication, the asserting party administrator must set up the container to handle HTTP Basic authentication for the SOAP URL.
Set the SAML Version as necessary.
If the SAML POST profile is used with the asserting party, set the Issuer to the issuer name, such as a host:port combination.
Save your work.
You can try SAML v1.x Web SSO using OpenAM by following the procedures in this section:
Install two separate OpenAM servers, one to act as asserting party, the other to act as relying party.
How you do this in practice is up to you.
You can, for example, set up two separate OpenAM servers on a single host by adding aliases for the hosts in your hosts file, and by using separate containers that listen on different ports.
For example, if your host is a laptop, you can add the aliases to the loopback address as in the following example line from an
/etc/hostsfile.127.0.0.1 localhost ap.example.net rp.example.com
Then, run one application server to listen on port 8080, and another to listen on port 9080.
Deploy and configure OpenAM server with the default configuration at
http://ap.example.net:8080/apfor the asserting party and athttp://rp.example.com:9080/rpfor the relying party. This allows you to use the default configuration for both servers.See the Installation Guide for instructions.
The procedures in this section use those example URLs to represent the OpenAM servers acting as asserting and relying parties.
On the asserting party server, login to OpenAM console as administrator, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click Local Site Properties.
Click the server's instance ID in the Site Identifiers table.
Record the asserting party Site ID for later use.
On the relying party server, login to OpenAM console as administrator, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click Local Site Properties.
Click the server's instance ID in the Site Identifiers table.
Record the asserting party Site ID for later use.
Follow these steps to configure the asserting party OpenAM server:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click Local Site Properties.
On the Local Site Properties page for the asserting party server, select Sign SAML Response.
The asserting party thus signs SAML responses with the private key for the default test certificate.
Save your work, and then click Back to Federation.
Click New in the Trusted Partners table to add the relying party as a trusted partner.
In the Destination area of the Select trusted partner type and profile page, select Artifact and Post (not SOAP Query), and then click Next.
Apply the following settings, adjusted for the host names you use.
If a field is not mentioned, accept the defaults.
Under Common Settings, use these settings:
Name: rp.example.com:9080 Source ID: relying party Site ID that you recorded Target: rp.example.com:9080 Under Destination > Artifact, use these settings:
SOAP URL: http://rp.example.com:9080/rp/SAMLAwareServlet Host List: rp.example.com Under Source > Post, set Post URL: http://rp.example.com:9080/rp/SAMLPOSTProfileServlet
Click Finish to save your work.
Follow these steps to configure the relying party OpenAM server:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator, browse to Federation > SAML 1.x Configuration, and then click New in the Trusted Partners table to add the asserting party as a trusted partner.
In the Source area of the Select trusted partner type and profile page, select Artifact and Post, and then click Next.
Apply the following settings, adjusted for the host names you use.
If a field is not mentioned, accept the defaults.
Under Common Settings, use these settings:
Name: ap.example.net:8080 Source ID: asserting party Site ID that you recorded Signing Certificate Alias: test Under Source > Artifact, set SOAP URL: http://ap.example.net:8080/ap/SAMLSOAPReceiver
Under Source > Post, set Issuer: ap.example.net:8080
Click Finish to save your work.
Once you have successfully configured both parties, try SAML v1.x Web SSO:
Log out of OpenAM console on both servers.
Try Web SSO using the SAML Artifact profile.
Simulate the OpenAM administrator browsing the asserting party's site, and selecting a link to the OpenAM console on the relying party's site.
The URL to simulate this action is something like
http://ap.example.net:8080/ap/SAMLAwareServlet?TARGET=http://rp.example.com:9080/rp.OpenAM requires that you authenticate.
Login as OpenAM demo user,
demowith default passwordchangeit, on the asserting party server.Notice that you are redirected to OpenAM console on the relying party server, and that you are successfully logged in as the demo user.
Log out of OpenAM console on both servers.
Try Web SSO using the SAML HTTP POST profile:
Simulate the OpenAM administrator browsing the asserting party's site, and selecting a link to the OpenAM console on the relying party's site.
The URL to simulate this action is something like
http://ap.example.net:8080/ap/SAMLPOSTProfileServlet?TARGET=http://rp.example.com:9080/rp.OpenAM requires that you authenticate.
Login as OpenAM administrator,
amadmin, on the asserting party server.Notice that you are redirected to OpenAM console on the relying party server, and that you are successfully logged in as
amadmin.
OpenAM provides a REST Security Token Service (STS) and a SOAP STS that allow OpenAM to bridge identities across web and enterprise Identity Access Management (IAM) systems through its token transformation process.
Web services and requestors (that is, consumers or clients) are typically deployed across different security domains and topologies. Each domain may require a specific security token type to assert authenticated identities. STS provides a means to exchange tokens across these different domains without re-authenticating or re-establishing trust relationships while allowing the requestor access to a web service's protected resources.
This chapter covers configuration of both OpenAM's REST and SOAP STS components. Developers should refer to the "Working With the Security Token Service" in the Developer's Guide for information about how to publish REST and SOAP STS instances programmatically and how to invoke these services.
The OpenAM STS issues, validates, and cancels tokens to establish trust relationships across different security domains. OpenAM STS provides the following key features:
REST STS. OpenAM provides a REST STS component that accepts REST API calls to OpenAM to transform security tokens. The OpenAM REST STS allows browser-based clients to use the HTTP protocol methods (GET and POST), cookies, and redirection to authenticate the client with the STS. Note that the REST STS does not conform to the WS-Trust specification, but provides a simpler deployment alternative to SOAP STS for token transformations.
SOAP STS. OpenAM provides a WS-Trust 1.4-compliant SOAP STS that lets OpenAM administrators publish or configure security token services. The SOAP STS provides for SOAP-enabled applications to send and receive SOAP messages without the need for HTTP redirection for authentication.
REST AND SOAP STS: Token Transformations. OpenAM STS issues OpenID Connect V1.0 (OIDC) and SAML V2.0 tokens (bearer, holder-of-key, sender vouches).
The REST STS provides the following token transformations for a single provider. (Note that the REST STS input type tokens do not conform to the WS-Trust specification):
• Username token → OIDC • OIDC → OIDC[8] • X.509 token → OIDC • OpenAM Session token → OIDC • Username token → SAML v2.0 • X.509 token → SAML v2.0 • OIDC token → SAML v2.0 • OpenAM Session token → SAML v2.0 The SOAP STS provides the following token transformations for a single provider:
• UsernameToken→ OIDC• OIDC → OIDC • X.509→ OIDC• OpenAM SessionToken → OIDC • UsernameToken→ SAML v2.0• X.509→ SAML v2.0• OpenAM SessionToken → SAML v2.0 In both cases, you can invalidate or validate the interim OpenAM session that was created during the authentication of the input token type after the creation of the output token.
REST AND SOAP STS: Publish Service. You can configure REST or SOAP STS instances using the OpenAM console or programmatically. OpenAM provides a REST STS publish service that allows you to publish these instances using a POST to the endpoints. Note that a published instance can have only a single encryption key. Therefore, you need one published instance per service provider that the web service invoking the STS intends to call. For more information, see "The Publish Service" in the Developer's Guide.
REST STS AND SOAP STS: Custom SAML Assertion Plugins. OpenAM supports customizable SAML assertion statements. You can create custom plug-ins for
Conditions,Subject,AuthenticationStatements,AttributeStatements, andAuthorizationDecisionStatementsstatements.REST STS: Custom Token Validators and Providers. The OpenAM REST STS provides the ability to customize tokens that are not supported by default by the STS. For example, you can configure STS to transform a token of type CUSTOM to a SAML V2.0 token.
SOAP STS: Client SDK. OpenAM provides a SOAP STS client SDK module to allow developers to use Apache CXF-STS classes. For details, see "About the SOAP STS Client SDK" in the Developer's Guide.
SOAP STS: ActAs and OnBehalfOf Elements. OpenAM STS supports delegated and proxied token relationships, as defined by the
ActAsandOnBehalfOfelements in WS-Trust, which is available for Username and OpenAM session tokens.SOAP STS: Security Binding Assertions. OpenAM SOAP STS supports the WS-SecurityPolicy binding assertions that protect communication to and from the STS: transport, asymmetric, symmetric.
SOAP STS: Custom WSDL. The OpenAM SOAP STS comes with a pre-configured WSDL file. You can customize the policy bindings governing the input or output messages to or from the STS. For specific information, see "Customizing the WSDL File".
SOAP STS: Logging Service. The OpenAM STS allows SOAP-STS log entries to be configured via
java.util.logging, which allows logging to be configured via thelogging.propertiesfile in the Tomcatconfdirectory.
The main differences between the OpenAM's REST and SOAP STS implementations are summarized in the table below:
| Features | REST STS | SOAP STS |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoints used by consumers | REST | SOAP |
| WS-Trust 1.4 compliant? | No | Yes |
| Input token types supported | Username, X.509, OpenAM session, OpenID Connect | Username, X.509, OpenAM session |
| Custom Token Type support | Yes | No |
| Apache CXF-based client SDK | No | Yes |
| ActAs/OnBehalfOf Support | No | Yes |
| Deployment | REST endpoints exposed upon instance creation | OpenAM .war and the SOAP STS .war
files mustbe deployed in separate web containers to expose
the SOAP endpoints |
A Security Token Service (STS) validates, issues, and cancels security tokens. OpenAM provides two Security Token Services:
REST STS. OpenAM provides a REST-based security token services. Note that the REST STS does not conform to the WS-Trust specification but provides a simpler deployment alternative than SOAP STS for token transformations.
SOAP STS. OpenAM supports a fully WS-Trust 1.4-compliant Security Token Service.
The WS-Trust specification introduces the concept of a centralized runtime component called the Security Token Service (STS), which issues, cancels, and validates security tokens in SOAP-based networks. A WS-Trust model involves communication between the components: a requestor, web service, and STS. The following terms are used throughout this chapter:
The requestor is a web client or programmatic agent that wants to use a service offered by the web service.
The web service allows authenticated and authorized clients to access resources or applications.
The identity provider stores claims about subjects and works with the STS to issue security tokens.
The STS acts as a trusted third-party web service that asserts the identity of a requestor across different security domains through the exchange of security tokens and brokers a trust relationship between the requestor and the web service provider. The STS issues tokens based on its configurations, which model the identity of a given identity provider, and issues tokens to a specific relying party.
A security token is a SOAP STS data structure representing a set of claims that assert the identity of a subject. A single claim is identity information, such as a subject's name, age, gender, and email address.
A security policy, defined in WS-SecurityPolicy, specifies the required elements, tokens, security bindings, supporting tokens, and protocol assertions, which are requirements for a web service to grant a subject access to its service. The security policy is defined in a WSDL document, which is an XML file that states what needs to be protected, what tokens are allowed for access, and transmission requirements for SOAP STS.
"Basic REST STS Model" illustrates a simple REST STS topology between a requestor, web service, and STS. The STS instance is set up with the identity provider which has an existing trust relationship with the web service. The difference between the REST STS versus the SOAP STS is that REST STS does not strictly follow the WS-Trust specification for input token and output token formats. However, the REST STS provides a simpler means to deploy an STS instance, compared to that of the SOAP STS.
A simple REST STS process flow is as follows:
A requestor makes an access request to a web resource.
The web service redirects the requestor to the STS.
The requestor sends an HTTP(S) POST to the STS endpoint. The request includes credentials, token input type and desired token output type. An example curl request is shown below:
$ curl \ --request POST \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5..." \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --data '{ "input_token_state": { "token_type": "USERNAME", "username": "demo", "password": "changeit" }, "output_token_state": { "token_type": "SAML2", "subject_confirmation": "BEARER" }, }' \ https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/rest-sts/username-transformer?_action=translateOr, you can run a command for an OIDC token:
$ curl \ --request POST --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5.." \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --data '{ "input_token_state": { "token_type": "USERNAME", "username": "demo", "password": "changeit" }, "output_token_state": { "token_type": "OPENIDCONNECT" , "nonce":"12345678", "allow_access":true } }' \ http://forgerock-am.openrock.org:8080/openam/rest-sts/username-transformer?_action=translateThe STS validates the signature, decodes the payload, and verifies that the requestor issued the transaction. The STS validates the requestor's credentials, creates an interim OpenAM session, and optionally creates a CTS token for the session. The STS then issues a token to the requestor. If STS is configured to invalidate the interim OpenAM session, it does so. The requestor gets redirected to the web service.
The requestor presents the token to the web service. The web service validates the signature, decodes the payload, and verifies that the requestor issued the request. It then extracts and validates the token and processes the request.
If a CTS token was created for the session, the web service can call the REST STS to invalidate the token and the corresponding OpenAM session upon request.
"Basic SOAP STS Model" illustrates a basic SOAP STS topology between a requestor, web service, and STS. The STS instance is set up with the identity provider which has an existing trust relationship with the web service.
A basic SOAP STS process flow is as follows:
A requestor first accesses a protected resource for a web service. The requestor gets the web service's WSDL file, which specifies the policy requirements to access its services.
The requestor creates and configures an
STSClientobject whose main task is to contact the STS.The
STSClientcontacts the STS to obtain its WSDL file. Each published STS instance exposes an API that is defined in its WSDL file. The WSDL file specifies the security policy bindings, which specify the type of token they must present to the API, and how this token is protected during transit.The
STSClientgenerates and sends a Request for Security Token (RST) to the STS. The RST specifies the what type of token is desired. The requestor'susernameTokenis embedded in the SOAP envelope that contains the RST and is used for authentication.The SOAP STS client SDK provides the classes, templates, and documentation to allow developers to set the state necessary to allow the Apache CXF runtime to generate the SOAP envelopt containing the RST, which satisfies the security policy bindings of the targeted STS.
The STS validates the requestor's
usernameToken, creates an interim OpenAM session, and optionally creates a CTS token for the session. Upon successful authentication, the STS constructs a Request for Security Token Response (RSTR), signs the SAML v2.0 token, and embeds the token within the RSTR. If STS is configured to invalidate the interim token, it does so. The STS sends a Request for Security Token Response (RSTR) to theSTSClient.The
STSClientextracts the security token and sends it in the request's message header. TheSTSClientsends the message to the web service.The web service extracts the SAML token and validates the signature to ensure that it came from the STS. The web service allows the user whose ID is specified in the SAML token to access its protected resource.
If a CTS token was created for the session, the web service can call the SOAP STS to invalidate the token and the corresponding OpenAM session upon request.
OpenAM 13 supports its own REST STS and a WS-Trust 1.4-compliant SOAP STS that transforms tokens from one type to SAML v2.0 or OIDC tokens. The STS can be deployed in existing federated systems to establish cross-domain trust relationships using token transformations.
OpenAM provides the ability for OpenAM administrators to publish or configure STS instances, each with its own distinct policy configurations, programmatically or via the OpenAM console.
The OpenAM SOAP STS is built upon the Apache CXF STS, an open-source implementation of JAX-WS and JAX-RS, as well as Apache WSS4j, an open-source Java implementation of the WS-Security specification.
OpenAM's REST STS service provides an easier deployment alternative to SOAP STS to issue OpenID Connect 1.0 or SAML v2.0 tokens for a single service provider. Each REST STS instance is configured with the following elements:
Issuer. The issuer corresponds to the IdP
EntityID.SP EntityID. The SP
EntityIDis used in theAudienceRestrictionelement of theConditionsstatement of the issued assertion.SP Assertion Consumer Service URL. The SP assertion consumer service URL is used as the
Recipientattribute of thesubjectConfirmationelement in theSubjectstatement, which is required for bearer assertions according to the Web SSO profile.
For signing and encryption support, each REST STS instance has a configuration state, which specifies the keystore location containing the signing and encryption keys:
If assertion signature is configured, the keystore path and password must be specified as well as the alias and password corresponding to the
PrivateKeyused to sign the assertion.If assertion encryption is configured, the keystore path and password must be specified, as well as the alias corresponding the the SP’s X509Certificate encapsulating the
PublicKeyused to encrypt the symmetric key used to encrypt the generated assertion.Note that the keystore location can be specified via an absolute path on the local filesystem, or a path relative to the OpenAM classpath. Either the entire assertion can be encrypted, or the
NameIDand/orAttributeStatementAttributes.
All statements constituting a SAML v2.0 assertion can be customized.
For each REST STS instance, you can provide custom plug-ins for
Conditions, Subject,
AuthenticationStatements,
AttributeStatements, and
AuthorizationDecisionStatements.
If you specify the custom plug-ins in the configuration state of the published
REST STS instance, the custom classes are consulted to provide the
specific statements. See the interfaces in the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements
package for details.
Each REST STS instance must specify the authentication context (that is,
AuthnContext) to be included in the
AuthenticationStatements of the generated assertion.
This AuthnContext allows
the generated SAML v2.0 assertion to specify the manner in which the
assertion’s subject was authenticated.
For a token transformation, this AuthnContext is
a function of the input token type. By default, the following
AuthnContext strings will be included in the SAML v2.0
assertion generated as part of the transformation of the following input
token types:
OpenAM:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PreviousSessionUsername Token and OpenID Connect Token:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransportX.509 Token:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:X509
Note that you can override these default mappings by implementing the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.token.provider.AuthnContextMapper
interface and specifying the name of this implementation in the
configuration of the published REST STS instance.
If you are interested in the REST STS, you should be familiar with the following specifications before setting up your deployment:
OpenAM 13 allows OpenAM administrators to publish WS-Trust 1.4-compliant STS instances, each with a distinct security policy configuration, and each issuing OpenID Connect (OIDC) v1.0 Tokens or SAML v2.0 (bearer, holder of key, and sender vouches) assertions.
The SOAP STS is deployed remotely from OpenAM in a Tomcat or Jetty container.
Deploying both the OpenAM .war and the SOAP STS
.war in the same container is not supported.
The remotely-deployed SOAP STS .war file authenticates to
OpenAM with SOAP STS agent credentials and pulls the configuration state for
all SOAP instances published in its realm, exposing WS-Trust-compliant SOAP
web services based on this configuration state.
For more information, see "Deploying SOAP STS Instances".
OpenAM is the authentication authority for the STS instances and its configured data stores, which store the attributes that are included in OIDC tokens and generated SAML v2.0 assertions.
You can publish any number of SOAP STS instances programmatically, or by using the OpenAM console. Each instance is published with a specific WS-SecurityPolicy binding, which specifies:
Type of supporting token that asserts the caller’s identity.
Manner in which the supporting token is protected (symmetric, asymmetric, or transport binding).
Each published SOAP STS instance is protected by a security policy binding, which specifies what sort of token must be presented to assert the caller's identity (also known as the supporting token), and how this supporting token is protected. There are three protection schemes: transport, symmetric, and asymmetric:
Transport Binding Assertion. Transport binding is used when the message is protected at the transport level, such as HTTPS, and thus requires no explicit enforcement at the security policy binding enforcement level. The SOAP keystore configuration allows a SOAP STS instance to be published referencing the keystore state necessary to enforce the symmetric and asymmetric bindings.
Symmetric Binding Assertion. Symmetric binding is used when only one party needs to generate security tokens. In a symmetric binding, the client generates symmetric key state used to sign and encrypt messages, and encrypts this symmetric key state with the STS’s public key, and includes the encrypted symmetric key in the request. Thus, the SOAP keystore configuration of a published STS instance, which is protected by the symmetric binding, must reference a keystore with the STS's
PrivateKeyEntry, so that it may decrypt the symmetric key generated by the client.Asymmetric Binding Assertion. Asymmetric binding is used when both the client and the service both have security tokens. In an asymmetric binding, client requests are signed with the client’s secret key, and encrypted with the STS’s public key. STS responses are signed with the STS’s private key and encrypted with the client’s public key. The client's X.509 certificate is included in the request, so that the STS can validate the client's signature and encrypt responses to the client without requiring the presence of the client's X.509 certificate in the STS's keystore. However, the SOAP keystore configuration of a published STS instance protected by an asymmetric binding must reference a keystore with the STS's PrivateKeyEntry, which allows the STS to both: 1) sign messages from STS to client, and 2) decrypt messages from the client.
Note
The Decryption Key Alias in a SOAP STS instance's configuration corresponds to the
PrivateKeyEntry.
The following bindings are available:
• UsernameToken over the Transport, Symmetric, and Asymmetric binding |
| • OpenAM Session Token over the Transport and Unprotected binding |
| • X.509 certificates examples seen in WS-SecurityPolicy Examples Version 1.0 |
A SAML v2.0 assertion, defined in
SAML V2.0,
contains a Subject element that identifies the principal,
which is the subject of the statements in the assertion.
The Subject element contains an identifier and zero
or more SubjectConfirmation elements, which allows a
relying party to verify the subject of the assertion with the entity with whom
the relying party is communicating.
The SubjectConfirmation element contains a required
Method attribute that specifies the URI identifying the
protocol used to confirm the subject.
The OpenAM STS supports the following subject confirmation methods:
Holder of Key. The holder of key subject confirmation method involves proving a relationship between the subject and claims. This is achieved by signing part of the SOAP message with a proof key sent in the SAML assertion. The additional proof key guards against any attempted man-in-the-middle attack by ensuring that the SAML assertion comes from the subject claiming to the be requestor.
URI: urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:holder-of-keySender Vouches. The sender vouches subject confirmation method is used in cases where you have a proxy gateway that propagates the client identity via the SOAP messages on behalf of the client. The proxy gateway must protect the SOAP message containing the SAML assertion, so that the web service can verify that it has not been tampered with.
URI: urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:sender-vouchesBearer. The bearer subject confirmation method assumes that a trust relationship exists between the subject and the claims, and thus no keys are required when using a bearer token. No additional steps are required to prove or establish a relationship.
Since browser-based clients use bearer tokens and no keys are required, you must protect the SOAP message using a transport-level mechanism, such as SSL, as this is the only means to protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
URI: urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:bearer
If you are interested in the SOAP STS, you should be familiar with the SOAP STS specifications:
SOAP STS supports the ability to issue SAML assertions with the sender vouches subject confirmation method. Sender vouches are used in proxy deployments, such as a proxying gateway, where the gateway requests a SAML assertion with a sender vouches confirmation from the STS.
In this case, the requestor's credentials are set in the
OnBehalfOf and ActAs elements in the
request security token (RST) request included in the Issue
invocation.
The gateway calls the STS, and the gateway’s
credentials satisfy the security policy bindings protecting the STS.
The presence of either the OnBehalfOf and
ActAs elements together with a token type of SAML v2.0
and a key type of PublicKey triggers the issuance of a
sender vouches SAML v2.0 assertion.
The STS runs token validators that validate the authenticity of the
ActAs or OnBehalfOf token.
The SOAP STS configuration indicates whether token delegation relationships
are supported in the STS in the ActAs and
OnBehalfOf elements. If token delegation is supported,
the configuration also indicates the token types that token validators
use to validate the ActAs and OnBehalfOf
token elements.
In the Request for Security Token (RST) invocation, Username
and OpenAM tokens are supported for the OnBehalfOf element.
In addition, you can specify that the SOAP STS instance be deployed with a
user-specified implementation of the token delegation handler interface,
org.apache.cxf.sts.token.delegation.TokenDelegationHandler.
A default token delegation handler is used if no custom token delegation
handler is configured.
The default token delegation handler
rejects the delegation relationship if the token principal set to null in the
token delegation parameters (that is, TokenDelegationParameters), as this is
the case when no token validators have validated the
ActAs and OnBehalfOf token. Thus, if
you want the STS instance to support the ActAs and
OnBehalfOf elements, you must specify one of the two
following configuration properties:
The Delegation Relationships Supported property.
One or more Delegated Token types. For example, OpenAM or
Usernamefor which token validators are deployed to validate theActAsorOnBehalfOftokens and/or a custom token delegation handler.Note
If you configure the
Usernametoken type as a delegated token type, OpenAM uses the configuration in the Authentication Target Mappings property to authenticateUsernametokens. OpenAM SSO tokens require no special configuration in the Authentication Target Mappings property.
Suppose you want to deploy the SOAP STS to receive requests from a proxy gateway and issue SAML v2.0 assertions with sender vouches subject confirmation method. The gateway sends the SAML v2.0 assertion that asserts the identity of the gateway client and vouches for its identity.
Suppose the SOAP STS deployment has a security policy binding requiring the presentation of an X.509 certificate. This security policy binding can be satisfied by presenting the gateway's X.509 certificate. However, the SOAP STS-issued SAML v2.0 assertion should assert the identity of the gateway client that presents its identity to the gateway as either a <username, password> combination or as an OpenAM session.
In this case, the published SOAP STS would specify an X.509-based security
policy, the delegation relationships to be supported, and whether both
OpenAM and Username token types should be supported. No
custom token delegation handler need be specified.
Furthermore, the SOAP STS instance must be published with Authentication
Target Mappings that specify how the Username token
should be presented to OpenAM's RESTful authentication context. The gateway
code would then create a request for security token (RST) invocation using
the classes in the
openam-sts/openam-soap-sts/openam-soap-sts-client
module, and include the gateway client's <username, password> or OpenAM
session state as the OnBehalfOf element. This setting
allows the gateway to consume the SOAP STS to issue SAML v2.0 assertions
with the sender vouches subject confirmation method, which asserts the
identity of the gateway client corresponding to the presented <username,
password> or OpenAM session state.
If, at a later date, you want to exclude or blacklist some users from attaining
SAML v2.0 assertions, regardless of their possession of valid
<username, password> or OpenAM session state, you can update the SOAP STS
with the class name of a token delegation handler implementation,
which would implement this blacklist functionality. The SOAP STS
.war file would have to be re-created with this file in the
classpath. The token delegation handler could reject the invocation for
users or principals on the blacklist.
STS token transformations validate input tokens before generating output tokens. STS uses OpenAM authentication modules and chains to perform token validation. When deploying STS, you must configure OpenAM authentication so that it can validate input tokens.
This section describes authentication configuration requirements for username, X.509, and OpenID Connect tokens. No special authentication configuration is required when using OpenAM session tokens as the input tokens in token transformations.
Because REST STS instances are not part of a secure framework like WS-Trust 1.4, this section also mentions security issues you should consider when sending tokens across a network to a REST STS instance.
In addition to configuring OpenAM authentication to support input token validation, you must identify the authentication module or chain to be used to validate each input token type. To do so, configure the Authentication Target Mappings property in the STS instance configuration. For more information about this property, see "Hints for Configuring STS Instances".
Username tokens passed to REST STS instance contain the username/password combination in clear text. Tokens can be validated using any module type that supports username/password authentication, including Data Store, LDAP, and so forth.
With usernames and passwords in clear text, be sure to configure your deployment with an appropriate level of security. Deploy REST STS instances that support input username token transformations on TLS.
REST STS instances can obtain X.509 certificates used as input tokens in two ways:
From the header key defined in the REST STS instance's Client Certificate Header Key property. In this case, STS also confirms that the request came from a host specified in the Trusted Remote Hosts property.
From the
javax.servlet.request.X509Certificateattribute in the ServletRequest. The REST STS instance obtains the X.509 certificate from the ServletRequest if no header key is configured in the Client Certificate Header Key property.
The OpenAM Certificate module authenticates the X.509 certificate input token. The module optionally performs certificate revocation list (CRL) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) checking, and can optionally check to see that the specified certificate is in a LDAP datastore.
If certificates are passed to REST STS using HTTP headers, you must configure the Trusted Remote Hosts and Http Header Name for Client Certificate properties in the Certificate module to match your REST STS instance's configuration.
To validate OpenID Connect input tokens, a REST STS instance must reference an OpenID Connect id_token bearer authentication module in the Authentication Target Mappings property.
Configure the authentication module as follows:
Specify a header in the Name of header referencing the ID Token property. The REST STS instance's Target Authentication Mapping property must reference the same header.
Specify the issuer name in the Token Issuer field, and configure the token issuer's discovery URL, JWK URL or client secret in the OpenID Connect validation configuration value property.
If incoming OpenID Connect tokens contain
azpclaims, specify valid claims in the "List of accepted authorized parties" property.If incoming OpenID Connect tokens contains
audclaims, specify the valid claim in the Audience property.Configure attribute mappings so that JWK claims map to attributes in the OpenAM user store.
For more information about OpenID Connect id_token bearer authentication module properties, see "Hints for the OpenID Connect id_token bearer Module".
Note
SOAP STS instances do not accept OpenID Connect tokens as input tokens in token transformations.
