Installation and configuration reference for the connectors that are supported with ForgeRock® Identity Management software. This reference includes installation and configuration instructions for each connector, and examples that demonstrate how to use the connectors in a deployment.
ForgeRock Identity Platform™ serves as the basis for our simple and comprehensive Identity and Access Management solution. We help our customers deepen their relationships with their customers, and improve the productivity and connectivity of their employees and partners. For more information about ForgeRock and about the platform, see https://www.forgerock.com.
This guide describes the OpenICF connectors that are supported in a deployment of ForgeRock Identity Management. The guide focuses on getting the connectors installed and configured with ForgeRock Identity Management software.
This guide does not describe all OpenICF connectors. Additional connectors are available from ForgeRock's BackStage site.
This guide is written for anyone using supported OpenICF connectors with ForgeRock Identity Management software.
You do not need to have a complete understanding of ForgeRock Identity Management to learn something from this guide, although a background in identity management and maintaining web application software can help. You do need some background in managing services on your operating systems and in your application servers. You can nevertheless get started with this guide, and learn more as you go along.
Most examples in the documentation are created in GNU/Linux or Mac OS X
operating environments.
If distinctions are necessary between operating environments,
examples are labeled with the operating environment name in parentheses.
To avoid repetition file system directory names are often given
only in UNIX format as in /path/to/server,
even if the text applies to C:\path\to\server as well.
Absolute path names usually begin with the placeholder
/path/to/.
This path might translate to /opt/,
C:\Program Files\, or somewhere else on your system.
Command-line, terminal sessions are formatted as follows:
$ echo $JAVA_HOME /path/to/jdk
Command output is sometimes formatted for narrower, more readable output even though formatting parameters are not shown in the command.
Program listings are formatted as follows:
class Test {
public static void main(String [] args) {
System.out.println("This is a program listing.");
}
}ForgeRock publishes comprehensive documentation online:
The ForgeRock Knowledge Base offers a large and increasing number of up-to-date, practical articles that help you deploy and manage ForgeRock software.
While many articles are visible to community members, ForgeRock customers have access to much more, including advanced information for customers using ForgeRock software in a mission-critical capacity.
ForgeRock product documentation, such as this document, aims to be technically accurate and complete with respect to the software documented. It is visible to everyone and covers all product features and examples of how to use them.
The ForgeRock.org site has links to source code for ForgeRock open source software, as well as links to the ForgeRock forums and technical blogs.
If you are a ForgeRock customer, raise a support ticket instead of using the forums. ForgeRock support professionals will get in touch to help you.
This chapter provides a high-level overview of the supported connectors.
For instructions on building connector configurations interactively, see "Configuring Connectors" in the Integrator's Guide.
- Generic LDAP Connector
The generic LDAP connector is based on JNDI, and can be used to connect to any LDAPv3-compliant directory server, such as ForgeRock Directory Services (DS), Active Directory, SunDS, Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition, IBM Security Directory Server, and OpenLDAP.
For information about installing and configuring the LDAP connector, see "Generic LDAP Connector".
- CSV File Connector
The CSV file connector is useful when importing users, either for initial provisioning or for ongoing updates. When used continuously in production, a CSV file serves as a change log, often containing only user records that have changed.
For information about installing and configuring the CSV file connector, see "CSV File Connector".
- Database Table Connector
The Database Table connector enables provisioning to a single table in a JDBC database.
For information about installing and configuring the Database Table connector, see "Database Table Connector".
- PowerShell Connector
The scripted PowerShell Connector toolkit allows you to create a connector customized to communicate with Microsoft systems such as Azure AD and Active Directory.
For information about installing and configuring the PowerShell connector, see "PowerShell Connector Toolkit".
- Groovy Connector
The scripted Groovy Connector toolkit enables you to run a Groovy script for any OpenICF operation, such as search, update, create, and others, on any external resource.
For information about installing and configuring the Groovy connector, see "Groovy Connector Toolkit".
- SAP Connector
The SAP connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector Toolkit that connects to any SAP system using the SAP JCo Java libraries.
For information about installing and configuring the SAP connector, see "SAP Connector".
- Google Apps Connector
The Google Apps connector enables you to interact with Google's web applications.
For information about installing and configuring the Google Apps connector, see "Google Apps Connector".
- Kerberos Connector
The Kerberos connector is an implementation of the SSH connector, and is based on Java Secure Channel (JSch) and the Java implementation of the Expect library (Expect4j). This connector enables you to manage Kerberos user principals from IDM.
For information about installing and configuring the Kerberos connector, see "Kerberos Connector".
- Salesforce Connector
The Salesforce connector enables provisioning, reconciliation, and synchronization between Salesforce and the IDM repository.
For information about installing and configuring the Salesforce connector, see "Salesforce Connector".
- Marketo Connector
The Marketo connector enables synchronization between IDM managed users and a Marketo Lead Database.
For information about installing and configuring the Marketo connector, see "Marketo Connector".
- Active Directory Connector
The Active Directory connector is a legacy connector, written in C# for the .NET platform.
For information about installing and configuring the Active Directory connector, see "Active Directory Connector".
- Office 365 Connector
The Office 365 connector uses the O365 Graph API to manage Azure AD users and groups. This connector uses the OData 3.0 specification and can be used, with minor modifications, to connect to any OData 3 provider.
For information about installing and configuring the Office 365 connector, see "Office 365 Connector".
- SCIM Connector
The SCIM connector is based on the Simple Cloud Identity Management (SCIM) protocol and enables you to manage user and group accounts on any SCIM-compliant resource provider, such as Slack, Facebook or SalesForce.
For information about installing and configuring the SCIM connector, see "SCIM Connector".
- Adobe Campaign Manager Connector
The Adobe Campaign Manager connector enables you to manage profiles in an Adobe Campaign data store.
For information about installing and configuring the Adobe Campaign Manager connector, see "Adobe Campaign Manager Connector".
The generic LDAP connector is based on JNDI, and can be used to connect to any LDAPv3-compliant directory server, such as ForgeRock Directory Services (DS), Active Directory, SunDS, Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition, IBM Security Directory Server, and OpenLDAP.
OpenICF provides a legacy Active Directory (AD) .NET connector. Note, however, that the AD Connector is deprecated and support for its use with IDM will be discontinued in a future release. For simple Active Directory (and Active Directory LDS) deployments, the generic LDAP Connector works better than the Active Directory connector, in most circumstances. Using the generic LDAP connector avoids the need to install a remote connector server in the overall deployment. In addition, the generic LDAP connector has significant performance advantages over the Active Directory connector. For more complex Active Directory deployments, use the PowerShell Connector Toolkit, as described in "PowerShell Connector Toolkit".
IDM bundles version 1.4.6.0 of the LDAP connector.
Three sample LDAP connector configurations are provided in the
path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/
directory:
provisioner.openicf-opendjldap.jsonprovides a sample LDAP connector configuration for a ForgeRock Directory Services (DS) server.provisioner.openicf-adldap.jsonprovides a sample LDAP connector configuration for an Active Directory server.provisioner.openicf-adldsldap.jsonprovides a sample LDAP connector configuration for an Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) server.
You should be able to adapt one of these sample configurations for any LDAPv3-compliant server.
The connectorRef configuration property provides
information about the LDAP connector bundle, and is the same in all three
sample LDAP connector configurations:
{
"connectorRef": {
"connectorHostRef": "#LOCAL",
"connectorName": "org.identityconnectors.ldap.LdapConnector",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.ldap-connector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.4.0.0,2.0.0.0)"
}
}
The connectorHostRef property is optional, if you use the
connector .jar provided in openidm/connectors, and you
use a local connector server.
The following excerpt shows the configuration properties in the sample LDAP connector for DS. These properties are described in detail later in this section. For additional information on the properties that affect synchronization, see "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes". For a complete list of the configuration properties for the LDAP connector, see "LDAP Connector Configuration":
"configurationProperties" : {
"host" : "localhost",
"port" : 1389,
"ssl" : false,
"startTLS" : false,
"privateKeyAlias" : null,
"alternateKeyStore" : null,
"alternateKeyStoreType" : null,
"alternateKeyStorePassword" " null,
"principal" : "cn=Directory Manager",
"credentials" : "password",
"baseContexts" : [
"dc=example,dc=com"
],
"baseContextsToSynchronize" : [
"dc=example,dc=com"
],
"accountSearchFilter" : null,
"accountSynchronizationFilter" : null,
"groupSearchFilter" : null,
"groupSynchronizationFilter" : null,
"passwordAttributeToSynchronize" : null,
"synchronizePasswords" : false,
"removeLogEntryObjectClassFromFilter" : true,
"modifiersNamesToFilterOut" : [ ],
"passwordDecryptionKey" : null,
"changeLogBlockSize" : 100,
"attributesToSynchronize" : [ ],
"changeNumberAttribute" : "changeNumber",
"passwordDecryptionInitializationVector" : null,
"filterWithOrInsteadOfAnd" : false,
"objectClassesToSynchronize" : [
"inetOrgPerson"
],
"vlvSortAttribute" : "uid",
"passwordAttribute" : "userPassword",
"useBlocks" : false,
"maintainPosixGroupMembership" : false,
"failover" : [ ],
"readSchema" : true,
"accountObjectClasses" : [
"top",
"person",
"organizationalPerson",
"inetOrgPerson"
],
"accountUserNameAttributes" : [
"uid"
],
"groupMemberAttribute" : "uniqueMember",
"passwordHashAlgorithm" : null,
"usePagedResultControl" : true,
"blockSize" : 100,
"uidAttribute" : "entryUUID",
"maintainLdapGroupMembership" : false,
"respectResourcePasswordPolicyChangeAfterReset" : false
},hostThe host name or IP address of the server on which the LDAP instance is running.
portThe port on which the LDAP server listens for LDAP requests. The sample configuration specifies a default port of 1389.
sslIf
true, the specified port listens for LDAPS connections.For instructions on using the LDAP connector over SSL, see "Configuring the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS".
startTLSSpecifies whether to use the startTLS operation to initiate a TLS/SSL session. To use startTLS, set
"startTLS":true,and"ssl":false. Your connection should use the insecure LDAP port (typically389or1389for a DS server).Specify the certificates that should be used for authentication, as described in "Configuring the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS".
principalThe bind DN that is used to connect to the LDAP server.
credentialsThe password of the
principalthat is used to connect to the LDAP server.baseContextsOne or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used when searching the tree. Searches are performed when discovering users from the LDAP server or when looking for the groups of which a user is a member. During reconciliation operations, IDM searches through the base contexts listed in this property for changes. (See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes").
baseContextsToSynchronizeOne or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used to determine if a change should be synchronized. During liveSync operations, IDM searches through the base contexts listed in this property for changes. If no value is specified here, the values in listed in the
baseContextsproperty are used. (See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes").accountSynchronizationFilterUsed during synchronization actions to filter out LDAP accounts. (See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes").
accountObjectClassesThis property lists all the object classes that represent an account. If this property has multiple values, an
ANDfilter is used to determine the affected entries. For example, if the value of this property is["organizationalPerson", "inetOrgPerson"], any entry with the object classorganizationalPersonAND the object classinetOrgPersonis considered as an account entry. You can override the value of this property by specifying the user object classes during the create operation.If no object class is specified when you create a user, this property is used as the default list of object classes for the new entry.
accountSearchFilterSearch filter that user accounts must match. (See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes").
accountUserNameAttributesAttributes holding the account's user name. Used during authentication to find the LDAP entry matching the user name.
attributesToSynchronizeList of attributes used during object synchronization. IDM ignores change log updates that do not include any of the specified attributes. If empty, IDM considers all changes. (See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes").
blockSizeBlock size for simple paged results and VLV index searches, reflecting the maximum number of entries retrieved at any one time.
changeLogBlockSizeBlock size used when fetching change log entries.
changeNumberAttributeChange log attribute containing the last change number.
failoverLDAP URLs specifying alternative LDAP servers to connect to if IDM cannot connect to the primary LDAP server specified in the
hostandportproperties.filterWithOrInsteadOfAndIn most cases, the filter to fetch change log entries is AND-based. If this property is set, the filter ORs the required change numbers instead.
groupMemberAttributeLDAP attribute holding members for non-POSIX static groups.
groupSearchFilterSearch filter that group entries must match.
maintainLdapGroupMembershipIf
true, IDM modifies group membership when entries are renamed or deleted.In the sample LDAP connector configuration file provided with IDM, this property is set to
false. This means that LDAP group membership is not modified when entries are renamed or deleted in IDM. To ensure that entries are removed from LDAP groups when the entries are deleted, set this property totrueor enable referential integrity on the LDAP server. For information about configuring referential integrity in DS, see Configuring Referential Integrity in the Developer's Guide for ForgeRock Directory Services.maintainPosixGroupMembershipIf
true, IDM modifies POSIX group membership when entries are renamed or deleted.modifiersNamesToFilterOutUse this property to avoid loops caused by changes made to managed user objects being synchronized. For more information, see "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes".
objectClassesToSynchronizeIDM synchronizes only entries that have these object classes. See also "Controlling What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes".
passwordAttributeAttribute to which IDM writes the predefined
PASSWORDattribute.passwordAttributeToSynchronizeIDM synchronizes password values on this attribute.
passwordDecryptionInitializationVectorThis is a legacy attribute, and its value should remain set to
null. To configure password synchronization between an LDAP server and IDM, use one of the password synchronization plugins, described in the Password Synchronization Plugin Guide.passwordDecryptionKeyThis is a legacy attribute, and its value should remain set to
null. To configure password synchronization between an LDAP server and IDM, use one of the password synchronization plugins, described in the Password Synchronization Plugin Guide.passwordHashAlgorithmHash password values with the specified algorithm, if the LDAP server stores them in clear text.
The hash algorithm can be one of the following:
NONE- Clear textWIN-AD- Used for password changes to Active DirectorySHA- Secure Hash AlgorithmSHA-1- A 160-bit hash algorithm that resembles the MD5 algorithmSSHA- Salted SHAMD5- A 128-bit message-digest algorithmSMD5- Salted MD5
readSchemaIf
true, read the schema from the LDAP server.This property is used only during the connector setup, to generate the object types.
If this property is
false, the LDAP connector provides a basic default schema that can manage LDAP users and groups. The default schema mapsinetOrgPersonto the OpenICF__ACCOUNT__property, andgroupOfUniqueNamesto the OpenICF__GROUP__property. The following LDAP object classes are also included in the default schema:organizationorganizationalUnitpersonorganizationalPersonaccountgroupOfNamesremoveLogEntryObjectClassFromFilterIf
true, the filter to fetch change log entries does not contain thechangeLogEntryobject class, and IDM expects no entries with other object types in the change log. The default setting istrue.respectResourcePasswordPolicyChangeAfterResetIf
true, bind with the Password Expired and Password Policy controls, and throwPasswordExpiredExceptionand other exceptions appropriately.synchronizePasswordsThis is a legacy attribute, and its value should remain set to
false. To configure password synchronization between an LDAP server and IDM, use one of the password synchronization plugins, described in the Password Synchronization Plugin Guide.uidAttributeSpecifies the LDAP attribute that should be used as the immutable ID for the entry. For a DS resource, you should use the
entryUUID. Although you can use a DN (or any unique attribute) for the_id, as a best practice, you should use an attribute that is both unique and immutable, such as theentryUUID.useBlocksIf
useBlocksisfalse, no pagination is used. IfuseBlocksistrue, the connector uses block-based LDAP controls, either the simple paged results control, or the virtual list view control, depending on the setting of theusePagedResultControlproperty.usePagedResultControlTaken into account only if
useBlocksistrue. IfusePagedResultControlisfalse, the connector uses the virtual list view (VLV) control, if it is available. IfusePagedResultControlistrue, the connector uses the simple paged results control for search operations.useTimestampsForSyncIf
true, use timestamps for liveSync operations, instead of the change log.By default, the LDAP connector has a change log strategy for LDAP servers that support a change log, such as ForgeRock Directory Services (DS) and Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition. If the LDAP server does not support a change log, or if the change log is disabled, liveSync for create and modify operations can still occur, based on the timestamps of modifications.
vlvSortAttributeAttribute used as the sort key for virtual list view.
sendCAUDTxIdIf
true, propagate the Common Audit Transaction ID to a DS server.
To use the LDAP connector over SSL, update your connector configuration file as follows:
For a connection over SSL, set the
sslproperty totrueand set theportto a secure port, for example,636.To initiate a connection using startTLS, set
"startTLS":true,and"ssl":false. Set theportto an insecure LDAP port, for example,389.If you are using a CA-signed server certificate, add that certificate to the IDM truststore, for example:
$ cd /path/to/openidm/security $ keytool \ -importcert \ -alias server-cert \ -keystore truststore \ -storepass changeit \ -file /path/to/server-cert.crt
Specify the certificate that the LDAP connector will use to authenticate to the remote LDAP server.
By default, the LDAP connector uses the self-signed certificate that is generated in the IDM keystore when IDM first starts up. You have two options to change this default behavior:
Set the
privateKeyAliasto the alias of a certificate in the IDM keystore. The alias name is case-sensitive.If you set
privateKeyAliastonull, no private key is sent during the SSL handshake, so only the server certificate is used. You must import the server certificate into the IDM truststore, as shown in the previous step.If
privateKeyAliasis set to an alias within the IDM keystore, the connector uses that private key for SSL mutual authentication.Specify a different keystore for the connector.
If you do not want to use the default IDM keystore, set the following properties:
alternateKeyStore- specifies the full path to an alternate keystore.alternateKeyStoreType- specifies alternate keystore type. Valid values areJKS,JCEKSandPKCS12.alternateKeyStorePassword- specifies password for the alternate keystore.
To control the set of LDAP entries that are affected by reconciliation and automatic synchronization operations, set the following properties in the provisioner configuration. Automatic synchronization operations includes liveSync (synchronization of changes from the LDAP server to IDM) and implicit sync (synchronization from IDM to the LDAP server).
baseContextsThe starting points in the LDAP tree that are used when searching the directory tree, for example,
dc=example,dc=com. These base contexts must include the set of users and the set of groups that must be searched during reconciliation operations.baseContextsToSynchronizeThe starting points in the LDAP tree that are used to determine if a change should be synchronized. This property is used only for automatic synchronization operations. Only entries that fall under these base contexts are considered during synchronization operations.
accountSearchFilterOnly user accounts that match this filter are searched, and therefore affected by reconciliation and synchronization operations. If you do not set this property, all accounts within the base contexts specified previously are searched.
accountSynchronizationFilterThis property is used during reconciliation and automatic synchronization operations, and filters out any LDAP accounts that you specifically want to exclude from these operations.
objectClassesToSynchronizeDuring automatic synchronization operations, only the object classes listed here are considered for changes. IDM ignores change log updates (or changes to managed objects) which do not have any of the object classes listed here.
attributesToSynchronizeDuring automatic synchronization operations, only the attributes listed here are considered for changes. Objects that include these attributes are synchronized. Objects that do not include these attributes are ignored. If this property is not set, IDM considers changes to all attributes specified in the mapping. Automatic synchronization includes liveSync and implicit synchronization operations. For more information, see "Types of Synchronization" in the Integrator's Guide
This attribute works only with LDAP servers that log changes in a change log, not with servers (such as Active Directory) that use other mechanisms to track changes.
modifiersNamesToFilterOutThis property enables you to define a list of DNs. During synchronization operations, the connector ignores changes made by these DNs.
