Connector reference
Connectors let you connect to external resources such as LDAP, Active Directory, flat files, and others. This guide describes all the connectors supported with Identity Cloud, IDM, and RCS, and how to configure them.
| Any available connector works with IDM, either directly or using RCS. Identity Cloud can use any available connector through RCS. |
All connectors are available for download from Backstage, but some connectors are already bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, and RCS. The following table identifies which connectors are bundled by default with each product:
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
No |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
No |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
No |
No |
Configurations in this guide are simplified to show essential aspects. Not all resources support all IDM operations; however, the resources shown here support most of the CRUD operations, reconciliation, and liveSync.
Resources are external systems, databases, directory servers, and other sources of identity data, that are managed and audited by IDM. To connect to resources, IDM loads the ForgeRock Open Identity Connector Framework (ICF). ICF avoids the need to install agents to access resources, instead using the resources' native protocols. For example, ICF connects to database resources using the database’s Java connection libraries or JDBC driver, to directory servers over LDAP, and to UNIX systems over ssh.
ForgeRock Identity Platform™ serves as the basis for our simple and comprehensive Identity and Access Management solution. We help our customers deepen their relationships with their customers, and improve the productivity and connectivity of their employees and partners. For more information about ForgeRock and about the platform, see https://www.forgerock.com.
The ForgeRock Common REST API works across the platform to provide common ways to access web resources and collections of resources.
Adobe Marketing Cloud connector
The Adobe Marketing Cloud connector lets you manage profiles in an Adobe Campaign data store. The connector supports a subset of the OpenICF operations, as listed in OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector.
| To use this connector, you need an Adobe ID. |
Before you start
Configure a new integration on AdobeIO, as shown in the following steps. Note that these steps assume a specific version of the AdobeIO user interface. For information on the current version, refer to the corresponding Adobe documentation.
|
The integration requires a public certificate and private key that will be used to sign the JWT token. |
-
You can use IDM’s generated self-signed certificate and private key to test the connector. In a production environment, use a CA-signed certificate and key.
Export IDM’s self-signed certificate as follows:
-
Export the certificate and key from JCEKS to standardized format PKCS #12:
keytool \ -importkeystore \ -srckeystore /path/to/openidm/security/keystore.jceks \ -srcstoretype jceks \ -destkeystore /path/to/keystore.p12 \ -deststoretype PKCS12 \ -srcalias openidm-localhost \ -deststorepass changeit \ -destkeypass changeit
-
Export the certificate:
openssl pkcs12 \ -in /path/to/keystore.p12 \ -nokeys \ -out /path/to/cert.pem
-
Export the unencrypted private key:
openssl pkcs12 \ -in /path/to/keystore.p12 \ -nodes \ -nocerts \ -out /path/to/key.pem
-
-
Log in to https://console.adobe.io/.
-
Click Integrations > New Integration.
-
Click Access an API > Continue.
-
Under the Experience Cloud item, click Adobe Campaign > Continue, then click New integration > Continue.
-
Enter a name and short description for the new integration. For example,
IDM-managed. -
Drag and drop your public certificate file into the Public keys certificates area. Alternatively, click Select a File, and browse to the file location.
-
Select a license, then click Create Integration.
-
Select Continue to integration details to obtain the Client Credentials required by the connector.
You will need these details for the connector configuration.
Install the Adobe Marketing Cloud connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/adobecm-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Adobe Marketing Cloud connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, you can create a connector configuration file and place it in your project’s conf/ directory. IDM bundles a sample configuration file (/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-adobe.json) that you can use as a starting point.
The following example shows an excerpt of the provisioner configuration. Enable the connector (set "enabled" : true) then edit at least the configurationProperties to match your Adobe IO setup:
"configurationProperties" : {
"endpoint" : "mc.adobe.io",
"imsHost" : "ims-na1.adobelogin.com",
"tenant" : "https://example.adobesandbox.com/",
"apiKey" : "",
"techAccId" : "example@techacct.adobe.com",
"orgId" : "example@AdobeOrg",
"clientSecret" : "CLIENT_SECRET",
"privateKey" : "PRIVATE_KEY"
},
...endpoint-
The Adobe IO endpoint for Marketing Cloud.
mc.adobe.ioby default - you should not have to change this value. imsHost-
The Adobe Identity Management System (IMS) host.
ims-na1.adobelogin.comby default - you should not have to change this value. tenant-
Your tenant (organization) name or sandbox host.
apiKey-
The API key (client ID) assigned to your API client account.
techAccId-
Your Technical account ID, required to generate the JWT.
orgId-
Your organization’s unique ID, for example
12345@AdobeOrg. clientSecret-
The client secret assigned to your API client account.
privateKey-
The private key used to sign the JWT token, corresponds to the public key certificate that you attached to the integration.
For a list of all the configurable properties, refer to Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector Configuration.
Test the Adobe Marketing Cloud connector
When your connector is configured correctly, you can test its status by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adobe?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "adobe",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/adobe",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.adobecm-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.acm.ACMConnector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)"
},
"displayName": "Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"account"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can reach the configured Adobe integration.
Adobe Marketing Cloud remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Adobe Marketing Cloud connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Adobe Marketing Cloud connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Adobe Marketing Cloud remote connector.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector
The Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector Configuration
The Adobe Marketing Cloud Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Adobe IO endpoint for Marketing Cloud. mc.adobe.io by default - you should not have to change this. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Adobe Identity Management System (IMS) host. ims-na1.adobelogin.com by default - you should not have to change this. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Your tenant (organization) name or sandbox host. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Adobe Integration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The API key (client ID) assigned to your API client account. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Your Technical account ID, required to generate the JWT. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Your organizations unique ID, for example 12345@AdobeOrg. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The client secret assigned to your API client account. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The private key used to sign the JWT token, corresponds to the public key certificate attached to the integration. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The OAuth Access Token for the application. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
AS400 connector
The AS400 connector enables you to manage and synchronize users between AS400 and the IDM managed user repository.
Before you start
These instructions assume you have an AS400 administrator account and you have access to AS400. You need the following information to configure the connector:
- Host Name
-
The name or IP address of the host where AS400 is running.
- Username
-
The AS400 Organizational Admin username.
- Password
-
The AS400 Organizational Admin password.
- Is Secure
-
Whether or not to enable a secure connection to AS400.
Install the AS400 connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/as400-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the AS400 connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select AS400 Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to AS400 Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the AS400 connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/as400?_action=test"
{
"name": "as400",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/as400",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.as400-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.as400.As400Connector"
},
"displayName": "AS400 Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__",
"__GROUP__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the AS400 system.
AS400 remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the AS400 connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the AS400 connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the AS400 remote connector.
Use the AS400 connector
The following resources are supported by AS400:
| ICF Native Type | AS400 Resource Type |
|---|---|
__ACCOUNT__ |
Users |
__GROUP__ |
Groups |
The following filter operators and attributes are supported by AS400:
| Object Type | Operators | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
__GROUP__ |
id filter |
Id |
You can perform the following actions with the AS400 connector:
Create an AS400 user
The following example creates a user with all available attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json"\
--request POST \
--data "{
"__NAME__":"BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__":"ASDE1234",
"PWDEXP":false,
"__ENABLE__":true,
"USRCLS":"*USER",
"ASTLVL":"*BASIC",
"CURLIB":"*CRTDFT",
"INLPGM":"*NONE",
"INLMNU":"MAIN",
"TEXT":"TEXTFILEDVALUE",
"SPCAUT":["*AUDIT"],
"SPCENV":"*S36",
"DSPSGNINF":"*YES",
"PWDEXPITV":"323",
"PWDCHGBLK":"93",
"LCLPWDMGT":true,
"LMTDEVSSN":"*NO",
"MAXSTG":"10000",
"PTYLMT":8,
"JOBD":"QDFTJOBD",
"OWNER":"*USRPRF",
"ACGCDE":"*BLANK",
"DOCPWD":"W12345",
"MSGQ":"*USRPRF",
"DLVRY":"*HOLD",
"SEV":"50",
"PRTDEV":"*SYSVAL",
"OUTQ":"*DEV",
"ATNPGM":"*ASSIST",
"SRTSEQ":"*HEX",
"LANGID":"ENG",
"CCSID":"*HEX",
"CHRIDCTL":"*DEVD",
"SETJOBATR":["*CCSID"],
"LOCALE":"*C",
"USROPT":["*HLPFULL"],
"UID":"*GEN",
"HOMEDIR":"*USRPRF",
"EIMASSOC":["*NOCHG"],
"USREXPITV":99,
"USREXPDATE":"*USREXPITV",
"LMTCPB":"*YES",
"CNTRYID":"*SYSVAL",
"GRPPRF":"AZURE",
"SUPGRPPRF":["AWS"]
}" \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/As400/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create&_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"USROPT" : [ "*HLPFULL" ],
"SEV" : "50",
"USREXPITV" : 99,
"IsAuthCollectionActive" : false,
"HOMEDIR" : "/home/BJENSEN",
"MAXSTG" : "10000",
"UID" : "1277",
"PTYLMT" : 8,
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"PRTDEV" : "*SYSVAL",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"LMTDEVSSN" : "*NO",
"__UID__" : "BJENSEN",
"SRTSEQ" : "*HEX",
"DSPSGNINF" : "*YES",
"PWDCHGBLK" : "93",
"GRPPRF" : "AZURE",
"USREXPDATE" : "12/06/22",
"CURLIB" : "*CRTDFT",
"LMTCPB" : "*YES",
"ASTLVL" : "*BASIC",
"SUPGRPPRF" : [ "AWS" ],
"MSGQ" : "/QSYS.LIB/QUSRSYS.LIB/BJENSEN.MSGQ",
"LANGID" : "ENG",
"CCSID" : "65535",
"PWDEXPITV" : "323",
"IsUserEntitlementRequired" : true,
"TEXT" : "TEXTFILEDVALUE",
"JOBD" : "/QSYS.LIB/QGPL.LIB/QDFTJOBD.JOBD",
"ActionAuditLevel" : "*BASIC",
"ObjectAuditValue" : "*NONE",
"PasswordChangedDate" : "Mon Aug 29 05:15:20 IST 2022",
"ATNPGM" : "/QSYS.LIB/QEZMAIN.PGM",
"LCLPWDMGT" : true,
"INLPGM" : "*NONE",
"USRCLS" : "*USER",
"SPCAUT" : [ "*AUDIT" ],
"SETJOBATR" : [ "*CCSID" ],
"SPCENV" : "*S36",
"ACGCDE" : "",
"IsPasswordNone" : false,
"DLVRY" : "*HOLD",
"IsAuthCollectionRepositoryExist" : false,
"UserExpirationAction" : "*DISABLE",
"INLMNU" : "/QSYS.LIB/%LIBL%.LIB/MAIN.MNU",
"LOCALE" : "*C",
"KBDBUF" : "*SYSVAL",
"OWNER" : "*USRPRF",
"PasswordExpireDate" : "Tue Jul 18 00:00:00 IST 2023",
"PWDEXP" : false,
"OUTQ" : "*DEV",
"CNTRYID" : "*SYSVAL",
"CHRIDCTL" : "*DEVD",
"StorageUsed" : "12"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least the
If the |
Query all users
The following example queries all users in the system:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id": "ADAM"},
{"_id": "BJENSEN"},
{"_id": "CHERYL"},
{"_id": "DAVID"},
{"_id": "EDDIE"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single user
The following example queries all users in the system:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN?prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"USROPT" : [ "*HLPFULL" ],
"SEV" : "50",
"USREXPITV" : 99,
"IsAuthCollectionActive" : false,
"HOMEDIR" : "/home/BJENSEN",
"MAXSTG" : "10000",
"UID" : "1277",
"PTYLMT" : 8,
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"PRTDEV" : "*SYSVAL",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"LMTDEVSSN" : "*NO",
"__UID__" : "BJENSEN",
"SRTSEQ" : "*HEX",
"DSPSGNINF" : "*YES",
"PWDCHGBLK" : "93",
"GRPPRF" : "AZURE",
"USREXPDATE" : "12/06/22",
"CURLIB" : "*CRTDFT",
"LMTCPB" : "*YES",
"ASTLVL" : "*BASIC",
"SUPGRPPRF" : [ "AWS" ],
"MSGQ" : "/QSYS.LIB/QUSRSYS.LIB/BJENSEN.MSGQ",
"LANGID" : "ENG",
"CCSID" : "65535",
"PWDEXPITV" : "323",
"IsUserEntitlementRequired" : true,
"TEXT" : "TEXTFILEDVALUE",
"JOBD" : "/QSYS.LIB/QGPL.LIB/QDFTJOBD.JOBD",
"ActionAuditLevel" : "*BASIC",
"ObjectAuditValue" : "*NONE",
"PasswordChangedDate" : "Mon Aug 29 05:15:20 IST 2022",
"ATNPGM" : "/QSYS.LIB/QEZMAIN.PGM",
"LCLPWDMGT" : true,
"INLPGM" : "*NONE",
"USRCLS" : "*USER",
"SPCAUT" : [ "*AUDIT" ],
"SETJOBATR" : [ "*CCSID" ],
"SPCENV" : "*S36",
"ACGCDE" : "",
"IsPasswordNone" : false,
"DLVRY" : "*HOLD",
"IsAuthCollectionRepositoryExist" : false,
"UserExpirationAction" : "*DISABLE",
"INLMNU" : "/QSYS.LIB/%LIBL%.LIB/MAIN.MNU",
"LOCALE" : "*C",
"KBDBUF" : "*SYSVAL",
"OWNER" : "*USRPRF",
"PasswordExpireDate" : "Tue Jul 18 00:00:00 IST 2023",
"PWDEXP" : false,
"OUTQ" : "*DEV",
"CNTRYID" : "*SYSVAL",
"CHRIDCTL" : "*DEVD",
"StorageUsed" : "12"
}
Modify a user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. You can use the AS400 connector to modify the following attributes:
-
PASSWORD -
PWDEXP -
STATUS -
USRCLS -
ASTLVL -
CURLIB -
INLPGM -
INLMNU -
LMTCPB -
TEXT -
SPCAUT -
SPCENV -
DSPSGNINF -
PWDEXPITV -
PWDCHGBLK -
LCLPWDMGT -
LMTDEVSSN -
KBDBUF -
MAXSTG -
PTYLMT -
JOBD -
OWNER -
ACGCDE -
DOCPWD -
MSGQ -
DLVRY -
SEV -
PRTDEV -
OUTQ -
ATNPGM -
SRTSEQ -
LANGID -
CNTRYID -
CCSID -
CHRIDCTL -
SETJOBATR -
LOCALE -
USROPT -
UID -
HOMEDIR -
USREXPDATE -
USREXPITV -
EIMASSOC -
GRPPRF -
SUPGRPPRF
The following request updates a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data "{
"__PASSWORD__":"ASDE1234",
"PWDEXP":false,
"__ENABLE__":true,
"USRCLS":"*USER",
"ASTLVL":"*BASIC",
"CURLIB":"*CRTDFT",
"INLPGM":"*NONE",
"INLMNU":"MAIN",
"TEXT":"TEXTFILEDVALUE",
"SPCAUT":["*AUDIT"],
"SPCENV":"*S36",
"DSPSGNINF":"*YES",
"PWDEXPITV":"323",
"PWDCHGBLK":"93",
"LCLPWDMGT":true,
"LMTDEVSSN":"*NO",
"MAXSTG":"10000",
"PTYLMT":8,
"JOBD":"QDFTJOBD",
"OWNER":"*USRPRF",
"ACGCDE":"*BLANK",
"DOCPWD":"W12345",
"MSGQ":"*USRPRF",
"DLVRY":"*HOLD",
"SEV":"50",
"PRTDEV":"*SYSVAL",
"OUTQ":"*DEV",
"ATNPGM":"*ASSIST",
"SRTSEQ":"*HEX",
"LANGID":"ENG",
"CCSID":"*HEX",
"CHRIDCTL":"*DEVD",
"SETJOBATR":["*CCSID"],
"LOCALE":"*C",
"USROPT":["*HLPFULL"],
"UID":"*GEN",
"HOMEDIR":"*USRPRF",
"EIMASSOC":["*NOCHG"],
"USREXPITV":99,
"USREXPDATE":"*USREXPITV",
"LMTCPB":"*YES",
"CNTRYID":"*SYSVAL",
"GRPPRF":"AZURE","SUPGRPPRF":["AWS"]
}" \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/As400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"USROPT" : [ "*HLPFULL" ],
"SEV" : "50",
"USREXPITV" : 99,
"IsAuthCollectionActive" : false,
"HOMEDIR" : "/home/BJENSEN",
"MAXSTG" : "10000",
"UID" : "1277",
"PTYLMT" : 8,
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"PRTDEV" : "*SYSVAL",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"LMTDEVSSN" : "*NO",
"__UID__" : "BJENSEN",
"SRTSEQ" : "*HEX",
"DSPSGNINF" : "*YES",
"PWDCHGBLK" : "93",
"GRPPRF" : "AZURE",
"USREXPDATE" : "12/06/22",
"CURLIB" : "*CRTDFT",
"LMTCPB" : "*YES",
"ASTLVL" : "*BASIC",
"SUPGRPPRF" : [ "AWS" ],
"MSGQ" : "/QSYS.LIB/QUSRSYS.LIB/BJENSEN.MSGQ",
"LANGID" : "ENG",
"CCSID" : "65535",
"PWDEXPITV" : "323",
"IsUserEntitlementRequired" : true,
"TEXT" : "TEXTFILEDVALUE",
"JOBD" : "/QSYS.LIB/QGPL.LIB/QDFTJOBD.JOBD",
"ActionAuditLevel" : "*BASIC",
"ObjectAuditValue" : "*NONE",
"PasswordChangedDate" : "Mon Aug 29 05:15:20 IST 2022",
"ATNPGM" : "/QSYS.LIB/QEZMAIN.PGM",
"LCLPWDMGT" : true,
"INLPGM" : "*NONE",
"USRCLS" : "*USER",
"SPCAUT" : [ "*AUDIT" ],
"SETJOBATR" : [ "*CCSID" ],
"SPCENV" : "*S36",
"ACGCDE" : "",
"IsPasswordNone" : false,
"DLVRY" : "*HOLD",
"IsAuthCollectionRepositoryExist" : false,
"UserExpirationAction" : "*DISABLE",
"INLMNU" : "/QSYS.LIB/%LIBL%.LIB/MAIN.MNU",
"LOCALE" : "*C",
"KBDBUF" : "*SYSVAL",
"OWNER" : "*USRPRF",
"PasswordExpireDate" : "Tue Jul 18 00:00:00 IST 2023",
"PWDEXP" : false,
"OUTQ" : "*DEV",
"CNTRYID" : "*SYSVAL",
"CHRIDCTL" : "*DEVD",
"StorageUsed" : "12"
}
Reset a user’s password
To reset the password for an AS400 user account, you can use the connector to change the user’s password:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data "{
"__PASSWORD__":"newpassword123"
}" \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"USROPT" : [ "*HLPFULL" ],
"SEV" : "50",
...
}
Activate a user
The following example activates a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data "{
"__ENABLE__": true
}
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
...
"__ENABLE__": true
...
}
Deactivate a user
The following example deactivates a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data "{"
""__ENABLE__": false
}" \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
...
"__ENABLE__": false
...
}
Delete a user
The following example deletes a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request DELETE \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/as400/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
...
}
Query all groups
The following example queries all AS400 Groups by their IDs:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/as400/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids&_prettyprint=true"
{
{
"result": [
{"_id": "AWS"},
{"_id": "AZURE"},
{"_id": "CLOUD"}
],
"resultCount" : 3,
"pagedResultsCookie" : null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy" : "NONE",
"totalPagedResults" : -1,
"remainingPagedResults" : -1
}
Query a single group
The following example queries a single AS400 group by its ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/as400/__GROUP__/AWS?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "AWS",
"GID" : "116",
"__NAME__" : "AWS",
"GRPAUT" : "*NONE",
"GRPAUTTYP" : "*PRIVATE",
"__UID__" : "AWS"
}
Account attributes
The following account attributes are supported by the AS400 connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
User Profile Name |
|
The password used to log in. |
|
The previous sign-on date. |
|
The last date the password was changed. |
|
Whether or not the password is *NONE. |
|
The user expiration action. |
|
The storage used. |
|
A value used for auditing the object. |
|
The Action Audit Level. |
|
When the user’s password is set to expire. |
|
The user’s status. Permitted values are |
|
The special access control for the user. |
|
Specifies which user interface to use. |
|
Specifies the name of the current library associated with the job. |
|
The initial program. |
|
The initial menu. |
|
Whether or not user entitlement is required. |
|
Whether or not authority collection is active. |
|
Limit capabilities. |
|
A free-form text field. |
|
The special access permissions for the user. |
|
The special environment. |
|
The display sign-on information. |
|
The password expiration interval. |
|
Whether or not to block password change. |
|
Local password management. |
|
Limit device session. |
|
Keyboard buffering. |
|
Maximum allowed storage. |
|
Highest schedule priority. |
|
Job description. |
|
The owner of the user profile. |
|
The accounting code. |
|
The document password. |
|
The message queue. |
|
Delivery. |
|
The severity code. |
|
The print device. |
|
The output queue. |
|
The attention program. |
|
The sort sequence. |
|
The language ID. |
|
The country or region ID. |
|
The Coded Character Set ID. |
|
The character identifier control. |
|
The local job attributes. |
|
The locale. |
|
The user options. |
|
The user ID number. |
|
The home directory. |
|
The user’s expiration date. |
|
The user’s expiration interval. |
|
Authority. |
|
The EIM association. |
|
The date the password expires. |
|
Specifies the user’s group profile name whose authority is used when there is no job-specific authority given to the user. |
|
Specifies the user’s supplemental group profiles. Used with |
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the AS400 Connector
The AS400 Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
AS400 Connector Configuration
The AS400 Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Host name or IP address of As400. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The username to login As400. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The password to login As400. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Enables or not secure connection to As400. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum life for an available connection. The default value is 86400000. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum amount of inactive time before an available connection is closed. The default value is 3600000. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum amount of time a connection can be in use before it is closed and returned to the pool. The default value is -1 indicating that there is no limit. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum number of times a connection can be used before it is replaced in the pool. The default value is -1 indicating that there is no limit. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether the maintenance thread is used to cleanup expired connections. The default is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether threads are used in communication with the host servers and for running maintenance. The default value is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Time interval for how often the maintenance daemon is run. The default value is 300000 milliseconds. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) connector
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service for securely controlling access to AWS services. The AWS connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between AWS and IDM managed user objects. An AWS administrator account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your AWS administrator account and note the following:
- Access Key ID
-
The access key ID is a globally unique IAM user identifier to access the AWS service API.
- Secret Key ID
-
The secret key is a password to access the AWS service API.
- Role ARN
-
Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the role which has IAM Full Access permissions.
- Credentials Expiration
-
Time (in seconds) to configure the duration in which the temporary credentials would expire. Optional.
- Region
-
The region where the AWS instance is hosted.
Install the AWS connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/aws-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the AWS connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select AWS Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to AWS Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the AWS connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws?_action=test"
{
"name": "aws",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/aws",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.aws-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.aws.AwsConnector"
},
"displayName": "AWS Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the AWS system.
AWS remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the AWS connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the AWS connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the AWS remote connector.
Use the AWS connector
The following AWS account attributes are supported by the AWS connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The username of the user. Only alphanumeric characters, and |
|
Auto-generated user id. |
|
The path to the created user (used to define a hierarchy-based structure). Default value is |
|
Password for the user account. |
|
Amazon Resource Name (ARN), used to uniquely identify the AWS resource. For more information on ARNs, refer to Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) in the AWS documentation. |
|
Date of profile creation, in ISO 8601 date-time format. |
|
Date the password was last used. |
|
The ARN of the policy that is used to set the permissions boundary for the user. |
|
A list of customizable key-value pairs. For more information about tags on AWS, refer to Tagging AWS resources in the AWS documentation. For example: |
You can use the AWS connector to perform the following actions on an AWS account:
Create an AWS user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "bjensen",
"Path": "/",
"UserId": "AIDAW3FY74V57KNBRIDU6",
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::470686885243:user/bjensen",
"CreatedDate": "Thu Jun 02 16:46:39 PDT 2022"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least |
Update an AWS user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. The following attributes can be modified on a user:
-
__USER__ -
__PASSWORD__ -
Path -
PermissionsBoundary -
Tags
For example, to add a new tag to a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Tags": [{
"Key": "Project",
"Value": "Meteor"
}]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__/bjensen"
{
"_id": "bjensen",
"Path": "/",
"UserId": "AIDAW3FY74V57KNBRIDU6",
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::470686885243:user/bjensen",
"CreatedDate": "Thu Jun 02 16:46:39 PDT 2022",
"Tags": [
{
"Project": "Meteor"
}
]
}
Query AWS users
The following example queries all AWS users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "bjensen"
},
{
"_id": "frank@example.com"
},
{
"_id": "testFR4User"
},
{
"_id": "testFR5User"
},
{
"_id": "testFR6User"
}
],
"resultCount": 5,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__/bjensen"
{
"_id": "bjensen",
"Path": "/",
"UserId": "AIDAW3FY74V57KNBRIDU6",
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::470686885243:user/bjensen",
"CreatedDate": "Thu Jun 02 16:46:39 PDT 2022",
"Tags": [
{
"Project": "Meteor"
}
]
}
Reset an AWS user account password
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{
"operation": "add",
"field": "__PASSWORD__",
"value": "Passw0rd@123!"
}]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__/bjensen"
{
"_id": "bjensen",
"Path": "/",
"UserId": "AIDAW3FY74V57KNBRIDU6",
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::470686885243:user/bjensen",
"CreatedDate": "Thu Jun 02 16:46:39 PDT 2022",
"Tags": [
{
"Project": "Meteor"
}
]
}
|
While the |
Delete an AWS user account
You can use the AWS connector to delete an account from the AWS IAM service.
The following example deletes an AWS account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/aws/__ACCOUNT__/bjensen"
{
"_id": "bjensen",
"Path": "/",
"UserId": "AIDAW3FY74V57KNBRIDU6",
"__NAME__": "bjensen",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::470686885243:user/bjensen",
"CreatedDate": "Thu Jun 02 16:46:39 PDT 2022",
"Tags": [
{
"Project": "Meteor"
}
]
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the AWS Connector
The AWS Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
AWS Connector Configuration
The AWS Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Access Key ID to access the AWS IAM Service API. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the Secret Key ID to access the AWS IAM Service API. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Amazon Resource Name specifying the Role. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Regions. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Page Size. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the temporary credentials expiration time in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the ProxyHost. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the ProxyPort. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Proxy Username. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Proxy Password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Maximum Connection Timeout in milliseconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the number of Maximum Connections. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Cerner connector
Cerner is a healthcare-related service which provides an integrated healthcare IT solution for large healthcare providers. The Cerner connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between Cerner and IDM managed user objects. A Cerner system account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your Cerner system account and note the following:
- Bearer token
-
The bearer token associated with your system account.
- Tenant
-
Your Cerner tenant ID.
- Region
-
The Cerner Cloud region where the tenant resides.
Install the Cerner connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/cerner-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Cerner connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Cerner Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Cerner Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the Cerner connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner?_action=test"
{
"name": "Cerner",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/Cerner",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.cerner-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.cerner.CernerConnector"
},
"displayName": "Cerner Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ORGANIZATION__",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ORGANIZATIONGROUP__",
"__ALL__",
"__PERSONNELGROUP__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector was configured correctly, and can authenticate to the Cerner system.
Cerner remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Cerner connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Cerner connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Cerner remote connector.
Use the Cerner connector
| Connector resource | Cerner resource type |
|---|---|
|
Personnel |
|
Organization |
|
Personnel Group |
|
Organization Group |
__ACCOUNT__ attributes
| Attribute | Notes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The user’s name, in a |
||||||||||||
|
Must be in |
||||||||||||
|
Accepted values are |
||||||||||||
|
The user’s first name. Required. |
||||||||||||
|
The user’s last name. Required. |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Accepted values are: |
||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
For a list of valid language tags, refer to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) language subtag registry. |
__ORGANIZATION__ attributes
| Attribute | Notes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The name of the organization. This corresponds to |
||||||||||||
|
The name of the organization. Required. |
||||||||||||
|
Alias types related to the organization. |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
For a list of valid language tags, refer to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) language subtag registry. |
||||||||||||
|
The postal codes indicating the area of coverage provided by the organization. |
||||||||||||
|
|
__PERSONNELGROUP__ attributes
| Attribute | Notes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A comma-separated name for the personnel group. |
||||||
|
The mnemonic determines the function of the personnel group. |
||||||
|
The type of the personnel group mnemonic. Usually either |
||||||
|
The name of the personnel group. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The type of alias. Requires |
||||||
|
The source of the alias value. Requires |
||||||
|
The unique identifier of alias. Requires |
__ORGANIZATIONGROUP__ attributes
| Attribute | Notes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A comma-separated name for the organization group. |
||||||
|
A list of organization IDs that are members of the organization group. |
||||||
|
The name of the organization group. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The type of alias. Requires |
||||||
|
The source of the alias value. Requires |
||||||
|
The unique identifier of alias. Requires |
You can use the Cerner connector to perform the following actions on a Cerner account:
Create a Cerner user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"updatedAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z",
"given": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Jensen"
},
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"languages": [],
"formattedName": "Barbara Jensen",
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"family": "Jensen",
"isManual": true,
"aliasSystem": "Barbara"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least |
Update a Cerner user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request:
For example, to add the user’s middle name:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara",
"name": {
"middle": "Simone"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"updatedAt": "2022-04-29T23:03:57Z",
"given": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"languages": [],
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"family": "Jensen",
"isManual": true,
"aliasSystem": "Barbara"
}
Query Cerner users
The following example queries all Cerner users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "7d9538c8-1c2a-4894-a403-129b35308f39"
},
{
"_id": "8f1c2671-9ebb-4105-9537-a3a0fc24afce"
},
{
"_id": "ac944860-705f-4487-99bf-6959c5e6157c"
},
{
"_id": "d308e459-51fa-469a-a07e-72f96906a4b4"
},
{
"_id": "ff9d6902-20be-4c6e-821a-5a0f3ccaebc8"
},
{
"_id": "bf2b9346-715e-4f59-9dc5-2bc89b8216cd"
},
{
"_id": "055def33-a845-4100-bcd1-2b59a3526ec5"
},
{
"_id": "167609b8-dfd0-4302-9022-4a3e8809b166"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "9f4ea23d-bacc-46ee-b8c9-75916a5f5128"
},
{
"_id": "a4d6be21-a5ce-4a56-91af-94c627701d4f"
}
],
"resultCount": 1020,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
|
Querying all ids can take a significant amount of time to return when the data set is large. Consider using paginated results instead, for example: curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=true&_fields=_id&_pageSize=2&_pagedResultsOffset=50"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "878c87d4-8322-4908-a858-555a1cb45e36"
},
{
"_id": "9ecaa98b-58df-4dd1-bc99-34341411b151"
}
],
"resultCount": 2,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
|
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"updatedAt": "2022-04-29T23:03:57Z",
"given": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"languages": [],
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"family": "Jensen",
"isManual": true,
"aliasSystem": "Barbara"
}
Delete a Cerner user account
You can use the Cerner connector to delete an account from the Cerner repository.
The following example deletes a Cerner account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"updatedAt": "2022-04-29T23:03:57Z",
"given": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"languages": [],
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"family": "Jensen",
"isManual": true,
"aliasSystem": "Barbara"
}
All supported resources can be queried. You can update user accounts, organizations, organization groups, and personnel groups, but only user accounts can be created or deleted. Available additional operations include:
Assign personnel groups to a user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara",
"name": {
"middle": "Simone"
},
"personnelGroupId": [
"8636d4c3-de7c-4f8a-828b-b709d6bfd636"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"family": "Jensen",
"updatedAt": "2022-10-25T23:50:31Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"given": "Barbara",
"organizationId": [],
"aliasSystem": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"languages": [],
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"isManual": true,
"personnelGroupId": [
"8636d4c3-de7c-4f8a-828b-b709d6bfd636"
],
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z"
}
Remove a user from a personnel group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara",
"name": {
"middle": "Simone"
},
"personnelGroupId": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"family": "Jensen",
"updatedAt": "2022-10-26T00:03:40Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"given": "Barbara",
"organizationId": [],
"aliasSystem": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"languages": [],
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"isManual": true,
"personnelGroupId": [],
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z"
}
Assign an organization member
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara",
"name": {
"middle": "Simone"
},
"organizationId": [
"c66f037b-50f5-4703-b51f-838f42a49e84"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"family": "Jensen",
"updatedAt": "2022-10-26T00:03:40Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"given": "Barbara",
"organizationId": [
"c66f037b-50f5-4703-b51f-838f42a49e84"
],
"aliasSystem": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"languages": [],
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"isManual": true,
"personnelGroupId": [],
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z"
}
Remove an organization member
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"given": "Barbara",
"family": "Jensen",
"aliasType": "USER",
"__NAME__": "Jensen, Barbara",
"name": {
"middle": "Simone"
},
"organizationId": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ACCOUNT__/5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6"
{
"_id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"formattedName": "Barbara Simone Jensen",
"__NAME__": "Jensen,Barbara",
"aliasValue": "Jensen",
"family": "Jensen",
"updatedAt": "2022-10-26T00:03:40Z",
"aliasType": "USER",
"given": "Barbara",
"organizationId": [],
"aliasSystem": "Barbara",
"name": {
"given": "Barbara",
"middle": "Simone",
"family": "Jensen",
"formatted": "Barbara Simone Jensen"
},
"languages": [],
"id": "5170a9cd-e501-4cbf-a1bf-9e6d293362c6",
"isManual": true,
"personnelGroupId": [],
"aliases": {
"type": "USER",
"value": "Jensen",
"system": "Barbara"
},
"createdAt": "2022-04-29T22:54:08Z"
}
Assign an organization to an organization group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"organizationId": [
"f90a6224-1880-4935-a838-e19d3079a23c",
"19b5157e-6fbe-4716-860b-28d6df90f331",
"c66f037b-50f5-4703-b51f-838f42a49e84"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ORGANIZATIONGROUP__/67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc"
{
"_id": "67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc",
"organizationId": [
"c66f037b-50f5-4703-b51f-838f42a49e84",
"f90a6224-1880-4935-a838-e19d3079a23c",
"19b5157e-6fbe-4716-860b-28d6df90f331"
],
"updatedAt": "2022-05-06T12:56:02Z",
"aliases": {
"type": "SOGI",
"value": "0001ORGVALUE",
"system": "0001System"
},
"id": "67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc",
"aliasType": "SOGI",
"aliasValue": "0001ORGVALUE",
"aliasSystem": "0001System",
"name": "ABC SK ORG GROUP",
"createdAt": "2022-05-06T12:56:02Z",
"__NAME__": "0001ORGVALUE,0001System"
}
Remove an organization from an organization group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"organizationId": [
"f90a6224-1880-4935-a838-e19d3079a23c",
"19b5157e-6fbe-4716-860b-28d6df90f331"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Cerner/__ORGANIZATIONGROUP__/67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc"
{
"_id": "67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc",
"organizationId": [
"f90a6224-1880-4935-a838-e19d3079a23c",
"19b5157e-6fbe-4716-860b-28d6df90f331"
],
"updatedAt": "2022-05-06T12:56:02Z",
"aliases": {
"type": "SOGI",
"value": "0001ORGVALUE",
"system": "0001System"
},
"id": "67203020-aae7-4f44-865f-c8591d618ffc",
"aliasType": "SOGI",
"aliasValue": "0001ORGVALUE",
"aliasSystem": "0001System",
"name": "ABC SK ORG GROUP",
"createdAt": "2022-05-06T12:56:02Z",
"__NAME__": "0001ORGVALUE,0001System"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Cerner Connector
The Cerner Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Cerner Connector Configuration
The Cerner Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the bearer token to authorize Cerner. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the tenant to authorize Cerner. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the region to authorize Cerner. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connection timeout in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Proxy Host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Proxy Port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Proxy Username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the Proxy Password. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
CSV file connector
The CSV file connector is useful when importing users, either for initial provisioning or for ongoing updates. When used continuously in production, a CSV file serves as a change log, often containing only user records that have changed.
|
This connector does not verify CSV data before attempting a synchronization. You must ensure that your CSV file is complete and properly formed before using the connector. Do not remove or replace CSV files that are the source or target of an active scheduled reconciliation or synchronization operation. |
Install the CSV file connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/csvfile-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the CSV file connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select CSV file Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to CSV file Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, use the sample CSV file connector configuration in openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-csvfile.json as a basis for your configuration.
The following example shows an excerpt of the connector configuration. The connectorHostRef property is optional and must be provided only if the connector runs remotely.
{
"connectorRef": {
"connectorHostRef": "#LOCAL",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.csvfile.CSVFileConnector",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.csvfile-connector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)"
}
}The only required configuration property is the path to the csvFile:
"configurationProperties" : {
"csvFile" : "&{idm.instance.dir}/data/csvConnectorData.csv"
}For a list of all configuration properties for this connector, refer to Configuration Properties.
|
If you change the structure of the CSV file resource, by adding or removing columns, you must update the corresponding object |
CSV file remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the CSV file connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the CSV file connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the CSV file remote connector.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the CSV File Connector
The CSV File Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Batch
-
Execute a series of operations in a single request.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
CSV File Connector Configuration
The CSV File Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
The CSV header that maps to the password for each row. Use this property when password-based authentication is required. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The character(s) used to replace spaces within column names. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The full path to the CSV file that is the data source for this connector. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The character string in the CSV file that is used to terminate each line. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The CSV header that maps to the uid (or name) for each row. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The character in the CSV file that is used to encapsulate strings. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The character in the CSV file that is used to escape characters. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The character in the CSV file that is used to separate field values. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The number of historical copies of the CSV file to retain when performing synchronization operations. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Database Table connector
The Database Table connector lets you provision to a single table in a JDBC database.
Install the Database Table connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/databasetable-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Database Table connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Database Table Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Database Table Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, use the sample connector configuration for the Database Table connector in samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-contractordb.json. The corresponding data definition language file is provided in samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-contractordb.sql.
The following excerpt shows a sample Database Table connector configuration:
"configurationProperties" : {
"url" : "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/contractordb?serverTimezone=UTC",
"driverClassName" : "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver",
"username" : "root",
"password" : "password",
"table" : "people",
"keyColumn" : "EMAIL",
"passwordColumn" : "",
"changeLogColumn" : "CHANGE_TIMESTAMP",
"disablePaging" : false,
"enableEmptyString" : false,
"quoting" : "",
"rethrowAllSQLExceptions" : true,
"nativeTimestamps" : false,
"allNative" : false,
"suppressPassword" : true,
"validationQueryTimeout" : -1,
"validationQuery" : "SELECT 1 FROM DUAL",
"validationInterval" : 3000,
"initialSize" : 10,
"maxIdle" : 100,
"minIdle" : 10,
"maxWait" : 30000,
"maxActive" : 100,
"maxAge" : 0,
"minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" : 60000,
"timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" : 5000,
"testWhileIdle" : false,
"testOnBorrow" : true
}The mandatory configurable properties are as follows:
url-
The JDBC database address that contains the table to which you are provisioning. The format of the url will change depending on the type of database, such as
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/contractordb?serverTimezone=UTC, orjdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:3306/contractordb. Note that the address includes the name of the database you are connecting to. driverClassName-
The class name of the driver you are using to connect to a database. The name varies depending on the type of database you are using, such as
oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver, orcom.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver. table-
The name of the table in the JDBC database that contains the user accounts.
keyColumn-
The column value that is used as the unique identifier for rows in the table.
If you want to map NAMEorUIDto an attribute in IDM, change thekeyColumnto a column in the SQL schema that does not match any of the target properties in your mapping; otherwise, a conflict occurs and IDM does not create the account. Previously, this column wasUNIQUE_ID.
Unless the database is configured to not need authentication, username and password are also required.
Tomcat JDBC connection pool
The Database Table connector uses the Apache Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool. Additional configurable properties and information are available in the Apache Tomcat documentation.
Database Table remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Database Table connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Database Table connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Database Table remote connector.
Implementation specifics
-
To use this connector for liveSync, add a changelog type column to the database and provide the name of this column in the
changeLogColumnproperty. Note that the Database Table connector supports liveSync for create and update operations only. To detect deletes in the database you must run a full reconciliation. -
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Database Table connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
-
The Database Table connector supports paged reconciliation queries only for the following databases:
-
MySQL
-
PostgreSQL
-
Oracle Database 11gR2 and later versions
-
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and later versions
Paging is enabled by default. If you are connecting to a database for which paging is not supported, you must disable it by setting "disablePaging" : truein the connector configuration.
For more information about configuring paged reconciliation queries, refer to Paging Reconciliation Query Results.
-
-
If your database does not support precise (nanosecond) timestamps, you can use the
inclusiveSyncconfiguration property to ensure that modified entries are not missed in liveSync operations. IfinclusiveSyncis set totrue, the connector synchronizes all entries whose change timestamp is greater than or equal to thesyncToken. Be aware that if you set this property totrue, the activity log creates a new entry every time liveSync occurs, even if entries are changed. This can lead to rapid growth of the activity audit log.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Database Table Connector
The Database Table Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Database Table Connector Configuration
The Database Table Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection properties that will be sent to our JDBC driver when establishing new connections. Format of the string must be [propertyName=property;]* NOTE - The "user" and "password" properties will be passed explicitly, so they do not need to be included here. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to propagate the interrupt state for a thread that has been interrupted (not clearing the interrupt state). Default value is false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true if you wish to put a facade on your connection so that it cannot be reused after it has been closed. This prevents a thread holding on to a reference of a connection it has already called closed on, to execute queries on it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default catalog of connections created by this pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
To avoid excess validation, run validation at most at this frequency (in milliseconds). If a connection is due for validation, but was validated within this interval, it will not be validated again. The default value is 3000 (3 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag whether ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to true if you want to ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to false if you want to fail the initialization of the pool by throwing exception. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Register the pool with JMX or not. The default value is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can complete the transaction by calling commit on the connection as it is returned to the pool If rollbackOnReturn==true then this attribute is ignored. Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to log stack traces for application code which abandoned a Connection. Logging of abandoned Connections adds overhead for every Connection borrow because a stack trace has to be generated. The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. Idle connections are checked periodically (if enabled) and connections that have been idle for longer than minEvictableIdleTimeMillis are released. The default value is derived from maxActive:100. (Also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated by the idle object evictor (if any). If an object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false and this property has to be set in order for the pool cleaner/test thread is to run (also see timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to remove abandoned connections if they exceed the removeAbandonedTimeout. If set to true a connection is considered abandoned and eligible for removal if it has been in use longer than the removeAbandonedTimeout Setting this to true can recover db connections from applications that fail to close a connection. See also logAbandoned The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connections that have been abandoned (timed out) wont get closed and reported up unless the number of connections in use are above the percentage defined by abandonWhenPercentageFull. The value should be between 0-100. The default value is 0, which implies that connections are eligible for closure as soon as removeAbandonedTimeout has been reached. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum number of established connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. The connection pool can shrink below this number if validation queries fail. The default value is derived from initialSize:10. (Also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default read-only state of connections created by this pool. If not set then the setReadOnly method will not be called. (Some drivers dont support read only mode, ex: Informix) |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before throwing an exception. Default value is 30000 (30 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to log errors during the validation phase to the log file. If set to true, errors will be logged as SEVERE. Default value is false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The fully qualified Java class name of the JDBC driver to be used. The driver has to be accessible from the same classloader as tomcat-jdbc.jar. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns the name of the connection pool. By default a JVM unique random name is assigned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns true if this connection pool is configured to wrap statements in order to enable equals() and hashCode() methods to be called on the closed statements if any statement proxy is set. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A custom query to be run when a connection is first created. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The timeout in seconds before a connection validation queries fail. This works by calling java.test_sample.Statement.setQueryTimeout(seconds) on the statement that executes the validationQuery. The pool itself doesnt timeout the query, it is still up to the JDBC driver to enforce query timeouts. A value less than or equal to zero will disable this feature. The default value is -1. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The SQL query that will be used to validate connections from this pool before returning them to the caller. If specified, this query does not have to return any data, it just cant throw a SQLException. The default value is null. Example values are SELECT 1(mysql), select 1 from dual(oracle), SELECT 1(MS Sql Server). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can terminate the transaction by calling rollback on the connection as it is returned to the pool Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
By default, the jdbc-pool will ignore the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, and simply return a previously pooled connection under the globally configured properties username and password, for performance reasons. The pool can however be configured to allow use of different credentials each time a connection is requested. To enable the functionality described in the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, simply set the property alternateUsernameAllowed to true. Should you request a connection with the credentials user1/password1 and the connection was previously connected using different user2/password2, the connection will be closed, and reopened with the requested credentials. This way, the pool size is still managed on a global level, and not on a per schema level. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of a class which implements the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.Validator interface and provides a no-arg constructor (may be implicit). If specified, the class will be used to create a Validator instance which is then used instead of any validation query to validate connections. The default value is null. An example value is com.mycompany.project.SimpleValidator. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout value in seconds. Similar to to the removeAbandonedTimeout value but instead of treating the connection as abandoned, and potentially closing the connection, this simply logs the warning if logAbandoned is set to true. If this value is equal or less than 0, no suspect checking will be performed. Suspect checking only takes place if the timeout value is larger than 0 and the connection was not abandoned or if abandon check is disabled. If a connection is suspect a WARN message gets logged and a JMX notification gets sent once. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish the ProxyConnection class to use String.equals and set to false when you wish to use == when comparing method names. This property does not apply to added interceptors as those are configured individually. The default value is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout in seconds before an abandoned(in use) connection can be removed. The default value is 60 (60 seconds). The value should be set to the longest running query your applications might have. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default auto-commit state of connections created by this pool. If not set, default is JDBC driver default (If not set then the setAutoCommit method will not be called). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns true if we should run the validation query when connecting to the database for the first time on a connection. Normally this is always set to false, unless one wants to use the validationQuery as an init query. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A semicolon separated list of classnames extending org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.JdbcInterceptor class. See Configuring JDBC interceptors below for more detailed description of syntaz and examples. These interceptors will be inserted as an interceptor into the chain of operations on a java.test_sample.Connection object. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The initial number of connections that are created when the pool is started. Default value is 10. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default TransactionIsolation state of connections created by this pool. One of the following: NONE, READ_COMMITTED, READ_UNCOMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE If not set, the method will not be called and it defaults to the JDBC driver. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used in tomcat-jdbc-pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The URL used to connect to the database. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool, and we will attempt to borrow another. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. In order to have a more efficient validation, see validationInterval. Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish that calls to getConnection should be treated fairly in a true FIFO fashion. This uses the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue implementation for the list of the idle connections. The default value is true. This flag is required when you want to use asynchronous connection retrieval. Setting this flag ensures that threads receive connections in the order they arrive. During performance tests, there is a very large difference in how locks and lock waiting is implemented. When fairQueue=true there is a decision making process based on what operating system the system is running. If the system is running on Linux (property os.name=Linux. To disable this Linux specific behavior and still use the fair queue, simply add the property org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue.ignoreOS=true to your system properties before the connection pool classes are loaded. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used. Access can be achieved by calling unwrap on the pooled connection. see javax.test_sample.DataSource interface, or call getConnection through reflection or cast the object as javax.test_sample.PooledConnection |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Time in milliseconds to keep this connection. When a connection is returned to the pool, the pool will check to see if the now - time-when-connected > maxAge has been reached, and if so, it closes the connection rather than returning it to the pool. The default value is 0, which implies that connections will be left open and no age check will be done upon returning the connection to the pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum amount of time an object may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction. The default value is 60000 (60 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle connection validation/cleaner thread. This value should not be set under 1 second. It dictates how often we check for idle, abandoned connections, and how often we validate idle connections. The default value is 5000 (5 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being returned to the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Return true if a lock should be used when operations are performed on the connection object. Should be set to false unless you plan to have a background thread of your own doing idle and abandon checking such as JMX clients. If the pool sweeper is enabled, then the lock will automatically be used regardless of this setting. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated from this pool at the same time. The default value is 100. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection username to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Enter the name of the table in the database that contains the accounts. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The connection password to be passed to the JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Select whether database column names for this resource should be quoted, and the quoting characters. By default, database column names are not quoted (None). For other selections (Single, Double, Back, or Brackets), column names will appear between single quotes, double quotes, back quotes, or brackets in the SQL generated to access the database. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
This mandatory column value will be used as the unique identifier for rows in the table. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Enter the name of the column in the table that will hold the password values. If empty, no validation is done on resources and passwords. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If true, optional paging in a query will be ignored by the connector. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Select to enable support for writing an empty string, instead of a NULL value, in character based columns defined as not-null in the table schema. This option does not influence the way strings are written for Oracle based tables. By default empty strings are written as a NULL value. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If this is not checked, SQL statements which throw SQLExceptions with a 0 ErrorCode will be have the exception caught and suppressed. Check it to have exceptions with 0 ErrorCodes rethrown. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Select to retrieve Timestamp data type of the columns in java.sql.Timestamp format from the database table. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Select to retrieve all data types of columns in native format from the database table. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The change log column stores the latest change time. Providing this value the Sync capabilities are activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true then the password will not be returned. Never. Even though it is explicitly requested. If set to false then the password will be returned if it is explicitly requested. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the SyncOp will query for ChangeLogColumn >= syncToken. One record will always be returned from the database in this case and be handled by the connector. If set to false, the SyncOp will query for ChangeLogColumn > syncToken. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true then the JDBC Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS is used for prepared statement. It may need to be set to false with Oracle JDBC driver for create() operation. Defaults to tue. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
DocuSign connector
The DocuSign connector lets you manage DocuSign service accounts and synchronize accounts between DocuSign and the IDM managed user repository.
This chapter describes how to install and configure the DocuSign connector, and how to perform basic tests to ensure that it’s running correctly.
For a complete example that includes the configuration required to synchronize users with this connector, refer to Synchronize data between IDM and DocuSign.
Before you start
The instructions in this guide assume that you have a DocuSign administrator account, and that you have added an Integrator Key, as described in the DocuSign Documentation. Before you configure the connector, log in to your administrator account and note the following information:
-
API User ID
-
API Account ID
-
Integration Key
You will also need to set up an RSA Keypair and copy the public and private keys to a location that will be accessible by the connector.
-
Docusign API Hostname
-
Docusign OAuth Hostname
You need these details to configure the connector to interact with your DocuSign environment.
The DocuSign connector uses Oauth to connect to DocuSign. You must grant authorization to the Integration Key by directing your browser to the following URL:
https://account-d.docusign.com/oauth/auth?response_type=code&scope=signature%20impersonation&client_id=your-integrator-key&redirect_uri=https://client.example.com/callback
In the resulting window, click Accept to grant the required authorization.
The connector requires signing groups to be enabled. Depending on your DocuSign plan, you might need to contact the DocuSign Support team to enable signing groups. For more information, refer to the DocuSign documentation.
Install the DocuSign connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/docusign-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Download the connector dependencies. The DocuSign connector has a dependency on the Java JWT library 4.4.0 (java-jwt-4.4.0.jar).
-
If you are running the connector locally, place the library in the