Use these hints to configure properties for REST and SOAP STS instances.
The following are general configuration properties for REST STS instances:
- Persist Issued Tokens in Core Token Store
Specifies whether to enable token persistence in the Core Token Service (CTS).
OpenAM saves all STS-issued tokens to CTS when token persistence is enabled. A token's lifetime in CTS has the same length as the Token Lifetime property specified for issued tokens.
STS token validation and cancellation capabilities require tokens to be present in CTS. Therefore, if your deployment requires token validation and cancellation, you must enable token persistence.
- Supported Token Transforms
Specifies one or more token transformations supported by this REST STS instance. Token transformations are listed in the OpenAM console using the notation
input_token_type -> output_token_type.For each supported token transformation, OpenAM provides an option to invalidate the interim OpenAM session. When transforming a token, the STS creates an OpenAM session. If desired, you can invalidate the OpenAM session after token transformation is complete.
- Custom Token Validators
Specifies a validator class for a custom token type.
Use the format
CUSTOM_TOKEN_TYPE|custom_validator_classto specify each validator class. For example,CUSTOM|org.mycompany.tokens.myCustomTokenValidator.For more information about custom token validators, see "Extending STS to Support Custom Token Types" in the Developer's Guide.
- Custom Token Providers
Specifies a provider class for a custom token type.
Use the format
CUSTOM_TOKEN_TYPE|custom_provider_class. To specify each provider class. For example,CUSTOM|org.mycompany.tokens.myCustomTokenProvider.For more information about custom token providers, see "Extending STS to Support Custom Token Types" in the Developer's Guide.
- Custom Token Transforms
Specifies one or more token transformations that take a custom token type as the input or output token. If you specify a custom token validator or provider, you must also specify a custom token transform.
Specify the custom transform using three values separated by the vertical bar character | as follows:
The input token type
The output token type
Whether to invalidate the OpenAM session created during token transformation. Specify
TRUEto invalidate the session orFALSEto let the session remain valid.
For example, a value of
CUSTOM|SAML2|TRUEconfigures a token transformation that transforms aCUSTOMtoken to a SAML v2.0 assertion and then invalidates the created OpenAM session.
The following are deployment configuration properties for REST STS instances:
- Deployment Url Element
Specifies a string that identifies this REST STS instance.
The Deployment Url Element is a component of the REST STS instance's endpoint. For example, if you specified
myRESTSTSInstanceas the Deployment Url Element, the REST STS endpoint would berest-sts/myRealm/myRESTSTSInstance.- Authentication Target Mappings
Specifies one or more mappings that define how the REST STS instance authenticates input tokens.
Each mapping is a set of arguments separated by the vertical bar character | as follows:
(Required) The input token type:
USERNAME,OPENAM,X509,OPENIDCONNECT, or a custom token type.(Required) The value
serviceormodule. If the third argument is an authentication chain, specifyservice. If the third argument is an authentication module, specifymodule.(Required) The name of an OpenAM authentication chain or module to which the input token is authenticated.
(Optional) The name of the header to place the token in when authenticating to OpenAM. Specify this parameter for input
X509andOPENIDCONNECTtokens as follows:For
X509input tokens, the format isx509_token_auth_target_header_key=Header Name.For
OPENIDCONNECTinput tokens, the format isoidc_id_token_auth_target_header_key=Header Name.
Be sure to specify the header names configured in the Certificate or OpenID Connect id_token bearer authentication module properties as the Header Name argument.
This argument can also be used with custom token types to specify the name of a header or cookie from which to obtain a token. When using this argument with a custom token type, its format is determined by the custom validator class that validates the custom token type.
The following are example mappings:
USERNAME|service|myLDAPChainconfigures STS to authenticate inputUSERNAMEtokens to themyLDAPChainauthentication chain.X509|module|CertModule|x509_token_auth_target_header_key=ClientCertconfigures STS to obtain an X.509 certificate from theClientCertheader, use it as the input token, and authenticate it using theCertModuleauthentication module.
- Client Certificate Header Key
Specifies the name of a header that a TLS offloader should use to use to transmit client certificates.
Token transformations that take an X.509 certificate as the input token require the certificate to be presented using two-way TLS, so that the TLS handshake can validate client certificate ownership. A common way of obtaining the client certificate with two-way TLS is to use the
javax.servlet.request.X509Certificateattribute in the servlet request.However, in deployments with TLS offloading, the offloader must use an HTTP header to transmit the certificate to its destination. This configuration property is the name of the HTTP header whose value contains the certificate.
- Trusted Remote Hosts
Specifies one or more IP addresses of hosts trusted to transmit client X.509 certificates in deployments with TLS offloading.
To allow any host to transmit a certificate, specify
anyas the value of this property.As with the Client Certificate Header Key property, configure this property for deployments with TLS offloading.
This section lists configuration properties associated with STS-issued SAML v2.0 assertions for both REST and SOAP STS instances. The properties fall into two categories:
Properties that determine content in STS-issued SAML v2.0 assertion. For information about SAML v2.0 assertions, see Assertions and Protocols for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0.
Properties that determine how the issued SAML v2.0 assertion is signed or encrypted.
- The SAML2 issuer Id
Specifies the IdP entity ID. Populates the
Issuerelement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.- Service Provider Entity Id
Specifies an audience attribute value. Populates the
AudienceRestrictionsubelement of theConditionselement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.This value is required when issuing Bearer assertions.
- Service Provider Assertion Consumer Service Url
Specifies a recipient attribute value. Populates the
Recipientsubelement of theSubjectConfirmationelement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.This value is required when issuing Bearer assertions.
- NameIdFormat
Specifies the name identifier format for the SAML v2.0 assertion.
- Token Lifetime
Specifies the lifetime, in seconds, for the assertion. The default is 600 seconds.
- Custom Conditions Provider Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates a
Conditionselement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theConditionselement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.ConditionsProviderinterface, and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Customs Subject Provider Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates a
Subjectelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theSubjectelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.SubjectProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom AuthenticationStatements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthnStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthnStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthenticationStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom AttributeStatements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AttributeStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAttributeStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AttributeStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Authorization Decision Statements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthzDecisionStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthzDecisionStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthzDecisionStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Attribute Mapper Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom attribute mapper class. An attribute mapper generates
attributeelements to be included in the SAML v2.0 assertion.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AttributeMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Authentication Context Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthnContextelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthnContextelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.By default, OpenAM generates the
AuthnContextelement based on the input token type as follows:For input OpenAM tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PreviousSessionFor input username tokens and OpenID Connect ID tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransportFor input X.509 tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:X509
- Attribute Mappings
Configures mappings between SAML v2.0 attribute names—map keys—and OpenAM user profile attributes or session properties in order to generate
Attributeelements in the SAML v2.0 assertion.OpenAM's default attribute mapper generates
Attributeelements as follows:The map key populates the
Attributeelement'sNameproperty.The user profile or session property value populates the
Attributeelement'sAttributeValueproperty.
When specifying map keys in the Attribute Mappings property, use the following format:
[NameFormatURI]|SAML_ATTRIBUTE_NAME.Map values enclosed in quotes are included in the attribute without mapping. Specify
';binary'at the end of a map value for attributes that have binary values.The following are examples of attribute mappings:
EmailAddress=mailAddress=postaladdressurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|urn:mace:dir:attribute-def:cn=cnpartnerID="staticPartnerIDValue"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|nameID="staticNameIDValue"photo=photo;binaryurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|photo=photo;binary
- Sign Assertion
Specifies whether or not to sign the SAML v2.0 assertion.
When enabling assertion signing, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, Signature Key Alias, and Signature Key Password properties.
- Encrypt Assertion
Specifies whether to encrypt the entire SAML v2.0 assertion. When enabling assertion encryption:
You must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
You must not specify the Encrypt Attributes or Encrypt NameID options.
The Encryption Key Alias corresponds to the public key of the service provider that is the intended audience of the assertion. SAML v2.0 assertion encryption works as follows:
OpenAM generates a symmetric key.
OpenAM encrypts the symmetric key with the recipient's public key.
OpenAM includes the encrypted key in the part of the assertion that is not symmetric key-encrypted.
The service provider—owner of the corresponding private key—uses the private key to decrypt the symmetric key included in the assertion.
The service provider can then use the decrypted symmetric key to decrypt the assertion.
- Encrypt Attributes
Specifies whether to encrypt the assertion's attributes only. When specifying this option, do not specify the Encrypt Assertion option.
When encrypting attributes, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
- Encrypt NameID
Specifies whether to encrypt the assertion's NameID only. When specifying this option, do not specify the Encrypt Assertion option.
When encrypting the NameID, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
- Encryption Algorithm
Specifies the encryption algorithm to use when encrypting the entire assertion, the assertion's attributes, or the NameID.
- KeystorePath
Specifies the path to the Java keystore to be used for encrypting all or part of the SAML assertion. Specify an absolute path or a location in the OpenAM classpath.
OpenAM provides two keystores with test keys that are located at the
/path/to/openam/openam/path. For more information about the OpenAM keystores, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".- Keystore Password
Specifies the encryption keystore's password.
- Encryption Key Alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the service provider's X.509 certificate encapsulating the public key used to encrypt the symmetric key used to encrypt the generated assertion.
- Signature Key Alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the assertion.
- Signature Key Password
Specifies the password of the private key used to sign the assertion.
This section lists configuration properties associated with STS-issued OpenID Connect tokens for both REST and SOAP STS instances. The properties fall into two categories:
Properties that determine content in the issued OpenID Connect ID token. For information about OpenID Connect ID tokens, see the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 specification.
Properties that determine how the issued token is signed.
An STS instance configured to issue OpenID Connect tokens models the
relationship between an OpenID Connect token provider and relying party. In
other words, an STS instance issues tokens for a particular OAuth 2.0
client. The tokens contain aud and azp
claims for the OAuth 2.0 client, and signing key state corresponding to a
token provider.
In this model, when users call an STS instance to generate an OpenID Connect ID token, the process is analogous to the exchange between an OAuth 2.0 authorization server and resource owner following the initial redirection from an OAuth 2.0 client initiating the implicit flow. The STS instance returns the OpenID Connect ID token that corresponds to the authorization server's authentication of the resource owner. OpenAM authenticates one of the following:
For REST STS, the token specified as the
input_token_statefor the token transformationFor SOAP STS, the supporting token necessary to traverse the SecurityPolicy bindings protecting the WS-Trust operation
Implicit in this model is the notion that an OpenID Connect ID token has value outside of an OAuth 2.0 flow, and that an OAuth 2.0 client, as a relying party, could be generalized as a SAML v2.0 service provider. The ID token is not simply an an entity-provided verifiable authorized access to a specific resource set, but rather a generic service provider that consumes an OpenID Connect ID token to authenticate and authorize the subject asserted by the token.
Therefore, the configuration of an STS instance that issues OpenID Connect ID tokens contains information that defines the token provider and relying party.
Note that the nonce claim in the ID token is not a
configuration property of an STS instance. STS consumers requesting an output
OpenID Connect token provide a nonce value when making
token transformation requests.
- The id of the OpenIdConnect Token Provider
Specifies the OpenID Connect token provider issuer ID. Populates the
issclaim of the ID token.- Token Lifetime
Specifies, in seconds, the ID token's expiration. Populates the
expclaim of the ID token.- Token signature algorithm
Specifies an HMAC or RSA algorithm used to sign ID tokens.
- Public key reference type
Specifies how public keys should be referenced in issued ID tokens signed with RSA. OpenID Connect ID tokens are issued as JSON web tokens (JWTs). Tokens can reference RSA public keys as JSON web keys (JWKs), or not at all.
Used with RSA signing.
- KeyStore Location
Specifies the path to the Java keystore used for signing the ID token. Specify an absolute path or a location in the OpenAM classpath.
Used with RSA signing.
OpenAM provides two keystores with test keys that are located at the
/path/to/openam/openam/path. For more information about the OpenAM keystores, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".- KeyStore password
Specifies the password of the keystore used for signing the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- KeyStore signing key alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- Signature key password
Specifies the password of the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- Client secret
Specifies the secret shared between the client and the ID token generator used to sign the ID token.
Used with HMAC signing.
- The audience for issued tokens
Specifies the intended audience for the ID token. Populates the
audclaim of the ID token.- The authorized party
Specifies the party to which the ID token is being issued. Populates the
azpclaim of the ID token.- Claim map
Specifies additional claim entries to be inserted into the ID token.
Specifies entries using the format
claim_name=user_profile_attribute. When issuing the ID token, OpenAM populates the claim value with the value of the attribute in the authenticated user's profile.For example, suppose the Claim map property had an entry with the value
email=mail. A generated OpenID Connect ID token for user Sam Carter would contain the claim"email":"scarter@example.com"if themailattribute in Sam Carter's user profile had the valuescarter@example.com.- Custom claim mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom claim mapper class. A claim mapper generates additional claims to be included in the OpenID Connect ID token.
The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.oidc.OpenIdConntectTokenClaimMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom authn context mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
acrclaim in the OpenID Connect ID token. Anacrclaim indicates which authentication context class was satisfied by the authentication of the principal asserted in the OpenID Connect ID token. Theacrclaim is optional and is not included in the generated ID token by default.For REST STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.rest.token.provider.oidc.OpenIdConnectTokenAuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.For SOAP STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.soap.token.provider.oidc.SoapOpenIdConnectTokenAuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled into the SOAP STS deployment.warfile.- Custom authn methods references mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
amrclaim in the OpenID Connect ID token. Anamrclaim indicates which authentication methods were used to authenticate the principal asserted in the OpenID Connect ID token. Theamrclaim is optional and is not included in the generated ID token by default.For REST STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.rest.token.provider.oidc.OpenIdConnectTokenAuthMethodReferencesMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.For SOAP STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.soap.token.provider.oidc.SoapOpenIdConnectTokenAuthnMethodReferencesMapperinterface and must be bundled into the SOAP STS deployment.warfile.
The following are general configuration properties for SOAP STS instances:
- Persist Issued Tokens in Core Token Store
Specifies whether to enable token persistence in the Core Token Service (CTS).
OpenAM saves all STS-issued tokens to CTS when token persistence is enabled. A token's lifetime in CTS has the same length as the Token Lifetime property specified for issued tokens.
STS token validation and cancellation capabilities require tokens to be present in CTS. Therefore, if your deployment requires token validation and cancellation, you must enable token persistence.
- Issued Tokens
Specifies the types of tokens that this SOAP STS instance issues as output tokens for token transformations.
- Security Policy Validated Token
Specifies the
SupportingTokentype in the WS-SecurityPolicy bindings in the SOAP STS deployment's WSDL, and whether the OpenAM session created during token transformation should be invalidated after the token is issued.
The following are deployment configuration properties for SOAP STS instances:
- Deployment Url Element
Specifies a string that identifies this SOAP STS instance.
The Deployment Url Element is a component of the SOAP STS instance's endpoint. For example, if you specified
mySOAPSTSInstanceas the Deployment Url Element, the SOAP STS endpoint would be SOAP STS .war File Name/myRealm/mySOAPSTSInstance.- Authentication Target Mappings
Specifies one or more mappings that define how the SOAP STS instance should authenticate input tokens.
Each mapping is a set of arguments separated by the | character as follows:
(Required) The input token type:
USERNAME,OPENAM, orX509.(Required) The value
serviceormodule. If the third argument is an authentication chain, specifyservice. If the third argument is an authentication module, specifymodule.(Required) The name of an OpenAM authentication chain or module to which the input token is authenticated.
(Optional) The name of the header in which to place the token when authenticating to OpenAM. For
X509input tokens, the format isx509_token_auth_target_header_key=Header Name.Be sure to specify the header name configured in the Certificate authentication module properties as the Header Name argument.
The following are example mappings:
USERNAME|service|myLDAPChainconfigures STS to authenticate inputUSERNAMEtokens to themyLDAPChainauthentication chain.X509|module|CertModule|x509_token_auth_target_header_key=ClientCertconfigures STS to obtain an X.509 certificate from theClientCertheader, use it as the input token, and authenticate it using theCertModuleauthentication module.
- Url of OpenAM
Specifies the OpenAM URL. For example,
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam.- Wsdl File Referencing Security Policy Binding Selection
Specifies a supporting token type and security policy binding to protect the SOAP STS instance. This choice will determine the SecurityPolicy bindings in the wsdl file defining the WS-Trust API.
If you select the
Custom wsdl fileoption, you must provide the path to a custom WSDL file in the Custom wsdl File property.- Custom wsdl File
Specifies the path to a custom WSDL file that defines the WS-Trust API.
- Custom Service QName
Specifies the
nameattribute of thewsdl:serviceelement. Configure this property when using a custom WSDL file.- Custom Port QName
Specifies the
nameattribute of thewsdl:portelement. Configure this property when using a custom WSDL file.- Delegation Relationships Supported
Enable this option if the request security token messages can include
wst14:ActAsorwst:OnBehalfOfparameters. Note that you must enable this option if the SOAP STS instance issues SAML v2.0 assertions withSenderVouchessubject confirmations.- Delegated Token Types
Specifies the types of validation support to enable in the SOAP STS instance for
USERNAMEandOPENAMtokens inwst14:ActAsorwst:OnBehalfOfparameters specified in request security token messages.If the SOAP STS instance supports delegated relationships, configure either the Delegated Token Types property or the Custom Delegation Handlers property, but not both properties.
- Custom Delegation Handlers
Specifies custom handlers that implement the
org.apache.cxf.sts.token.delegation.TokenDelegationHandlerinterface. The handlers provide validation support for the tokens inwst14:ActAsorwst:OnBehalfOfparameters specified in request security token messages. Custom delegation handlers are typically used when the tokens are custom tokens.If the SOAP STS instance supports delegated relationships, configure either the Delegated Token Types property or the Custom Delegation Handlers property, but not both properties.
The following are SOAP keystore configuration properties for SOAP STS instances:
- Soap Keystore Location
Specifies a keystore containing keys that enforce security policy when using the symmetric and asymmetric bindings with SOAP messaging.
Note that the Wsdl File Referencing Security Policy Binding Selection property determines the binding for a SOAP STS instance.
- Keystore Password
Specifies the SOAP keystore's password.
- Signature Key Alias
Specifies the alias of the key used to sign messages from this SOAP STS instance. You must configure this property when using asymmetric binding.
- Signature Key Password
Specifies the password for the signature key.
- Decryption Key Alias
Specifies the alias of the key used by this SOAP STS instance to decrypt client messages for the asymmetric binding, and to decrypt the client-generated symmetric key for the symmetric binding.
- Decryption Key Password
Specifies the decryption key's password.
This section lists configuration properties associated with STS-issued SAML v2.0 assertions for both REST and SOAP STS instances. The properties fall into two categories:
Properties that determine content in STS-issued SAML v2.0 assertion. For information about SAML v2.0 assertions, see Assertions and Protocols for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0.
Properties that determine how the issued SAML v2.0 assertion is signed or encrypted.
- The SAML2 issuer Id
Specifies the IdP entity ID. Populates the
Issuerelement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.- Service Provider Entity Id
Specifies an audience attribute value. Populates the
AudienceRestrictionsubelement of theConditionselement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.This value is required when issuing Bearer assertions.
- Service Provider Assertion Consumer Service Url
Specifies a recipient attribute value. Populates the
Recipientsubelement of theSubjectConfirmationelement of the SAML v2.0 assertion.This value is required when issuing Bearer assertions.
- NameIdFormat
Specifies the name identifier format for the SAML v2.0 assertion.
- Token Lifetime
Specifies the lifetime, in seconds, for the assertion. The default is 600 seconds.
- Custom Conditions Provider Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates a
Conditionselement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theConditionselement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.ConditionsProviderinterface, and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Customs Subject Provider Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates a
Subjectelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theSubjectelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.SubjectProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom AuthenticationStatements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthnStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthnStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthenticationStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom AttributeStatements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AttributeStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAttributeStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AttributeStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Authorization Decision Statements Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthzDecisionStatementelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthzDecisionStatementelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthzDecisionStatementsProviderinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Attribute Mapper Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom attribute mapper class. An attribute mapper generates
attributeelements to be included in the SAML v2.0 assertion.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AttributeMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom Authentication Context Class Name
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
AuthnContextelement in the SAML v2.0 assertion. This property is optional: use a custom class when theAuthnContextelement created by the default provider does not meet your needs.The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.saml2.statements.AuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.By default, OpenAM generates the
AuthnContextelement based on the input token type as follows:For input OpenAM tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PreviousSessionFor input username tokens and OpenID Connect ID tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransportFor input X.509 tokens:
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:X509
- Attribute Mappings
Configures mappings between SAML v2.0 attribute names—map keys—and OpenAM user profile attributes or session properties in order to generate
Attributeelements in the SAML v2.0 assertion.OpenAM's default attribute mapper generates
Attributeelements as follows:The map key populates the
Attributeelement'sNameproperty.The user profile or session property value populates the
Attributeelement'sAttributeValueproperty.
When specifying map keys in the Attribute Mappings property, use the following format:
[NameFormatURI]|SAML_ATTRIBUTE_NAME.Map values enclosed in quotes are included in the attribute without mapping. Specify
';binary'at the end of a map value for attributes that have binary values.The following are examples of attribute mappings:
EmailAddress=mailAddress=postaladdressurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|urn:mace:dir:attribute-def:cn=cnpartnerID="staticPartnerIDValue"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|nameID="staticNameIDValue"photo=photo;binaryurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:uri|photo=photo;binary
- Sign Assertion
Specifies whether or not to sign the SAML v2.0 assertion.
When enabling assertion signing, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, Signature Key Alias, and Signature Key Password properties.
- Encrypt Assertion
Specifies whether to encrypt the entire SAML v2.0 assertion. When enabling assertion encryption:
You must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
You must not specify the Encrypt Attributes or Encrypt NameID options.
The Encryption Key Alias corresponds to the public key of the service provider that is the intended audience of the assertion. SAML v2.0 assertion encryption works as follows:
OpenAM generates a symmetric key.
OpenAM encrypts the symmetric key with the recipient's public key.
OpenAM includes the encrypted key in the part of the assertion that is not symmetric key-encrypted.
The service provider—owner of the corresponding private key—uses the private key to decrypt the symmetric key included in the assertion.
The service provider can then use the decrypted symmetric key to decrypt the assertion.
- Encrypt Attributes
Specifies whether to encrypt the assertion's attributes only. When specifying this option, do not specify the Encrypt Assertion option.
When encrypting attributes, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
- Encrypt NameID
Specifies whether to encrypt the assertion's NameID only. When specifying this option, do not specify the Encrypt Assertion option.
When encrypting the NameID, you must also specify the KeystorePath, Keystore Password, and Encryption Key Alias properties.
- Encryption Algorithm
Specifies the encryption algorithm to use when encrypting the entire assertion, the assertion's attributes, or the NameID.
- KeystorePath
Specifies the path to the Java keystore to be used for encrypting all or part of the SAML assertion. Specify an absolute path or a location in the OpenAM classpath.
OpenAM provides two keystores with test keys that are located at the
/path/to/openam/openam/path. For more information about the OpenAM keystores, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".- Keystore Password
Specifies the encryption keystore's password.
- Encryption Key Alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the service provider's X.509 certificate encapsulating the public key used to encrypt the symmetric key used to encrypt the generated assertion.
- Signature Key Alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the assertion.
- Signature Key Password
Specifies the password of the private key used to sign the assertion.
This section lists configuration properties associated with STS-issued OpenID Connect tokens for both REST and SOAP STS instances. The properties fall into two categories:
Properties that determine content in the issued OpenID Connect ID token. For information about OpenID Connect ID tokens, see the OpenID Connect Core 1.0 specification.
Properties that determine how the issued token is signed.
An STS instance configured to issue OpenID Connect tokens models the
relationship between an OpenID Connect token provider and relying party. In
other words, an STS instance issues tokens for a particular OAuth 2.0
client. The tokens contain aud and azp
claims for the OAuth 2.0 client, and signing key state corresponding to a
token provider.
In this model, when users call an STS instance to generate an OpenID Connect ID token, the process is analogous to the exchange between an OAuth 2.0 authorization server and resource owner following the initial redirection from an OAuth 2.0 client initiating the implicit flow. The STS instance returns the OpenID Connect ID token that corresponds to the authorization server's authentication of the resource owner. OpenAM authenticates one of the following:
For REST STS, the token specified as the
input_token_statefor the token transformationFor SOAP STS, the supporting token necessary to traverse the SecurityPolicy bindings protecting the WS-Trust operation
Implicit in this model is the notion that an OpenID Connect ID token has value outside of an OAuth 2.0 flow, and that an OAuth 2.0 client, as a relying party, could be generalized as a SAML v2.0 service provider. The ID token is not simply an an entity-provided verifiable authorized access to a specific resource set, but rather a generic service provider that consumes an OpenID Connect ID token to authenticate and authorize the subject asserted by the token.
Therefore, the configuration of an STS instance that issues OpenID Connect ID tokens contains information that defines the token provider and relying party.
Note that the nonce claim in the ID token is not a
configuration property of an STS instance. STS consumers requesting an output
OpenID Connect token provide a nonce value when making
token transformation requests.
- The id of the OpenIdConnect Token Provider
Specifies the OpenID Connect token provider issuer ID. Populates the
issclaim of the ID token.- Token Lifetime
Specifies, in seconds, the ID token's expiration. Populates the
expclaim of the ID token.- Token signature algorithm
Specifies an HMAC or RSA algorithm used to sign ID tokens.
- Public key reference type
Specifies how public keys should be referenced in issued ID tokens signed with RSA. OpenID Connect ID tokens are issued as JSON web tokens (JWTs). Tokens can reference RSA public keys as JSON web keys (JWKs), or not at all.
Used with RSA signing.
- KeyStore Location
Specifies the path to the Java keystore used for signing the ID token. Specify an absolute path or a location in the OpenAM classpath.
Used with RSA signing.
OpenAM provides two keystores with test keys that are located at the
/path/to/openam/openam/path. For more information about the OpenAM keystores, see "Managing Certificates and Keystores".- KeyStore password
Specifies the password of the keystore used for signing the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- KeyStore signing key alias
Specifies the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- Signature key password
Specifies the password of the alias corresponding to the private key used to sign the ID token.
Used with RSA signing.
- Client secret
Specifies the secret shared between the client and the ID token generator used to sign the ID token.
Used with HMAC signing.
- The audience for issued tokens
Specifies the intended audience for the ID token. Populates the
audclaim of the ID token.- The authorized party
Specifies the party to which the ID token is being issued. Populates the
azpclaim of the ID token.- Claim map
Specifies additional claim entries to be inserted into the ID token.
Specifies entries using the format
claim_name=user_profile_attribute. When issuing the ID token, OpenAM populates the claim value with the value of the attribute in the authenticated user's profile.For example, suppose the Claim map property had an entry with the value
email=mail. A generated OpenID Connect ID token for user Sam Carter would contain the claim"email":"scarter@example.com"if themailattribute in Sam Carter's user profile had the valuescarter@example.com.- Custom claim mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom claim mapper class. A claim mapper generates additional claims to be included in the OpenID Connect ID token.
The class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.tokengeneration.oidc.OpenIdConntectTokenClaimMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.- Custom authn context mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
acrclaim in the OpenID Connect ID token. Anacrclaim indicates which authentication context class was satisfied by the authentication of the principal asserted in the OpenID Connect ID token. Theacrclaim is optional and is not included in the generated ID token by default.For REST STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.rest.token.provider.oidc.OpenIdConnectTokenAuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.For SOAP STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.soap.token.provider.oidc.SoapOpenIdConnectTokenAuthnContextMapperinterface and must be bundled into the SOAP STS deployment.warfile.- Custom authn methods references mapper class
Specifies the name of a custom class that generates an
amrclaim in the OpenID Connect ID token. Anamrclaim indicates which authentication methods were used to authenticate the principal asserted in the OpenID Connect ID token. Theamrclaim is optional and is not included in the generated ID token by default.For REST STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.rest.token.provider.oidc.OpenIdConnectTokenAuthMethodReferencesMapperinterface and must be bundled in the OpenAM.warfile.For SOAP STS instances, the class must implement the
org.forgerock.openam.sts.soap.token.provider.oidc.SoapOpenIdConnectTokenAuthnMethodReferencesMapperinterface and must be bundled into the SOAP STS deployment.warfile.