When a managed user object is updated, and that change is synchronized to the LDAP server, the change made on the LDAP server is recorded in the change log. A liveSync operation picks up the change, and attempts to replay the change on the managed user object, effectively resulting in a loop of updates.
To avoid this situation, you can specify a unique user in your LDAP directory, that will be used only for the LDAP connector. The unique user must be something other than
cn=directory manager, for examplecn=openidmuser. You can then include that user DN as the value ofmodifiersNamesToFilterOut. When a change is made through the LDAP connector, and that change is recorded in the change log, the modifier's name (cn=openidmuser) is flagged and IDM does not attempt to replay the change back to the managed user repository. So you are effectively indicating that IDM should not synchronized changes back to managed user that originated from managed user, thus preventing the update loop.This attribute works only with LDAP servers that log changes in a change log, not with servers (such as Active Directory) that use other mechanisms to track changes.
The LDAP connector provides functionality specifically for managing Active Directory users and groups. The connector can handle the following operational attributes to manage Active Directory accounts:
ENABLE- uses theuserAccountControlattribute to get or set the account status of an object.The LDAP connector reads the
userAccountControlto determine if an account is enabled or disabled. The connector modifies the value of theuserAccountControlattribute if IDM changes the value of__ENABLE__.__ACCOUNT_EXPIRES__- gets or sets theaccountExpiresattribute of an Active Directory object.__LOCK_OUT__- uses themsDS-User-Account-Control-Computedsystem attribute to check if a user account has been locked.If IDM sets the
__LOCK_OUT__toFALSE, the LDAP connector sets the Active DirectorylockoutTimeto0to unlock the account.If IDM sets the
__LOCK_OUT__toTRUE, the LDAP connector ignores the change and logs a message.__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__- uses themsDS-User-Account-Control-Computedsystem attribute to check if a user password has expired.To force password expiration (to force a user to change their password when they next log in),
pwdLastSetmust be set to0. The LDAP connector setspwdLastSetto0, if IDM sets__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__toTRUE.To remove password expiration,
pwdLastSetmust be set to0and then-1. This sets the value ofpwdLastSetto the current time. The LDAP connector setspwdLastSetto-1if IDM sets__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__toFALSE.Note
Active Directory does not allow you to create an enabled account with an expired password. If you are using
__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__to force a new user to change their password when they next log in, you can create the user account as disabled initially (__ENABLE__=false). You can then patch the new user account to enable it. You can use the same workaround for synchronization operations, creating new user accounts as disabled, then issuing anopenidm.patchcall in apostCreatescript to enable the account.
The sample connector configuration file
(openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-adldap.json)
includes these operational attributes.
If you create or update users in Active Directory, and those user entries include passwords, you must use the LDAP connector over SSL. You cannot create or update an Active Directory user password in clear text. To use the connector over SSL, follow the instructions in "Configuring the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS".
The following command adds an Active Directory user. The output shows the operational attributes described in the previous section:
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=Brian Smith,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com",
"cn": "Brian Smith",
"sAMAccountName": "bsmith",
"userPrincipalName": "bsmith@example.com",
"userAccountControl": "512",
"givenName": "Brian",
"mail": "bsmith@example.com",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd"
}' \
http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/account?_action=create
{
"_id": "<GUID=cb2f8cbc032f474c94c896e69db2feb3>",
"mobile": null,
"postalCode": null,
"st": null,
"employeeType": null,
"objectGUID": "<GUID=cb2f8cbc032f474c94c896e69db2feb3>",
"cn": "Brian Smith",
"department": null,
"l": null,
"description": null,
"info": null,
"manager": null,
"sAMAccountName": "bsmith",
"sn": null,
"whenChanged": "20151217131254.0Z",
"userPrincipalName": "bsmith@example.com",
"userAccountControl": "512",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"displayName": null,
"givenName": "Brian",
"middleName": null,
"facsimileTelephoneNumber": null,
"lastLogon": "0",
"countryCode": "0",
"employeeID": null,
"co": null,
"physicalDeliveryOfficeName": null,
"pwdLastSet": "2015-12-17T13:12:54Z",
"streetAddress": null,
"homePhone": null,
"__PASSWORD_NOTREQD__": false,
"telephoneNumber": null,
"dn": "CN=Brian Smith,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com",
"title": null,
"mail": "bsmith@example.com",
"postOfficeBox": null,
"__SMARTCARD_REQUIRED__": false,
"uSNChanged": "86144",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"initials": null,
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"company": null,
"employeeNumber": null,
"accountExpires": "0",
"c": null,
"whenCreated": "20151217131254.0Z",
"uSNCreated": "86142",
"division": null,
"groups": [],
"__DONT_EXPIRE_PASSWORD__": false,
"otherHomePhone": []
}
Note that the command sets the userAccountControl to
512, which is an enabled account.
The value of the userAccountControl determines the
account policy. The following list describes the common values for the
userAccountControl.
512Enabled account.
514Disabled account.
544Enabled account, password not required.
546Disabled account, password not required.
66048Enabled account, password does not expire.
66050Disabled account, password does not expire.
66080Enabled account, password does not expire and is not required.
66082Disabled account, password does not expire and is not required.
262656Enabled account, smartcard required.
262658Disabled account, smartcard required.
262688Enabled account, smartcard required, password not required.
262690Disabled account, smartcard required, password not required.
328192Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328192Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328194Disabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328224Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire and is not required.
328226Disabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire and is not required.
The following command creates a basic Active Directory group with the LDAP connector:
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=Employees,DC=example,DC=com"
}' \
http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/group?_action=create
{
"_id": "<GUID=240da4e959d81547ad8629f5b2b5114d>"
}
The LDAP connector exposes two special attributes to handle Active
Directory group scope and type: GROUP_SCOPE and
GROUP_TYPE.
The GROUP_SCOPE attribute is defined in the provisioner
configuration as follows:
...
"__GROUP_SCOPE__" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeName" : "__GROUP_SCOPE__",
"nativeType" : "string"
},
The value of the GROUP_SCOPE attribute can be
global, domain, or
universal. If no group scope is set when the group is
created, the scope is global by default. For more
information about the different group scopes, see the corresponding Microsoft documentation.
The GROUP_TYPE attribute is defined in the provisioner
configuration as follows:
...
"__GROUP_TYPE__" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeName" : "__GROUP_TYPE__",
"nativeType" : "string"
},
The value of the GROUP_TYPE attribute can be
security or distribution. If no
group type is set when the group is created, the type is
security by default. For more information about the
different group types, see the corresponding Microsoft documentation.
The following example creates a new distribution group, with universal scope:
$ curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=NewGroup,DC=example,DC=com",
"__GROUP_SCOPE__": "universal",
"__GROUP_TYPE__": "distribution"
}' \
http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/group?_action=create
{
"_id": "<GUID=f189df8a276f91478ad5055b1580cbcb>"
}Most dates in Active Directory are represented as the number of 100-nanosecond intervals since January 1, 1601 (UTC). For example:
pwdLastSet: 130698687542272930
IDM generally represents dates as an ISO 8601-compliant string
with yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssZ format. For example:
2015-03-02T20:17:48Z
The generic LDAP connector therefore converts any dates from Active
Directory to ISO 8601 format, for fields such as pwdLastSet,
accountExpires, lockoutTime, and
lastLogon.
In a multi-domain Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest, the global catalog (GC) provides a read-only (searchable) representation of every object in the forest. Each domain controller (DC) in the forest stores a writable replica of the objects in its domain. Therefore, a DC can locate only the objects in its domain.
If your Active Directory deployment has only one domain controller, you can configure the connector to connect to that single domain controller. If your deployment spans multiple domains, you must configure the connector to connect to the Global Catalog (GC) to have a comprehensive view of all the domains.
Using a GC as the authoritative data source has the following limitations:
Only a subset of attributes is replicated from other domains to the GC.
Certain attributes required by the LDAP connector might be missing. To avoid this problem, modify the Active Directory schema to ensure that the required attributes are replicated to the GC.
Delete operations are not detected immediately.
A liveSync operation will therefore not update IDM with the result of a delete operation. Delete operations are detected by a reconciliation operation, so data stores are only temporarily "out of sync" with regard to deletes.
Not all group types are supported.
Group membership information is replicated to the GC for universal groups only. You must therefore use universal groups if your directory service has more than one domain.
Note
You can use the USN value for liveSync but
must connect to the GC in this case, and ensure that
you never failover to a different GC or to a DC. Using the USN for
liveSync instead of the timestamp mechanism is generally preferred,
because of the issue with detecting delete operations.
The LDAP connector constructs an LDAP search filter using a combination of filters, in the following order:
(& (native filter) (user filter) (object class filter) )
The filter components are as follows:
- Native Filter
The native filter is the query filter that has been translated to an LDAP query. For example,
uid+eq+"user123"is translated touid=user123.This part of the filter is processed first.
- User Filter
You can define a user filter with the properties
accountSearchFilterandgroupSearchFilterin the connector configuration.These properties enable you to construct a more granular or specific search filter. If a user filter is specified, the connector does not use the object class filter. If no user filter is specified, (
accountSearchFilterandgroupSearchFilterset tonullor absent from the connector configuration), the connector uses the object class filter.- Object Class Filter
This part of the filter includes the object classes that the entry must have in order to be returned by the search.
The
__ACCOUNT__and__GROUPS__object classes are defined by the propertiesaccountObjectClassesandgroupObjectClassesin the connector configuration. For example, the following excerpt of a sampleprovisioner.openicf-ldap.jsonfile indicates that theaccountObjectClassesinclude the LDAP object classestop,person,organizationalPerson, andinetOrgPerson:"configurationProperties" : { ... "accountObjectClasses" : [ "top", "person", "organizationalPerson", "inetOrgPerson" ] ...With this configuration, the search filter for accounts is constructed as follows:
(&(objectClass=top)(objectClass=person)(objectClass=organizationalPerson)(objectClass=inetOrgPerson))
If no
accountObjectClassesorgroupObjectClassesare defined in the connector configuration, the connector uses the name of the OpenICF ObjectClass in the filter. For example, an object of typeorganizationUnitwill result in:(&(objectClass=organizationUnit)
The LDAP Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The LDAP Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
filterWithOrInsteadOfAnd
|
boolean
|
false
|
| ||
|
Normally the filter used to fetch change log entries is an and-based filter retrieving an interval of change entries. If this property is set, the filter will or together the required change numbers instead. | |||||
|
| |||||
objectClassesToSynchronize
|
String[]
|
['inetOrgPerson']
|
| ||
|
The object classes to synchronize. The change log is for all objects; this filters updates to just the listed object classes. You should not list the superclasses of an object class unless you intend to synchronize objects with any of the superclass values. For example, if only "inetOrgPerson" objects should be synchronized, but the superclasses of "inetOrgPerson" ("person", "organizationalperson" and "top") should be filtered out, then list only "inetOrgPerson" here. All objects in LDAP are subclassed from "top". For this reason, you should never list "top", otherwise no object would be filtered. | |||||
|
| |||||
baseContextsToSynchronize
|
String[]
|
[]
|
| ||
|
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used to determine if a change should be synchronized. The base contexts attribute will be used to synchronize a change if this property is not set. | |||||
|
| |||||
attributesToSynchronize
|
String[]
|
[]
|
| ||
|
The names of the attributes to synchronize. This ignores updates from the change log if they do not update any of the named attributes. For example, if only "department" is listed, then only changes that affect "department" will be processed. All other updates are ignored. If blank (the default), then all changes are processed. | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordDecryptionInitializationVector
|
GuardedByteArray
|
null
|
| ||
|
The initialization vector to decrypt passwords with when performing password synchronization. | |||||
|
| |||||
synchronizePasswords
|
boolean
|
false
|
| ||
|
If true, the connector will synchronize passwords. The Password Capture Plugin needs to be installed for password synchronization to work. | |||||
|
| |||||
changeNumberAttribute
|
String
|
changeNumber
|
| ||
|
The name of the change number attribute in the change log entry. | |||||
|
| |||||
modifiersNamesToFilterOut
|
String[]
|
[]
|
| ||
|
The list of names (DNs) to filter from the changes. Changes with the attribute "modifiersName" that match entries in this list will be filtered out. The standard value is the administrator name used by this adapter, to prevent loops. Entries should be of the format "cn=Directory Manager". | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordDecryptionKey
|
GuardedByteArray
|
null
|
| ||
|
The key to decrypt passwords with when performing password synchronization. | |||||
|
| |||||
credentials
|
GuardedString
|
null
| |||
|
Password for the principal. | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordAttributeToSynchronize
|
String
|
null
|
| ||
|
The name of the password attribute to synchronize when performing password synchronization. | |||||
|
| |||||
changeLogBlockSize
|
int
|
100
|
| ||
|
The number of change log entries to fetch per query. | |||||
|
| |||||
useTimestampsForSync
|
boolean
|
false
|
| ||
|
If true, the connector will use the createTimestamp and modifyTimestamp system attributes to detect changes (Create/Update) on the directory instead of native change detection mechanism (cn=changelog on OpenDJ or Update Sequence Number -USN- on Active Directory for instance). Default value is false. | |||||
|
| |||||
accountSynchronizationFilter
|
String
|
null
|
| ||
|
An optional LDAP filter for the objects to synchronize. Because the change log is for all objects, this filter updates only objects that match the specified filter. If you specify a filter, an object will be synchronized only if it matches the filter and includes a synchronized object class. | |||||
|
| |||||
removeLogEntryObjectClassFromFilter
|
boolean
|
true
|
| ||
|
If this property is set (the default), the filter used to fetch change log entries does not contain the "changeLogEntry" object class, expecting that there are no entries of other object types in the change log. | |||||
|
| |||||
alternateKeyStorePassword
|
GuardedString
|
null
| |||
|
Password to use for the alternate keystore | |||||
|
| |||||
groupSynchronizationFilter
|
String
|
null
|
| ||
|
An optional LDAP filter for the objects to synchronize. Because the change log is for all objects, this filter updates only objects that match the specified filter. If you specify a filter, an object will be synchronized only if it matches the filter and includes a synchronized object class. | |||||
|
| |||||
groupMemberAttribute
|
String
|
uniqueMember
| |||
|
The name of the group attribute that will be updated with the distinguished name of the user when the user is added to the group. | |||||
|
| |||||
accountSearchFilter
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
An optional LDAP filter to control which accounts are returned from the LDAP resource. If no filter is specified, only accounts that include all specified object classes are returned. | |||||
|
| |||||
privateKeyAlias
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
Specifies the name of a private key alias from the keystore that should be used for SSL mutual authentication. If null, no private key is sent during SSL handshake so only server cert is used. This alias name is case sensitive. | |||||
|
| |||||
ssl
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Select the check box to connect to the LDAP server using SSL. | |||||
|
| |||||
maintainPosixGroupMembership
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
When enabled and a user is renamed or deleted, update any POSIX groups to which the user belongs to reflect the new name. Otherwise, the LDAP resource must maintain referential integrity with respect to group membership. | |||||
|
| |||||
groupSearchFilter
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
An optional LDAP filter to control which groups are returned from the LDAP resource. If no filter is specified, only groups that include all specified object classes are returned. | |||||
|
| |||||
referralsHandling
|
String
|
follow
| |||
|
Defines how to handle LDAP referrals. Possible values can be follow, ignore or throw. | |||||
|
| |||||
host
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
The name or IP address of the host where the LDAP server is running. | |||||
|
| |||||
maintainLdapGroupMembership
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
When enabled and a user is renamed or deleted, update any LDAP groups to which the user belongs to reflect the new name. Otherwise, the LDAP resource must maintain referential integrity with respect to group membership. | |||||
|
| |||||
resetSyncToken
|
String
|
never
| |||
|
Connector can reset the sync token if ever the value of the sync token is greater than the last change number in the directory changelog. Defaults to "never" (no reset). If set to "first" it will reset the sync token to the value of the firstChangeNumber changelog attribute. If set to "last" it will reset the sync token to the value of the lastChangeNumber changelog attribute. | |||||
|
| |||||
vlvSortAttribute
|
String
|
uid
| |||
|
Specify the sort attribute to use for VLV indexes on the resource. | |||||
|
| |||||
baseContexts
|
String[]
|
[]
| |||
|
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used when searching the tree. Searches are performed when discovering users from the LDAP server or when looking for the groups of which a user is a member. | |||||
|
| |||||
blockSize
|
int
|
100
| |||
|
The maximum number of entries that can be in a block when retrieving entries in blocks. | |||||
|
| |||||
groupObjectClasses
|
String[]
|
['top',
'groupOfUniqueNames']
| |||
|
The default list of object classes that will be used when creating new group objects in the LDAP tree. This can be overridden by specifying the group object classes during the Create operation. | |||||
|
| |||||
accountUserNameAttributes
|
String[]
|
['uid',
'cn']
| |||
|
Attribute or attributes which holds the account's user name. They will be used when authenticating to find the LDAP entry for the user name to authenticate. | |||||
|
| |||||
failover
|
String[]
|
[]
| |||
|
List all servers that should be used for failover in case the preferred server fails. If the preferred server fails, JNDI will connect to the next available server in the list. List all servers in the form of "ldap://ldap.example.com:389/", which follows the standard LDAP v3 URLs described in RFC 2255. Only the host and port parts of the URL are relevant in this setting. | |||||
|
| |||||
port
|
int
|
389
| |||
|
TCP/IP port number used to communicate with the LDAP server. | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordAttribute
|
String
|
userPassword
| |||
|
The name of the LDAP attribute that holds the password. When changing a users password, the new password is set to this attribute. | |||||
|
| |||||
useDNSSRVRecord
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
If true, the connector will do a DNS query to find SRV records associated with the value set for host property ("_ldap._tcp.example.com" for example). Defaults to false. | |||||
|
| |||||
getGroupMemberId
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Specifies whether to add an extra _memberId attribute to get the group members __UID__ | |||||
|
| |||||
startTLS
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Specifies whether to use the startTLS operation to initiate a TLS/SSL session. | |||||
|
| |||||
allowTreeDelete
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Connector can delete an entry (node) with leaf entry if this value is set to true (defaults to false). The LDAP control LDAP_SERVER_TREE_DELETE_OID (1.2.840.113556.1.4.805) is used. | |||||
|
| |||||
respectResourcePasswordPolicyChangeAfterReset
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
When this resource is specified in a Login Module (i.e., this resource is a pass-through authentication target) and the resource's password policy is configured for change-after-reset, a user whose resource account password has been administratively reset will be required to change that password after successfully authenticating. | |||||
|
| |||||
uidAttribute
|
String
|
entryUUID
| |||
|
The name of the LDAP attribute that is mapped to the OpenICF UID attribute. | |||||
|
| |||||
principal
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
The distinguished name with which to authenticate to the LDAP server. | |||||
|
| |||||
accountObjectClasses
|
String[]
|
['top',
'person',
'organizationalPerson',
'inetOrgPerson']
| |||
|
The default list of object classes that will be used when creating new user objects in the LDAP tree. This can be overridden by specifying the user object classes during the Create operation. | |||||
|
| |||||
alternateKeyStoreType
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
Defines the type of the alternate key store. Valid values are JKS, JCEKS and PKCS12 | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordHashAlgorithm
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
Indicates the algorithm that the Identity system should use to hash the password. Currently supported values are SSHA, SHA, SMD5, MD5 and WIN-AD (when AD is the target). A blank value indicates that the system will not hash passwords. This will cause clear text passwords to be stored in LDAP unless the LDAP server performs the hash (as Forgerocks OpenDJ does, for example). | |||||
|
| |||||
alternateKeyStore
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
Defines the filename of an alternate keystore. If specified, the connector will not use the default keystore specified by the javax.net.ssl.keyStore property. | |||||
|
| |||||
authType
|
String
|
simple
| |||
|
The authentication mechanism to use: Simple or SASL-GSSAPI. Defaults to "simple". | |||||
|
| |||||
useBlocks
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Specifies whether to use block-based LDAP controls, like the simple paged results or VLV control. When performing search operations on large numbers of entries, the entries are returned in blocks to reduce the amount of memory used by the operation. | |||||
|
| |||||
readSchema
|
boolean
|
true
| |||
|
If true, the connector will read the schema from the server. If false, the connector will provide a default schema based on the object classes in the configuration. This property must be true in order to use extended object classes. | |||||
|
| |||||
usePagedResultControl
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
When enabled, the LDAP Paged Results control is preferred over the VLV control when retrieving entries. | |||||
|
| |||||
sendCAUDTxId
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Connector can send the Common Audit Transaction Id (if present) to the target OpenDJ server when this value is set to true (defaults to false). The LDAP control TransactionIdControl (1.3.6.1.4.1.36733.2.1.5.1) is used. | |||||
|
| |||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | |||||
The CSV file connector is useful when importing users, either for initial provisioning or for ongoing updates. When used continuously in production, a CSV file serves as a change log, often containing only user records that have changed.