/path/to/openidm/libdirectory:mv ~/Downloads/java-jwt-4.4.0.jar /path/to/openidm/lib/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place the library in the
/path/to/openicf/libdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the DocuSign connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select DocuSign Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to DocuSign Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file. IDM provides a sample connector configuration file in the /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners directory. Copy this sample file (provisioner.openicf-docusign.json) to your project’s conf directory.
The following excerpt shows sample configuration properties:
"configurationProperties": {
"host" : "_CHANGEME_",
"oAuthHost" : "_CHANGEME_",
"accountId" : "_CHANGEME_",
"integratorKey" : "_CHANGEME_",
"privateKeyFilePath" : "_CHANGEME_",
"publicKeyFilePath" : "_CHANGEME_",
"userId" : "_CHANGEME_",
...
}host-
The Docusign API hostname, for example,
demo.docusign.net. oAuthHost-
The Docusign OAuth hostname, for example,
https://account.docusign.com/oauth. userId-
The API User ID of the DocuSign user that will authenticate to the REST server. You can locate this ID under Admin > Integrations > API and Keys when you log in to your DocuSign account.
accountId-
The API Account ID of the user specified previously. You can locate this account ID under Admin > Integrations > API and Keys when you log in to your DocuSign account.
integratorKey-
The DocuSign Integration Key or client ID. You can locate the Integrator Key under Admin > Integrations > API and Keys when you log in to your DocuSign account. For more information, refer to the corresponding DocuSign documentation.
privateKeyFilePath-
The full path to the Private Key of the RSA Keypair. To obtain the Private Key, select Admin > Integrations > API and Keys, then select Add RSA Keypair. Copy the value of the Private Key to a file and specify the file path in this property, for example:
"privateKeyFilePath" : "/path/to/private-key.txt". publicKeyFilePath-
The full path to the Public Key of the RSA Keypair. To obtain the Public Key, select Admin > Integrations > API and Keys, then select Add RSA Keypair. Copy the value of the Public Key to a file and specify the file path in this property, for example:
"publicKeyFilePath" : "/path/to/public-key.txt".
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the UI.
Test the DocuSign connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign?_action=test"
{
"name": "docusign",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/docusign",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.docusign-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.docusign.DocuSignConnector"
},
"displayName": "DocuSign Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"userSignature",
"signingGroup",
"__ALL__",
"account",
"contact"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly, and can authenticate to the DocuSign server.
DocuSign remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the DocuSign connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the DocuSign connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the DocuSign remote connector.
Configure Connection Pooling
The DocuSign connector supports connection pooling, which can substantially improve the performance of the connector. The basic connection pooling configuration is described in Connection pooling configuration.
Use the DocuSign Connector
You can use the DocuSign connector to perform the following actions on a DocuSign account.
Create a DocuSign User
This example creates a user with the minimum required attributes.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"password": "Passw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account?_action=create"
{
"_id": "dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"accountManagementGranular": [
{
"canManageUsers": "false"
},
{
"canManageAdmins": "false"
},
{
"canManageGroups": "false"
},
{
"canManageSharing": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageReporting": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSecuritySettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageSigningGroups": "false"
}
],
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"enableConnectForUser": "false",
"lastName": "Garcia",
"createdDateTime": "2018-10-18T07:48:39.3870000Z",
"userSettings": [
{
"name": "expressSendOnly",
"value": "false"
}
],
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"sendActivationOnInvalidLogin": "false",
"userStatus": "ActivationSent",
"firstName": "Carlos",
"groupList": [
{
"groupName": "Everyone",
"groupType": "everyoneGroup",
"groupId": "4428049"
}
],
"uri": "/users/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"isAdmin": "False",
"userType": "CompanyUser"
}
When you create a new user, you must specify at least the userName, email, and password. The value of the userName attribute determines how the remaining name attributes (firstName, lastName, and so on) are set in the new DocuSign user entry.
If you create the user with a single word as the value of the userName attribute, for example, cgarcia, the user’s userName and lastName attributes in DocuSign are both set to cgarcia.
If you create the user with multiple words as the value of the userName attribute, for example, Carlos Garcia), the user’s userName attribute is set to Carlos Garcia, their firstName attribute is set to Carlos, and their lastName attribute is set to Garcia.
Only the first three words of the userName attribute are parsed, into the firstName, middleName, and lastName attributes. Any additional words are ignored.
|
By default, DocuSign accounts have a strict password strength setting. If a create operation fails with a Caused by: org.identityconnectors.framework.common.exceptions.ConnectorException: Invalid forgotten password challenge. You can also set a custom curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"password": "Passw0rd",
"forgottenPasswordInfo": {
"forgottenPasswordQuestion1": "my question",
"forgottenPasswordAnswer1": "my answer"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account?_action=create"
|
Query DocuSign User Entries
This example queries all DocuSign users by their IDs:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "bc9f0464-808a-4703-b4c2-c1e6a77f0c3a",
"userName": "Babs Jensen"
},
{
"_id": "dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"userName": "Carlos Garcia"
},
{
"_id": "94be4fed-cfd7-47d5-9fcc-813405084f17",
"userName": "Olayinka Kuti"
}
],
"resultCount": 3,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91"
{
"_id": "dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"accountManagementGranular": [
{
"canManageUsers": "false"
},
{
"canManageAdmins": "false"
},
{
"canManageGroups": "false"
},
{
"canManageSharing": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageReporting": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSecuritySettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageSigningGroups": "false"
}
],
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"enableConnectForUser": "false",
"lastName": "Garcia",
"createdDateTime": "2018-10-18T07:48:39.3870000Z",
"userSettings": [
{
"name": "expressSendOnly",
"value": "false"
}
],
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"sendActivationOnInvalidLogin": "false",
"userStatus": "ActivationSent",
"firstName": "Carlos",
"groupList": [
{
"groupName": "Everyone",
"groupType": "everyoneGroup",
"groupId": "4428049"
}
],
"uri": "/users/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"isAdmin": "False",
"userType": "CompanyUser"
}
Modify a DocuSign User Entry
You can modify an existing user with a PATCH request or with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. You can use the connector to modify the following attributes of a user entry:
-
title -
firstName -
middleName -
lastName -
suffix -
userName
After creation, a user’s email address is read-only and you cannot modify it using the connector.
If forgotten password recovery has been enabled for the DocuSign user account, (forgottenPasswordQuestion and forgottenPasswordAnswer have been set) you can use the connector to change a user’s password. You must include the following attributes in a password change request:
-
currentPassword -
newPassword -
email -
forgottenPasswordQuestion -
forgottenPasswordAnswer -
forgottenPasswordInfo
The following example changes Carlos Garcia’s password:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-type: application/json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[
{
"operation": "replace",
"field": "password",
"value": "MyPassw0rd"
}
]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91"
{
"_id": "dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"accountManagementGranular": [
{
"canManageUsers": "false"
},
{
"canManageAdmins": "false"
},
{
"canManageGroups": "false"
},
{
"canManageSharing": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageReporting": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSecuritySettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageSigningGroups": "false"
}
],
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"userProfileLastModifiedDate": "2018-10-18T01:10:59.4230000Z",
"enableConnectForUser": "false",
"lastName": "Garcia",
"createdDateTime": "2018-10-18T07:48:39.3870000Z",
"userSettings": [
{
"name": "expressSendOnly",
"value": "false"
}
],
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"sendActivationOnInvalidLogin": "false",
"userStatus": "ActivationSent",
"firstName": "Carlos",
"groupList": [
{
"groupName": "Everyone",
"groupType": "everyoneGroup",
"groupId": "4428049"
}
],
"uri": "/users/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"isAdmin": "False",
"userType": "CompanyUser"
}
If the naming component attributes are sent in an update, these attribute values are set on the DocuSign user. The user’s userName attribute is re-generated from the individual naming components. If both the userName and additional naming component attributes (such as firstName or lastName are sent in the update request, the supplied userName attribute is ignored and its value is regenerated from the individual naming components.
Close a DocuSign User Account
You cannot use the DocuSign connector to delete an account from the DocuSign repository. However, you can use a DELETE request to set the userStatus attribute of the account to Closed.
The following example closes Carlos Garcia’s DocuSign account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/docusign/account/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91"
{
"_id": "dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"accountManagementGranular": [
{
"canManageUsers": "false"
},
{
"canManageAdmins": "false"
},
{
"canManageGroups": "false"
},
{
"canManageSharing": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageReporting": "false"
},
{
"canManageAccountSecuritySettings": "false"
},
{
"canManageSigningGroups": "false"
}
],
"userName": "Carlos Garcia",
"userProfileLastModifiedDate": "2018-10-18T01:10:59.4230000Z",
"enableConnectForUser": "false",
"lastName": "Garcia",
"createdDateTime": "2018-10-18T07:48:39.3870000Z",
"userSettings": [
{
"name": "expressSendOnly",
"value": "false"
}
],
"email": "cgarcia@example.com",
"sendActivationOnInvalidLogin": "false",
"userStatus": "ActivationSent",
"firstName": "Carlos",
"groupList": [
{
"groupName": "Everyone",
"groupType": "everyoneGroup",
"groupId": "4428049"
}
],
"uri": "/users/dc1c6940-1de7-4434-a91e-1407424cac91",
"isAdmin": "False",
"userType": "CompanyUser"
}
|
A closed account remains in the DocuSign repository and can still be queried by its ID. |
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the DocuSign Connector
The DocuSign Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
DocuSign Connector Configuration
The DocuSign Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The DNS name or IP address of the DocuSign REST server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The OAuth host URL to the DocuSign REST server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The DocuSign Account ID to manage. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The DocuSign integrator key for accessing the REST API. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The path to the private key used to generate a JSON web token (JWT). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The path to the public key used to generate a JSON web token (JWT). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The user ID of the user creating the JSON web token (JWT). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Advanced Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies that the HTTP client accepts self-signed certificates. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies that the HTTP client does not verify the host name. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The hostname of the HTTP proxy (if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the DocuSign server). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The proxy port number (if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the DocuSign server). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies that there is consent from the organization. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Dropbox connector
Before you start
-
Create a Dropbox developer account.
-
Create a new application with full Dropbox access. Add the required read and write permissions for team, member, and group. Remember to save the app key and app secret.
-
Get a refresh token.
Install the Dropbox connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/dropbox-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Dropbox connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Dropbox Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Dropbox Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Base Connector Details
-
Dropbox Endpoint: https://api.dropboxapi.com/2 -
Use Basic Auth For OAuth Token Neg:true|false -
Max connections: max size of the http connection pool used. Defaults to10. -
Connection Timeout (seconds): Defines a timeout for the underlying http connection in seconds. Defaults to30.
Authentication
-
Token Endpoint: https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token -
Client ID: Your Client ID. -
Client Secret: Your Client Secret. -
Refresh Token: Your Refresh Token.
Object Types
If necessary, add or edit your object types to have these three objects with their properties:
__ACCOUNT__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
YES |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
__GROUP__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
YES |
|
String |
String |
YES |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Integer |
Integer |
NO |
Role
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
If configuring the connector over REST or through the filesystem, specify the connection details to the Dropbox resource provider in the configurationProperties for the connector. If you are using OAuth for your connection, the minimum required properties are serviceUri, tokenEndpoint, refreshToken, clientId, and clientSecret.
Sample Configuration
{
"configurationProperties" : {
"tokenExpiration" : null,
"accessToken" : null,
"serviceUri" : "https://api.dropboxapi.com/2",
"login" : null,
"password" : null,
"authenticationMethod" : "OAUTH",
"tokenEndpoint" : "https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token",
"clientId" : "k3..........5g",
"clientSecret" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"refreshToken" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"authToken" : null,
"acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : false,
"disableHostNameVerifier" : false,
"disableHttpCompression" : false,
"clientCertAlias" : null,
"clientCertPassword" : null,
"maximumConnections" : "10",
"httpProxyHost" : null,
"httpProxyPort" : null,
"httpProxyUsername" : null,
"httpProxyPassword" : null,
"connectionTimeout" : "30",
"grantType" : null,
"scope" : null,
"authorizationTokenPrefix" : "Bearer",
"useBasicAuthForOauthTokenNeg" : true
}
}
On startup, IDM encrypts the value of the clientSecret.
|
Mapping
From Dropbox users to OpenIDM Users
Attributes Grid
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
mail
From OpenIDM Users to Dropbox Users
Attributes Grid
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
email
From Dropbox groups to OpenIDM Groups
| When a member is added or removed from a group, it is necessary to perform a reconciliation from dropbox members to IDM members to keep the members of a group up to date. |
Attributes Grid
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
var result = source.group_external_id;
if(result == undefined){
result = source.group_id;
}
result;
|
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
groupExternalId
From OpenIDM Groups to Dropbox groups
Attributes Grid
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
group_id,group_external_id
Test the Dropbox connector
Test that the connector was configured correctly:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request POST 'http://localhost:8080/system/Dropbox?_action=test'
{
"name" : "Dropbox",
"enabled" : true,
"config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/Dropbox",
"connectorRef" : {
"bundleVersion" : [1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0),
"bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.dropbox-connector",
"connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.dropbox.DropboxConnector"
},
"displayName" : "Dropbox Connector",
"objectTypes" : [
"__GROUP__",
"role",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok" : true
}
MEMBERS
Invite a member
To invite a member, it is necessary to at least provide the email field. The fields given_name, surname, role_id are not required, but it is advisable to fill them in because these fields cannot be modified later. To get the list of roles go here:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"email" : "NEW.MEMBER@EMAIL.COM",
"given_name" : "GIVENNAME",
"surname" : "SURNAME",
"role_id" : "ROLE ID"
}'
--request POST 'http://localhost:8080/system/Dropbox/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create'
{
"_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID",
"role_id" : "ROLE_ID",
"email" : "NEW.MEMBER@EMAIL.COM",
...
}
Get members
Retrieve a list of team members ids from Dropbox. The limit of results and the default value are 1000:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "001"
},
{
"_id" : "002"
},
{
"_id" : "003"
},
...
]
}
Get member
Retrieve a team member from Dropbox. The team member id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__ACCOUNT__/TEAM_MEMBER_ID'
{
"_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID",
"groups" : [
{
"access_type" : "member",
"group_id" : "GROUP_ID"
}
],
"email" : "test@email.com",
"abbreviated_name" : "gs",
"joined_on" : "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"surname" : "surname",
"member_status" : "active",
"email_verified" : true,
"given_name" : "givenname",
"membership_type" : "full",
"role_id" : "ROLE_ID"
}
Get member email
Retrieve a team member in Dropbox filtering by email field. The team member id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__ACCOUNT__/TEAM_MEMBER_ID?_fields=email'
{
"_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID",
"email" : "test@email.com"
}
Delete member
Delete a member from a team. The team member id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request DELETE 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__ACCOUNT__/TEAM_MEMBER_ID'
{
"_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID",
"email" : "deleted.member@email.com",
...
}
GROUPS
Create a new empty group
Group name must be provided at least when creating a new group. group_management_type can be user_managed or company_managed, default is company_managed.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"group_name" : "GROUP NAME",
"group_management_type" : "company_managed",
"group_external_id" : "GROUP EXTERNAL ID"
}'
--request POST 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__GROUP__?_action=create' \
{
"_id" : "_id",
"group_id" : "GROUP_ID",
"member_count" : 0,
"group_name" : "GROUP NAME",
"group_external_id" : "GROUP EXTERNAL ID",
"group_management_type" : "company_managed",
"members" : []
}
Get groups
Retrieves a list of groups showing only the ids. The limit of results and the default value are 1000:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "001"
},
{
"_id" : "002"
},
{
"_id" : "003",
},
...
]
}
Update a group
| The default group in Dropbox cannot be updated. |
The fields that can be updated for a group are group_name, group_external_id, group_management_type (company_managed or user_managed). To add a member to a group, you need to provide the type of access and the team member id; to delete a member, delete the object. The group id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'If-Match: *' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"group_name" : "new name",
"group_management_type" : "company_managed",
"group_external_id" : "new external id",
"members" : [
{
"access_type" : "member",
"team_member_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID"
}
]
}
--request PUT 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__GROUP__/GROUP_ID'
{
"group_id" : "GROUP_ID",
"group_external_id" : "new extenal id",
"group_name" : "new name",
"member_count" : 1,
"group_management_type" : "company_managed",
"members" : [
{
"access_type" : "member",
"team_member_id" : "TEAM_MEMBER_ID"
}
]
}
Delete a group
The group id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request DELETE 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/__GROUP__/GROUP_ID'
{
"_id" : "GROUP_ID",
"group_name" : "group name",
...
}
ROLES
Get available roles from Dropbox members.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Dropbox/role/?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result" : [
{
"_id" : "ROLE_ID",
"name" : "Name role",
"description" : "Description role"
},
...
]
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Dropbox Connector
The Dropbox Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Dropbox Connector Configuration
The Dropbox Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Dropbox endpoint URI. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Dropbox login name. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The Dropbox user password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which method is to be used to authenticate on the remote server. Options are BASIC (username/password), OAUTH (Client id/secret) or TOKEN (static token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When using OAUTH as authentication method, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be queried for (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The client identifier for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Secure client secret for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Static authentication token. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Content compression is enabled by default. Set this property to true to disable it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed, set this to the certificate alias from the keystore. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed and the client certificate (private key) password is different from the keystore password, set this to the client private key password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the max size of the HTTP connection pool used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Hostname if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Port if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines Proxy Username if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Defines Proxy Password if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a timeout for the underlying HTTP connection in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Used by the refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 grant type to use (client_credentials or refresh_token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 scope to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The prefix to be used in the Authorization HTTP header for Token authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Authentication method for refresh token (Basic Authentication or Sending the ClientId and Client Secret in the Header). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Epic connector
Epic is a healthcare-related service which handles patient medical records. The Epic connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between Epic and the IDM managed user objects. An Epic administrator account on the Epic system you wish to connect to is required for this connector to work.
| The Epic connector only supports EMP user records. |
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your Epic administrator account and note the following:
-
Client ID
-
Username
-
Password
-
Private key (Generate an RSA keypair and convert to PKCS8)
To generate your private key:
-
Generate and download an RSA key pair.
-
Run the following command to convert the RSA private key to PKCS8 format:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -nocrypt -in privatekey.pem -out epic_pkcs8_private_key.pem
-
After generating the private key in PKCS8 format, remove
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----and-----END PRIVATE KEY-----from the generated PKCS8 private key file. -
Remove any escape characters such as
\nor\r.
-
-
REST endpoint (Optional)
-
SOAP endpoint (Optional)
-
Max records (Optional)
-
User template file path (Optional)
-
User sub template file path (Optional)
-
In Basket classification file path (Optional)
-
Group file path (Optional)
|
The user template, user sub template, in basket, and group file paths are local paths that are accessible to the IDM or RCS instance. |
Install the Epic connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/epic-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Epic connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Epic Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Epic Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the Epic connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic?_action=test"
{
"name": "Epic",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/Epic",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.epic-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.epic.EpicConnector"
},
"displayName": "Epic Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the Epic server.
Epic remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Epic connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Epic connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Epic remote connector.
Configure connection pooling
The Epic connector supports connection pooling, which can substantially improve the performance of the connector. The basic connection pooling configuration is described in Connection pooling configuration.
Use the Epic connector
| The Epic connector only supports EMP user records. |
The following resources are supported by the Epic connector:
| Connector Resource | Epic Resource Type |
|---|---|
|
Users |
|
Departments |
|
Groups |
|
Linked Provider |
|
User Template |
|
User Sub Template |
|
In Basket Classifications |
You can use the Epic connector to perform the following actions on an Epic account:
Create an Epic user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json"\
--request POST \
--data '{
"UserID": "8675309”,
"__NAME__": "Walter, Taylor"
}'\
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"ContactComment": "Initial contact created via web service",
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": true
}
|
Query Epic user entries
The following example queries all Epic users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "dsully"
},
{
"_id": "999999999"
},
{
"_id": "admin@ACECompany.com"
},
{
"_id": "extuser320"
},
{
"_id": "Achong"
},
{
"_id": "dsewell"
},
{
"_id": "8675309"
},
{
"_id": "atestuser"
},
{
"_id": "Amaraphornc"
},
{
"_id": "jocampo"
}
],
"resultCount": 10,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"ContactComment": "Initial contact created via web service",
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": true
}
Modify an Epic user entry
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. You can use the Epic connector to modify the following attributes:
User accounts
-
__ENABLE__ -
__GROUP__ -
__NAME__(Required) -
__PASSWORD__ -
UserID -
UserIDType -
UserAlias -
UserPhotoPath -
Sex -
Notes -
Provider -
LinkedProviderID -
Department -
ContactComment -
ContactDate -
SystemLoginID -
LDAPOverrideID -
DefaultLoginDepartmentID -
ReportGrouper1 -
ReportGrouper2 -
ReportGrouper3 -
CategoryReportGrouper -
InBasketClassifications -
UsersManagers -
PrimaryManager -
DefaultTemplateID -
UserTemplate -
UserSubtemplateIDs -
UserComplexName-UserComplexNamehas the following sub-attributes:-
FirstName -
GivenNameInitials -
MiddleName -
LastName -
LastNamePrefix -
SpouseLastName -
SpousePrefix -
SpouseLastNameFirst -
Suffix
When updating a user, __NAME__overrides theFirstName,LastNameandMiddleNameofUserComplexNameattributes. -
-
IsActive -
BlockStatus-BlockStatushas the following sub-attributes:-
IsBlocked -
BlockStatus.Comment
-
In Basket Classifications
-
__UID__ -
__NAME__
Groups
-
__UID__ -
__NAME__ -
Type
User Templates
-
__UID__ -
__NAME__
User Sub Templates
-
__UID__ -
__NAME__
Provider
-
__NAME__ -
__UID__ -
ExternalID -
Title -
NPI ID -
Provider Type -
Specialty -
Practice Name -
Street Address -
Phone
For example, to add a Suffix to a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Walter, Taylor",
"UserComplexName": {
"Suffix": "Junior"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "Jr.",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR JR.",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": true
}
Reset an Epic user account password
To reset the password for Epic user account, you can use the connector to change a user’s password.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd@123!",
"__NAME__": "Walter, Taylor"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": true
}
Activate an Epic user
The following example activates a user with the minimum required attributes, and updates their name:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Walter, Taylorupdate",
"__ENABLE__": "true"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylorupdate",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLORUPDATE",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": true
}
Deactivate an Epic user
The following example deactivates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{ \
"__NAME__": "TAYLOR, WALTER",
"__ENABLE__": false
}'\
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": false
}
Close an Epic user account
You can use the Epic connector to delete an account from the Epic repository.
|
A deleted account technically remains in the Epic repository, but cannot be queried by its ID. |
The following example deletes an Epic account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"_id": "8675309",
"UserComplexName": {
"FirstName": "Taylor",
"GivenNameInitials": "",
"MiddleName": "",
"LastName": "Walter",
"LastNamePrefix": "",
"SpouseLastName": "",
"SpousePrefix": "",
"Suffix": "",
"AcademicTitle": "",
"PrimaryTitle": "",
"SpouseLastNameFirst": false,
"FatherName": "",
"GrandfatherName": ""
},
"BlockStatus": {
"IsBlocked": false,
"Reason": "",
"Comment": ""
},
"__GROUP__": [],
"UserID": "8675309",
"__NAME__": "WALTER, TAYLOR",
"UsersManagers": [],
"InBasketClassifications": [],
"__ENABLE__": false
}
You can then confirm the account has been deleted by querying the UserID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__/8675309"
{
"code": 404,
"reason": "Not Found",
"message": "Object 8675309 not found on system/Epic/__ACCOUNT__"
}
Additionally, all supported resources can be queried:
Query Epic departments
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/Department?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "40"
},
{
"_id": "56"
},
{
"_id": "71"
},
{
"_id": "77"
},
{
"_id": "58"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "46"
},
{
"_id": "10120160"
},
{
"_id": "1002020"
},
{
"_id": "31"
},
{
"_id": "83"
},
{
"_id": "115"
}
],
"resultCount": 548,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Query Epic providers
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/Provider?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "116"
},
{
"_id": "E3087"
},
{
"_id": "E4000"
},
{
"_id": "E4913"
},
{
"_id": "E5335"
},
{
"_id": "E4716"
},
{
"_id": "E5370"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "E4001"
},
{
"_id": "E4002"
},
{
"_id": "E5137"
},
{
"_id": "E5199"
},
{
"_id": "E4003"
},
{
"_id": "E4694"
},
{
"_id": "E4004"
},
{
"_id": "E4005"
},
{
"_id": "E5019"
},
{
"_id": "E4843"
}
],
"resultCount": 2560,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/Provider/E4716"
{
"_id": "E4716",
"Specialty": "Family Medicine",
"__UID__": "E4716",
"Provider Type": "Physician",
"__NAME__": "WELLHIVE, PROVIDER"
}
Query user templates
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/UserTemplate?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "T00004"
},
{
"_id": "T00024"
},
{
"_id": "T00033"
},
{
"_id": "T00038"
},
{
"_id": "T00076"
},
{
"_id": "T00077"
},
{
"_id": "T00078"
},
{
"_id": "T00088"
},
{
"_id": "T00089"
},
{
"_id": "T00090"
},
{
"_id": "T1000601"
},
{
"_id": "T1002020"
},
{
"_id": "T1020101"
},
{
"_id": "T1020102"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "T8888001"
},
{
"_id": "T8889901"
},
{
"_id": "T9998001"
}
],
"resultCount": 431,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/UserTemplate/T8888001"
{
"_id": "T8888001",
"__UID__": "T8888001",
"__NAME__": "RESEARCH ADMINISTRATOR TEMPLATE"
}
Query user sub templates
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/UserSubTemplate?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "ST00007"
},
{
"_id": "ST00030"
},
{
"_id": "ST10200"
},
{
"_id": "ST10201"
},
{
"_id": "ST10202"
},
{
"_id": "ST10203"
},
{
"_id": "ST10204"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "ST10401"
},
{
"_id": "ST10402"
},
{
"_id": "ST10700"
},
{
"_id": "ST107001"
},
{
"_id": "T5080002"
},
{
"_id": "T99901"
},
{
"_id": "TCVREPSUB"
}
],
"resultCount": 91,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/UserSubTemplate/T00007"
{
"_id": "T00007",
"__NAME__": "EXCEL MEDICAL",
"__UID__": "T00007"
}
Query In Basket classifications
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/InBasketClassifications?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "1"
},
{
"_id": "2"
},
{
"_id": "15"
},
{
"_id": "29"
},
{
"_id": "30"
},
{
"_id": "31"
},
{
"_id": "84"
},
{
"_id": "85"
},
{
"_id": "100"
},
{
"_id": "140"
},
{
"_id": "141"
},
{
"_id": "212"
}
],
"resultCount": 12,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/InBasketClassifications/140"
{
"_id": "140",
"__NAME__": "Model AP Pt Clinical Msg Pool",
"__UID__": "140"
}
Query Epic groups
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "1"
},
{
"_id": "2"
},
{
"_id": "3"
},
{
"_id": "4"
},
{
"_id": "5"
},
{
"_id": "6"
},
{
"_id": "7"
},
{
"_id": "1000"
},
{
"_id": "1001"
},
{
"_id": "1002"
},
{
"_id": "1003"
},
{
"_id": "1004"
},
{
"_id": "1005"
},
{
"_id": "1006"
}
],
"resultCount": 14,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Epic/__GROUP__/1000"
{
"_id": "1000",
"__NAME__": "Community",
"__UID__": "1000",
"Type": "Community",
"Undefined3": "Customer~Epic Customer"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Epic Connector
The Epic Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Epic Connector Configuration
The Epic Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Client ID to authorize the Epic APIs. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the Private key in pkcs8 format. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Username required for Connection. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the Password required for Connection. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the location of User Template file. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the location of User Subtemplate file. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the location of In Basket Classifications File. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the location of Group File. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Maximum records for search operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Maximum connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Maximum Connection Timeout in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the Access token to establish connectivity with the target. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Validity period of the token. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Password. |
||||
|
|
|
No |
|
The HTTP URL for the REST End point (https://myserver.com/service/). |
||||
|
|
|
No |
|
The HTTP URL for the SOAP End point (https://myserver.com/service/). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Google Apps connector
The Google Apps connector is bundled with IDM and Identity Cloud. A sample connector configuration is also included with IDM. The Google Apps connector lets you interact with Google’s web applications.
The Google Apps connector is subject to the API Limits and Quotas imposed by Google. The connector also adheres to the implementation guidelines set out by Google for implementing exponential backoff.
Google project requirements
Use of the Google Apps connector requires a properly configured Google project. The basic steps for configuring a Google project should be used as an outline, as the specific options, menus, and features may have changed.
-
Log in to the Google Apps Developers Console and update your existing project or create a new project.
-
Enable the following APIs for your project:
Failure to enable the specified APIs results in the following depending on the Google Apps connector version:
-
For version 1.5.20.19 and earlier, connector requests hang indefinitely with no error message.
-
For version 1.5.20.20 and later, the connector logs an error.
-
-
Set up an OAuth2 Client.
The Google Apps connector uses OAuth2 to authorize the connection to the Google service:
-
In the Google Apps Developers Console, select Credentials > Create Credentials > OAuth client ID.
-
Click Configure Consent Screen, select Internal, and click Create.
-
On the OAuth consent screen, enter an Application name; for example,
RCS, and click Save.This name displays for all applications registered in this project.
-
Select Credentials > Create Credentials > OAuth client ID > Web application, and enter information in the following fields:
- Authorized JavaScript origins
-
The URI that clients use to access your application. The default URI is
https://localhost:8443.The URI that you enter here must be the same you use to access RCS. - Authorized redirect URIs
-
The OAuth redirect URI,
https://localhost:8443/admin/oauth.htmlby default.
-
Click Create.
-
On the OAuth client created pop-up, make a note of your Client ID and Client Secret.
-
-
Add RCS to the Trusted Apps list:
-
Log in to the Google Admin Console.
-
From the top left menu, select Security > API Controls.
-
Select MANAGE THIRD-PARTY APP ACCESS, click Change Access, and change the RCS app settings to Trusted.
-
Install the Google Apps connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/googleapps-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Google Apps connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Google Apps Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Google Apps Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
A Sign in with Google page displays.
-
Log in.
After you log in, Google requests access for the project.
-
Click Allow.
If you click Deny, you must return to the Connector Configuration > Details tab in the admin UI, and save your changes again.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
The Google Apps connector uses OAuth2 to authorize the connection to the Google service. To use this authorization mechanism, you must supply a clientId and clientSecret, to obtain an access token from Google. You can get the clientId and clientKey from the Google Developers Console after you have configured your Web Application.
A sample Google Apps connector configuration file is provided in samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-google.json with IDM.
This excerpt shows a sample Google Apps connector configuration. The default location of the connector .jar file is openidm/connectors. Therefore, the value of the connectorHostRef property must be "#LOCAL":
{
"connectorHostRef": "#LOCAL",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps.GoogleAppsConnector",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps-connector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)"
},The required configuration properties are as follows:
"configurationProperties": {
"domain": "",
"clientId": "",
"clientSecret": null,
"refreshToken": null
},domain-
Set to the domain name for OAuth 2-based authorization.
clientId-
A client identifier, as issued by the OAuth 2 authorization server. For more information, refer to the following section of RFC 6749: Client Identifier.
clientSecret-
Sometimes also known as the client password. OAuth 2 authorization servers can support the use of
clientIdandclientSecretcredentials, as noted in the following section of RFC 6749: Client Password. - refreshToken
-
A client can use an OAuth 2 refresh token to continue accessing resources. For more information, refer to the following section of RFC 6749: Refresh Tokens.
For a sample Google Apps configuration that includes OAuth 2-based entries for configurationProperties, refer to Synchronize accounts with the Google Apps connector.
Test the Google Apps connector
You can test the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/googleapps?_action=test"
{
"name": "googleapps",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/googleapps",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.googleapps.GoogleAppsConnector"
},
"displayName": "GoogleApps Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"Role",
"OrgUnit",
"LicenseAssignment",
"__GROUP__",
"__ALL__",
"RoleAssignment",
"Privilege",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"Member"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector was configured correctly, and can authenticate to the Google Cloud Platform system.
Google Apps remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Google Apps connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Google Apps connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Google Apps remote connector.
Use the Google Apps connector with a proxy server
If the IDM server is hosted behind a firewall and requests to the Google Apps server are routed through a proxy, you must specify the proxy host and port in the connector configuration so that the connector can pass this information to the lower Google API.
To specify the proxy server details, set the proxyHost, proxyPort and validateCertificate properties in the connector configuration. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"proxyHost": "myproxy.home.com",
"proxyPort": 8080,
"validateCertificate": true,
...
}The validateCertificate property indicates whether the proxy server should validate the server certificate from the local truststore.
Supported resource types
The Google Apps connector uses the Google Enterprise License Manager and Directory APIs to perform CRUD operations against resources within a Google Apps domain.
The following table lists the resource types that are supported by the Google Apps connector:
| ICF Native Type | Google Resource Type | Naming Attribute |
|---|---|---|
__ACCOUNT__ |
user |
primaryEmail |
__GROUP__ |
group |
|
Member |
member |
{groupKey}/email |
OrgUnit |
orgUnit |
{parentOrgUnitPath}/__NAME__ |
LicenseAssignment |
licenseAssignment |
{productId}/sku/{skuId}/user/{primaryEmail} |
Role |
role |
{roleId} |
RoleAssignment |
roleassignment |
{roleAssignmentId} |
Privilege |
privilege |
Supported user attributes
The Google Apps connector supports the following user resource attributes:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
An array of addresses for the user account. |
||
|
Whether the user has agreed to the Terms of Service. |
||
|
An array of aliases for the user account. |
||
|
Whether the user account is archived. |
||
|
Whether the user must change their password at next login. |
||
|
The user creation time. |
||
|
An ID used to identify the customer. |
||
|
Define custom fields for user accounts. |
||
|
The user deletion time. |
||
|
This attribute is managed using other attributes ( |
||
|
The ETag of the user account. Read-only attribute. |
||
|
An array of external IDs for the user account. |
||
|
The hash function for the user’s password. |
||
|
The unique ID for the user. |
||
|
An array of instant messenger accounts for the user. |
||
|
Whether to include the user in the global address list. |
||
|
Whether the user’s IP is allowlisted. |
||
|
Whether the user is an admin. |
||
|
Whether the user is a delegated administrator. |
||
|
Whether the user is enforcing two-step verification. |
||
|
Whether the user is enrolled in two-step verification. |
||
|
Whether the user’s mailbox is set up. |
||
|
The kind of user, typically |
||
|
An array of the user’s language preferences. |
||
|
The last time the user logged in. |
||
|
An object containing the |
||
|
An array of non-editable aliases for the user account. |
||
|
An array of organizations for the user account. |
||
|
The full path of the parent organization associated with the user. If the parent organization is top-level, it is represented as a forward slash ( |
||
|
The user’s password. |
||
|
An array of phone numbers for the user account. |
||
|
The user’s primary email address. |
||
|
The user’s recovery email address. |
||
|
The user’s recovery phone number. |
||
|
An array of relations for the user account. |
||
(Deprecated) |
Do not use this attribute.
|
||
|
An array of the user’s email addresses, excluding their primary email address and all editable and non-editable aliases. |
||
|
Whether the user is suspended. |
||
|
The reason the user account is suspended. |
||
|
The url to a user’s thumbnail photo. |
Functional limitations
The Google Apps connector is subject to the following functional limitations:
-
In an UPDATE request, the old object (before the update) is returned in the request result. This behavior differs from that for other connectors, where the updated object is returned.
Although the update is processed correctly, there is a significant delay from Google, and IDM sends its GET request to return the object before the update has taken effect. This behavior has no impact on the success of the update.
-
The connector does not implement the ICF Sync operation so you cannot use the connector for liveSync of supported Google Apps resources to IDM managed objects.
-
The connector does not implement the Authenticate operation so you cannot use the connector to perform pass-through authentication between IDM and a Google Apps domain. You can also not use this connector to perform password Change operations (as opposed to password Reset) because the connector cannot authenticate on behalf of the end user.
-
Support for Filters when performing Search operations is limited to those attributes described in connector-reference:google.adoc#google-apps-search-filters.
-
Google Apps creates a new User Alias each time the
primaryEmailaddress associated with the User object is modified. You cannot delete User Aliases with the Google Apps connector, so you must manage Aliases directly from within the Google Apps console. -
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Google Apps connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
Supported search filters
The Google Apps connector supports filtered searches against Google Apps resources. However, limitations imposed by the APIs provided by the Google Apps Admin SDK prevent filtering of resource types based on arbitrary attributes and values.
The following filter operators and attributes are supported for Search operations with the Google Apps connector:
| Object Type | Operators | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
__ACCOUNT__ |
And, Contains1, StartsWith, Equals |
name, email, givenName, familyName, orgUnitPath, im, externalId, address, addressPoBox, addressExtended, addressStreet, addressLocality, addressRegion, addressPostalCode, addressCountry, orgName, orgTitle, orgDepartment, orgDescription, orgCostCenter |
__GROUP__ |
Contains1, Equals |
customer (Equals only), userKey (Equals only), _MEMBERS_ (Contains only) |
Member |
And, Equals |
groupKey, memberKey (And only) |
OrgUnit |
StartsWith |
orgUnitPath |
LicenseAssignment |
N/A |
|
Role |
N/A |
|
RoleAssignment |
N/A |
|
Privilege |
N/A |
1 "Contains" looks for a whole word match, in the given order. For example, an API request with _queryFilter=givenName+co+'Ana' matches users with givenName values of "Ana" and "Ana Lucia" but not "Anabelle". A multi-word query for _queryFilter=givenName+co+'Ana Lucia' would match values of "Ana Lucia Evans" and "Ana Lucia Ball" but not "Lucia Ana".
Product licenses
The Google Apps connector can query all available licenses and return details of individual product licenses.
Query all available product licenses
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/googleapps/License?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "Google-Apps/1010020027",
"__NAME__": "Google Workspace Business Starter",
"productId": "Google-Apps",
"productName": "Google Workspace",
"skuId": "1010020027",
"skuName": "Google Workspace Business Starter"
},
{
"_id": "Google-Drive-storage/Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"__NAME__": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"productId": "Google-Drive-storage",
"productName": "Google-Drive-storage",
"skuId": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"skuName": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB"
}
],
"resultCount": 2,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read a product license
To read the details of a license, perform a GET request on the endpoint:
system/googleapps/License/{PRODUCT_ID}/{SKU_ID}curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/googleapps/License/Google-Drive-storage/Google-Drive-storage-20GB"
{
"_id": "Google-Drive-storage/Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"__NAME__": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"productId": "Google-Drive-storage",
"productName": "Google-Drive-storage",
"skuId": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB",
"skuName": "Google-Drive-storage-20GB"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the GoogleApps Connector
The GoogleApps Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
GoogleApps Connector Configuration
The GoogleApps Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Internet domain name. See https://support.google.com/a/answer/177483?hl=en. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Client identifier issued to the client during the registration process. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Client secret issued to the client during the registration process. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The refresh token allows you to get a new access token that is good for another hour. Refresh tokens never expire, they can only be revoked by the user or programatically by your app. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines an HTTP proxy host to use with the connection (example: "myproxy.home.com"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines an HTTP proxy port to use with the connection (defaults to 8080). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies whether the validation of the server certificate from the locally stored truststore is enabled. (defaults to true). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Users to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 500, inclusive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Groups to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 200, inclusive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Members to return. Acceptable values are greater than 1. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Licenses to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 1000, inclusive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Licenses to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 1000, inclusive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
All Google Licenses that will be queried when requesting licenses assigned to a user. The format of the license is ProductId/SkuId (e.g. Google-Apps/101002002). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Licenses to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 100, inclusive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of Licenses to return. Acceptable values are 1 to 100, inclusive. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Google Cloud Platform connector
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services offered by Google. The GCP connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between GCP and IDM managed user objects. A GCP administrator account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your GCP administrator account and note the following:
- Domain name
-
The domain name of the account on GCP — for example, example.com.
- Private key
-
The private key is required to sign the JWT token used to authenticate with GCP.
- Service account
-
The GCP connector uses a service account with two-legged OAuth to connect to GCP. A service account is identified by its email address, which is unique to the account.
- Admin user
-
The GCP administrator username.
|
The Admin SDK API must also be enabled to allow viewing and managing users in the Google Cloud Platform. |
Install the GCP connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/gcp-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the GCP connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select GCP Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to GCP Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the GCP connector
You can test the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp?_action=test"
{
"name": "gcp",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/gcp",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.gcp-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.gcp.GcpConnector"
},
"displayName": "GCP Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector was configured correctly, and can authenticate to the Google Cloud Platform system.
GCP remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the GCP connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the GCP connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the GCP remote connector.
Use the GCP connector
The following GCP account attributes are supported by the GCP connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The username of the user. This maps to a user’s |
|
Password for the user account. Required. |
|
The first name of the user. Required. |
|
The last name of the user. Required. |
|
The user ID for the user account. |
|
A list of emails associated with the user account. For example: |
|
A list of addresses associated with the user account. For example: |
|
A list of organizations the user account is associated with. For example: |
|
A list of phone numbers associated with the user account. For example: |
|
A list of the user’s relationships to other users. For example: |
|
A list of external IDs for the user, such as employee or network IDs. For example: |
For a full list of attributes on GCP user accounts, refer to the GCP documentation.
You can use the GCP connector to perform the following actions on a GCP account:
Create a GCP user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd!",
"givenName": "Barbara",
"familyName": "Jensen"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least |
Update a GCP user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. The following attributes can be modified on a user:
-
primaryEmail -
__PASSWORD__ -
givenName -
familyName -
organizations -
addresses -
emails -
externalIds -
relations -
phones
For example, to add a new phone to a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"phones": [{
"type": "mobile",
"value": "+1 888 555 2312",
"primary": true
}]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__/115637914640083360831"
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831",
"givenName": "Barbara",
"__UID__": "115637914640083360831",
"phones": [
{
"value": "+1 888 555 2312",
"type": "mobile"
}
],
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"familyName": "Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"emails": [
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com",
"primary": true
},
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com.test-google-a.com"
}
]
}
|
The updated data may not appear in the initial response, but appears on any future queries of that user. |
Query GCP users
The following example queries all GCP users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "103181194086915091216"
},
{
"_id": "104153234757881174617"
},
{
"_id": "105181741894703739324"
},
{
"_id": "105644268361304742523"
},
{
"_id": "101682225764075422695"
},
{
"_id": "101516788947553424126"
},
{
"_id": "102825554929567443783"
},
{
"_id": "101429904015255587067"
},
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831"
}
],
"resultCount": 9,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__/115637914640083360831"
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831",
"givenName": "Barbara",
"__UID__": "115637914640083360831",
"phones": [
{
"value": "+1 888 555 2312",
"type": "mobile"
}
],
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"familyName": "Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"emails": [
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com",
"primary": true
},
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com.test-google-a.com"
}
]
}
Reset a GCP account password
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{
"operation": "add",
"field": "__PASSWORD__",
"value": "Passw0rd@123!"
}]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__/115637914640083360831"
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831",
"givenName": "Barbara",
"__UID__": "115637914640083360831",
"phones": [
{
"value": "+1 888 555 2312",
"type": "mobile"
}
],
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"familyName": "Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"emails": [
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com",
"primary": true
},
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com.test-google-a.com"
}
]
}
|
While the |
Delete a GCP account
You can use the GCP connector to delete an account from the GCP service.
The following example deletes a GCP account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/gcp/__ACCOUNT__/115637914640083360831"
{
"_id": "115637914640083360831",
"givenName": "Barbara",
"__UID__": "115637914640083360831",
"phones": [
{
"value": "+1 888 555 2312",
"type": "mobile"
}
],
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"familyName": "Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"emails": [
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com",
"primary": true
},
{
"address": "bjensen@example.com.test-google-a.com"
}
]
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the GCP Connector
The GCP Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
GCP Connector Configuration
The GCP Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the domain name for GCP. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides private key to authenticate GCP. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides service account for fetching users from GCP. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides admin user for fetching users from GCP. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides user max results for fetching users from GCP. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connection timeout in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connections. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy connector toolkit
The generic Groovy connector toolkit runs a Groovy script for any ICF operation, such as search, update, create, and others, on any external resource.
The Groovy connector toolkit is not a complete connector in the traditional sense. Instead, it is a framework where you must write your own Groovy scripts to address your implementation requirements.
Configure scripted Groovy connectors
You cannot configure a scripted Groovy connector through the UI. Configure the connector over REST, as described in Configure Connectors Over REST.
Alternatively, create a connector configuration file in your project’s conf
directory. A number of sample configurations for scripted Groovy implementations are provided in openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-scriptedimplementation.json. Use these as the basis for configuring your own scripted connector.
Samples describes a number of scripted connector implementations. The scripts provided with these samples demonstrate how the Groovy connector toolkit can be used. These scripts cannot be used as is in your deployment but are a good starting point to base your customization. For information about writing your own scripts, refer to Scripted connectors with Groovy.
Validate pooled connections
The scripted SQL connector uses the Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool to manage its connections. Occasionally, a JDBC resource accessed by the scripted SQL connector might become unavailable for a period. When the resource comes back online, IDM is able to recover automatically and resume operations. However, the connector might not be able to refresh its connection pool and might then pass a closed connection to its scripts. This can affect operations until IDM is restarted.
To avoid this situation, you can configure connection validation, where connections are validated before being borrowed from the connection pool.
To configure connection validation, add the following properties to the configurationProperties object in your connector configuration:
testOnBorrow-
Validates the connection object before it is borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it is dropped from the pool and the connector attempts to borrow another object.
For this property to have an effect, you must set
validationQueryto a non-null string. validationQuery-
The SQL query used to validate connections from the pool before returning them to the caller.
The precise query will differ, depending on the database that you are accessing. The following list provides sample queries for common databases:
- HyperSQL DataBase (HSQLDB)
-
select 1 from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SYSTEM_USERS - Oracle DB
-
select 1 from dual - DB2
-
select 1 from sysibm.sysdummy1 - MySQL
-
select 1 - Microsoft SQL
-
select 1 - PostgreSQL
-
select 1 - Ingres Database
-
select 1 - Apache Derby
-
values 1 - H2 Database
-
select 1 - Firebird SQL
-
select 1 from rdb$database
validationInterval-
Specifies the maximum frequency (in milliseconds) at which validation is run. If a connection is due for validation but was previously validated within this interval, it is not validated again.
The larger the value, the better the connector performance. However, with a large value you increase the chance of a stale connection being presented to the connector.
Connection validation can have an impact on performance and should not be done too frequently. With the following configuration, connections are validated no more than every 34 seconds:
{
...
"configurationProperties" : {
...
"testOnBorrow" : true,
"validationQuery" : "select 1 from dual",
"validationInterval" : 34000,
...
},
...
}Use custom properties in scripts
The customConfiguration and customSensitiveConfiguration properties enable you to inject custom properties into your scripts. Properties listed in customSensitiveConfiguration are encrypted.
For example, the following excerpt of the scripted Kerberos provisioner file shows how these properties inject the Kerberos user and encrypted password into the scripts, using the kadmin command.
"customConfiguration" : "kadmin { cmd = '/usr/sbin/kadmin.local'; user='<KADMIN USERNAME>'; default_realm='<REALM>' }",
"customSensitiveConfiguration" : "kadmin { password = '<KADMIN PASSWORD>'}",Debug Groovy scripts
When you call a Groovy script from the Groovy connector, you can use the SLF4J logging facility to obtain debug information.
For instructions on how to use this facility, refer to the KnowledgeBase article How do I add logging to Groovy scripts in IDM.
Run scripts through the connector
Groovy toolkit connectors have two operations that allow you to run arbitrary script actions: runScriptOnConnector and runScriptOnResource. runScriptOnConnector is an operation that sends the script action to the connector to be compiled and executed. runScriptOnResource is an operation that sends the script to another script to be handled.
runScriptOnConnector
The runScriptOnConnector script lets you run an arbitrary script action through the connector. This script takes the following variables as input:
configuration-
A handler to the connector’s configuration object.
options-
A handler to the Operation Options.
operation-
The operation type that corresponds to the action (
RUNSCRIPTONCONNECTORin this case). log-
A handler to the connector’s log.
To run an arbitrary script on a Groovy toolkit connector, define the script in the systemActions property of your provisioner file:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]If you want to define your script in the provisioner file itself rather than in a separate file, you can use the actionSource property instead of the actionFile one. A simple example follows:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionSource" : "2 * 2"
}
]
}
]
It is optional to prepend the last script statement in actionSource with return.
|
Running MyScript will return:
{
"actions" : [
{
"result": 4
}
]
}If your script accepts parameters, you may supply them in the request body or the query string. For example:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data-raw '{"param1":"value1"}'
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=MyScript¶m2=value2"**
You can also call it through the IDM script engine. Note that the system can accept arbitrary parameters, as demonstrated here:
openidm.action("/system/groovy", "script", {"contentParameter": "value"}, {"scriptId": "MyScript", "additionalParameter1": "value1", "additionalParameter2": "value2"})runScriptOnResource
To run an arbitrary script using runScriptOnResource, you must add some configuration details to your provisioner file. These details include a scriptOnResourceScriptFileName which references a script file located in a path contained in the scriptRoots array.
Define these properties in your provisioner file as follows:
"configurationProperties": {
"scriptRoots": [
"path/to/scripts"
],
"scriptOnResourceScriptFileName": "ScriptOnResourceScript.groovy"
},
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "script-1",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]When you have defined the script, you can call it over REST on the system endpoint, as follows:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=scriptOnResourceScript&scriptExecuteMode=resource"
Script compilation and caching
The first time a script is read, it is compiled from Groovy script to Java bytecode and cached in memory. Each time the script is called, the Groovy script engine checks the last modified of the script file to determine if it has changed. If it has not changed, the cached bytecode is executed. If it has changed, the script is reloaded, compiled and cached.
Implemented interfaces
The following tables list the ICF interfaces that are implemented for non-poolable and poolable connector implementations:
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Scripted Groovy Connector
The Scripted Groovy Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector
The Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Configuration properties
The following tables list the configuration properties for non-poolable and poolable connector implementations:
Scripted Groovy Connector Configuration
The Scripted Groovy Connector has the following configurable properties:
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector Configuration
The Scripted Poolable Groovy Connector has the following configurable properties:
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
HubSpot connector
The HubSpot connector lets you synchronize HubSpot contacts and companies with managed objects in an IDM repository.
This topic describes how to install and configure the HubSpot connector, and how to perform basic tests to ensure that it’s running correctly.
For a complete example that includes the configuration required to synchronize users with this connector, refer to Synchronize data between IDM and HubSpot.
Before you configure the HubSpot connector, you must have a client app in HubSpot, with the corresponding clientID, clientSecret and refreshToken.
Install the HubSpot connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/hubspot-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the HubSpot connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select HubSpot Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to HubSpot Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file. IDM provides a sample connector configuration file in the /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners directory. Copy this sample file (provisioner.openicf-hubspot.json) to your project’s conf directory.
Adjust the configurationProperties to match your HubSpot application details. You must provide a clientId, clientSecret, and refreshToken. Other properties are optional:
"configurationProperties" : {
"clientId" : "daa533ae-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-6e66d84e6448",
"clientSecret" : "c598a365-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-24b32b6ae04d",
"refreshToken" : "f37e1132-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-4b9e724ce4a0",
"acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : true,
"readSchema" : "true",
"disableHostNameVerifier" : false,
"maximumConnections" : "10",
"permitsPerSecond" : "10",
"httpProxyHost" : null,
"httpProxyPort" : null
}IDM encrypts the clientSecret and refreshToken as soon as the connector is enabled.
Test the HubSpot connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "hubspot",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/hubspot",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.hubspot-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.hubspot.HubspotConnector"
},
"displayName": "Hubspot Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"company",
"contactProperties",
"__ALL__",
"companyProperties",
"contact"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can connect to HubSpot.
HubSpot remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the HubSpot connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the HubSpot connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the HubSpot remote connector.
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The HubSpot connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
Using the HubSpot connector With a proxy server
If the IDM server is hosted behind a firewall and requests to the resource provider are routed through a proxy, you must specify the proxy host and port in the connector configuration.
To specify the proxy server details, set the httpProxyHost, and httpProxyPort properties in the connector configuration. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"httpProxyHost": "myproxy.home.com",
"httpProxyPort": 8080,
...
}OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Hubspot Connector
The Hubspot Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Hubspot Connector Configuration
The Hubspot Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Client ID of the OAuth application in Hubspot. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Client Secret for the preceding Client ID. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Refresh token for application in Hubspot. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Advanced Connection Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies whether the HubSpot server should accept self-signed certificates. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If false, the Hubspot connector provides a default schema for Hubspot contacts and companies. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If hostname verification is disabled, the HubSpot server accepts connections from any host. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Maximum number of simultaneous connections to HubSpot. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Number of Api calls to be made per second. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies the Hostname if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and HubSpot. Defaults to null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies the Port number if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and HubSpot . Defaults to null. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Kerberos connector
The Kerberos connector is an implementation of the SSH connector, and is based on Java Secure Channel (JSch) and the Java implementation of the Expect library (Expect4j).
The Kerberos connector lets you manage Kerberos user principals from IDM. The connector bundles a number of Groovy scripts, to interact with a Kerberos admin server. You should not edit the bundled Groovy scripts. The scripts use the kadmin utility to communicate with the Kerberos server.
The Kerberos connector lets you perform the following operations on Kerberos user principals:
-
List the existing principals.
-
Display the details of a principal.
-
Add a user principal.
-
Change the password of a user principal and unlock the principal.
-
Delete a user principal.
Kerberos connector schema
The Kerberos connector can only be used to manage the Kerberos principal object type (which maps to the ICF __ACCOUNT__ object). The following attributes are supported in the schema:
-
principal- (maps to__NAME__and__UID__) -
__PASSWORD__- updatable, required when an object is created -
__LOCK_OUT__- updatable only; unlock an account by setting this attribute tofalse -
policy- the password policy used by the principal -
expirationDate- the date that the user principal expires -
passwordExpiration- the date that the password expires -
maximumTicketLife- the maximum ticket life for the principal. At the end of the ticket lifetime, the ticket can no longer be used. However, if the renewable lifetime (maximumRenewableLife) is longer than the ticket lifetime, the ticket holder can present the ticket to the KDC and request a new ticket. -
maximumRenewableLife- the period during which the ticket can be renewed. A renewed ticket usually has a new ticket lifetime, dating from the time that it was renewed, that is constrained by the renewable ticket lifetime.
In addition, the following read-only attributes are supported:
-
lastPasswordChange -
lastModified -
lastSuccessfulAuthentication -
lastFailedAuthentication -
failedPasswordAttempts
Install the Kerberos connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/kerberos-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Kerberos connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Kerberos Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Kerberos Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file. A sample connector configuration (provisioner.openicf-kerberos.json) is provided in the /path/to/openidm/samples/sync-with-kerberos/conf/ directory with IDM. Copy the sample connector configuration to your project’s conf/ directory, and adjust it to match your Kerberos environment.
-
Set the authentication properties, as described in Configure Authentication to the SSH Server. In addition, set at least the following properties:
customConfiguration-
Specify the details of the user principal and the default realm here. The sample connector configuration is as follows:
"customConfiguration" : "kadmin { cmd = '/usr/sbin/kadmin.local'; user = '<KADMIN USERNAME>'; default_realm = '<REALM, e.g. EXAMPLE.COM>' }"A complete custom configuration will look something like this:
"customConfiguration" : "kadmin { cmd = '/usr/sbin/kadmin.local'; user = 'openidm/admin'; default_realm = 'EXAMPLE.COM' }"
customSensitiveConfiguration-
Set the password for the user principal here. The sample connector configuration is as follows:
"customSensitiveConfiguration" : "kadmin {password = '<KADMIN PASSWORD>'}"Change this to reflect your user principal password, for example:
"customSensitiveConfiguration" : "kadmin {password = 'Passw0rd'}"
Basic Kerberos Connector Configuration
This list describes the basic Kerberos connector configuration properties. For a complete list, refer to Configuration Properties:
host-
The host name or IP address of the SSH server on which the
kadmincommand is run. port-
The port number on which the SSH server listens.
Default:
22(the default SSH port) user-
The username of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
This is not the same as your Kerberos user principal. This account must be able to
sshinto the server on which Kerberos is running, with the password provided in the next parameter.If you use the
rootuser, thesudocommand in the Test script will never get the'pass::'prompt. Instead of using therootuser, create a regular user and add that user to the group that hassudoprivileges. Alternatively, modify the Test script so that it does not usesudo. password-
The password of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
prompt-
A string representing the remote SSH session prompt. This must be the exact prompt string, in the format
username@target:, for exampleroot@localhost:~$.If the prompt includes a trailing space, you must include the space in the value of this property.
Consider customizing your Linux prompt with the
PS1andPS2variables, to set a safe prompt. For information about customizing prompts, refer to this article. sudoCommand-
A string that shows the full path to the
sudocommand; for example/usr/bin/sudo. echoOff-
If set to
true(the default), the input command echo is disabled. If set tofalse, every character that is sent to the server is sent back to the client in theexpect()call. terminalType-
Sets the terminal type to use for the session. The list of supported types is determined by your Linux/UNIX system. For more information, refer to the
terminfomanual page (man terminfo).Default:
vt102 setLocale-
If set to
true, indicates that the default environment locale should be changed to the value of thelocaleproperty.Default:
false locale-
Sets the locale for LC_ALL, LANG, and LANGUAGE environment variables, if
setLocaleis set totrue.Default:
en_US.utf8 connectionTimeout-
Specifies the connection timeout to the remote server, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000 expectTimeout-
Specifies the timeout used by the
expect()calls in scripts, in milliseconds.Default:
5000 authenticationType-
Sets the authentication type, either
PASSWORDorPUBKEY. For more information, refer to connector-reference:ssh.adoc#ssh-authentication.Default:
PASSWORD throwOperationTimeoutException-
If
true, the connector throws an exception when the timeout is reached for an operation. Otherwise, the operation fails silently.Default:
true scriptRoots-
The path to the Groovy scripts that perform the ICF operations, relative to your installation directory. For the Kerberos connector, the scripts are bundled in the connector .jar file, so the sample connector configuration uses the path
jar:file:connectors/kerberos-connector-1.5.20.21.jar!/scripts/kerberos/. classpath-
The directory in which the compiler should look for compiled classes. The default classpath, if not is specified, is
install-dir/lib. ScriptFileName-
The script that is used for each ICF operation. Do not change these script names in the bundled Kerberos connector.
Kerberos remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Kerberos connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Kerberos connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Kerberos remote connector.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Kerberos Connector
The Kerberos Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Kerberos Connector Configuration
The Kerberos Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The hostname to connect to. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
TCP port to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The user name used to login to remote server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The password used to login to remote server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The passphrase used to read the private key when using Public Key authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The base 64 encoded value (PEM) of the private key used for Public Key authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which authentication type should be use: PASSWORD or PUBKEY. |
||||
|
|
`root@localhost:# ` |
|
Yes |
A string representing the remote SSH session prompt. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
A string representing the sudo command. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Disable the input command echo. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the terminal type to use for the session. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Define the locale for LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables to use if setLocale=true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines if the default environment locale should be changed with the value provided for locale. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the connection timeout to the remote server in milliseconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the timeout used by the expect() calls in the scripts in milliseconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines if an OperationTimeoutException should be thrown if any call to expect times out. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the "prompt ready" timeout for the promptReady() command in milliseconds. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
LDAP connector
The LDAP connector is based on the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI), and can connect to any LDAPv3-compliant directory server, such as ForgeRock Directory Services (DS), Active Directory, SunDS, Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition, IBM Security Directory Server, and OpenLDAP.
Because it is based on JNDI, the LDAP connector is restricted to the attribute types that are supported by JNDI. JNDI supports only strings and an array of bytes. If you attempt to use different attribute value types, the connector throws a malformed attribute value exception. For more information, refer to the corresponding JNDI documentation.
Install the LDAP connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/ldap-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the LDAP connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select LDAP Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to LDAP Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file. IDM provides several sample LDAP connector configurations in the path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/ directory. Copy one of the sample connector configurations to your project’s conf directory, and adjust it to match your LDAP environment:
-
provisioner.openicf-ldap.json—a sample LDAP connector configuration for a generic LDAP server. -
provisioner.openicf-dsldap.json—a sample LDAP connector configuration for a ForgeRock Directory Services (DS) server. -
provisioner.openicf-adldap.json—a sample LDAP connector configuration for an Active Directory server.
You should be able to adapt one of these sample configurations for any LDAPv3-compliant server.
Sample LDAP connector configuration
This configuration shows the properties for an LDAP connector connecting to DS. For more information about the properties that affect synchronization, refer to Control what the LDAP connector synchronizes. For a complete list of the configuration properties for the LDAP connector, refer to LDAP Connector Configuration:
"configurationProperties" : {
"host" : "localhost",
"port" : 1389,
"ssl" : false,
"startTLS" : false,
"privateKeyAlias" : null,
"alternateKeyStore" : null,
"alternateKeyStoreType" : null,
"alternateKeyStorePassword" : null,
"principal" : "uid=admin",
"credentials" : "password",
"baseContexts" : [
"dc=example,dc=com"
],
"baseContextsToSynchronize" : [
"dc=example,dc=com"
],
"accountSearchFilter" : null,
"accountSynchronizationFilter" : null,
"groupSearchFilter" : null,
"groupSynchronizationFilter" : null,
"removeLogEntryObjectClassFromFilter" : true,
"modifiersNamesToFilterOut" : [ ],
"changeLogBlockSize" : 100,
"attributesToSynchronize" : [ ],
"changeNumberAttribute" : "changeNumber",
"filterWithOrInsteadOfAnd" : false,
"objectClassesToSynchronize" : [
"inetOrgPerson"
],
"vlvSortAttribute" : "uid",
"passwordAttribute" : "userPassword",
"useBlocks" : false,
"maintainPosixGroupMembership" : false,
"failover" : [ ],
"readSchema" : true,
"accountObjectClasses" : [
"top",
"person",
"organizationalPerson",
"inetOrgPerson"
],
"accountUserNameAttributes" : [
"uid"
],
"groupMemberAttribute" : "uniqueMember",
"passwordHashAlgorithm" : null,
"usePagedResultControl" : true,
"blockSize" : 100,
"uidAttribute" : "entryUUID",
"maintainLdapGroupMembership" : false,
"respectResourcePasswordPolicyChangeAfterReset" : false
},host-
The host name or IP address of the server on which the LDAP instance is running.
port-
The port on which the LDAP server listens for LDAP requests. The sample configuration specifies a default port of 1389.
ssl-
If
true, the specified port listens for LDAPS connections.For instructions on using the LDAP connector over SSL, refer to Configure the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS.
startTLS-
Specifies whether to use the startTLS operation to initiate a TLS/SSL session. To use startTLS, set
"startTLS":true,and"ssl":false. Your connection should use the insecure LDAP port (typically389or1389for a DS server).Specify the certificates that should be used for authentication, as described in Configure the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS.
principal-
The bind DN that is used to connect to the LDAP server.
credentials-
The password of the
principalthat is used to connect to the LDAP server. baseContexts-
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used when searching the tree. Searches are performed when discovering users from the LDAP server or when looking for the groups of which a user is a member. During reconciliation operations, IDM searches through the base contexts listed in this property for changes. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
baseContextsToSynchronize-
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used to determine if a change should be synchronized. During liveSync operations, IDM searches through the base contexts listed in this property for changes. If no value is specified here, the values in listed in the
baseContextsproperty are used. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes. accountSynchronizationFilter-
Used during synchronization actions to filter out LDAP accounts. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
accountObjectClasses-
This property lists all the object classes that represent an account. If this property has multiple values, an
ANDfilter is used to determine the affected entries. For example, if the value of this property is["organizationalPerson", "inetOrgPerson"], any entry with the object classorganizationalPersonAND the object classinetOrgPersonis considered as an account entry. You can override the value of this property by specifying the user object classes during the create operation.If no object class is specified when you create a user, this property is used as the default list of object classes for the new entry.
accountSearchFilter-
Search filter that user accounts must match. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
accountUserNameAttributes-
Attributes holding the account’s user name. Used during authentication to find the LDAP entry matching the user name.
attributesToSynchronize-
List of attributes used during object synchronization. IDM ignores change log updates that do not include any of the specified attributes. If empty, IDM considers all changes. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
blockSize-
Block size for simple paged results and VLV index searches, reflecting the maximum number of entries retrieved at any one time.
changeLogBlockSize-
Block size used when fetching change log entries.
changeNumberAttribute-
Change log attribute containing the last change number.
failover-
LDAP URLs specifying alternative LDAP servers to connect to if IDM cannot connect to the primary LDAP server specified in the
hostandportproperties. filterWithOrInsteadOfAnd-
In most cases, the filter to fetch change log entries is AND-based. If this property is set, the filter ORs the required change numbers instead.
groupMemberAttribute-
LDAP attribute holding members for non-POSIX static groups.
groupSearchFilter-
Search filter that group entries must match.
maintainLdapGroupMembership-
If
true, IDM modifies group membership when entries are renamed or deleted.Does not apply to Active Directory.
In the sample LDAP connector configuration, this property is set to
false. This means that LDAP group membership is not modified when entries are renamed or deleted in IDM. To ensure that entries are removed from LDAP groups when the entries are deleted, set this property totrueor enable referential integrity on the LDAP server. For information about configuring referential integrity in DS, refer to Referential Integrity in the Configuration Guide for ForgeRock Directory Services. maintainPosixGroupMembership-
If
true, IDM modifies POSIX group membership when entries are renamed or deleted. modifiersNamesToFilterOut-
Use this property to avoid loops caused by changes made to managed user objects being synchronized. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
objectClassesToSynchronize-
IDM synchronizes only entries that have these object classes. For more information, refer to Control What the LDAP Connector Synchronizes.
passwordAttribute-
Attribute to which IDM writes the predefined
PASSWORDattribute. passwordHashAlgorithm-
Hash password values with the specified algorithm, if the LDAP server stores them in clear text. The only supported algorithm is
WIN-AD(used when Active Directory is the target). A blank value indicates the system will not hash passwords. This will cause clear text passwords to be stored in LDAP, unless the LDAP server performs the hash. readSchema-
If
true, read the schema from the LDAP server.This property is used only during the connector setup, to generate the object types.
If this property is
false, the LDAP connector provides a basic default schema that can manage LDAP users and groups. The default schema mapsinetOrgPersonto the OpenICF__ACCOUNT__property, andgroupOfUniqueNamesto the OpenICF__GROUP__property. The following LDAP object classes are also included in the default schema:-
organization -
organizationalUnit -
person -
organizationalPerson -
account -
groupOfNames
-
removeLogEntryObjectClassFromFilter-
If
true, the filter to fetch change log entries does not contain thechangeLogEntryobject class, and IDM expects no entries with other object types in the change log. The default setting istrue. respectResourcePasswordPolicyChangeAfterReset-
If
true, bind with the Password Expired and Password Policy controls, and throwPasswordExpiredExceptionand other exceptions appropriately. uidAttribute-
Specifies the LDAP attribute that should be used as the immutable ID for the entry. You can use a DN (or any unique attribute) for the
id. As a best practice, you _should use an attribute that is both unique and immutable, such as theentryUUID. For a DS resource, you must use theentryUUIDas theuidAttribute, otherwise you might encounter problems with synchronizing delete operations. useBlocks-
If
useBlocksisfalse, no pagination is used. IfuseBlocksistrue, the connector uses block-based LDAP controls, either the simple paged results control, or the virtual list view control, depending on the setting of theusePagedResultControlproperty. usePagedResultControl-
Taken into account only if
useBlocksistrue. IfusePagedResultControlisfalse, the connector uses the virtual list view (VLV) control, if it is available. IfusePagedResultControlistrue, the connector uses the simple paged results control for search operations. useTimestampsForSync-
If
true, use timestamps for liveSync operations, instead of the change log.By default, the LDAP connector has a change log strategy for LDAP servers that support a change log, such as ForgeRock Directory Services (DS) and Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition. If the LDAP server does not support a change log, or if the change log is disabled, liveSync for create and modify operations can still occur, based on the timestamps of modifications.
Regardless of the
useTimestampsForSyncvalue, the connector uses a timestamp strategy for liveSync for the following LDAP server types:-
MS Active Directory Global Catalog
-
OpenLDAP
-
Unknown
An LDAP server type is marked Unknown if it is anything other than IBM, Novell, UnboundIDD, RedHat/Fedora 389, CA LDAP, OpenDS, ForgeRock OpenDJ / DS, Sun DSEE Directory, Microsoft Active Directory, Microsoft Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (LDS), Microsoft Active Directory Global Catalog, or OpenLDAP.
-
timestampSyncOffset-
An optional offset, specified in seconds, that is negatively applied to the timestamp for timestamp-based sync operations. This setting is useful when there are replication delays between LDAP instances. The default value is
0, or no offset. vlvSortAttribute-
Attribute used as the sort key for virtual list view.
sendCAUDTxId-
If
true, propagate the Common Audit Transaction ID to a DS server.
LDAP remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the LDAP connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the LDAP connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the LDAP remote connector.
Configure the LDAP connector to use SSL and StartTLS
To use the LDAP connector over SSL, update your connector configuration as follows:
-
For a connection over SSL, set the
sslproperty totrueand set theportto a secure port, for example,636.To initiate a connection using startTLS, set
"startTLS":true,and"ssl":false. Set theportto an insecure LDAP port, for example,389. -
If you are using a CA-signed server certificate, add that certificate to the IDM truststore, for example:
keytool \ -importcert \ -alias server-cert \ -keystore /path/to/openidm/security/truststore \ -storepass changeit \ -file /path/to/server-cert.crt
-
Specify the certificate that the LDAP connector will use to authenticate to the remote LDAP server.
By default, the LDAP connector uses the self-signed certificate that is generated in the IDM keystore when IDM first starts up. You have two options to change this default behavior:
-
Set the
privateKeyAliasto the alias of a certificate in the IDM keystore. The alias name is case-sensitive.If you set
privateKeyAliastonull, no private key is sent during the SSL handshake, so only the server certificate is used. You must import the server certificate into the IDM truststore, as shown in the previous step.If
privateKeyAliasis set to an alias within the IDM keystore, the connector uses that private key for SSL mutual authentication. -
Specify a different keystore for the connector.
If you do not want to use the default IDM keystore, set the following properties:
-
alternateKeyStore- specifies the full path to an alternate keystore. -
alternateKeyStoreType- specifies alternate keystore type. Valid values areJKS,JCEKSandPKCS12. -
alternateKeyStorePassword- specifies password for the alternate keystore.
-
-
-
Enable hostname verification to prevent a third party from manipulating DNS entries or spoofing the LDAP Server IP.
When hostname verification is enabled, the connector compares the hostname in the certificate
subjectandsubjectAltNamewith a simple hostname pattern defined in thehostNameVerificationproperty.To enable hostname verification, set
"hostNameVerification" : trueand set thehostNameVerificationproperty to the hostname you want to match. If the pattern matches, the connector is initialized successfully. If the pattern does not match, connector initialization throws an error. ThehostNameVerificationproperty supports wild card matching.Assume, for example, a server certificate principal hostname of
server1.example.com. With the following connector configuration, IDM starts up and the connector is initialized:"configurationProperties" : { ... "hostNameVerification" : true, "hostNameVerifierPattern" : "server1.example.com", ... }Similarly, with the following connector configuration, IDM starts up and the connector is initialized:
"configurationProperties" : { ... "hostNameVerification" : true, "hostNameVerifierPattern" : "*.example.com", ... }With the following connector configuration, IDM starts up but connector initialization throws an error:
"configurationProperties" : { ... "hostNameVerification" : true, "hostNameVerifierPattern" : "server2.example.com", ... }The error returned is similar to the following:
The host name from the server certificate'CN=server1.example.com' does not match the provided pattern 'server2.example.com'
Control what the LDAP connector synchronizes
To control the set of LDAP entries that are affected by reconciliation and automatic synchronization operations, set the following properties in the provisioner configuration. Automatic synchronization includes liveSync (synchronization of changes from the LDAP server to IDM) and implicit sync (synchronization from IDM to the LDAP server). For more information, refer to Synchronization types.
accountSearchFilter-
Only user accounts that match this filter are searched, and therefore affected by reconciliation and synchronization operations. If you do not set this property, all accounts within the base contexts specified previously are searched.
accountSynchronizationFilter-
This property is used during reconciliation and automatic synchronization operations, and filters out any LDAP accounts that you specifically want to exclude from these operations.
attributesToSynchronize-
During automatic synchronization operations, only the attributes listed here are considered for changes. Objects that include these attributes are synchronized. Objects that do not include these attributes are ignored. If this property is not set, IDM considers changes to all attributes specified in the mapping.
This attribute works only with LDAP servers that log changes in a change log, not with servers (such as Active Directory) that use other mechanisms to track changes.
baseContexts-
The starting points in the LDAP tree that are used when searching the directory tree; for example,
dc=example,dc=com. These base contexts must include the set of users and the set of groups that must be searched during reconciliation operations. baseContextsToSynchronize-
The starting points in the LDAP tree that are used to determine if a change should be synchronized. This property is used only for automatic synchronization operations. Only entries that fall under these base contexts are considered during synchronization operations.
modifiersNamesToFilterOut-
This property lets you define a list of DNs. During synchronization operations, the connector ignores changes made by these DNs.
When a managed user object is updated, and that change is synchronized to the LDAP server, the change made on the LDAP server is recorded in the change log. A liveSync operation picks up the change, and attempts to replay the change on the managed user object, effectively resulting in a loop of updates.
To avoid this situation, you can specify a unique user in your LDAP directory, that will be used only for the LDAP connector. The unique user must be something other than
uid=admin; for example,cn=idmuser. You can then include that user DN as the value ofmodifiersNamesToFilterOut. When a change is made through the LDAP connector, and that change is recorded in the change log, the modifier’s name (cn=idmuser) is flagged, and IDM does not attempt to replay the change back to the managed user repository. So, you are effectively indicating that IDM should not synchronize changes back to managed user that originated from managed user, thus preventing the update loop.This attribute works only with LDAP servers that log changes in a change log, not with servers (such as Active Directory) that use other mechanisms to track changes.
objectClassesToSynchronize-
During automatic synchronization operations, only the object classes listed here are considered for changes. IDM ignores change log updates (or changes to managed objects) which do not have any of the object classes listed here.
Use the LDAP connector with Active Directory
The LDAP connector provides functionality specifically for managing Active Directory users and groups. The connector can handle the following operational attributes to manage Active Directory accounts:
__ENABLE__-
Uses the
userAccountControlattribute to get or set the account status of an object.The LDAP connector reads the
userAccountControlto determine if an account is enabled or disabled. The connector modifies the value of theuserAccountControlattribute if IDM changes the value of__ENABLE__. __ACCOUNT_EXPIRES__-
Sets the
accountExpiresattribute of an Active Directory object to reset an expired account, or to set a future expiration date.To set an account that never expires, set
"__ACCOUNT_EXPIRES__": "0".To set an expiration date, set
"__ACCOUNT_EXPIRES__": "date", wheredateis in ISO8601 format. For example:curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "__ACCOUNT_EXPIRES__": "2020-12-31T00:00:00Z" }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/AD/account/e1418d64-096c-4cb0-b903-ebb66562d99d" { "sn": "jensen", "__LOCK_OUT__": false, "__ENABLE__": true, "objectGUID": "e1418d64-096c-4cb0-b903-ebb66562d99d", "dn": "CN=bjensen,OU=create,DC=example,DC=com", "accountExpires": "2020-12-31T00:00:00Z" } __LOCK_OUT__-
Uses the
msDS-User-Account-Control-Computedsystem attribute to check if a user account has been locked.If IDM sets
__LOCK_OUT__toFALSE, the LDAP connector sets the Active DirectorylockoutTimeto0to unlock the account.If IDM sets
__LOCK_OUT__toTRUE, the LDAP connector ignores the change and logs a message. __PASSWORD_EXPIRED__-
Uses the
msDS-User-Account-Control-Computedsystem attribute to check if a user password has expired.To force password expiration (that is, to force a user to change their password when they next log in), set
pwdLastSetto0. The LDAP connector setspwdLastSetto0, if IDM sets__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__toTRUE.To remove password expiration, set
pwdLastSetto0and then to-1. This sets the value ofpwdLastSetto the current time. The LDAP connector setspwdLastSetto-1if IDM sets__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__toFALSE.Active Directory does not allow you to create an enabled account with an expired password. If you are using __PASSWORD_EXPIRED__to force a new user to change their password when they next log in, you can create the user account as disabled initially (__ENABLE__=false). You can then patch the new user account to enable it. You can use the same workaround for synchronization operations, creating new user accounts as disabled, then issuing anopenidm.patchcall in apostCreatescript to enable the account. __CURRENT_PASSWORD__-
For a password change request, the connector supplies the
__CURRENT_PASSWORD__, along with the new password. The connector can also do a password reset where only the new password is supplied.
The sample connector configuration file (openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-adldap.json) includes these operational attributes. Note that the passwordAttribute property in this provisioner file is set to unicodePwd. This property specifies the attribute in Active Directory that holds the user password. When a user’s password is changed, the new value is set in this attribute.
Manage Active Directory users with the LDAP connector
If you create or update users in Active Directory, and those user entries include passwords, you must use the LDAP connector over SSL. You cannot create or update an Active Directory user password in clear text. To use the connector over SSL, follow the instructions in Configure the LDAP Connector to Use SSL and StartTLS.
The following command adds an Active Directory user. The output shows the operational attributes described in the previous section:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=Brian Smith,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com",
"cn": "Brian Smith",
"sAMAccountName": "bsmith",
"userPrincipalName": "bsmith@example.com",
"userAccountControl": "512",
"givenName": "Brian",
"mail": "bsmith@example.com",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/account?_action=create"
{
"_id": "e1418d64-096c-4cb0-b903-ebb66562d99d",
"mobile": null,
"postalCode": null,
"st": null,
"employeeType": [],
"objectGUID": "e1418d64-096c-4cb0-b903-ebb66562d99d",
"cn": "Brian Smith",
"department": null,
"l": null,
"description": null,
"info": null,
"manager": null,
"sAMAccountName": "bsmith",
"sn": null,
"whenChanged": "20151217131254.0Z",
"userPrincipalName": "bsmith@example.com",
"userAccountControl": "512",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"displayName": null,
"givenName": "Brian",
"middleName": null,
"facsimileTelephoneNumber": null,
"lastLogon": "0",
"countryCode": "0",
"employeeID": null,
"co": null,
"physicalDeliveryOfficeName": null,
"pwdLastSet": "2015-12-17T13:12:54Z",
"streetAddress": null,
"homePhone": null,
"__PASSWORD_NOTREQD__": false,
"telephoneNumber": null,
"dn": "CN=Brian Smith,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com",
"title": null,
"mail": "bsmith@example.com",
"postOfficeBox": null,
"__SMARTCARD_REQUIRED__": false,
"uSNChanged": "86144",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"initials": null,
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"company": null,
"employeeNumber": null,
"accountExpires": "0",
"c": null,
"whenCreated": "20151217131254.0Z",
"uSNCreated": "86142",
"division": null,
"groups": [],
"__DONT_EXPIRE_PASSWORD__": false,
"otherHomePhone": []
}
|
Note that the command sets the userAccountControl to 512, which is an enabled account. The value of the userAccountControl determines the account policy. The following list describes the common values for the userAccountControl.
512-
Enabled account.
514-
Disabled account.
544-
Enabled account, password not required.
546-
Disabled account, password not required.
66048-
Enabled account, password does not expire.
66050-
Disabled account, password does not expire.
66080-
Enabled account, password does not expire and is not required.
66082-
Disabled account, password does not expire and is not required.
262656-
Enabled account, smartcard required.
262658-
Disabled account, smartcard required.
262688-
Enabled account, smartcard required, password not required.
262690-
Disabled account, smartcard required, password not required.
328192-
Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328192-
Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328194-
Disabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire.
328224-
Enabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire and is not required.
328226-
Disabled account, smartcard required, password does not expire and is not required.
Manage Active Directory groups with the LDAP connector
The following command creates a basic Active Directory group with the LDAP connector:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=Employees,DC=example,DC=com"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/group?_action=create"
{
"_id": "240da4e9-59d8-1547-ad86-29f5b2b5114d"
}
The LDAP connector exposes two special attributes to handle Active Directory group scope and type: GROUP_SCOPE and GROUP_TYPE.
The GROUP_SCOPE attribute is defined in the provisioner configuration as follows:
...
"__GROUP_SCOPE__" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeName" : "__GROUP_SCOPE__",
"nativeType" : "string"
},The value of the GROUP_SCOPE attribute can be global, domain, or universal. If no group scope is set when the group is created, the scope is global by default. For more information about the different group scopes, refer to the corresponding Microsoft documentation.
The GROUP_TYPE attribute is defined in the provisioner configuration as follows:
...
"__GROUP_TYPE__" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeName" : "__GROUP_TYPE__",
"nativeType" : "string"
},The value of the GROUP_TYPE attribute can be security or distribution. If no group type is set when the group is created, the type is security by default. For more information about the different group types, refer to the corresponding Microsoft documentation.
The following example creates a new distribution group, with universal scope:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"dn": "CN=NewGroup,DC=example,DC=com",
"__GROUP_SCOPE__": "universal",
"__GROUP_TYPE__": "distribution"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/group?_action=create"
{
"_id": "f189df8a-276f-9147-8ad5-055b1580cbcb"
}
Support for nested Active Directory groups
By default, Active Directory does not return members of a nested group when querying the parent group. Some additional configuration is required to return members of a nested Active Directory group.
To include members of a nested group, create a new nestedMembers attribute in your provisioner file:
"nestedMembers" : {
"type" : "array",
"items" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeType" : "string"
},
"nativeName" : "memberOf:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:",
"nativeType" : "string",
"flags" : [
"NOT_CREATABLE",
"NOT_UPDATEABLE",
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
},Note that the nativeName property includes 1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941, which is the OID of LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAIN and LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_TRANSITIVE_EVAL. This is what tells Active Directory to include members of nested groups.
Querying this attribute will return results that include members of any nested groups of the queried group. For example:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/ad/account?_queryFilter=nestedMembers+eq+"CN=ParentGroup,DC=example,DC=com"&_fields=cn"
Handle Active Directory dates
Most dates in Active Directory are represented as the number of 100-nanosecond intervals since January 1, 1601 (UTC). For example:
pwdLastSet: 130698687542272930
IDM generally represents dates as an ISO 8601-compliant string with yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ssZ format. For example:
2015-03-02T20:17:48Z
The generic LDAP connector therefore converts any dates from Active Directory to ISO 8601 format, for fields such as pwdLastSet, accountExpires, lockoutTime, and lastLogon.
Multiple Active Directory domains
In a multi-domain Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest, the global catalog (GC) provides a read-only (searchable) representation of every object in the forest. Each domain controller (DC) in the forest stores a writable replica of the objects in its domain. Therefore, a DC can locate only the objects in its domain.
If your Active Directory deployment has only one domain controller, you can configure the connector to connect to that single domain controller. If your deployment spans multiple domains, you must configure the connector to connect to the Global Catalog (GC) to have a comprehensive view of all the domains.
Using a GC as the authoritative data source has the following limitations:
-
Only a subset of attributes is replicated from other domains to the GC.
Certain attributes required by the LDAP connector might be missing. To avoid this problem, modify the Active Directory schema to ensure that the required attributes are replicated to the GC.
-
Delete operations are not detected immediately.
A liveSync operation will therefore not update IDM with the result of a delete operation. Delete operations are detected by a reconciliation operation, so data stores are only temporarily "out of sync" with regard to deletes.
-
Not all group types are supported.
Group membership information is replicated to the GC for universal groups only. You must therefore use universal groups if your directory service has more than one domain.
|
You can use the |
LDAP search filters
The LDAP connector constructs an LDAP search filter using a combination of filters, in the following order:
(& (native filter) (user filter) (object class filter) )
The filter components are as follows:
- Native Filter
-
The native filter is the query filter that has been translated to an LDAP query. For example,
uid+eq+"user123"is translated touid=user123.This part of the filter is processed first.
- User Filter
-
You can define a user filter with the properties
accountSearchFilterandgroupSearchFilterin the connector configuration.These properties enable you to construct a more granular or specific search filter. If a user filter is specified, the connector does not use the object class filter. If no user filter is specified, (
accountSearchFilterandgroupSearchFilterset tonullor absent from the connector configuration), the connector uses the object class filter. - Object Class Filter
-
This part of the filter includes the object classes that the entry must have in order to be returned by the search.
The
__ACCOUNT__and__GROUPS__object classes are defined by the propertiesaccountObjectClassesandgroupObjectClassesin the connector configuration. For example, the following configuration indicates that theaccountObjectClassesinclude the LDAP object classestop,person,organizationalPerson, andinetOrgPerson:"configurationProperties" : { ... "accountObjectClasses" : [ "top", "person", "organizationalPerson", "inetOrgPerson" ], ... }With this configuration, the search filter for accounts is constructed as follows:
(&(objectClass=top)(objectClass=person)(objectClass=organizationalPerson)(objectClass=inetOrgPerson))
If no
accountObjectClassesorgroupObjectClassesare defined in the connector configuration, the connector uses the name of the ICF ObjectClass in the filter. For example, an object of typeorganizationUnitwill result in:(&(objectClass=organizationUnit)
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the LDAP Connector
The LDAP Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
LDAP Connector Configuration
The LDAP Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Normally the filter used to fetch change log entries is an and-based filter retrieving an interval of change entries. If this property is set, the filter will or together the required change numbers instead. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The object classes to synchronize. The change log is for all objects; this filters updates to just the listed object classes. You should not list the superclasses of an object class unless you intend to synchronize objects with any of the superclass values. For example, if only "inetOrgPerson" objects should be synchronized, but the superclasses of "inetOrgPerson" ("person", "organizationalperson" and "top") should be filtered out, then list only "inetOrgPerson" here. All objects in LDAP are subclassed from "top". For this reason, you should never list "top", otherwise no object would be filtered. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used to determine if a change should be synchronized. The base contexts attribute will be used to synchronize a change if this property is not set. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The names of the attributes to synchronize. This ignores updates from the change log if they do not update any of the named attributes. For example, if only "department" is listed, then only changes that affect "department" will be processed. All other updates are ignored. If blank (the default), then all changes are processed. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
An optional offset, specified in seconds to be negatively applied to the timestamp for Timestamp based Sync operations. Default value is 0, or no offset. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the change number attribute in the change log entry. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The list of names (DNs) to filter from the changes. Changes with the attribute "modifiersName" that match entries in this list will be filtered out. The standard value is the administrator name used by this adapter, to prevent loops. Entries should be of the format "cn=Directory Manager". |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Password for the principal. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The number of change log entries to fetch per query. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
If true, the connector will use the createTimestamp and modifyTimestamp system attributes to detect changes (Create/Update) on the directory instead of native change detection mechanism (cn=changelog on OpenDJ or Update Sequence Number -USN- on Active Directory for instance). Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
An optional LDAP filter for the objects to synchronize. Because the change log is for all objects, this filter updates only objects that match the specified filter. If you specify a filter, an object will be synchronized only if it matches the filter and includes a synchronized object class. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
If this property is set (the default), the filter used to fetch change log entries does not contain the "changeLogEntry" object class, expecting that there are no entries of other object types in the change log. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Password to use for the alternate keystore. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
An optional LDAP filter for the objects to synchronize. Because the change log is for all objects, this filter updates only objects that match the specified filter. If you specify a filter, an object will be synchronized only if it matches the filter and includes a synchronized object class. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of the group attribute that will be updated with the distinguished name of the user when the user is added to the group. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
An optional LDAP filter to control which accounts are returned from the LDAP resource. If no filter is specified, only accounts that include all specified object classes are returned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the name of a private key alias from the keystore that should be used for SSL mutual authentication. If null, no private key is sent during SSL handshake so only server cert is used. This alias name is case sensitive. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Select the check box to connect to the LDAP server using SSL. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When enabled and a user is renamed or deleted, update any POSIX groups to which the user belongs to reflect the new name. Otherwise, the LDAP resource must maintain referential integrity with respect to group membership. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum interval (seconds) at which the target directory is polled when a connection is reused from the pool. Defaults to 60 seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
An optional LDAP filter to control which groups are returned from the LDAP resource. If no filter is specified, only groups that include all specified object classes are returned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines how to handle LDAP referrals. Possible values can be follow, ignore or throw. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name or IP address of the host where the LDAP server is running. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When enabled and a user is renamed or deleted, update any LDAP groups to which the user belongs to reflect the new name. Otherwise, the LDAP resource must maintain referential integrity with respect to group membership. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connector can reset the sync token if ever the value of the sync token is greater than the last change number in the directory changelog. Defaults to "never" (no reset). If set to "first" it will reset the sync token to the value of the firstChangeNumber changelog attribute. If set to "last" it will reset the sync token to the value of the lastChangeNumber changelog attribute. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specify the sort attribute to use for VLV indexes on the resource. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Converts the Greenwich Time to ISO8601 format. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
One or more starting points in the LDAP tree that will be used when searching the tree. Searches are performed when discovering users from the LDAP server or when looking for the groups of which a user is a member. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the connector will verify the hostname in the certificate (subject + alternative subject) against the defined hostNameVerifierPattern. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of entries that can be in a block when retrieving entries in blocks. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default list of object classes that will be used when creating new group objects in the LDAP tree. This can be overridden by specifying the group object classes during the Create operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Attribute or attributes which holds the account’s user name. They will be used when authenticating to find the LDAP entry for the user name to authenticate. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
List all servers that should be used for failover in case the preferred server fails. If the preferred server fails, JNDI will connect to the next available server in the list. List all servers in the form of "ldap://ldap.example.com:389/", which follows the standard LDAP v3 URLs described in RFC 2255. Only the host and port parts of the URL are relevant in this setting. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
TCP/IP port number used to communicate with the LDAP server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Converts the AD Interval to ISO8601. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A simple pattern used to match the hostname from the certificate. It can contains * character (server1.example.com, *.example.com). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of the LDAP attribute that holds the password. When changing a users password, the new password is set to this attribute. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the connector will do a DNS query to find SRV records associated with the value set for host property ("_ldap._tcp.example.com" for example). Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies whether to add an extra _memberId attribute to get the group members UID. CAUTION: Setting this property to true can incur a large performance cost on group handling. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The last time the connector was checked to see if it was alive |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When set to true, The ldapGroups attribute will search group membership through static groups only. If false, it will leverage the "memberOf" attribute of an object (defaults to true). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies whether to use the startTLS operation to initiate a TLS/SSL session. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connector can delete an entry (node) with leaf entry if this value is set to true (defaults to false). The LDAP control LDAP_SERVER_TREE_DELETE_OID (1.2.840.113556.1.4.805) is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When this resource is specified in a Login Module (i.e., this resource is a pass-through authentication target) and the resource’s password policy is configured for change-after-reset, a user whose resource account password has been administratively reset will be required to change that password after successfully authenticating. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of the LDAP attribute that is mapped to the OpenICF UID attribute. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The distinguished name with which to authenticate to the LDAP server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default list of object classes that will be used when creating new user objects in the LDAP tree. This can be overridden by specifying the user object classes during the Create operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the type of the alternate key store. Valid values are JKS, JCEKS and PKCS12. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates the algorithm that the Identity system should use to hash the password. The only supported value is WIN-AD (for when Active Directory is the target). A blank value indicates that the system will not hash passwords. This will cause clear text passwords to be stored in LDAP unless the LDAP server performs the hash (as Forgerocks OpenDJ does, for example). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the filename of an alternate keystore. If specified, the connector will not use the default keystore specified by the javax.net.ssl.keyStore property. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The authentication mechanism to use: Simple or SASL-GSSAPI. Defaults to "simple". |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The timeout (in ms) before the connection attempt is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A list of custom octet string attributes to be declared so that the LDAP connector manipulates these attributes as byte arrays. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies whether to use block-based LDAP controls, like the simple paged results or VLV control. When performing search operations on large numbers of entries, the entries are returned in blocks to reduce the amount of memory used by the operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the connector will read the schema from the server. If false, the connector will provide a default schema based on the object classes in the configuration. This property must be true in order to use extended object classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When enabled, the LDAP Paged Results control is preferred over the VLV control when retrieving entries. If disabled, paged queries will be ignored. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connector used to transform the AD ObjectGUID in the form <GUID=xxxxxx>. It now used dashed notation (xxxx-xx-xx-xxxx-xxxxxx) by default. Set to true to keep the old format. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connector can send the Common Audit Transaction Id (if present) to the target OpenDJ server when this value is set to true (defaults to false). The LDAP control TransactionIdControl (1.3.6.1.4.1.36733.2.1.5.1) is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the name used in the JAAS configuration file to define the JAAS login configuration. If null, it defaults to "org.identityconnectors.ldap.LdapConnector". |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Marketo connector
The Marketo connector lets you synchronize between IDM managed users and a Marketo leads database. You can synchronize any managed user to Marketo—those who have been added directly to the IDM repository, and those who have registered themselves through a Social Identity Provider.
The Marketo connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector, and lets you interact with leads in a Marketo database, using Groovy scripts for the ICF operations.
To use the Marketo connector, you need:
-
A Marketo account
-
A client ID and client secret
-
The REST API URL for your IDM service
-
A custom list created in your Marketo leads database
To obtain these details from Marketo, refer to the Marketo documentation.
Install the Marketo connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/marketo-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Marketo connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Marketo Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Marketo Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file.
A sample connector configuration file is bundled with IDM, provided at /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-marketo.json. Copy the sample connector configuration file to your project’s conf/ directory.
This sample connector configuration shows the mandatory properties:
Sample Marketo connector configuration
{
"displayName" : "MarketoConnector",
"description" : "Connector used to sync users to Marketo leads",
"author" : "ForgeRock",
"enabled" : true,
"connectorRef" : {
"bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo-connector",
"bundleVersion" : "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo.MarketoConnector"
},
...
"configurationProperties" : {
"instance" : "<INSTANCE_FQDN>",
"clientId" : "<CLIENT_ID>",
"clientSecret" : "<CLIENT_SECRET>",
"leadFields" : null,
"partitionName" : null,
"listName" : "<LEAD_LIST_NAME>",
"scriptRoots" : [
"jar:file:connectors/marketo-connector-1.5.20.20.jar!/scripts/marketo/"
],
...
},
...
}- instance
-
To locate the REST API endpoint URL in Marketo, select Admin > Web Services, scroll down to REST API, and find the endpoint. Use that REST endpoint as the value of the
instanceproperty in your connector configuration. Remove the protocol and/restfrom the URL. For example, if the endpoint ishttps://some-number.mktorest.com/rest, the value of theinstanceproperty must besome-number.mktorest.com. - clientId
-
Locate the client ID in the details of your Marketo service
LaunchPoint. - clientSecret
-
Locate the client secret in the details of your Marketo service
LaunchPoint. - listName
-
The name of the custom list created in your Marketo Leads database.
- scriptRoots
-
The path to the Groovy scripts that perform the ICF operations, relative to your installation directory. For the Marketo connector, the scripts are bundled in the connector .jar file, so the sample connector configuration uses the path
jar:file:connectors/marketo-connector-1.5.20.20.jar!/scripts/marketo/.
| For a complete list of configuration properties, refer to Marketo Connector Configuration. |
Test the Marketo connector
When the connector is configured correctly, you can test its status by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "marketo",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/marketo",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"account"
],
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.marketo.MarketoConnector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)"
},
"displayName": "Marketo Connector",
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can reach your Marketo database.
Marketo remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Marketo connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Marketo connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Marketo remote connector.
Reconcile users with a Marketo leads database
The Marketo connector lets you reconcile IDM users (including managed users and users who have registered through a social identity provider) with a Marketo leads database. To set up reconciliation to a Marketo database, copy the following sample mapping file to your project’s conf directory:
/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/marketo/sync.json
This file sets up a mapping from the managed user repository to Marketo user accounts. The file includes transformations for user accounts registered through Facebook and LinkedIn. You can use these transformations as a basis for transformations from other social identity providers.
If you have an existing mapping configuration, add the content of this sample sync.json to your existing mapping.
The sample mapping restricts reconciliation to users who have accepted the marketing preferences with the following validSource script:
"validSource" : {
"type" : "text/javascript",
"globals" : {
"preferences" : [
"marketing"
]
},
"file" : "ui/preferenceCheck.js"
}When a user registers with IDM, they can choose to accept this condition. As a regular user, they can also select (or deselect) the condition in the End User UI by logging into IDM at http://localhost:8080/, and selecting Preferences.
If a user deselects the marketing preference after their account has been reconciled to Marketo, the next reconciliation run will remove the account from the Marketo database.
For more information on how preferences work in a mapping, refer to User preferences.
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Marketo connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Marketo Connector
The Marketo Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Marketo Connector Configuration
The Marketo Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Marketo-assigned FQDN for your instance. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Your OAuth2 client ID. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Your OAuth2 client secret. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Comma-delimited list of lead fields to fetch; Leave empty for default set. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Name of the partition in which to create and update leads; May be left empty. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Name of the Marketo static list the connector will use to manage leads. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The access token for the application. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The expiration token for the application. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Microsoft Graph API connector
The Microsoft (MS) Graph API connector uses the Microsoft Graph SDK for Java and the Authentication Providers for the Microsoft Graph Java SDK. Unlike the PowerShell connector for Azure, the MS Graph API connector is a Java connector and does not need .NET RCS to run. As a Java connector, the MS Graph API connector functions like any standard IDM connector.
The MS Graph API connector can read, search, and fetch data from Microsoft Azure when Azure is the authoritative data source. It can also provision to Azure when IDM or Identity Cloud is the authoritative data source.
The MS Graph API connector is bundled with IDM and Identity Cloud, and is also available from the ForgeRock Download Center. The connector bundles all its dependencies.
| Microsoft Graph API doesn’t support paging for all relationships/resources. Refer to the Microsoft Documentation. |
Next steps:
Microsoft Azure requirements
Before you can use the connector, you must register an application with Azure. You need a Microsoft Azure subscription to complete this procedure:
-
Log in to the MS Azure portal as an administrative user.
-
Under Azure services , select App registrations.
-
On the Register an application page, enter a name for the application; for example, FR-Connector.
-
Select the supported account types, and enter a Redirect URI.
The redirect URI is the IDM URI that Azure should redirect to after successful authentication; for example,
https://idm.example.com:8443/. -
On the new registration page for your application, make a note of the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID. You will need these to configure the connector:

-
Generate a client secret:
-
Select Certificates & secrets > New client secret .
-
Enter a description, select an expiration date, and click Add.
-
Copy the client secret Value:

You will not be able to retrieve the client secret in cleartext after you exit this screen. -
-
Set the API permissions:
-
Select API permissions, click Microsoft Graph, and then click Application permissions.

-
From the User item, select the following permissions:
-
User.Export.All -
User.ManageIdentities.All -
User.Read.All -
User.ReadWrite.All
-
-
From the Group item, select the following permissions:
-
Group.Create -
Group.Read.All -
Group.ReadWrite.All
-
-
From the Directory item, select the following permissions:
-
Directory.Read.All -
Directory.ReadWrite.All
-
-
Click Add permissions .
-
-
Grant admin consent for the API permissions:
On the Configured permissions page, Grant admin consent for org-name, then click Yes.

Install the MS Graph API connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/msgraphapi-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the MS Graph API connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select MS Graph API Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to MS Graph API Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, copy the sample connector configuration file from /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-azuread.json to your project’s conf/ directory.
Set at least the Azure tenant, clientId and clientSecret in the configurationProperties. For example:
"configurationProperties" : {
"tenant" : "your tenant ID",
"clientId" : "your client ID",
"clientSecret" : "your client secret"
}MS Graph API remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the MS Graph API connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the MS Graph API connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the MS Graph API remote connector.
Test the connector
One simple method for testing the connector configuration is using the test action on the openidm/system endpoint:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
{
"name": "azuread",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/azuread",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.msgraphapi-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.msgraphapi.MSGraphAPIConnector"
},
"displayName": "MSGraphAPI Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"servicePrincipal",
"__GROUP__",
"roleEligibilitySchedule",
"roleEligibilityScheduleInstance",
"__ALL__",
"roleEligibilityScheduleRequest",
"directoryRole",
"team",
"roleAssignmentSchedule",
"roleDefinition",
"servicePlan",
"directoryRoleTemplate",
"application",
"roleAssignmentScheduleRequest",
"roleAssignmentScheduleInstance",
"subscribedSku",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"roleAssignment"
],
"ok": true (1)
}
| 1 | A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector is configured correctly. |
Synchronize accounts between IDM and Azure
To use the MS Graph API connector to synchronize accounts between IDM and Azure, set up a mapping between the two data stores.
You can use the sample configuration file at /path/to/openidm/samples/sync-with-azuread/conf/sync.json as a starting point.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the MSGraphAPI Connector
The MSGraphAPI Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
MSGraphAPI Connector Configuration
The MSGraphAPI Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Azure AD tenant name or id. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The clientID used by the connector during the OAuth flow. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The client secret used by the connector during the OAuth flow. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The Http proxy host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The Http proxy port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The Http proxy user name. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The Http proxy user password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true, the Azure object will be deleted permanently on delete operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for read operations either per seconds ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for write operations (create/update/delete) either per second ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the expiry time for cached license information (in minutes). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Use the connector (MS Graph API)
After you configure the MS Graph API connector, you can use it to synchronize, read, and edit resources:
| Microsoft Graph API doesn’t support paging for all relationships/resources. Refer to the Microsoft Documentation. |
Users and groups (MS Graph API)
You can use the MS Graph API connector to list, create, update, and delete users and groups.
List user entries
This command retrieves a list of users in your Azure tenant. You can also use any system-enabled filter, such as those described in Construct Queries:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31"
},
{
"_id": "c7fe57e2-3159-45e1-b67a-435232fd88d9"
},
{
"_id": "9e714b5c-345a-430c-93f5-d8c6f9a2f225"
},
...
],
...
}
Return a user entry
This command retrieves a specific user entry from your Azure tenant:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31"
{
"_id": "c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31",
"surname": "Jensen",
"displayName": "Babs Jensen",
"memberOf": [
"036f288c-6f71-41ae-9d09-6a68c8ba315b"
],
"mail": "babs.jensen@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"onPremisesExtensionAttributes": {
...
},
"usageLocation": "FR",
"userType": "Member",
"identities": [
{
"signInType": "userPrincipalName",
"issuerAssignedId": "00991235@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"issuer": "example.onmicrosoft.com"
}
],
"businessPhones": [],
"createdDateTime": "2020-11-20T11:09:15Z",
"accountEnabled": true,
"userPrincipalName": "00991235@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"proxyAddresses": [
"smtp:00991235@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"SMTP:babs.jensen@example.onmicrosoft.com"
],
"imAddresses": [],
"passwordPolicies": "None",
"mailNickname": "00991235",
"givenName": "Babs",
"__NAME__": "00991235@example.onmicrosoft.com"
}
Create users or groups
This command creates a new user in your Azure tenant:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '{
"surname": "Carter",
"displayName": "Steve Carter",
"givenName": "Steve",
"userType": "Member",
"accountEnabled": true,
"mailNickname": "00654321",
"userPrincipalName": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com",
"__PASSWORD__": "MyPassw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user?_action=create"
{
"_id": "9fa6c765-0872-45f6-8714-1dcd1ed94859",
"surname": "Carter",
"displayName": "Steve Carter",
"memberOf": [],
"onPremisesExtensionAttributes": {
"extensionAttribute14": null,
...
},
"userType": "Member",
"identities": [
{
"signInType": "userPrincipalName",
"issuerAssignedId": "00654321@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"issuer": "example.onmicrosoft.com"
}
],
"businessPhones": [],
"createdDateTime": "2020-12-18T13:23:58Z",
"accountEnabled": true,
"userPrincipalName": "00654321@example.onmicrosoft.com",
"proxyAddresses": [],
"imAddresses": [],
"mailNickname": "00654321",
"givenName": "Steve",
"__NAME__": "00654321@example.onmicrosoft.com"
}
Update entries
This command changes the password for the user created previously:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request PATCH \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '[ {
"operation": "replace",
"field": "__PASSWORD__",
"value": "MyNewPassw0rd"
} ]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/9fa6c765-0872-45f6-8714-1dcd1ed94859"
{
"_id": "9fa6c765-0872-45f6-8714-1dcd1ed94859",
"surname": "Carter",
"displayName": "Steve Carter",
"memberOf": [],
"onPremisesExtensionAttributes": {
"extensionAttribute14": null,
...
},
"userType": "Member",
"identities": [
{
"signInType": "userPrincipalName",
"issuerAssignedId": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com",
"issuer": "forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com"
}
],
"businessPhones": [],
"createdDateTime": "2020-12-18T13:23:58Z",
"accountEnabled": true,
"userPrincipalName": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com",
"proxyAddresses": [],
"imAddresses": [],
"mailNickname": "00654321",
"givenName": "Steve",
"__NAME__": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com"
}
Delete users and groups
This command deletes a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/9fa6c765-0872-45f6-8714-1dcd1ed94859"
{
"_id": "9fa6c765-0872-45f6-8714-1dcd1ed94859",
"surname": "Carter",
"displayName": "Steve Carter",
"memberOf": [],
"onPremisesExtensionAttributes": {
"extensionAttribute14": null,
...
},
"userType": "Member",
"identities": [
{
"signInType": "userPrincipalName",
"issuerAssignedId": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com",
"issuer": "forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com"
}
],
"businessPhones": [],
"createdDateTime": "2020-12-18T13:23:58Z",
"accountEnabled": true,
"userPrincipalName": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com",
"proxyAddresses": [],
"imAddresses": [],
"mailNickname": "00654321",
"givenName": "Steve",
"__NAME__": "00654321@forgedemo.onmicrosoft.com"
}
Service plans (MS Graph API)
Use the MS Graph API connector to list the service plans in your Azure data source, get details on service plans, and manage service plans for specific users.
List available service plans in Azure
This command lists the values of the read-only servicePlan object:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePlan?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113",
"__NAME__": "EXCHANGE_S_DESKLESS",
"appliesTo": "User",
"subscribedSkuId": "9xdl4ChCwk2okl0_8zYaEIRZWEsbZYpEnlM7EPBpz38",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"servicePlanId": "4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113"
}
],
"resultCount": 1,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
List service plans details
This command lists the details of a specific servicePlan:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePlan/4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113"
{
"_id": "4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113",
"__NAME__": "EXCHANGE_S_DESKLESS",
"appliesTo": "User",
"subscribedSkuId": "9xdl4ChCwk2okl0_8zYaEIRZWEsbZYpEnlM7EPBpz38",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"servicePlanId": "4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113"
}
Add service plans to a user
Add service plans to a user by supplying the __servicePlanIds__ array of strings with the format skuId:servicePlanId. This command adds two service plans to a specific user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-None-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__servicePlanIds__": [
"4b585984-651b-448a-9e53-3b10f069cf7f:a82fbf69-b4d7-49f4-83a6-915b2cf354f4",
"4b585984-651b-448a-9e53-3b10f069cf7f:b76fb638-6ba6-402a-b9f9-83d28acb3d86"
]
}
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/5e85a7a1-2e57-4be2-b912-3e50bc26c856"
{
"_id": "5e85a7a1-2e57-4be2-b912-3e50bc26c856",
"__NAME__": "mciowixxlrcnbob@{AZURE_DOMAIN}",
"__servicePlanIds__": [
"4b585984-651b-448a-9e53-3b10f069cf7f:a82fbf69-b4d7-49f4-83a6-915b2cf354f4",
"4b585984-651b-448a-9e53-3b10f069cf7f:b76fb638-6ba6-402a-b9f9-83d28acb3d86"
],
"country": "US",
"givenName": "mciowixx",
"userPrincipalName": "mciowixxlrcnbob@{AZURE_DOMAIN}",
"licenses": [
{
"skuPartNumber": "DESKLESSPACK",
"servicePlans": [
{
"servicePlanName": "VIVAENGAGE_CORE",
"provisioningStatus": "Success",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "a82fbf69-b4d7-49f4-83a6-915b2cf354f4"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "VIVA_LEARNING_SEEDED",
"provisioningStatus": "Success",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "b76fb638-6ba6-402a-b9f9-83d28acb3d86"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "Nucleus",
"provisioningStatus": "Success",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "db4d623d-b514-490b-b7ef-8885eee514de"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "MICROSOFTBOOKINGS",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "199a5c09-e0ca-4e37-8f7c-b05d533e1ea2"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "RMS_S_BASIC",
"provisioningStatus": "Success",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "31cf2cfc-6b0d-4adc-a336-88b724ed8122"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "POWER_VIRTUAL_AGENTS_O365_F1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "ba2fdb48-290b-4632-b46a-e4ecc58ac11a"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "CDS_O365_F1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "90db65a7-bf11-4904-a79f-ef657605145b"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "PROJECT_O365_F3",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "7f6f28c2-34bb-4d4b-be36-48ca2e77e1ec"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "DYN365_CDS_O365_F1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "ca6e61ec-d4f4-41eb-8b88-d96e0e14323f"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "PROJECTWORKMANAGEMENT",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "b737dad2-2f6c-4c65-90e3-ca563267e8b9"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "KAIZALA_O365_P1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "73b2a583-6a59-42e3-8e83-54db46bc3278"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "MICROSOFT_SEARCH",
"provisioningStatus": "Success",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "94065c59-bc8e-4e8b-89e5-5138d471eaff"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "WHITEBOARD_FIRSTLINE1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "36b29273-c6d0-477a-aca6-6fbe24f538e3"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "OFFICEMOBILE_SUBSCRIPTION",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "c63d4d19-e8cb-460e-b37c-4d6c34603745"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "BPOS_S_TODO_FIRSTLINE",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "80873e7a-cd2a-4e67-b061-1b5381a676a5"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "FORMS_PLAN_K",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "f07046bd-2a3c-4b96-b0be-dea79d7cbfb8"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "STREAM_O365_K",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "3ffba0d2-38e5-4d5e-8ec0-98f2b05c09d9"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "FLOW_O365_S1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "bd91b1a4-9f94-4ecf-b45b-3a65e5c8128a"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "POWERAPPS_O365_S1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "e0287f9f-e222-4f98-9a83-f379e249159a"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "TEAMS1",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "57ff2da0-773e-42df-b2af-ffb7a2317929"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "Deskless",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "8c7d2df8-86f0-4902-b2ed-a0458298f3b3"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "MCOIMP",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "afc06cb0-b4f4-4473-8286-d644f70d8faf"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "SHAREPOINTWAC",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "e95bec33-7c88-4a70-8e19-b10bd9d0c014"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "SWAY",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "a23b959c-7ce8-4e57-9140-b90eb88a9e97"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "INTUNE_O365",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingActivation",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "882e1d05-acd1-4ccb-8708-6ee03664b117"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "YAMMER_ENTERPRISE",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "7547a3fe-08ee-4ccb-b430-5077c5041653"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "SHAREPOINTDESKLESS",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "902b47e5-dcb2-4fdc-858b-c63a90a2bdb9"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "EXCHANGE_S_DESKLESS",
"provisioningStatus": "Disabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "4a82b400-a79f-41a4-b4e2-e94f5787b113"
}
],
"id": "9xdl4ChCwk2okl0_8zYaEIRZWEsbZYpEnlM7EPBpz38",
"skuId": "4b585984-651b-448a-9e53-3b10f069cf7f"
}
],
"usageLocation": "US"
}User licenses (MS Graph API)
The MS Graph API connector lets you list the available licenses in your Azure data source and manage those licenses for specific users.
List available licenses in Azure
This command lists the values of the read-only subscribedSku object. For more information about this object class, refer to the corresponding Microsoft documentation:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/subscribedSku?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "5ee8xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-76dc2c2c30bc_f245ecc8-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx114de5f3",
"prepaidUnits": {
"warning": 0,
"enabled": 1,
"suspended": 0
},
"skuId": "f245ecc8-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx114de5f3",
"skuPartNumber": "O365_BUSINESS_PREMIUM",
"capabilityStatus": "Enabled",
"appliesTo": "User",
"consumedUnits": 1,
"__NAME__": "O365_BUSINESS_PREMIUM",
"servicePlans": [
{
"servicePlanName": "RMS_S_BASIC",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "31cxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx122"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "POWER_VIRTUAL_AGENTS_O365_P2",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "041xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxaee"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "CDS_O365_P2",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "User",
"servicePlanId": "95bxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx95a"
},
...
]
}
],
...
}
List a user’s licenses
Each user object can include a read-only licenses property that contains an array of objects (maps).
This command lists a specific user’s licenses:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31?_fields=licenses"
{
"_id": "c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31",
"licenses": [
{
"skuPartNumber": "O365_BUSINESS_PREMIUM",
"servicePlans": [
{
"servicePlanName": "RMS_S_BASIC",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "31cxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx122"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "POWER_VIRTUAL_AGENTS_O365_P2",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "041xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxaee"
},
{
"servicePlanName": "CDS_O365_P2",
"provisioningStatus": "PendingProvisioning",
"appliesTo": "Company",
"servicePlanId": "95bxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx95a"
},
...
],
"id": "c8noxxxxsEqoxxxxLCwwxxxxRfKvxxxxth8nxxxx5fM",
"skuId": "f24xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx5f3"
}
]
}
Add and remove a user’s licenses
You cannot manipulate a user’s licenses property directly because it is read-only. To add or remove licenses for a user, set the addLicenses or removeLicenses properties when you create or update the user.
|
The connector does not currently support PATCH |
This command updates an existing user entry to add a license with the `skuId`f24xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx5f3:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-None-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"addLicenses": [
{
"skuId": "f24xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx5f3"
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31"
This command updates the user entry to remove the license with `skuId`f24xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx5f3:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"removeLicenses": "f24xxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx5f3"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/c48be8cc-5846-4059-95e8-a7acbf6aec31"
Contacts (MS Graph API)
A contact is a resource type in Microsoft Outlook used to organize and store information about an associated object. Contacts use the /user endpoint. For more information, refer to the Microsoft Graph documentation.
The MS Graph API connector offers limited support for contacts and includes the following write-only attributes:
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"nativeType": "object"
},
"nativeName": "__addContacts__",
"nativeType": "object",
"flags": [
"NOT_READABLE",
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
},
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string",
"nativeType": "string"
},
"nativeName": "__removeContacts__",
"nativeType": "string",
"flags": [
"NOT_READABLE",
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
},
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"nativeType": "object"
},
"nativeName": "__updateContacts__",
"nativeType": "object",
"flags": [
"NOT_READABLE",
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
}Add contacts to a user
| You must add contacts to an existing user. |
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"__addContacts__": {
"givenName": "Test-Contact",
"businessAddress": {
"city": "exampleCity",
"state": "exampleState",
"postalCode": "99999",
"street": "example st",
"countryOrRegion": "United States"
}
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7"
Return a user entry with contacts
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request GET \ 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7?_fields="_id,contacts"'
{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"contacts": [
{
"id": "{CONTACT-ID}",
"givenName": "Test-Contact",
"businessAddress": {
"city": "exampleCity",
"state": "exampleState",
"postalCode": "99999",
"street": "example st",
"countryOrRegion": "United States"
}
}
]
}Update a user’s contacts
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"__updateContacts__": {
"id": "{CONTACT-ID}",
"givenName": "Test-Contact-Updated",
"businessAddress": {
"city": "exampleCity",
"state": "exampleState",
"postalCode": "99999",
"street": "example st",
"countryOrRegion": "United States"
}
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7"
After updating the user’s contacts, a subsequent read on the user with the contacts field returns the updated contacts:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request GET \ 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7?_fields="_id,contacts"'
{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"contacts": [
{
"id": "{CONTACT-ID}",
"givenName": "Test-Contact-Updated",
"businessAddress": {
"city": "exampleCity",
"state": "exampleState",
"postalCode": "99999",
"street": "example st",
"countryOrRegion": "United States"
}
}
]
}Remove a user’s contacts
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"__removeContacts__": [
"{CONTACT-ID}"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7"
After removing the user’s contacts, a subsequent read on the user with the contacts field returns an empty contacts array:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request GET \ 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/user/671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7?_fields="_id,contacts"'
{
"_id": "671fa173-ad81-41c3-89bf-af939426eee7",
"contacts": []
}Role eligibility schedules (MS Graph API)
The MS Graph API connector lets you read and manage role eligibility schedules.
Create a role eligibility schedule request
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"action": "adminAssign",
"justification": "Justification is required",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"principalId": "2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2022-04-10T00:00:00Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleEligibilityScheduleRequest"
{
"_id": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"isValidationOnly": false,
"targetScheduleId": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.143Z",
"__NAME__": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"principalId": "2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"action": "adminAssign",
"ticketInfo": {},
"completedDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.167Z",
"justification": "Justification is required",
"status": "Provisioned",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.168101400Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
},
"createdBy": {
"user": {
"id": "f516bdc4-0171-42ba-823a-4cbdff160d0f"
}
}
}
Read a role eligibility schedule request
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleEligibilityScheduleRequest/0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7"
{
"_id": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"isValidationOnly": false,
"targetScheduleId": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.143Z",
"__NAME__": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"principalId": "2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"action": "adminAssign",
"ticketInfo": {},
"completedDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.167Z",
"justification": "Justification is required",
"status": "Provisioned",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.168101400Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
},
"createdBy": {
"user": {
"id": "f516bdc4-0171-42ba-823a-4cbdff160d0f"
}
}
}
Get role eligibility schedules for a user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleEligibilitySchedule?_queryFilter=principalId%20eq%20'2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe'"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"modifiedDateTime": "0001-01-01T08:00Z",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.450Z",
"principalId": "2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-15T23:59:45.450Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
},
"createdUsing": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"status": "Provisioned",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"__NAME__": "0d8a7bbe-e4ab-4798-8539-728c410ac7b7",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"memberType": "Direct"
}
],
...
}
Get role eligibility schedule instance
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleEligibilityScheduleInstance?_queryFilter=principalId+eq+'2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe'"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "UX6spHTVBkG5_Zv86oJthH0ZIKwfxAZIp1uoOmyPt1I-1-e",
"roleDefinitionId": "a4ac7e51-d574-4106-b9fd-9bfcea826d84",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"roleEligibilityScheduleId": "1248840c-f57d-4168-9e2c-1e0d0e9a46f4",
"__NAME__": "UX6spHTVBkG5_Zv86oJthH0ZIKwfxAZIp1uoOmyPt1I-1-e",
"principalId": "2588c7f0-776e-407e-a1dc-f3a77a28e4fe",
"startDateTime": "2023-02-03T21:29:03.217Z",
"memberType": "Direct"
}
],
...
}
Role assignment schedules (MS Graph API)
The MS Graph API connector lets you read and manage role assignment schedules.
Create a role assignment schedule request
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"action": "adminAssign",
"justification": "Justification is required",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"principalId": "a4375665-cba5-4208-a4f2-12a0d2fc0e85",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2022-04-10T00:00:00Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleAssignmentScheduleRequest"
{
"_id": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.079921Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
},
"isValidationOnly": false,
"createdBy": {
"user": {
"id": "f516bdc4-0171-42ba-823a-4cbdff160d0f"
}
},
"ticketInfo": {},
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"principalId": "f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e",
"__NAME__": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"completedDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.080Z",
"targetScheduleId": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"action": "adminAssign",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"status": "Provisioned",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.070Z",
"justification": "Justification is required"
}Read a role assignment schedule request
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleAssignmentScheduleRequest/4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0"
{
"_id": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.079921Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
},
"isValidationOnly": false,
"createdBy": {
"user": {
"id": "f516bdc4-0171-42ba-823a-4cbdff160d0f"
}
},
"ticketInfo": {},
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"principalId": "f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e",
"__NAME__": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"completedDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.080Z",
"targetScheduleId": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"action": "adminAssign",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"status": "Provisioned",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:04.070Z",
"justification": "Justification is required"
}Get role assignment schedules for a user
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleAssignmentSchedule?_queryFilter=principalId%20eq%20’f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e'"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"__NAME__": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"status": "Provisioned",
"memberType": "Direct",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"principalId": "f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e",
"createdDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:07.727Z",
"assignmentType": "Assigned",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"createdUsing": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"scheduleInfo": {
"startDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:07.727Z",
"expiration": {
"type": "noExpiration"
}
}
}
],
...
}Get role assignment schedule instance
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/roleAssignmentScheduleInstance?_queryFilter=principalId+eq+'f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e'"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "UafX_Qu2SkSYTAJlL-j6HOgTZPlmE25CqyRNk4DxHi4-1",
"assignmentType": "Assigned",
"memberType": "Direct",
"principalId": "f96413e8-1366-426e-ab24-4d9380f11e2e",
"startDateTime": "2023-02-16T22:21:07.727Z",
"__NAME__": "UafX_Qu2SkSYTAJlL-j6HOgTZPlmE25CqyRNk4DxHi4-1",
"roleAssignmentScheduleId": "4b49df1e-4b59-4a93-a7c7-ad3b13ad98b0",
"directoryScopeId": "/",
"roleDefinitionId": "fdd7a751-b60b-444a-984c-02652fe8fa1c",
"roleAssignmentOriginId": "UafX_Qu2SkSYTAJlL-j6HOgTZPlmE25CqyRNk4DxHi4-1"
}
],
...
}Applications (MS Graph API)
The MS Graph API connector lets you read and manage applications.
Query all applications
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/application?_queryFilter=true"
Read an application
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/application/e2dcfa77-5222-4715-a043-98baac00683d"
{
"_id": "e2dcfa77-5222-4715-a043-98baac00683d",
"tags": [],
"spa": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"parentalControlSettings": {
"legalAgeGroupRule": "Allow",
"countriesBlockedForMinors": []
},
"api": {
"requestedAccessTokenVersion": 2,
"knownClientApplications": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"preAuthorizedApplications": []
},
"passwordCredentials": [],
"info": {},
"addIns": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"publicClient": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"verifiedPublisher": {},
"identifierUris": [],
"web": {
"implicitGrantSettings": {
"enableAccessTokenIssuance": false,
"enableIdTokenIssuance": false
},
"redirectUris": []
},
"publisherDomain": "example.com",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:40:02Z",
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoles": [],
"isDeviceOnlyAuthSupported": false,
"appId": "bc146d82-be72-4e16-814d-76e977ad198e",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"requiredResourceAccess": [
{
"resourceAppId": "00000002-0000-0000-c000-000000000000",
"resourceAccess": [
{
"id": "311a71cc-e848-46a1-bdf8-97ff7156d8e6",
"type": "Scope"
}
]
}
]
}Create an application
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"requiredResourceAccess": [
{
"resourceAppId": "00000002-0000-0000-c000-000000000000",
"resourceAccess": [
{
"id": "311a71cc-e848-46a1-bdf8-97ff7156d8e6",
"type": "Scope"
}
]
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/application"
{
"_id": "e2dcfa77-5222-4715-a043-98baac00683d",
"tags": [],
"spa": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"parentalControlSettings": {
"legalAgeGroupRule": "Allow",
"countriesBlockedForMinors": []
},
"api": {
"requestedAccessTokenVersion": 2,
"knownClientApplications": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"preAuthorizedApplications": []
},
"passwordCredentials": [],
"info": {},
"addIns": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"publicClient": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"verifiedPublisher": {},
"identifierUris": [],
"web": {
"implicitGrantSettings": {
"enableAccessTokenIssuance": false,
"enableIdTokenIssuance": false
},
"redirectUris": []
},
"publisherDomain": "example.com",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:40:02Z",
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoles": [],
"isDeviceOnlyAuthSupported": false,
"appId": "bc146d82-be72-4e16-814d-76e977ad198e",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"requiredResourceAccess": [
{
"resourceAppId": "00000002-0000-0000-c000-000000000000",
"resourceAccess": [
{
"id": "311a71cc-e848-46a1-bdf8-97ff7156d8e6",
"type": "Scope"
}
]
}
]
}Add a password (client secret) to an application
Adding passwordCredential when creating applications is not supported. You must use the addPassword method to add passwords or secrets to an application.
Some actions require more than a UUID on return and have no object to follow up with a subsequent read. In this instance, you can use the scriptOnConnector action, which requires at least the builtinAction parameter. Adding client secrets using this method requires the parameter builtinAction=addPassword. You can learn more about the other required parameter applicationId and optional parameters in the Microsoft Graph documentation.
The above also requires a dummy system action. For example:
{
"scriptId": "addPassword",
"actions": [
{
"systemType": ".*MSGraphAPIConnector",
"actionSource": "return;",
"actionType": "Groovy"
}
]
}The actionSource is ignored for these builtIn requests, but still required to invoke the scriptOnConnector action.
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/?_action=script&scriptId=addPassword&displayName=TestSecretGenesis&applicationId=f619a0ac-0548-4e90-9314-84d967088d2b&builtinAction=addPassword"
{
"actions": [
{
"result": {
"secretText": "{GENERATED-CLIENT-SECRET}",
"startDateTime": {
"dateTime": {
"date": {
"month": 5,
"year": 2023,
"day": 5
},
"time": {
"hour": 20,
"nano": 771787000,
"minute": 40,
"second": 27
}
},
"offset": {
"totalSeconds": 0
}
},
"displayName": "TestSecretGenesis",
"hint": "LS8",
"keyId": "8f48fb5e-a295-4969-b988-a723a02f2f28",
"endDateTime": {
"dateTime": {
"date": {
"month": 5,
"year": 2025,
"day": 5
},
"time": {
"hour": 20,
"nano": 771787000,
"minute": 40,
"second": 27
}
},
"offset": {
"totalSeconds": 0
}
}
}
}
]
}Update an application
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[
{
"operation": "replace",
"field": "/displayName",
"value": "Test-Application-Updated"
}
]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/application/4eff1242-bd95-463b-9c8c-f221ec489ba1"
{
"_id": "4eff1242-bd95-463b-9c8c-f221ec489ba1",
"tags": [],
"spa": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"parentalControlSettings": {
"legalAgeGroupRule": "Allow",
"countriesBlockedForMinors": []
},
"api": {
"requestedAccessTokenVersion": 2,
"knownClientApplications": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"preAuthorizedApplications": []
},
"passwordCredentials": [],
"info": {},
"addIns": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"publicClient": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"verifiedPublisher": {},
"identifierUris": [],
"web": {
"implicitGrantSettings": {
"enableAccessTokenIssuance": false,
"enableIdTokenIssuance": false
},
"redirectUris": []
},
"publisherDomain": "example.com",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:40:11Z",
"displayName": "Test-Application-Updated",
"appRoles": [],
"appId": "68e06ad2-569f-407d-b117-6cc1d9f5d787",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"requiredResourceAccess": []
}Delete an application
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "If-Match: *" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/application/579d5781-6e39-4b94-b741-1748d1e14199"
{
"_id": "579d5781-6e39-4b94-b741-1748d1e14199",
"tags": [],
"spa": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"parentalControlSettings": {
"legalAgeGroupRule": "Allow",
"countriesBlockedForMinors": []
},
"api": {
"requestedAccessTokenVersion": 2,
"knownClientApplications": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"preAuthorizedApplications": []
},
"passwordCredentials": [],
"info": {},
"addIns": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"publicClient": {
"redirectUris": []
},
"verifiedPublisher": {},
"identifierUris": [],
"web": {
"implicitGrantSettings": {
"enableAccessTokenIssuance": false,
"enableIdTokenIssuance": false
},
"redirectUris": []
},
"publisherDomain": "example.com",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:40:18Z",
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoles": [],
"appId": "6e26b7a3-53ef-45ea-8492-fed30f1dd2ad",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"requiredResourceAccess": []
}servicePrincipal (MS Graph API)
The servicePrincipal resource type represents an instance of an application in a directory. For more information, refer to the Microsoft Graph documentation.
Query all servicePrincipal objects
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal?_queryFilter=true"
Read a servicePrincipal
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/1c696b95-7f68-4018-b627-6c9601faa80b"
{
"_id": "1c696b95-7f68-4018-b627-6c9601faa80b",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"a293dbaf-ba5d-4692-8898-521a1da51bac"
],
"appId": "a293dbaf-ba5d-4692-8898-521a1da51bac",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Create a servicePrincipal
A servicePrincipal requires an appId.
|
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"appId": "0b9179f4-f617-4ab8-9c33-18a870c76722"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal"
{
"_id": "7d164d58-6210-4c25-84db-d3dfce1171b4",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"0b9179f4-f617-4ab8-9c33-18a870c76722"
],
"appId": "0b9179f4-f617-4ab8-9c33-18a870c76722",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Add a password (client secret) to a servicePrincipal
Adding passwordCredential when creating a servicePrincipal is not supported. You must use the addPassword method to add passwords or secrets to a servicePrincipal.
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/?_action=script&scriptId=addPassword&displayName=TestSecretGenesis&servicePrincipalId=32e18e7a-cb23-4453-b5f4-286bc1a629b8&builtinAction=addPassword"
{
"actions": [
{
"result": {
"secretText": "{GENERATED-CLIENT-SECRET}",
"startDateTime": {
"dateTime": {
"date": {
"month": 5,
"year": 2023,
"day": 5
},
"time": {
"hour": 20,
"nano": 91094000,
"minute": 41,
"second": 8
}
},
"offset": {
"totalSeconds": 0
}
},
"displayName": "TestSecretGenesis",
"hint": "rJn",
"keyId": "862c0883-45ac-4e13-8adc-ce9bf3036570",
"endDateTime": {
"dateTime": {
"date": {
"month": 5,
"year": 2025,
"day": 5
},
"time": {
"hour": 20,
"nano": 91094000,
"minute": 41,
"second": 8
}
},
"offset": {
"totalSeconds": 0
}
}
}
}
]
}Update a servicePrincipal
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[
{
"operation": "replace",
"field": "/appRoleAssignmentRequired",
"value": true
}
]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/7d164d58-6210-4c25-84db-d3dfce1171b4"
{
"_id": "7d164d58-6210-4c25-84db-d3dfce1171b4",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"0b9179f4-f617-4ab8-9c33-18a870c76722"
],
"appId": "0b9179f4-f617-4ab8-9c33-18a870c76722",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": true
}Delete a servicePrincipal
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "If-Match: *" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/1df34a52-3491-4b3a-8ec7-51d77ab50860"
{
"_id": "1df34a52-3491-4b3a-8ec7-51d77ab50860",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"a2179b48-33f0-4933-8c59-39639469bb13"
],
"appId": "a2179b48-33f0-4933-8c59-39639469bb13",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Application permissions (MS Graph API)
Application permissions are also known as app roles or app role assignments. You can grant application permissions directly by adding an app role assignment to an object, such as user, group, or servicePrincipal. For more information about app role assignments, refer to the Microsoft Graph documentation.
|
The following table displays what the different id’s involved in app role assignment represent:
|
Add an app role assignment to a servicePrincipal
| This process is identical for users and groups. |
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__addAppRoleAssignments__": {
"principalId": "05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879",
"resourceId": "b3e4e58e-16fa-4b3d-a7b5-f134b7387e62",
"appRoleId": "df021288-bdef-4463-88db-98f22de89214"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879"
{
"_id": "05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [
{
"resourceDisplayName": "Microsoft Graph",
"resourceId": "b3e4e58e-16fa-4b3d-a7b5-f134b7387e62",
"principalDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleId": "df021288-bdef-4463-88db-98f22de89214",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:41:15.373168300Z",
"principalId": "05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879",
"id": "IZG0BfULnkeKThQCEmSIeS7n5ay2n99BiFNwyj97w8Y",
"principalType": "ServicePrincipal"
}
],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"93dd36a4-61ca-4a1d-89cf-eac96587de35"
],
"appId": "93dd36a4-61ca-4a1d-89cf-eac96587de35",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Remove an app role assignment from a servicePrincipal
| This process is identical for users and groups. |
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__removeAppRoleAssignments__": "IZG0BfULnkeKThQCEmSIeS7n5ay2n99BiFNwyj97w8Y"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879"
{
"_id": "05b49121-0bf5-479e-8a4e-140212648879",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"93dd36a4-61ca-4a1d-89cf-eac96587de35"
],
"appId": "93dd36a4-61ca-4a1d-89cf-eac96587de35",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Add an app role to a principal (user/group/servicePrincipal) via a servicePrincipal
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__addAppRoleAssignedTo__": {
"principalId": "87f5b3f8-6a8c-4e50-8fd6-0467d5e97e0c",
"resourceId": "bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8",
"appRoleId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8"
{
"_id": "bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"62212657-8f49-40b3-874b-9d1c25cb4388"
],
"appId": "62212657-8f49-40b3-874b-9d1c25cb4388",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [
{
"resourceDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"resourceId": "bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8",
"principalDisplayName": "qcmozfwwygkebie",
"appRoleId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"createdDateTime": "2023-05-05T20:41:25.405071800Z",
"principalId": "87f5b3f8-6a8c-4e50-8fd6-0467d5e97e0c",
"id": "-LP1h4xqUE6P1gRn1el-DCzqXtqJH6NBt0Fr0lT0g2g",
"principalType": "User"
}
],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}Remove an app role from a principal (user/group/servicePrincipal) via a servicePrincipal
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__removeAppRoleAssignedTo__": "-LP1h4xqUE6P1gRn1el-DCzqXtqJH6NBt0Fr0lT0g2g"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azuread/servicePrincipal/bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8"
{
"_id": "bf960539-a1d8-4eab-a46e-e9ce0b3f15c8",
"addIns": [],
"replyUrls": [],
"keyCredentials": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"displayName": "Test-Application",
"appRoleAssignments": [],
"alternativeNames": [],
"resourceSpecificApplicationPermissions": [],
"appDisplayName": "Test-Application",
"accountEnabled": true,
"appOwnerOrganizationId": "9e91bf24-7a08-433e-b111-5542416b4f20",
"passwordCredentials": [],
"servicePrincipalNames": [
"62212657-8f49-40b3-874b-9d1c25cb4388"
],
"appId": "62212657-8f49-40b3-874b-9d1c25cb4388",
"signInAudience": "AzureADandPersonalMicrosoftAccount",
"notificationEmailAddresses": [],
"servicePrincipalType": "Application",
"tags": [],
"appRoleAssignedTo": [],
"info": {},
"appRoles": [],
"appRoleAssignmentRequired": false
}MongoDB connector
The MongoDB connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy Connector. This connector lets you interact with a MongoDB document database using Groovy scripts for the ICF operations.
| The MongoDB connector uses Java MongoDB driver v4.5.1. For MongoDB version compatibility information, refer to Compatibility in the MongoDB Documentation. |
Before you start
In a production environment, enable access control on your MongoDB database. If your connector will manage MongoDB users and roles, you must create an administrative user in the admin database. If your connector will manage collections in a database, this administrative user must create a specific user and role for the connector for the target database.
For information about enabling access control in MongoDB, refer to the MongoDB documentation.
The commands in this chapter assume an administrative user named myUserAdmin with password Passw0rd who has the readWrite role on the test database.
Install the MongoDB connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/mongodb-connector-1.5.20.16.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the MongoDB connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select MongoDB Connector - 1.5.20.16.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to MongoDB Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, configure the connector with a configuration file. A sample connector configuration file (provisioner.openicf-mongodb.json) is provided in the /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners directory in IDM. Copy the sample connector configuration to your project’s conf/ directory, and adjust the configurationProperties to match your MongoDB instance:
"configurationProperties" : {
"connectionURI" : "mongodb://localhost:27017",
"host" : "localhost",
"port" : "27017",
"user" : "myUserAdmin",
"password" : "Passw0rd",
"userDatabase" : "admin",
"database" : "test",
...
}Set "enabled" : true to enable the connector.
Test the MongoDB connector
When your connector is configured correctly, you can test its status by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "mongodb",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/mongodb",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.mongodb-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.mongodb.MongoDBConnector"
},
"displayName": "MongoDB Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"account",
"role"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the MongoDB connector can connect to the database.
MongoDB remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the MongoDB connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the MongoDB connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the MongoDB remote connector.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the MongoDB Connector
The MongoDB Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
MongoDB Connector Configuration
The MongoDB Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
The MongoDB client connection URI, for example "mongodb://localhost:27017". Overrides other connection parameters. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The MongoDB server host name. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The MongoDB server port number. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The MongoDB username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The password used to connect to MongoDB. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of the database in which the MongoDB user is defined. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A list of additional mongodbDB servers when connecting to a MongoDB cluster (["host1:27017","host2:27017",…]"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the list of attributes to convert to MongoDB BSON Date type on create/update. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The database to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the list of attributes that should be considered as BSON Arrays. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true, retains null values in the target MongoDB document. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true, retains null values in the target MongoDB document. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the date format to use for MongoDB Date attributes (defaults to ISO 8601 "yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the timezone to use for MongoDB Date attributes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the name to use in the target MongoDB document for the ICF NAME attribute. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Connection Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Use secure socket layer to connect to MongoDB. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines if host name should be validated when SSL is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum idle time for a pooled connection in ms (0 means no limit). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum life time for a pooled connection in ms (0 means no limit). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum number of connections per host (must be >= 0). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of connections per host (must be > 0). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Oracle EBS connector
The Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) connector enables you to manage EBS accounts and synchronize accounts between EBS and the IDM managed user repository.
Before you start
These instructions assume you have an EBS administrator account and access to an Oracle EBS Database. You will need the following information to configure the connector:
- Username
-
Your EBS administrator account username.
- Password
-
Your EBS administrator account password.
- JDBC Connection URL
-
The URL to establish the connection between the connector and the EBS application.
For more information, refer to the Oracle E-Business Suite documentation.
Install the EBS connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/ebs-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Download the Oracle JDBC driver (ojdbc8.jar).
-
If you are running the connector locally, place the library in the
/path/to/openidm/lib/directory:mv ~/Downloads/ojdbc8.jar /path/to/openidm/lib/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place the library in the
/path/to/openicf/libdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the EBS connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select EBS Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to EBS Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the EBS connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS?_action=test&_prettyPrint=true"
{
"name" : "EBS",
"enabled" : true,
"config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/EBS",
"connectorRef" : {
"bundleVersion" : [1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0),
"bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.ebs-connector",
"connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.oracleebs.OracleEbsConnector"
},
"displayName" : "Oracle EBS Connector",
"objectTypes" : [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok" : true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the Oracle EBS server.
EBS remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the EBS connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the EBS connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the EBS remote connector.
Configure Connection Pooling
The EBS connector embeds Tomcat JDBC pool. For more information, refer to Apache Tomcat 9 JDBC Connection Pool.
Attributes
The following attributes are supported by the connector:
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s User ID |
|
The user’s username |
|
The user’s encrypted password |
|
Number of sessions |
|
Start date for the created user |
|
End date for the created user |
|
The user’s description |
|
Last logged on date |
|
The date the current password was set |
|
The number of accesses left for the password |
|
The number of accesses allowed for the password |
|
The number of days allowed for the password |
|
The user’s email address |
|
The user’s fax number |
Use the EBS connector
The EBS connector can perform the following actions:
Create a user
The following example creates a user with all the creatable attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data
'{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Test@123",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER": "2",
"START_DATE": "03-Nov-22",
"END_DATE": "08-Nov-22",
"LAST_LOGON_DATE": "08-DEC-2021",
"PASSWORD_DATE": "08-JUN-2021",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT": "1",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES": "1",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS": "1"
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create&_prettyPrint=true"
{
"_id": "1015488",
"USER_ID": "1015488",
"START_DATE": "03-Nov-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN": 1015131,
"USER_NAME": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER": 2,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE": "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT": 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES": 1,
"END_DATE": "08-Nov-22",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS": 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE": "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE": "02-Dec-22"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least the
|
Query a user by id
The following queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__/1015488?_prettyPrint=true”
{
"_id": "1015488",
"USER_ID": "1015488",
"START_DATE": "03-Nov-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN": 1015131,
"USER_NAME": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER": 7,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE": "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT": 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES": 1,
"END_DATE": "08-Nov-22",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS": 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE": "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DESCRIPTION": "ebsuser",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE": "02-Dec-22"
}
Query all users
The following example queries all users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result":[
{"_id":"1000001"},
{"_id":"3"},
{"_id":"2"},
{"_id":"0"},
{"_id":"1001"},
{"_id":"1555"},
{"_id":"1003"},
{"_id":"1004"},
{"_id":"1005"},
{"_id":"1007"}
],
"resultCount":10,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
}
Update a user
The EBS Connector can modify the following attributes of a user entry:
-
__PASSWORD__ -
__ENABLE__ -
EMAIL_ADDRESS -
START_DATE -
END_DATE
The following example updates a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Test@123",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER": "7",
"START_DATE": "03-Nov-22",
"END_DATE": "08-Nov-22",
"LAST_LOGON_DATE": "08-DEC-2021",
"PASSWORD_DATE": "08-JUN-2021",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT": "1",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES": "1",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS": "1",
"DESCRIPTION": "ebsuser"
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__/1015488?_prettyPrint=true"
{
"_id" : "1015488",
"USER_ID" : "1015488",
"START_DATE" : "03-Nov-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN" : 1015131,
"USER_NAME" : "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__" : false,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER" : 7,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE" : "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT" : 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES" : 1,
"END_DATE" : "08-Nov-22",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS" : 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE" : "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"DESCRIPTION" : "ebsuser",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE" : "02-Dec-22"
}
Reset a user’s password
To reset the password for a user account, update the user’s "__PASSWORD__" attribute:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__": "RRvts125!"
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__/1015488?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "1015488",
"USER_ID" : "1015488",
"START_DATE" : "03-Nov-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN" : 1015131,
"USER_NAME" : "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__" : false,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER" : 7,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE" : "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT" : 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES" : 1,
"END_DATE" : "08-Nov-22",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS" : 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE" : "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DESCRIPTION" : "ebsuser",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE" : "02-Dec-22"
}
Activate a user
The following example activates a user:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__":"BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__":"Rvts12345",
"__ENABLE__": true
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__/1015488?_prettyPrint=true"
{
"_id" : "1015488",
"USER_ID" : "1015488",
"START_DATE" : "02-Dec-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN" : -1,
"USER_NAME" : "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER" : 7,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE" : "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT" : 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES" : 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS" : 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE" : "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"DESCRIPTION" : "ebsuser",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE" : "02-Dec-22"
}
Deactivate a user
The following example deactivates a user:
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__":"BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__":"Rvts12345",
"__ENABLE__": false
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/EBS/__ACCOUNT__/1015488?_prettyPrint=true"
{
"_id" : "1015488",
"USER_ID" : "1015488",
"START_DATE" : "03-Nov-22",
"LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN" : -1,
"USER_NAME" : "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__" : false,
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "bjensen@forgerock.com",
"SESSION_NUMBER" : 7,
"LAST_LOGON_DATE" : "08-Dec-21",
"PASSWORD_ACCESSES_LEFT" : 1,
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_ACCESSES" : 1,
"END_DATE" : "02-Dec-22",
"PASSWORD_LIFESPAN_DAYS" : 1,
"PASSWORD_DATE" : "08-Jun-21",
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"DESCRIPTION" : "ebsuser",
"LAST_UPDATE_DATE" : "02-Dec-22"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Oracle EBS Connector
The Oracle EBS Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Oracle EBS Connector Configuration