This section describes the process for deploying SOAP STS instances. To
deploy a SOAP STS instance, you create an agent that the SOAP STS deployment
uses to authenticate to OpenAM, then configure the instance, prepare a
deployment directory, run a wizard to package the instance into a
.war file, and deploy the .war file
into a web container.
When multiple SOAP STS instances are configured in the same realm, the SOAP
STS deployment created by the wizard supports all of the realm's SOAP STS
instances. Their configurations are packaged together into a
single .war file, and they use the same agent to
authenticate to OpenAM.
SOAP STS deployments must run in a separate web container from OpenAM. They access OpenAM to perform the following tasks:
To obtain the configuration of SOAP STS instances published in the SOAP STS deployment realm
To authenticate supporting tokens specified in security policy bindings
To request token creation
To request token cancellation
In order to access OpenAM to perform these tasks, SOAP STS deployments need an identity that they can use to authenticate to OpenAM before they can request OpenAM services.
SOAP STS deployments use an agent identity to authenticate to OpenAM. Note that even if you have multiple SOAP STS instances in a deployment, you need only a single agent identity for the entire deployment, and not one agent identity per SOAP STS instance.
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > SOAP STS Agent.
Click New to create a new agent.
Specify an agent name and password.
Specify the Poll Interval.
The Poll Interval property soecifies how often the SOAP STS deployment contacts OpenAM to obtain changes to the configuration of SOAP STS instances published in the SOAP STS deployment. Polling OpenAM enables the SOAP STS deployment to detect configuration changes to SOAP STS instances, deletion of SOAP STS instances in the deployment, and the addition of new SOAP STS instances to the deployment.
Click Create.
In a subsequent step in the deployment process, you run the Create a Soap STS Deployment wizard. The wizard prompts you to provide the SOAP STS agent name and password, and then configures the SOAP STS deployment to use the agent identity to authenticate to OpenAM.
To configure a new SOAP STS instance using the OpenAM console, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances, and then click Add.
See "SOAP STS Configuration Properties" for detailed information about STS configuration properties.
You can also configure a SOAP STS instance programmatically. See "Publishing SOAP STS Instances" in the Developer's Guide for more information.
Before you can run the Create a SOAP STS Deployment wizard, which creates
a .war file for the SOAP STS instance, you must prepare a
directory with content that the wizard uses as input.
Prepare the deployment directory as follows:
Create a subdirectory in the OpenAM installation directory named
soapstsdeployment:$ cd /path/to/openam $ mkdir soapstsdeployment
Create the SOAP STS server
.warfile and copy it to the deployment directory:If you have not already done so, download the git repository containing the OpenAM source code.
You can find information about downloading and compiling the OpenAM source code on the forgerock.org website. The website also lists prerequisites for compiling the source code. Make sure that your system meets these prerequisites before proceeding.
Check out the tag in the source code repository for this release of OpenAM.
Build the SOAP STS server
.warfile:$ cd /path/to/openam-source $ cd openam-sts/openam-soap-sts/openam-soap-sts-server $ mvn install
Copy the SOAP STS server
.warfile to the deployment directory:$ cd target $ cp openam-soap-sts-server-13.5.2.war /path/to/openam/soapstsdeployment
Copy all keystores specified in all SOAP STS instance configurations in the realm to the
/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory. Keystores are configured in the following fields under Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances > Instance Name:Soap Keystore Location (in the Soap Keystore Configuration section)
KeystorePath (in the Issued SAML2 Token Configuration section)
KeystoreLocation (in the OpenIdConnect Token Configuration section)
If you specified custom WSDL files in the SOAP STS instance configuration for one or more SOAP STS instances in the realm, copy all of the custom WSDL files to the
/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory. Custom WSDL files are specified under Custom wsdl File.For more information about custom WDSL files in a SOAP STS deployment, see "Customizing the WSDL File".
After you have prepared the deployment directory, you are ready to run the
wizard that creates a SOAP STS deployment .war file.
Run the wizard as follows:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard, where Realm Name is the realm in which you configured one or more SOAP STS instances.
Click Create a Soap STS Deployment.
The Common Tasks > Create a Soap STS Deployment page appears.
Click Create a Soap STS Deployment again.
The Configure a Soap STS Deployment page appears.
Specify values in the Configure a Soap STS Deployment page as follows:
- Realm of Soap STS Deployment
The realm in which you have configured one or more SOAP STS instances.
- OpenAM URL
OpenAM's deployment URL. For example,
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam.- SOAP STS Agent Name, SOAP STS Agent Password
The agent name and password that you defined when you created the SOAP STS agent. Creating the SOAP STS agent is described in "Creating a SOAP STS Agent".
- Custom wsdl file names
The file names of all custom WSDL files that are defined in the SOAP STS instance configurations in the realm. All the files that you specify in this field should have been copied to the
/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory when you prepared the deployment directory.- KeyStore file names
The file names of all keystores that are defined in the SOAP STS instance configurations in the realm. All the files that you specify in this field should have been copied to the
/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory when you prepared the deployment directory.
Click Create.
If the wizard runs successfully, a message appears letting you know that OpenAM successfully created a SOAP STS deployment
.warfile nameddeployable-soap-sts-server_timestamp.war. in the/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory.If the wizard does not run successfully, correct the error and rerun the wizard.
You can extend the default capabilities of a SOAP STS deployment with the following types of customized classes:
Token delegation handlers that validate credentials set in
ActAsandOnBehalfOfelements of request security tokens.Customized token delegation handlers are configured under Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances > Instance Name > Deployment > Custom Delegation Handlers.
Classes that override the default
AuthnContextstrings included in generated SAML v2.0 assertions.These classes are configured under Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances > Instance Name > Issued SAML2 Token Configuration > Custom Authentication Context Class Name.
Classes that provide
acrclaims in generated OpenID Connect tokens.These classes are configured under Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances > Instance Name > OpenIdConnect Token Configuration > Custom authn context mapper class.
Classes that provide
amrclaims in generated OpenID Connect tokens.These classes are configured under Realms > Realm Name > STS > SOAP STS Instances > Instance Name > OpenIdConnect Token Configuration > Custom authn methods references mapper class.
To include any of the preceding customizations in a SOAP STS deployment,
bundle the customized classes into the SOAP STS deployment
.war file under
deployment-context/WEB-INF/classes.
After you run the Create a Soap STS Deployment wizard, you deploy the
SOAP STS .war file created by the wizard to a web
container.
Deploy the .war file as follows:
OpenAM supports the following web containers for SOAP STS deployments:
Apache Tomcat 6, 7, or 8
Jetty 7, 8, or 9
Install an instance of one of these web containers for the SOAP STS deployment, making sure the port numbers you specify in the web container's configuration do not conflict with any active ports on the host on which you will run the web container.
Copy the SOAP STS deployment
.warfile from the/path/to/openam/soapstsdeploymentdirectory to the/path/to/soap-sts-web-container/webappsdirectory, renaming the file to eliminate colons in the file name. For example:$ cd /path/to/openam/soapstsdeployment $ cp deployable-soap-sts-server_timestamp.war mySOAPSTSDeployment.war $ cp mySOAPSTSDeployment.war /path/to/soap-sts-web-container/webapps
Simplifying the
.warfile name eliminates web container startup errors that occur when the file name contains certain characters.Start the SOAP STS deployment web container.
Review the web container's log file for errors. If errors are detected, correct the errors and restart the web container.
If you want to verify that the SOAP STS agent successfully connects to OpenAM, enable message-level debug logging on OpenAM, and then restart the SOAP STS deployment web container. For details about how to enable message-level debug logging, see "Debug Logging".
Review the
Sessiondebug log. You should see entries in the log that demonstrate that the SOAP STS agent successfully authenticated to OpenAM, and that the agent has a session with OpenAM.When you have finished verification, remember to turn off message-level debugging.
You can publish SOAP STS instances that reference a custom WSDL file.
The custom WSDL can also contains a user-entered port and service
QNames (qualified names), which reference the to-be-exposed
port and service defined in the WSDL file. You can customize the WSDL
files, which must be diffs of the existing WSDL files defined in
openam-sts/openam-soap-sts/openam-soap-sts-server/src/main/resources.
The following two customizations are supported:
You can copy the
Bindingelement in the specification of one WSDL file into another, so that a SOAP STS instance can be published and protected by two policy bindings. In other words, theExactlyOneelement of a given policy can have two binding definitions, so that the satisfaction of either will allow access to the SOAP STS.You can customize the
Policybindings governing the input or output messages to or from the SOAP STS instance.Note
The existing set of security policy bindings specified in the pre-configured WSDL files are taken from Apache CXF-sanctioned definitions, and thus are correctly realized by Apache CXF/WSS4J. Any deviations from the standard definitions specified in the WSDL files in the OpenAM code base at
openam-sts/openam-soap-sts/openam-soap-sts-server/src/main/resourcesother than those specified above will not be supported.
Assume that you have the following WSDL definition:
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="signed_body_input_policy">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<sp:SignedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:SignedParts>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="signed_body_output_policy">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<sp:SignedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:SignedParts>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>Then, you can make the following changes:
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="signed_body_input_policy">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<sp:SignedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:SignedParts>
<sp:EncryptedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:EncryptedParts>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="signed_body_output_policy">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<sp:SignedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:SignedParts>
<sp:EncryptedParts>
<sp:Body/>
</sp:EncryptedParts>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>
OpenAM SOAP STS logs to the Simple Logging Facade for Java (SLF4J) API.
Because the Apache CXF framework, by default, logs to the java.util.logging
object, the OpenAM SOAP STS is built with a maven dependency upon
slf4j-jdk14, which allows OpenAM SOAP STS log entries
to be configured via java.util.logging.
As a result, you can implement both OpenAM SOAP STS and Apache CXF logging
to be configured via the logging.properties file in the
Tomcat conf directory.
You can configure and customize Apache CXF-related logging according to directions given at the following web site: http://cxf.apache.org/docs/debugging-and-logging.html
Note
Because the OpenAM SOAP STS code logs to the SLF4J API, the manner in which
these logs are realized is a function of the jar file state bundled in the
OpenAM SOAP STS server .war file.
If you implement the OpenAM SOAP STS logs using a different framework,
you can replace the slf4j-jdk14 Maven dependency in the
OpenAM SOAP STS server pom.xml file by the desired dependency
and rebuild the .war file. Or you can change the generated
OpenAM SOAP STS server .war file
to include the desired .jar file, which will realize the
SLF4J API with the desired logging framework.
Also, note that the debugfiles.properties included in the
OpenAM SOAP STS server .war
file does not configure logging. It is present only because some OpenAM code
leveraged by the SOAP STS continues to have dependencies upon the legacy,
OpenAM debug logger. The presence of this file minimizes the number of
harmless error logs generated by the initialization of this legacy debug
logger. OpenAM SOAP STS does not utilize this logger.
This chapter shows how to configure the OpenAM Dashboard service.
The Dashboard Service provides the end user with an interface to access applications secured by OpenAM, both cloud-based applications like SalesForce and internal applications protected by policy agents. The Dashboard Service uses SSO to login to the applications when the user clicks on the application icon. For some apps, like SalesForce, you will want to limit access to only a few users. Other apps, like Google Mail or Drive, you will probably want to make available to all users.
The Dashboard Service is meant to give users a single place to access their applications. Keep in mind that this does not limit user access, only what appears on the user dashboard.
There are three stages to setting up the Dashboard Service:
Setup the Dashboard Service and add applications.
Add the service to the realms.
Assign users applications so that they appear on the users' dashboards. This can be done manually or through a provisioning solution.
User dashboard pages require the XUI, which is enabled by default in OpenAM. To verify that XUI is enabled, log in to the OpenAM console as administrator and navigate to Configure > Authentication, click Core Attributes, and then enable XUI Interface.
Once the Dashboard Service is configured for a user,
the user can access their dashboard after logging in through the XUI
under /XUI/#dashboard/.
For example, the full URL depending on the deployment might be
at https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/#dashboard/.
Making some applications universally available ensures that all users have the same basic applications. However, some of your applications should be protected from the majority of your users. You will need to single out which users will include the application on their dashboard.
There are three default applications in the Dashboard Service: Google, SalesForce, and ZenDesk.
You can add applications to the Dashboard Service with the following steps. All fields except the dashboard class name and ICF Identifier are required for the application to work properly from the dashboard:
Log in to the OpenAM console as OpenAM Administrator,
amadmin.Navigate to Configure > Global Services, click Dashboard, and then click New to add a new application to the Dashboard Service and to provide the information needed to connect to the app.
Provide a unique name for the application.
Add a Dashboard Class Name that identifies how the end user will access the app, such as
SAML2ApplicationClassfor a SAML v2.0 application.Add a Dashboard Name for the application.
Add a Dashboard Display Name. This name is what the end user will see, such as Google.
Add the Dashboard Icon you would like the end user to see for the application. Either use a fully-qualified URL or an appropriate relative URL so that the icon is rendered properly on the user dashboard.
Add the Dashboard Login URL to point to the location the end user will go to once they click on the icon.
Leave the ICF Identifier blank.
Click Add when you are done.
You must add the Dashboard Service to a realm before it will be available. The following instructions show you how to add an application to a single realm. Before you begin, make sure you have the name of the application as it appears on the Secondary Configuration Instance table under Configure > Global Services > Dashboard:
Select Realms > Realm Name > Services, and then click Add a Service.
Select the Dashboard service, and then click Create.
Add or remove the applications you would like to appear on the Dashboard service for the realm.
Click Save Changes when you are done.
You may need to remove an application from user's dashboard, but you do not want to entirely delete the user. The following steps walk you through removing an application from a user's dashboard:
Select Realms > Realm Name > Subjects and click the user identifier to edit the user's profile.
Under Services, click Dashboard.
Delete the application beside the user name under the user's Assigned Dashboard list.
Click Save.
This chapter describes how to configure OpenAM as a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server that can accept authentication requests from RADIUS clients.
RADIUS is a lightweight, datagram-based protocol formally specified in RFC 2865 that is supported by many devices and servers for external authentication. VPN concentrators, routers, switches, wireless access points, and many other devices have native RADIUS support. Such devices are known as RADIUS clients. Using the RADIUS protocol, they converse with RADIUS servers to authenticate entities, such as users attempting to access their resources.
The RADIUS protocol itself is quite simple. There are four packet types:
Access-Requestpackets are sent from a client to a server to begin a new authentication conversation, or to respond to a previous response in an existing conversation and provide requested information.Access-Acceptpackets are sent from a server to a client to indicate a successful authentication.Access-Rejectpackets are sent from a server to a client to indicate a failed authentication.Access-Challengepackets are sent from a server to a client to solicit more information from the entity being authenticated.
Each packet type defines:
A set of fields that must be included
Other fields that can be included to convey:
Additional requirements
Information about the context of the conversation
Attributes of the entity after successful authentication
For example, an Access-Request
packet should always contain user name and password fields, and it can
contain other fields that provide information about the client making the
request. For example, inclusion of the optional State
field indicates that a packet is part of an authentication conversation
already in progress. Its absence indicates the start of a new conversation.
An authentication conversation always begins with an
Access-Request packet that does not have a
State field. If the RADIUS server only requires the user
name and password for authentication, then conversations will complete after
the server sends an Access-Accept or
Access-Reject packet, depending on whether the
authentication credentials were valid. However, if more information is
required by the server, such as an SMS-relayed one-time password sent to the
user's phone, the additional requirement can be solicited using an
Access-Challenge response to the client, followed by an
Access-Request packet that has a State
field that associates it with the existing conversation. The conversation
completes with an Access-Accept or
Access-Reject packet depending on whether the one-time
password supplied in the second request matches the password sent to the
user's phone.
This conversational style in which the server accepts, rejects, or solicits more information makes RADIUS an excellent match for leveraging OpenAM's authentication infrastructure. OpenAM performs authentication using chains of authentication modules found in realms. These modules identify authentication requirements that are conveyed to clients wishing to authenticate. The modules then accept values submitted by the user for verification. The mechanism for modules to convey these requirements to OpenAM is through a finite set of constructs known as callbacks. By leveraging OpenAM's flexible and extensible authentication mechanism, organizations can craft an authentication experience suitable for their needs, while using the same mechanisms for both HTTP and RADIUS authentication.
Two OpenAM features support the RADIUS protocol: the RADIUS authentication module and the RADIUS Server service.
The RADIUS authentication module enables OpenAM to act as a RADIUS client, delegating authentication to an external RADIUS server:
Use the RADIUS authentication module when you want OpenAM to pass user names and passwords through to an external RADIUS server so that the RADIUS server can authenticate the users.
For information about configuring the RADIUS authentication module, see "Hints for the RADIUS Authentication Module".
The RADIUS Server service provides a RADIUS server within OpenAM. The server authenticates RADIUS clients that are external to OpenAM. The server is backed by OpenAM's authentication chains and modules, thereby providing the possibility of multi-factor authentication in addition to simple user name and password authentication.
The following example shows the flow of a successful simple user name and password authentication attempt from a RADIUS client:
The following example shows the flow of a successful multi-factor authentication scenario in which the RADIUS Server service is backed by an authentication chain that includes the LDAP and the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) authentication modules. First, the LDAP authentication module requires the user to provide a user name and password. Then the ForgeRock Authenticator (OATH) module requires the user to enter a one-time password obtained from the authenticator app on a mobile phone:
The rest of this chapter covers the configuration of the RADIUS Server service in an OpenAM deployment.
The OpenAM RADIUS server is disabled by default. To enable it, perform the following steps:
Login to the OpenAM console as the top-level administrative user, such as
amadmin.Navigate to Configure > Global Services, and then click RADIUS Server.
Under Secondary Configuration Instance, click New.
OpenAM uses secondary configuration instances in the RADIUS Server service to encapsulate RADIUS clients. You must configure one secondary configuration instance, also known as a subconfiguration, for each client that will connect to the RADIUS Server.
Configure attributes for the subconfiguration. See "RADIUS Server" in the Reference for information about configuring the subconfiguration attributes.
Click Add to add the configuration for the RADIUS client to the overall RADIUS Server service's configuration.
If you have multiple RADIUS clients that will connect to the OpenAM RADIUS server, add a subconfiguration for each client. It is not necessary to configure all your RADIUS clients when you configure the RADIUS Server service initially—you can add and remove clients over time as you need them.
Configure global attributes of the RADIUS Server service. At a minimum, set the Enabled field to
YESto start the RADIUS server immediately after you save the RADIUS Server service configuration.See "RADIUS Server" in the Reference for information about configuring the RADIUS Server service's global attributes.
On the main configuration page for the RADIUS Server service, click Save.
The RADIUS server starts immediately after you save the configuration if the
Enabled field has the value YES. Any time you make changes
to the RADIUS Server service configuration, they take effect as soon as you
save the changes.
This section covers how to configure OpenAM to troubleshoot the RADIUS Server service, describes how to run a sample client included with OpenAM, and provides details about some specific issues that you might run into when using the RADIUS Server service.
If you need to troubleshoot the RADIUS Server service, enable message-level debugging in OpenAM. For information about enabling OpenAM debug logging, see "Debug Logging".
With message-level debug logging enabled, OpenAM writes messages to the
Radius debug log file when notable events occur,
including the following:
RADIUS server startup
Changes to the RADIUS server configuration
Successful and unsuccessful client connections
Various error events
You can also configure the RADIUS Server service to log the packets sent between RADIUS clients and OpenAM. To enable packet logging, use the Log Packet Contents for this Client property when configuring RADIUS clients in the RADIUS Server service.
The openam-radius-server-13.5.2-15.jar
includes a sample client that you can use to test simple connectivity to
the RADIUS Server service.
The following procedure describes how to set up and run the sample client:
Configure the RADIUS Server service. Be sure to enable the service. Include a secondary configuration instance for the sample client as part of the service configuration.
For more information on the RADIUS Server service configuration properties, see "RADIUS Server" in the Reference.
Create a file named
radius.propertiesin the current working directory. The file consists of the following key-value pairs:secret- Mandatory property specifying the RADIUS client's shared secret. This property's value must be identical to the value of the Client Secret property for the RADIUS client in the OpenAM RADIUS Server service configuration.host- Mandatory property specifying the host name or IP address of the OpenAM server.port- Mandatory property specifying the port number on which OpenAM's RADIUS server listens. This property's value must be identical to the Listener Port property in the OpenAM RADIUS Server service configuration.show-traffic- Optional property specifying whether to show traffic packet during client operation. Valid values aretrueandfalse. Packet traffic is not shown if this property is not specified.
The following is an example
radius.propertiesfile:secret=cangetin host=openam.example.com port=1812 show-traffic=true
Make sure that your current working directory is the directory in which you created the
radius.propertiesfile, then execute the sample client. Messages from the sample client indicate success or failure authenticating. If you specifyshow-traffic=truein theradius.propertiesfile, the packets to and from the OpenAM RADIUS server appear in standard output:$ java -jar //path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-radius-server-13.5.2-15.jar ? Username: demo ? Password: changeit Packet To openam.example.com:1812 ACCESS_REQUEST [1] - USER_NAME : demo - USER_PASSWORD : ******* - NAS_IP_ADDRESS : openam.example.com/192.168.10.10 - NAS_PORT : 0 Packet From openam.example.com:1812 ACCESS_ACCEPT [1] ---> SUCCESS! You've Authenticated!
This section offers solutions to issues that you might encounter when configuring communication between RADIUS clients and the RADIUS Server service. The solutions assume that you have enabled message-level debugging for the RADIUS Server service in OpenAM and have access to the debug logs.
- Client Cannot Connect
When a RADIUS client connects to OpenAM's RADIUS server and hangs without receiving a response, the problem could be one of four possible issues:
The OpenAM RADIUS Server service is not enabled.
An entry similar to the following in the
Radiusdebug log indicates that OpenAM's RADIUS Server was started:amRadiusServer:10/12/2015 12:00:14:814 PM PDT: Thread[RADIUS-1812-Listener,5,main]: TransactionId[27350419-8c21-429e-b580-35abf64604cf] RADIUS Listener is Active. Port : 1812 Threads Core : 2 Threads Max : 10 Thread Keep-alive : 10 sec Request Queue : 10
If no such entry exists in the debug log, re-examine the configuration for the RADIUS Server service and correct the problem.
The client is not defined.
An entry similar to the following in the
Radiusdebug log indicates the inability of a client to connect:amRadiusServer:10/12/2015 04:05:53:681 PM PDT: Thread[RADIUS-1812-Listener,5,main]: TransactionId[270084d5-b7d0-42e4-8709-eeaeaf435aff] WARNING: No Defined RADIUS Client matches IP address /192.168.10.10. Dropping request.
To fix the problem, correct the client configuration in the RADIUS Server service.
The handler class for the client is incorrect.
An entry similar to the following in the
Radiusdebug log indicates an incorrect handler class:ERROR: Configuration setting handlerClass in RADIUS Client configuration named 'TestClient' is invalid. Requests from this client will be ignored.
To fix the problem, correct the client configuration in the RADIUS Server service.
Traffic is not arriving at the OpenAM server.
No specific debug log entries appear for this problem.
This is likely a network communication problem. Investigate the route for traffic between the RADIUS client and the OpenAM RADIUS server to see where communication is lost.
- Authentication Always Fails
When authentication always fails, the probable cause is one of the following three issues:
The client secret configured for the client in the RADIUS Server service is incorrect.
In an
Access-Requestpacket, the shared secret is used along with the random value sent in the request authenticator field to encrypt the password field value that is passed across the wire. If the client and server's shared secrets are not identical, the password expected by the server will not match the password sent by the client, resulting in authentication always failing. The user's password is always incorrect in such a scenario and there is no way for the server to differentiate between the client secret being incorrect and the password sent from the client being incorrect. The log file indicates that OpenAM has sent anAccess-Rejectpacket to the client, similar to the action that would be taken if the shared secret matched on the client and server and the user entered an invalid password:amRadiusServer:10/12/2015 04:27:55:785 PM PDT: Thread[RADIUS-1812-Listener,5,main]: TransactionId[270084d5-b7d0-42e4-8709-eeaeaf435aff] finalPacketType sent in response to auth request: 'ACCESS_REJECT'
Since the shared secret is specific to each client, such messages might appear for one RADIUS client, while other clients can authenticate successfully.
To fix this problem, correct the configuration for your client in the RADIUS Server service.
The realm configured for the client in the RADIUS Server service is incorrect.
An entry similar to the following in the
Radiusdebug log indicates an invalid realm in the RADIUS Server service configuration:ERROR: Unable to start login process. Denying Access. com.sun.identity.authentication.spi.AuthLoginException: Domain is invalid| invalid_domain.jsp
If the realm is missing from the configuration, an error similar to the following appears:
ERROR: Unable to initialize declared handler class 'org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.OpenAMAuthHandler' for RADIUS client ''. Rejecting access. java.lang.IllegalStateException: Configuration property 'realm' not found in handler configuration. It must be added to the Configuration Properties for this class in the Radius Client's configuration.
To fix this problem, correct the client configuration in the RADIUS Server service.
The authentication chain configured for the client in the RADIUS Server service is incorrect.
An entry similar to the following in the
Radiusdebug log indicates an invalid authentication chain in the RADIUS Server service configuration:amRadiusServer:10/12/2015 05:32:21:771 PM PDT: Thread[pool-5-thread-2,5,main]: TransactionId[378a41cf-0581-4b62-a92f-be2b008ab4d3] ERROR: Unable to start login process. Denying Access.
If the chain is missing from the configuration, an error similar to the following appears:
ERROR: Unable to initialize declared handler class 'org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.OpenAMAuthHandler' for RADIUS client ''. Rejecting access. java.lang.IllegalStateException: Configuration property 'chain' not found in handler configuration. It must be added to the Configuration Properties for this class in the Radius Client's configuration.
To fix this problem, correct the client configuration in the RADIUS Server service.
- Configuration Is Correct but Authentication Fails
In this case, you might have a client-specific problem. OpenAM provides a tool that you can use to eliminate OpenAM and its configuration as the cause of the problem. You can declare an alternate handler class implementation in the RADIUS Server service configuration. Two test handlers are available for troubleshooting purposes:
The
org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.AcceptAllHandlerhandler always returns anAccess-Acceptpacket, indicating successful authentication for all requests.The
org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.RejectAllHandlerhandler always returns anAccess-Rejectpacket, indicating failed authentication for all requests.
In a case where you believe that configuration is correct but authentication always fails, you could specify the
org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.AcceptAllHandlerhandler class in the RADIUS Server service configuration for your client. With packet logging enabled, all requests received from the client should log packet contents traffic similar to the following even if the password is incorrect:WARNING: Packet from TestClient: ACCESS_REQUEST [1] - USER_NAME : demo - USER_PASSWORD : ******* - NAS_IP_ADDRESS : /127.0.0.1 - NAS_PORT : 0This is followed by:
WARNING: Packet to TestClient: ACCESS_ACCEPT [1]
If the client still indicates that authentication has failed, refer to the documentation for the client to determine why the
Access-Acceptresponse is rejected. Most likely, the client expects specific fields in theAccess-Acceptresponse that are not provided by OpenAM. There is currently no facility in OpenAM to return fields inAccess-Acceptresponses.- Authentication Always Succeeds, Even With a Bad Password
This would be a very unusual situation, probably due to the
org.forgerock.openam.radius.server.spi.handlers.AcceptAllHandlerhandler being left in place after troubleshooting an error scenario in which authentication always suceeds.To resolve the problem, verify that the correct handler class is specified in the RADIUS Server service configuration for the client. If it is not specified, review the authentication modules in the chain that authenticates users and determine whether one of the modules might be accepting all authentication requests. This situation could also occur because of incorrectly-specified module criteria in the chain's definition.
Deploying OpenAM's RADIUS server lets an organization consolidate RADIUS and HTTP authentication into a single solution, facilitating reuse of existing authentication mechanisms between both types of clients. However, there are several limitations:
Because RADIUS authentication attempts always start with a user name and password transmitted in an
Access-Requestpacket, the first module in an authentication chain used for RADIUS clients must accept a user name and a password.Some OpenAM callback types are not applicable to RADIUS clients. For example, a
RedirectCallbackdirects HTTP clients, such as browsers, to HTTP resources to be used for some aspect of authentication. Redirects make no sense to RADIUS clients and cannot be consumed in any meaningful way.A
ConfirmationCallbackalso presents challenges for RADIUS clients.As a result, some OpenAM authentication modules cannot be used with RADIUS clients. Before attempting to use an authentication module with RADIUS clients, review the module's callbacks to determine whether the module will support RADIUS clients. You can use the REST API to determine the callbacks for an authentication module as described in "Authentication and Logout" in the Developer's Guide.