A sample CSV file connector configuration is provided in
openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-csv.json.
The following example shows an excerpt of the provisioner configuration.
The connectorHostRef property is optional and must be
provided only if the connector runs remotely.
{
"connectorRef": {
"connectorHostRef": "#LOCAL",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.csvfile.CSVFileConnector",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.csvfile-connector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.1.4,1.6.0.0)"
}
}The following excerpt shows the required configuration properties:
"configurationProperties" : {
"csvFile" : "&{launcher.project.location}/data/csvConnectorData.csv"
},-
csvFile The path to the CSV file that is the data source for this connector.
The CSV file connector also supports following optional configuration properties:
-
headerUid The CSV header that maps to the
uid(or name) for each row.Default:
uidencodingDefault:
utf-8headerPasswordThe CSV header that maps to the password for each row. Use this property when password-based authentication is required.
fieldDelimiterThe character in the CSV file that is used to separate field values.
Default:
,-
quoteCharacter The character in the CSV file that is used to encapsulate strings.
Default:
"-
newlineString The character string in the CSV file that is used to terminate each line.
Default:
\n-
syncFileRetentionCount The number of historical copies of the CSV file to retain when performing synchronization operations.
Default:
3
The CSV File Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Batch
Execute a series of operations in a single request.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The CSV File Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
headerPassword
|
String
|
password
| ||
|
Name of the password column as found in the CSV file | ||||
|
| ||||
csvFile
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Full path to the CSV file | ||||
|
| ||||
newlineString
|
String
|
| ||
|
Character(s) used to terminate a line in the CSV file | ||||
|
| ||||
headerUid
|
String
|
uid
| ||
|
Name of the uid column as found in the CSV file | ||||
|
| ||||
quoteCharacter
|
String
|
"
| ||
|
Character used to quote fields | ||||
|
| ||||
fieldDelimiter
|
String
|
,
| ||
|
Character used to delimit columnar fields | ||||
|
| ||||
syncFileRetentionCount
|
int
|
3
| ||
|
Number of sync history files to retain | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Database Table connector enables provisioning to a single table in a JDBC database.
A sample connector configuration for the Database Table connector is
provided in
samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-contractordb.json.
The corresponding data definition language file is provided in
samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-contractordb.sql.
The following excerpt shows the settings for the connector configuration properties in the sample Database Table connector:
"configurationProperties" :
{
"quoting" : "",
"host" : "localhost",
"port" : "3306",
"user" : "root",
"password" : "",
"database" : "contractordb",
"table" : "people",
"keyColumn" : "UNIQUE_ID",
"passwordColumn" : "",
"jdbcDriver" : "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver",
"jdbcUrlTemplate" : "jdbc:mysql://%h:%p/%d",
"enableEmptyString" : false,
"rethrowAllSQLExceptions" : true,
"nativeTimestamps" : true,
"allNative" : false,
"validConnectionQuery" : null,
"changeLogColumn" : "CHANGE_TIMESTAMP",
"datasource" : "",
"jndiProperties" : null
},The mandatory configurable properties are as follows:
databaseThe JDBC database that contains the table to which you are provisioning.
tableThe name of the table in the JDBC database that contains the user accounts.
keyColumnThe column value that is used as the unique identifier for rows in the table.
To use this connector for liveSync, add a changelog type column to the
database and provide the name of this column in the
changeLogColumn property. Note that the Database Table
connector supports liveSync for create and update operations only. To detect
deletes in the database you must run a full reconciliation.
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Database Table connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
The Database Table Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Database Table Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
quoting
|
String
|
| |||
|
Select whether database column names for this resource should be quoted, and the quoting characters. By default, database column names are not quoted (None). For other selections (Single, Double, Back, or Brackets), column names will appear between single quotes, double quotes, back quotes, or brackets in the SQL generated to access the database. | |||||
|
| |||||
host
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the name of the host on which the database is running. | |||||
|
| |||||
port
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the port number on which the database server is listening. | |||||
|
| |||||
user
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the name of the mandatory Database user with permission to access the accounts table. | |||||
|
| |||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| |||
|
Enter a user account that has permission to access the accounts table. | |||||
|
| |||||
database
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the name of the database on the database server that contains the table. | |||||
|
| |||||
table
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the name of the table in the database that contains the accounts. | |||||
|
| |||||
keyColumn
|
String
|
| |||
|
This mandatory column value will be used as the unique identifier for rows in the table. | |||||
|
| |||||
passwordColumn
|
String
|
| |||
|
Enter the name of the column in the table that will hold the password values. If empty, no validation is done on resources and passwords. | |||||
|
| |||||
jdbcDriver
|
String
|
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
| |||
|
Specify the JDBC Driver class name. For Oracle: oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver. For MySQL: org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver. Can be empty if datasource is provided. | |||||
|
| |||||
jdbcUrlTemplate
|
String
|
jdbc:oracle:thin:@%h:%p:%d
| |||
|
Specify the JDBC Driver Connection URL. Oracle template is jdbc:oracle:thin:@[host]:[port(1521)]:[DB]. MySQL template is jdbc:mysql://[host]:[port(3306)]/[db], for more info, read the JDBC driver documentation. Could be empty if datasource is provided. | |||||
|
| |||||
enableEmptyString
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Select to enable support for writing an empty string, instead of a NULL value, in character based columns defined as not-null in the table schema. This option does not influence the way strings are written for Oracle based tables. By default empty strings are written as a NULL value. | |||||
|
| |||||
rethrowAllSQLExceptions
|
boolean
|
true
| |||
|
If this is not checked, SQL statements which throw SQLExceptions with a 0 ErrorCode will be have the exception caught and suppressed. Check it to have exceptions with 0 ErrorCodes rethrown. | |||||
|
| |||||
nativeTimestamps
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Select to retrieve Timestamp data type of the columns in java.sql.Timestamp format from the database table. | |||||
|
| |||||
allNative
|
boolean
|
false
| |||
|
Select to retrieve all data types of columns in native format from the database table. | |||||
|
| |||||
validConnectionQuery
|
String
|
null
| |||
|
Specify whether the check connection alive query should be used. If empty, the default implementation checks the connection by switching autocommit on/off. It might be more efficient to test the connection by selecting 1 from a dummy table. | |||||
|
| |||||
changeLogColumn
|
String
|
|
| ||
|
The change log column stores the latest change time. Providing this value the Sync capabilities are activated. | |||||
|
| |||||
datasource
|
String
|
| |||
|
If specified, the connector will attempt to connect using only this data source, and will ignore other specified resource parameters. For example: jdbc/SampleDataSourceName | |||||
|
| |||||
jndiProperties
|
String[]
|
null
| |||
|
Could be empty or enter the JDBC JNDI Initial context factory, context provider in a format: key = value. | |||||
|
| |||||
suppressPassword
|
boolean
|
true
| |||
|
If set to true then the password will not be returned. Never. Even though it is explicitly requested. If set to false then the password will be returned if it is explicitly requested. | |||||
|
| |||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | |||||
The PowerShell Connector Toolkit is not a complete connector in the traditional sense. Rather, it is a framework within which you must write your own PowerShell scripts to address the requirements of your Microsoft Windows ecosystem. You can use the PowerShell Connector Toolkit to create connectors that can provision any Microsoft system, including, but not limited to, Active Directory, MS SQL, MS Exchange, SharePoint, Azure, and Office365. Essentially, any task that can be performed with PowerShell can be executed through connectors based on this toolkit.
The PowerShell Connector Toolkit is available from ForgeRock's BackStage site.
IDM includes Active Directory and Azure sample scripts for the PowerShell connector that can help you get started with this toolkit. For more information, see "Connecting to Active Directory With the PowerShell Connector" in the Samples Guide and "Connecting to Azure AD With the PowerShell Connector" in the Samples Guide.
The sample scripts illustrate the following scenarios:
Synchronization of users between Windows AD DS and IDM.
Synchronization of users between Windows Azure AD and IDM.
To implement a scripted PowerShell connector, you must install the following:
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5 or later. Connectors created with the PowerShell Connector Toolkit run on the .NET platform and require the installation of a .NET connector server on the Windows system. To install the .NET connector server, follow the instructions in "Installing and Configuring a .NET Connector Server" in the Integrator's Guide.
PowerShell version 4.0 or above.
The PowerShell Connector Toolkit.
To run the commands in this procedure, start with the PowerShell command line. Some of the commands in this procedure require administrative privileges.
Install, configure, and start the .NET connector server on a Windows host. If you are running an Active Directory Domain Controller, install the .NET connector server on the same host on which the Windows PowerShell module is installed.
For instructions on installing the .NET connector server, see "Installing and Configuring a .NET Connector Server" in the Integrator's Guide.
Configure IDM to connect to the .NET connector server.
To do so, copy the remote connector provisioner file from the
openidm\samples\provisionersdirectory to your project'sconf\directory, and edit the file to match your configuration.PS C:\ cd \path\to\openidm PS C:\path\to\openidm cp samples\provisioners\provisioner.openicf.connectorinfoprovider.json conf
For instructions on editing this file, see "Configuring IDM to Connect to the .NET Connector Server" in the Integrator's Guide.
Download the PowerShell Connector Toolkit archive (
mspowershell-connector-1.4.4.0.zip) from ForgeRock's BackStage site.Extract the archive and move the
MsPowerShell.Connector.dllto the folder in which the connector server application executable file (ConnectorServerService.exe) is located.Sample PowerShell scripts are provided in the
openidm\samples\directory. Thescripted-powershell-with-addirectory contains scripts for a connection to Active Directory, and thescripted-powershell-with-azure-adcontains scripts for a connection to Azure AD. Copy these scripts to the host on which the .NET connector server is installed.The full path to the scripts must be referenced in your connector configuration file (
provisioner.openicf-*.json), for example:"CreateScriptFileName" : "C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADCreate.ps1", ...
Copy the sample connector configuration for the PowerShell connector from the
samples\provisionersdirectory to your project'sconfdirectory.IDM includes two sample PowerShell connector configurations:
Active Directory:
provisioner.openicf-adpowershell.jsonAzure AD:
provisioner.openicf-azureadpowershell.json
Verify that at least the path to the scripts and the connection and authentication details are correct for your deployment. The following section describes the configurable properties in the sample connector configuration files.
Note
Paths in these files must use forward slash characters and not the backslash characters that you would expect in a Windows path.
Your PowerShell connector configuration file should include the following properties:
| Property | Type | Example | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
operationScriptFileName
|
String
|
C:/openidm/AD/ADCreate.ps1,
C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-azure-ad/azureADScripts/AzureADDelete.ps1
| ||
|
The full path to the script that implements the corresponding OpenICF operation. | ||||
VariablesPrefix
|
String
|
Connector
| ||
|
To avoid variable namespace conflicts, you can define a prefix for the connector variables. All variables are injected into the script under that prefix and can be used with the dotted notation. | ||||
QueryFilterType
|
String
|
AdPsModule (for AD), Map (for
Azure AD)
| ||
|
A configurable query filter visitor property that defines the format in which the query will be injected into the connector. Possible values are:
| ||||
ReloadScriptOnExecution
|
Boolean
|
true
| ||
|
When | ||||
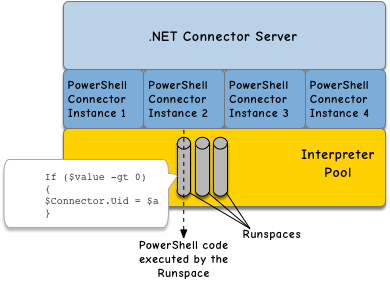
UseInterpretersPool
|
Boolean
|
true
| ||
|
If | ||||
MaxInterpretersPoolSize
|
Integer
|
5
| ||
|
The maximum size of the interpreter pool. | ||||
MinInterpretersPoolSize
|
Integer
|
1
| ||
|
The minimum size of the interpreter pool. | ||||
SubstituteUidAndNameInQueryFilter
|
Boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Specifies whether the | ||||
UidAttributeName
|
String
|
ObjectGUID (AD), ObjectId (AzureAD)
| ||
|
The attribute on the resource that contains the object | ||||
NameAttributeName
|
String
|
DistinguishedName (AD), UserPrincipalName (AzureAD)
| ||
|
The attribute on the resource that contains the object
| ||||
PsModulesToImport
|
Array
|
["ActiveDirectory"] (AD), ["MSOnline"] (AzureAD)
| ||
|
An array of additional PowerShell modules that the connector must import | ||||
Host
|
String
|
| ||
|
The host name or IP address of the resource (Active Directory or Azure AD) | ||||
Port
|
Integer
| null | ||
|
The port number on which the remote resource listens for connections | ||||
Login
|
String
| "" | ||
|
The user account in the remote resource that is used for the connection | ||||
Password
|
String
| null | ||
|
The password of the user account that is used for the connection | ||||
CustomProperties
|
Array
| [ ] | ||
|
An array of Strings to define custom configuration properties. Each
property takes the format "configurationProperties" : {
...
"CustomProperties" : ["baseContext = CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com" ],
... }, The custom property can then be read from the PowerShell
scripts as follows:
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in IDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
Start IDM with the configuration for your PowerShell connector project.
The following tests assume that the configuration is in the default
path/to/openidm directory. If your PowerShell project
is in a different directory, use the startup command
with the -p option to point to that directory.
$ cd path/to/openidm $ ./startup.sh
To test that the PowerShell connector has been configured correctly, run the following REST call:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
{
"name" : "azureadpowershell",
"enabled" : true,
"config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/azureadpowershell",
"objectTypes" : [ "__ALL__", "group", "account" ],
"connectorRef" : {
"connectorName" : "Org.Forgerock.OpenICF.Connectors.MsPowerShell.MsPowerShellConnector",
"bundleName" : "MsPowerShell.Connector",
"bundleVersion" : "[1.4.3.0,1.5.0.0)"
},
"displayName" : "PowerShell Connector",
"ok" : true
}The displayed output demonstrates a successful configuration of an Azure AD connector.
When you run this test, you should also see a log entry associated with the
.NET connector server, in the logs/ subdirectory of
that server.
You can use the connector, with a PowerShell search script, to retrieve
information from a target system. The PowerShell search script accepts
IDM queries, including query-all-ids and
_queryFilter
With the following command, you can retrieve a list of existing users on an Azure AD system. You can also use any system-enabled filter, such as those described in "Presence Expressions" in the Integrator's Guide.
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell/account?_queryId=query-all-ids"
You can use the connector to create new users or groups on the target
system, based on options listed in the relevant
provisioner.openicf-* configuration file.
For example, the following command creates a new user on a remote Azure AD instance:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '{
"PasswordNeverExpires": false,
"AlternateEmailAddresses": ["Robert.Smith@example.com"],
"LastName": "Smith",
"PreferredLanguage": "en-US",
"FirstName": "Robert",
"UserPrincipalName": "Robert.Smith@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"DisplayName": "Robert Smith"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell/account?_action=create"
The PowerShell scripts associated with update functionality support changes to the following properties:
Password
Principal Name
License
Common user attributes
As an example, you could use the following command to change the password
for the user with the noted _id:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request PATCH \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '{
"operation": "replace",
"Field": "password",
"value": "Passw1rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell/account/1d4c9276-6937-4d9e-9c60-67e8b4207f4e"
You can use the PowerShell connector to delete user and group objects.
As an example, the following command deletes one user from an Azure AD
deployment, based on their _id:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell/account/1d4c9276-6937-4d9e-9c60-67e8b4207f4e"
The PowerShell connector uses runspaces to execute the scripts for each action (create, update, search, and so on). A runspace is an instance of the Windows PowerShell interpreter within the PowerShell connector. A runspace essentially creates a new thread on an existing process. The connector can also use an interpreter pool and have several runspace instances running within the connector. This makes the connector more efficient under a heavy load. The interpreter pool can be shared between connector instances.
The following image shows how multiple connector instances use an interpreter pool with multiple runspaces:
PowerShell 5.0 includes several cmdlets related to runspace debugging. These cmdlets allow you to debug arbitrary runspaces, that is, runspaces other than the default PowerShell console or PowerShell ISE.
The examples shown in this section assume the following setup. Adjust the examples for your particular setup:
You are using IDM 5.5.1.3 and version 1.4.4.0 of the PowerShell connector.
IDM is running on a local UNIX host, distinct from the Windows host on which the PowerShell connector runs.
You have already installed and configured version 1.5.4.0 of the .NET connector server on the remote Windows host. You have also installed and tested the PowerShell connector. See "Setting Up the PowerShell Connector" for more information.