The Oracle EBS Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection properties that will be sent to our JDBC driver when establishing new connections. Format of the string must be [propertyName=property;]* NOTE - The "user" and "password" properties will be passed explicitly, so they do not need to be included here. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to propagate the interrupt state for a thread that has been interrupted (not clearing the interrupt state). Default value is false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The SQL query that will be used to validate connections from this pool before returning them to the caller. If specified, this query does not have to return any data, it just cant throw a SQLException. The default value is null. Example values are SELECT 1(mysql), select 1 from dual(oracle), SELECT 1(MS Sql Server). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can terminate the transaction by calling rollback on the connection as it is returned to the pool Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true if you wish to put a facade on your connection so that it cannot be reused after it has been closed. This prevents a thread holding on to a reference of a connection it has already called closed on, to execute queries on it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default catalog of connections created by this pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
To avoid excess validation, run validation at most at this frequency (in milliseconds). If a connection is due for validation, but was validated within this interval, it will not be validated again. The default value is 3000 (3 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag whether ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to true if you want to ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to false if you want to fail the initialization of the pool by throwing exception. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Register the pool with JMX or not. The default value is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can complete the transaction by calling commit on the connection as it is returned to the pool If rollbackOnReturn==true then this attribute is ignored. Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to log stack traces for application code which abandoned a Connection. Logging of abandoned Connections adds overhead for every Connection borrow because a stack trace has to be generated. The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
By default, the jdbc-pool will ignore the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, and simply return a previously pooled connection under the globally configured properties username and password, for performance reasons. The pool can however be configured to allow use of different credentials each time a connection is requested. To enable the functionality described in the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, simply set the property alternateUsernameAllowed to true. Should you request a connection with the credentials user1/password1 and the connection was previously connected using different user2/password2, the connection will be closed, and reopened with the requested credentials. This way, the pool size is still managed on a global level, and not on a per schema level. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of a class which implements the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.Validator interface and provides a no-arg constructor (may be implicit). If specified, the class will be used to create a Validator instance which is then used instead of any validation query to validate connections. The default value is null. An example value is com.mycompany.project.SimpleValidator. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. Idle connections are checked periodically (if enabled) and connections that have been idle for longer than minEvictableIdleTimeMillis are released. The default value is derived from maxActive:100. (Also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated by the idle object evictor (if any). If an object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false and this property has to be set in order for the pool cleaner/test thread is to run (also see timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to remove abandoned connections if they exceed the removeAbandonedTimeout. If set to true a connection is considered abandoned and eligible for removal if it has been in use longer than the removeAbandonedTimeout Setting this to true can recover db connections from applications that fail to close a connection. See also logAbandoned The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout value in seconds. Similar to to the removeAbandonedTimeout value but instead of treating the connection as abandoned, and potentially closing the connection, this simply logs the warning if logAbandoned is set to true. If this value is equal or less than 0, no suspect checking will be performed. Suspect checking only takes place if the timeout value is larger than 0 and the connection was not abandoned or if abandon check is disabled. If a connection is suspect a WARN message gets logged and a JMX notification gets sent once. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish the ProxyConnection class to use String.equals and set to false when you wish to use == when comparing method names. This property does not apply to added interceptors as those are configured individually. The default value is true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout in seconds before an abandoned(in use) connection can be removed. The default value is 60 (60 seconds). The value should be set to the longest running query your applications might have. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default auto-commit state of connections created by this pool. If not set, default is JDBC driver default (If not set then the setAutoCommit method will not be called). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns true if we should run the validation query when connecting to the database for the first time on a connection. Normally this is always set to false, unless one wants to use the validationQuery as an init query. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connections that have been abandoned (timed out) wont get closed and reported up unless the number of connections in use are above the percentage defined by abandonWhenPercentageFull. The value should be between 0-100. The default value is 0, which implies that connections are eligible for closure as soon as removeAbandonedTimeout has been reached. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A semicolon separated list of classnames extending org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.JdbcInterceptor class. See Configuring JDBC interceptors below for more detailed description of syntaz and examples. These interceptors will be inserted as an interceptor into the chain of operations on a java.test_sample.Connection object. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum number of established connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. The connection pool can shrink below this number if validation queries fail. The default value is derived from initialSize:10. (Also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default read-only state of connections created by this pool. If not set then the setReadOnly method will not be called. (Some drivers dont support read only mode, ex: Informix). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The initial number of connections that are created when the pool is started. Default value is 10. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before throwing an exception. Default value is 30000 (30 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default TransactionIsolation state of connections created by this pool. One of the following: NONE, READ_COMMITTED, READ_UNCOMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE If not set, the method will not be called and it defaults to the JDBC driver. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used in tomcat-jdbc-pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The URL used to connect to the database. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool, and we will attempt to borrow another. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. In order to have a more efficient validation, see validationInterval. Default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish that calls to getConnection should be treated fairly in a true FIFO fashion. This uses the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue implementation for the list of the idle connections. The default value is true. This flag is required when you want to use asynchronous connection retrieval. Setting this flag ensures that threads receive connections in the order they arrive. During performance tests, there is a very large difference in how locks and lock waiting is implemented. When fairQueue=true there is a decision making process based on what operating system the system is running. If the system is running on Linux (property os.name=Linux. To disable this Linux specific behavior and still use the fair queue, simply add the property org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue.ignoreOS=true to your system properties before the connection pool classes are loaded. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to log errors during the validation phase to the log file. If set to true, errors will be logged as SEVERE. Default value is false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used. Access can be achieved by calling unwrap on the pooled connection. see javax.test_sample.DataSource interface, or call getConnection through reflection or cast the object as javax.test_sample.PooledConnection. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Time in milliseconds to keep this connection. When a connection is returned to the pool, the pool will check to see if the now - time-when-connected > maxAge has been reached, and if so, it closes the connection rather than returning it to the pool. The default value is 0, which implies that connections will be left open and no age check will be done upon returning the connection to the pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum amount of time an object may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction. The default value is 60000 (60 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle connection validation/cleaner thread. This value should not be set under 1 second. It dictates how often we check for idle, abandoned connections, and how often we validate idle connections. The default value is 5000 (5 seconds). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being returned to the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. The default value is false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The fully qualified Java class name of the JDBC driver to be used. The driver has to be accessible from the same classloader as tomcat-jdbc.jar. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns the name of the connection pool. By default a JVM unique random name is assigned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns true if this connection pool is configured to wrap statements in order to enable equals() and hashCode() methods to be called on the closed statements if any statement proxy is set. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Return true if a lock should be used when operations are performed on the connection object. Should be set to false unless you plan to have a background thread of your own doing idle and abandon checking such as JMX clients. If the pool sweeper is enabled, then the lock will automatically be used regardless of this setting. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A custom query to be run when a connection is first created. The default value is null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated from this pool at the same time. The default value is 100. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection username to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The timeout in seconds before a connection validation queries fail. This works by calling java.test_sample.Statement.setQueryTimeout(seconds) on the statement that executes the validationQuery. The pool itself doesnt timeout the query, it is still up to the JDBC driver to enforce query timeouts. A value less than or equal to zero will disable this feature. The default value is -1. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Oracle EBS login password to authenticate the user. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Page size of search. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
PeopleSoft connector
The PeopleSoft connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between Oracle PeopleSoft and IDM managed user objects. A PeopleSoft administrator account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your PeopleSoft administrator account and note the following:
- Host
-
The host address of the PeopleSoft instance.
- Port
-
The port for the PeopleSoft instance.
- User ID
-
The username to log into the PeopleSoft instance.
- Password
-
The password to log into the PeopleSoft instance.
- Domain Connect Password
-
The domain connection password for the PeopleSoft WebLogic application server.
Install the PeopleSoft connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/peoplesoft-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Download the connector dependencies.
-
psjoa.jaris a file unique to each installation of PeopleSoft. It is compiled and provided by your PeopleSoft administrator. If it is not provided to you, refer to Generatepsjoa.jar -
psft.jaris generated by the following commands:set CLASSPATH=%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar;%CLASSPATH% jar cvf psft.jar .\PeopleSoft\Generated\CompIntfc*.class
Generate psjoa.jar
This procedure is only required if your PeopleSoft Administrator did not provide psjoa.jar.
|
-
Start PeopleSoft Application Designer, and open any Component Interface definition.
-
Select Build > PeopleSoft APIs.
The Build PeopleSoft API Bindings window displays.
-
Under the Java Classes group box, select Build, and specify a target directory.
-
To build the selected bindings, click OK.
The app builds the selected bindings in the specified directory. If the operation is successful, a Done message appears in the PeopleSoft Application Designer Build window.
-
Compile the generated APIs:
cd %PS_HOME%\class\PeopleSoft\Generated\CompIntfc javac −classpath %PS_HOME%\class\psjoa.jar *.java cd c:\pt8\class\PeopleSoft\ Generated\ PeopleSoft javac −classpath %PS_HOME%\class\psjoa.jar *.java
cd $PS_HOME/class/PeopleSoft/Generated/CompIntfc javac classpath $PS_HOME/class/psjoa.jar *.java cd $PS_HOME/class/PeopleSoft/Generated/PeopleSoft javac classpath $PS_HOME/class/psjoa.jar *.java
-
Copy
psjoa.jarand generated jar into/path/to/openicf/lib.
Configure the PeopleSoft connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select PeopleSoft Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to PeopleSoft Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the PeopleSoft connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft?_action=test"
{
"name": "peoplesoft",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/peoplesoft",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.peoplesoft-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.peoplesoft.PeopleSoftConnector"
},
"displayName": "PeopleSoft Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the PeopleSoft system.
PeopleSoft remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the PeopleSoft connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the PeopleSoft connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the PeopleSoft remote connector.
Use the PeopleSoft connector
The following PeopleSoft account attributes are supported by the PeopleSoft connector:
| Attribute | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The name of the user. Required. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ID of the user. Required. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The type of ID and ID value for the user. Required. This is an object, containing
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Alias ID of the user. This should be a fully qualified email address. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A description of the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Primary permission list for the user. Displays which permissions the user is granted in the primary permission list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Row security permission list for the user. Displays which permissions the user is granted in the row security permission list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Process profile permission list for the user. Displays which permissions the user is granted in the process profile permission list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Navigator home permission list for the user. Displays which permissions the user is granted in the navigator home permission list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The symbolic ID of the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The user’s language preference.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enable support for multiple languages for the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Whether the user account is locked. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three letter code for the user’s preferred currency. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The number of failed logins for the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Whether the user is marked as an expert. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The type of operation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Determines whether the user has access to user switching. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number of worklist entries associated with the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Whether there is a worklist associated with the user. Must be either |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Email preference of the user. Must be either |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fallback user to route to if the user is unavailable. This must be filled out if you specify |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Effective start date that a user will be unavailable. Must be in |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Effective end date, marking when a user will become available again. Must be in |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of email addresses associated with the user. This is an object, with
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of roles the user has. Users inherit permissions based on the roles the user has. This is an object, with |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The password for the user. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Used to confirm the password of the user. This needs to match the user’s password. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Status showing whether or not the user profile is encrypted. |
Operations on PeopleSoft accounts
You can use the PeopleSoft connector to perform the following actions on a PeopleSoft account:
Create a PeopleSoft user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"IDTypes": [{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "Y",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "Y",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least |
Update a PeopleSoft user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. The following attributes can be modified on a user:
-
UserIDAlias -
UserDescription -
PrimaryPermissionList -
RowSecurityPermissionList -
ProcessProfilePermissionList -
NavigatorHomePermissionList -
SymbolicID -
LanguageCode -
MultiLanguageEnabled -
AccountLocked -
CurrencyCode -
FailedLogins -
ExpertEntry -
Opertype -
AllowSwitchUser -
WorklistUser -
EmailUser -
AlternateUserID -
EffectiveDateFrom -
EffectiveDateTo -
EmailAddresses -
Roles -
IDTypes -
Password -
ConfirmPassword -
Encrypted
For example, to update the EmailAddresses for a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"IDTypes": [{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}],
"EmailAddresses": [{
"EmailType":"BUS",
"EmailAddress":"test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail":"Y"
}]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "Y",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "Y",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
Query PeopleSoft users
The following example queries all PeopleSoft users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "AZIGLAR"
},
{
"_id": "BCHALMERS"
},
{
"_id": "BDAVIS"
},
{
"_id": "BFRANCISCO"
},
{
"_id": "BGONZALES"
},
{
"_id": "BJENSEN"
},
{
"_id": "BLOCHERTY"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "SUNDERWOOD"
},
{
"_id": "SVANDERSTEEN"
},
{
"_id": "SWALTERS"
},
{
"_id": "TCORY"
},
{
"_id": "TELLIS"
}
],
"resultCount": 300,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "Y",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "Y",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
Reset a PeopleSoft user account password
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__CURRENT_PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "Y",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "Y",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
|
While the |
Enable a PeopleSoft user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": 1
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "N",
"__ENABLE__": 1,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "N",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
Disable a PeopleSoft user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"__ENABLE__": 0
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "N",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "N",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
Delete a PeopleSoft user account
You can use the PeopleSoft connector to delete an account from the PeopleSoft service.
The following example deletes an PeopleSoft account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"ExpertEntry": 0,
"LanguageCode": "ENG",
"EmailUser": "N",
"__ENABLE__": 0,
"__NAME__": "Barbara Jensen",
"IDTypes": [
{
"IDType": "EMP",
"AttributeValue": "0001"
}
],
"Encrypted": 1,
"EmailAddresses": [
{
"EmailType": "BUS",
"EmailAddress": "test@example.com",
"PrimaryEmail": "Y"
}
],
"UserID": "BJENSEN",
"Opertype": 0,
"MultiLanguageEnabled": 0,
"WorklistUser": "N",
"WorklistEntriesCount": 0,
"AllowSwitchUser": 0,
"FailedLogins": 0
}
Operations on other objects
The following operations are supported for other objects, including Employee, Permission, External Job Applicant, and Role:
Query all employees
The following example queries all employees' details:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__EMPLOYEE__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id":"0001"},
{"_id":"21"},
{"_id":"22"},
{"_id":"25"},
{"_id":"AA0001"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single employee
The following example queries a single employee’s details:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__EMPLOYEE__/BJENSEN?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"LAST_NAME" : "Jensen",
"PROP_DERIVED_EMP" : "N",
"COLL_NAME_TYPE_VW" : [ {
"KEYPROP_NAME_TYPE" : "PRI",
"FIRST_NAME" : "Barbara",
"LAST_NAME" : "Jensen"
}, {
"KEYPROP_NAME_TYPE" : "PRF",
"FIRST_NAME" : "Barbara",
"LAST_NAME" : "Jensen"
} ],
"PROP_NAME" : "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__" : "BJENSEN",
"COLL_ADDRESS_TYPE_VW" : [ {
"KEYPROP_ADDRESS_TYPE" : "",
"KEYPROP_EFFDT" : "11/14/2022",
"PROP_EFF_STATUS" : "A",
"PROP_COUNTRY" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS1" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS2" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS3" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS4" : "",
"PROP_CITY" : "",
"PROP_NUM1" : "",
"PROP_NUM2" : "",
"PROP_HOUSE_TYPE" : "",
"PROP_ADDR_FIELD1" : "",
"PROP_ADDR_FIELD2" : "",
"PROP_ADDR_FIELD3" : "",
"PROP_COUNTY" : "",
"PROP_STATE" : "",
"PROP_POSTAL" : "",
"PROP_GEO_CODE" : "",
"PROP_IN_CITY_LIMIT" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS1_AC" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS2_AC" : "",
"PROP_ADDRESS3_AC" : "",
"PROP_CITY_AC" : "",
"PROP_REG_REGION" : ""
} ],
"COLL_PERSONAL_PHONE" : [ {
"KEYPROP_PHONE_TYPE" : "",
"PROP_COUNTRY_CODE" : "",
"PROP_PHONE" : "",
"PROP_EXTENSION" : "",
"PROP_PREF_PHONE_FLAG" : "N"
} ],
"COLL_EMAIL_ADDRESSES" : [ {
"KEYPROP_E_ADDR_TYPE" : "",
"PROP_EMAIL_ADDR" : "",
"PROP_PREF_EMAIL_FLAG" : "N"
} ]
}
Query all permissions
The following example queries all employee permissions:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__PERMISSION__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id":"11"},
{"_id":"CI_PERSONAL_DATA"},
{"_id":"CRM8000"},
{"_id":"CRRW1000"},
{"_id":"EOCB_CLIENT_USER"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single permission
The following example queries a single permission’s details:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__PERMISSION__/HCCPCSALL?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "HCCPCSALL",
"__UID__" : "HCCPCSALL",
"__NAME__" : "Campus - Hidden Objects",
"KEYPROP_CLASSID" : "HCCPCSALL"
}
Query all external job applicants
The following example queries all external job applicants:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__EXTERNAL_JOB_APPLICANT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id":"500000"},
{"_id":"500001"},
{"_id":"500002"},
{"_id":"500003"},
{"_id":"500004"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single external job applicant
The following example queries a single external job applicant’s details:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__EXTERNAL_JOB_APPLICANT__/500258?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "500258",
"__NAME__" : "500258",
"__UID__" : "500258"
}
Query all roles
The following example queries all employee roles:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ROLE__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id":"ACM Administrator"},
{"_id":"ADS Designer"},
{"_id":"AG Composer Administrator"},
{"_id":"AG Composer User"},
{"_id":"AM Administrator"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single role
The following example queries a single role’s details:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/peoplesoft/__ROLE__/HR%20Matrix%20Manager?_prettyprint=true"
{
"_id" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"PSROLEGRANTORVW" : [ {
"GRANTROLENAME" : "",
"ROLENAME" : "HR Matrix Manager"
} ],
"PC_FUNCTION_NAME" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"__UID__" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"DESCRLONG" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"ALLOWNOTIFY" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"ROLE_PCODE_RULE_ON" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"__NAME__" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"PSROLECANGRANT" : [ {
"GRANTROLENAME" : "",
"ROLENAME" : "HR Matrix Manager"
} ],
"DESCR" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"QRYNAME" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"ROLE_QUERY_RULE_ON" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"RECNAME" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"FIELDNAME" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"PSROLEMEMBER" : [ {
"ROLEUSER" : "",
"ROLENAME" : "HR Matrix Manager"
} ],
"PSROLEDYNMEMBER" : [ {
"ROLEUSER" : "",
"ROLENAME" : "HR Matrix Manager"
} ],
"ALLOWLOOKUP" : "HR Matrix Manager",
"PSROLECLASS" : [ {
"CLASSID" : "HCCPHR9435"
} ],
"LDAP_RULE_ON" : "HR Matrix Manager"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the PeopleSoft Connector
The PeopleSoft Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
PeopleSoft Connector Configuration
The PeopleSoft Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Host name or IP address to connect to PeopleSoft server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Port to connect to PeopleSoft server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The userid used to login to PeopleSoft server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The password used to login to PeopleSoft server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The password for PeopleSoft app server domain. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
PingOne connector
The PingOne connector lets you manage and synchronize data between PingOne and IDM and Identity Cloud. A PingOne administrator account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your PingOne administrator account and note the following:
- Username
-
The username used to log in to PingOne.
- Password
-
The password used to log in to PingOne.
- Environment ID
-
The PingOne environment ID for your organization.
Install the PingOne connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/pingone-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the PingOne connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select PingOne Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to PingOne Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Example PingOne configuration
This excerpt shows a sample PingOne connector configuration:
{
"connectorRef" : {
"displayName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.pingone.PingOneConnector",
"bundleVersion" : "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"systemType" : "provisioner.openicf",
"bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.pingone-connector",
"connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.pingone.PingOneConnector",
"connectorHostRef" : ""
},
"poolConfigOption" : {
"maxObjects" : 10,
"maxIdle" : 10,
"maxWait" : 150000,
"minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" : 120000,
"minIdle" : 1
},
"resultsHandlerConfig" : {
"enableNormalizingResultsHandler" : false,
"enableFilteredResultsHandler" : false,
"enableCaseInsensitiveFilter" : false,
"enableAttributesToGetSearchResultsHandler" : true
},
"operationTimeout" : {
"CREATE" : -1,
"UPDATE" : -1,
"DELETE" : -1,
"TEST" : -1,
"SCRIPT_ON_CONNECTOR" : -1,
"SCRIPT_ON_RESOURCE" : -1,
"GET" : -1,
"RESOLVEUSERNAME" : -1,
"AUTHENTICATE" : -1,
"SEARCH" : -1,
"VALIDATE" : -1,
"SYNC" : -1,
"SCHEMA" : -1
},
"configurationProperties" : {
"environmentId" : null,
"serviceUri" : null,
"login" : null,
"password" : null,
"authenticationMethod" : "OAUTH",
"tokenEndpoint" : null,
"clientId" : null,
"clientSecret" : null,
"authToken" : null,
"acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : false,
"disableHostNameVerifier" : false,
"disableHttpCompression" : false,
"clientCertAlias" : null,
"clientCertPassword" : null,
"maximumConnections" : 10,
"httpProxyHost" : null,
"httpProxyPort" : null,
"httpProxyUsername" : null,
"httpProxyPassword" : null,
"connectionTimeout" : 30,
"refreshToken" : null,
"grantType" : null,
"scope" : null,
"authorizationTokenPrefix" : "Bearer",
"useBasicAuthForOauthTokenNeg" : true
},
"enabled" : true,
"objectTypes" : {
"__GROUP__" : {
"$schema" : "http://json-schema.org/draft-03/schema",
"id" : "__GROUP__",
"type" : "object",
"nativeType" : "__GROUP__",
...
}
},
"__POPULATION__" : {
"$schema" : "http://json-schema.org/draft-03/schema",
"id" : "__POPULATION__",
"type" : "object",
"nativeType" : "__POPULATION__",
...
}
},
"__ACCOUNT__" : {
"$schema" : "http://json-schema.org/draft-03/schema",
"id" : "__ACCOUNT__",
"type" : "object",
"nativeType" : "__ACCOUNT__",
...
}
},
"__AVAILABLE_ROLE__" : {
"$schema" : "http://json-schema.org/draft-03/schema",
"id" : "__AVAILABLE_ROLE__",
"type" : "object",
"nativeType" : "__AVAILABLE_ROLE__",
...
}
},
"__ROLE__" : {
"$schema" : "http://json-schema.org/draft-03/schema",
"id" : "__ROLE__",
"type" : "object",
"nativeType" : "__ROLE__",
...
}
}
}
}Test the PingOne connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone?_action=test"
{
"name": "pingone",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/pingone",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.pingone-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.pingone.PingOneConnector"
},
"displayName": "PingOne Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__GROUP__",
"__POPULATION__",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__",
"__AVAILABLE_ROLE__",
"__ROLE__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the PingOne environment.
PingOne remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the PingOne connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the PingOne connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the PingOne remote connector.
Implementation specifics
Any sync mapping that uses PingOne as the source or target must include the following in the mapping configuration:
The default recon query page size for IDM and Identity Cloud is too large for PingOne resources. You must set the source and target to 1000 or less. For example:
{
"reconSourceQueryPageSize" : 1000,
"reconTargetQueryPageSize" : 1000,
...
}For more information about sync mappings, refer to:
Use the PingOne connector
You can use the PingOne connector to perform various actions on the following PingOne resources:
| Connector resource | PingOne resource type |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Users
Create a PingOne user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"username": "A_20240223183659857",
"nickname": "A_2024022",
"email": "A_20240223183659857@example.com",
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "dc3c02ab-5a22-4537-b5cb-7f3a0c164ab1",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:01.889Z",
"email": "A_20240223183659857@example.com",
"__NAME__": "A_20240223183659857",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "A_20240223183659857",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:01.889Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "A_2024022",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least the |
Create a PingOne user with group memberships and role assignments
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"username": "20240223183659857_gm",
"nickname": "2024022318",
"email": "20240223183659857_gm@example.com",
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"__groupMemberships__": [
"336c9e3e-5480-4f32-8706-ccd944531286",
"aa4c33a9-6726-4526-b70f-7cd63fce5c28"
],
"__roleAssignments__": [
"9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2",
"9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:ce00e15f-f845-4df1-abf3-fdc4ff4e176c"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "e9c4a878-d26d-4a2e-9da7-3d83b5d6a8b9",
"__groupMemberships__": [
"336c9e3e-5480-4f32-8706-ccd944531286",
"aa4c33a9-6726-4526-b70f-7cd63fce5c28"
],
"__roleAssignments__": [
"9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2",
"9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:ce00e15f-f845-4df1-abf3-fdc4ff4e176c"
],
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:09.365Z",
"email": "20240223183659857_gm@example.com",
"__NAME__": "20240223183659857_gm",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "20240223183659857_gm",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:09.967Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "2024022318",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
},
"groupMemberships": [
{
"name": "20240223183659857_A",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"id": "336c9e3e-5480-4f32-8706-ccd944531286",
"isExternal": false,
"type": "DIRECT"
},
{
"name": "20240223183659857_B",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"id": "aa4c33a9-6726-4526-b70f-7cd63fce5c28",
"isExternal": false,
"type": "DIRECT"
}
],
"roleAssignments": [
{
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"role": {
"id": "0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2"
},
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e",
"type": "ENVIRONMENT"
},
"readOnly": false,
"id": "2c48fdd6-fec3-47f6-80d7-c993bafc8802",
"type": "DIRECT",
"user": {
"id": "fd5e0c14-ba9b-479b-85f8-80ac9222cc97"
}
},
{
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"role": {
"id": "ce00e15f-f845-4df1-abf3-fdc4ff4e176c"
},
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e",
"type": "ENVIRONMENT"
},
"readOnly": false,
"id": "c5eda229-fdc7-4e4a-b887-833b53b3ec87",
"type": "DIRECT",
"user": {
"id": "fd5e0c14-ba9b-479b-85f8-80ac9222cc97"
}
}
]
}
Update a PingOne user
To modify an existing user, include all user attributes in the PUT request. The following user attributes can’t be modified:
-
population -
mfaEnabled -
verifyStatus -
identityProvider -
linkedAccounts
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"username": "A_20240223183659857",
"nickname": "A_2024022",
"email": "update@email.com",
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__/4da38ae8-50dc-4555-9c76-6d2f9a984007"
{
"_id": "4da38ae8-50dc-4555-9c76-6d2f9a984007",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:04.668Z",
"email": "update@email.com",
"__NAME__": "A_20240223183659857",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "C_20240223183659857",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:05.866Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "A_2024022",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
}
Query all PingOne user IDs
The following example queries all PingOne users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "ffc979b8-6279-4cb9-b327-98db745ff60b"
},
{
"_id": "e0e0258a-87de-43c5-8e25-91915959317d"
},
...
],
"resultCount": 5,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read all PingOne users
The following example reads all PingOne users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "ffc979b8-6279-4cb9-b327-98db745ff60b",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:35:33.304Z",
"email": "OCPSGYHOARDL@example.com",
"__NAME__": "OCPSGYHOARDL",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "OCPSGYHOARDL",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:35:33.304Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "OCPSGY",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
},
{
"_id": "e0e0258a-87de-43c5-8e25-91915959317d",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:35:34.219Z",
"email": "FQHCIODRAYIK@example.com",
"__NAME__": "FQHCIODRAYIK",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "FQHCIODRAYIK",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:35:34.219Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "FQHCIO",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
},
...
],
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read a single PingOne user
The following example reads PingOne user dfdb1068-174c-4c05-8a73-8c91e3f20f83:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__/dfdb1068-174c-4c05-8a73-8c91e3f20f83"
{
"_id": "dfdb1068-174c-4c05-8a73-8c91e3f20f83",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:06.471Z",
"email": "D_20240223183659857@example.com",
"__NAME__": "D_20240223183659857",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "D_20240223183659857",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:06.471Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "D_2024022",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
}
Delete a PingOne user
The following example deletes a PingOne account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ACCOUNT__/dfdb1068-174c-4c05-8a73-8c91e3f20f83"
{
"_id": "dfdb1068-174c-4c05-8a73-8c91e3f20f83",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:06.471Z",
"email": "D_20240223183659857@example.com",
"__NAME__": "D_20240223183659857",
"identityProvider": {
"type": "PING_ONE"
},
"primaryPhone": "123 123 123",
"enabled": true,
"lifecycle": {
"status": "ACCOUNT_OK"
},
"verifyStatus": "NOT_INITIATED",
"username": "D_20240223183659857",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:37:06.471Z",
"mfaEnabled": true,
"nickname": "D_2024022",
"account": {
"canAuthenticate": true,
"status": "OK"
},
"population": {
"id": "1a0348b5-c6f5-41b0-a71a-194ed76f703f"
}
}
Groups
Create a group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--data '{
"name": "A_20240223183647490",
"description": "standard description"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__GROUP__?_action=create'
{
"_id": "bb6534d0-39a0-4e8e-b4b1-efe595063540",
"directMemberCounts": {
"users": 0,
"groups": 0
},
"__NAME__": "A_20240223183647490",
"name": "A_20240223183647490",
"description": "standard description"
}
|
When you create a new group, you must specify at least the |
Query all group IDs
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "c42b514f-56c9-4c63-a91c-679d006ac248"
},
{
"_id": "bb6534d0-39a0-4e8e-b4b1-efe595063540"
},
{
"_id": "1ce940ce-dde6-4066-8869-9435072c4089"
},
...
],
"resultCount": 14,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Query a specific group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__GROUP__/c42b514f-56c9-4c63-a91c-679d006ac248"
{
"_id": "c42b514f-56c9-4c63-a91c-679d006ac248",
"directMemberCounts": {
"users": 0,
"groups": 0
},
"__NAME__": "PY_GROUP_20240223183647490",
"name": "PY_GROUP_20240223183647490",
"description": "standard description"
}
Update a group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'If-Match: *' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"name": "C_20240223183647490",
"description": "updated description"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__GROUP__/bb6534d0-39a0-4e8e-b4b1-efe595063540'
{
"_id": "bb6534d0-39a0-4e8e-b4b1-efe595063540",
"directMemberCounts": {
"users": 0,
"groups": 0
},
"__NAME__": "A_20240223183647490",
"name": "A_20240223183647490",
"description": "updated description"
}
Delete a group
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request DELETE \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__GROUP__/1ce940ce-dde6-4066-8869-9435072c4089'
{
"_id": "1ce940ce-dde6-4066-8869-9435072c4089",
"directMemberCounts": {
"users": 0,
"groups": 0
},
"__NAME__": "D_20240223183647490",
"name": "D_20240223183647490",
"description": "standard description"
}
Populations
A PingOne population defines a particular set of users.
Create a population
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--data '{
"name": "C_20240223183654888",
"description": "standard description"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__POPULATION__?_action=create'
{
"_id": "e40936b4-36ec-4250-96dd-1c37ee8773e5",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:56.710Z",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"description": "standard description",
"default": "false",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:56.710Z",
"name": "C_20240223183654888",
"userCount": 0,
"__NAME__": "C_20240223183654888"
}
|
When you create a new population, you must specify at least the |
Read a single population
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__POPULATION__/e40936b4-36ec-4250-96dd-1c37ee8773e5"
{
"_id": "e40936b4-36ec-4250-96dd-1c37ee8773e5",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:56.710Z",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"description": "standard description",
"default": "false",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:56.710Z",
"name": "C_20240223183654888",
"userCount": 0,
"__NAME__": "C_20240223183654888"
}
Update a population
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'If-Match: *' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"name": "C_20240223183654888",
"description": "updated description"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__POPULATION__/e40936b4-36ec-4250-96dd-1c37ee8773e5'
{
"_id": "e40936b4-36ec-4250-96dd-1c37ee8773e5",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:56.710Z",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"description": "updated description",
"default": "false",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:57.125Z",
"name": "C_20240223183654888",
"userCount": 0,
"__NAME__": "C_20240223183654888"
}
Delete a population
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'If-Match: *' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request DELETE \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__POPULATION__/93c83bc9-a546-4728-bd1f-f75a6436616c'
{
"_id": "93c83bc9-a546-4728-bd1f-f75a6436616c",
"createdAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:57.463Z",
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"description": "standard description",
"default": "false",
"updatedAt": "2024-02-24T02:36:57.463Z",
"name": "D_20240223183654888",
"userCount": 0,
"__NAME__": "D_20240223183654888"
}
Roles
Read all roles
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ROLE__?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "1813bc13-8d13-4e88-a825-d40bfe82777b",
"applicableTo": [
"ORGANIZATION"
],
"name": "Organization Admin",
"description": "Organization Admin",
"permissions": [
{
"id": "advancedservices:read:config",
"classifier": "config",
"description": "Retrieve PingOne Advanced Services customer configuration"
},
{
"id": "authz:update:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Update PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "pingintelligence:create:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Creates a Orchestration flow for Ping Intelligence deployment"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Read PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Create a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:test:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Test a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Create a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:recentdecisions",
"classifier": "recentdecisions",
"description": "Read Recent Decisions of a PingOne Authorize Decision Endpoint"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:read:organization",
"classifier": "organization",
"description": "Read organizations"
},
{
"id": "pingenterprise:update:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Updates Orchestration flow for Ping Enterprise deployment"
},
...
],
"__NAME__": "Organization Admin"
},
...
],
"resultCount": 13,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read a single role
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__ROLE__/1813bc13-8d13-4e88-a825-d40bfe82777b"
{
"_id": "1813bc13-8d13-4e88-a825-d40bfe82777b",
"applicableTo": [
"ORGANIZATION"
],
"name": "Organization Admin",
"description": "Organization Admin",
"permissions": [
{
"id": "advancedservices:read:config",
"classifier": "config",
"description": "Retrieve PingOne Advanced Services customer configuration"
},
{
"id": "authz:update:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Update PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "pingintelligence:create:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Creates a Orchestration flow for Ping Intelligence deployment"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Read PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Create a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:test:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Test a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Create a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:recentdecisions",
"classifier": "recentdecisions",
"description": "Read Recent Decisions of a PingOne Authorize Decision Endpoint"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:read:organization",
"classifier": "organization",
"description": "Read organizations"
},
{
"id": "pingenterprise:update:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Updates Orchestration flow for Ping Enterprise deployment"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Read a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:test:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Test a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "pingenterprise:create:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Creates a Orchestration flow for Ping Enterprise deployment"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:read:environment",
"classifier": "environment",
"description": "Read environments"
},
{
"id": "authz:update:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Update a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "pingintelligence:update:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Updates Orchestration flow for Ping Intelligence deployment"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:read:deployment",
"classifier": "deployment",
"description": "Read deployment resource"
},
{
"id": "authz:update:tag",
"classifier": "tag",
"description": "Create and Update PingOne Authorize Policy Version Tag"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:decisionendpoint",
"classifier": "decisionendpoint",
"description": "Create PingOne Authorize Decision Endpoint"
},
{
"id": "advancedservices:delete:environment",
"classifier": "environment",
"description": "Delete PingOne Advanced Services environment"
},
{
"id": "authz:create:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Create PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "authz:test:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Test PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:condition",
"classifier": "condition",
"description": "Delete a PingOne Authorize Condition"
},
{
"id": "authz:update:decisionendpoint",
"classifier": "decisionendpoint",
"description": "Update PingOne Authorize Decision Endpoint"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:entity",
"classifier": "entity",
"description": "Delete PingOne Authorize Entity"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:update:environment",
"classifier": "environment",
"description": "Update environment"
},
{
"id": "integrations:read:integration",
"classifier": "integration",
"description": "Read an integration in integration catalog"
},
{
"id": "authz:read:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Read a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "authz:authorize:decisionendpoint",
"classifier": "decisionendpoint",
"description": "Request Decision from a PingOne Authorize Decision Endpoint"
},
{
"id": "visualization:create:exploration",
"classifier": "exploration",
"description": "Create data exploration"
},
{
"id": "bootstrap:read:bootstrap",
"classifier": "bootstrap",
"description": "Read bootstrap"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:service",
"classifier": "service",
"description": "Delete a PingOne Authorize Service"
},
{
"id": "visualization:read:template",
"classifier": "template",
"description": "Read data exploration template"
},
{
"id": "pingenterprise:read:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Retrieve Orchestration flow for Ping Enterprise deployment"
},
{
"id": "ratelimiting:read:rateLimits",
"classifier": "rateLimits",
"description": "Read rate limits"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:attribute",
"classifier": "attribute",
"description": "Delete a PingOne Authorize Attribute"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:adaptiveTrustPolicy",
"classifier": "adaptiveTrustPolicy",
"description": "Delete a PingOne Adaptive Trust Policy"
},
{
"id": "pingenterprise:delete:orchestration",
"classifier": "orchestration",
"description": "Deletes Orchestration flow for Ping Enterprise deployment"
},
{
"id": "visualization:read:exploration",
"classifier": "exploration",
"description": "Read data exploration"
},
{
"id": "authz:delete:processor",
"classifier": "processor",
"description": "Delete a PingOne Authorize Processor"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:delete:environment",
"classifier": "environment",
"description": "Delete environment"
},
{
"id": "orgmgt:promote:environment",
"classifier": "environment",
"description": "Promote environment"
},
...
],
"__NAME__": "Organization Admin"
}
Available roles
Available roles is a virtual object class, not a native PingOne resource. The _id is a concatenation of two other GUIDs and the level of access the role grants in the following format:
scopeId:scopeType:roleId
|
The id for the associated scope type |
|
|
|
The role id |
Example available role:
{
"_id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2",
"role": {
"id": "0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2" (1)
},
"name": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin",
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e", (2)
"type": "ENVIRONMENT" (3)
},
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"__NAME__": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin"
}| 1 | roleId |
| 2 | scopeId |
| 3 | scopeType |
Read all available roles
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__AVAILABLE_ROLE__?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2",
"role": {
"id": "0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2"
},
"name": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin",
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e",
"type": "ENVIRONMENT"
},
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"__NAME__": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin"
},
{
"_id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:ce00e15f-f845-4df1-abf3-fdc4ff4e176c",
"role": {
"id": "ce00e15f-f845-4df1-abf3-fdc4ff4e176c"
},
"name": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Read Only",
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e",
"type": "ENVIRONMENT"
},
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"__NAME__": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Read Only"
},
...
],
"resultCount": 10,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read a single available role
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/pingone/__AVAILABLE_ROLE__/9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2'
{
"_id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e:ENVIRONMENT:0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2",
"role": {
"id": "0bd9c966-7664-4ac1-b059-0ff9293908e2"
},
"name": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin",
"scope": {
"id": "9da69b4c-8101-4db8-8cef-66a9a167b02e",
"type": "ENVIRONMENT"
},
"environment": {
"id": "d182d341-2739-4082-975f-bc94396a9651"
},
"__NAME__": "ENVIRONMENT - Administrators: Identity Data Admin"
}
Supported search filters
The PingOne connector supports filtered searches against PingOne resources. However, certain limitations imposed by the PingOne APIs prevent the filtering of resource types based on arbitrary attributes and values. For a complete list, refer to Limiting and Filtering data in the PingOne documentation.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the PingOne Connector
The PingOne Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
PingOne Connector Configuration
The PingOne Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The environment identifier. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The service endpoint URI. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The service login name. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The service user password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which method is to be used to authenticate on the remote server. Options are BASIC (username/password), OAUTH (Client id/secret) or TOKEN (static token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When using OAUTH as authentication method, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be queried for (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The client identifier for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Secure client secret for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Static authentication token. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Content compression is enabled by default. Set this property to true to disable it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed, set this to the certificate alias from the keystore. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed and the client certificate (private key) password is different from the keystore password, set this to the client private key password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the max size of the HTTP connection pool used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Hostname if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Port if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines Proxy Username if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Defines Proxy Password if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a timeout for the underlying HTTP connection in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Used by the refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 grant type to use (client_credentials or refresh_token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 scope to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The prefix to be used in the Authorization HTTP header for Token authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Authentication method for refresh token (Basic Authentication or Sending the ClientId and Client Secret in the Header). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
PowerShell connector toolkit
The PowerShell connector toolkit is not a complete connector in the traditional sense. Rather, it is a framework within which you must write your own PowerShell scripts to address your Microsoft Windows ecosystem requirements. You can use the PowerShell connector toolkit to create connectors that can provision any Microsoft system, including, but not limited to, Active Directory, Microsoft SQL, MS Exchange, SharePoint, Azure, and Office365. Any task you can perform with PowerShell can be executed through connectors based on this toolkit.
The PowerShell connector toolkit is available from the ForgeRock BackStage download site. It is also bundled with the .NET remote connector server.
To use this connector, you must write a PowerShell script for each operation that you want the connector to perform (create, read, update, delete, authenticate, and so on). Sample scripts for core operations are included with the .NET RCS.
Before you start
To implement a scripted PowerShell connector, you must install the following:
-
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6.2 or later. Connectors created with the PowerShell connector toolkit run on the .NET platform and require the installation of a .NET connector server on the Windows system. To install the .NET connector server, follow the instructions in Install .NET RCS.
-
PowerShell version 4.0 or above.
-
The PowerShell connector toolkit.
Install the PowerShell connector
To run the commands in this procedure, start with the PowerShell command line. Some commands require administrative privileges.
-
Install, configure, and start the .NET connector server on a Windows host. If you are running an Active Directory Domain Controller, install the .NET connector server on the same host on which the Windows PowerShell module is installed.
-
The PowerShell connector toolkit comes bundled with the .NET RCS. To confirm it is installed, check the .NET RCS installation directory for a
MsPowerShell.Connector.dllfile. -
Sample scripts are provided with the .NET remote connector server.
Reference the full path to the scripts in your connector configuration, for example:
"CreateScriptFileName" : "C:/Program Files (x86)/ForgeRock/OpenICF/samples/ADCreate.ps1", ...
Configure the PowerShell connector
-
You cannot configure a PowerShell connector through the UI. Configure the connector over REST, as described in Configure Connectors Over REST.
-
Alternatively, copy the sample connector configuration file (
provisioner.openicf-adpowershell.json) from thesamples\example-configurations\provisionersdirectory to your project’sconfdirectory.Paths in these files must use forward slash characters and not the backslash characters that you would expect in a Windows path. -
Verify that at least the path to the scripts and the connection and authentication details are correct for your deployment.
PowerShell Connector Configuration Properties Property Type Example Encrypted[2] Required[3] operationScriptFileNameStringC:/openidm/AD/ADCreate.ps1,