Some client mechanisms leveraged by authentication modules might not be applicable to RADIUS clients. For example, suppose a customized SMS one-time password module sends a one-time password over an SMS service, and then provides a
ChoiceCallbackthat enables the user to set a cookie in their browser that expires after 30 days. Such a module might first determine whether the cookie was available, still valid, and applicable to the current user before reissuing a new one-time and soliciting the value from the user.RADIUS clients are unable to process HTTP cookies. Therefore, although RADIUS clients can support a
ChoiceCallback, the customized feature described in the previous paragraph would not function correctly for RADIUS clients and therefore should not be deployed with RADIUS clients. As a result, some callback sets within an authentication module will differ depending on the type of client being authenticated.The RADIUS Server service logs only to the ForgeRock common audit logger introduced in OpenAM 13. It does not log to the classic OpenAM audit logs that were available prior to OpenAM 13.
When building custom authentication modules, consider their suitability to handle the types of clients that might use them, and make adjustments to callbacks as needed.
You can configure the default behavior OpenAM will take when a REST call does not specify explicit version information using either of the following procedures:
The available options for default behavior are as follows:
- Latest
The latest available supported version of the API is used.
This is the preset default for new installations of OpenAM.
- Oldest
The oldest available supported version of the API is used.
This is the preset default for upgraded OpenAM instances.
Note
The oldest supported version may not be the first that was released, as APIs versions become deprecated or unsupported. See "Deprecated Functionality" in the Release Notes.
- None
No version will be used. When a REST client application calls a REST API without specifying the version, OpenAM returns an error and the request fails.
Log in as OpenAM administrator,
amadmin.Click Configure > Global Services, and then click REST APIs.
In Default Version, select the required response to a REST API request that does not specify an explicit version:
Latest,Oldest, orNone.(Optional) Optionally, enable
Warning Headerto include warning messages in the headers of responses to requests.Save your work.
Use the
ssoadm set-attr-defscommand with theopenam-rest-apis-default-versionattribute set to eitherLATEST,OLDESTorNONE, as in the following example:$ ssh openam.example.com $ cd /path/to/openam-tools/admin/openam/bin $ ./ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --servicename RestApisService \ --schematype Global \ --attributevalues openam-rest-apis-default-version=NONE Schema attribute defaults were set.
OpenAM stores configuration data in an LDAP directory server and in files. The directory service replicates configuration data between directory servers, allowing OpenAM to share configuration data across servers in a site. During normal production operations, you rely on directory replication to maintain multiple, current copies of OpenAM service configuration. To recover from the loss of a server or from a serious administrative error, back up directory data and configuration files.
This chapter shows how to backup and restore OpenAM configuration data by backing up and restoring local configuration files and local (embedded) configuration directory server data. If your deployment uses an external configuration directory server, then refer to the documentation for your external directory server or work with your directory server administrator to back up and restore configuration data stored in the external directory service.
For OpenDJ directory server you can find more information in the chapter on Backing Up and Restoring Data.
This chapter aims to cover the following uses of backup data.
Recovery from server failure:
Recovery from serious administrative error:
This procedure backs up all the configuration data stored with the server. This backup is to be restored when rebuilding a failed server.
Have the following points in mind when using this procedure:
Use this procedure only when OpenAM stores configuration data in the embedded OpenDJ directory server, which means that the embedded OpenDJ directory server files are co-located with other OpenAM configuration files.
If your deployment uses an external configuration directory server, then refer to the documentation for your external directory server or work with your directory server administrator to back up and restore configuration data stored in the external directory service. For OpenDJ directory server you can find more information in the chapter on Backing Up and Restoring Data.
Do not restore configuration data from a backup of a different release of OpenAM. The structure of the configuration data can change from release to release.
In OpenAM deployments where configuration directory data is replicated, you must take the following points into consideration:
Directory replication mechanically applies new changes to ensure that replicated data is the same everywhere. When you restore older backup data, directory replication applies newer changes to the older data.
This includes new changes that the administrator sees as mistakes. To recover from administrative error, you must work around this behavior either by performing a change to be replicated that repairs the error or by restoring all replicas to a state prior to the error.
When preparing directory server backup and restore operations, also know that data replication purge operations affect the useful lifetime of any data that you back up.
Replication relies on historical data to resolve any conflicts that arise. If directory servers did not eventually purge this historical data, the data would continue to grow until it filled all available space. Directory servers therefore purge older historical data. OpenDJ purges historical data older than 3 days by default.
When the directory server encounters a gap in historical data it cannot correctly complete replication operations. You must make sure, therefore, that any data you restore from backup is not older than the replication purge delay. Otherwise your restoration operation could break replication with the likely result that you must restore all servers from backup, losing any changes that occurred in the meantime.
For more information about purge delay, see the OpenDJ Administration Guide section on To Restore a Replica.
Follow these steps for each OpenAM server that you want to back up:
Stop OpenAM or the container in which it runs.
Back up OpenAM configuration files including those of the configuration directory server but skipping log and lock files.
The following example uses the default configuration location. $HOME is the home directory of the user who runs the web container where OpenAM is deployed, and OpenAM is deployed in Apache Tomcat under
openam:$ cd $HOME $ zip \ --recurse-paths \ /path/to/backup-`date -u +i5%F-%m-%S`.zip \ openam .openamcfg/AMConfig_path_to_tomcat_webapps_openam_ \ --exclude openam/openam/debug/* openam/openam/log/* openam/openam/stats* \ openam/opends/logs/* openam/opends/locks/* ... $ ls /path/to/backup-2014-12-01-12-00.zip /path/to/backup-2014-12-01-12-00.zip
The backup is valid until the end of the purge delay.
Start OpenAM or the container in which it runs.
This procedure applies when rebuilding a failed server.
Have the following points in mind when using this procedure:
This procedure restores all the configuration data for a server, where the configuration data has been backed up as described in "To Back Up All Server Configuration Data".
Use this procedure only when OpenAM stores configuration data in the embedded OpenDJ directory server, which means that the embedded OpenDJ directory server files are co-located with other OpenAM configuration files.
If your deployment uses an external configuration directory server, then refer to the documentation for your external directory server or work with your directory server administrator to back up and restore configuration data stored in the external directory service. For OpenDJ directory server, you can find more information in the chapter on Backing Up and Restoring Data.
Do not restore configuration data from a backup of a different release of OpenAM. The structure of the configuration data can change from release to release.
If OpenAM also stores CTS data in the embedded OpenDJ directory server, then the restore operation overwrites current CTS data with older data. After you restore from backup, users authenticate again as necessary.
If your deployment has long-lived sessions and you do not currently use session failover, you can limit the extent of reauthentication by implementing session failover. For details, see "Setting Up OpenAM Session Failover" in the Installation Guide.
In OpenAM deployments where configuration directory data is replicated, you must take the following points into consideration:
Directory replication mechanically applies new changes to ensure that replicated data is the same everywhere. When you restore older backup data, directory replication applies newer changes to the older data.
This includes new changes that the administrator sees as mistakes. To recover from administrative error, you must work around this behavior either by performing a change to be replicated that repairs the error or by restoring all replicas to a state prior to the error.
When preparing directory server backup and restore operations, also know that data replication purge operations affect the useful lifetime of any data that you back up.
Replication relies on historical data to resolve any conflicts that arise. If directory servers did not eventually purge this historical data, the data would continue to grow until it filled all available space. Directory servers therefore purge older historical data. OpenDJ purges historical data older than 3 days by default.
When the directory server encounters a gap in historical data it cannot correctly complete replication operations. You must make sure, therefore, that any data you restore from backup is not older than the replication purge delay. Otherwise your restoration operation could break replication with the likely result that you must restore all servers from backup, losing any changes that occurred in the meantime.
For more information about purge delay, see the OpenDJ Administration Guide section on To Restore a Replica.
Follow these steps for each OpenAM server to restore. If you are restoring OpenAM after a failure, make sure you make a copy of any configuration and log files that you need to investigate the problem before restoring OpenAM from backup:
Stop OpenAM or the container in which it runs.
Restore files in the configuration directory as necessary, making sure that you restore from a valid backup, one that is newer than the replication purge delay:
$ cd $HOME $ unzip /path/to/backup-2014-12-01-12-00.zip Archive: /path/to/backup-2014-12-01-12-00.zip replace openam/.configParam? [y]es, [n]o, [A]ll, [N]one, [r]ename: A ...
Start OpenAM or the container in which it runs.
LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF) is a standard, text-based format for storing LDAP directory data. You can use LDIF excerpts to make changes to directory data.
This procedure takes an LDIF backup of OpenAM configuration data only. Use this LDIF data when recovering from a serious configuration error:
Make sure that OpenAM's configuration is in correct working order before exporting configuration data.
Use the OpenDJ export-ldif command to run a task that exports only configuration data, not CTS data.
You can run this command without stopping OpenAM.
Find OpenDJ commands under the file system directory that contains OpenAM configuration files.
The bind password for Directory Manager is the same as the password for the OpenAM global administrator (amadmin):
$ $HOME/openam/opends/bin/export-ldif \ --port 4444 \ --hostname openam.example.com \ --bindDN "cn=Directory Manager" \ --bindPassword password \ --backendID userRoot \ --includeBranch dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org \ --excludeBranch ou=tokens,dc=openam,dc=forgerock,dc=org \ --ldifFile /path/to/backup-`date -u +%F-%m-%s`.ldif \ --start 0 \ --trustAll Export task 20141208113331302 scheduled to start Dec 8, 2014 11:33:31 AM CET
When the task completes, the LDIF file is at the expected location:
$ ls /path/to/*.ldif /path/to/backup-2014-12-08-12-1418034808.ldif
A serious configuration error is an error that you cannot easily repair by using OpenAM configuration tools, such as OpenAM console or the ssoadm command.
Use this procedure to recover from a serious configuration error by manually restoring configuration data to an earlier state. This procedure depends on LDIF data that you exported as described in "To Export Only Configuration Data".
Read the OpenDJ change log to determine the LDAP changes that caused the configuration problem.
The OpenDJ change log provides an external change log mechanism that allows you to read changes made to directory data for replicated directory servers.
For instructions on reading the change log, see the OpenDJ Administration Guide section on Change Notification For Your Applications.
Based on the data in the change log, determine what changes would reverse the configuration error.
For changes that resulted in one attribute value being replaced by another, you can recover the information from the change log alone.
For deleted content not contained in the change log, use the LDIF resulting from "To Export Only Configuration Data" to determine a prior, working state of the configuration entry before the configuration error.
Prepare LDIF to modify configuration data in a way that repairs the error by restoring the state of directory entries before the administrative error.
Use the OpenDJ ldapmodify command to apply the modification.
For instructions on making changes to directory data see the section on Updating the Directory in the OpenDJ Directory Server Developer's Guide.
This chapter shows you how to manage scripts used for client-side and server-side scripted authentication, custom policy conditions, and handling OpenID Connect claims using the OpenAM console and the ssoadm command.
For information on managing scripts by using the OpenAM REST API, see "RESTful Script Management" in the Developer's Guide. For information on configuring Scripting Service settings, see "Scripting" in the Reference.
The following procedures describe how to create, modify, and delete scripts using the OpenAM console:
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Scripts.
Click New Script.
The New Script page appears:
Specify a name for the script.
Select the type of script from the Script Type drop-down list.
Click Create.
The Script Name page appears:
Enter values on the Script Name page as follows:
Enter a description of the script.
Choose the script language, either JavaScript or Groovy. Note that not every script type supports both languages.
Enter the source code in the Script field.
On supported browsers, you can click Upload, navigate to the script file, and then click Open to upload the contents to the Script field.
Click Validate to check for compilation errors in the script.
Correct any compilation errors, and revalidate the script until all errors have been fixed.
Save your changes.
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Scripts.
Select the script you want to modify from the list of scripts.
The Script Name page appears.
Modify values on the Script Name page as needed. Note that if you change the Script Type, existing code in the script is replaced.
If you modified the code in the script, click Validate to check for compilation errors.
Correct any compilation errors, and revalidate the script until all errors have been fixed.
Save your changes.
Log in to the console as an OpenAM administrator, for example,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Scripts.
Choose one or more scripts to delete by activating the checkboxes in the relevant rows. Note that you can only delete user-created scripts—you cannot delete the global sample scripts provided with OpenAM.
Click Delete.
Use the ssoadm command's create-sub-cfg, get-sub-cfg, and delete-sub-cfg subcommands to manage OpenAM scripts.
Create an OpenAM script as follows:
Create a script configuration file as follows:
script-file=/path/to/script-file language=JAVASCRIPT|GROOVY name=myScript context=AUTHENTICATION_SERVER_SIDE|AUTHENTICATION_CLIENT_SIDE|POLICY_CONDITION|OIDC_CLAIMS
Run the ssoadm create-sub-cfg command. The
--datafileargument references the script configuration file you created in the previous step:$ ssoadm \ create-sub-cfg \ --realm /myRealm \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --servicename ScriptingService \ --subconfigname scriptConfigurations/scriptConfiguration \ --subconfigid myScript \ --datafile /path/to/myScriptConfigurationFile Sub Configuration scriptConfigurations/scriptConfiguration was added to realm /myRealm
To list the properties of a script, run the ssoadm get-sub-cfg command:
$ ssoadm \ get-sub-cfg \ --realm /myRealm \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --servicename ScriptingService \ --subconfigname scriptConfigurations/myScript createdBy= lastModifiedDate= lastModifiedBy= name=myScript context=POLICY_CONDITION description= language=JAVASCRIPT creationDate= script=...Script output follows...
To delete a script, run the ssoadm delete-sub-cfg command:
$ ssoadm \ delete-sub-cfg \ --realm /myRealm \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --servicename ScriptingService \ --subconfigname scriptConfigurations/myScript Sub Configuration scriptConfigurations/myScript was deleted from realm /myRealm
This chapter shows how to work with certificates and keystores used to protect network communication and to sign and encrypt information.
Digital signatures are constructed and verified as follows:
The signer computes a hash of the data to sign, and encrypts the hash using a private key to get the signature.
The signer then attaches the signature to the data, and sends the message with the recipient.
To validate the digital signature on the message, the recipient decrypts the signature using the public key certificate that corresponds to the private key of the signer.
The recipient computes the hash of the data, then checks that the decrypted signature (the decrypted hash) matches the computed hash.
Parties signing requests, responses, or assertions must share the public key certificates for signing keys. The certificates can either be shared in advance and imported into the trusted partners' trust stores, then referenced in the configuration by their trust store aliases, or shared in each signed message.
You should not have to concern yourself with certificates
when working with OpenAM. OpenAM's core services and Java EE policy agents depend
on the certificates installed for use with the web application container in
which they run. OpenAM web policy agents depend on the certificates installed
for use with the web server. Each certificate has been signed
by a well-known certificate authority (CA), whose certificate is already
installed in the Java CA certificates trust store
($JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/cacerts, default password
changeit) and in browsers, and so is recognized by other
software used without you having to configure anything.
However, you may want to configure OpenAM advanced features such as SAML v2.0, OpenID Connect 1.0, and others, which require certificates and key aliases to be maintained in a keystore whose location is configured in OpenAM.
You can use either CA or self-signed certificates with OpenAM, although you should have in mind that you will need to configure your applications to trust your self-signed certificates. For more information about installing OpenAM in a secure container with a self-signed certificate, see "To Set Up OpenAM With HTTPS and Self-Signed Certificates". For more information about sharing self-signed certificates among applications, see "To Share Self-Signed Certificates".
The container in which you install OpenAM requires a certificate in order to set up secure connections. Perform the following steps to set up Apache Tomcat 8.0 (Tomcat) with an HTTPS connector, using the Java keytool command to create a self-signed key pair:
Stop Tomcat.
Create a certificate and store it in a new keystore:
$ cd /path/to/tomcat/conf/ $ keytool -genkey -alias openam.example.com -storetype JCEKS -keyalg RSA -keystore keystore.jceks Enter keystore password: What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: openam.example.com What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: Eng What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: ForgeRock.com What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: Grenoble What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: Isere What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: FR Is CN=openam.example.com, OU=Eng, O=ForgeRock.com, L=Grenoble, ST=Isere, C=FR correct? [no]: yes Enter key password for <openam.example.com> (RETURN if same as keystore password):
Uncomment the SSL connector configuration in Tomcat's
conf/server.xml, and specify your keystore file, type, and password:<!-- Define a SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443 This connector uses the JSSE configuration, when using APR, the connector should be using the OpenSSL style configuration described in the APR documentation --> <!-- --> <Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" SSLEnabled="true" maxThreads="150" scheme="https" secure="true" keystoreFile="/path/to/tomcat/conf/keystore.jceks" keystorePass="changeit" keystoreType="JCEKS" clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" />You may need different settings depending on your configuration and version of Apache Tomcat. See the documentation for your version for more information.
Start Tomcat.
Verify that you can connect to Tomcat on port 8443 over HTTPS.
Your browser does not trust the certificate, because the certificate is self-signed and not signed by any of the CAs stored in your browser.
You recognize the subject and issuer of your certificate, and so can choose to trust the certificate, saving it into your browser's trust store.
Deploy and configure OpenAM.
To share the self-signed certificate in your container with other applications or servers, see "To Share Self-Signed Certificates".
OpenAM supports two possible keystore types to store certificates and keys: JCEKS, configured by default, and JKS.
During installation, OpenAM deploys a keystore of each type with several self-signed key aliases for demo and test purposes only. For production deployments, you should generate your own key aliases and configure OpenAM to use them.
Most OpenAM features that require storing key aliases for signing or encryption use the default keystore configuration. However, some features may require or support different configurations:
The Forgerock Authenticator (OATH) module and the Forgerock Authenticator (PUSH) module support configuring a specific keystore to encrypt device profiles instead of using the default keystore.
The Security Token Service supports configuring separate keystores for encrypting issued SAML v2.0 and OpenID Connect tokens.
The Audit Logging Service requires configuring a JKS keystore for tamper proofing.
SAML v2.0 identity providers support setting up a specific file to store the password of the key pair used for signing or encryption, instead of using the password file for the default keystore.
For a comparison between the default configuration of the JCEKS and the JKS keystores in OpenAM, see the following table:
| JCEKS | JKS | |
|---|---|---|
| By default in OpenAM? | Yes [a] | No |
| In which path is it? | $HOME/openam/openam/keystore.jceks | $HOME/openam/openam/keystore.jks |
| Where is its password stored? [b] |
$HOME/openam/openam/.storepass
| $HOME/openam/openam/.storepass
|
| Which test aliases does it contain? [c] |
|
|
| Where is the private key password file? [d] |
$HOME/openam/openam/.keypass
|
$HOME/openam/openam/.keypass
|
[a] New OpenAM installations use the JCEKS keystore as the default keystore. Upgrading an OpenAM installation does not change the keystore type in that installation, which in OpenAM 13 and earlier was a JKS keystore type by default. [b]
The password of the JCEKS and JKS keystores is
[c]
The password of all the test key aliases in both JCEKS and JKS is
[d] The password is encrypted. For more information on recreating this file, see "To Encrypt Keystore Passwords". | ||
OpenAM provides the JCEKS keystore by default on new installations. If you have upgraded from OpenAM 13 or previous versions, OpenAM would use the JKS keystore by default, unless you reconfigured OpenAM to use the JCEKS keystore.
This procedure assumes that your keystore is configured with the key
aliases that you need, and that the password for the keystore and for the
key aliases have been encrypted. For more information about replacing
the test key alias, see "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ",
and for more information about encrypting passwords for your already created
keystore and key aliases, see "To Encrypt Keystore Passwords".
To configure OpenAM to use a JCEKS or a JKS keystore, or to modify OpenAM's keystore configuration, perform the following steps:
Determine whether you want to configure the keystore for all your servers, or configure the keystore on a per-server basis:
If you want to configure the keystore for all your servers, navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Security > Key Store.
If you want to configure the keystore on a per-server basis, nagivate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Security > Key Store.
For more information about inherited properties, see "Configuring Servers" in the Reference.
Enter the keystore file name in the Keystore File field. For example,
keystore.jceks.Set the Keystore Type to
JKSorJCEKS.In the Keystore Password File field, enter the location of the keystore password file.
In the Private Key Password File field, enter the location of the private key password file.
In the Certificate Alias field, enter the alias of the private key to sign SAML v1.x XML files. If you do not require SAML v1.x functionality, you can leave the default
testalias.Save your changes, and restart the OpenAM server or servers affected by the configuration changes.
The steps in this procedure describe how to encrypt keystore and key alias passwords after you have changed them. The procedure assumes you have a keystore with your required key aliases already created and that all the key aliases have the same password. However, you can modify this procedure to encrypt passwords for SAML v2.0 keys if you want to keep them different from those already in the keystore.
To encrypt keystore and key alias passwords, perform the following steps:
Back up your original files, for example, the
$HOME/openam/openam/.storepassand the$HOME/openam/openam/.keypassfiles.Change the passwords of your keystore and key aliases as required.
Create two files, each containing only a password in cleartext. You can create the files in a temporary location:
storepass.cleartextcontains the cleartext keystore password.keypass.cleartextcontains the cleartext key password for the key aliases that reside in the keystore.
(Optional) If you have not already done so, install the administration tools as described in "To Set Up Administration Tools" in the Installation Guide.
Prepare encrypted password files for use by OpenAM:
$ ./ampassword --encrypt storepass.cleartext > .storepass $ ./ampassword --encrypt keypass.cleartext > .keypass
Remove the
*.cleartextfiles after preparing the encrypted versions.Replace the password files with the ones that you have created. For example:
$ cp .storepass .keypass ~/openam/openam/
(Optional) In a multi-server environment, every server has its own keystore file. Make sure key aliases and certificates are maintained in every server by doing the same changes in all, or copying over the keystore and the
.keypassand.storepassfiles.(Optional) (Optional) If the password files created have different names than the default
.storepassand.keypass, perform the following steps to change the keystore configuration:Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrative user, for example,
amadmin.Determine whether you want to configure the keystore for all your servers, or configure the keystore on a per-server basis:
If you want to configure the keystore for all your servers, navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Security > Key Store.
If you want to configure the keystore on a per-server basis, nagivate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Security > Key Store.
For more information about inherited properties, see "Configuring Servers" in the Reference.
In the Keystore Password File field, enter the location of the keystore password file.
In the Private Key Password File field, enter the location of the private key password file.
Save your changes.
(Optional)If you created a password file specifically for signing SAML assertions, navigate to Federation > Entity Providers > Provider Name and insert the name of the password file in the Key Pass property. Save your changes.
Restart the OpenAM server or servers affected by the configuration changes.
When deleting or adding key aliases, you should consider the following points:
By default, OpenAM uses the
testkey alias as follows:To sign persistent cookies: in Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > Security > Persistent Cookie Encryption Certificate Alias.
To sign SAML v1.x XML files: in Configure > Server Defaults > Security > Key Store > Certificate Alias.
To sign and encrypt stateless sessions: in Configure > Global Configuration > Session.
For more information about replacing the
testkey alias, see "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key ".
There may be more than one key alias in the keystore. For instance, you may have one key alias for SAML 2.0 configuration, and two more key aliases for the user self-service features, and others.
The key aliases' passwords must be encrypted in a file, and configured in OpenAM:
For SAML v2.0 identity providers, you can create a password file for the key aliases used to sign assertions. For more information, see "Modifying an Identity Provider's Configuration".
For the Forgerock Authenticator (OATH) and the Forgerock Authenticator (PUSH) modules, you can create a password file for the key aliases used to encrypt device profiles. For more information, see "Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication".
For other purposes (SAML v1.x, user self-service, stateless sessions, and others), the key aliases in the keystore must have the same password. This password must be then encrypted in a file and configured in OpenAM.
For more information about encrypting the password file, see "To Encrypt Keystore Passwords".
The password for the keystore and the password of the key aliases do not need to match.
In a multi-server environment, every server has its own keystore file. Make sure key aliases and certificates are maintained in every server.
You must restart OpenAM if you make any changes to the keystore, for example, adding or removing keys, changing key passwords, or changing the keystore password.
For recommendations on which algorithm to use for different OpenAM features, see the following table:
| Usage | Recommended Algorithm |
|---|---|
| User self-service encryption key | RSA with SHA-256, minimum 2048-bit |
| User self-service signing secret | HMAC with SHA-256 |
| SAML v1.x | RSA with SHA-256, minimum 2048-bit |
| SAML v2.0 | RSA with SHA-256, minimum 2048-bit |
| Persistent Cookie Encryption | RSA with SHA-256, minimum 2048-bit |
| Stateless Sessions | See "Configuring the JWT Signature" |
The steps in this procedure cover how to change the test
key alias that is configured by default in OpenAM, for another key:
Back up the
$HOME/openam/openam/keystore.jceks,$HOME/openam/openam/.storepass, and$HOME/openam/openam/.keypassfiles.Acquire a new key from your certificate authority, or generate new self-signed keys.
You can generate a new key (self-signed or not) and add it to the existing keystore configured in OpenAM, you can generate a new key and a new keystore, or you can import a key to a keystore. When you create or import a new key, the keytool command adds the new alias to the specified keystore if it exists, or creates a new keystore if it does not exist.
For this example, the step uses self-signed keys for example purposes, and creates a new keystore
keystore.jceksfile in a temporary location with a new asymmetric key alias callednewkey.The passwords entered in this step are encrypted manually in the next step, keep track of them:
$ cd /tmp $ keytool \ -genkeypair \ -alias newkey \ -keyalg RSA \ -keysize 2048 \ -validity 730 \ -storetype JCEKS \ -keystore keystore.jceks Enter keystore password: Reenter new password: What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: openam.example.com What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: Eng What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: ForgeRock.com What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: Grenoble What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: Isere What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: FR Is CN=openam.example.com, OU=Eng, O=ForgeRock.com, L=Grenoble, ST=Isere, C=FR correct? [no]: yes Enter key password for <newkey> (RETURN if same as keystore password): Reenter new password:
Create two files, each containing only a password in cleartext:
storepass.cleartextcontains the cleartext keystore password.keypass.cleartextcontains the cleartext key password for the key aliases that reside in the keystore.
(Optional) If you have not already done so, install the administration tools as described in "To Set Up Administration Tools" in the Installation Guide.
Prepare encrypted password files for use by OpenAM:
$ ./ampassword --encrypt storepass.cleartext > .storepass $ ./ampassword --encrypt keypass.cleartext > .keypass
Remove the
*.cleartextfiles after preparing the encrypted versions.Replace the default OpenAM keystore and password files with the ones that you have created. For example:
$ cp keystore.jceks .storepass .keypass ~/openam/openam/
(Optional) If you have an authentication chain configured with the Persistent Cookie module, perform the following steps:
Log in to the OpenAM console as an administrative user, for example,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Settings > Security.
Change the value in the Persistent Cookie Encryption Certificate Alias field from
testtonewkey.Save your changes.
(Optional) In a multi-server environment, every server has its own keystore file. Make sure key aliases and certificates are maintained in every server by doing the same changes in all, or copying over the keystore and the
.keypassand.storepassfiles.Restart the OpenAM server or servers affected by the configuration changes to use the new keystore and encrypted password files.
Log in to the OpenAM console as administrator, for example,
amadmin.Replace the
testkey alias in the features in use, for example:If you have already configured a SAML v2.0 identity provider, navigate to Federation > Provider Name > Assertion Content > Signing and Encryption, and then edit the signing key certificate alias.
Save your changes.
Navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Security > Key Store and replace the
testkey alias in the Certificate Alias property for SAML v1.x usage.
(Optional) (Optional) Self-signed keys are not automatically recognized by other entities. If you created new self-signed key aliases, you must share them as described in "To Share Self-Signed Certificates".
(Optional) (Optional) Share updated metadata with other entities in your circle of trust as described in "Configuring Identity Providers, Service Providers, and Circles of Trust".
User self-service requires a key pair for encryption and a signing secret key to be available before configuring any of its features.
OpenAM provides the demo selfserviceenctest key alias
for encrypting, and the demo selfservicesigntest
signing secret key alias.