The remote Windows host includes the PowerShell module version 5.0 (available with the Windows Management Framework 5.0).
You are using the PowerShell scripts and configuration provided with the sample described in "Connecting to Azure AD With the PowerShell Connector" in the Samples Guide.
Before you start, check that the interpreters pool is configured as follows
in your PowerShell connector configuration
(provisioner.openicf-azureadpowershell.json):
"configurationProperties" : {
...
"UseInterpretersPool" : true,
"MinInterpretersPoolSize" : 1,
"MaxInterpretersPoolSize" : 1,
...
},This configuration will make debugging easier.
Then follow these steps to set up debugging:
Connect the PowerShell ISE to the connector server.
Start the PowerShell ISE in Administrator mode.
From the PowerShell ISE, open the
AzureADSearch.ps1sample script:In the PowerShell ISE console, use the
Get-Processcmdlet to obtain the process identifier of the Connector Server service:PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF> Get-Process -Name "connector*" Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName ------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- ----------- 576 56 79748 89484 1.16 1628 1 ConnectorServerServiceUse the
EnterPSHostProcesscmdlet to connect to the Connector Server service, specifying its process identifier:PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF> Enter-PSHostProcess -Id 1628 [Process:1628]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>
Use the
Get-Runspaceto look at the PowerShell interpreter pool that is embedded by the connector:[Process:1628]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF> Get-Runspace Id Name ComputerName Type State Availability -- ---- ------------ ---- ----- ------------ 1 Runspace1 localhost Local Opened Available 2 RemoteHost localhost Local Opened Busy
Note that there is one Runspace (
Runspace1) open. Because you have set the maximum pool size to 1, that number should not increase.
Enter Debug mode and call a script:
First, use the
Debug-RunSpacecmdlet to attach to the available Runspace:[Process:1628]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF> Debug-Runspace -Id 1 Debugging Runspace: Runspace1 To end the debugging session type the 'Detach' command at the debugger prompt, or type 'Ctrl+C' otherwise.
Run any action over the IDM REST interface.
The following example queries all user accounts:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell/account?_queryFilter=true" Stopped at: $proceed = $TRUE [DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>>
The output indicates that the debugger has been triggered and that it is stopped at the first line of code.
Type
hto list the debugging commands:[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> h s, stepInto Single step (step into functions, scripts, etc.) v, stepOver Step to next statement (step over functions, scripts, etc.) o, stepOut Step out of the current function, script, etc. c, continue Continue operation q, quit Stop operation and exit the debugger d, detach Continue operation and detach the debugger. k, Get-PSCallStack Display call stack l, list List source code for the current script. Use "list" to start from the current line, "list <m>" to start from line <m>, and "list <m> <n>" to list <n> lines starting from line <m> <enter> Repeat last command if it was stepInto, stepOver or list ?, h displays this help message. For instructions about how to customize your debugger prompt, type "help about_prompt".To inspect the variables injected into the scripts by the connector, type
$Connector:[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> $Connector Key Value --- ----- Result Org.ForgeRock.OpenICF.Connectors.MsPowerShell.MsPowerShellSearchResults Action SEARCH Operation SEARCH Configuration Org.ForgeRock.OpenICF.Connectors.MsPowerShell.MsPowerShellConfiguration ObjectClass ObjectClass: __ACCOUNT__ Options OperationOptions: Org.IdentityConnectors.Common.ReadOnlyDictionary`2[System.String,System.Object]
Because the
$Connectorvariable is a hash table, you can use dotted notation to inspect the various items.The following example inspects the connector configuration:
[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> $Connector.Configuration AuthenticateScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADAuthenticate.ps1 CreateScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADCreate.ps1 DeleteScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADDelete.ps1 ResolveUsernameScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADResolveUsername.ps1 SchemaScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADSchema.ps1 SearchScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADSearch.ps1 SyncScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADSync.ps1 TestScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADTest.ps1 UpdateScriptFileName : C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADUpdate.ps1 VariablesPrefix : Connector QueryFilterType : AdPsModule ReloadScriptOnExecution : True UseInterpretersPool : True SubstituteUidAndNameInQueryFilter : True UidAttributeName : ObjectGUID NameAttributeName : DistinguishedName PsModulesToImport : {ActiveDirectory} Host : 192.168.1.103 Port : 389 Login : CN=bjensen,CN=users,DC=example,DC=com Password : Org.IdentityConnectors.Common.Security.GuardedString MinInterpretersPoolSize : 1 MaxInterpretersPoolSize : 1 ...The following example inspects the Search query:
[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> $Connector.Query Key Value --- ----- Not False Operation STARTSWITH Left DisplayName Right Sprint ...
Use the
sandvcommands to step over and step into your scripts:[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> s Stopped at: $searchBase = $Connector.Configuration.PropertyBag.baseContext [DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> v Stopped at: $attrsToGet = "*" [DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>>
Note
You cannot use breakpoints with the debugger because it is running in memory.
Use the
lcommand to check where you are in the script:[DBG]: [Process:1628]: [Runspace1]: PS C:\Program Files (x86)\ForgeRock\OpenICF>> l 78: 79: # Always put code in try/catch statement and make sure exceptions are re-thrown to connector 80: try 81: { 82: $searchBase = $Connector.Configuration.PropertyBag.baseContext 83:* $attrsToGet = "*" 84: $filter = "*" 85: 86: if ( $Connector.Query ) {$filter = $Connector.Query} 87: 88: switch ($Connector.ObjectClass.Type) 89: { 90: "__ACCOUNT__" 91: { 92: Get-ADUser -Filter $filter -SearchBase $searchBase -Properties $attrsToGet | Process-Results 93: }Close the session.
When the script has completed, you will see the following message in the debugger console:
Command or script completed. To end the debugging session type the 'Detach' command at the debugger prompt, or type 'Ctrl+C' otherwise.
Type
Ctrl+Cto return to the process prompt orexitto exit the process and return to the console prompt.To debug the same script again, or to debug another script, you must call
Debug-Runspaceagain before you send the query over the IDM REST interface.
OpenICF provides a generic Groovy Connector Toolkit that enables you to run a Groovy script for any OpenICF operation, such as search, update, create, and others, on any external resource.
The Groovy Connector Toolkit is not a complete connector in the traditional sense. Rather, it is a framework within which you must write your own Groovy scripts to address the requirements of your implementation.
The Groovy Connector Toolkit is bundled in the JAR
openidm/connectors/groovy-connector-1.4.4.0.jar.
A number of sample scripted connector implementations are provided in the Samples Guide, specifically in "Connecting to DS With ScriptedREST" in the Samples Guide, and "Connecting to DS With ScriptedCREST" in the Samples Guide. The scripts provided with these samples demonstrate how the Groovy Connector Toolkit can be used. These scripts cannot be used as is in your deployment, but are a good starting point on which to base your customization. For information about writing your own scripts, see "Writing Scripted Connectors With the Groovy Connector Toolkit" in the Connector Developer's Guide.
You specify the connector configuration in your project's
conf/provisioner.openicf-connector.json file. A number of
sample configurations for scripted Groovy implementations are provided in
openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-scriptedimpementation.json.
Use these as the basis for configuring your own scripted connector.
The scripted SQL connector uses the Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool to managed its connections. Occasionally, a JDBC resource that is accessed by the scripted SQL connector might become unavailable for a period. When the resource comes back online, IDM is generally able to recover automatically and resume operations. However, the connector might not be able to refresh its connection pool and might then pass a closed connection to its scripts. This can affect operations until IDM is restarted.
To avoid this situation, you can configure connection validation, where connections are validated before being borrowed from the connection pool.
To configure connection validation, add the following properties to the
configurationProperties object in your connector
configuration:
testOnBorrowValidates the connection object before it is borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it is dropped from the pool and the connector attempts to borrow another object.
For this property to have an effect, you must set
validationQueryto a non-null string.validationQueryThe SQL query used to validate connections from the pool before returning them to the caller.
The precise query will differ, depending on the database that you are accessing. The following list provides sample queries for common databases:
- HyperSQL DataBase (HSQLDB)
select 1 from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SYSTEM_USERS
- Oracle DB
select 1 from dual
- DB2
select 1 from sysibm.sysdummy1
- MySQL
select 1
- MS SQL
select 1
- PostgreSQL
select 1
- Ingres Database
select 1
- Apache Derby
values 1
- H2 Database
select 1
- Firebird SQL
select 1 from rdb$database
validationIntervalSpecifies the maximum frequency (in milliseconds) at which validation is run. If a connection is due for validation but was previously validated within this interval, it is not validated again.
The larger this value, the better the connector performance. However, with a large value you increase the chance of a stale connection being presented to the connector.
Connection validation can have an impact on performance and should not be done too frequently. With the following configuration, connections are validated no more than every 34 seconds:
{
"name" : "scriptedsql",
...
"configurationProperties" : {
...
"testOnBorrow" : true,
"validationQuery" : "select 1 from dual",
"validationInterval" : 34000,
The following tables list the OpenICF interfaces that are implemented for each scripted connector implementation:
The Scripted Groovy Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Scripted CREST Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Scripted REST Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Scripted SQL Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The following tables list the configuration properties for each scripted connector implementation:
The Scripted Groovy Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Scripted CREST Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
serviceAddress
|
URI
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
proxyAddress
|
URI
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultAuthMethod
|
String
|
BASIC
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
username
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
An example GuardedString property | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Scripted REST Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
serviceAddress
|
URI
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultContentType
|
String
|
application/json
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
proxyAddress
|
URI
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultAuthMethod
|
String
|
BASIC
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultRequestHeaders
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
username
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
An example GuardedString property | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Scripted SQL Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
password
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The connection password to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. | ||||
|
| ||||
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
connectionProperties
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The connection properties that will be sent to our JDBC driver when establishing new connections. Format of the string must be [propertyName=property;]* NOTE - The "user" and "password" properties will be passed explicitly, so they do not need to be included here. The default value is null. | ||||
|
| ||||
propagateInterruptState
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Set this to true to propagate the interrupt state for a thread that has been interrupted (not clearing the interrupt state). Default value is false for backwards compatibility. | ||||
|
| ||||
useDisposableConnectionFacade
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Set this to true if you wish to put a facade on your connection so that it cannot be reused after it has been closed. This prevents a thread holding on to a reference of a connection it has already called closed on, to execute queries on it. | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultCatalog
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The default catalog of connections created by this pool. | ||||
|
| ||||
validationInterval
|
long
|
30000
| ||
|
avoid excess validation, only run validation at most at this frequency - time in milliseconds. If a connection is due for validation, but has been validated previously within this interval, it will not be validated again. The default value is 30000 (30 seconds). | ||||
|
| ||||
ignoreExceptionOnPreLoad
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Flag whether ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to true if you want to ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to false if you want to fail the initialization of the pool by throwing exception. | ||||
|
| ||||
jmxEnabled
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Register the pool with JMX or not. The default value is true. | ||||
|
| ||||
commitOnReturn
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If autoCommit==false then the pool can complete the transaction by calling commit on the connection as it is returned to the pool If rollbackOnReturn==true then this attribute is ignored. Default value is false. | ||||
|
| ||||
logAbandoned
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Flag to log stack traces for application code which abandoned a Connection. Logging of abandoned Connections adds overhead for every Connection borrow because a stack trace has to be generated. The default value is false. | ||||
|
| ||||
maxIdle
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
The maximum number of connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. Default value is maxActive:100 Idle connections are checked periodically (if enabled) and connections that been idle for longer than minEvictableIdleTimeMillis will be released. (also see testWhileIdle) | ||||
|
| ||||
testWhileIdle
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
The indication of whether objects will be validated by the idle object evictor (if any). If an object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false and this property has to be set in order for the pool cleaner/test thread is to run (also see timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis) | ||||
|
| ||||
removeAbandoned
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Flag to remove abandoned connections if they exceed the removeAbandonedTimeout. If set to true a connection is considered abandoned and eligible for removal if it has been in use longer than the removeAbandonedTimeout Setting this to true can recover db connections from applications that fail to close a connection. See also logAbandoned The default value is false. | ||||
|
| ||||
abandonWhenPercentageFull
|
int
|
0
| ||
|
Connections that have been abandoned (timed out) wont get closed and reported up unless the number of connections in use are above the percentage defined by abandonWhenPercentageFull. The value should be between 0-100. The default value is 0, which implies that connections are eligible for closure as soon as removeAbandonedTimeout has been reached. | ||||
|
| ||||
minIdle
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The minimum number of established connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. The connection pool can shrink below this number if validation queries fail. Default value is derived from initialSize:10 (also see testWhileIdle) | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultReadOnly
|
Boolean
|
null
| ||
|
The default read-only state of connections created by this pool. If not set then the setReadOnly method will not be called. (Some drivers dont support read only mode, ex: Informix) | ||||
|
| ||||
maxWait
|
int
|
30000
| ||
|
The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before throwing an exception. Default value is 30000 (30 seconds) | ||||
|
| ||||
logValidationErrors
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Set this to true to log errors during the validation phase to the log file. If set to true, errors will be logged as SEVERE. Default value is false for backwards compatibility. | ||||
|
| ||||
driverClassName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The fully qualified Java class name of the JDBC driver to be used. The driver has to be accessible from the same classloader as tomcat-jdbc.jar | ||||
|
| ||||
name
|
String
|
Tomcat Connection Pool[1-2106622700]
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
initSQL
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
A custom query to be run when a connection is first created. The default value is null. | ||||
|
| ||||
validationQueryTimeout
|
int
|
-1
| ||
|
The timeout in seconds before a connection validation queries fail. This works by calling java.sql.Statement.setQueryTimeout(seconds) on the statement that executes the validationQuery. The pool itself doesnt timeout the query, it is still up to the JDBC driver to enforce query timeouts. A value less than or equal to zero will disable this feature. The default value is -1. | ||||
|
| ||||
validationQuery
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The SQL query that will be used to validate connections from this pool before returning them to the caller. If specified, this query does not have to return any data, it just cant throw a SQLException. The default value is null. Example values are SELECT 1(mysql), select 1 from dual(oracle), SELECT 1(MS Sql Server) | ||||
|
| ||||
rollbackOnReturn
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If autoCommit==false then the pool can terminate the transaction by calling rollback on the connection as it is returned to the pool Default value is false. | ||||
|
| ||||
alternateUsernameAllowed
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
By default, the jdbc-pool will ignore the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, and simply return a previously pooled connection under the globally configured properties username and password, for performance reasons. The pool can however be configured to allow use of different credentials each time a connection is requested. To enable the functionality described in the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, simply set the property alternateUsernameAllowed to true. Should you request a connection with the credentials user1/password1 and the connection was previously connected using different user2/password2, the connection will be closed, and reopened with the requested credentials. This way, the pool size is still managed on a global level, and not on a per schema level. | ||||
|
| ||||
dataSourceJNDI
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The JNDI name for a data source to be looked up in JNDI and then used to establish connections to the database. See the dataSource attribute. Default value is null | ||||
|
| ||||
validatorClassName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The name of a class which implements the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.Validator interface and provides a no-arg constructor (may be implicit). If specified, the class will be used to create a Validator instance which is then used instead of any validation query to validate connections. The default value is null. An example value is com.mycompany.project.SimpleValidator. | ||||
|
| ||||
suspectTimeout
|
int
|
0
| ||
|
Timeout value in seconds. Similar to to the removeAbandonedTimeout value but instead of treating the connection as abandoned, and potentially closing the connection, this simply logs the warning if logAbandoned is set to true. If this value is equal or less than 0, no suspect checking will be performed. Suspect checking only takes place if the timeout value is larger than 0 and the connection was not abandoned or if abandon check is disabled. If a connection is suspect a WARN message gets logged and a JMX notification gets sent once. | ||||
|
| ||||
useEquals
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Set to true if you wish the ProxyConnection class to use String.equals and set to false when you wish to use == when comparing method names. This property does not apply to added interceptors as those are configured individually. The default value is true. | ||||
|
| ||||
removeAbandonedTimeout
|
int
|
60
| ||
|
Timeout in seconds before an abandoned(in use) connection can be removed. The default value is 60 (60 seconds). The value should be set to the longest running query your applications might have. | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultAutoCommit
|
Boolean
|
null
| ||
|
The default auto-commit state of connections created by this pool. If not set, default is JDBC driver default (If not set then the setAutoCommit method will not be called.) | ||||
|
| ||||
testOnConnect
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
jdbcInterceptors
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
A semicolon separated list of classnames extending org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.JdbcInterceptor class. See Configuring JDBC interceptors below for more detailed description of syntaz and examples. These interceptors will be inserted as an interceptor into the chain of operations on a java.sql.Connection object. The default value is null. | ||||
|
| ||||
initialSize
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The initial number of connections that are created when the pool is started. Default value is 10 | ||||
|
| ||||
defaultTransactionIsolation
|
int
|
-1
| ||
|
The default TransactionIsolation state of connections created by this pool. One of the following: NONE, READ_COMMITTED, READ_UNCOMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE If not set, the method will not be called and it defaults to the JDBC driver. | ||||
|
| ||||
numTestsPerEvictionRun
|
int
|
0
| ||
|
Property not used in tomcat-jdbc-pool. | ||||
|
| ||||
url
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
testOnBorrow
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool, and we will attempt to borrow another. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. In order to have a more efficient validation, see validationInterval. Default value is false | ||||
|
| ||||
fairQueue
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Set to true if you wish that calls to getConnection should be treated fairly in a true FIFO fashion. This uses the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue implementation for the list of the idle connections. The default value is true. This flag is required when you want to use asynchronous connection retrieval. Setting this flag ensures that threads receive connections in the order they arrive. During performance tests, there is a very large difference in how locks and lock waiting is implemented. When fairQueue=true there is a decision making process based on what operating system the system is running. If the system is running on Linux (property os.name=Linux. To disable this Linux specific behavior and still use the fair queue, simply add the property org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue.ignoreOS=true to your system properties before the connection pool classes are loaded. | ||||
|
| ||||
accessToUnderlyingConnectionAllowed
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Property not used. Access can be achieved by calling unwrap on the pooled connection. see javax.sql.DataSource interface, or call getConnection through reflection or cast the object as javax.sql.PooledConnection | ||||
|
| ||||
maxAge
|
long
|
0
| ||
|
Time in milliseconds to keep this connection. When a connection is returned to the pool, the pool will check to see if the now - time-when-connected > maxAge has been reached, and if so, it closes the connection rather than returning it to the pool. The default value is 0, which implies that connections will be left open and no age check will be done upon returning the connection to the pool. | ||||
|
| ||||
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis
|
int
|
60000
| ||
|
The minimum amount of time an object may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction. The default value is 60000 (60 seconds). | ||||
|
| ||||
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis
|
int
|
5000
| ||
|
The number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle connection validation/cleaner thread. This value should not be set under 1 second. It dictates how often we check for idle, abandoned connections, and how often we validate idle connections. The default value is 5000 (5 seconds). | ||||
|
| ||||
testOnReturn
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being returned to the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false. | ||||
|
| ||||
useLock
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
maxActive
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated from this pool at the same time. The default value is 100 | ||||
|
| ||||
username
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The connection username to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
When you call a Groovy script from the Groovy connector, you can use the SLF4J logging facility to obtain debug information.