The full path to the script that implements the corresponding OpenICF operation.
VariablesPrefixStringConnector

To avoid variable namespace conflicts, you can define a prefix for the connector variables. All variables are injected into the script under that prefix and can be used with the dotted notation.
QueryFilterTypeStringAdPsModule(for Active Directory)

A configurable query filter visitor property that defines the format in which the query will be injected into the connector. Possible values are:
-
Map- the query filter is a map -
Ldap- the query filter is in LDAP search format; for example,"(cn=Joe)" -
Native- the query filter is a native OpenICF query filter -
AdPsModule- the query filter is compatible with the Active Directory PowerShell module,Get-ADUser Filter
ReloadScriptOnExecutionBooleantrue

When
true, the connector reloads the script from disk every time it is executed. This can be useful for debugging purposes. Set tofalsein production.UseInterpretersPoolBooleantrue

If
true, the connector leverages the PowerShell RunSpace Pool.MaxInterpretersPoolSizeInteger5

The maximum size of the interpreter pool.
MinInterpretersPoolSizeInteger1

The minimum size of the interpreter pool.
PoolCleanupIntervalDouble60

Specifies the interval (in minutes) at which unused interpreter instances are discarded. To avoid cleaning up unused interpreter instances, set this property to
0.SubstituteUidAndNameInQueryFilterBooleantrue

Specifies whether the
__UID__and__NAME__should be replaced by the value defined in theNameAttributeNameandUidAttributeNamein the query filter.UidAttributeNameStringObjectGUID

The attribute on the resource that contains the object
__UID__.NameAttributeNameStringDistinguishedName

The attribute on the resource that contains the object
__NAME__.PsModulesToImportArray["ActiveDirectory","C:/openidm/samples/scripted-powershell-with-ad/tools/ADSISearch.psm1"]

An array of additional PowerShell modules that the connector must import.
HostStringad.example.com

The host name or IP address of the Active Directory server.
PortIntegernull

The port number on which the remote resource listens for connections.
LoginString""

The user account in the remote resource that is used for the connection.
PasswordStringnull

The password of the user account that is used for the connection.
CustomPropertiesArray[ ]