The steps in this procedure cover how to change the demo key aliases
for different keys. This procedure assumes that you
will not create a new keystore. If you need to create a new keystore and
replace the default test key alias as well, see
"To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key " before continuing with this
procedure.
Perform the following steps:
Back up the
$HOME/openam/openam/keystore.jceksfile.Acquire a new key from your certificate authority, or generate new self-signed keys. The password of the new keys for the user self-service features must match the passwords of those keys already present in the keystore and configured in Configure > Server Defaults > Security > Key Store > Private Key Password File.
For this example, the step generates a self-signed key for encryption for example purposes, and a new signing secret key to an existing keystore, but you could also import the keys to the keystore.
Create the new self-signed encryption key alias:
$ cd ~/openam/openam/ $ keytool \ -genkeypair \ -alias newenckey \ -keyalg RSA \ -keysize 2048 \ -validity 730 \ -storetype JCEKS \ -keystore keystore.jceks Enter keystore password: What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: openam.example.com What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: Eng What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: ForgeRock.com What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: Grenoble What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: Isere What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: FR Is CN=openam.example.com, OU=Eng, O=ForgeRock.com, L=Grenoble, ST=Isere, C=FR correct? [no]: yes Enter key password for <newenckey> (RETURN if same as keystore password): Re-enter new password:
Create the new signing secret key alias:
$ cd ~/openam/openam/ $ keytool \ -genseckey \ -alias newsigkey \ -keyalg HmacSHA256 \ -keysize 256 \ -storetype JCEKS \ -keystore keystore.jceks Enter keystore password: Enter key password for <newsigkey> (RETURN if same as keystore password): Re-enter new password:
(Optional) In a multi-server environment, every server has its own keystore file. Make sure key aliases and certificates are maintained in every server by doing the same changes in all, or copying over the keystore and the
.keypassand.storepassfiles.Restart the OpenAM server or servers affected by the configuration changes.
Configure user self-service to use the new keys. For more information, see "To Configure Self Service Key Aliases".
(Optional) (Optional) The passwords for the user self-service key aliases must match the password of those key aliases already present in the keystore. If you only have SAML v2.0 keys with their own password files, you need to generate an encrypted password file for the user self-service keys. For more information, see "To Encrypt Keystore Passwords".
[9] Alternatively,
you can specify the trust store for a Java application, such as
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/path/to/truststore.jks
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit.
This chapter covers how to monitor OpenAM services to ensure appropriate performance and service availability.
OpenAM lets you monitor OpenAM over protocol through web pages, Java Management Extensions (JMX), or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). The services are based on JMX.
To configure monitoring services, login to OpenAM console as OpenAM administrator, and navigate to Configure > Global Services > System, and then click Monitoring. Alternatively, you can use the ssoadm set-attr-defs command:
$ ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --servicename iPlanetAMMonitoringService \ --schematype Global \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --attributevalues iplanet-am-monitoring-enabled=true
Restart OpenAM for the changes to take effect. You must also restart OpenAM if you disable monitoring.
You can configure OpenAM to allow you to access a web based view of
OpenAM MBeans on port 8082 where the core server runs, such as
http://openam-ter.example.com:8082/. Either use the
console, or use the ssoadm command:
$ ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --servicename iPlanetAMMonitoringService \ --schematype Global \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --attributevalues iplanet-am-monitoring-http-enabled=true
The default authentication file allows you to authenticate over HTTP
as user demo, password changeit. The
user name and password are kept in the file specified, with the password
encrypted:
$ cat openam/openam/openam_mon_auth demo AQICMBCKlwx6G3vzK3TYYRbtTpNYAagVIPNP
Or:
$ cat openam/openam/opensso_mon_auth demo AQICvSe+tXEg8TUUT8ekzHb8IRzVSvm1Lc2u
You can encrypt a new password using the ampassword command. After changing the authentication file, you must restart OpenAM for the changes to take effect.
You can configure OpenAM to allow you to listen for Java Management eXtension (JMX) clients, by default on port 9999. Either use the OpenAM console page under Configure > Global Services > System > Monitoring and make sure both Monitoring Status and Monitoring RMI interface status are both set to Enabled, or use the ssoadm command:
$ ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --servicename iPlanetAMMonitoringService \ --schematype Global \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --attributevalues iplanet-am-monitoring-enabled=true \ iplanet-am-monitoring-rmi-enabled=true
A number of tools support JMX, including jvisualvm
and jconsole. When you use jconsole
to browse OpenAM MBeans for example, the default URL for the OpenAM running
on the local system is
service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://localhost:9999/server.
$ jconsole service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://localhost:9999/server &
You can also browse the MBeans by connecting to your web application container, and browsing to the OpenAM MBeans. By default, JMX monitoring for your container is likely to be accessible only locally, using the process ID.
Also see Monitoring and Management Using JMX for instructions on how to connect remotely, how to use SSL, and so forth.
Important
JMX has a limitation in that some Operations and CTS tables cannot be properly serialized from OpenAM to JMX. As a result, only a portion of OpenAM's monitoring information is available through JMX. SNMP is a preferred monitoring option over JMX and exposes all OpenAM tables, especially for CTS, with no serialization limitations.
You can configure OpenAM to allow you to listen on port 8085 for SNMP monitoring. Either use the console, or use the ssoadm command:
$ ssoadm \ set-attr-defs \ --servicename iPlanetAMMonitoringService \ --schematype Global \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --attributevalues iplanet-am-monitoring-snmp-enabled=true
The "Configuring the Core Token Service" in the Installation Guide (CTS) provides persistent and highly available token storage for a several components within OpenAM, including user sessions, OAuth 2.0, SAML v2.0 and UMA tokens.
Depending on system load and usage, the CTS can produce a large quantity of tokens, which can be short lived. This style of usage is significantly different from typical LDAP usage. As such, systems administrators may be interested in monitoring this usage as part of LDAP directory maintenance.
The CTS functions only with one external LDAP service, OpenDJ.
To that end, the current state of CTS tokens on a system can be monitored over SNMP. The current state of different types of CTS tokens are associated with different Object Identifiers (OIDs) in a Management Information Base (MIB).
To enable SNMP, see "SNMP Monitoring"
Once activated, SNMP monitoring works over UDP by default. You may want to install one of many available network monitoring tools. For the purpose of this section, basic SNMP service and monitoring tools have been installed on a GNU/Linux system. The same commands should work on a Mac OS X system.
SNMP depends on labels known as Object Identifiers (OIDs). These
are uniquely defined labels, organized in tree format. For OpenAM, they
are configured in a .mib file named
FORGEROCK-OPENAM-CTS.mib, found
inside the /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-mib-schema-13.5.2-15.jar
file of the OpenAM deployment.
For detailed information on configured OIDs, see "Core Token Service (CTS) Object Identifiers" in the Reference.
With the OIDs in hand, you can set up an SNMP server to collect the data. You would also need SNMP utility commands with associated OIDs to measure the current state of a component. First, to verify the operation of SNMP on a GNU/Linux system, over port 8085, using SNMP version 2c, run the following command:
# snmpstatus -c public -v 2c localhost
The output should normally specify communications over UDP. If you
get a timeout message, the SNMP service may not be
running.
You can get the value for a specific OID. For example, the following command would retrieve the cumulative count for CTS create operations, over port 8085:
# snmpget -c public -v 2c :8085 enterprises.36733.1.2.3.3.1.1.1
If your version of the tool does not support the enterprises OID string,
use 1.3.6.1.4.1 instead, as in 1.3.6.1.4.1.36733.1.2.3.3.1.1.1.
For one view of the tree of OIDs, you can use the snmpwalk command. For example, the following command lists all OIDs related to CTS:
# snmpwalk -c public -v 2c :8085 enterprises.36733.1.2.3
A number of CTS OIDs are listed with a Counter64 value.
As defined in
RFC 2578, an OID so configured has a maximum
value of 2^64 - 1.
You can monitor policy evaluation performance over SNMP. OpenAM records statistics for up to a number of recent policy evaluation requests. (You can configure the number in OpenAM console under Configuration > System > Monitoring. For details, see the system configuration reference section, "Monitoring" in the Reference.)
Interface Stability: Evolving
As described in "CTS SNMP Monitoring",
SNMP uses OIDs defined in the .mib file,
FORGEROCK-OPENAM-POLICY.mib, found inside the
/path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-mib-schema-13.5.2-15.jar
file of the OpenAM deployment. This file specifies the statistics OpenAM
keeps for policy evaluation operations.
Adapt the examples in "CTS SNMP Monitoring"
to read monitoring statistics about policy evaluation on the command line.
When monitoring is active, OpenAM records statistics about both the numbers and rates of policy evaluations performed, and also the times taken to process policy evaluations.
The statistics are all read-only.
The base OID for policy evaluation statistics is
enterprises.36733.1.2.2.1.
The following table describes the values that you can read:
| OID | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Cumulative number of policy evaluations for specific resources (self) |
|
|
|
Average rate of policy evaluations for specific resources (self) |
|
|
|
Minimum rate of policy evaluations for specific resources (self) |
|
|
|
Maximum rate of policy evaluations for specific resources (self) |
|
|
|
Cumulative number of policy evaluations for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Average rate of policy evaluations for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Minimum rate of policy evaluations for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Maximum rate of policy evaluations for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Average length of time to evaluate a policy for a specific resource (self) |
|
|
|
Slowest evaluation time for a specific resource (self) |
|
|
|
Average length of time to evaluate a policy for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Slowest evaluation time for a tree of resources (subtree) |
|
|
|
Slowest individual policy evaluation time overall |
|
You can monitor stateful session statistics over SNMP. OpenAM records statistics for up to a configurable number of recent sessions. (You can configure the number in OpenAM console under Configuration > System > Monitoring. For details, see the system configuration reference section, "Monitoring" in the Reference.)
SNMP monitoring is not available for stateless sessions.
Interface Stability: Evolving
As described in "CTS SNMP Monitoring",
SNMP uses OIDs defined in a .mib file
that specifies the statistics OpenAM keeps for policy evaluation operations, the
FORGEROCK-OPENAM-SESSION.mib file. This file is found
inside the /path/to/tomcat/webapps/openam/WEB-INF/lib/openam-mib-schema-13.5.2-15.jar
file of the OpenAM deployment.
Adapt the examples in "CTS SNMP Monitoring"
to read monitoring statistics about sessions on the command line.
When monitoring is active, OpenAM records statistics about both the numbers of internal, remote, and CTS sessions, and also the times taken to process sessions.
The statistics are all read-only.
The base OID for session statistics is
enterprises.36733.1.2.1.
Times are expressed in nanoseconds rather than milliseconds,
as many operations take less than one millisecond.
The following table describes the values that you can read:
| OID | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Total number of current internal sessions |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to refresh an internal session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to logout an internal session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to destroy an internal session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to set a property on an internal session |
|
|
|
Total number of current remote sessions |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to refresh a remote session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to logout a remote session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to destroy a remote session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to set a property on a remote session |
|
|
|
Total number of sessions currently in the Core Token Service (CTS) |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to refresh a CTS session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to logout a CTS session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to destroy a CTS session |
|
|
|
Average time it takes to set a property on a CTS session |
|
You can check over HTTP whether OpenAM is up, using
isAlive.jsp. Point your application to the file
under the OpenAM URL, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/openam/isAlive.jsp.
If you get a success code (with Server is ALIVE: in
the body of the page returned), then OpenAM is in operation.
OpenAM services capture a variety of information in debug logs. Unlike audit log records, debug log records are unstructured. Debug logs contain a variety of types of information that is useful when troubleshooting OpenAM, including stack traces. The level of debug log record output is configurable. Debug log records are always written to flat files.
To adjust the debug level while OpenAM is running, login to the OpenAM console as OpenAM administrator and navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Debugging. The default level for debug logging is Error. This level is appropriate for normal production operations, in which case no debug log messages are expected.
Setting the debug log level to Warning increases the volume of messages. Setting the debug log level to Message dumps detailed trace messages. Unless told to do so by qualified support personnel, do not use Warning and Message levels in production.
By default, certain components that run in OpenAM's JVM—for example,
embedded OpenDJ configuration stores—do not generate trace-level
messages when you configure the debug log level to Message. If you need
trace-level messages for these components, navigate to Deployment >
Servers > Server Name > Advanced, create a
org.forgerock.openam.slf4j.enableTraceInMessage
property, and set its value to true.
During development, you might find it useful to log all debug messages
to a single file. In order to do so, set Merge Debug Files to
on.
OpenAM logs to a single file immediately after you change this property. You do not need to restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for the change to take effect.
OpenAM lets you capture debug log messages selectively for a specific service. This can be useful when you must turn on debugging in a production system where you want to avoid excessive logging, but must gather messages when you reproduce a problem.
Perform these steps to capture debug messages for a specific service:
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator,
amadmin.Browse to
Debug.jsp, for examplehttp://openam.example.com:8080/openam/Debug.jsp.No links to this page are provided in the console.
Select the service to debug and also the level required given the hints provided in the
Debug.jsppage.The changes takes effect immediately.
Promptly reproduce the problem you are investigating.
After reproducing the problem, immediately return to the
Debug.jsppage, and revert to normal log levels to avoid filling up the disk where debug logs are stored.
By default OpenAM does not rotate debug logs. To rotate debug logs,
edit WEB-INF/classes/debugconfig.properties where
OpenAM is deployed.
The debugconfig.properties file includes
the following properties:
org.forgerock.openam.debug.prefixSpecifies the debug log file prefix applied when OpenAM rotates a debug log file. The property has no default. It takes a string as the property value.
org.forgerock.openam.debug.suffixSpecifies the debug log file suffix applied when OpenAM rotates a debug log file. The property takes a
SimpleDateFormatstring. The default is-MM.dd.yyyy-kk.mm.org.forgerock.openam.debug.rotationSpecifies an interval in minutes between debug log rotations. Set this to a value greater than zero to enable debug log rotation based on time passed.
org.forgerock.openam.debug.rotation.maxsizeSpecifies a maximum log file size in megabytes between debug log rotations. Set this to a value greater than zero to enable debug log rotation based on log file size.
Changes to properties in the
debugconfig.properties file
take effect immediately.
You do not need to restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for
the changes to take effect.
The OpenAM recording facility lets you initiate events to monitor OpenAM while saving output that is useful when performing troubleshooting.
OpenAM recording events save four types of information:
OpenAM debug logs
Thread dumps, which show you the status of every active thread, with output similar to a JStack stack trace
Important run-time properties
The OpenAM configuration
You initiate a recording event by invoking the
ssoadm start-recording command or by using the
start action of the /json/records
REST API endpoint. Both methods use JSON to control the recording event.
This section describes starting and stopping recording using the
ssoadm command, using a JSON file to configure the
recording event, and locating the output recorded information.
For information about using the /json/records REST API
endpoint to activate and deactivate recording, see
"RESTful Troubleshooting Information Recording" in the Developer's Guide.
Start OpenAM recording with the ssoadm start-recording command. For example:
$ ssoadm \
start-recording \
--servername http://openam.example.com:8080/openam \
--adminid amadmin \
--password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \
--jsonfile recording.json
{
"recording":true,
"record": {
"issueID":103572,
"referenceID":"policyEvalFails",
"description":"Record everything",
"zipEnable":false,
"threadDump": {
"enable":true,
"delay": {
"timeUnit":"SECONDS",
"value":5
}
},
"configExport": {
"enable":true,
"password":"admin password",
"sharePassword":true
},
"debugLogs": {
"debugLevel":"message",
"autoStop": {
"time": {
"timeUnit":"MILLISECONDS",
"value":15000
},
"fileSize": {
"sizeUnit":"KB",
"value":1048576
}
}
},
"status":"RUNNING",
"folder":"/home/openam/debug/record/103572/policyEvalFails/"
}
}
Note
The ssoadm command output in the preceding example is shown in indented format for ease of reading. The actual output is not indented.
In the preceding ssoadm start-recording command example,
the recording.json file specifies the information
to be recorded and under what conditions recording automatically terminates.
This file is known as the recording control file.
"The Recording Control File" describes the format of recording control
files and provides an annotated example.
An active recording event stops when:
You explicitly tell OpenAM to stop recording by executing the ssoadm stop-recording command. See the Reference for details about this command.
Another ssoadm start-recording command is sent to OpenAM that specifies an issue ID other that differs from the active recording event's issue ID. In this case, the initial recording session terminates and the new recording event starts. Note that you can determine whether an OpenAM recording event is active by using the ssoadm get-recording-status command.
A timer configured in the recording control file determines that the maximum amount of time for the recording event has been reached.
A file size monitor configured in the recording control file determines that the maximum amount of information in debug logs has been reached.
A JSON file that is input to the ssoadm start-recording command controls the amount of information OpenAM records, the recording duration, and the location of recording output files.
The following properties comprise the recording control file:
issueIDType: Number
Required. The issue identifier—a positive integer stored internally as a Java
longdata type. A case number is a good choice for theissueIDvalue.The
issueIDis a component of the path at which recorded information is stored. See "Retrieving Recording Information" for more information.referenceIDType: String
Required. A second identifier for the recording event. Use this property to segregate multiple recording events for the same issue.
The
referenceIDis a component of the path at which recorded information is stored. See "Retrieving Recording Information" for more information.Note that spaces are not allowed in the
referenceIDvalue.DescriptionType: String
Required. A textual description of the recording event.
zipEnableType: Boolean
Required. Whether to compress the output directory into a zip file when recording has stopped.
configExportType: Object
Required. An object containing the following properties:
enableType: Boolean
Required. Whether to export the OpenAM configuration upon completion of the recording event. Exporting the OpenAM configuration is a best practice, because it is extremely useful to have access to the configuration when troubleshooting.
passwordType: String
Required if
enableistrue. A key required to import the exported configuration. The key is used the same way that the ssoadm export-svc-cfg command uses the-eargument.sharePasswordType: Boolean
Required if
enableistrue. Whether to show thepasswordvalue in the ssoadm start-recording, ssoadm get-recording-status, and ssoadm stop-recording output, and in theinfo.jsonfile, which is output during recording events, and which contains run-time properties.
debugLogsType: Object
Required. An object containing the following properties:
debugLevelType: String
Required. The debug level to set for the recording event. Set the value of
debugLeveltoMESSAGEto get the most troubleshooting information from your recording period. Other acceptable but less commonly used values areERRORandWARNING.autoStopType: Object
Optional. Contains another object used to specify an event that automatically ends a recording period. For time-based termination, specify a
timeobject; for termination based on uncompressed file size, specify afileSizeobject. If you specify bothtimeandfileSizeobjects, the event that occurs first causes recording to stop.Specifying
fileSizeandtimeobjects is a best practice, because it ensures that the recorded output does not occupy a larger than expected amount of space on your file system, and that recording events end in a timely fashion.timeType: Object
Optional; must be specified in the
autoStopobject iffileSizeis not specified. Configures a recording period to terminate recording after this amount of time.timeUnitType: String
Required. Acceptable values are
MILLISECONDS,SECONDS,MINUTES,HOURS, andDAYS.valueType: Numeric
Required. Values in
MILLISECONDSare rounded down to the second. The minimum acceptable value forautoStopis one second.
fileSizeType: Object
Optional; must be specified in the
autoStopobject iftimeis not specified. Configures a recording period to terminate after the aggregate size of uncompressed debug logs has reached this size.sizeUnitType: String
Required. Acceptable values are
B,KB,MB, andGB.valueType: Numeric
Required.
threadDumpType: Object
Required. An object containing the following properties:
enableType: Boolean
Required. Whether to dump threads during the recording event. Thread dumps are especially useful when troubleshooting performance issues and issues with unresponsive servers.
delayType: Object
Required if
enableistrue. Contains another object used to specify an interval at which thread dumps are taken. The initial thread dump is taken at the start of the recording event; subsequent thread dumps are taken at multiples of thedelayinterval.timeUnitType: String
Required. Acceptable values are
MILLISECONDS,SECONDS,MINUTES,HOURS, andDAYS.valueType: Numeric
Required. The minimum acceptable value is one second. Time units that are smaller than seconds, such as
MILLISECONDS, are rounded to the closest second.
The following is an example of a recording control file:
{
"issueID": 103572,
"referenceID": "policyEvalFails",
"description": "Troubleshooting artifacts in support of case 103572",
"zipEnable": true,
"configExport": {
"enable": true,
"password": "5x2RR70",
"sharePassword": false
},
"debugLogs": {
"debugLevel": "MESSAGE",
"autoStop": {
"time": {
"timeUnit": "SECONDS",
"value": 15
},
"fileSize": {
"sizeUnit": "GB",
"value": 1
}
}
},
"threadDump" : {
"enable": true,
"delay" : {
"timeUnit": "SECONDS",
"value": 5
}
}
}
The recording control file properties in the preceding example affect the recording output as follows:
| Recording Control File Property | Value | Effect |
|---|---|---|
issueID, referenceID
|
103572, policyEvalFails
|
Recording output is stored at the path
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFails_timestamp.zip.
For more information about the location of recording output, see
"Retrieving Recording Information".
|
Description
|
Troubleshooting artifacts in support of case 103572
| No effect. |
zipEnable
|
true
| Recording output is compressed into a zip file. |
configExport / enable
|
true
| The OpenAM configuration is exported at the start of the recording event. |
configExport / password
|
5x2RR70
| Knowledge of this password will be required to access the OpenAM configuration that was saved during recording. |
configExport / sharePassword
|
false
|
The password is not displayed in output messages displayed during
the recording event or in the info.json file.
|
debugLogs / debugLevel
|
MESSAGE
| Recording enables message-level debug logs during the recording event. |
debugLogs / autoStop / time
|
SECONDS, 15
|
Because both the time and
fileSize properties are set, recording stops after
15 seconds, or after the size of the debug logs exceeds 1 GB,
whichever occurs first.
|
debugLogs / autoStop / fileSize
|
GB, 1
|
Because both the time and
fileSize properties are set, recording stops after
15 seconds, or after the size of the debug logs exceeds 1 GB,
whichever occurs first.
|
threadDump / enable
|
true
| Thread dumps are taken throughout the recording event. |
threadDump / delay
|
SECONDS, 5
| The first thread dump is taken when the recording event starts. Additional thread dumps are taken every five seconds hence. |
Information recorded by OpenAM is stored at the path
debugFileLocation/record/issueID/referenceID.
For example, if the debug file location is
/home/openam/debug, the issue ID
103572, and the reference ID
policyEvalFails, the path containing
recorded information is
/home/openam/debug/record/103572/policyEvalFails.
When there are multiple recording events with the same
issueID and referenceID,
OpenAM appends a timestamp to the referenceID
of the earliest paths. For example, multiple recording events for
issue ID 103572 and reference ID
policyEvalFails might be stored at the
following paths:
Most recent recording:
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFailsNext most recent recording:
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFails_2015-10-24-11-48-51-902-PDTEarliest recording:
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFails_2015-08-10-15-15-10-140-PDT
OpenAM compresses the output from recording events when you set the
zipEnable property to true. The output
file can be found at the path
debugFileLocation/record/issueID/referenceID_timestamp.zip.
For example, compressed output for a recording event for
issue ID 103572 and reference ID
policyEvalFails might be stored at the
following path:
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFails_2015-08-12-12-19-02-683-PDT.zip.
Use the referenceID property value to segregate
output from multiple problem recreations associated with the same case.
For example, while troubleshooting case 103572, you notice that you only
have a problem when evaluating policy for members of the Finance realm.
You could trigger two recording events as follows:
| OpenAM Behavior | referenceIDValue | Recording Output Path |
|---|---|---|
| Policy evaluation behaves as expected for members of the Engineering realm. |
policyEvalSucceeds
|
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalSucceeds
|
| Policy evaluation unexpectedly fails for members of the Finance realm. |
policyEvalFails
|
debugFileLocation/record/103572/policyEvalFails
|
The OpenAM console lets the administrator view and manage active user sessions on the Sessions tab page.
Session management from the OpenAM console is only available for stateful sessions. Stateless sessions do not appear in the Sessions tab page.
To end a user session manually, select the user's session, and then click the Invalidate Session button. As a result, the user has to authenticate again.
Note
Deleting a user does not automatically remove any of the user's sessions. After deleting a user, check for any sessions for the user and remove them under the Console's Sessions tab.
This chapter covers key OpenAM tunings to ensure smoothly performing access and federation management services, and to maximize throughput while minimizing response times.
Note
The recommendations provided here are guidelines for your testing rather than hard and fast rules for every situation. Said another way, the fact that a given setting is configurable implies that no one setting is right in all circumstances.
The extent to which performance tuning advice applies depends to a large extent on your requirements, on your workload, and on what resources you have available. Test suggestions before rolling them out into production.
The suggestions in this chapter pertain to OpenAM deployments with the following characteristics:
The host running the OpenAM server has a large amount of memory.
The deployment has a dedicated OpenDJ directory server for the Core Token Service. The host running this directory server is a high-end server with a large amount of memory and multiple CPUs.
The OpenAM server is configured to use stateful sessions.
As a rule of thumb, an OpenAM server in production with a 3 GB heap configured to use stateful sessions can handle 100,000 sessions. Although you might be tempted to use a larger heap with a 64-bit JVM, smaller heaps are easier to manage. Thus, rather than scaling single servers up to increase the total number of simultaneous sessions, consider scaling out by adding more servers instead.
OpenAM has a number of settings that can be tuned to increase performance.
The following general points apply:
Set debug level to
error.Set container-level logging to a low level, such as
errororsevere.
Tune your LDAP data stores, your LDAP authentication modules, and connection pools for CTS and configuration stores.
To change LDAP data store settings, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores > Data Store Name in the OpenAM console. Each data store has its own connection pool and therefore each data store needs its own tuning:
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| LDAP Connection Pool Minimum Size | 1 |
The minimum LDAP connection pool size; a good tuning value for this property is 10. ( |
| LDAP Connection Pool Maximum Size | 10 |
The maximum LDAP connection pool size; a high tuning value for this property is 65, though you might well be able to reduce this for your deployment. Ensure your LDAP server can cope with the maximum number of clients across all the OpenAM servers. ( |
To change connection pool settings for the LDAP authentication module, in the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Authentication, and then click Core Attributes.
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Default LDAP Connection Pool Size | 1:10 |
The minimum and maximum LDAP connection pool used by the LDAP authentication module. This should be tuned to 10:65 for production. ( |
When tuning LDAP connection pool settings for the Core Token Service (CTS), what you change depends on whether the directory service backing the CTS is the same directory service backing OpenAM configuration.
When the same directory service backs both the CTS and also OpenAM configuration (the default), then the same connection pool is shared for any LDAP operations requested by the CTS or by a service accessing the OpenAM configuration. In this case, one connection is reserved for cleanup of expired CTS tokens. Roughly half of the connections are allocated for CTS operations, to the nearest power of two.[10] The remaining connections are allocated to services accessing the OpenAM configuration. For a default configuration, where the maximum number of connections in the pool is ten, one connection is allocated for cleanup of expired CTS tokens, four connections are allocated for other CTS operations, and five connections are allocated for services accessing the configuration. If the Maximum Connection Pool size is 20, one connection is allocated for cleanup of expired CTS tokens, eight connections are allocated for other CTS operations, and 11 connections are allocated for services accessing the configuration. If the pool size is 65, then the numbers are 1, 32, and 32, and so on.
The minimum number of connections is 6.
When the directory service backing the CTS is external (differs from the directory service backing the OpenAM configuration) then the connection pool used to access the directory service for the CTS is separate from the pool used to access the directory service for the OpenAM configuration. One connection is reserved for cleanup of expired CTS tokens. Remaining connections are allocated for CTS operations such that the number of connections allocated is equal to a power of two. In this case, set the maximum number of connections to 2^n+1, as in 9, 17, 33, 65, and so forth.
If the same directory service backs both the CTS and also OpenAM configuration, then set the Maximum Connection Pool property size under Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Directory Configuration.
If the directory service backing the CTS is external (differs from the directory service backing the OpenAM configuration), then set the Maximum Connection property size under Deployment > Servers > Server Name > CTS > CTS Token Store.