For instructions on how to use this facility, see the KnowledgeBase article How do I add logging to Groovy scripts in IDM.
The SAP connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector Toolkit that connects to any SAP system using the SAP JCo Java libraries. This chapter describes how to install and configure the scripted SAP connector, and how to test the sample scripts that are bundled with the connector.
The sample scripts illustrate the following scenarios:
Synchronization of users between an SAP HR module and IDM
Synchronization of users between IDM and an SAP (R/3) system
The SAP connector requires the SAP Java Connector (JCo) libraries, version 3.0.12 or later. ForgeRock distributes the SAP connector without these JCo libraries. Before you can use the SAP connector, you must obtain the JCo libraries that correspond to your architecture.
Download the SAP connector from ForgeRock's BackStage site.
Copy the SAP connector JAR file (
sap-connector-1.4.2.0.jar) to theopenidm/connectorsdirectory:$ cp ~/Downloads/sap-connector-1.4.2.0.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors
Copy the SAP JCo libraries that correspond to your architecture to the
/path/to/openidm/libdirectory. For example:$ cp sapjco3.jar /path/to/openidm/lib $ cp libsapjco3.so /path/to/openidm/lib
Change your IDM logging configuration to log messages from the SAP connector.
By default, IDM logs nothing for the SAP connector. To troubleshoot any issues with the connector, set the following properties in your project's
conf/logging.propertiesfile:# SAP Connector Logging org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.level=FINER samples.r3.level=FINER samples.hr.level=FINER samples.level=FINER
The SAP HR sample scripts enable you to manage the email address and global employee UID of records in an SAP HR system.
The following sections explain how to configure IDM to use these sample scripts, how to test the connection to the SAP HR system, and how to update user records.
Create a connector configuration file for the SAP connector and place it in your project's
conf/directory.You can use this sample provisioner.openicf-saphr.json as a guide.
Edit that file with the connection details for your SAP HR system. Specifically, set at least the following properties:
destinationAn alias to the SAP system to which you are connecting, for example,
SAP1. If you are connecting to more than one SAP system, thedestinationproperty for each system must be unique.The sample connector configuration assumes a connection to a single SAP system, so the value for this property in the sample configuration is
OPENIDM.asHostThe FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example
sap.example.com.userYour SAP user account.
passwordThe password of this SAP user account.
clientThe SAP Client number that will be used to connect to the SAP system.
systemNumberThe SAP system number.
directConnectionA boolean (true/false). If
true, the connection goes directly to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. Iffalse, the connection goes to a group of SAP instances, through an SAP message server.sapRouterThe IP address and port of the SAP router, if applicable. The syntax is
/H/host[/S/port], for example/H/203.0.113.0/S/3299.poolCapacityThe maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. If there is no connection pooling, set this to
0. The default value is1.For optimum performance, set this value to an integer between
5and10.
To test this connector, you can use the sample Groovy scripts available from the ForgeRock Artifact Repository Browser. You can find the source for these scripts in this location, in the
samples/directory, as well as thesamples/hr/subdirectory.TestSAP.groovySearchSAPHR.groovyUpdateSAPHR.groovySchemaSAPHR.groovyEmplComm.groovyUpdate your connector configuration to point to those scripts. The sample connector configuration assumes the following locations for the scripts (relative to the value of the
scriptRootsproperty):"testScriptFileName" : "samples/TestSAP.groovy", "searchScriptFileName" : "samples/hr/SearchSAPHR.groovy", "updateScriptFileName" : "samples/hr/UpdateSAPHR.groovy", "schemaScriptFileName" : "samples/hr/SchemaSAPHR.groovy",
The
EmplComm.groovymust be placed in the same location as the Search, Update, and Schema scripts.Important
The Groovy scripts belong to a specific package. The parent directory where the scripts are located must be the same as the package name. So the
TestSAP.groovyscript must be under asamplesdirectory (because it belongs to thesamplespackage) and the remaining HR scripts must be under asamples/hrdirectory (because they belong to thehrpackage).
Start IDM with the configuration for your SAP connector project.
This procedure assumes that the configuration is in the default
path/to/openidmdirectory. If your SAP project is in a different directory, use the-poption with the startup command to point to that directory.$ cd path/to/openidm $ ./startup.sh
Test that the connector has been configured correctly and that the SAP HR system can be reached:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/?_action=test" { "name" : "saphr", "enabled" : true, "config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/saphr2", "objectTypes" : [ "__ALL__", "employee" ], "connectorRef" : { "connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.SapConnector", "bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap-connector", "bundleVersion" : "1.4.2.0" }, "displayName" : "Sap Connector", "ok" : true }Retrieve a list of the existing users (with their employee number) in the SAP HR system:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee?_queryId=query-all-ids" { "result" : [ { "_id" : "00000010", "__NAME__" : "00000010" }, { "_id" : "00000069", "__NAME__" : "00000069" }, { "_id" : "00000070", "__NAME__" : "00000070" }, ...Retrieve the complete record of an employee in the SAP HR system by including the employee's ID in the URL.
The following command retrieves the record for employee Maria Gonzales:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" { "_id" : "55099307", "PERSONAL_DATA" : { "PERNO" : "55099307", "INFOTYPE" : "0002", "TO_DATE" : "Fri Dec 31 00:00:00 CET 9999", "FROM_DATE" : "Tue Mar 30 00:00:00 CET 1954", "SEQNO" : "000", "CH_ON" : "Thu Mar 27 00:00:00 CET 2003", "CHANGED_BY" : "MAYROCK", "LAST_NAME" : "Gonzales", "FIRSTNAME" : "Maria", "NAME_FORM" : "00", "FORMOFADR" : "2", "GENDER" : "2", "BIRTHDATE" : "Tue Mar 30 00:00:00 CET 1954", "LANGU" : "D", "NO_O_CHLDR" : "0", "BIRTHYEAR" : "1954", "BIRTHMONTH" : "03", "BIRTHDAY" : "30", "LASTNAME_M" : "GONZALES", "FSTNAME_M" : "MARIA" }, ... }
The following sample commands show how the SAP connector is used to manage
the email account of user Maria Gonzales, retrieved in the previous step.
Management of the global UID (SYS-UNAME) works in the same
way.
Check if Maria Gonzales already has an email account on the SAP HR system by filtering a query on her user account for the
EMAILfield:$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307?_fields=EMAIL" { "_id" : "55099307", }No email account is found for Maria Gonzales.
Add an email account by sending a PUT request. The JSON payload should include the email address as the value of the
IDproperty:$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales@example.com" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" { "_id" : "55099307", "EMAIL" : [ { "EMPLOYEENO" : "55099307", "SUBTYPE" : "0010", "VALIDEND" : "Fri Dec 31 00:00:00 CET 9999", "VALIDBEGIN" : "Fri March 18 00:00:00 CET 2016", "RECORDNR" : "000", "COMMTYPE" : "0010", "NAMEOFCOMMTYPE" : "E-mail", "ID" : "Maria.Gonzales@example.com" } ], ...By default, the connector sets the
VALIDBEGINdate to the current date, and theVALIDENDdate to the SAP "END" date (12/31/9999). You can specify different temporal constraints by including these properties in the JSON payload, with the formatYYYYMMDD. For example:{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales@example.com" "VALIDBEGIN": "20160401", "VALIDEND": "20161231" } }To change the value of an existing email account, provide a new value for the
ID.The JSON payload of the change request must also include the
RECORDNRattribute, as well as theVALIDBEGINandVALIDENDdates, in SAP format (YYYYMMDD).The following example changes Maria Gonzales' email address to
maria.gonzales-admin@example.com:$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales-admin@example.com", "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307"To change the temporal constraint (
VALIDENDdate) of the record, include the existingVALIDENDdata in the JSON payload, and specify the new end date as a value of theDELIMIT_DATEattribute.The following example changes the end date of Maria Gonzale's new mail address to December 31st, 2016:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales-admin@example.com", "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101", "DELIMIT_DATE": "20161231" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307"To delete the email address of the record, send a PUT request with the current
RECORDNR,VALIDBEGIN, andVALIDENDattributes, but without theID.The following request removes the email address from Maria Gonzales' record:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307"
The SAP Connector enables you to perform the following operations on SAP system user accounts:
List all users
List all activity groups (roles)
Manage user profiles
List all user companies
Obtain a user's details
Create a user
Update a user
Assign roles to a user
Lock a user account
Unlock a user account
Delete a user account
Currently, the SAP connector cannot detect changes on the SAP system in real time. You must run a reconciliation operation to detect changes on the SAP system.
Create a connector configuration file for the SAP connector and place it in your project's
conf/directory.You can use this sample provisioner.openicf-sapr3.json as a guide.
Edit that file with the connection details for your SAP R/3 system. Specifically, set at least the following properties:
destinationAn alias to the SAP system to which you are connecting, for example,
SAP1. If you are connecting to more than one SAP system, thedestinationproperty for each system must be unique.The sample connector configuration assumes a connection to a single SAP system,
MYSAP.asHostThe FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example
sap.example.com.userYour SAP user account.
passwordThe password of this SAP user account.
clientThe SAP Client number that will be used to connect to the SAP system.
systemNumberThe SAP system number.
directConnectionA boolean (true/false). If
true, the connection goes directly to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. Iffalse, the connection goes to a group of SAP instances, through an SAP message server.sapRouterThe IP address and port of the SAP router, if applicable. The syntax is
/H/host[/S/port], for example/H/203.0.113.0/S/3299.poolCapacityThe maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. If there is no connection pooling, set this to
0. The default value is1.For optimum performance, set this value to an integer between
5and10.
To test this connector, you can use the sample Groovy scripts available from the ForgeRock Artifact Repository Browser. You can find the source for these scripts in this location, in the
samples/directory, as well as thesamples/r3/subdirectory.TestSAP.groovySearchSAPR3.groovyCreateSAPR3.groovyUpdateSAPR3.groovyDeleteSAPR3.groovySchemaSAPR3.groovyUpdate your connector configuration to point to those scripts. The sample connector configuration assumes the following locations for the scripts (relative to the value of the
scriptRootsproperty):"testScriptFileName" : "samples/TestSAP.groovy", "searchScriptFileName" : "samples/r3/SearchSAPR3.groovy", "createScriptFileName" : "samples/r3/CreateSAPR3.groovy", "updateScriptFileName" : "samples/r3/UpdateSAPR3.groovy", "deleteScriptFileName" : "samples/r3/DeleteSAPR3.groovy", "schemaScriptFileName" : "samples/r3/SchemaSAPR3.groovy",
Important
The Groovy scripts belong to a specific package. The parent directory where the scripts are located must be the same as the package name. So the
TestSAP.groovyscript must be under asamplesdirectory (because it belongs to thesamplespackage) and the R/3 scripts must be under asamples/r3directory (because they belong to ther3package).
Start IDM with the configuration for your SAP R/3 project.
This procedure assumes that the configuration is in the default
path/to/openidmdirectory. If your SAP project is in a different directory, use the-poption with the startup command to point to that directory.$ cd path/to/openidm $ ./startup.sh
Test that the connector has been configured correctly and that the SAP R/3 system can be reached:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/?_action=test" { "name": "mysap", "enabled": true, "config": "config/provisioner.openicf/mysap", "objectTypes": [ "__ALL__", "user", "activity_group", "company", "profile" ], "connectorRef": { "connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.SapConnector", "bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap-connector", "bundleVersion": "1.4.2.0" }, "displayName": "Sap Connector", "ok": true }
This section provides sample commands for managing users in an SAP system.
The following command returns a list of the existing users in the SAP system, with their IDs:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
},
{
"_id": "DDIC",
"__NAME__": "DDIC"
},
...
{
"_id": "USER4",
"__NAME__": "USER4"
},
{
"_id": "USER6",
"__NAME__": "USER6"
},
{
"_id": "USER7",
"__NAME__": "USER7"
}
],
"resultCount": 9,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}The following command uses the SAP connector to obtain a user's details from a target SAP system:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"__ENABLE_DATE__": "2015-09-01",
"__DISABLE_DATE__": "2016-09-01",
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"ADDTEL": [
{
"COUNTRY": "DE",
"TELEPHONE": "19851444",
...
},
...
],
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "T_ALM_CONF",
...
}
],
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
...
},
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "MW_ADMIN",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-07-15",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31",
"AGR_TEXT": "Middleware Administrator"
},
...
],
"DEFAULTS": {
...
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"ADDRESS": {
...
},
"UCLASS": {
...
},
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2015-07-15",
"MODTIME": "14:22:57"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2015-09-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-09-01",
...
},
"_id": "BJENSEN"
}In addition to the standard user attributes, the GET request returns the following OpenICF operational attributes:
__ENABLE__- indicates whether the account is enabled, based on the value of theLOGONDATAattribute__ENABLE_DATE__- set to the value ofLOGONDATA/GLTGV(date from which the user account is valid)__DISABLE_DATE__- set to the value ofLOGONDATA/GLTGB(date to which the user account is valid)__LOCK_OUT__- indicates whether the account is locked
To create a user, you must supply at least a username and password. If you do not provide a lastname, the connector uses the value of the username.
The following command creates a new SAP user, SCARTER:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"ADDRESS": {
...
},
"__NAME__": "SCARTER",
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-20",
"MODTIME": "04:14:29"
},
"UCLASS": {
"COUNTRY_SURCHARGE": "0",
"SUBSTITUTE_FROM": "0000-00-00",
"SUBSTITUTE_UNTIL": "0000-00-00"
},
"__ENABLE__": true,
"DEFAULTS": {
"SPDB": "H",
"SPDA": "K",
"DATFM": "1",
"TIMEFM": "0"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
...
},
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "U",
"GLOB_LOCK": "U",
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
}
}The SAP account that is created is valid and enabled, but the password is expired by default. To log into the SAP system, the newly created user must first provide a new password.
To create a user with a valid (non-expired) password, include the
__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__ attribute in the JSON payload, with
a value of false. For example:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
To create an account that is locked by default, include the
__LOCK_OUT__ attribute in the JSON payload, with a value
of true. For example:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__LOCK_OUT__": true
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"__NAME__": "SCARTER",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"__LOCK_OUT__": true,
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "0000-00-00",
"GLTGB": "0000-00-00",
"USTYP": "A",
"LTIME": "00:00:00",
"BCODE": "2FC0D86C99AA5862",
"CODVN": "B",
"PASSCODE": "1DBBD983287D7CB4D8177B4333F439F808A395FA",
"CODVC": "F",
"PWDSALTEDHASH": "{x-issha, 1024}zrs3Zm/fX/l/KFGATp3kvOGlis3zLLiPmPVCDpJ9XF0=",
"CODVS": "I"
},
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2015-10-01",
"MODTIME": "15:25:18"
},
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "L", // "L" indicates that the user is locked on the local system
"GLOB_LOCK": "U",
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
},
...For the most part, the SAP connector uses the standard SAP schema to create a user account. The most common attributes in an SAP user account are as follows:
ADDRESS- user address dataLOGONDATA- user logon dataDEFAULTS- user account defaultsCOMPANY- the company to which the user is assignedREF_USER- the usernames of the Reference UserALIAS- an alias for the usernameUCLASS- license-related user classificationLASTMODIFIED- read-only attribute that indicates the date and time that the account was last changedISLOCKED- read-only attribute that indicates the lockout status of the accountIDENTITY- assignment of a personal identity to the user accountPROFILES- any profiles assigned to the user account (see "Managing User Profiles").ACTIVITYGROUPS- activity groups assigned to the userADDTEL- telephone numbers assigned to the user
In addition, the SAP connector supports the following OpenICF operational attributes for CREATE requests:
LOCK_OUTPASSWORDPASSWORD_EXPIRED
The following example creates a user, KVAUGHAN, with all of the standard attributes:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "KVAUGHAN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2016-04-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-12-01",
"USTYP": "A"
},
"ADDRESS": {
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"TEL1_NUMBR": "33297603177",
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"FUNCTION": "Test User"
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "EXAMPLE.COM"
},
"ALIAS": {
"USERALIAS": "KVAUGHAN"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "KVAUGHAN",
"ADDRESS": {
"PERS_NO": "0000010923",
"ADDR_NO": "0000010765",
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"FULLNAME": "Katie Vaughan",
...
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"LANGU_CR_P": "E",
"LANGUCPISO": "EN"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2016-04-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-12-01",
...
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"__ENABLE__": true,
"ADDTEL": [
{
...
}
],
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "U",
"GLOB_LOCK": "U",
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
},
"UCLASS": {
"COUNTRY_SURCHARGE": "0",
"SUBSTITUTE_FROM": "0000-00-00",
"SUBSTITUTE_UNTIL": "0000-00-00"
},
"ALIAS": {
"USERALIAS": "KVAUGHAN"
},
"__NAME__": "KVAUGHAN",
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-20",
"MODTIME": "04:55:08"
},
"__ENABLE_DATE__": "2016-04-01", // (Value of LOGONDATA/GLTGV)
"DEFAULTS": {
"SPDB": "H",
"SPDA": "K",
"DATFM": "1",
"TIMEFM": "0"
},
"__DISABLE_DATE__": "2016-12-01" // (Value of LOGONDATA/GLTGB)
}
The following sections provide sample commands for updating an existing user account.
To lock or unlock a user's account, send a PUT request, and set the value
of the user's __LOCK_OUT__ attribute to
true.
The following example locks user KVAUGHAN's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__LOCK_OUT__": true
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"The following example unlocks KVAUGHAN's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__LOCK_OUT__": false
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"To update a user's standard attributes, send a PUT request to the user ID. The JSON payload must respect the structure for each attribute, as indicated in "Schema Used by the SAP Connector For User Accounts".
The following command updates the ADDRESS attribute of
user KVAUGHAN:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ADDRESS": {
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"FULLNAME": "Katie Vaughan",
"FUNCTION": "Administrator",
"TITLE": "Company",
"NAME": "EXAMPLE.COM",
"CITY": "San Francisco",
"POSTL_COD1": "94105",
"STREET": "Sacramento St",
"HOUSE_NO": "2912",
"COUNTRY": "US",
"COUNTRYISO": "US",
"LANGU": "E",
"LANGU_ISO": "EN",
"REGION": "CA",
"TIME_ZONE": "PST",
"TEL1_NUMBR": "33297603177",
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"LANGU_CR_P": "E",
"LANGUCPISO": "EN"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
To reset the user's password, provide the new password as the value of the
__PASSWORD__ attribute, in a PUT request. The following
command resets KVAUGHAN's password to MyPassw0rd:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "MyPassw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
Note that unless you set the __PASSWORD_EXPIRED__
attribute to false, the user will be required to reset
her password the next time she logs into the SAP system.