An array of Strings to define custom configuration properties. Each property takes the format
"name=value". For example:"configurationProperties" : { ... "CustomProperties" : ["baseContext = CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com" ], ... }The custom property can then be read from the PowerShell scripts as follows:
$base = $Connector.Configuration.PropertyBag.baseContext
-
Test the PowerShell connector
These examples show you how to test the connector is configured correctly and operating as expected.
Check the connector configuration
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
{
"name" : "adpowershell",
"enabled" : true,
"config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/adpowershell",
"objectTypes" : [ "__ALL__", "group", "account" ],
"connectorRef" : {
"connectorName" : "Org.Forgerock.OpenICF.Connectors.MsPowerShell.MsPowerShellConnector",
"bundleName" : "MsPowerShell.Connector",
"bundleVersion" : "[1.4.3.0,1.5.0.0)"
},
"displayName" : "PowerShell Connector",
"ok" : true
}
When you run this test, a log entry associated with the .NET connector server should be created in the logs/
directory of that server.
Search user entries
You can use the connector, with a PowerShell search script, to retrieve information from a target system. The PowerShell search script accepts IDM queries, including query-all-ids and _queryFilter.
The following command retrieves a list of users in an Active Directory server. You can also use any system-enabled filter, such as those described in Presence Expressions:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adpowershell/account?_queryId=query-all-ids"
Create users or groups
This command creates a new user in Active Directory:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '{
"distinguishedName" : "CN=Robert Smith,CN=Users,DC=EXAMPLE,DC=COM",
"sAMAccountName" : "robert.smith",
"sn" : "Smith",
"cn" : "Robert Smith",
"userPrincipalName": "Robert.Smith@example.com",
"enabled" : true,
"password" : "Passw0rd",
"telephoneNumber" : "0052-611-091"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adpowershell/account?_action=create"
Update entries
You can update the following properties with the sample scripts:
-
Password
-
Principal Name
-
License
-
Common user attributes
This command changes the password for the user with the specified _id:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request PATCH \
--header "content-type: application/json" \
--data '{
"operation": "replace",
"Field": "password",
"value": "Passw1rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adpowershell/account/1d4c9276-6937-4d9e-9c60-67e8b4207f4e"
Delete Users and Groups
This command deletes an Active Directory user entry with the specified _id:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adpowershell/account/1d4c9276-6937-4d9e-9c60-67e8b4207f4e"
Run Scripts Through the Connector
The runScriptOnConnector operation lets you run an arbitrary script action through the connector. This operation takes the following variables as input:
configuration-
A handler to the connector’s configuration object.
options-
A handler to the Operation Options.
operation-
The operation type that corresponds to the action (
RUNSCRIPTONCONNECTORin this case). log-
A handler to the log.
The script can return any object that can be serialized by OpenICF, such as Boolean, String, Array, or Dictionary. If the object type cannot be serialized, such as Hashtable, the script fails with the error:
"error": "No serializer for class: System.Collections.Hashtable"
To run an arbitrary script on the PowerShell connector, define the script in the systemActions property of your provisioner file:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*PowerShellConnector",
"actionType" : "PowerShell",
"actionFile" : "scripts/Myactionscript.ps1"
}
]
}
]When you have defined the script, you can call it over REST on the system endpoint, as follows:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/adpowershell?_action=script&scriptId=MyScript¶m1=value1¶m2=value2"
You can also call it through the IDM script engine, as follows:
openidm.action("/system/adpowershell", "script", {}, {"scriptId": "MyScript", "param1": "value1", "param2": "value2"})|
Because the action script is stored locally with IDM, it must be transmitted across the network every time it is called. An alternative approach is to write a PowerShell module and to load it using the The following example uses the |
Manage Azure AD Objects With the PowerShell Connector
ForgeRock provides two sets of sample scripts to let you manage objects in Azure AD with the PowerShell connector:
-
Version 1: These scripts are based on the older Microsoft Online (MSOL) V1 PowerShell module. For information on connecting to your Azure AD with this module, refer to the corresponding Microsoft documentation. Microsoft has expressed its intention to deprecate this module when its functionality has been completely migrated to the newer Azure Active Directory PowerShell for Graph Module. These scripts are supported only up to Windows 2012 R2.
The Version 1 scripts can manage security groups but not dynamic groups.
-
Version 2: These scripts are based on the Azure Active Directory PowerShell for Graph Module. For information on connecting to your Azure AD with this module, refer to the corresponding Microsoft documentation. The cmdlets in this module let you perform CRUD operations on an Azure AD instance, and configure the directory and its features.
The Version 2 scripts can manage user password policies, security and mail groups, dynamic groups, and devices.
Follow these procedures to use the sample Azure AD scripts with the PowerShell connector:
Set Up a Remote Connector Server
-
Install a .NET connector server on your Windows host. These steps assume a Windows hostname of
windows-host.example.com. -
On
windows-host.example.com, install the PowerShell connector.When you have installed the PowerShell connector, make sure that the ICF .NET connector server is still running. If it is not running, restart the connector server and check the logs. In some cases, Windows blocks the PowerShell connector .dll files. If the connector server fails to start, right-click on
MsPowerShell.Connector.dlland select Properties > Security -
If the following text displays:
This file came from another computer and might be blocked to help protect this computer.
Click Unblock to unblock the connector .dll file. Then, restart the connector server.
-
On
windows-host.example.com, install the Windows Azure AD Module that corresponds to the version of the scripts you are using.-
For Version 1 scripts, install the MSOnline module.
-
For Version 2 scripts, install the Azure AD module.
-
-
These instructions assume that you have an existing Azure AD instance.
Create a specific administrative account in Azure AD, to run the PowerShell connector scripts.
-
In a PowerShell window on
windows-host.example.com, verify that your Windows host can connect to your Azure AD tenant:-
For Version 1 scripts, run
Connect-MsolService. -
For Version 2 scripts, run
Connect-AzureAD.
-
Set Up the PowerShell Azure AD Scripts
When all your systems are installed and running, and you have verified that your Windows host can connect to your Azure AD, set up the sample scripts as follows:
-
On
windows-host.example.com, create a directory for the PowerShell scripts, for example:PS C:\> mkdir -Path openidm\scripted-powershell-with-azure-ad\scripts
Whatever location you choose for the scripts will be referenced in your connector configuration (provisioner file).
-
Download the Azure AD scripts from the ForgeRock stash repository.
Download either the V1 or V2 scripts, depending on your Azure AD module, and place them in the scripts directory you created in the previous step:
ls C:\openidm\scripted-powershell-with-azure-ad\scripts Directory: C:\openidm\scripted-powershell-with-azure-ad\scripts Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 10965 AzureADCreate.ps1 -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 3547 AzureADDelete.ps1 -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 6952 AzureADSchema.ps1 -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 8149 AzureADSearch.ps1 -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 2465 AzureADTest.ps1 -a--- 7/21/2020 4:00 AM 10840 AzureADUpdate.ps1
By default, Windows does not trust downloaded scripts. To be able to run the scripts, you might need to do the following:
-
Run the Unblock-File cmdlet. This cmdlet unblocks PowerShell script files that were downloaded from the Internet so that you can run them, regardless of the PowerShell execution policy.
-
Change the PowerShell execution policy to let you run the scripts.
-
-
In IDM, configure the connection to the .NET connector server.
-
In IDM, configure the PowerShell connector.
The ForgeRock stash repository includes a sample provisioner file for both versions of the scripts. Use those files as a starting point. Set at least the following properties:
connectorHostRefThe name of the connector server referenced in the previous step.
*ScriptFileNameSet the path to the script directory that you created on
windows-host.example.com.
Test the PowerShell Connector With Azure AD
-
Test that the connector has been configured correctly and can reach the Azure AD:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/azureadpowershell?_action=test" { "name": "azureadpowershell", "enabled": true, "config": "config/provisioner.openicf/azureadpowershell", "objectTypes": [ "__ALL__", "account", "group" ], "connectorRef": { "bundleName": "MsPowerShell.Connector", "connectorName": "Org.ForgeRock.OpenICF.Connectors.MsPowerShell.MsPowerShellConnector", "bundleVersion": "[1.4.3.0,1.5.0.0)" }, "displayName": "PowerShell Connector ", "ok": true }If there is no response from this connector test, check your connector configuration and the connection to the .NET connector server.
IBM RACF connector
IBM Resource Access Control Facility (RACF) is an access control system for IBM mainframes running z/OS. The RACF connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between RACF and IDM managed user objects. A RACF administrator account is required for this connector to work.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your RACF administrator account and note the following:
- Host name
-
The domain name or IP address of the host where RACF is running.
- Port
-
The port RACF is configured to use.
- User ID
-
The RACF administrator user ID.
- Password
-
The password for the RACF administrator account.
- Segments
-
A list of RACF user profile segments that are supported. Refer to RACF segments and attributes for a list of available segments.
- Accept self-signed certificates
-
A boolean determining whether RACF is configured to allow self-signed certificates. This should usually be
falsein production environments, but may betrueduring development. - Client certificate alias
-
Alias name for the client certificate.
- Client certificate password
-
Password for the client certificate.
Install the RACF connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/racf-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the RACF connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select RACF Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to RACF Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the RACF connector
You can test the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf?_action=test"
{
"name": "racf",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/racf",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.racf-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.racf.RacfConnector"
},
"displayName": "RACF Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__",
"__GROUP__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector was configured correctly, and can authenticate to the RACF system.
RACF remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the RACF connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the RACF connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the RACF remote connector.
RACF segments and attributes
The following tables list available attributes by segment. Attributes listed in the Base segment are available by default. To use any other attributes, include the segment name in the list of segments in the RACF connector configuration.
User accounts support create, update, query, and delete actions. Groups only support query actions.
Account attributes
The following attributes are available to the __ACCOUNT__ resource object:
Base segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s ID. Required. |
|
The user’s system name. Must match |
|
The user’s name. |
|
Owner of the user’s profile. |
|
Default group of the user. |
|
User’s authority in the default group. |
|
The user’s password. |
|
Optional password phrase. |
|
Expiration date for the user’s system access. |
|
Date a user’s system access is restored. |
|
Days of the week and hours of the day the user has access to the system. |
|
Classes in which the user can define profiles. |
|
Name of the data model profile used when creating new data profiles (either generic or discrete). |
|
The group the user belongs to. |
|
The user’s default security label. |
|
Whether other group members have access to any other group set the user protects. |
|
Indicates that when checking global access, the account will not be used to allow access to a resource. |
|
Gives the user the system-wide auditor attribute. |
|
Gives the user the system-wide operations attribute. |
|
Gives the user the system-wide special attribute. |
|
Indicates all permanent data sets this user creates should be discrete profiles in RACF. |
CICS segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The classes the user is assigned in CICS. Determines which basic mapping support (BMS) messages are routed to the user. Represented as a number ranging from |
|
A 1-3 character identification of the user for use by BMS. |
|
The number ( |
|
The resource security level (RSL) keys assigned to the user. |
|
The time in hours and minutes (either |
|
The transaction security level (TLS) keys assigned to the user. |
|
Indicates whether the user should be signed out when an XRF takeover occurs. |
DCE segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Single Sign On (SSO) processing. Either |
|
The user’s DCE principal name. |
|
The user’s DCE home cell. |
|
The user’s DCE UUID. |
|
The user’s principal DCE UUID. |
DFP segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s DFP data application identifier. |
|
The user’s default data class for attributes used during allocation of any new data sets. |
|
The user’s default management class for attributes used in managing a data set after it is allocated. |
|
The user’s default storage class for logical storage attributes. |
KERB segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s encryption key types. Available values include: |
|
The user’s local principal name. The value specified must be unique. |
|
The maximum Kerberos ticket life specified in seconds. Note that |
LANGUAGE segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s primary language. |
|
The user’s secondary language. |
LNOTES segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s short name for use with Lotus Notes in z/OS. |
NDS segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s name for use with Novell Directory Services |
NETVIEW segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Master Console Station (MCS) console identifier. |
|
Specifies whether a security check is performed for this user. Either |
|
The domain identifier for any domains where the user can start a cross-domain session. |
|
The initial command or list of commands to be executed by NetView when the user logs in. |
|
Indicates whether the user can receive unsolicited messages. |
|
Indicates whether the user can use the NetView graphic monitor facility. |
|
NetView scope classes the user has authority with. The class value is a number from |
OMVS segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s z/OS maximum address space size. |
|
The user’s z/OS maximum CPU time allowed. |
|
The user’s z/OS maximum number of files allowed per process. |
|
The user’s z/OS home directory path. |
|
The user’s z/OS non-shared memory size limit. |
|
The user’s z/OS maximum memory map size. |
|
The user’s maximum number of processes per UID in z/OS. |
|
The user’s z/OS path name, such as a default shell program. |
|
The user’s z/OS maximum shared memory size. |
|
The user’s z/OS maximum number of threads per process. |
|
The user’s z/OS user ID. |
OPERPARM segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Alternative console group used for recovery. |
|
The user’s command authority. |
|
Name of the system to which the user is connected for command processing. |
|
Indicates whether the console can receive delete operator message (DOM) requests. |
|
Indicates whether this console should receive all messages that are directed to hardcopy. |
|
Indicates whether or not a console should receive messages directed to the internal console. |
|
Indicates a data retrieval key used to search for user consoles using the |
|
Message level the user should receive. Available values include |
|
Indicates whether command responses received by the user are logged. |
|
Specifies the format messages are displayed in. Available values include |
|
Indicates whether the user should receive a migration console ID. |
|
List of events the user can monitor. |
|
List of the systems this console can receive unsolicited messages from. |
|
Routing codes for messages this console receives. |
|
The amount of virtual storage (in megabytes) the console is allowed for message queuing. |
|
Specifies whether this console should receive undelivered messages. |
|
Indicates whether a console should receive messages directed to unknown console IDs. |
OVM segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s OpenExtensions for z/VM user ID. |
|
The user’s OpenExtensions for z/VM file system root directory path. |
|
The user’s OpenExtensions for z/VM home directory path. |
|
The user’s OpenExtensions for z/VM program path, such as a default shell program. |
PROXY segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The URL of the LDAP server which the z/OS LDAP server contacts when acting as a proxy. |
|
The distinguished name (DN) which the z/OS LDAP server uses when acting as a proxy. |
TSO segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s default TSO account number. |
|
The user’s default hold class. |
|
The user’s default job class. |
|
The user’s maximum region size. |
|
The user’s default message class. |
|
The name of the user’s default login procedure. |
|
The user’s default region size. |
WORKATTR segment
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
User name on |
|
Building on |
|
Department on |
|
Room on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Account number. |
|
User email address. |
Group attributes
The following attributes are available to the __GROUP__ resource object:
Group attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
ID of the group. |
|
Name of the group. |
|
Owner of the group. |
|
List of subgroups part of this group. |
|
List of groups this group is part of. |
|
List of users part of this group. |
Use the RACF connector
You can use the RACF connector to perform the following actions on a RACF account:
Create a RACF user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"userId": "BJENSEN"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"NAME": "UNKNOWN",
"LAST-ACCESS": "UNKNOWN",
"DFLTGRP": "SYS1",
"WHEN": {
"DAYS": "ANYDAY",
"TIME": "ANYTIME"
},
"PASS-INTERVAL": "N/A",
"PHRASEDATE": "N/A",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"SECLABEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"ATTRIBUTES": [
"PROTECTED"
],
"PASSDATE": "N/A",
"SECLEVEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"__GROUP__": [
{
"GROUP": "SYS1",
"OWNER": "IBMUSER",
"AUTH": "USE",
"UACC": "NONE"
}
],
"OWNER": "IBMUSER"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least |
Update a RACF user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. For a list of attributes, refer to RACF segments and attributes.
For example, to add a work email and update the name of the user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"WORKATTR_WAEMAIL": "bjensen@example.com",
"NAME": "Barbara Jensen"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"NAME": "BARBARA JENSEN",
"LAST-ACCESS": "UNKNOWN",
"DFLTGRP": "SYS1",
"WORKATTR_WAEMAIL": "bjensen@example.com",
"WHEN": {
"DAYS": "ANYDAY",
"TIME": "ANYTIME"
},
"PASS-INTERVAL": "N/A",
"PHRASEDATE": "N/A",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"SECLABEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"ATTRIBUTES": [
"PROTECTED"
],
"PASSDATE": "N/A",
"SECLEVEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"__GROUP__": [
{
"GROUP": "SYS1",
"OWNER": "IBMUSER",
"AUTH": "USE",
"UACC": "NONE"
}
],
"OWNER": "IBMUSER"
}
Query RACF users
The following example queries all RACF users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "ADCDY"
},
{
"_id": "ADCDZ"
},
{
"_id": "BJENSEN"
},
{
"_id": "BPXOINIT"
},
{
"_id": "CEA"
},
{
"_id": "CFZSRV"
},
{
"_id": "CICSUSER"
},
{
"_id": "DANY101"
},
{
"_id": "DANY102"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "ZOSCAGL"
},
{
"_id": "ZOSCSRV"
},
{
"_id": "ZOSMFAD"
},
{
"_id": "ZOSUGST"
},
{
"_id": "ZWESIUSR"
},
{
"_id": "ZWESVUSR"
}
],
"resultCount": 162,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"NAME": "BARBARA JENSEN",
"LAST-ACCESS": "UNKNOWN",
"DFLTGRP": "SYS1",
"WORKATTR_WAEMAIL": "bjensen@example.com",
"WHEN": {
"DAYS": "ANYDAY",
"TIME": "ANYTIME"
},
"PASS-INTERVAL": "N/A",
"PHRASEDATE": "N/A",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"SECLABEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"ATTRIBUTES": [
"PROTECTED"
],
"PASSDATE": "N/A",
"SECLEVEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"__GROUP__": [
{
"GROUP": "SYS1",
"OWNER": "IBMUSER",
"AUTH": "USE",
"UACC": "NONE"
}
],
"OWNER": "IBMUSER"
}
Reset a RACF account password
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{
"operation": "add",
"field": "__PASSWORD__",
"value": "Passw0rd@123!"
}]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"NAME": "BARBARA JENSEN",
"LAST-ACCESS": "22.304/12:17:39",
"DFLTGRP": "SYS1",
"WORKATTR_WAEMAIL": "bjensen@example.com",
"WHEN": {
"DAYS": "ANYDAY",
"TIME": "ANYTIME"
},
"PASS-INTERVAL": "180",
"PHRASEDATE": "00.000",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"SECLABEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"ATTRIBUTES": [
"NOPASSWORD",
"PASSPHRASE"
],
"PASSDATE": "N/A",
"SECLEVEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"__GROUP__": [
{
"GROUP": "SYS1",
"OWNER": "IBMUSER",
"AUTH": "USE",
"UACC": "NONE"
}
],
"OWNER": "IBMUSER"
}
|
While the |
Delete a RACF account
You can use the RACF connector to delete an account from the RACF service.
The following example deletes a RACF account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/racf/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"NAME": "BARBARA JENSEN",
"LAST-ACCESS": "22.304/12:17:39",
"DFLTGRP": "SYS1",
"WORKATTR_WAEMAIL": "bjensen@example.com",
"WHEN": {
"DAYS": "ANYDAY",
"TIME": "ANYTIME"
},
"PASS-INTERVAL": "180",
"PHRASEDATE": "00.000",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"SECLABEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"ATTRIBUTES": [
"NOPASSWORD",
"PASSPHRASE"
],
"PASSDATE": "N/A",
"SECLEVEL": "NONE SPECIFIED",
"__GROUP__": [
{
"GROUP": "SYS1",
"OWNER": "IBMUSER",
"AUTH": "USE",
"UACC": "NONE"
}
],
"OWNER": "IBMUSER"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the RACF Connector
The RACF Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
RACF Connector Configuration
The RACF Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Host name or IP address of RACF. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
TCP/IP port number used to communicate with the RACF. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The user id used to login to RACF. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The password used to login to RACF. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
To retrieve data based on RACF segments. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Specifies whether to accept or not self-signed certificates. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Alias for the client certificate. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Password for the client certificate. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connection timeout in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Proxy Host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Proxy Port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the Proxy Username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the Proxy Password. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Salesforce connector
The Salesforce connector lets you provision, reconcile, and synchronize users between Salesforce and the IDM managed user repository.
This topic describes how to install and configure the Salesforce connector, and how to perform basic tests to ensure that it’s running correctly.
For a complete example that includes the configuration required to synchronize users with this connector, refer to Synchronize users between Salesforce and IDM.
Before you configure the Salesforce connector
The instructions in this topic assume that you have an existing Salesforce organization, a Salesforce administrative account, and a Connected App with OAuth enabled.
For instructions on setting up a Connected App, refer to the corresponding Salesforce documentation. When you have set up the Connected App, locate the Consumer Key and Consumer Secret. You will need these details to configure the connector.
The Salesforce connector is bundled with IDM and Identity Cloud and has no specific installation requirements.
Install the Salesforce connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/salesforce-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Salesforce connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Salesforce Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
The Login URL is the OAuth endpoint used to make the OAuth authentication request to Salesforce.
When you create your connected app, you are instructed to wait 2-10 minutes for the settings to propagate across all the Salesforce data centers. If you are using a Salesforce test tenant, such as https://eu26.lightning.force.com, you can specify a custom URL here and enter the FQDN of the test tenant. This lets you test the connector without waiting for the new app settings to be propagated.For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Salesforce Connector Configuration The connector attempts to access your Salesforce organization.
-
Enter your Salesforce login credentials.
-
On the permission request screen, click Allow to enable IDM to access your Salesforce Connected App.
-
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Configure the Salesforce connector with a configuration file
IDM provides a sample connector configuration file in the /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners directory.
Copy this sample file (provisioner.openicf-salesforce.json) to your project’s conf directory and set at least the following properties, based on the grant type:
"configurationProperties" : {
"grantType" : "refresh_token",
"refreshToken" : "refreshToken",
"loginUrl" : "loginURL",
"clientSecret" : "clientSecret",
"clientId" : "clientId",
"instanceUrl" : "instanceURL"
}"configurationProperties" : {
"grantType" : "client_credentials",
"loginUrl" : "loginURL",
"clientSecret" : "clientSecret",
"clientId" : "clientId",
"instanceUrl" : "instanceURL"
}loginUrl-
The OAuth endpoint that will be used to make the OAuth authentication request to Salesforce.
The default endpoint for a production system is
https://login.salesforce.com/services/oauth2/token. The default endpoint for a sandbox (test) system ishttps://test.salesforce.com/services/oauth2/token. clientSecret-
The Consumer Secret associated with your Connected App.
clientId-
The Consumer Key associated with your Connected App.
grantType-
The OAuth2 grant type to use (
client_credentialsorrefresh_token).client_credentials-
This grant type requires
clientId,clientSecret,loginURL, andinstanceURL. refresh_token-
This grant type requires
clientId,clientSecret,loginURL, andinstanceURL, andrefreshToken.
refreshToken-
The admin UI gets the
refreshTokenautomatically during connector configuration. Required when the grant type isrefresh_token. To manually get the value, refer to Get therefreshTokenandinstanceURL. instanceURL-
The admin UI gets the
instanceURLautomatically during connector configuration when using therefresh_tokengrant type. For theclient_credentialsgrant type, you must provide the value. This is typically a well-known value, but to manually get the value, refer to Get therefreshTokenandinstanceURL.
Get the refreshToken and instanceURL
-
Browse to the following URL:
SALESFORCE_URL/services/oauth2/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=CONSUMER_KEY&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&scope=id+api+refresh_token
-
SALESFORCE_URL is one of the following:
-
A production URL (
https://login.salesforce.com) -
A sandbox URL (
https://test.salesforce.com) -
A custom Salesforce MyDomain URL, such as
https://ic-example-com--SUP1.cs21.my.salesforce.com
-
-
CONSUMER_KEY is the Consumer Key associated with the Connected App that you created within your Salesforce organization.
-
REDIRECT_URI is the IDM URI Salesforce should redirect to during authentication. It must match the Redirect URI specified within your Salesforce Connect App configuration, for example:
https://localhost:8443/
-
-
You are redirected to Salesforce, and prompted to give this application access to your Salesforce account. When you have given consent, you should receive a response URL that looks similar to the following:
https://localhost:8443/admin/index.html#connectors/edit//&code=aPrxJZTK7Rs03PU634VK8Jn9o_U3ZY1ERxM7IiklF...The
&codepart of this URL is an authorization code, that you need for the following step.This authorization code expires after 10 minutes. If you do not complete the OAuth flow within that time, you will need to start this process again. -
Copy the authorization code from the response URL and use it as the value of the
codeparameter in the following REST call. The consumer-key, redirect-uri, and SALESFORCE_URL must match what you used in the first step of this procedure:curl \ --verbose \ --data "grant_type=authorization_code" \ --data "client_id=consumer-key" \ --data "client_secret=consumer-secret" \ --data "redirect_uri=https://localhost:8443/" \ --data "code=access-token-code" \ "SALESFORCE_URL/services/oauth2/token" { "access_token": "00DS0000003K4fU!AQMAQOzEU.8tCjg8Wk79yKPKCtrtaszX5jrHtoT4NBpJ8x...", "signature": "2uREX1lseXdg3Vng/2+Hrlo/KHOWYoim+poj74wKFtw=", "refresh_token": "5Aep861KIwKdekr90I4iHdtDgWwRoG7O_6uHrgJ.yVtMS0UaGxRqE6WFM77W7...", "token_type": "Bearer", "instance_url": "https://example-com.cs1.my.salesforce.com", "scope": "id api refresh_token", "issued_at": "1417182949781", "id": "https://login.salesforce.com/id/00DS0000003K4fUMAS/00530000009hWLcAAM" }The output includes the
refresh_tokenandinstance_urlyou need to configure the connector. -
Set
"enabled" : trueto enable the connector. -
Save the connector configuration.
Use the Salesforce connector with a proxy server
If the IDM server is hosted behind a firewall and requests to the resource server are routed through a proxy, you must specify the proxy information in the connector configuration. The Salesforce connector supports two mutually exclusive configuration properties for specifying the proxy: proxyHost and proxyUri.
To specify the proxy server details using an HTTP scheme, set the proxyHost and proxyPort properties in the connector configuration. If the proxy requires authentication, set the proxyUsername and proxyPassword properties. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"proxyHost": "myproxy.example.com",
"proxyPort": 8080,
"proxyUsername": "hgale815",
"proxyPassword": "password123",
...
}To specify the proxy server details using a URI, set the proxyUri property in the connector configuration. The proxyUri property contains the scheme, host, and port. If the proxy requires authentication, set the proxyUsername and proxyPassword properties. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"proxyUri": "https://myproxy.example.com:8080",
"proxyUsername": "hgale815",
"proxyPassword": "password123",
...
}Test the Salesforce connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/salesforce?_action=test"
{
"name": "salesforce",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/salesforce",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.salesforce-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.salesforce.SalesforceConnector"
},
"displayName": "Salesforce Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ALL__",
"User"
],
"ok": true
}
+
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly, and can authenticate to Salesforce.
Salesforce remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Salesforce connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Salesforce connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Salesforce remote connector.
Implementation Specifics
-
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Salesforce connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value. Salesforce does not support multi-valued attributes.
-
Attributes themselves cannot be removed from Salesforce. The connector therefore performs an update with
""as the value of the attribute being removed. This sets the value of the removed attribute tonull.Salesforce does not support application user DELETE requests. -
The Salesforce connector supports any Salesforce object that is available to the API. To check which objects are available, log in to Salesforce Workbench to access the API explorer. This URL points to Version 49 of the API. Adjust the URL for the latest API version.
Because the number of Salesforce objects is potentially very large, the Salesforce connector configuration includes a
supportedObjectTypesproperty that lets you specify the objects you want to support. The connector checks the metadata in Salesforce for each of the objects you list in this property, and dynamically builds the required schema. The sample connector configuration file (provisioner.openicf-salesforce.json) generates the schema only for the User object:{ ... "configurationProperties": { ... "supportedObjectTypes": [ "User" ] }, }You can add any object to the list of
supportedObjectTypes, and the connector will build the schema for that object. -
The Salesforce API restricts how query results can be paged. The default, and maximum page size is
2000. The minimum page size is200. The Salesforce API does not guarantee that the requested page size is the actual page size. Returned results might vary, to maximize performance.For example, the following query (with
"pageSize=1") might return more than one user if more than one user exists in Salesforce:http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/salesforce/user?_queryId=query-all-ids&_pageSize=1For more information, refer to the Salesforce documentation.
Permission sets and groups
The Salesforce connector can display and allow you to interact with a user’s groups and permissions on the user’s data model. This is done through the __PermissionSetIds__ and __GroupIds__ attributes.
Configure permission sets and groups
To configure these attributes, add the following to the user object in your provisioner file:
[...]
"__PermissionSetIds__" : {
"type" : "array",
"items" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeType" : "string"
},
"nativeName" : "__PermissionSetIds__",
"nativeType" : "string",
"absentIfEmpty" : true,
"flags" : [
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
},
"__GroupIds__" : {
"type" : "array",
"items" : {
"type" : "string",
"nativeType" : "string"
},
"nativeName" : "__GroupIds__",
"nativeType" : "string",
"absentIfEmpty" : true,
"flags" : [
"NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT"
]
}
Both __PermissionSetIds__ and __GroupIds__ should have the NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT flag enabled.
|
Get a user’s permission sets and groups
When getting a user object, you must specifically request that the system return the __PermissionSetIds__ and __GroupIds__ fields. For example:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User?_queryFilter=Alias+eq+"bjensen"&_fields=_id,__PermissionSetIds__,__GroupIds__"
| Salesforce assigns a default permission set to each created user. |
Create a user with permissions sets and groups
To create a user object with associated permissions and groups, include the __PermissionSetIds__ and __GroupIds__ fields in the POST request. These fields are an array of strings.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"Username": "bjensen@example.com",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"Email": "bjensen@example.com",
"Alias": "bjensen",
"LocaleSidKey": "en_US",
"LanguageLocaleKey": "en_US",
"FirstName": "Barbara"
"TimeZoneSidKey": "America/Los_Angeles",
"CommunityNickname": "bjensen"
"ProfileId": "00e200000001ehhP"
"__PermissionSetIds__": ["0P50300000QIbGAM"],
"__GroupIds__": ["0J40700000DIg3Hm"]
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User?_action=create"
Update a user’s permission sets and groups
You can update a user’s permission sets and groups through the API using a PUT call. The following request adds a permission set and group to scarter, a user with id 00503000002XmQqAAK.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"OutOfOfficeMessage": "",
"LastName": "Carter",
"UserPreferencesSortFeedByComment": true,
"UserPreferencesPathAssistantCollapsed": false,
"BannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/B",
"EmailPreferencesAutoBcc": true,
"TimeZoneSidKey": "America/Los_Angeles",
"UserPreferencesHideLightningMigrationModal": false,
"UserPreferencesFavoritesWTShown": false,
"MediumPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/M",
"UserPreferencesHideS1BrowserUI": false,
"UserType": "Standard",
"UserPreferencesDisableSharePostEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesCreateLEXAppsWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesApexPagesDeveloperMode": false,
"EmailPreferencesStayInTouchReminder": true,
"UserPreferencesDisMentionsCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"Username": "scarter@example.com",
"EmailEncodingKey": "UTF-8",
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesSuppressTaskSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesHideSfxWelcomeMat": true,
"LanguageLocaleKey": "en_US",
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToExternalUsers": false,
"LastViewedDate": "2022-11-09T17:15:08.000+0000",
"UserPermissionsAvantgoUser": false,
"UserPreferencesHideCSNGetChatterMobileTask": false,
"UserPreferencesPipelineViewHideHelpPopover": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableLikeEmail": true,
"UserPermissionsSupportUser": false,
"UserPermissionsChatterAnswersUser": false,
"FirstName": "Sam",
"ForecastEnabled": false,
"ReceivesAdminInfoEmails": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableAllFeedsEmail": false,
"LocaleSidKey": "en_US",
"UserPreferencesHideCSNDesktopTask": false,
"SystemModstamp": "2022-11-09T17:14:58.000+0000",
"Id": "00503000002XmQqAAK",
"UserPreferencesLightningExperiencePreferred": true,
"UserPreferencesDisableBookmarkEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesEventRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"UserPreferencesDisableMentionsPostEmail": false,
"CommunityNickname": "scarter",
"UserPreferencesShowCityToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToExternalUsers": false,
"IsProfilePhotoActive": false,
"UserPreferencesDisProfPostCommentEmail": false,
"CreatedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPermissionsMobileUser": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableLaterCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesPreviewCustomTheme": false,
"UserPermissionsCallCenterAutoLogin": false,
"UserPreferencesPreviewLightning": false,
"IsActive": true,
"UserPreferencesDisableFileShareNotificationsForApi": false,
"BadgeText": "",
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesHasCelebrationBadge": false,
"UserPreferencesTaskRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"LastReferencedDate": "2022-11-09T17:15:08.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesDisableChangeCommentEmail": false,
"FullPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/F",
"UserPreferencesDisableEndorsementEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesActivityRemindersPopup": true,
"UserPreferencesEnableAutoSubForFeeds": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsOfflineUser": false,
"UserPreferencesDisCommentAfterLikeEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToGuestUsers": false,
"SmallBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/D",
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"MediumBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/E",
"UserPreferencesShowProfilePicToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToGuestUsers": false,
"EmailPreferencesAutoBccStayInTouch": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesReminderSoundOff": false,
"UserPreferencesUserDebugModePref": false,
"LastModifiedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPreferencesDisableFollowersEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesHideEndUserOnboardingAssistantModal": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToGuestUsers": false,
"ReceivesInfoEmails": false,
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesExcludeMailAppAttachments": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToGuestUsers": false,
"DigestFrequency": "D",
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeReservedWTShown": false,
"UserPermissionsMarketingUser": false,
"UserPreferencesHideBiggerPhotoCallout": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableProfilePostEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToExternalUsers": false,
"LastModifiedDate": "2022-11-09T17:14:57.000+0000",
"ProfileId": "00e30000001ehhPAAQ",
"Name": "Sam Carter",
"UserPreferencesNewLightningReportRunPageEnabled": false,
"UserPermissionsSFContentUser": false,
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToExternalUsers": true,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavBarWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCityToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeSectionCollapseWTShown": false,
"Alias": "scarter",
"DefaultGroupNotificationFrequency": "N",
"__NAME__": "00503000002XmQqAAK",
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavGridMenuWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesHideChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"UserPreferencesSuppressEventSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesFavoritesShowTopFavorites": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableMessageEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesCacheDiagnostics": false,
"SmallPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/T",
"IsExtIndicatorVisible": false,
"Email": "scarter@example.com",
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToExternalUsers": false,
"CreatedDate": "2022-11-09T17:14:57.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesHideSecondChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"__PermissionSetIds__": [
"0PS30000000LFR9GAO"
],
"__GroupIds__": [
"00G03000001V8p5EAC"
]
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User/00503000002XmQqAAK"
Feature licenses
The Salesforce connector can query all supported feature licenses and return details of individual feature licenses. The feature licenses available to your organization depend on your Salesforce instance. For more information, refer to View Your Organization’s Feature Licenses in the Salesforce help site.
Configure supported feature licenses
To configure supported feature licenses, make the following changes to your connector configuration (provisioner.openicf-salesforce.json):
-
Add the supported feature licenses. For a complete list of licenses, refer to
supportedFeatureLicensesin the Salesforce Connector Configuration.For example, to add
UserPermissionsOfflineUser,UserPermissionsMarketingUser, andUserPermissionsWorkDotComUserFeatureas supported feature licenses:"supportedFeatureLicenses": [ "UserPermissionsOfflineUser", "UserPermissionsMarketingUser", "UserPermissionsWorkDotComUserFeature" ] -
Add the
__FeatureLicenses__property to theUserobject:"User" : { ... "properties" : { "__NAME__" : { "type" : "string", "nativeName" : "__NAME__", "nativeType" : "string" }, "Id" : { "type" : "string", "nativeName" : "Id", "nativeType" : "string" }, "__FeatureLicenses__" : { "type" : "array", "items" : { "type" : "string", "nativeType" : "string" }, "nativeName" : "__FeatureLicenses__", "nativeType" : "string", "absentIfEmpty" : true, "flags" : [ "NOT_RETURNED_BY_DEFAULT" ] }, ...
Get a user’s feature licenses
When getting a user object, you must specifically request the system return the __FeatureLicenses__ field. For example:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User?_queryFilter=Alias+eq+"birdch"&_fields=_id,__FeatureLicenses__"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "00503000004PDoeAAG",
"__FeatureLicenses__": [
"UserPermissionsOfflineUser"
]
}
],
"resultCount": 1,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}Create a user with feature licenses
To create a user object with associated feature licenses, include the __FeatureLicenses__ field in the POST request. This field is an array of strings.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"Username": "birdyjbirch@example.com",
"LastName": "birdyjbirch",
"Email": "birdyjbirch@example.com",
"Alias": "birdch",
"LocaleSidKey": "en_US",
"LanguageLocaleKey": "en_US",
"EmailEncodingKey": "UTF-8",
"FirstName": "birdyjbirch",
"TimeZoneSidKey": "America/Los_Angeles",
"CommunityNickname": "birdyjbirch",
"ProfileId": "00e30000001ehhPAAQ",
"__FeatureLicenses__": ["UserPermissionsOfflineUser"]
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User?_action=create"
{
"_id": "00503000004PDoeAAG",
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToExternalUsers": false,
"ForecastEnabled": false,
"DigestFrequency": "D",
"UserPreferencesPipelineViewHideHelpPopover": false,
"UserPermissionsMarketingUser": false,
"UserPreferencesPreviewCustomTheme": false,
"UserPreferencesDisMentionsCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsCallCenterAutoLogin": false,
"UserPreferencesApexPagesDeveloperMode": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToGuestUsers": false,
"Id": "00503000004PDoeAAG",
"UserPreferencesHasCelebrationBadge": false,
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToExternalUsers": false,
"IsExtIndicatorVisible": false,
"BadgeText": "",
"UserPreferencesDisableProfilePostEmail": false,
"Username": "birdyjbirch@example.com",
"UserPreferencesLightningExperiencePreferred": true,
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"EmailPreferencesStayInTouchReminder": true,
"UserPreferencesHideLightningMigrationModal": false,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavGridMenuWTShown": false,
"EmailEncodingKey": "UTF-8",
"UserPreferencesDisProfPostCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesHideCSNDesktopTask": false,
"LastModifiedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesHideBiggerPhotoCallout": false,
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesSuppressEventSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsMobileUser": false,
"CreatedDate": "2023-07-21T23:39:02.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesFavoritesWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableLikeEmail": true,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableSharePostEmail": false,
"IsActive": true,
"LastName": "birdyjbirch",
"FirstName": "birdyjbirch",
"DefaultGroupNotificationFrequency": "N",
"UserPermissionsAvantgoUser": false,
"UserPreferencesHideCSNGetChatterMobileTask": false,
"CommunityNickname": "birdyjbirch",
"UserPreferencesShowCityToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableChangeCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesHideSfxWelcomeMat": true,
"EmailPreferencesAutoBcc": true,
"BannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/B",
"UserPreferencesCacheDiagnostics": false,
"UserPreferencesHideEndUserOnboardingAssistantModal": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCityToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsSupportUser": false,
"UserPreferencesShowProfilePicToGuestUsers": false,
"SmallPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/T",
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToGuestUsers": false,
"SystemModstamp": "2023-07-21T23:39:02.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesDisableLaterCommentEmail": false,
"LocaleSidKey": "en_US",
"UserPreferencesSuppressTaskSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableBookmarkEmail": false,
"__NAME__": "00503000004PDoeAAG",
"UserPermissionsOfflineUser": true, (1)
"UserPreferencesActivityRemindersPopup": true,
"UserPreferencesEnableAutoSubForFeeds": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesReminderSoundOff": false,
"UserPreferencesCreateLEXAppsWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableMentionsPostEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesExcludeMailAppAttachments": false,
"OutOfOfficeMessage": "",
"SmallBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/D",
"UserPreferencesDisableFileShareNotificationsForApi": false,
"UserPreferencesEventRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeSectionCollapseWTShown": false,
"MediumBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/E",
"UserPreferencesUserDebugModePref": false,
"UserPreferencesHideS1BrowserUI": false,
"MediumPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/M",
"UserPreferencesPathAssistantCollapsed": false,
"Email": "birdyjbirch@example.com",
"UserType": "Standard",
"UserPreferencesDisableMessageEmail": false,
"ReceivesInfoEmails": false,
"EmailPreferencesAutoBccStayInTouch": false,
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToGuestUsers": false,
"IsProfilePhotoActive": false,
"LastModifiedDate": "2023-07-21T23:39:02.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesTaskRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"UserPreferencesDisableEndorsementEmail": false,
"FullPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/F",
"Name": "birdyjbirch birdyjbirch",
"UserPreferencesDisCommentAfterLikeEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesSortFeedByComment": true,
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeReservedWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavBarWTShown": false,
"TimeZoneSidKey": "America/Los_Angeles",
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToGuestUsers": false,
"ProfileId": "00e30000001ehhPAAQ",
"UserPreferencesHideSecondChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToExternalUsers": true,
"UserPreferencesNewLightningReportRunPageEnabled": false,
"UserPermissionsChatterAnswersUser": false,
"LanguageLocaleKey": "en_US",
"ReceivesAdminInfoEmails": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToGuestUsers": false,
"Alias": "birdch",
"UserPreferencesPreviewLightning": false,
"UserPreferencesHideChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToExternalUsers": false,
"CreatedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPreferencesDisableFollowersEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableAllFeedsEmail": false,
"UserPermissionsSFContentUser": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesFavoritesShowTopFavorites": false
}| 1 | UserPermissionsOfflineUser is now true. |
Update a user’s feature licenses
You can update a user’s feature licenses through the API using a PUT call. The following request adds a feature license to birdj, a user with id 00503000004PDmsAAG:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToExternalUsers": false,
"ForecastEnabled": false,
"DigestFrequency": "D",
"UserPreferencesPipelineViewHideHelpPopover": false,
"UserPermissionsMarketingUser": false,
"LastReferencedDate": "2023-07-21T23:29:42.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesPreviewCustomTheme": false,
"UserPreferencesDisMentionsCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsCallCenterAutoLogin": false,
"UserPreferencesApexPagesDeveloperMode": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToGuestUsers": false,
"Id": "00503000004PDmsAAG",
"UserPreferencesHasCelebrationBadge": false,
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToExternalUsers": false,
"IsExtIndicatorVisible": false,
"BadgeText": "",
"UserPreferencesDisableProfilePostEmail": false,
"Username": "birdyjbird@example.com",
"UserPreferencesLightningExperiencePreferred": true,
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"EmailPreferencesStayInTouchReminder": true,
"UserPreferencesHideLightningMigrationModal": false,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavGridMenuWTShown": false,
"EmailEncodingKey": "UTF-8",
"UserPreferencesDisProfPostCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesHideCSNDesktopTask": false,
"LastModifiedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPreferencesShowStreetAddressToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesHideBiggerPhotoCallout": false,
"UserPreferencesShowWorkPhoneToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesSuppressEventSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowPostalCodeToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsMobileUser": false,
"CreatedDate": "2023-07-21T23:29:41.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesFavoritesWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableLikeEmail": true,
"UserPreferencesShowMobilePhoneToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableSharePostEmail": false,
"IsActive": true,
"LastName": "birdyjbird",
"FirstName": "birdyjbird",
"DefaultGroupNotificationFrequency": "N",
"UserPermissionsAvantgoUser": false,
"UserPreferencesHideCSNGetChatterMobileTask": false,
"CommunityNickname": "birdyjbird",
"UserPreferencesShowCityToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToGuestUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableChangeCommentEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesHideSfxWelcomeMat": true,
"EmailPreferencesAutoBcc": true,
"LastViewedDate": "2023-07-21T23:29:42.000+0000",
"BannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/B",
"UserPreferencesCacheDiagnostics": false,
"UserPreferencesHideEndUserOnboardingAssistantModal": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCityToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPermissionsSupportUser": false,
"UserPreferencesShowProfilePicToGuestUsers": false,
"SmallPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/T",
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToGuestUsers": false,
"SystemModstamp": "2023-07-21T23:29:41.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesDisableLaterCommentEmail": false,
"LocaleSidKey": "en_US",
"UserPreferencesSuppressTaskSFXReminders": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableBookmarkEmail": false,
"__NAME__": "00503000004PDmsAAG",
"UserPermissionsOfflineUser": false,
"UserPreferencesActivityRemindersPopup": true,
"UserPreferencesEnableAutoSubForFeeds": false,
"UserPreferencesShowEmailToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesReminderSoundOff": false,
"UserPreferencesCreateLEXAppsWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableMentionsPostEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesExcludeMailAppAttachments": false,
"OutOfOfficeMessage": "",
"SmallBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/D",
"UserPreferencesDisableFileShareNotificationsForApi": false,
"UserPreferencesEventRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeSectionCollapseWTShown": false,
"MediumBannerPhotoUrl": "/profilephoto/005/E",
"UserPreferencesUserDebugModePref": false,
"UserPreferencesHideS1BrowserUI": false,
"MediumPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/M",
"UserPreferencesPathAssistantCollapsed": false,
"Email": "birdyjbird@example.com",
"UserType": "Standard",
"UserPreferencesDisableMessageEmail": false,