In both cases, if you must change the default connection timeouts, set the following advanced properties under Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced:
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Connection Pool | 10 |
Find this setting in OpenAM console under Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Directory Configuration. When the same directory service backs both the CTS and also OpenAM configuration, consider increasing this to at least 19 to allow 9 connections for the CTS, and 10 connections for access to the OpenAM configuration (including for example looking up policies). |
| Max Connections | 10 |
Find this setting in OpenAM console under Deployment > Servers > Server Name > CTS > External Store Configuration. When the directory service backing the CTS is external and the load on the CTS is high, consider setting this to 2^n+1, where n = 4, 5, 6, and so on. In other words, try setting this to 17, 33, 65, and so on when testing performance under load.
( |
| CTS connection timeout (advanced property) | 10 (seconds) |
Most CTS requests to the directory server are handled quickly, so the default timeout is fine for most cases.
If you choose to vary this setting for performance testing,
set the advanced property,
You must restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for changes to take effect. |
| CTS reaper timeout (advanced property) | None |
The CTS token cleanup connection generally should not time out as it is used to request long-running queries that can return many results.
If you choose to vary this setting for performance testing,
set the advanced property,
You must restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for changes to take effect. |
| Configuration management connection timeout (advanced property) | 10 (seconds) |
Most configuration management requests to the directory server are handled quickly, so the default timeout is fine for most cases.
If you choose to vary this setting for performance testing,
set the advanced property,
You must restart OpenAM or the container in which it runs for changes to take effect. |
OpenAM has two thread pools used to send notifications to clients. The Service Management Service (SMS) thread pool can be tuned in the OpenAM console under Configure > Server Defaults > SDK > Data Store:
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Notification Pool Size | 10 |
This is the size of the thread pool used to send notifications. In production this value should be fine unless lots of clients are registering for SMS notifications. ( |
The session service has its own thread pool to send notifications to listeners about changes to stateful sessions. This is configured under Configure > Server Defaults > Session > Notification:
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Notification Pool Size | 10 |
This is the size of the thread pool used to send notifications. In production this should be around 25-30. ( |
| Notification Thread Pool Threshold | 5000 |
This is the maximum number of notifications in the queue waiting to be sent. The default value should be fine in the majority of installations. ( |
The session service has additional properties to tune, which are configured under Configure > Server Defaults > Session > Session Limits. The following suggestions apply to deployments using stateful sessions:
| Property | Default Value | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Sessions | 5000 |
In production, this value can safely be set into the 100,000s. The maximum session limit is really controlled by the maximum size of the JVM heap which must be tuned appropriately to match the expected number of concurrent sessions. ( |
| Sessions Purge Delay | 0 |
This should be zero to ensure sessions are purged immediately. ( |
This section gives some initial guidance on configuring the JVM for running OpenAM. These settings provide a strong foundation to the JVM before a more detailed garbage collection tuning exercise, or as best practice configuration for production:
| JVM Parameters | Suggested Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| At least 1 GB (2 GB with embedded OpenDJ), in production environments at least 2 GB to 3 GB. This setting depends on the available physical memory, and on whether a 32- or 64-bit JVM is used. | - |
| - | Ensures the server JVM is used |
| Set both to 256 MB | Controls the size of the permanent generation in the JVM |
| Set both to 256 MB | Controls the size of the metaspace in the JVM |
| 60000 | Controls the read timeout in the Java HTTP client implementation This applies only to the Sun/Oracle HotSpot JVM. |
| High setting: 30000 (30 seconds) | Controls the connect timeout in the Java HTTP client implementation When you have hundreds of incoming requests per second, reduce this value to avoid a huge connection queue. This applies only to the Sun/Oracle HotSpot JVM. |
| JVM Parameters | Suggested Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Controls the protocols used for outbound HTTPS connections from OpenAM. This applies only to Sun/Oracle Java environments. |
| JVM Parameters | Suggested Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| - | Verbose garbage collection reporting |
|
| Location of the verbose garbage collection log file |
| - | Prints a heap histogram when a SIGTERM signal is received by the JVM |
| - | Prints detailed information about garbage collection |
| - | Prints detailed garbage collection timings |
| - | Out of Memory errors generate a heap dump automatically |
|
| Location of the heap dump |
| - | Use the concurrent mark sweep garbage collector |
| - | Aggressive compaction at full collection |
| - | Allow class unloading during CMS sweeps |
OpenAM caches data to avoid having to query user and configuration data stores each time it needs the information. By default, OpenAM makes use of LDAP persistent search to receive notification of changes to cached data. For this reason, caching works best when data are stored in a directory server that supports LDAP persistent search.
OpenAM has two kinds of cache on the server side that you can configure, one for configuration data and the other for user data. Generally use the default settings for configuration data cache. This section mainly covers the configuration choices you have for caching user data.
OpenAM implements the global user data cache for its user data stores. Prior to OpenAM 11.0, OpenAM supported a secondary Time-to-Live (TTL) data store caching layer, which has since been removed in OpenAM 11.0 and later versions.
The user data store also supports a DN Cache, used to cache DN lookups
that tend to occur in bursts during authentication.
The DN Cache can become out of date when a user is moved or renamed in the
underlying LDAP store, events that are not always reflected in a persistent search result.
You can enable the DN cache when the underlying LDAP store supports persistent
search and mod DN operations (that is, move or rename DN).
The following diagram depicts the two kinds of cache, and also the two types of caching available for user data:
The rest of this section concerns mainly settings for global user data cache and for SDK clients. For a look at data store cache settings, see "LDAP Data Store Settings".
By default OpenAM has caching enabled both for configuration data and
also for user data. This setting is governed by the server property
com.iplanet.am.sdk.caching.enabled, which by default is
true. When you set this advanced property to
false, then you can enable caching independently for
configuration data and for user data.
Disabling caching can have a severe negative impact on performance. This is because when caching is disabled, OpenAM must query a data store each time it needs data.
If, however, you have at least one user data store that does not support LDAP persistent search, such as a relational database or an LDAP directory server that does not support persistent search, then you must disable the global cache for user data. Otherwise user data caches cannot stay in sync with changes to user data entries:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Advanced.
Set the value of the
com.iplanet.am.sdk.caching.enabledproperty tofalseto disable caching overall.Set the value of the
com.sun.identity.sm.cache.enabledproperty totrueto enable configuration data caching.All supported configuration data stores support LDAP persistent search, so it is safe to enable configuration data caching.
You must explicitly set this property to
true, because setting the value of the propertycom.iplanet.am.sdk.caching.enabledtofalsein the previous step disables both user and configuration data caching.Save your work.
OpenAM starts persistent searches on user data stores when possible [11] in order to monitor changes. With user data store caching disabled, OpenAM still starts the persistent searches, even though it no longer uses the results.
Therefore, if you disable user data store caching, you should also disable persistent searches on user data stores in your deployment to improve performance. To disable persistent search on a user data store, remove the value of the Persistent Search Base DN configuration property and leave it blank. Locate this property under Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores > Data Store Name > Persistent Search Controls.
With a large user data store and active user base, the number of user entries in cache can grow large.
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Configuration > Server Defaults > SDK.
Change the value of SDK Caching Maximum Size.
There is no corresponding setting for configuration data, as the number of configuration entries in a large deployment is not likely to grow nearly as large as the number of user entries.
Policy agents and other OpenAM SDK clients can also cache user data, using most of the same properties as OpenAM server as described in "OpenAM Cache Properties" . Clients, however, can receive updates by notification from OpenAM or, if notification fails, by polling OpenAM for changes.
This procedure describes how to enable change notification and polling for policy agent user data cache updates. When configuring a custom OpenAM SDK client using a .properties file, use the same properties as for the policy agent configuration:
In the OpenAM console, navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Agents > Agent Type > Agent Name to view and edit the policy agent profile.
On the Global tab page, check that the Agent Notification URL is set.
When notification is enabled, the agent registers a notification listener with OpenAM for this URL.
The corresponding property is
com.sun.identity.client.notification.url.For any changes you make, Save your work.
You must restart the policy agent for the changes to take effect.
The table below provides a quick reference, primarily for user data cache settings.
Notice that many properties for configuration data cache have
sm (for Service Management) in their names, whereas those
for user data have idm (for Identity Management) in their
names:
| Property | Description | Default | Applies To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum number of user entries cached. | 10000 | Server and SDK |
|
Whether to enable caching for both configuration data and also for user data. If If |
| Server & SDK |
|
How often in minutes the SDK client, such as a policy agent should poll OpenAM for modified user data entries. The SDK also uses this value to determine the age of the oldest changes requested. The oldest changes requested are 2 minutes older than this setting. In other words, by default the SDK polls for entries changed in the last 3 minutes. Set this to 0 or a negative integer to disable polling. | 1 (minute) | SDK |
|
How long OpenAM stores a given change to a cached entry, so that clients polling for changes do not miss the change. | 30 (minutes) | Server only |
|
If Otherwise, set this to |
| Server & SDK |
|
How many minutes to store a user data entry in the global user data cache. | 30 (minutes) | Server & SDK |
|
Whether user data entries in the global user data cache should expire over time. |
| Server & SDK |
|
Whether the SDK client, such as a policy agent should register a notification listener for user data changes with the OpenAM server. The SDK client uses the URL specified by
If notifications cannot be enabled for some reason, then the SDK client falls back to polling for changes. |
| SDK |
|
If Otherwise, set this to |
| Server & SDK |
|
Set this to |
| Server & SDK |
|
Sets the cache size. |
| Server & SDK |
When you change the OpenAM host name, you must make manual changes to the configuration. This chapter describes what to do. If you must also move an embedded configuration directory from one host to another, see the OpenDJ Administration Guide chapter, Moving Servers.
Changing OpenAM host names involves the following high-level steps.
Adding the new host name to the Realm/DNS Aliases list.
Exporting, editing, then importing the configuration.
This step relies on the ssoadm command, which you install separately from OpenAM as described in "To Set Up Administration Tools" in the Installation Guide.
Stopping OpenAM and editing configuration files.
Removing the old host name from the Realm/DNS Aliases list.
Before you start, make sure you have a current backup of your current installation. See "Backing Up and Restoring OpenAM Configurations" for instructions.
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator,
amadmin.Under Realms > Realm Name, click Properties, add the new host name to the Realm/DNS Aliases list, and then save your work.
Export the service configuration:
$ ssoadm \ export-svc-cfg \ --adminid amadmin \ --encryptsecret myEncryptSecretString1234 \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --outfile config.xml Service Configuration was exported.
OpenAM uses the value entered in
--encryptsecretto encrypt passwords stored in the backup file. It can be any value, and is required when restoring a configuration.Edit the service configuration file:
Change the fully qualified domain name, such as
openam.example.com, throughout the file.If you are changing the context path, such as
/openam, then make the following changes:Change the value of
com.iplanet.am.services.deploymentDescriptor.Change contextPath in the value of the
propertiesViewBeanURL="contextPath/auth/ACServiceInstanceList".Change contextPath in the value of
propertiesViewBeanURL="contextPath/auth/ACModuleList".Change the context path in a <Value> element that is a child of an <AttributeValuePair> element.
Change the context path where it occurs throughout the file in the full URL to OpenAM, such as
http://openam.example.com:8080/contextPath.
If you are changing the port number, then change the value of
com.iplanet.am.server.port.Also change the port number in
host:portcombinations throughout the file.If you are changing the domain name, then change the cookie domain, such as
<Value>.example.com</Value>throughout the file.
Import the updated service configuration:
$ ssoadm \ import-svc-cfg \ --adminid amadmin \ --encryptsecret myEncryptSecretString1234 \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --xmlfile config.xml Directory Service contains existing data. Do you want to delete it? [y|N] y Please wait while we import the service configuration... Service Configuration was imported.
Stop OpenAM or the web container where it runs.
Edit the bootstrap file, such as
/home/user/openam/bootstrap, changing the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN), port, and context path for OpenAM as necessary.If you are changing the context path, then move the folder containing OpenAM configuration, such as
/home/user/openam/, to match the new context path, such as/home/user/openam2/.If you are changing the location or context path, change the name of the file in the
/home/user/.openamcfgfolder, such asAMConfig_path_to_tomcat_webapps_openam_, to match the new location and context path.Also edit the path name in the file to match the change you made when moving the folder.
Restart OpenAM or the web container where it runs.
Log in to OpenAM console as administrator,
amadmin.Under Realms > Realm Name, click Properties, remove the old host name from the Realm/DNS Aliases list, and then save your work.
This chapter identifies best practices for securing your OpenAM deployment.
OpenAM includes default settings to make it easier for you to evaluate the software. Avoid these default settings in production deployments:
When connecting to LDAP, bind with a specific administrative account rather than a root DN account, if possible.
Change the default
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie name both in OpenAM (com.iplanet.am.cookie.name) and in your policy agent profiles (com.sun.identity.agents.config.cookie.name).When installing OpenAM, do not use
/openamor/openssoas the deployment URI.Create an administrator in the Top Level Realm with a different ID than the default
amadmin.Create specific administrator users to track better who makes configuration changes.
Remove the demo user account. For example, if you configure the embedded OpenDJ directory server as a configuration and CTS store, the default demo user account gets created during the installation process. You should remove the user using the OpenAM console under Realms > Top Level Realm > Subjects > User.
Set the list of Valid
gotoURL Resources. By default, OpenAM redirects the user to the URL specified in thegotoandgotoOnFailquery string parameters supplied to the authentication interface in the login URL.To increase security against possible phishing attacks through open redirect, you can specify a list of valid URL resources against which OpenAM validates these URLs. OpenAM only redirects a user if the
gotoandgotoOnFailURL matches any of the resources specified in this setting. If no setting is present, it is assumed that thegotoorgotoOnFailURL is valid.To set the Valid
gotoURL Resources, use the OpenAM console, and navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services. Click Add a Service, select Validation Service, and add one or more validgotoURLs, and then click Create.When setting valid
gotoURLs, you can use the "*" wildcard, where "*" matches all characters except "?". For more specific patterns, use resource names with wildcards as described in the procedure, "Configuring Valid goto URL Resources".Disable module based authentication for all OpenAM realms. Module based authentication lets users authenticate using the
module=module-namelogin parameter. To disable module based authentication for a realm, select the realm in the OpenAM console, then select Authentication > Settings > Security and clear the Module Based Authentication check box.
Anytime users interact with a web service, there are risks. With OpenAM, you can reduce those risks by limiting what is exposed through the firewall using the following strategy:
Use a reverse proxy in front of OpenAM to allow access only to the necessary URLs. A reverse proxy exposes only those endpoints needed for an application. For example, if you need to expose the OAuth2/OpenID Connect endpoints and REST interface, then you should implement a reverse proxy.
The following figure shows the recommended architecture with a reverse proxy.
Leave
ssoadm.jspdisabled in production. (Advanced property:ssoadm.disabled=true).If possible in your deployment, control access to OpenAM console by network address, such that administrators can only connect from well-known systems and networks.
Restrict access to URIs that you do not use, and prevent internal endpoints, such as
/sessionservicefrom being reachable over the Internet.For a full list of endpoints, see "Service Endpoints" in the Reference.
Create realms for your organization(s) and separate administrative users from end users. For instructions, see "Configuring Realms".
To direct relevant users to the correct realms, you can then either:
Use the
realm=realm-namequery string parameter.Create fully qualified domain name DNS aliases for the realms.
When customizing
config/auth/default*/Login.jsp, make sure that you do not introduce any security vulnerabilities, such as cross-site scripting due to unvalidated input.Create a policy agent profile for each policy agent. See "Configuring Policy Agent Profiles" for instructions.
Keep communications secure by using encryption, properly configured cookies, and request and response signatures:
Protect network traffic by using HTTPS and LDAPS where possible.
When using HTTPS, use secure cookies, which are transmitted only over secured connections.
To configure OpenAM server to use secure cookies, in the OpenAM console, navigate to Configure > Server Defaults > Security. On the Cookie tab, select Secure Cookie, and then click Save Changes.
HttpOnly cookies are meant to be transmitted only over HTTP and HTTPS, and not through non-HTTP methods, such as JavaScript functions.
If you are using the classic UI, you can configure the OpenAM server to use HttpOnly cookies by navigating to Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced, and setting the
com.sun.identity.cookie.httponlyproperty's value totrue. Save your changes. Note that the XUI does not currently support HttpOnly cookies.Where possible, use subdomain cookies, and control subdomains in a specific DNS master.
Use cookie hijacking protection with restricted tokens, where each policy agent uses different SSO tokens for the same user. See "To Protect Against Cookie Hijacking" for instructions.
Use your own key, not the
testkey provided with OpenAM, to sign:SAML 2.0 authentication requests, authentication responses, and single logout requests
XUI authentication IDs
See "To Change OpenAM Default test Signing Key " for instructions.
When using SAML v2.0, if the other entities in your circle of trust can handle encryption, then use encryption in addition to signing requests and responses.
The built-in amadmin account cannot be disabled, deleted, or
renamed, since it is hard-coded in the source code of several
files.
If you want a user to have administration rights in OpenAM other than
amadmin, delegate realm administration privileges
to the new user. For more information about delegating realm administration
privileges, see "Delegating Realm Administration Privileges".
In this section you will find procedures to change the password of the
top-level administrator amadmin, when:
OpenAM is configured using an external configuration store.
See "To Change the amadmin User's Password: External Configuration Store".
OpenAM is configured using the embedded OpenDJ instance as the configuration store. It may be configured with an external data store, or with the embedded OpenDJ instance as a data store.
See "To Change the amadmin User's Password: Embedded Configuration Store".
If OpenAM is configured to use an external configuration store,
perform the following steps to change the
amadmin user's password:
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Top Level Realm > Subjects, and then click
amAdmin.On the Edit User page, select Edit next to Password.
On the Change Password page, enter the new password in the New Password field.
Click OK to save your changes.
If your deployment has multiple OpenAM servers, the new password replicates across all servers.
If OpenAM is configured to use the embedded OpenDJ instance for
the configuration store, you must change the passwords of the following
two users in the embedded OpenDJ accounts to match the new
amadmin password:
You must change these two passwords in the embedded OpenDJ instance regardless of whether you use an external or embedded data store.
The
cn=Directory Manageruser, created during installation.The global administrator, created in OpenDJ by OpenAM after a second OpenAM server has been added to the deployment.
Some functionality might not work if the OpenDJ directory manager, OpenAM
administrator amadmin, and OpenDJ global administrator
passwords are not identical. For example, adding new servers to the
deployment.
To change the OpenAM amadmin, OpenDJ directory manager, and
OpenDJ global administrator passwords and the required bindings,
perform the following steps:
Back up your deployment as described in "Backing Up and Restoring OpenAM Configurations".
Log in to the OpenAM console as the administrator,
amadmin.Navigate to Realms > Top Level Realm > Subjects, and then click
amAdmin.On the Edit User page, select Edit next to Password.
On the Change Password page, enter the new password in the New Password field.
Click OK to save your changes.
If your deployment has multiple OpenAM servers, the new password replicates across all servers.
OpenAM binds to the embedded OpenDJ server using the
cn=Directory Manageraccount. Change thecn=Directory Manageraccount's bind password in the OpenAM configuration as follows:Change the password for the configuration store binding:
Navigate to Deployment > Servers > Server Name > Directory Configuration.
Enter the new bind password, which is the new
amadminpassword, and save your changes.Make this change for each of your OpenAM servers.
(Optional) If you use the embedded OpenDJ instance as a data store, change the following bind passwords:
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores > embedded:
Enter the new bind password, which is the new
amadminpassword, and save your changes.Make this change in every OpenAM realm that uses the embedded OpenDJ as a data store.
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Services > Policy Configuration:
Enter the new bind password, which is the new
amadminpassword, and save your changes.Make this change in every OpenAM realm that uses the embedded OpenDJ as a data store.
Navigate to Realms > Realm Name > Authentication > Modules, and select LDAP:
Enter the new bind password, which is the new
amadminpassword, and save your changes.Make this change in every OpenAM realm that uses the embedded OpenDJ as a data store.
To change the
cn=Directory Managerand the global administrator passwords in the embedded OpenDJ, see Resetting Administrator Passwords in the OpenDJ Administration Guide.
This chapter covers how to get debugging information and troubleshoot issues in OpenAM deployments.
Solutions to Common Issues
This section offers solutions to common problems when working with OpenAM.
28.1. OpenAM Installation | |
Q: | OpenAM configuration could not write to the configuration directory. Where must I change permissions, and what permissions are required? |
A: | If the user running the web container has a $HOME directory, then
the configuration directory is stored there, and you probably do not have
this problem. If you do not know the user running the web container, use
the ps command to check. In the following example, the
user is $ ps -ef | grep tomcat mark 1739 1 0 14:47... For a container installed from native packages with a dedicated
user, $HOME may not be where you think it is. Look at the user's entry in
If you cannot change the permissions to the user's home directory,
you can, as a workaround, unpack $ cd ~/Downloads/openam/OpenAM-13.5.2.war $ mkdir unpacked ; cd unpacked $ jar xf ../OpenAM-13.5.2.war $ vi WEB-INF/classes/bootstrap.properties $ grep ^config WEB-INF/classes/bootstrap.properties configuration.dir=/my/readwrite/config/dir $ jar cf ../openam.war * |
Q: | Deployment failed due to lack of memory. What do I do? |
A: | OpenAM requires at least a maximum heap size of 1024 MB, with a 256
MB maximum permanent generation heap size. For the Sun JVM, ensure the
container starts with If you do not know the settings used when the web container was
started, use the ps command to check. In the following
example, the web container is $ ps -ef | grep tomcat | grep Xm ... -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m ... Make sure you have at least 2 GB of RAM on the system where you run OpenAM to avoid running out of memory. If you make it through deployment and seem to be running out of
memory later, you can confirm memory errors in OpenAM by searching the
|
Q: | Deployment failed due to invalid hostname configuration. What do I do? |
A: | OpenAM requires that you use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that the host can resolve: $ ping openam-ter.example.com PING openam-ter (192.168.56.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from openam (192.168.56.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.025 ms 64 bytes from openam (192.168.56.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.032 ms 64 bytes from openam (192.168.56.2): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.030 ms For a test deployment (at home, on a laptop), you can use fake FQDNs
in $ cat /etc/hosts | grep openam 192.168.56.2 openam openam.example.com 192.168.56.3 openam-bis openam-bis.example.com 192.168.56.5 openam-ter openam-ter.example.com |
Q: | I configured OpenAM, and now am seeing the configuration screen again. Who deleted my configuration? |
A: | OpenAM uses a file in $ cat ~/.openamcfg/AMConfig_path_to_tomcat_webapps_openam_ /home/amuser/openam If OpenAM cannot find its configuration, then it displays the configuration screen. |
28.2. OpenAM Upgrades | |
Q: | I have upgraded OpenAM, now my tools are not working properly. What happened? |
A: | Every OpenAM component must be upgraded, not just the main
OpenAM |
28.3. OpenAM Administration | |
Q: | I cannot use the browser-based equivalent of
ssoadm,
|
A: | For security reasons, the |
Q: | The ssoadm command is very slow on my virtual machine (VMWare, VirtualBox, and so forth). How can I speed it up? |
A: | Virtual machine random devices do not always produce enough random data. The ssoadm command can hang while reading random data from the virtual machine's random device, with the result that you can wait a minute or more for a single command to finish. To work around this limitation on virtual machines, make sure you install something that generates enough random data, such as a timer entropy daemon. |
Q: | I have OpenAM deployed on WebLogic 12.1.1 and am running Java 6. What can I do to fix the exceptions and strange results that I am seeing when I use the ssoadm command? |
A: | Edit the start up script for WebLogic as described in "Preparing Oracle WebLogic" in the Installation Guide, and then restart WebLogic. |
Q: | I added OpenDJ as a data store, and now I cannot add a user. OpenAM gives me the following error: ERROR: LDAPv3Repo.create failed. errorCode=65 Entry |
A: | When you set up a New Data Store to use OpenDJ as an identity repository under Realms > Realm Name > Data Stores > New..., you need to check the Load schema when saved box if you want OpenAM to add the schema to OpenDJ. The box is not selected by default. The full version of OpenAM includes directory server schema in the
$ /path/to/opendj/bin/ldapmodify \ --port 1389 \ --bindDN "cn=Directory Manager" \ --bindPassword password \ --filename ~/Downloads/openam/ldif/fam_sds_schema.ldif Processing MODIFY request for CN=schema MODIFY operation successful for DN CN=schema |
Q: | I have OpenAM installed in WebSphere application server with IBM Java. I am doing REST-based user registration or forgotten password reset, or setting up the HOTP authentication module, sending mail to an SMTP server over SSL. How come OpenAM cannot send mail over SSL? |
A: | If you see in the OpenAM Authentication debug log that the SSL handshake is failing when connecting to the mail server, then it is likely that the SSL certificate presented by the mail server is not trusted. This is a WebSphere/IBM Java issue, rather than an OpenAM issue. To work around the problem, follow these steps to make sure that WebSphere trusts the mail server SSL certificate:
After WebSphere restarts, it should trust the mail server SSL certificate. OpenAM therefore should be able to connect to the mail server over SSL. For more information, see the WebSphere documentation. |
Q: | My container log file is filling up with messages from OpenAM's OAuth authorization service and OpenID Connect provider. What can I do to prevent all these messages from being logged? |
A: | This behavior is governed by the log settings for RESTlet, which is used by OpenAM for OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0. Use log configuration settings to turn off logging from RESTlet. For example, if your container is Apache Tomcat (Tomcat), follow these steps:
|
Q: | I have session failover configured for an OpenAM site. I see many
connections in |
A: | When you have session failover configured for a site, OpenAM servers run health checks against other servers in the same site. By default, the health checks are run every second (1000 milliseconds) with a timeout of 1 second (1000 milliseconds). If there is network latency between servers in a site, for example, if you are running your servers in virtual machines, the default settings might not be right for your deployment. In that case, consider changing the following advanced server properties:
To set advanced properties, either use the OpenAM console page under Configure > Server Defaults > Advanced, or set the properties using the ssoadm update-server-cfg command as in the following example, which updates the default server configuration: $ ./ssoadm \ update-server-cfg \ --servername default \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/pwd.txt \ --attributevalues com.iplanet.am.session.failover.cluster.stateCheck.timeout=2000 |
Q: | I want to change the password for the |
A: | To change the You can then change the password for the $ cd /path/to/SSOAdminTools/bin $ ./ssoadm \ set-identity-attrs \ --realm / \ --idname amService-UrlAccessAgent \ --idtype user \ --adminid amadmin \ --password-file /tmp/passwd \ --attributevalues userpassword=changeit Attribute values of identity, amService-UrlAccessAgent of type, user in realm, / was modified. The new password will take effect the next time you start OpenAM. |
Q: | How do I set the TCP connection timeout for outbound HTTP connections created by OpenAM? |
A: | The default connection timeout is 10 seconds (10000ms). You can
change the default timeout by setting the
On the OpenAM console, go to Configuration > Server & Sites > Server Instance > Advanced, and then set the property with a value representing the TCP connection timeout in milliseconds. |
- Access control
Control to grant or to deny access to a resource.
- Account lockout
The act of making an account temporarily or permanently inactive after successive authentication failures.
- Actions
Defined as part of policies, these verbs indicate what authorized subjects can do to resources.
- Advice
In the context of a policy decision denying access, a hint to the policy enforcement point about remedial action to take that could result in a decision allowing access.
- Agent administrator
User having privileges only to read and write policy agent profile configuration information, typically created to delegate policy agent profile creation to the user installing a policy agent.
- Agent authenticator
Entity with read-only access to multiple agent profiles defined in the same realm; allows an agent to read web service profiles.
- Application
In general terms, a service exposing protected resources.
In the context of OpenAM policies, the application is a template that constrains the policies that govern access to protected resources. An application can have zero or more policies.
- Application type
Application types act as templates for creating policy applications.
Application types define a preset list of actions and functional logic, such as policy lookup and resource comparator logic.
Application types also define the internal normalization, indexing logic, and comparator logic for applications.
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
Access control that is based on attributes of a user, such as how old a user is or whether the user is a paying customer.
- Authentication
The act of confirming the identity of a principal.
- Authentication chaining
A series of authentication modules configured together which a principal must negotiate as configured in order to authenticate successfully.
- Authentication level
Positive integer associated with an authentication module, usually used to require success with more stringent authentication measures when requesting resources requiring special protection.
- Authentication module
OpenAM authentication unit that handles one way of obtaining and verifying credentials.
- Authorization
The act of determining whether to grant or to deny a principal access to a resource.