The following command resets KVAUGHAN's password to
MyPassw0rd, and ensures that she does not have to reset
her password the next time she logs in:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "MyPassw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false
}'
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"To delete a user account, send a DELETE request to the user ID. The following example deletes KVAUGHAN:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
The command returns the complete user object that was deleted.
An SAP system uses profiles to manage authorization. The following examples demonstrate how to add, change, and remove a user's profiles.
Profiles are added as an array of one or more objects.
The following command creates a user BJENSEN, with the system administrator
profile (S_A.SYSTEM):
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"PROFILES": [
{"BAPIPROF": "S_A.SYSTEM"}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "S_A.SYSTEM",
"BAPIPTEXT": "System administrator (Superuser)",
"BAPITYPE": "S",
"BAPIAKTPS": "A"
}
],
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}Note that the additional information regarding that profile is added to the user account automatically.
To update a user's profiles, send a PUT request to the user's ID,
specifying the new profiles as an array of values for the
PROFILES attribute. The values provided in the PUT
request will replace the current profiles, so you must include the existing
profiles in the request.
The following example adds the SAP_ALL profile to user
BJENSEN's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"PROFILES": [
{"BAPIPROF": "S_A.SYSTEM"},
{"BAPIPROF": "SAP_ALL"}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "SAP_ALL",
"BAPIPTEXT": "All SAP System authorizations",
"BAPITYPE": "C",
"BAPIAKTPS": "A"
},
{
"BAPIPROF": "S_A.SYSTEM",
"BAPIPTEXT": "System administrator (Superuser)",
"BAPITYPE": "S",
"BAPIAKTPS": "A"
}
],
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}To remove all profiles from a user's account, update the account with an empty array. The following example removes all profiles from BJENSEN's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"PROFILES": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}
The output shows no PROFILES attribute, as this
attribute is now empty for this user.
SAP user roles (or activity groups) are an alternative mechanism to grant authorization to an SAP system. Essentially, a role encapsulates a set of one or more profiles.
Roles can be granted with temporal constraints, that is, a period during which the role is valid. If no temporal constraints are specified, the SAP connector sets the FROM date to the current date and the TO date to 9999-12-31.
Roles are added as an array of one or more objects.
The following command creates a user SCARTER, with two roles:
SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR and
SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR. The auditor role has a temporal
constraint, and is valid only from May 1st, 2016 to April 30th, 2017. The
format of the temporal constraint is YYYY-mm-dd:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-05-01",
"TO_DAT": "2017-04-30"
},
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR"
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "T_ALM_CONF",
"BAPIPTEXT": "Profile for the Role SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"BAPITYPE": "G",
"BAPIAKTPS": "A"
}
],
...
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-04-20",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31",
"AGR_TEXT": "Alert Management Administrator"
},
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-05-01",
"TO_DAT": "2017-04-30",
"AGR_TEXT": "AIS - System Audit - Users and Authorizations"
}
],
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}When a role is granted, the corresponding profiles are attached to the user account automatically.
To update a user's roles, send a PUT request to the user's ID,
specifying the new roles as an array of values of the
ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute. The values provided in the PUT
request will replace the current ACTIVITYGROUPS.
The following example removes the SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR
role and changes the temporal constraints on the
SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR role for SCARTER's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-06-02",
"TO_DAT": "2016-06-02"
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "T_ALM_CONF",
"BAPIPTEXT": "Profile for the Role SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"BAPITYPE": "G",
"BAPIAKTPS": "A"
}
],
...
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-06-02",
"TO_DAT": "2016-06-02",
"AGR_TEXT": "Alert Management Administrator"
}
],
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
To remove all roles from a user's account, update the value of the
ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute with an empty array. The
following example removes all roles from SCARTER's account:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
...
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-21",
"MODTIME": "04:27:00"
},
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
The output shows no ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute, as this
attribute is now empty.
The SAP connector supports an SNC (Secure Network Connection) configuration. SNC is a software layer in the SAP System architecture that provides an interface to an external security product.
For a list of the configuration properties specific to SNC, see "SAP Secure Network Connection Configuration Properties".
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The SAP connector implements the add, remove, and replace operations but the sample scripts provided with the connector implement only the replace operation. If you use these sample scripts, a PATCH request will therefore always replace the entire attribute value with the new value.
Synchronization of passwords to the SAP system requires that you configure SNC and SSO. If you do not configure these two elements correctly, passwords that are updated by IDM are set as initial passwords rather than productive passwords, and users are forced to change their passwords on login.
To configure the SAP connector to use SNC, set the
sncModeproperty to"1".To configure the connector to use SSO with SNC, set the
sncSSOproperty to"1".The logon session during which a productive password is set must be secured using the authentication method Single Sign-On (SSO) using Secure Network Communications (SNC). IDM must request and receive an SSO logon ticket from the SAP system to allow the
BAPI_USER_CHANGEprocess to set a productive password. For more information, see the corresponding SAP Note 1287410 at https://service.sap.com/sap/support/notes/1287410.To configure the connector to request this logon ticket, set the value of the
x509Certproperty as follows:If you are using an X509 certificate to negotiate with the SAP server, set the
x509Certproperty to the base 64-encoded certificate.Note that the certificate must be a valid, CA-signed certificate. You cannot use a self-signed certificate here.
If you are not using an X509 certificate to negotiate with the SAP server, set the
x509Certproperty tonull.In this case, the connector will use the
userandpasswordspecified in the connector configuration to request the SSO logon ticket.
The SAP Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The SAP Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
x509Cert
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
asHost
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example sap.example.com | ||||
|
| ||||
gwHost
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
SAP gateway host name | ||||
|
| ||||
gwServ
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
SAP gateway service | ||||
|
| ||||
user
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
SAP Logon user | ||||
|
| ||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
SAP Logon password | ||||
|
| ||||
client
|
String
|
000
| ||
|
SAP client | ||||
|
| ||||
systemNumber
|
String
|
00
| ||
|
SAP system number | ||||
|
| ||||
language
|
String
|
EN
| ||
|
SAP Logon language | ||||
|
| ||||
destination
|
String
|
OPENIDM
| ||
|
SAP JCo destination name | ||||
|
| ||||
directConnection
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
If true, direct connection to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. If false connection to a group of SAP instances through an SAP message server | ||||
|
| ||||
sapRouter
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
SAP router string to use for a system protected by a firewall. (/H/host[/S/port]) | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
trace
|
String
|
0
| ||
|
Enable/disable RFC trace (0 or 1) | ||||
|
| ||||
cpicTrace
|
String
|
0
| ||
|
Enable/disable CPIC trace [0..3] | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
msHost
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the host that the message server is running on | ||||
|
| ||||
group
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the group name of the application servers, used when you log in to a logon group that uses load balancing | ||||
|
| ||||
msServ
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Name of the service where the message server can be reached | ||||
|
| ||||
r3Name
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the name of the SAP system, used when you log in to a logon group that uses load balancing | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
sncMode
|
String
|
0
| ||
|
Flag used to activate SNC. Possible values are 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON). | ||||
|
| ||||
sncQoP
|
String
|
3
| ||
|
Specifies the security level to use for the connection. Possible values are 1 - Authentication only, 2 - Integrity protection, 3 - Privacy protection, 8 - Use the value from snc/data_protection/use on the application server, 9 - Use the value from snc/data_protection/max on the application server | ||||
|
| ||||
sncLibrary
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the path to the external library that provides Secure Network Connection service. The default is the system-defined library as defined in the environment variable SNC_LIB. | ||||
|
| ||||
sncPartnerName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the AS ABAP SNC name, for example, "p:CN=ABC, O=MyCompany, C=US". You can find the application server SNC name in the profile parameter snc/identity/as on the AS ABAP. | ||||
|
| ||||
sncMyName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Specifies the connector SNC name, for example, "p:CN=OpenIDM, O=MyCompany, C=US". This parameter is optional, but you should set it to make sure that the correct SNC name is used for the connection. | ||||
|
| ||||
sncSSO
|
String
|
0
| ||
|
Specifies whether the connection should be configured for single sign-on (SSO). Possible values are 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON). | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
poolCapacity
|
String
|
1
| ||
|
Maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. 0 = no connection pooling. Default is 1. | ||||
|
| ||||
expirationTime
|
String
|
60000
| ||
|
Time in ms after that a free connection can be closed. Default is one minute. | ||||
|
| ||||
maxGetTime
|
String
|
30000
| ||
|
Maximum time in ms to wait for a connection, if the maximum allowed number of connections is allocated by the pool. Default is 30 seconds. | ||||
|
| ||||
peakLimit
|
String
|
0
| ||
|
Maximum number of active connections that can be created for a destination simultaneously. The default is 0 (unlimited). | ||||
|
| ||||
expirationPeriod
|
String
|
60000
| ||
|
Period in ms after that the destination checks the released connections for expiration. Default is one minute | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The SSH connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector Toolkit, and is based on Java Secure Channel (JSch) and the Java implementation of the Expect library (Expect4j). This connector enables you to interact with any SSH server, using Groovy scripts for the OpenICF operations.
The SSH connector is a poolable connector. This means that each connector instance is placed into a connection pool every time an action is completed. Subsequent actions can re-use connector instances from the connector pool. When a new connector instance is created, a new SSH client connection is created against the target SSH server. This SSH connection remains open as long as the connector instance is in the connection pool. Note that when a new action is performed, it finds the SSH connection in the exact state that it was left by the previous action.
The following image shows the relationship between SSH connector instances and SSH connections to the target server:
The SSH connector authenticates to the SSH server using either a
login/password or a public/private key. The authentication method is
specified in the authenticationType property in the
connector configuration file
(conf/provisioner.openicf-ssh.json).
- Authenticating with a login and password
To authenticate with a login and password, set the
authenticationTypetoPASSWORDin the connector configuration file, and set auserandpassword. For example:"configurationProperties" : { ... "authenticationType" : "PASSWORD", "user" : "<USERNAME>", "password" : "<PASSWORD>", ...The password is encrypted when IDM loads the provisioner file.
- Authenticating with a passphrase and private key
To authenticate with a secure certificate, generate a pair of public/private keys. Install the public key on the server side and the private key on the IDM host (where the connector is located). Set the
authenticationTypetoPUBKEYin the connector configuration file and set theuser,password,passphraseandprivateKeyproperties. For example:"configurationProperties" : { ... "authenticationType" : "PUBKEY", "user" : "<USERNAME>", "password" : "<PASSWORD>", "passphrase" : "secret", "privateKey" : ["-----BEGIN DSA PRIVATE KEY-----", "MIIBugIBAAKBgQDcB0ztVMCFptpJhqlLNZSdN/5cDL3S7aOVy52Ae7vwwCqQPCQr", "6NyUk+wtkDr07NlYd3sg7a9hbsEnlYChsuX+/WUIvbOKdMfeqcQ+jKK26YdkTCGj", "g86dBj9JYhobSHDoQ9ov31pYN/cfW5BAZwkm9TdpEjHPvMIaOxx7GPGKWwIVALbD", "CEuf1yJk9UB7v0dmJS7bKkbxAoGARcbAuDP4rB6MsgAAkVwf+1sHXEiGPShYWrVV", "qBgCZ/S45ELqUuiaN/1N/nip/Cc/0SBPKqwl7o50CUg9GH9kTAjmXiwmbkwvtUv+", "Xjn5vCHS0w18yc3rGwyr2wj+D9KtDLFJ8+T5HmsbPoDQ3mIZ9xPmRQuRFfVMd9wr", "DY0Rs7cCgYAxjGjWDSKThowsvOUCiE0ySz6tWggHH3LTrS4Mfh2t0tnbUfrXq2cw", "3CN+T6brgnpYbyX5XI17p859C+cw90MD8N6vvBxaN8QMDRFk+hHNUeSy8gXeem9x", "O0vdIxCgKvA4dh5nSVb5VGKENEGNEHRlYxEPzbqlPa/C/ZvzIvdKXQIUQMoidPFC", "n9z+mE2dAADnPf2m9vk=", "-----END DSA PRIVATE KEY-----" ], ...The default value for the
passphraseproperty isnull. If you do not set a passphrase for the private key, the passphrase value must be equal to an empty string.You must set a value for the
passwordproperty, because the connector uses sudo to perform actions on the SSH server.The private key (PEM certificate) must be defined as a JSON String array.
The values of the
passphrase,passwordandprivateKeyare encrypted when IDM loads the provisioner file.
IDM provides a sample connector configuration
(provisioner.openicf-ssh.json) in the
/path/to/openidm/samples/ssh/conf/ directory.
You can copy the sample connector configuration to your project's
conf/ directory, and adjust it to match your Kerberos
environment.
Set the authentication properties, as described in "Configuring Authentication to the SSH Server". In addition, set at least the following properties:
hostSpecify the hostname or IP address of the SSH server.
portSet the port on which the SSH server listens.
Default:
22userThe username of the account that connects to the SSH server.
This account must be able to
sshinto the server, with the password provided in the next parameter.passwordThe password of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
promptA string representing the remote SSH session prompt. This must be the exact prompt string, in the format
username@target:, for exampleadmin@myserver:~$. Include any trailing spaces.
The following list describes the configuration properties of the SSH connector shown in the sample connector configuration file. You can generally use the defaults provided in the sample connector configuration file, in most cases. For a complete list of all the configuration properties of the SSH connector, see "Configuration Properties".
sudoCommandA string that shows the full path to the sudo command, for example
/usr/bin/sudo.echoOffIf set to
true(the default), the input command echo is disabled. If set tofalse, every character that is sent to the server is sent back to the client in theexpect()call.terminalTypeSets the terminal type to use for the session. The list of supported types is determined by your Linux/UNIX system. For more information, see the
terminfomanual page ($ man terminfo).Default:
vt102setLocaleIf set to
true, indicates that the default environment locale should be changed to the value of thelocaleproperty.Default:
falselocaleSets the locale for the LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables, if
setLocaleis set totrue.Default:
en_US.utf8connectionTimeoutSpecifies the connection timeout to the remote server, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000expectTimeoutSpecifies the timeout used by the
expect()calls in scripts, in milliseconds.Default:
5000authenticationTypeSets the authentication type, either
PASSWORDorPUBKEY. For more information, see "Configuring Authentication to the SSH Server".Default:
PASSWORDthrowOperationTimeoutExceptionIf
true, the connector throws an exception when theexpectTimeoutis reached for an operation. Otherwise, the operation fails silently.Default:
truescriptRootsThe path to the Groovy scripts that will perform the OpenICF operations, relative to your IDM installation directory. The sample connector configuration expects the scripts in
project-dir/tools, so this parameter is set to&{launcher.project.location}/toolsin the sample configuration.classpathThe directory in which the compiler should look for compiled classes. The default classpath, if not is specified, is
install-dir/lib.reloadScriptOnExecutionBy default, scripts are loaded and compiled when a connector instance is created and initialized. Setting
reloadScriptOnExecutionto true makes the connector load and compile the script every time it is called. Do not set this property totruein a production environment, because it will have a significant impact on performance.Default:
false*ScriptFileNameThe name of the Groovy script that is used for each OpenICF operation.
The SSH Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The SSH Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
host
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The hostname to connect to | ||||
|
| ||||
port
|
int
|
22
| ||
|
TCP port to use (defaults to 22) | ||||
|
| ||||
user
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The user name used to login to remote server | ||||
|
| ||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The password used to login to remote server | ||||
|
| ||||
passphrase
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The passphrase used to read the private key when using Public Key authentication | ||||
|
| ||||
privateKey
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
The base 64 encoded value (PEM) of the private key used for Public Key authentication | ||||
|
| ||||
authenticationType
|
String
|
PASSWORD
| ||
|
Defines which authentication type should be use: PASSWORD or PUBKEY (defaults to PASSWORD) | ||||
|
| ||||
prompt
|
String
|
root@localhost:#
| ||
|
A string representing the remote SSH session prompt (defaults to root@localhost:# ) | ||||
|
| ||||
sudoCommand
|
String
|
/usr/bin/sudo
| ||
|
A string representing the sudo command (defaults to /usr/bin/sudo) | ||||
|
| ||||
echoOff
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Disable the input command echo (default to true) | ||||
|
| ||||
terminalType
|
String
|
vt102
| ||
|
Defines the terminal type to use for the session (default to vt102) | ||||
|
| ||||
locale
|
String
|
en_US.utf8
| ||
|
Define the locale for LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables to use if setLocale=true | ||||
|
| ||||
setLocale
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
Defines if the default environment locale should be changed with the value provided for locale (defaults to false) | ||||
|
| ||||
connectionTimeout
|
int
|
5000
| ||
|
Defines the connection timeout to the remote server in milliseconds (default to 5000) | ||||
|
| ||||
expectTimeout
|
long
|
5000
| ||
|
Defines the timeout used by the expect() calls in the scripts in milliseconds (default to 5000) | ||||
|
| ||||
throwOperationTimeoutException
|
boolean
|
true
| ||
|
Defines if an OperationTimeoutException should be thrown if any call to expect times out (defaults to true) | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
IDM bundles a Google Apps connector, along with a sample connector configuration. The Google Apps connector enables you to interact with Google's web applications.
The Google Apps connector is subject to the API Limits and Quotas that are imposed by Google. The connector also adheres to the implementation guidelines set out by Google for implementing exponential backoff.
The Google Apps connector uses OAuth2 to authorize the connection to the
Google service. To use this authorization mechanism, you must supply a
clientId and clientSecret in order to
obtain an access token from Google. You can obtain the
clientId and clientKey from the Google
Developers Console after you have configured your Web Application.
A sample Google Apps connector configuration file is provided in
samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-google.json
The following is an excerpt of the provisioner configuration file. This
example shows an excerpt of the provisioner configuration. The
default location of the connector .jar is
openidm/connectors. Therefore the value of the
connectorHostRef property must be
"#LOCAL":
{
"connectorHostRef": "#LOCAL",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps.GoogleAppsConnector",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps-connector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.4.0.0,2.0.0.0)"
}, The following excerpt shows the required configuration properties:
"configurationProperties": {
"domain": "",
"clientId": "",
"clientSecret": null,
"refreshToken": null
}, These configuration properties are fairly straightforward:
domainSet to the domain name for OAuth 2-based authorization.
clientIdA client identifier, as issued by the OAuth 2 authorization server. For more information, see the following section of RFC 6749: Client Identifier.
clientSecretSometimes also known as the client password. OAuth 2 authorization servers can support the use of
clientIdandclientSecretcredentials, as noted in the following section of RFC 6749: Client Password.- refreshToken
A client can use an OAuth 2 refresh token to continue accessing resources. For more information, see the following section of RFC 6749: Refresh Tokens.
For a sample Google Apps configuration that includes OAuth 2-based entries
for configurationProperties, see
"Synchronizing Accounts With the Google Apps Connector" in the Samples Guide.
The GoogleApps Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The GoogleApps Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
domain
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Internet domain name. See https://support.google.com/a/answer/177483?hl=en | ||||
|
| ||||
clientId
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Client identifier issued to the client during the registration process. | ||||
|
| ||||
clientSecret
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Client secret issued to the client during the registration process. | ||||
|
| ||||
refreshToken
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The refresh token allows you to get a new access token that is good for another hour. Refresh tokens never expire, they can only be revoked by the user or programatically by your app. | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Google Apps connector uses the Google Enterprise License Manager and Directory APIs to perform CRUD operations against resources within a Google Apps domain.
The following table lists the resource types that are supported by the Google Apps connector:
| OpenICF Native Type | Google Resource Type | Naming Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| __ACCOUNT__ | user | primaryEmail |
| __GROUP__ | group | |
| Member | member | {groupKey}/email |
| OrgUnit | orgUnit | {parentOrgUnitPath}/__NAME__ |
| LicenseAssignment | licenseAssignment | {productId}/sku/{skuId}/user/{primaryEmail} |
The Google Apps connector is subject to the following functional limitations:
The connector does not implement the OpenICF Sync operation so you cannot use the connector for liveSync of supported Google Apps resources to IDM managed objects.
The connector does not implement the Authenticate operation so you cannot use the connector to perform pass-through authentication between IDM and a Google Apps domain. You can also not use this connector to perform password Change operations (as opposed to password Reset) because the connector cannot authenticate on behalf of the end-user.
Support for Filters when performing Search operations is limited to those attributes described in "Supported Search Filters".
Google Apps creates a new User Alias each time the
primaryEmailaddress associated with the User object is modified. You cannot delete User Aliases with the Google Apps connector so you must manage Aliases directly from within the Google Apps console.The Google Apps connector does not support custom schemas. The connector is therefore not able to read or update attributes associated with custom schemas in your Google Apps domain.
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Google Apps connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
The Google Apps connector supports filtered searches against Google Apps resources. However, limitations imposed by the APIs provided by the Google Apps Admin SDK prevent filtering of resource types based on arbitrary attributes and values.
The following filter operators and attributes are supported for Search operations with the Google Apps connector:
| Object Type | Operators | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| __ACCOUNT__ | And, Contains, StartsWith, Equals | primaryEmail |
| __GROUP__ | Contains, Equals | |
| Member | Equals | {groupKey}/email |
| OrgUnit | StartsWith | {parentOrgUnitPath}/__NAME__ |
| LicenseAssignment | Equals | {productId}/sku/{skuId}/user/{primaryEmail} |
The Kerberos connector is an implementation of the SSH connector, and is based on Java Secure Channel (JSch) and the Java implementation of the Expect library (Expect4j). The connector depends on the following files, provided with IDM:
/path/to/openidm/lib/ssh-connector-1.4.2.0.jar/path/to/openidm/lib/expect4j-<version>.jar/path/to/openidm/lib/jsch-<version>.jar
The Kerberos connector enables you to manage Kerberos user principals from
IDM. The connector is provided in
/path/to/openidm/connectors/kerberos-connector-1.4.3.0.jar
and bundles a number of Groovy scripts to interact with a Kerberos admin
server. Users of the Kerberos connector are not expected to edit the bundled
Groovy scripts. The bundled scripts use the kadmin utility
to communicate with the Kerberos server.
The Kerberos connector enables you to perform the following operations on Kerberos user principals.
List the existing principals
Display the details of a principal
Add a user principal
Change the password of a user principal and unlock the principal
Delete a user principal
The Kerberos connector can only be used to manage the Kerberos
principal object type (which maps to the OpenICF
__ACCOUNT__ object). The following attributes are
supported in the schema:
principal- (maps to__NAME__and__UID__)__PASSWORD__- updatable, required when an object is created__LOCK_OUT__- updatable only; unlock an account by setting this attribute tofalsepolicy- the password policy used by the principalexpirationDate- the date that the user principal expirespasswordExpiration- the date that the password expiresmaximumTicketLife- the maximum ticket life for the principal. At the end of the ticket lifetime, the ticket can no longer be used. However, if the renewable lifetime (maximumRenewableLife) is longer than the ticket lifetime, the ticket holder can present the ticket to the KDC and request a new ticket.maximumRenewableLife- the period during which the ticket can be renewed. A renewed ticket usually has a new ticket lifetime, dating from the time that it was renewed, that is constrained by the renewable ticket lifetime.
In addition, the following read-only attributes are supported:
lastPasswordChangelastModifiedlastSuccessfulAuthenticationlastFailedAuthenticationfailedPasswordAttempts
A sample connector configuration
(provisioner.openicf-kerberos.json) is provided in the
/path/to/openidm/samples/sync-with-kerberos/conf/ directory.
You can copy the sample connector configuration to your project's
conf/ directory, and adjust it to match your Kerberos
environment.
Set the authentication properties, as described in "Configuring Authentication to the SSH Server". In addition, set at least the following properties:
customConfigurationSpecify the details of the user principal and the default realm here. The sample provisioner file has the following custom configuration:
"customConfiguration" : "kadmin{ cmd = '/usr/sbin/kadmin.local'; user = '<KADMIN USERNAME>'; default_realm = '<REALM, e.g. EXAMPLE.COM>' }",A complete custom configuration will look something like this:
"customConfiguration" : "kadmin { cmd = '/usr/sbin/kadmin.local'; user = 'openidm/admin'; default_realm = 'EXAMPLE.COM' }",customSensitiveConfigurationSet the password for the user principal here. The sample provisioner has the following configuration:
"customSensitiveConfiguration" : "kadmin { password = '<KADMIN PASSWORD>'}",Change this to reflect your user principal password, for example:
"customSensitiveConfiguration" : "kadmin { password = 'Passw0rd'}"
The following section describes the configuration parameters in the sample Kerberos connector configuration. For a complete list of the configuration properties for the Kerberos connector, see "Configuration Properties":
hostThe host name or IP address of the SSH server on which the kadmin command is run.
portThe port number on which the SSH server listens.
Default:
22(the default SSH port)userThe username of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
Note
This is not the same as your Kerberos user principal. This account must be able to
sshinto the server on which Kerberos is running, with the password provided in the next parameter.passwordThe password of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
promptA string representing the remote SSH session prompt. This must be the exact prompt string, in the format
username@target:, for exampleroot@localhost:~$.If the prompt includes a trailing space, you must include the space in the value of this property.
Consider customizing your Linux prompt with the
PS1andPS2variables, to set a safe prompt. For information about customizing promtps, see this article.sudoCommandA string that shows the full path to the sudo command, for example
/usr/bin/sudo.echoOffIf set to
true(the default), the input command echo is disabled. If set tofalse, every character that is sent to the server is sent back to the client in theexpect()call.terminalTypeSets the terminal type to use for the session. The list of supported types is determined by your Linux/UNIX system. For more information, see the
terminfomanual page ($ man terminfo).Default:
vt102setLocaleIf set to
true, indicates that the default environment locale should be changed to the value of thelocaleproperty.Default:
false- locale
Sets the locale for LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables, if
setLocaleis set totrue.Default:
en_US.utf8connectionTimeoutSpecifies the connection timeout to the remote server, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000expectTimeoutSpecifies the timeout used by the
expect()calls in scripts, in milliseconds.Default:
5000authenticationTypeSets the authentication type, either
PASSWORDorPUBKEY. For more information, see "Configuring Authentication to the SSH Server".Default:
PASSWORDthrowOperationTimeoutExceptionIf
true, the connector throws an exception when the timeout is reached for an operation. Otherwise, the operation fails silently.Default:
truescriptRootsThe path to the Groovy scripts that will perform the OpenICF operations, relative to your installation directory. For the Kerberos connector, the scripts are bundled up in the connector JAR file, so this path is set to
jar:file:connectors/kerberos-connector-1.4.3.0.jar!/script/kerberos/in the sample connector configuration.classpathThe directory in which the compiler should look for compiled classes. The default classpath, if not is specified, is
install-dir/lib.reloadScriptOnExecutionBy default, scripts are loaded and compiled when a connector instance is created and initialized. Setting
reloadScriptOnExecutionto true makes the connector load and compile the script every time it is called. Do not set this property totruein a production environment, because it will have a significant impact on performance.Default:
false*ScriptFileNameThe script that is used for each OpenICF operation. Do not change these script names in the bundled Kerberos connector.
The Kerberos Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Kerberos Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
host
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
port
|
int
|
22
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
user
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
passphrase
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
privateKey
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticationType
|
String
|
PASSWORD
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
prompt
|
String
|
root@localhost:#
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
sudoCommand
|
String
|
/usr/bin/sudo
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
echoOff
|
boolean
|
true
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
terminalType
|
String
|
vt102
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
locale
|
String
|
en_US.utf8
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
setLocale
|
boolean
|
false
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
connectionTimeout
|
int
|
5000
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
expectTimeout
|
long
|
5000
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
throwOperationTimeoutException
|
boolean
|
true
| ||||
|
Description is not available | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
IDM provides a Salesforce connector, along with a sample connector configuration. The Salesforce connector enables provisioning, reconciliation, and synchronization between Salesforce and the IDM repository.
The Salesforce Connector is not an OpenICF connector, but a separate IDM module, based on the ForgeRock Common Resource API.
To use this connector, you need a Salesforce account, and a Connected App that has OAuth enabled, which will allow you to retrieve the required consumer key and consumer secret.
For additional instructions, and a sample Salesforce configuration, see "Synchronizing Users Between Salesforce and IDM" in the Samples Guide.
The Marketo connector enables synchronization between IDM managed users and a Marketo Lead Database.
This connector forms part of ForgeRock's support for customer data management (CDM). You can synchronize any managed user to Marketo - those who have been added directly to the IDM repository, and those who have registered themselves through one of the Social Identity Providers described in "Configuring Social Identity Providers" in the Integrator's Guide.
The Marketo connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector Toolkit, and enables you to interact with leads in a Marketo database, using Groovy scripts for the OpenICF operations.
To use the Marketo connector, you need a Marketo account, a client ID, client secret, and the REST API URL for your IDM service, and a custom list created in your Marketo Leads database. For information on obtaining these details from Marketo, see the Marketo documentation.
A sample connector configuration file is available, at
/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-marketo.json.
To test the Marketo connector, copy that file to your project's
conf/ directory, and edit at least the
configurationProperties to provide the REST API URL, client
ID and client secret. To locate the REST API endpoint URL, select Admin > Web
Services in Marketo, scroll down to REST API, and find the endpoint. Use that
REST endpoint as the value of the instance property in your
connector configuration. Remove the protocol and /rest from
the URL. For example, if the endpoint is
https://140-OCV-xxx.mktorest.com/rest, the value of the
instance property must be
140-OCV-xxx.mktorest.com.
Set the enabled property in the connector configuration to
true. IDM encrypts the client secret on startup.
Optionally, you can specify the listName to which leads
should be added when they are synchronized from IDM. The following
excerpt of a sample connector configuration file shows the properties that you
must set:
{
"name" : "marketo",
"displayName" : "MarketoConnector",
"description" : "Connector used to sync users to Marketo leads",
"version" : "1.4.3.0",
"author" : "ForgeRock",
"enabled" : true,
...
"configurationProperties" : {
"instance" : "140-OCV-xxx.mktorest.com",
"clientId" : "1b5fxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx6a2c",
"clientSecret" : "19jf910703j19012790j0123i-d1",
"leadFields" : null,
"partitionName" : null,
"listName" : "DecemberPromotion",
...You can also configure the Marketo connector through the Admin UI. Select Configure > Connectors, click New Connector, and complete at least the required configuration properties, described in "Marketo Connector Configuration".
When your connector is configured correctly, you can test its status by running the following command:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "marketo",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/marketo",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"account"
],
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo.MarketoConnector",
"bundleVersion": "1.4.3.0"
},
"displayName": "Marketo Connector",
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can
reach your Marketo database.
For additional instructions on how to set up reconciliation from IDM to Marketo, see "Setting Up Users for Marketo Lead Generation" in the Integrator's Guide.
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Marketo connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
The Marketo Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Authenticate
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Script on Resource
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Marketo Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
customSensitiveConfiguration
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
customConfiguration
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper | ||||
|
| ||||
tokenExpiration
|
Long
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
accessToken
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
instance
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The Marketo-assigned FQDN for your instance | ||||
|
| ||||
clientId
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Your OAuth2 client ID | ||||
|
| ||||
clientSecret
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Your OAuth2 client secret | ||||
|
| ||||
leadFields
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Comma-delimited list of lead fields to fetch; Leave empty for default set | ||||
|
| ||||
partitionName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Name of the partition in which to create and update leads; May be left empty | ||||
|
| ||||
listName
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Name of the Marketo static list the connector will use to manage leads | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
createScriptFileName
|
String
|
CreateMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
customizerScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
| ||||
|
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
authenticateScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
scriptOnResourceScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
deleteScriptFileName
|
String
|
DeleteMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
resolveUsernameScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
searchScriptFileName
|
String
|
SearchMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
updateScriptFileName
|
String
|
UpdateMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
schemaScriptFileName
|
String
|
SchemaMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
testScriptFileName
|
String
|
TestMarketo.groovy
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
syncScriptFileName
|
String
|
null
|
| |||
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. | ||||||
|
| ||||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
targetDirectory
|
File
|
null
| ||
|
Directory into which to write classes. | ||||
|
| ||||
warningLevel
|
int
|
1
| ||
|
Warning Level of the compiler | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptExtensions
|
String[]
|
['groovy']
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
minimumRecompilationInterval
|
int
|
100
| ||
|
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptBaseClass
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script) | ||||
|
| ||||
scriptRoots
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. | ||||
|
| ||||
tolerance
|
int
|
10
| ||
|
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. | ||||
|
| ||||
debug
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, debugging code should be activated | ||||
|
| ||||
classpath
|
String[]
|
[]
| ||
|
Classpath for use during compilation. | ||||
|
| ||||
disabledGlobalASTTransformations
|
String[]
|
null
| ||
|
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. | ||||
|
| ||||
verbose
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If true, the compiler should produce action information | ||||
|
| ||||
sourceEncoding
|
String
|
UTF-8
| ||
|
Encoding for source files | ||||
|
| ||||
recompileGroovySource
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
If set to true recompilation is enabled | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Active Directory connector is a legacy connector, written in C# for the .NET platform. OpenICF connects to Active Directory over ADSI, the native connection protocol for Active Directory. The connector therefore requires a .NET connector server that has access to the ADSI .dll files.
Important
The AD Connector is deprecated and support for its use with IDM will be discontinued in a future release. For simple Active Directory (and Active Directory LDS) deployments, the generic LDAP Connector works better than the Active Directory connector, in most circumstances. Using the generic LDAP connector avoids the need to install a remote connector server in the overall deployment. In addition, the generic LDAP connector has significant performance advantages over the Active Directory connector. For more complex Active Directory deployments, use the PowerShell Connector Toolkit, as described in "PowerShell Connector Toolkit".
Before you configure the Active Directory Connector, make sure that the .NET Connector Server is installed, configured and started, and that IDM has been configured to use the Connector Server. For more information, see "Installing and Configuring a .NET Connector Server" in the Integrator's Guide.
Download the Active Directory (AD) Connector from ForgeRock's BackStage site.
Extract the contents of the AD Connector zip file into the directory in which you installed the Connector Server (by default
c:\Program Files (x86)\Identity Connectors\Connector Server>).Note that the files, specifically the connector itself (
ActiveDirectory.Connector.dll) must be directly under thepath\to\Identity Connectors\Connector Serverdirectory, and not in a subdirectory.Note
If the account that is used to install the Active Directory connector is different from the account under which the Connector Server runs, you must give the Connector Server runtime account the rights to access the Active Directory connector log files.
A sample Active Directory Connector configuration file is provided in
openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-ad.json. On the IDM host, copy the sample Active Directory connector configuration file to your project'sconf/directory:$ cd /path/to/openidm $ cp samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-ad.json project-dir/conf/
Edit the Active Directory connector configuration to match your Active Directory deployment.
Specifically, check and edit the
configurationPropertiesthat define the connection details to the Active Directory server.Also, check that the
bundleVersionof the connector matches the version of theActiveDirectory.Connector.dllin the Connector Server directory. The bundle version can be a range that includes the version of the connector bundle. To check the .dll version:Right click on the
ActiveDirectory.Connector.dllfile and select Properties.Select the Details tab and note the Product Version.
The following configuration extract shows sample values for the
connectorRefandconfigurationProperties:... "connectorRef" : { "connectorHostRef" : "dotnet", "connectorName" : "Org.IdentityConnectors.ActiveDirectory.ActiveDirectoryConnector", "bundleName" : "ActiveDirectory.Connector", "bundleVersion" : "[1.4.0.0,1.5.0.0)" }, ... "configurationProperties" : { "DirectoryAdminName" : "EXAMPLE\\Administrator", "DirectoryAdminPassword" : "Passw0rd", "ObjectClass" : "User", "Container" : "dc=example,dc=com", "CreateHomeDirectory" : true, "LDAPHostName" : "192.0.2.0", "SearchChildDomains" : false, "DomainName" : "example", "SyncGlobalCatalogServer" : null, "SyncDomainController" : null, "SearchContext" : "" },The main configurable properties are as follows:
connectorHostRefMust point to an existing connector info provider configuration in
project-dir/conf/provisioner.openicf.connectorinfoprovider.json. TheconnectorHostRefproperty is required because the Active Directory connector must be installed on a .NET connector server, which is always remote, relative to IDM.DirectoryAdminNameandDirectoryAdminPasswordSpecify the credentials of an administrator account in Active Directory, that the connector will use to bind to the server.
The
DirectoryAdminNamecan be specified as a bind DN, or in the formatDomainName\\samaccountname.SearchChildDomainsSpecifies if a Global Catalog (GC) should be used. This parameter is used in search and query operations. A Global Catalog is a read-only, partial copy of the entire forest, and is never used for create, update or delete operations.
Boolean, false by default.
LDAPHostNameSpecifies a particular Domain Controller (DC) or Global Catalog (GC), using its hostname. This parameter is used for query, create, update, and delete operations.
If
SearchChildDomainsis set totrue, this specific GC will be used for search and query operations. If theLDAPHostNameis null (as it is by default), the connector will allow the ADSI libraries to pick up a valid DC or GC each time it needs to perform a query, create, update, or delete operation.SyncGlobalCatalogServerSpecifies a Global Catalog server name for sync operations. This property is used in combination with the
SearchChildDomainsproperty.If a value for
SyncGlobalCatalogServeris set (that is, the value is notnull) andSearchChildDomainsis set totrue, this GC server is used for sync operations. If no value forSyncGlobalCatalogServeris set andSearchChildDomainsis set totrue, the connector allows the ADSI libraries to pick up a valid GC.SyncDomainControllerSpecifies a particular DC server for sync operations. If no DC is specified, the connector picks up the first available DC and retains this DC in future sync operations.