- Authorization Server
In OAuth 2.0, issues access tokens to the client after authenticating a resource owner and confirming that the owner authorizes the client to access the protected resource. OpenAM can play this role in the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework.
- Auto-federation
Arrangement to federate a principal's identity automatically based on a common attribute value shared across the principal's profiles at different providers.
- Bulk federation
Batch job permanently federating user profiles between a service provider and an identity provider based on a list of matched user identifiers that exist on both providers.
- Circle of trust
Group of providers, including at least one identity provider, who have agreed to trust each other to participate in a SAML v2.0 provider federation.
- Client
In OAuth 2.0, requests protected web resources on behalf of the resource owner given the owner's authorization. OpenAM can play this role in the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework.
- Conditions
Defined as part of policies, these determine the circumstances under which which a policy applies.
Environmental conditions reflect circumstances like the client IP address, time of day, how the subject authenticated, or the authentication level achieved.
Subject conditions reflect characteristics of the subject like whether the subject authenticated, the identity of the subject, or claims in the subject's JWT.
- Configuration datastore
LDAP directory service holding OpenAM configuration data.
- Cross-domain single sign-on (CDSSO)
OpenAM capability allowing single sign-on across different DNS domains.
- Delegation
Granting users administrative privileges with OpenAM.
- Entitlement
Decision that defines which resource names can and cannot be accessed for a given subject in the context of a particular application, which actions are allowed and which are denied, and any related advice and attributes.
- Extended metadata
Federation configuration information specific to OpenAM.
- Extensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML)
Standard, XML-based access control policy language, including a processing model for making authorization decisions based on policies.
- Federation
Standardized means for aggregating identities, sharing authentication and authorization data information between trusted providers, and allowing principals to access services across different providers without authenticating repeatedly.
- Fedlet
Service provider application capable of participating in a circle of trust and allowing federation without installing all of OpenAM on the service provider side; OpenAM lets you create Java Fedlets.
- Hot swappable
Refers to configuration properties for which changes can take effect without restarting the container where OpenAM runs.
- Identity
Set of data that uniquely describes a person or a thing such as a device or an application.
- Identity federation
Linking of a principal's identity across multiple providers.
- Identity provider (IdP)
Entity that produces assertions about a principal (such as how and when a principal authenticated, or that the principal's profile has a specified attribute value).
- Identity repository
Data store holding user profiles and group information; different identity repositories can be defined for different realms.
- Java EE policy agent
Java web application installed in a web container that acts as a policy agent, filtering requests to other applications in the container with policies based on application resource URLs.
- Metadata
Federation configuration information for a provider.
- Policy
Set of rules that define who is granted access to a protected resource when, how, and under what conditions.
- Policy Agent
Agent that intercepts requests for resources, directs principals to OpenAM for authentication, and enforces policy decisions from OpenAM.
- Policy Administration Point (PAP)
Entity that manages and stores policy definitions.
- Policy Decision Point (PDP)
Entity that evaluates access rights and then issues authorization decisions.
- Policy Enforcement Point (PEP)
Entity that intercepts a request for a resource and then enforces policy decisions from a PDP.
- Policy Information Point (PIP)
Entity that provides extra information, such as user profile attributes that a PDP needs in order to make a decision.
- Principal
Represents an entity that has been authenticated (such as a user, a device, or an application), and thus is distinguished from other entities.
When a Subject successfully authenticates, OpenAM associates the Subject with the Principal.
- Privilege
In the context of delegated administration, a set of administrative tasks that can be performed by specified subjects in a given realm.
- Provider federation
Agreement among providers to participate in a circle of trust.
- Realm
OpenAM unit for organizing configuration and identity information.
Realms can be used for example when different parts of an organization have different applications and user data stores, and when different organizations use the same OpenAM deployment.
Administrators can delegate realm administration. The administrator assigns administrative privileges to users, allowing them to perform administrative tasks within the realm.
- Resource
Something a user can access over the network such as a web page.
Defined as part of policies, these can include wildcards in order to match multiple actual resources.
- Resource owner
In OAuth 2.0, entity who can authorize access to protected web resources, such as an end user.
- Resource server
In OAuth 2.0, server hosting protected web resources, capable of handling access tokens to respond to requests for such resources.
- Response attributes
Defined as part of policies, these allow OpenAM to return additional information in the form of "attributes" with the response to a policy decision.
- Role based access control (RBAC)
Access control that is based on whether a user has been granted a set of permissions (a role).
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
Standard, XML-based language for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers.
- Service provider (SP)
Entity that consumes assertions about a principal (and provides a service that the principal is trying to access).
- Session
The interval that starts with the user authenticating through OpenAM and ends when the user logs out, or when their session is terminated. For browser-based clients, OpenAM manages user sessions across one or more applications by setting a session cookie. See also Stateful session and Stateless session.
- Session failover (SFO)
Capability to allow another OpenAM server to manage a session when the OpenAM server that initially authenticated the principal goes offline.
- Session token
Unique identifier issued by OpenAM after successful authentication. For a Stateful session, the session token is used to track a principal's session.
- Single log out (SLO)
Capability allowing a principal to end a session once, thereby ending her session across multiple applications.
- Single sign-on (SSO)
Capability allowing a principal to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without authenticating again.
- Site
Group of OpenAM servers configured the same way, accessed through a load balancer layer.
The load balancer handles failover to provide service-level availability. Use sticky load balancing based on
amlbcookievalues to minimize cross-talk in the site.The load balancer can also be used to protect OpenAM services.
- Standard metadata
Standard federation configuration information that you can share with other access management software.
- Stateful session
An OpenAM session that resides in the OpenAM server's memory and, if session failover is enabled, is also persisted in the Core Token Service's token store. OpenAM tracks stateful sessions in order to handle events like logout and timeout, to permit session constraints, and to notify applications involved in SSO when a session ends.
- Stateless session
An OpenAM session for which state information is encoded in OpenAM and stored on the client. The information from the session is not retained in OpenAM's memory. For browser-based clients, OpenAM sets a cookie in the browser that contains the session information.
- Subject
Entity that requests access to a resource
When a subject successfully authenticates, OpenAM associates the subject with the Principal that distinguishes it from other subjects. A subject can be associated with multiple principals.
- User data store
Data storage service holding principals' profiles; underlying storage can be an LDAP directory service, a relational database, or a custom
IdRepoimplementation.- Web policy agent
Native library installed in a web server that acts as a policy agent with policies based on web page URLs.
This appendix includes ForgeRock definitions for product release levels and interface stability.
ForgeRock defines Major, Minor, Maintenance, and Patch product release levels. The release level is reflected in the version number. The release level tells you what sort of compatibility changes to expect.
| Release Label | Version Numbers | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Major |
Version: x[.0.0] (trailing 0s are optional) |
|
|
Minor |
Version: x.y[.0] (trailing 0s are optional) |
|
|
Maintenance, Patch |
Version: x.y.z[.p]
The optional |
|
ForgeRock products support many protocols, APIs, GUIs, and command-line interfaces. Some of these interfaces are standard and very stable. Others offer new functionality that is continuing to evolve.
ForgeRock acknowledges that you invest in these interfaces, and therefore must know when and how ForgeRock expects them to change. For that reason, ForgeRock defines interface stability labels and uses these definitions in ForgeRock products.
| Stability Label | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Stable |
This documented interface is expected to undergo backwards-compatible changes only for major releases. Changes may be announced at least one minor release before they take effect. |
|
Evolving |
This documented interface is continuing to evolve and so is expected to change, potentially in backwards-incompatible ways even in a minor release. Changes are documented at the time of product release. While new protocols and APIs are still in the process of standardization, they are Evolving. This applies for example to recent Internet-Draft implementations, and also to newly developed functionality. |
|
Deprecated |
This interface is deprecated and likely to be removed in a future release. For previously stable interfaces, the change was likely announced in a previous release. Deprecated interfaces will be removed from ForgeRock products. |
|
Removed |
This interface was deprecated in a previous release and has now been removed from the product. |
|
Technology Preview |
Technology previews provide access to new features that are evolving new technology that are not yet supported. Technology preview features may be functionally incomplete and the function as implemented is subject to change without notice. DO NOT DEPLOY A TECHNOLOGY PREVIEW INTO A PRODUCTION ENVIRONMENT. Customers are encouraged to test drive the technology preview features in a non-production environment and are welcome to make comments and suggestions about the features in the associated forums. ForgeRock does not guarantee that a technology preview feature will be present in future releases, the final complete version of the feature is liable to change between preview and the final version. Once a technology preview moves into the completed version, said feature will become part of the ForgeRock platform. Technology previews are provided on an “AS-IS” basis for evaluation purposes only and ForgeRock accepts no liability or obligations for the use thereof. |
|
Internal/Undocumented |
Internal and undocumented interfaces can change without notice. If you depend on one of these interfaces, contact ForgeRock support or email info@forgerock.com to discuss your needs. |
A
- Admin Console
- overview, OpenAM Web-Based Console
- Administration tools, Administration Interfaces and Tools
- Authentication
- authentication
- multi-factor, Multi-Factor Authentication
- passwordless, Creating Authentication Chains for Push Authentication
- push, About Push Authentication
- Authorization, About Authorization in OpenAM
C
- Caching, Caching in OpenAM
- Certificates
- Configuring Keystore Properties, Configuring Keystores in OpenAM
- Self-Signed Certificates , About Certificates in OpenAM
- SSL
- Keystores, Managing Certificates and Keystores
- To Encrypt Keystore and Key Alias Passwords, Configuring Keystores in OpenAM
- Change amadmin Password, Changing the amadmin User's Password
- command-line tools
- overview, OpenAM Command-Line Tools
- Cross-domain single sign-on (CDSSO), Configuring Cross-Domain Single Sign-On
D
- Dashboard Service, Configuring the Dashboard Service, Adding Applications to a User's Dashboard
- Data stores
- Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM), Hints for Configuring Active Directory Application Mode Data Stores
- Generic LDAPv3, Hints for Configuring Generic LDAPv3 Data Stores
- OpenDJ, Hints for Configuring OpenDJ Data Stores
- Oracle DSEE, Hints for Configuring Sun/Oracle DSEE Data Stores
- Tivoli Directory Server, Hints for Configuring Tivoli Directory Server Data Stores
- Debug logging
- Level, Setting Debug Logging Levels
- Rotation, Rotating Debug Logs
- Service selection, Debug Logging By Service
- Single file, Debug Logging to a Single File
- Delegating privileges, Delegating Realm Administration Privileges
E
- Enabling ssoadm.jsp, OpenAM ssoadm.jsp
F
- Federation, About SAML v2.0 SSO and Federation
- Changing signing key, Managing Key Aliases in OpenAM
- Configuring, Creating a Hosted Identity Provider, Creating a Hosted Service Provider, Configuring a Remote Identity Provider, Configuring a Remote Service Provider, Modifying an Identity Provider's Configuration, Modifying a Service Provider's Configuration, Modifying a Circle of Trust's Configuration, Configuring Google Apps as a Remote Service Provider, Configuring Salesforce CRM as a Remote Service Provider, Configuring OpenAM for the ECP Profile
- Linking accounts, Managing Federated Accounts
- SAML v1.x, Managing SAML v1.x Single Sign-On
- SAML v2.0 Single Logout (SLO), Implementing SAML v2.0 Single Sign-On and Single Logout
- SAML v2.0 Single Sign-On (SSO), Implementing SAML v2.0 Single Sign-On and Single Logout
G
- Google Apps, Configuring Google Apps as a Remote Service Provider
K
- Keystore, Configuring Keystores in OpenAM
L
- Logging
- Audit, Configuring Audit Logging
- Debug, Debug Logging
M
- Mobile Connect
- provider service
- configuring, Using OpenAM with Mobile Connect
- Monitoring, Monitoring Interfaces
- CTS, Monitoring CTS Tokens
- Health check, Is OpenAM Running?
- JMX, JMX Monitoring
- Policy evaluation, SNMP Monitoring for Policy Evaluation
- Sessions, SNMP Monitoring for Sessions
- SNMP, SNMP Monitoring
N
- Notifications
- Service configuration changes, Notification Settings
- Stateful session changes, Notification Settings
O
- OAuth 2.0
- Device flow, OAuth 2.0 Device Flow
- OAuth 2.0 clients
- configuring, Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients
- OpenAM Console Responsiveness, OpenAM Console Responsiveness
- OpenAM Console Search Feature, OpenAM Console Search Feature
- OpenID Connect
- provider service
- configuring, Configuring OpenAM As OpenID Connect Provider
- OpenID Connect 1.0, Managing OpenID Connect 1.0 Authorization
- configuring, Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients
- stateless
- OpenIG, OpenIG or Policy Agent?
P
- Performance, Tuning OpenAM
- Policies, OpenAM Resource Types, Policy Sets, and Policies
- Configuring, Managing UMA Policies
- Policy
- Configuring, Configuring Policies Using the OpenAM Console
- Delegating management, Delegating Policy Management
- Import, Export, Importing and Exporting Policies
- policy agent
- profiles, Types of Agent
- types of, Types of Agent
- policy agent profiles
- agent administrators
- creating, Delegating Agent Profile Creation
- creating, Creating Agent Profiles
- delegating creation of, Delegating Agent Profile Creation
- policy agent properties
- web policy agents
- creating, Configuring Web Policy Agent Properties
- Policy agents
- Configuring, Configuring Java EE Policy Agents, Configuring Version 2.2 Policy Agents, Configuring Agent Authenticators
- Group inheritance, Creating Agent Profiles
- OAuth 2.0 clients
- configuring, Configuring OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect 1.0 Clients
- profiles, Configuring Policy Agent Profiles
- Policy Sets, OpenAM Resource Types, Policy Sets, and Policies
- Configuring, Configuring Policy Sets Using the OpenAM Console
R
- RADIUS
- authentication module, RADIUS Authentication Module
- OpenAM as a RADIUS server, Configuring OpenAM as a RADIUS Server
- Protocol, The RADIUS Protocol
- RADIUS Server service, RADIUS Server Service
- sample client, Running the Sample RADIUS Client
- server configuration, Configuring the RADIUS Server Service
- server limitations, RADIUS Server Limitations
- server troubleshooting, Troubleshooting the RADIUS Server Service
- Realms, Configuring Realms
- Resource Types, OpenAM Resource Types, Policy Sets, and Policies
- REST API, Configuring REST APIs
- Restore, Backing Up and Restoring OpenAM Configurations
- Restoring, Backing Up and Restoring OpenAM Configurations
S
- Salesforce CRM, Configuring Salesforce CRM as a Remote Service Provider
- SAML v1.x, Managing SAML v1.x Single Sign-On
- Scripts
- Managing, Managing Scripts
- Securing OpenAM, Securing OpenAM
- Session state
- and cross-domain single sign-on, Configuring Cross-Domain Single Sign-On
- and SAML 1.x, Managing SAML v1.x Single Sign-On
- iPlanetDirectoryPro cookie, Potential Problems
- Sessions, Session Management
- Silent installation, OpenAM Command-Line Tools
- Single Sign-On (SSO), Configuring Single Sign-On Within One Domain
- SOAP STS agents
- Configuring, Configuring SOAP STS Agents
- ssoadm.jsp
- enabling, OpenAM ssoadm.jsp
T
- Troubleshooting, Troubleshooting
U
- UMA, Managing UMA Authorization, Managing UMA Policies
- User Self-Service, Configuring User Self-Service Features
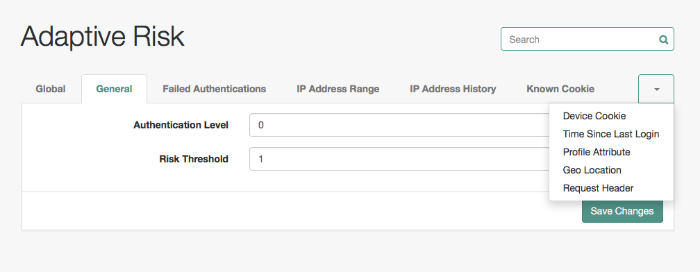
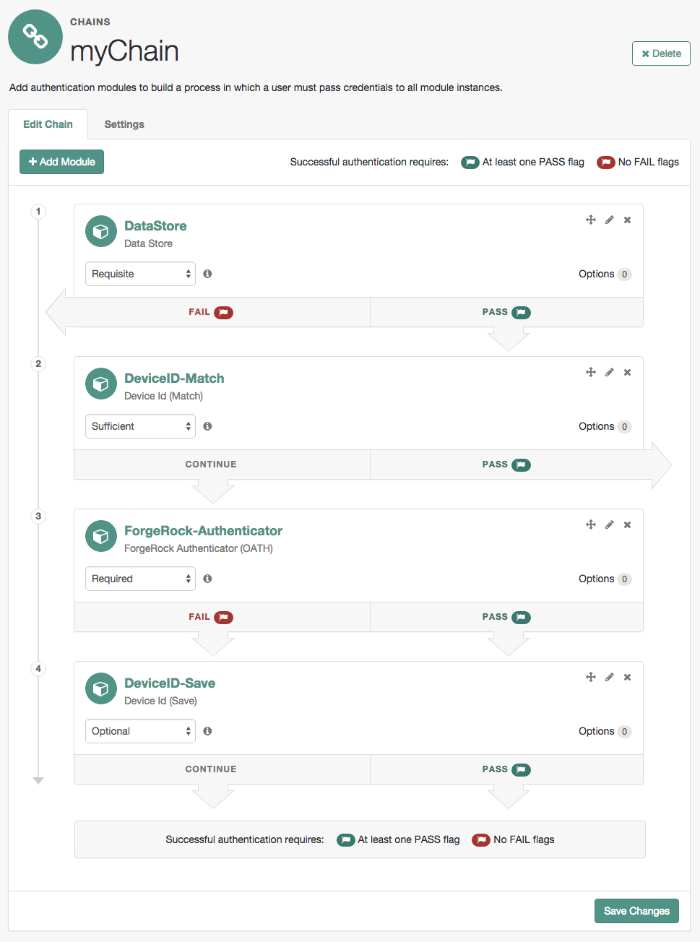
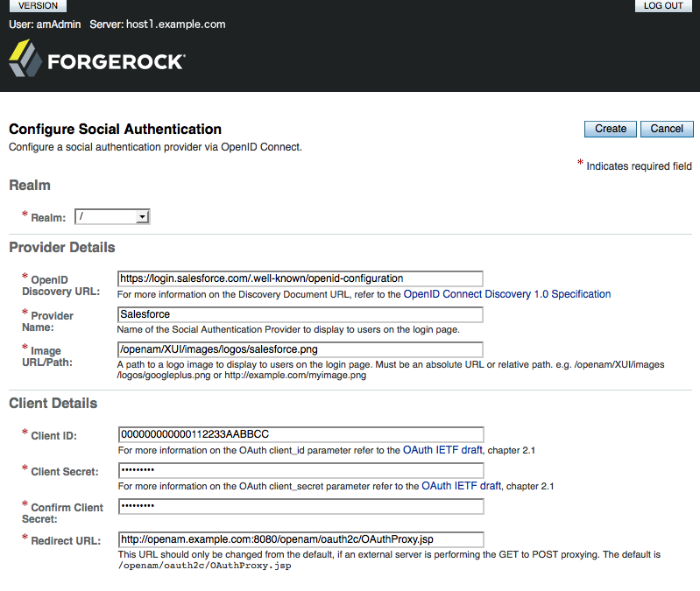
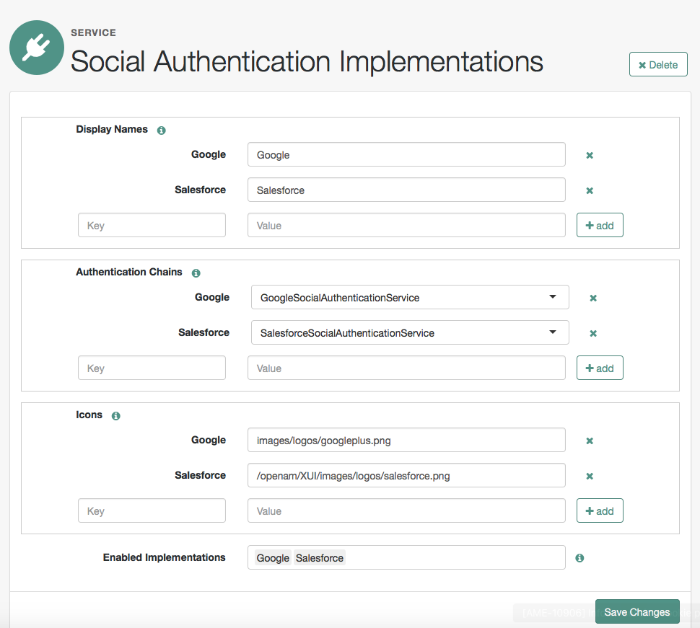
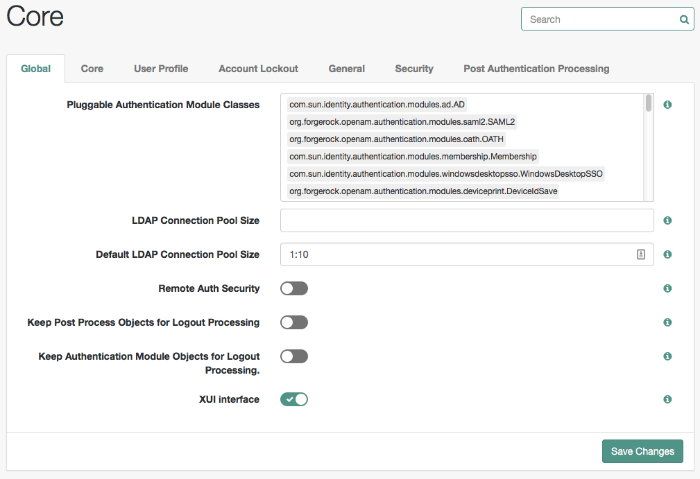
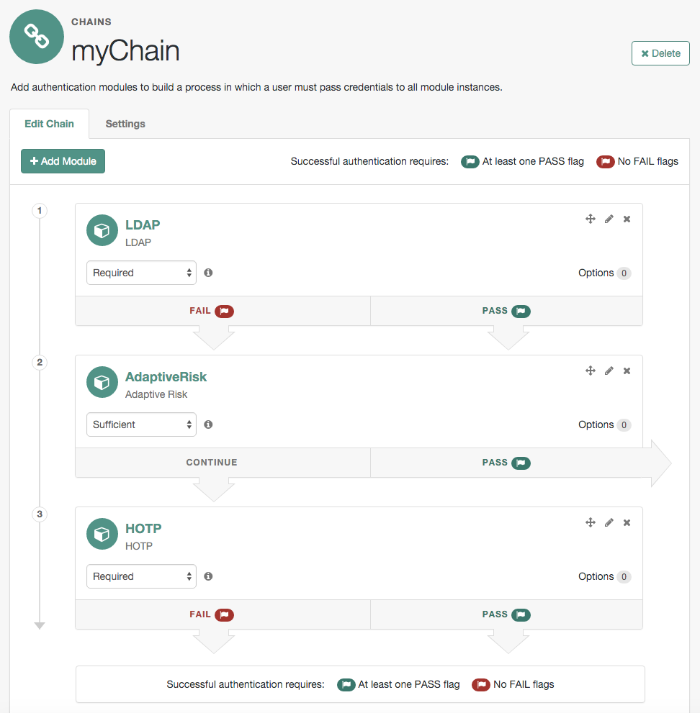
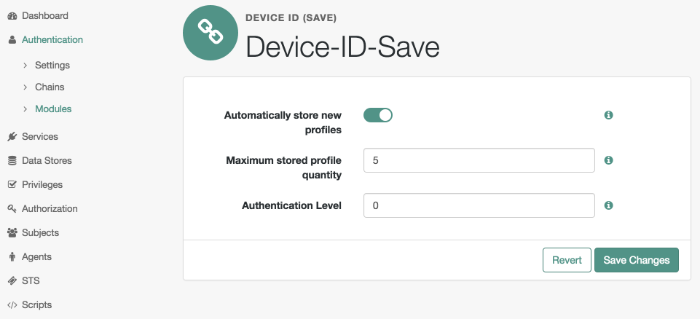
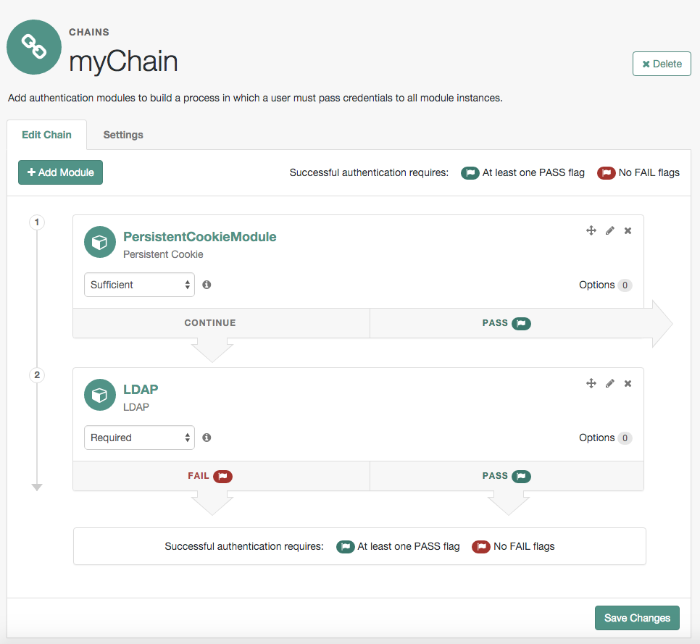
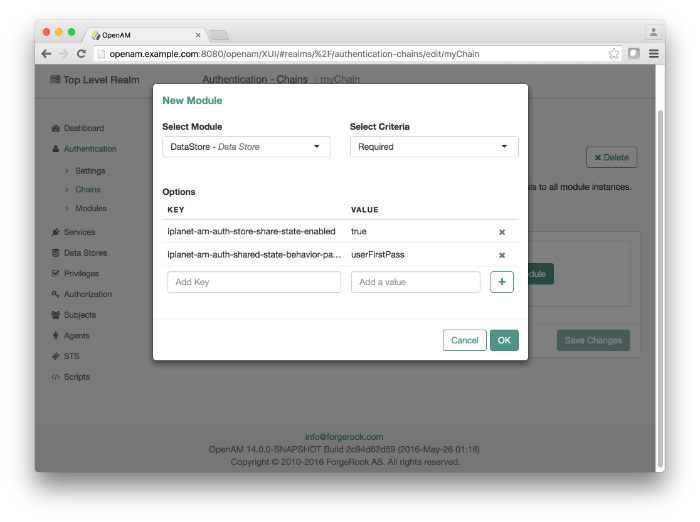
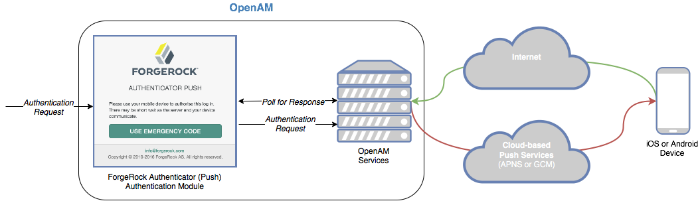

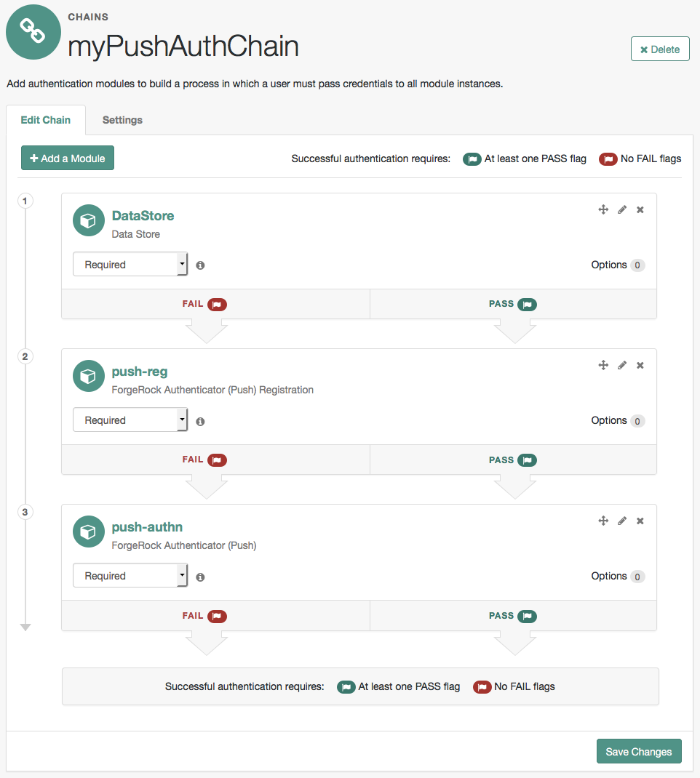
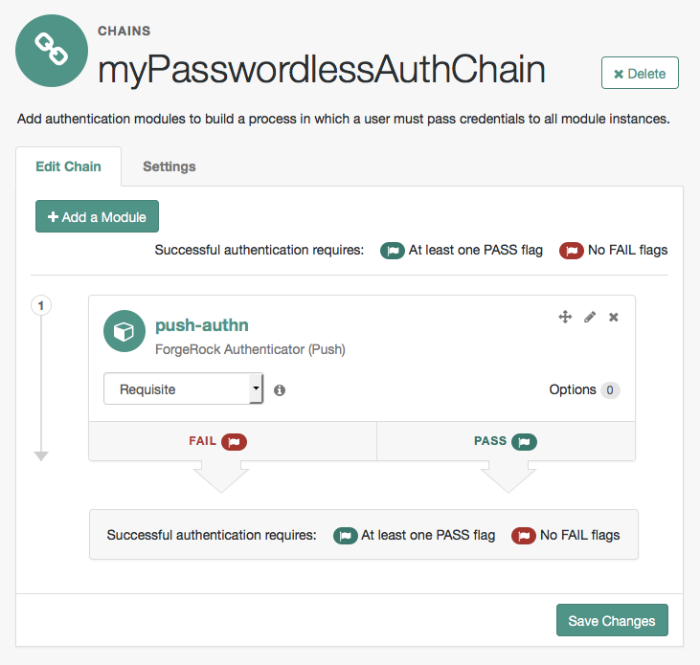
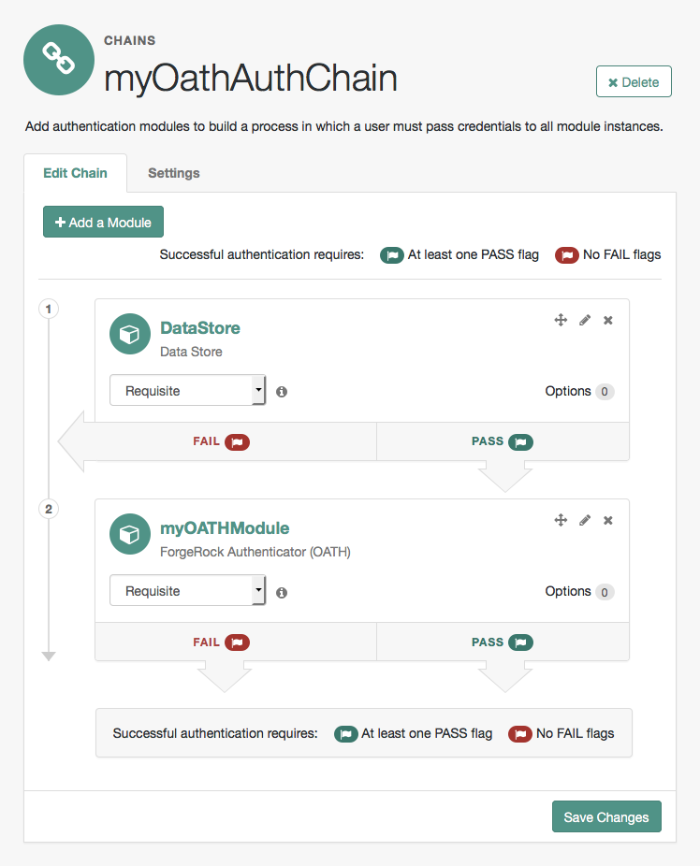



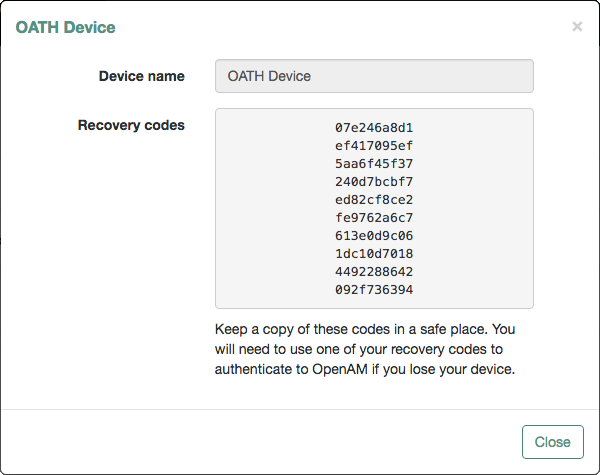
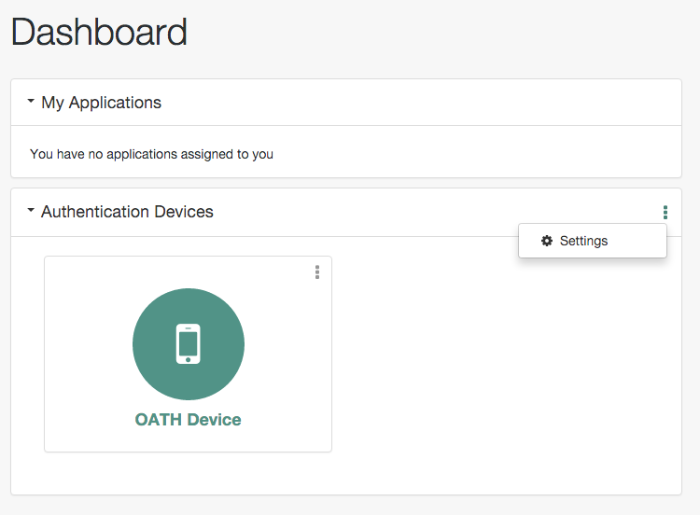
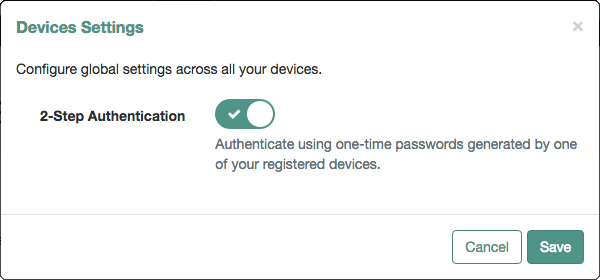
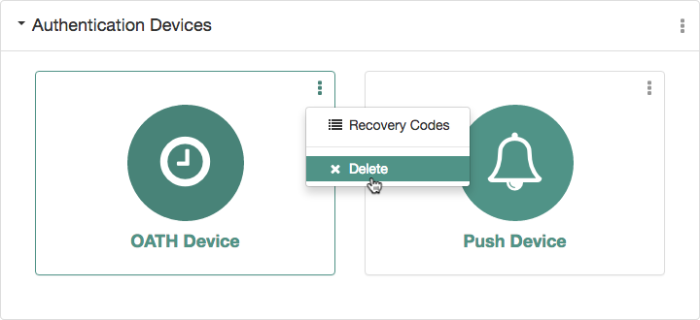



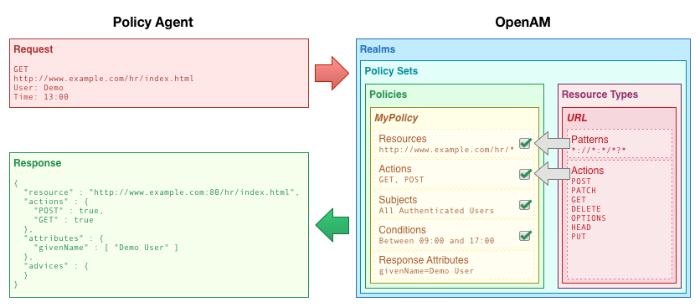
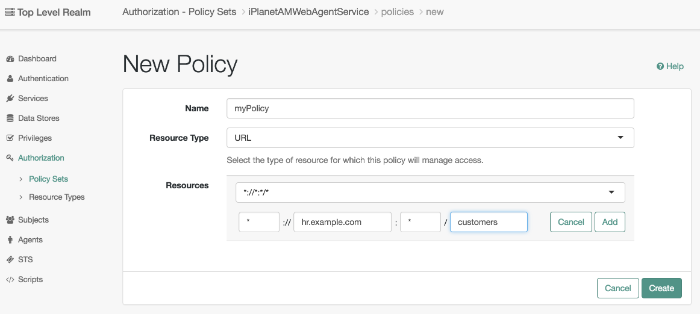
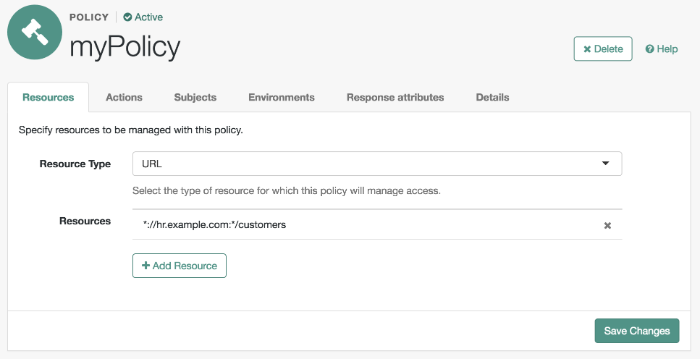

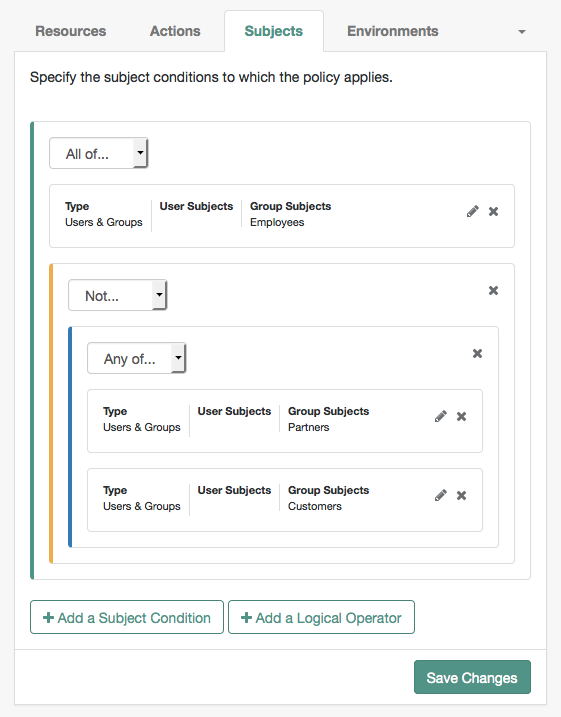
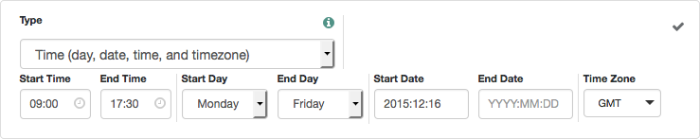
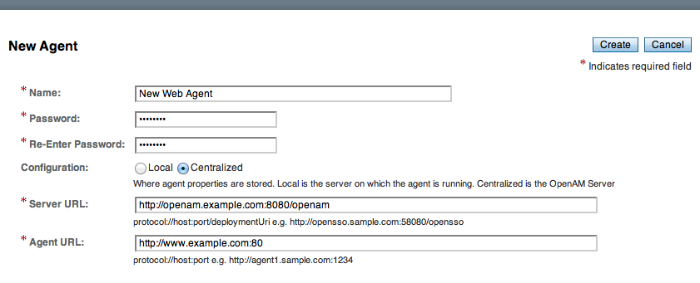
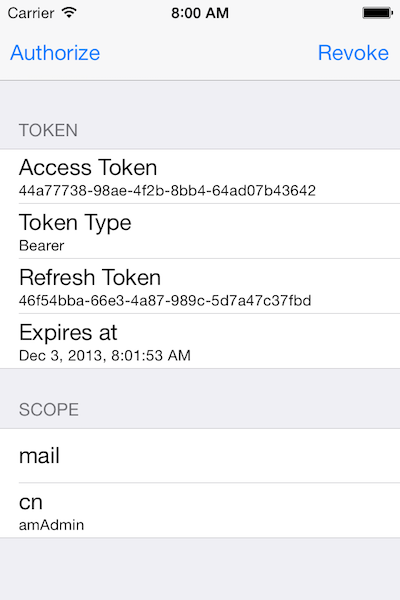
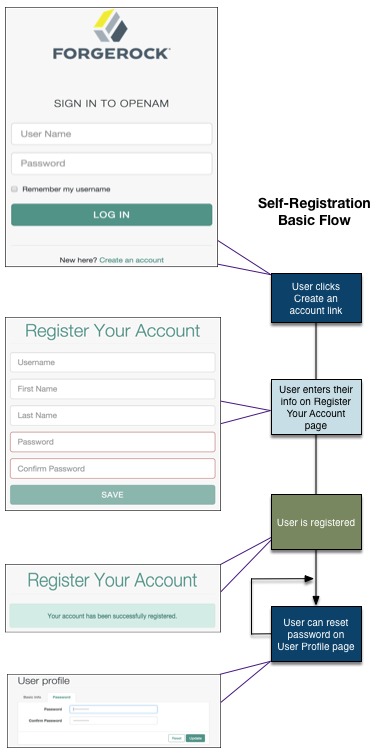
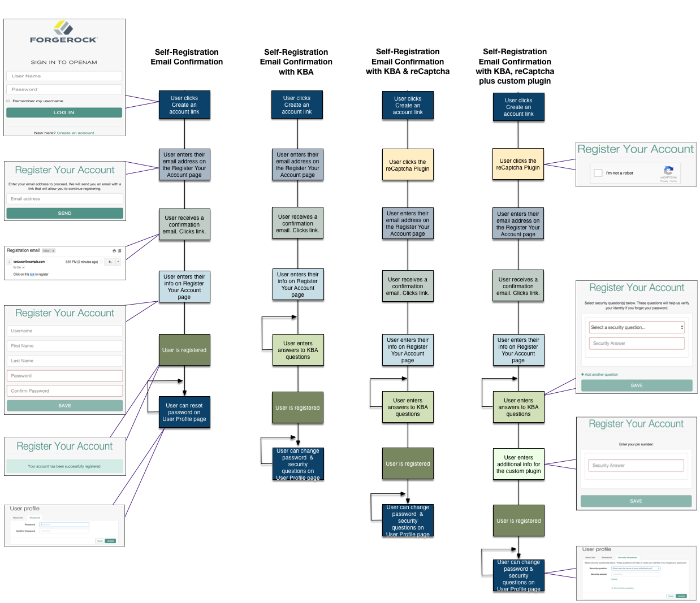
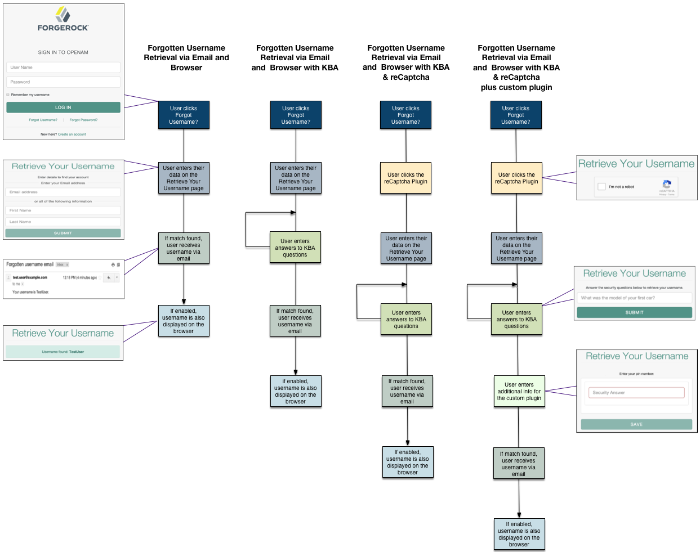
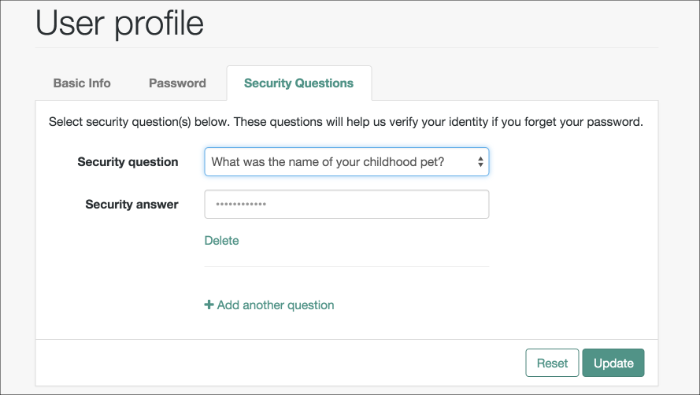
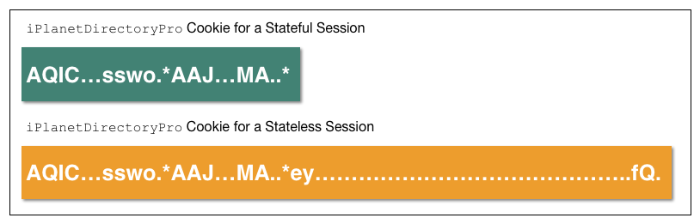
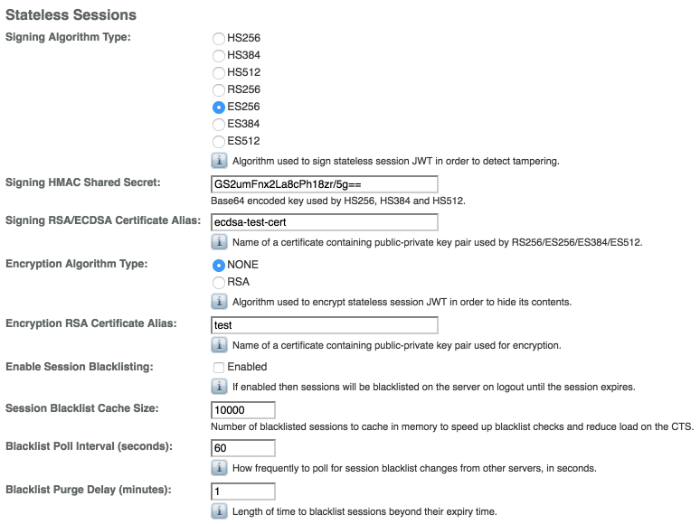
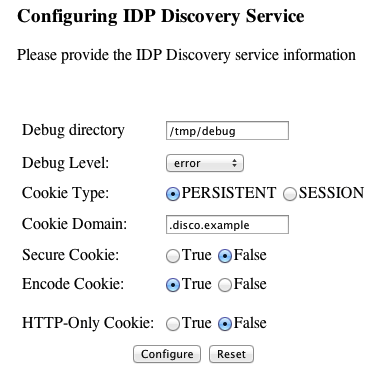
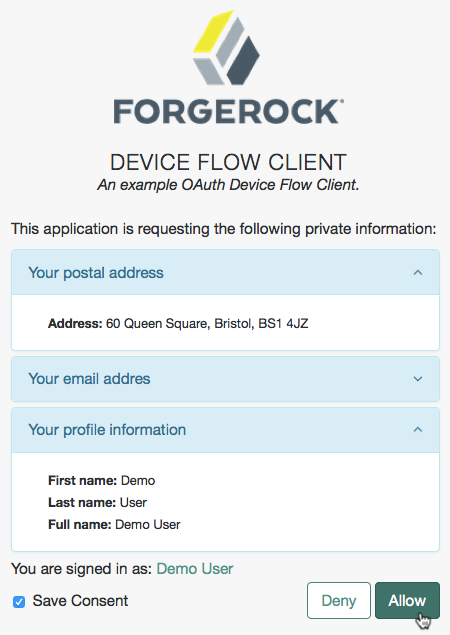


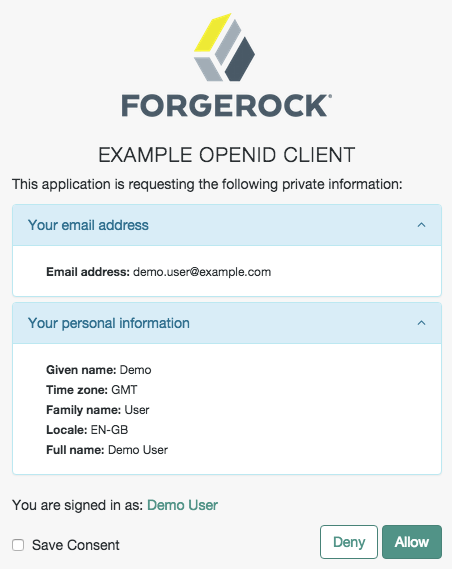


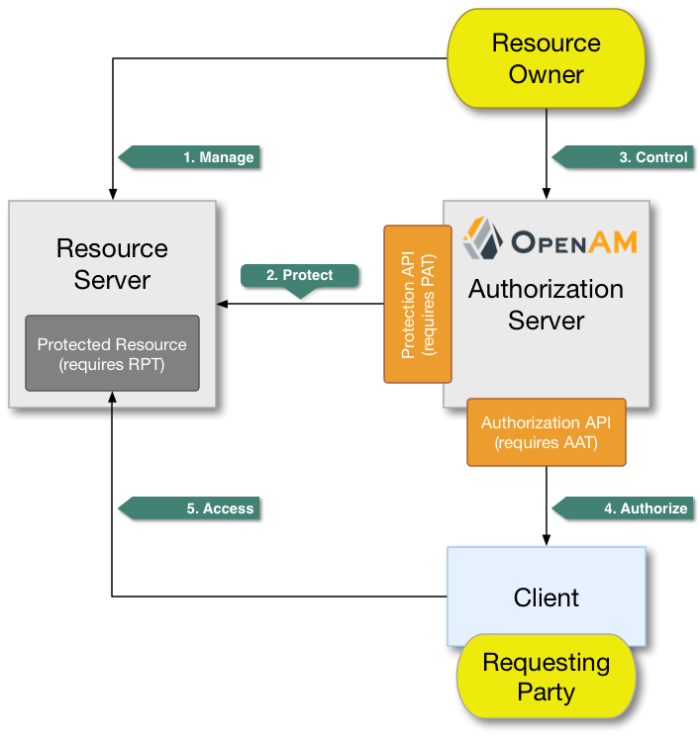
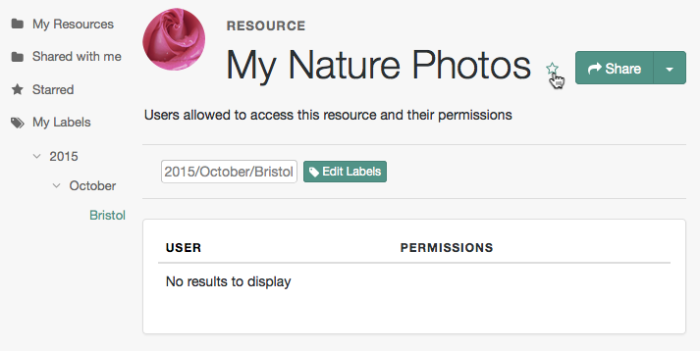


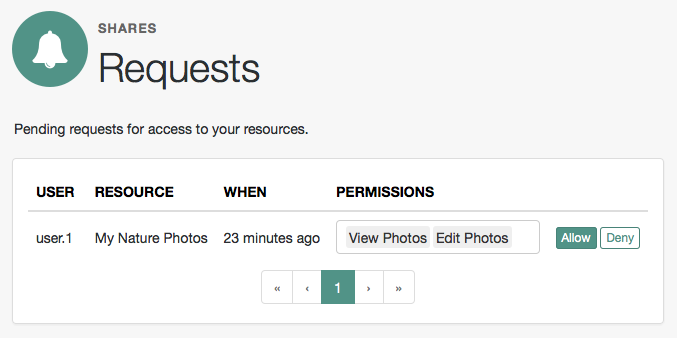
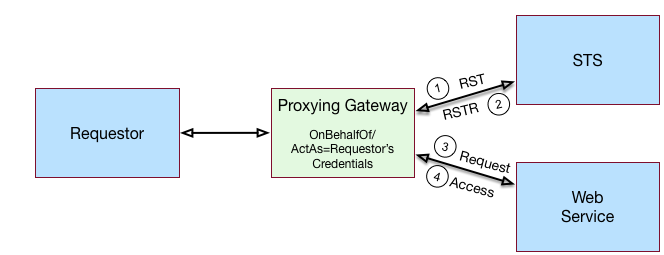
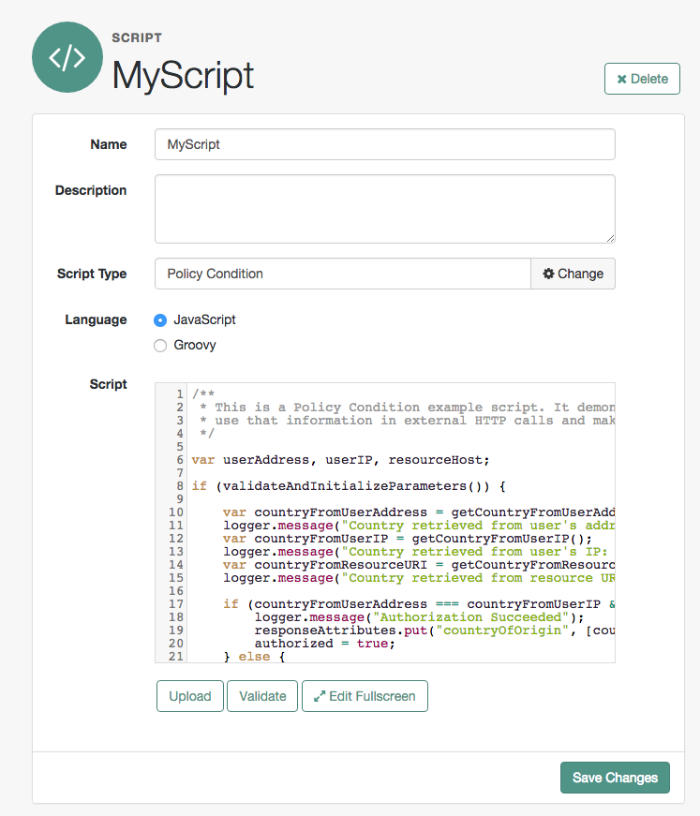
2.3.1. Configuring Pre-Populated Social Authentication Providers
OpenAM provides wizards to quickly enable authentication with Facebook, Google, and Microsoft. Most settings are pre-populated, only a Client ID and Client Secret are required.
To obtain a Client ID and Client Secret you should register an application with the third party provider, at the following links:
Facebook App Quickstart
Google Developers Console
Note
You must enable the Google+ API in order to authenticate with Google. To enable the Google+ API, login to the Google Developers Console, select your project, navigate to APIs and auth > APIs, and then set the status of the
Google+ APItoON.Microsoft account Developer Center
Once you have registered an application and obtained credentials from the social authentication provider, follow the steps below to configure authentication with the provider:
Select Realms > Realm Name > Dashboard > Configure Social Authentication, and then click the link for the social authentication provider you want to configure—Configure Facebook Authentication, Configure Google Authentication, or Configure Microsoft Authentication.
On the configure third party authentication page:
Select the realm in which to enable social authentication.
Enter the Client ID obtained from the third party authentication provider.
Enter the Client Secret obtained from the third party authentication provider, and repeat it in the
Confirm Client Secretfield.Leave the default
Redirect URL, unless you are using an external server as a proxy.Click
Create.On completion, the wizard displays a message confirming the successful creation of a new authentication module and an authentication chain for the provider, and either the creation of a new Social Authentication Implementations service named
socialAuthNService, or an update if it already existed.You can configure the authentication module, authentication chain, and Social Authentication Implementations service that you created by using the wizards in the same way as manually created versions. For more information, see "Configuring Authentication Modules", "Configuring Authentication Chains", and "Configuring the Social Authentication Implementations Service".