The updated configuration is applied immediately.
Check that the connector has been configured correctly by running the following command:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
The command must return
"ok" : truefor the Active Directory connector.The connector is now configured. To verify the configuration, perform a RESTful GET request on the remote system URL, for example:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ActiveDirectory/account?_queryId=query-all-ids"
This request should return the user accounts in the Active Directory server.
(Optional) To configure reconciliation or liveSync between IDM and Active Directory, create a synchronization configuration file (
sync.json) in your project'sconf/directory.The synchronization configuration file defines the attribute mappings and policies that are used during reconciliation.
The following is a simple example of a
sync.jsonfile for Active Directory:{ "mappings" : [ { "name" : "systemADAccounts_managedUser", "source" : "system/ActiveDirectory/account", "target" : "managed/user", "properties" : [ { "source" : "cn", "target" : "displayName" }, { "source" : "description", "target" : "description" }, { "source" : "givenName", "target" : "givenName" }, { "source" : "mail", "target" : "email" }, { "source" : "sn", "target" : "familyName" }, { "source" : "sAMAccountName", "target" : "userName" } ], "policies" : [ { "situation" : "CONFIRMED", "action" : "UPDATE" }, { "situation" : "FOUND", "action" : "UPDATE" }, { "situation" : "ABSENT", "action" : "CREATE" }, { "situation" : "AMBIGUOUS", "action" : "EXCEPTION" }, { "situation" : "MISSING", "action" : "UNLINK" }, { "situation" : "SOURCE_MISSING", "action" : "DELETE" }, { "situation" : "UNQUALIFIED", "action" : "DELETE" }, { "situation" : "UNASSIGNED", "action" : "DELETE" } ] } ] }To test the synchronization, run a reconciliation operation as follows:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/recon?_action=recon&mapping=systemADAccounts_managedUser"
If reconciliation is successful, the command returns a reconciliation run ID, similar to the following:
{"_id":"0629d920-e29f-4650-889f-4423632481ad","state":"ACTIVE"}Query the internal repository, using either a curl command, or the IDM Admin UI, to make sure that the users in your Active Directory server were provisioned into the repository.
The Active Directory connector supports PowerShell scripting. The following example shows a simple PowerShell script that is referenced in the connector configuration and can be called over the REST interface.
Note
External script execution is disabled on system endpoints by default. For
testing purposes, you can enable script execution over REST, on system
endpoints by adding the script action to the system
object, in the access.js file. For example:
$ more /path/to/openidm/script/access.js
...
{
"pattern" : "system/ActiveDirectory",
"roles" : "openidm-admin",
"methods" : "action",
"actions" : "script"
}, Be aware that scripts passed to clients imply a security risk in production environments. If you need to expose a script for direct external invocation, it might be better to write a custom authorization function to constrain the script ID that is permitted. Alternatively, do not expose the script action for external invocation, and instead, expose a custom endpoint that can make only the desired script calls. For more information about using custom endpoints, see "Creating Custom Endpoints to Launch Scripts" in the Integrator's Guide.
The following PowerShell script creates a new MS SQL user with a username
that is specified when the script is called. The script sets the user's
password to Passw0rd and, optionally, gives the user a
role. Save this script as
project-dir/script/createUser.ps1:
if ($loginName -ne $NULL) {
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('Microsoft.SqlServer.SMO') | Out-Null
$sqlSrv = New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') ('WIN-C2MSQ8G1TCA')
$login = New-Object -TypeName ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Login') ($sqlSrv, $loginName)
$login.LoginType = 'SqlLogin'
$login.PasswordExpirationEnabled = $false
$login.Create('Passw0rd')
# The next two lines are optional, and to give the new login a server role, optional
$login.AddToRole('sysadmin')
$login.Alter()
} else {
$Error_Message = [string]"Required variables 'loginName' is missing!"
Write-Error $Error_Message
throw $Error_Message
}
Now edit the Active Directory connector configuration to reference the
script. Add the following section to the connector configuration file
(project-dir/conf/provisioner.openicf-ad.json):
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "ConnectorScriptName",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ActiveDirectoryConnector",
"actionType" : "Shell",
"actionSource" : "@echo off \r\n echo %loginName%\r\n"
},
{
"systemType" : ".*ActiveDirectoryConnector",
"actionType" : "PowerShell",
"actionFile" : "script/createUser.ps1"
}
]
}
] To call the PowerShell script over the REST interface, use the following request, specifying the userName as input:
$ curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ActiveDirectory/?_action=script&scriptId=ConnectorScriptName&scriptExecuteMode=resource&loginName=myUser"
The Office 365 connector uses the O365 Graph API to manage Azure AD users and groups. This connector uses the OData 3.0 specification and can be used, with minor modifications, to connect to any OData 3 provider. Note that OData 2, 3 and 4 are not interchangeable and this connector can only function against OData 3 providers.
The Office 365 connector is available from ForgeRock's BackStage site. If you want to use this connector in production, contact ForgeRock Support.
This chapter lists the implemented interfaces and configurable properties for the Office 365 connector.
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Office 365 connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
The O365 Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Resolve Username
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The O365 Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
tenant
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Name of your Office365 tenant | ||||
|
| ||||
clientId
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
This value is provided by Office365 | ||||
|
| ||||
clientSecret
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
This value is provided by Office365 | ||||
|
| ||||
accessToken
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
This value is provided by Office365 | ||||
|
| ||||
tokenExpiration
|
Long
|
null
| ||
|
This value is provided by Office365 | ||||
|
| ||||
refreshToken
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
This value is provided by Office365 | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
accountEntitySet
|
String
|
User
| ||
|
The name AzureAD uses to declare account objects in its data payloads | ||||
|
| ||||
accountURIComponent
|
String
|
users
| ||
|
The name used in a URI path to specify an account target object | ||||
|
| ||||
groupEntitySet
|
String
|
Group
| ||
|
The name AzureAD uses to declare group objects in its data payloads | ||||
|
| ||||
groupURIComponent
|
String
|
groups
| ||
|
The name used in a URI path to specify an account target object | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The SCIM connector is based on the Simple Cloud Identity Management (SCIM) protocol and enables you to manage user
and group accounts on any SCIM-compliant resource provider, such as Slack or Facebook. The SCIM connector
implements both 1.1 and 2.0 endpoints. The SCIM connector is bundled with IDM in the connectors/ directory.
The SCIM connector uses the Apache HTTP client, which leverages the HTTP client connection pool, not the connector pool.
Download provisioner.openicf-scim.json to your project's
conf/directory.Edit
conf/provisioner.openicf-scim.json, as necessary. The following changes are required:"enabled" : trueTo specify the connection details to the SCIM resource provider, set the
configurationProperties. The required properties vary, based on theauthenticationMethod:OAUTHThe minimum required properties are
grantType,SCIMEndpoint,tokenEndpoint,clientId, andclientSecret.BASICThe minimum required properties are
userandpassword.TOKENThe minimum required property is
authToken.
Sample Configuration Using OAUTH:
"configurationProperties" : { "SCIMEndpoint" : "https://example.com/scim", "SCIMVersion" : 1, "authenticationMethod" : "OAUTH", "user" : null, "password" : null, "tokenEndpoint" : "https://example.com/oauth2/token", "clientId" : "Kdvl...................j3fka", "clientSecret" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : true, "disableHostNameVerifier" : true, "maximumConnections" : 10, "httpProxyHost" : null, "httpProxyPort" : null },Note
On startup, IDM encrypts the value of the
clientSecret.
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
The New Connector page displays.
In the General Details area, from the Connector Type drop-down list, select Scim Connector - Version#.
Enter other details, as necessary, and click Save.
After the connector is properly configured, you can test its status:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "SCIM",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/SCIM",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.scim-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.scim.ScimConnector",
"bundleVersion": "1.4.0.0"
},
"displayName": "Scim Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__",
"__GROUP__"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the SCIM connector
can reach the configured resource provider.
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The SCIM connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
The Scim Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Scim Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SCIMEndpoint
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The HTTP URL defining the root for the SCIM endpoint (https://myserver.com/service/scim) | ||||
|
| ||||
SCIMVersion
|
Integer
|
1
| ||
|
Defines the SCIM protocol version. Values can be either 1 or 2. Default is 1 | ||||
|
| ||||
authenticationMethod
|
String
|
OAUTH
| ||
|
Defines which method is to be used to authenticate on the remote server. Options are BASIC (username/password), OAUTH (Client id/secret) or TOKEN (static token). Defaults to OAUTH | ||||
|
| ||||
user
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
In case of BASIC authentication type, this property defines the remote user. | ||||
|
| ||||
password
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
In case of BASIC authentication type, this property defines the remote password. | ||||
|
| ||||
tokenEndpoint
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
When using OAUTH, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be queried for (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token) | ||||
|
| ||||
clientId
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
The client identifier | ||||
|
| ||||
clientSecret
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Secure client secret for OAUTH | ||||
|
| ||||
authToken
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Some service providers (Slack for instance) use static authentication tokens. | ||||
|
| ||||
acceptSelfSignedCertificates
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. Defaults to false | ||||
|
| ||||
disableHostNameVerifier
|
boolean
|
false
| ||
|
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. Defaults to false | ||||
|
| ||||
clientCertAlias
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed, set this to the certificate alias from the keystore. | ||||
|
| ||||
clientCertPassword
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed and the client certificate (private key) password is different than the keystore password, set this to the client private key password. | ||||
|
| ||||
maximumConnections
|
Integer
|
10
| ||
|
Defines the max size of the http connection pool used. Defaults to 10. | ||||
|
| ||||
httpProxyHost
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Defines the Hostname if an Htpp proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. | ||||
|
| ||||
httpProxyPort
|
Integer
|
null
| ||
|
Defines the Port if an Htpp proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
The Adobe Campaign Manager connector enables you to manage profiles in an Adobe Campaign data store. The connector supports a subset of the OpenICF operations, as listed in "OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector".
To use this connector, you need an Adobe ID.
The Adobe Campaign Manager connector requires the following libraries:
Before you start, download these libraries and copy them to the
/path/to/openidm/lib directory.
You must also configure a new integration on AdobeIO, as shown in the following steps. Note that these steps assume a specific version of the AdobeIO user interface. For information on the current version, see the corresponding Adobe documentation.
The integration requires a public certificate and private key that will be used to sign the JWT token.
You can use IDM's generated self-signed certificate and private key to test the connector. In a production environment, use a CA-signed certificate and key.
Export IDM's self-signed certificate as follows:
Export the certificate and key from JCEKS to standardized format PKCS #12:
$ cd /path/to/openidm/security $ keytool \ -importkeystore \ -srckeystore keystore.jceks \ -srcstoretype jceks \ -destkeystore keystore.p12 \ -deststoretype PKCS12 \ -srcalias openidm-localhost \ -deststorepass changeit \ -destkeypass changeit
Export the certificate:
$ openssl pkcs12 \ -in keystore.p12 \ -nokeys \ -out cert.pem
Export unencrypted private key:
$ openssl pkcs12 \ -in keystore.p12 \ -nodes \ -nocerts \ -out key.pem
Log in to https://console.adobe.io/ and select Integrations > New Integration.
Select Access an API > Continue.
Under the Experience Cloud item, select Adobe Campaign > Continue, then select New integration > Continue.
Enter a name for the new integration, for example,
IDM-managed, and a short description.Drag the public certificate that you exported previously into the Public keys certificates box.
Select a license, then select Create Integration.
Select Continue to integration details to obtain the Client Credentials required by the connector.
You will need these details for the connector configuration.
Create a connector configuration file for the Adobe Campaign Manager
connector and place it in your project's conf/
directory.
IDM bundles a sample configuration file
(/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-adobe.json)
that you can use as a starting point. Alternatively, you can create the
configuration by using the Admin UI. Select Configure > Connectors > New
Connector and select Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector - 1.5.0.0
as the connector type.
The following example shows an excerpt of the provisioner configuration.
Enable the connector (set "enabled" : true) then edit at
least the configurationProperties to match your Adobe IO
setup:
"configurationProperties" : {
"endpoint" : "mc.adobe.io",
"imsHost" : "ims-na1.adobelogin.com",
"tenant" : "https://example.adobesandbox.com/",
"apiKey" : "",
"techAccId" : "example@techacct.adobe.com",
"orgId" : "example@AdobeOrg",
"clientSecret" : "CLIENT_SECRET",
"privateKey" : "PRIVATE_KEY"
},
...-
endpoint The Adobe IO endpoint for Marketing Cloud.
mc.adobe.ioby default - you should not have to change this value.-
imsHost The Adobe Identity Management System (IMS) host.
ims-na1.adobelogin.comby default - you should not have to change this value.-
tenant Your tenant (organization) name or sandbox host.
-
apiKey The API key (client ID) assigned to your API client account.
-
techAccId Your Technical account ID, required to generate the JWT.
-
orgId Your organization's unique ID, for example
12345@AdobeOrg.-
clientSecret The client secret assigned to your API client account.
-
privateKey The private key used to sign the JWT token, corresponds to the public key certificate that you attached to the integration.
For a list of all the configurable properties, see "Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector Configuration".
When your connector is configured correctly, you can test its status by running the following command:
$ curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "adobe",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/adobe",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.adobecm-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.acm.ACMConnector",
"bundleVersion": "1.5.0.0"
},
"displayName": "Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"account"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can
reach the configured Adobe integration.
The Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces.
- Create
Creates an object and its
uid.- Delete
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid.- Schema
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector. Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration.The script has access to any script-arguments passed in by the application.
- Search
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
Tests the connector configuration. Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
The Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector has the following configurable properties.
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
accessToken
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
Description is not available | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
endpoint
|
String
|
mc.adobe.io
| ||
|
The Adobe IO endpoint for Marketing Cloud. mc.adobe.io by default - you should not have to change this. | ||||
|
| ||||
imsHost
|
String
|
ims-na1.adobelogin.com
| ||
|
Adobe Identity Management System (IMS) host. ims-na1.adobelogin.com by default - you should not have to change this. | ||||
|
| ||||
tenant
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Your tenant (organization) name or sandbox host. | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted [a] | Required [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
apiKey
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The API key (client ID) assigned to your API client account | ||||
|
| ||||
technicalAccountID
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Your Technical account ID, required to generate the JWT | ||||
|
| ||||
organizationID
|
String
|
null
| ||
|
Your organizations unique ID, for example 12345@AdobeOrg | ||||
|
| ||||
clientSecret
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The client secret assigned to your API client account | ||||
|
| ||||
privateKey
|
GuardedString
|
null
| ||
|
The private key used to sign the JWT token, corresponds to the public key certificate attached to the integration | ||||
|
| ||||
[a] Indicates whether the property value is considered confidential, and therefore encrypted in OpenIDM. [b] A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations. | ||||
This chapter describes all of the interfaces supported by the OpenICF framework, along with notes about their implementation. Specific connectors may support only a subset of these interfaces.
Normalize attributes to ensure consistent filtering.
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password. If the connector does not implement the AuthenticateOp interface it can not be used in OpenIDM to provide pass-through authentication.
Execute a series of operations in a single request. If a resource does not support batch operations, the connector will not implement the batch operation interface. The OpenICF framework will still support batched requests but the operations will be executed iteratively through the connector.
Subscribe for notification of any specified event on the target resource. This operation can be used in the context of IoT device reports, to receive notification of events such as low battery signals, inactive devices, and so on.
Create an object and return its uid.
Delete an object by its uid.
Get an object by its uid.
Use pools of target resources.
Resolve an object to its uid based on its username.
Describe supported object types, operations, and options.
Allow script execution on connector.
Allow script execution on the resource.
Allow searches for resource objects.
Connectors that implement only this interface can only be used for reconciliation operations.
Poll for synchronization events, which are native changes to target objects.
Subscribe for notification of synchronization events, which are native changes to target objects.
Test the connection configuration, including connecting to the resource.
Allows an authorized caller to update (modify or replace) objects on the target resource.
Allows an authorized caller to update (modify or replace) attribute values on
the target resource. This operation is more advanced than the
UpdateOp operation, and provides better performance and
atomicity semantics.
This chapter describes all of the predefined operation options by the OpenICF framework, along with notes about their use. Specific connectors may support only a subset of these options.
An option to use with Search (in conjunction with Container) that specifies how far beneath the specified container to search. Must be one of the following values:
SCOPE_OBJECT
SCOPE_ONE_LEVEL
SCOPE_SUBTREE
An option to use with Search that specifies the container under which to perform the search. Must be of type QualifiedUid. Should be implemented for those object classes whose ObjectClassInfo.isContainer() returns true.
An option to use with Script on Resource and possibly others that specifies an account under which to execute the script/operation. The specified account will appear to have performed any action that the script/operation performs.
An option to use with Script on Resource and possibly others that specifies a password under which to execute the script/operation.
Determines which attributes to retrieve during Search and Sync. This option overrides the default behavior, which is for the connector to return exactly the set of attributes that are identified as returned by default in the schema for that connector. This option allows a client application to request additional attributes that would not otherwise not be returned (generally because such attributes are more expensive for a connector to fetch and to format) and/or to request only a subset of the attributes that would normally be returned.
An option to use with Search that specifies an opaque cookie which is used by the connector to track its position in the set of query results.
An option to use with Search that specifies the index within the result set of the first result which should be returned.
An option to use with Search that specifies the requested page results page size.
An option to use with Search that specifies the sort keys which should be used for ordering the ConnectorObject returned by search request.
This option is used with the Batch operation, to specify whether the batch process should be aborted when the first error is encountered. The default behavior is to continue processing regardless of errors.
This option instructs the connector to execute batched requests in a serial manner if possible. The default behavior of the Batch operation is to execute requests in parallel, for speed and efficiency. In either case the task ID must be reflected in the response for each task, so that tasks can be correctly reordered.
Certain connectors support the ability to be pooled. For a pooled connector, OpenICF maintains a pool of connector instances and reuses these instances for multiple provisioning and reconciliation operations. When an operation must be executed, an existing connector instance is taken from the connector pool. If no connector instance exists, a new instance is initialized. When the operation has been executed, the connector instance is released back into the connector pool, ready to be used for a subsequent operation.
For an unpooled connector, a new connector instance is initialized for every operation. When the operation has been executed, OpenICF disposes of the connector instance.
Because the initialization of a connector is an expensive operation, reducing the number of connector initializations can substantially improve performance.
To configure connection pooling, set the following values in the connector
configuration file poolConfigOptions property:
"maxObjects"- the maximum number of connector instances in the pool (both idle and active). The default value is10instances."maxIdle"- the maximum number of idle connector instances in the pool. The default value is10idle instances."maxWait"- the maximum period to wait for a free connector instance to become available before failing. The default period is150000milliseconds, or 15 seconds."minEvictableIdleTimeMillis"- the minimum period to wait before evicting an idle connector instance from the pool. The default period is120000milliseconds, or 12 seconds."minIdle"- the minimum number of idle connector instances in the pool. The default value is1instance.