"ReceivesInfoEmails": false,
"EmailPreferencesAutoBccStayInTouch": false,
"UserPreferencesShowManagerToGuestUsers": false,
"IsProfilePhotoActive": false,
"LastModifiedDate": "2023-07-21T23:29:41.000+0000",
"UserPreferencesTaskRemindersCheckboxDefault": true,
"UserPreferencesDisableEndorsementEmail": false,
"FullPhotoUrl": "https://example.force.com/profilephoto/005/F",
"Name": "birdyjbird birdyjbird",
"UserPreferencesDisCommentAfterLikeEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesSortFeedByComment": true,
"UserPreferencesRecordHomeReservedWTShown": false,
"UserPreferencesGlobalNavBarWTShown": false,
"TimeZoneSidKey": "America/Los_Angeles",
"UserPreferencesShowFaxToGuestUsers": false,
"ProfileId": "00e30000001ehhPAAQ",
"UserPreferencesHideSecondChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"UserPreferencesShowTitleToExternalUsers": true,
"UserPreferencesNewLightningReportRunPageEnabled": false,
"UserPermissionsChatterAnswersUser": false,
"LanguageLocaleKey": "en_US",
"ReceivesAdminInfoEmails": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToGuestUsers": false,
"Alias": "birdj",
"UserPreferencesPreviewLightning": false,
"UserPreferencesHideChatterOnboardingSplash": false,
"UserPreferencesShowStateToExternalUsers": false,
"CreatedById": "00530000009hWLcAAM",
"UserPreferencesDisableFollowersEmail": false,
"UserPreferencesDisableAllFeedsEmail": false,
"UserPermissionsSFContentUser": false,
"UserPreferencesShowCountryToExternalUsers": false,
"UserPreferencesFavoritesShowTopFavorites": false,
"__FeatureLicenses__": [ (1)
"UserPermissionsOfflineUser"
]
}' \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/salesforce/User/00503000004PDmsAAG"
| 1 | The __FeatureLicenses__ array of strings to add to the user. |
Query all supported feature licenses
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/salesforce/FeatureLicense?_queryFilter=true"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "UserPermissionsOfflineUser",
"__NAME__": "UserPermissionsOfflineUser"
},
{
"_id": "UserPermissionsMarketingUser",
"__NAME__": "UserPermissionsMarketingUser"
},
{
"_id": "UserPermissionsInteractionUser",
"__NAME__": "UserPermissionsInteractionUser"
}
],
"resultCount": 3,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Read a feature license
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/salesforce/FeatureLicense/UserPermissionsMarketingUser"
{
"_id": "UserPermissionsMarketingUser",
"__NAME__": "UserPermissionsMarketingUser"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Salesforce Connector
The Salesforce Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Salesforce Connector Configuration
The Salesforce Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The client identifier. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The secure client secret for OAUTH. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The OAuth2 grant type to use (client_credentials or refresh_token). |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The refresh token for the application. Required for refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
|
The endpoint from which a new access token should be queried (https://login.salesforce.com/services/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The URL of the Salesforce instance (such as https://example-com.cs1.my.salesforce.com). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The Salesforce API version. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum connection timeout. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The hostname of an HTTP proxy used between the connector and the Salesforce service provider. Mutually exclusive with proxyUri and uses http scheme. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The proxy port number, if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the Salesforce service provider. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum size of the HTTP connection pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a list of Salesforce objects that will be used to dynamically build the provisioner schema. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The URI of an HTTP proxy that contains the scheme, host, and port number for that proxy. Mutually exclusive with proxyHost. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The proxy username to use with a proxy that requires authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The proxy user password to use with a proxy that requires authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a list of Salesforce feature licenses that can be assigned. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP connector
The SAP connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy connector toolkit that connects to any SAP system using the SAP JCo Java libraries. This topic describes how to install and configure the scripted SAP connector and how to test the sample scripts bundled with the connector.
| You can configure the SAP connector to work with either SAP HR or SAP ERP systems. |
The sample scripts illustrate the following scenarios:
-
Synchronization of users between an SAP HR module and IDM
-
Synchronization of users between IDM and an SAP (R/3) system
Install the SAP connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/sap-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Download the connector dependencies.
-
The SAP connector requires the SAP Java Connector (JCo) libraries, version 3.0.12 or later. ForgeRock distributes the SAP connector without these JCo libraries. Before you can use the SAP connector, you must obtain the JCo libraries that correspond to your architecture.
Copy the required SAP JCo libraries to the
/path/to/openidm/libdirectory. For example:cp sapjco3.jar /path/to/openidm/lib cp libsapjco3.so /path/to/openidm/lib
Change your IDM logging configuration to log messages from the SAP connector. By default, IDM logs nothing for the SAP connector. To troubleshoot any issues with the connector, set the following properties in your project’s conf/logging.properties file:
# SAP Connector Logging
org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.level=FINER
scripts.sap.r3.level=FINER
scripts.sap.hr.level=FINER
scripts.sap.level=FINERUsing the SAP connector with an SAP HR system
The SAP HR sample scripts let you manage the email address and global employee UID of records in an SAP HR system.
The following sections explain how to configure IDM to use these sample scripts, how to test the connection to the SAP HR system, and how to update user records.
Setting up IDM for the SAP HR samples
-
Create a connector configuration file for the SAP connector and place it in your project’s
conf/directory.Edit that file with the connection details for your SAP HR system. Specifically, set at least the following properties:
destination-
An alias to the SAP system to which you are connecting, for example,
SAP1. If you are connecting to more than one SAP system, thedestinationproperty for each system must be unique.The sample connector configuration assumes a connection to a single SAP system, so the value for this property in the sample configuration is
OPENIDM. asHost-
The FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example
sap.example.com. user-
Your SAP user account.
password-
The password of this SAP user account.
client-
The SAP Client number that will be used to connect to the SAP system.
systemNumber-
The SAP system number.
directConnection-
A boolean (true/false). If
true, the connection goes directly to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. Iffalse, the connection goes to a group of SAP instances through an SAP message server. sapRouter-
The IP address and port of the SAP router, if applicable. The syntax is
/H/hostport], for example/H/203.0.113.0/S/3299. poolCapacity-
The maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. If there is no connection pooling, set this to
0. The default value is1.For optimum performance, set this value to an integer between
5and10.
-
The connector bundles a number of sample Groovy scripts:
-
TestSAP.groovy -
SearchSAPHR.groovy -
UpdateSAPHR.groovy -
SchemaSAPHR.groovy -
EmplComm.groovyIf necessary, you can customize these scripts to suit your deployment by extracting them from the connector JAR and updating the connector configuration to point to the new file path.
The sample connector configuration assumes the following locations for the scripts (relative to the value of the
scriptRootsproperty):"testScriptFileName" : "TestSAP.groovy", "searchScriptFileName" : "hr/SearchSAPHR.groovy", "updateScriptFileName" : "hr/UpdateSAPHR.groovy", "schemaScriptFileName" : "hr/SchemaSAPHR.groovy",You must place the
EmplComm.groovyin the same location as the Search, Update, and Schema scripts.The Groovy scripts belong to a specific package. The parent directory where the scripts are located must be the same as the package name. So the TestSAP.groovyscript must be under ascripts/sapdirectory (because it belongs to thescripts/sappackage) and the remaining HR scripts must be under ascripts/sap/hrdirectory (because they belong to thehrpackage).
-
Testing the connection to the SAP HR system
-
Start IDM with the configuration for your SAP connector project.
This procedure assumes that the configuration is in the default
path/to/openidmdirectory. If your SAP project is in a different directory, use the-poption with the startup command to point to that directory:path/to/openidm/startup.sh
-
Test that the connector has been configured correctly and that the SAP HR system can be reached:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/?_action=test" { "name" : "saphr", "enabled" : true, "config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/saphr2", "objectTypes" : [ "__ALL__", "employee" ], "connectorRef" : { "connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.SapConnector", "bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap-connector", "bundleVersion" : "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)" }, "displayName" : "Sap Connector", "ok" : true } -
Retrieve a list of the existing users (with their employee number) in the SAP HR system:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee?_queryId=query-all-ids" { "result" : [ { "_id" : "00000010", "__NAME__" : "00000010" }, { "_id" : "00000069", "__NAME__" : "00000069" }, { "_id" : "00000070", "__NAME__" : "00000070" }, ... ] } -
Retrieve the complete record of an employee in the SAP HR system by including the employee’s ID in the URL.
The following command retrieves the record for employee Maria Gonzales:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" { "_id" : "55099307", "PERSONAL_DATA" : { "PERNO" : "55099307", "INFOTYPE" : "0002", "TO_DATE" : "Fri Dec 31 00:00:00 CET 9999", "FROM_DATE" : "Tue Mar 30 00:00:00 CET 1954", "SEQNO" : "000", "CH_ON" : "Thu Mar 27 00:00:00 CET 2003", "CHANGED_BY" : "MAYROCK", "LAST_NAME" : "Gonzales", "FIRSTNAME" : "Maria", "NAME_FORM" : "00", "FORMOFADR" : "2", "GENDER" : "2", "BIRTHDATE" : "Tue Mar 30 00:00:00 CET 1954", "LANGU" : "D", "NO_O_CHLDR" : "0", "BIRTHYEAR" : "1954", "BIRTHMONTH" : "03", "BIRTHDAY" : "30", "LASTNAME_M" : "GONZALES", "FSTNAME_M" : "MARIA" }, ... }
Using the SAP connector to manage employee information (SAP HR)
The following sample commands show how you can use the SAP connector to manage the email account of user Maria Gonzales, retrieved in the previous step. Management of the global UID (SYS-UNAME) works in the same way.
-
Check if Maria Gonzales already has an email account on the SAP HR system by filtering a query on her user account for the
EMAILfield:curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307?_fields=EMAIL" { "_id" : "55099307", }No email account is found for Maria Gonzales.
-
Add an email account by sending a PUT request. The JSON payload should include the email address as the value of the
IDproperty:curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales@example.com" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" { "_id" : "55099307", "EMAIL" : [ { "EMPLOYEENO" : "55099307", "SUBTYPE" : "0010", "VALIDEND" : "Fri Dec 31 00:00:00 CET 9999", "VALIDBEGIN" : "Fri March 18 00:00:00 CET 2016", "RECORDNR" : "000", "COMMTYPE" : "0010", "NAMEOFCOMMTYPE" : "E-mail", "ID" : "Maria.Gonzales@example.com" } ], ... }By default, the connector sets the
VALIDBEGINdate to the current date, and theVALIDENDdate to the SAP "END" date (12/31/9999). You can specify different temporal constraints by including these properties in the JSON payload, with the formatYYYYMMDD. For example:{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales@example.com" "VALIDBEGIN": "20160401", "VALIDEND": "20161231" } } -
To change the value of an existing email account, provide a new value for the
ID.The JSON payload of the change request must also include the
RECORDNRattribute, as well as theVALIDBEGINandVALIDENDdates, in SAP format (YYYYMMDD).The following example changes Maria Gonzales' email address to
maria.gonzales-admin@example.com:curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales-admin@example.com", "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" -
To change the temporal constraint (
VALIDENDdate) of the record, include the existingVALIDENDdata in the JSON payload, and specify the new end date as a value of theDELIMIT_DATEattribute.The following example changes the end date of Maria Gonzales' new mail address to December 31st, 2016:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "ID": "maria.gonzales-admin@example.com", "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101", "DELIMIT_DATE": "20161231" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307" -
To delete the email address of the record, send a PUT request with the current
RECORDNR,VALIDBEGIN, andVALIDENDattributes, but without theID.The following request removes the email address from Maria Gonzales' record:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --request PUT \ --data '{ "EMAIL": { "RECORDNR" : "000", "VALIDEND" : "99991231", "VALIDBEGIN" : "20000101" } }' \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphr/employee/55099307"
Using the SAP connector to manage SAP Basis System (R/3) users
The SAP connector enables you to perform the following operations on SAP system user accounts:
-
List all users
-
List all activity groups (roles)
-
List all user profiles
-
List all user companies
-
List all user groups
-
Obtain a user’s details
-
Create a user
-
Update a user
-
Assign roles to a user
-
Lock a user account
-
Unlock a user account
-
Delete a user account
Setting up IDM for the SAP R/3 samples
-
Create a connector configuration file for the SAP connector and place it in your project’s
conf/directory.Edit that file with the connection details for your SAP R/3 system. Specifically, set at least the following properties:
destination-
An alias to the SAP system to which you are connecting, for example,
SAP1. If you are connecting to more than one SAP system, thedestinationproperty for each system must be unique.The sample connector configuration assumes a connection to a single SAP system,
MYSAP. asHost-
The FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example
sap.example.com. user-
Your SAP user account.
password-
The password of this SAP user account.
client-
The SAP Client number that will be used to connect to the SAP system.
systemNumber-
The SAP system number.
directConnection-
A boolean (true/false). If
true, the connection goes directly to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. Iffalse, the connection goes to a group of SAP instances through an SAP message server. sapRouter-
The IP address and port of the SAP router, if applicable. The syntax is
/H/hostport], for example/H/203.0.113.0/S/3299. poolCapacity-
The maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. If there is no connection pooling, set this to
0. The default value is1.For optimum performance, set this value to an integer between
5and10.
-
The connector bundles a number of sample Groovy scripts:
-
TestSAP.groovy -
SearchSAPR3.groovy -
CreateSAPR3.groovy -
UpdateSAPR3.groovy -
DeleteSAPR3.groovy -
SyncSAPR3.groovy -
SchemaSAPR3.groovy -
ListR3Objects.groovy -
R3User.groovy -
R3UserActivityGroup.groovy -
R3UserAddress.groovy -
R3UserGroup.groovy -
R3UserLogonData.groovy -
R3UserProfile.groovy -
R3Config.groovy -
ListTablesR3Objects.groovy -
QueryTable.groovyIf necessary, you can customize these scripts to suit your deployment by extracting them from the connector JAR and updating the connector configuration to point to the new file path.
The sample connector configuration assumes the following locations for the scripts (relative to the value of the
scriptRootsproperty):"testScriptFileName" : "TestSAP.groovy", "searchScriptFileName" : "r3/SearchSAPR3.groovy", "createScriptFileName" : "r3/CreateSAPR3.groovy", "updateScriptFileName" : "r3/UpdateSAPR3.groovy", "deleteScriptFileName" : "r3/DeleteSAPR3.groovy", "syncScriptFileName" : "r3/SyncSAPR3.groovy", "schemaScriptFileName" : "r3/SchemaSAPR3.groovy",The Groovy scripts belong to a specific package. The parent directory where the scripts are located must be the same as the package name. So the TestSAP.groovyscript must be under ascripts/sapdirectory (because it belongs to thescripts/sappackage) and the R/3 scripts must be under ascripts/sap/r3directory (because they belong to ther3package).
-
Testing the connection to the SAP R/3 system
-
Start IDM with the configuration for your SAP R/3 project.
This procedure assumes that the configuration is in the default
path/to/openidmdirectory. If your SAP project is in a different directory, use the-poption with the startup command to point to that directory:/path/to/openidm/startup.sh
-
Test that the connector has been configured correctly and that the SAP R/3 system can be reached:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/?_action=test" { "name": "mysap", "enabled": true, "config": "config/provisioner.openicf/mysap", "objectTypes": [ "__ALL__", "user", "activity_group", "company", "profile", "group" ], "connectorRef": { "connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap.SapConnector", "bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.sap-connector", "bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)" }, "displayName": "Sap Connector", "ok": true }
Using the SAP connector to manage SAP R/3 users
This section provides sample commands for managing users in an SAP system.
Listing the users in the SAP system
The following command returns a list of the existing users in the SAP system, with their IDs:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
},
{
"_id": "DDIC",
"__NAME__": "DDIC"
},
...
{
"_id": "USER4",
"__NAME__": "USER4"
},
{
"_id": "USER6",
"__NAME__": "USER6"
},
{
"_id": "USER7",
"__NAME__": "USER7"
}
],
"resultCount": 9,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Obtaining the details of an SAP user
The following command uses the SAP connector to obtain a user’s details from a target SAP system:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"__ENABLE_DATE__": "2015-09-01",
"__DISABLE_DATE__": "2016-09-01",
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"ADDTEL": [
{
"COUNTRY": "DE",
"TELEPHONE": "19851444",
...
},
...
],
"PROFILES": [
"T_ALM_CONF",
...
],
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
...
},
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "MW_ADMIN",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-07-15",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31"
},
...
],
"DEFAULTS": {
...
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"ADDRESS": {
...
},
"UCLASS": {
...
},
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2015-07-15",
"MODTIME": "14:22:57"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2015-09-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-09-01",
...
},
"GROUPS": {
"USERGROUP": "SUPER"
...
},
"_id": "BJENSEN"
}
When using Central User Administration (CUA), the system also returns the SUBSYSTEMS attribute. Additionally, PROFILES and ACTIVITYGROUPS have a different definition:
"SYSTEMS": [
"TE9CLNT200",
"TE9CLNT300",
\...
],
"PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "T_ALM_CONF",
"SUBSYSTEM: "TE9CLNT200"
},
{
"BAPIPROF": "T_ALM_CONF",
"SUBSYSTEM: "TE9CLNT300"
},
\...
],
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "MW_ADMIN",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-07-15",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31",
"SUBSYSTEM": "TE9CLNT200"
},
{
"AGR_NAME": "MW_ADMIN",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-07-15",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31",
"SUBSYSTEM": "TE9CLNT300"
},
\...
]
...
In addition to the standard user attributes, the GET request returns the following ICF operational attributes:
-
__ENABLE__- indicates whether the account is enabled, based on the value of theLOGONDATAattribute -
__ENABLE_DATE__- set to the value ofLOGONDATA/GLTGV(date from which the user account is valid) -
__DISABLE_DATE__- set to the value ofLOGONDATA/GLTGB(date to which the user account is valid) -
__LOCK_OUT__- indicates whether the account is locked
Creating SAP user accounts
To create a user, you must supply at least a username and password. If you do not provide a lastname, the connector uses the value of the username.
The following command creates a new SAP user, SCARTER:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"ADDRESS": {
...
},
"__NAME__": "SCARTER",
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-20",
"MODTIME": "04:14:29"
},
"UCLASS": {
"COUNTRY_SURCHARGE": "0",
"SUBSTITUTE_FROM": "0000-00-00",
"SUBSTITUTE_UNTIL": "0000-00-00"
},
"__ENABLE__": true,
"DEFAULTS": {
"SPDB": "H",
"SPDA": "K",
"DATFM": "1",
"TIMEFM": "0"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
...
},
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "U",
"GLOB_LOCK": "U",
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
}
}
The SAP account that is created is valid and enabled, but the password is expired by default. To log in to the SAP system, the newly created user must first provide a new password.
To create a user with a valid (non-expired) password, include the __PASSWORD_EXPIRED__ attribute in the JSON payload with a value of false. For example:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
To create an account that is locked by default, include the __LOCK_OUT__ attribute in the JSON payload with a value of true. For example:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__LOCK_OUT__": true
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"__NAME__": "SCARTER",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"__LOCK_OUT__": true,
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "0000-00-00",
"GLTGB": "0000-00-00",
"USTYP": "A",
"LTIME": "00:00:00"
},
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2015-10-01",
"MODTIME": "15:25:18"
},
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "L", (1)
"GLOB_LOCK": "U", (2)
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
},
...
}
| 1 | "L" indicates that the user is locked on the local system. |
| 2 | On CUA Systems "GLOB_LOCK" will be marked as locked instead of "LOCAL_LOCK". |
Schema used by the SAP connector for user accounts
For the most part, the SAP connector uses the standard SAP schema to create a user account. The most common attributes in an SAP user account are as follows:
-
ADDRESS- user address data -
LOGONDATA- user logon data -
DEFAULTS- user account defaults -
COMPANY- the company to which the user is assigned -
REF_USER- the usernames of the Reference User -
ALIAS- an alias for the username -
UCLASS- license-related user classification -
LASTMODIFIED- read-only attribute that indicates the date and time that the account was last changed -
ISLOCKED- read-only attribute that indicates the lockout status of the account -
IDENTITY- assignment of a personal identity to the user account -
PROFILES- any profiles assigned to the user account (see connector-reference:sap.adoc#user-profiles). -
ACTIVITYGROUPS- activity groups assigned to the user (Roles) -
ADDTEL- telephone numbers assigned to the user -
GROUPS- groups assigned to the user -
SYSTEMS- subsystems assigned to the user (Only on CUA systems)
In addition, the SAP connector supports the following ICF operational attributes for CREATE requests:
-
LOCK_OUT -
PASSWORD -
PASSWORD_EXPIRED
The following example creates a user, KVAUGHAN, with all the standard attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "KVAUGHAN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2016-04-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-12-01",
"USTYP": "A"
},
"ADDRESS": {
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"TEL1_NUMBR": "33297603177",
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"FUNCTION": "Test User"
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "EXAMPLE.COM"
},
"ALIAS": {
"USERALIAS": "KVAUGHAN"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "KVAUGHAN",
"ADDRESS": {
"PERS_NO": "0000010923",
"ADDR_NO": "0000010765",
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"FULLNAME": "Katie Vaughan",
...
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"LANGU_CR_P": "E",
"LANGUCPISO": "EN"
},
"LOGONDATA": {
"GLTGV": "2016-04-01",
"GLTGB": "2016-12-01",
...
},
"COMPANY": {
"COMPANY": "SAP AG"
},
"__ENABLE__": true,
"ADDTEL": [
{
...
}
],
"ISLOCKED": {
"WRNG_LOGON": "U",
"LOCAL_LOCK": "U",
"GLOB_LOCK": "U",
"NO_USER_PW": "U"
},
"UCLASS": {
"COUNTRY_SURCHARGE": "0",
"SUBSTITUTE_FROM": "0000-00-00",
"SUBSTITUTE_UNTIL": "0000-00-00"
},
"ALIAS": {
"USERALIAS": "KVAUGHAN"
},
"__NAME__": "KVAUGHAN",
"__LOCK_OUT__": false,
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-20",
"MODTIME": "04:55:08"
},
"__ENABLE_DATE__": "2016-04-01", (1)
"DEFAULTS": {
"SPDB": "H",
"SPDA": "K",
"DATFM": "1",
"TIMEFM": "0"
},
"__DISABLE_DATE__": "2016-12-01" (2)
}
| 1 | Value of LOGONDATA/GLTGV. |
| 2 | Value of LOGONDATA/GLTGB. |
Updating SAP user accounts
The following sections provide sample commands for updating an existing user account.
Locking and unlocking an account
To lock or unlock a user’s account, send a PUT request, and set the value of the user’s __LOCK_OUT__ attribute to true.
The following example locks user KVAUGHAN’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__LOCK_OUT__": true
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
The following example unlocks KVAUGHAN’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__LOCK_OUT__": false
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
Updating the standard attributes of a user’s account
To update a user’s standard attributes, send a PUT request to the user ID. The JSON payload must respect the structure for each attribute, as indicated in connector-reference:sap.adoc#sap-user-schema.
The following command updates the ADDRESS attribute of user KVAUGHAN:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ADDRESS": {
"FIRSTNAME": "Katie",
"LASTNAME": "Vaughan",
"FULLNAME": "Katie Vaughan",
"FUNCTION": "Administrator",
"TITLE": "Company",
"NAME": "EXAMPLE.COM",
"CITY": "San Francisco",
"POSTL_COD1": "94105",
"STREET": "Sacramento St",
"HOUSE_NO": "2912",
"COUNTRY": "US",
"COUNTRYISO": "US",
"LANGU": "E",
"LANGU_ISO": "EN",
"REGION": "CA",
"TIME_ZONE": "PST",
"TEL1_NUMBR": "33297603177",
"E_MAIL": "katie.vaughan@example.com",
"LANGU_CR_P": "E",
"LANGUCPISO": "EN"
}
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
Resetting a user’s password
To reset the user’s password, provide the new password as the value of the __PASSWORD__ attribute in a PUT request. The following command resets KVAUGHAN’s password to MyPassw0rd:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "MyPassw0rd"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
Note that unless you set the __PASSWORD_EXPIRED__ attribute to false, the user will be required to reset her password the next time she logs into the SAP system.
The following command resets KVAUGHAN’s password to MyPassw0rd, and ensures that she does not have to reset her password the next time she logs in:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__PASSWORD__": "MyPassw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false
}'
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
Deleting user accounts
To delete a user account, send a DELETE request to the user ID. The following example deletes KVAUGHAN:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request DELETE \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/KVAUGHAN"
The command returns the complete user object that was deleted.
Get the latest changes with LiveSync
The following example updates the user’s data since the last synchronization:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=liveSync&source=system/mysap/__ACCOUNT__"
{
"connectorData": {
"nativeType": "string",
"syncToken": "20230707160932"
},
"_rev": "b69ca221-6610-484a-983f-142e8544e519-101",
"_id": "SYSTEMMYSAP\__ACCOUNT__"
}
Managing user profiles
An SAP system uses profiles to manage authorization. The following examples demonstrate how to add, change, and remove a user’s profiles.
Creating a user with one or more profiles
Profiles are added as an array of one or more strings.
The following command creates a user BJENSEN with the system administrator profile (S_A.SYSTEM):
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "BJENSEN",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"PROFILES": [
"S_A.SYSTEM"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"PROFILES": [
"S_A.SYSTEM"
],
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}
Note that the additional information regarding that profile is added to the user account automatically.
Updating a user’s profiles
To update a user’s profiles, send a PUT request to the user’s ID, specifying the new profiles as an array of values for the PROFILES attribute. The values provided in the PUT request will replace the current profiles, so you must include the existing profiles in the request.
The following example adds the SAP_ALL profile to user BJENSEN’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"PROFILES": [
"S_A.SYSTEM",
"SAP_ALL"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"PROFILES": [
"SAP_ALL",
"S_A.SYSTEM"
],
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}
Removing all profiles from a user account
To remove all profiles from a user’s account, update the account with an empty array. The following example removes all profiles from BJENSEN’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"PROFILES": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
...
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN"
}
The output shows no PROFILES attribute, as this attribute is now empty for this user.
|
When using CUA systems, each "PROFILES": [
{
"BAPIPROF": "SAP_ALL",
"SUBSYSTEM: "TE9CLNT200"
},
{
"BAPIPROF": "S_A.SYSTEM",
"SUBSYSTEM: "TE9CLNT200"
},
],
...
|
Managing user roles
SAP user roles (or activity groups) are an alternative mechanism to grant authorization to an SAP system. Essentially, a role encapsulates a set of one or more profiles.
Roles can be granted with temporal constraints, that is, a period during which the role is valid. If no temporal constraints are specified, the SAP connector sets the FROM date to the current date and the TO date to 9999-12-31.
Creating a user with one or more profiles
Roles are added as an array of one or more objects.
The following command creates a user SCARTER, with two roles: SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR and SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR. The auditor role includes a temporal constraint, which is only valid from May 1st, 2016 to April 30th, 2017. The format of the temporal constraint is YYYY-mm-dd:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-05-01",
"TO_DAT": "2017-04-30"
},
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR"
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"PROFILES": [
"T_ALM_CONF"
],
...
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-04-20",
"TO_DAT": "9999-12-31"
},
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR",
"FROM_DAT": "2016-05-01",
"TO_DAT": "2017-04-30"
}
],
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
When a role is granted, the corresponding profiles are attached to the user account automatically.
Updating a user’s roles
To update a user’s roles, send a PUT request to the user’s ID specifying the new roles as an array of values of the ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute. The values provided in the PUT request will replace the current ACTIVITYGROUPS.
The following example removes the SAP_AUDITOR_SA_CCM_USR role and changes the temporal constraints on the SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR role for SCARTER’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-06-02",
"TO_DAT": "2016-06-02"
}
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"PROFILES": [
"T_ALM_CONF"
],
...
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-06-02",
"TO_DAT": "2016-06-02"
}
],
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
Removing all roles from a user account
To remove all roles from a user’s account, update the value of the ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute with an empty array. The following example removes all roles from SCARTER’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"ACTIVITYGROUPS": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
...
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-21",
"MODTIME": "04:27:00"
},
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
The output shows no ACTIVITYGROUPS attribute, as this attribute is now empty.
|
On CUA systems, each "ACTIVITYGROUPS": [
{
"AGR_NAME": "SAP_ALM_ADMINISTRATOR",
"SUBSYSTEM": "T9CLNT200",
"FROM_DAT": "2015-06-02",
"TO_DAT": "2016-06-02"
}
],
...
|
Managing user groups
One of the Primary uses of user groups is to sort users into logical groups. This allows users to be categorized in a method that is not dependent on roles, AG’s, Responsibilities, Profiles, and so on.
User Groups also allow segregation of user maintenance, this is especially useful in a large organisation as you can control who your user admin team can maintain - an example would be giving a team leader the authority to change passwords for users in their team.
Creating a user with one or more groups
You add groups as an array of one or more strings.
The following command creates a user SCARTER, with two groups, SUPER and TEST_GROUP:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__" : "SCARTER",
"__PASSWORD__": "Passw0rd",
"__PASSWORD_EXPIRED__": false,
"GROUPS": [
"SUPER",
"TEST_GROUP"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/?_action=create"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
"GROUPS": [
"SUPER",
"TEST_GROUP"
],
...
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
Updating a user’s groups
To update a user’s groups, send a PUT request to the user’s ID, specifying the new groups as an array of values of the GROUPS attribute. The values provided in the PUT request replaces the current GROUPS.
The following example removes the SUPER group for SCARTER’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"GROUPS": [
"TEST_GROUP"
]
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
...
"GROUPS": [
"TEST_GROUP"
],
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
Removing all groups from a user account
To remove all groups from a user’s account, update the value of the GROUPS attribute with an empty array. The following example removes all groups from SCARTER’s account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match: *" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"GROUPS": []
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/mysap/user/SCARTER"
{
"_id": "SCARTER",
...
"LASTMODIFIED": {
"MODDATE": "2016-04-21",
"MODTIME": "04:27:00"
},
"__NAME__": "SCARTER"
}
The output shows no GROUPS attribute, as this attribute is now empty.
Configuring the SAP connector for OpenIDM user interface for R3
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select SAP Connector - 1.5.20.21.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to SAP Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Base Connector Details
To run the connector, you need the following minimum configuration:
-
Gateway Host: Host name or IP address of the SAP Gateway Server -
Application Server Host: Host name or IP address of the SAP Application Server (or SAP Netweaver Gateway) -
Client: Name of the SAP logon client -
Language: Language of the remote SAP System -
SAP Router -
User: Logon used for authenticating on the remote SAP System -
Password: Password of the previously specified logon, used for authenticating on the remote SAP System -
Scripts Root: Full Path To Script Files -
Search Script -
Create Script -
Update Script -
Delete Script -
Sync Script -
Test Script -
Schema Script
Object Types
You must add or edit your Object Types including the following four objects with the listed minimum properties:
__ACCOUNT__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED | ITEM TYPE | ITEM NATIVE TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
__NAME__ |
String |
String |
YES |
- |
- |
__PASSWORD__ |
String |
JAVA_TYPE_GUARDEDSTRING |
YES |
- |
- |
ALIAS |
String |
String |
YES |
- |
- |
LOGONDATA |
Object |
Object |
NO |
- |
- |
COMPANY |
Object |
Object |
NO |
- |
- |
ADDRESS |
Object |
Object |
YES |
- |
- |
__LOCK_OUT__ |
Boolean |
JAVA_TYPE_PRIMITIVE_BOOLEAN |
NO |
- |
- |
ACTIVITYGROUPS |
Array |
Object |
NO |
Object |
Object |
PROFILES (2) |
Array |
String |
NO |
String |
String |
GROUPS |
Array |
String |
NO |
String |
String |
SYSTEMS (1) |
Array |
String |
NO |
String |
String |
(1) On CUA Systems only.
(2) On CUA Systems it works as an array of objects.
profile
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
MANDT |
String |
String |
NO |
BAPIPTEXT |
String |
String |
NO |
PROFN |
String |
String |
NO |
TYP |
String |
String |
NO |
SUBSYSTEMS (1) |
Array |
String |
NO |
SUB_PROF (2) |
Array |
String |
NO |
(1) On CUA Systems only.
(2) Currently on non CUA Systems only.
activity_group
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
AGR_NAME |
String |
String |
NO |
MANDT |
String |
String |
NO |
SUBSYSTEMS (1) |
Array |
String |
NO |
SUB_AGR (2) |
Array |
String |
NO |
PROFILES (2) |
Array |
String |
NO |
T_CODES (2) |
Array |
String |
NO |
(1) On CUA Systems only.
(2) Currently on non CUA Systems only.
group
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
USERGROUP |
String |
String |
NO |
MANDT |
String |
String |
NO |
system
This object type is available on CUA Systems only
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
SYSNAME |
String |
String |
NO |
SYSTEMTYPE |
String |
String |
NO |
RFCDEST |
String |
String |
NO |
RCVSYSTEM |
String |
String |
NO |
NEW_SYSTEM |
String |
String |
NO |
MODEL |
String |
String |
NO |
SYSCLIENT |
String |
String |
NO |
CLIENT |
String |
String |
NO |
Configuring the SAP connector for SNC
The SAP connector supports an SNC (Secure Network Connection) configuration. SNC is a software layer in the SAP System architecture that provides an interface to an external security product.
For a list of the configuration properties specific to SNC, refer to SAP Secure Network Connection Configuration Properties.
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The SAP connector implements the add, remove, and replace operations but the sample scripts provided with the connector implement only the replace operation. If you use these sample scripts, a PATCH request will therefore always replace the entire attribute value with the new value.
Setting productive passwords on the SAP system
Synchronization of passwords to the SAP system requires that you configure SNC and SSO. If you do not configure these two elements correctly, passwords that are updated by IDM are set as initial passwords rather than productive passwords, and users are forced to change their passwords on login.
-
To configure the SAP connector to use SNC, set the
sncModeproperty to"1".To configure the connector to use SSO with SNC, set the
sncSSOproperty to"1". -
The logon session during which a productive password is set must be secured using the authentication method Single Sign-On (SSO) using Secure Network Communications (SNC). IDM must request and receive an SSO logon ticket from the SAP system to allow the
BAPI_USER_CHANGEprocess to set a productive password. For more information, refer to SAP Note 1287410.To configure the connector to request this logon ticket, set the value of the
x509Certproperty as follows:-
If you are using an X509 certificate to negotiate with the SAP server, set the
x509Certproperty to the base 64-encoded certificate.Note that the certificate must be a valid, CA-signed certificate. You cannot use a self-signed certificate here.
-
If you do not use an X509 certificate to negotiate with the SAP server, set the
x509Certproperty tonull.In this case, the connector will use the
userandpasswordspecified in the connector configuration to request the SSO logon ticket.
-
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the SAP Connector
The SAP Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
SAP Connector Configuration
The SAP Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
SAP gateway host name. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
SAP gateway service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The FQDN of your SAP Application Server, for example sap.example.com. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
SAP Logon user. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
SAP Logon password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
SAP client. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
SAP system number. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
SAP Logon language. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
SAP JCo destination name. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If true, direct connection to an SAP ABAP Application server or SAP router. If false connection to a group of SAP instances through an SAP message server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
SAP router string to use for a system protected by a firewall. (/H/host[/S/port]). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Advanced Configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the name of the SAP system, used when you log in to a logon group that uses load balancing. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the host that the message server is running on. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Name of the service where the message server can be reached. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the group name of the application servers, used when you log in to a logon group that uses load balancing. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP Secure Network Connection Configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The X509 certificate supplied for authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the AS ABAP SNC name, for example, "p:CN=ABC, O=MyCompany, C=US". You can find the application server SNC name in the profile parameter snc/identity/as on the AS ABAP. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the security level to use for the connection. Possible values are 1 - Authentication only, 2 - Integrity protection, 3 - Privacy protection, 8 - Use the value from snc/data_protection/use on the application server, 9 - Use the value from snc/data_protection/max on the application server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the connector SNC name, for example, "p:CN=OpenIDM, O=MyCompany, C=US". This parameter is optional, but you should set it to make sure that the correct SNC name is used for the connection. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Flag used to activate SNC. Possible values are 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies whether the connection should be configured for single sign-on (SSO). Possible values are 0 (OFF) and 1 (ON). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the path to the external library that provides Secure Network Connection service. The default is the system-defined library as defined in the environment variable SNC_LIB. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
JCo Connection Pool Configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of active connections that can be created for a destination simultaneously. The value 0 means unlimited. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum number of idle connections kept open by the destination. 0 = no connection pooling. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Time in ms after that a free connection can be closed. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Period in ms after that the destination checks the released connections for expiration. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Maximum time in ms to wait for a connection, if the maximum allowed number of connections is allocated by the pool. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP Jco Logs Configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Enable/disable CPIC trace [0..3]. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Enable/disable RFC trace (0 or 1). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP HANA Database connector
Before you start
These connector instructions require a SAP HANA Database account with elevated privileges to add roles, system, and application privileges. The following information is required to configure the connector:
- Username
-
Your SAP HANA Database username.
- Password
-
Your SAP HANA Database password.
- JDBC Connection URL
-
The URL to establish the connection between the connector and the SAP HANA Database.
- Driver class name
-
The class name driver path.
For more information, refer to the Connect to SAP HANA via JDBC documentation.
Install the SAP HANA Database connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/saphanadb-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Download the Sap Hana JDBC driver.
| The minimum required JDBC version is 2.16.14. |
-
If you are running the connector locally, place the library in the
/path/to/openidm/lib/directory:mv ~/Downloads/ngdbc-version.jar /path/to/openidm/lib/ -
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the SAP HANA Database connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select SAP HANA Database Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to SAP HANA Database Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Base connector details
username
|
The username for logging in to the database. |
password
|
The user password for logging in to the database. |
url
|
The database connection string in the form of |
driverClassName
|
The file directory location of DBC driver files. |
pageSize
|
Defines the page size to be displayed to users. |
ignoreUsers
|
Database users to ignore. Typically, these are internal database users to avoid for security reasons. |
Object types
You can add or edit the object type to obtain any of the following objects and their properties:
__ACCOUNT__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
GuardedString |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Boolean |
Boolean |
NO |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
ROLES
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES
PROPERTY NAME |
TYPE |
NATIVE TYPE |
REQUIRED |
|
String |
String |
NO |
SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES
PROPERTY NAME |
TYPE |
NATIVE TYPE |
REQUIRED |
|
String |
String |
NO |
To configure the connector over REST or using the filesystem, specify the connection details to the SAP HANA Database resource provider in the configurationProperties for the connector. The minimum required properties are username, password, url and driverClassName.
Sample configuration
{
"configurationProperties" : {
"connectionProperties" : null,
"propagateInterruptState" : false,
"useDisposableConnectionFacade" : true,
"defaultCatalog" : null,
"validationInterval" : 3000,
"ignoreExceptionOnPreLoad" : false,
"jmxEnabled" : true,
"commitOnReturn" : false,
"logAbandoned" : false,
"maxIdle" : 100,
"testWhileIdle" : false,
"removeAbandoned" : false,
"abandonWhenPercentageFull" : 0,
"minIdle" : 10,
"defaultReadOnly" : null,
"maxWait" : 30000,
"logValidationErrors" : false,
"name" : "Tomcat Connection Pool[1-20280544]",
"useStatementFacade" : true,
"initSQL" : null,
"validationQueryTimeout" : -1,
"validationQuery" : null,
"rollbackOnReturn" : false,
"alternateUsernameAllowed" : false,
"dataSourceJNDI" : null,
"validatorClassName" : null,
"suspectTimeout" : 0,
"useEquals" : true,
"removeAbandonedTimeout" : 60,
"defaultAutoCommit" : null,
"testOnConnect" : false,
"jdbcInterceptors" : null,
"initialSize" : 10,
"defaultTransactionIsolation" : -1,
"numTestsPerEvictionRun" : 0,
"url" : "jdbc:sap://HOST:PORT",
"testOnBorrow" : false,
"fairQueue" : true,
"accessToUnderlyingConnectionAllowed" : true,
"maxAge" : 0,
"minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" : 60000,
"timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" : 5000,
"testOnReturn" : false,
"useLock" : false,
"maxActive" : 100,
"username" : "USERNAME",
"password" : "PASSWORD",
"pageSize" : "50",
"driverClassName" : "com.sap.db.jdbc.Driver",
"ignoreUsers" : [
"SYS",
"SYSTEM"
]
}
}Mapping
From SAP HANA Database users to IDM or Identity Cloud users
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
USER_NAME
From IDM or Identity Cloud users to SAP HANA Database users
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Association>Association Rules>Correlation Queries
-
Link Qualifier: default
-
Any of the following fields:
USER_NAME
Test the SAP HANA Database connector
Test the connector configuration:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request POST \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb?_action=test'
{
"name": "saphanadb",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/saphanadb",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": [1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0),
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.saphanadb-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.saphanadb.SapHanaDBConnector"
},
"displayName": "SAP HANA Database Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES",
"ROLES",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
Use the SAP HANA Database connector
Database user
Create a user
To create a new user, you must include at least the USER_NAME and PASSWORD fields.
The default configuration requires passwords to have:
-
a minimum of 8 characters.
-
at least one number.
-
at least one uppercase letter.
-
at least one lowercase letter.
Special characters are optional, but the default password setting (Aa1) only accepts underscores (_). For more information, refer to Password Policy Configuration Options.
|
If the IS_RESTRICTED field is true, a restricted user is created. A restricted user has no default roles and an unrestricted user has the default PUBLIC role.
The possible date format for the fields VALID_FROM and VALID_UNTIL is: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm AM/PM.
When assigning SAML Providers to a User, only those providers that already exist within the database can be assigned during a create operation.
To grant and revoke roles, application or system privileges, some requirements are necessary, as detailed here.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--data '{
"USER_NAME" : "SAPHANADB_NEWUSER",
"PASSWORD" : "Password123",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "SAPHANADB_NEWUSER@example.com",
"CLIENT" : "001",
"TIME_ZONE" : "GMT",
"VALID_FROM" : "2024-12-12 12:30",
"VALID_UNTIL" : "2025-12-12 15:00",
"IS_SAML_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"ROLES" : [
"MODELING"
],
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES" : [
"sap.hana.backup::Admin"
],
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES" : [
"REPO.EXPORT",
"REPO.IMPORT",
"REPO.MAINTAIN_DELIVERY_UNITS"
]
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/__ACCOUNT__'
{
"USER_NAME" : "SAPHANADB_NEWUSER",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "SAPHANADB_NEWUSER@example.com",
"IS_RESTRICTED" : false,
"CLIENT" : "001",
"TIME_ZONE" : "GMT",
"USER_MODE" : "LOCAL"
"VALID_FROM": "2024-12-12 12:30",
"VALID_UNTIL": "2025-12-12 15:00",
"IS_SAML_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED" : true,
"PASSWORD_CHANGE_NEEDED" : false,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"HAS_REMOTE_USERS" : false,
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY" : false,
"CREATOR" : "USER_CREATOR",
"ROLES" : [
"PUBLIC",
"MODELING"
],
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES" : [
"sap.hana.backup::Admin"
],
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES" : [
"REPO.EXPORT",
"REPO.IMPORT",
"REPO.MAINTAIN_DELIVERY_UNITS"
]
}Get users
Retrieve a list of database user ids from SAP HANA Database:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "001"
},
{
"_id" : "002"
},
{
"_id" : "003"
},
...
]
}
Get a user
Retrieve a user from SAP HANA Database. You must specify the id in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/__ACCOUNT__/USER_ID'
{
"USER_NAME" : "NEW_USER",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "NEW_USER@example.com",
"IS_RESTRICTED" : false,
"CLIENT" : "000",
"TIME_ZONE" : "GMT",
"USER_MODE" : "LOCAL",
"VALID_FROM": "2023-09-06",
"VALID_UNTIL": "2023-12-31",
"IS_SAML_ENABLED" : fale,
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED" : false,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED" : true,
"PASSWORD_CHANGE_NEEDED" : false,
"HAS_REMOTE_USERS" : false,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY" : "999",
"CREATOR" : "USER_CREATOR",
"ROLES": [
"PUBLIC",
"MODELING"
],
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES" : [
"sap.hana.backup::Admin"
],
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES" : [
"REPO.EXPORT",
],
"SAML_PROVIDERS" : [
{
"SAML_PROVIDER_NAME" : "PROVIDER_NAME",
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY" : null
}
]
}
Update a user
Update a user from the database. You must specify the id in the URI path.
The roles field combines the catalog and repository roles. To grant and revoke roles, application or system privileges, some requirements are necessary, as detailed here.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "NEW_MAIL@EMAIL.COM",
"CLIENT" : "002",
"TIME_ZONE" : "PST",
"VALID_FROM" : "2023-09-06",
"VALID_UNTIL" : "2023-12-31",
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_SAML_ENABLED" : true,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED" : true,
"PASSWORD_CHANGE_NEEDED": true,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY": "999",
"ROLES": [
"PUBLIC",
"RESTRICTED_USER_JDBC_ACCESS"
]
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/__ACCOUNT__/USER_ID'
{
"USER_NAME": "USERNAME",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": "NEW_MAIL@EMAIL.COM",
"IS_RESTRICTED": false,
"CLIENT": "002",
"TIME_ZONE": "PST",
"USER_MODE": "LOCAL",
"VALID_FROM": "2023-09-06",
"VALID_UNTIL": "2023-12-31",
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED": true,
"IS_SAML_ENABLED": true,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED": true,
"PASSWORD_CHANGE_NEEDED": true,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY": "999",
"HAS_REMOTE_USERS": false,
"CREATOR": "USER_CREATOR",
"ROLES": [
"PUBLIC",
"RESTRICTED_USER_JDBC_ACCESS",
],
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES": [],
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES": [],
"SAML_PROVIDERS" : []
}
Delete a user
Delete a user from a database. You must specify the id in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request DELETE \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/__ACCOUNT__/USER_ID'
{
"USER_NAME" : "NEW_USER",
"EMAIL_ADDRESS" : "NEW_USER@EMAIL.COM",
"IS_RESTRICTED" : false,
"CLIENT" : "001",
"TIME_ZONE" : "GMT",
"USER_MODE" : "LOCAL"
"VALID_FROM": "2024-12-12",
"VALID_UNTIL": "2025-12-12",
"IS_SAML_ENABLED" : false,
"IS_KERBEROS_ENABLED" : false,
"IS_PASSWORD_ENABLED" : true,
"PASSWORD_CHANGE_NEEDED" : false,
"IS_CLIENT_CONNECT_ENABLED": true,
"HAS_REMOTE_USERS" : false,
"EXTERNAL_IDENTITY" : "999",
"CREATOR" : "USER_CREATOR",
"ROLES": [
"PUBLIC"
],
"APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES" : [],
"SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES" : [],
"SAML_PROVIDERS" : []
}
Get roles
Retrieve roles from a SAP HANA Database:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/ROLES?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "2361418",
"ROLE_NAME": "ABAP_READ",
"ROLE_ID": "2361418",
"ROLE_MODE": "LOCAL",
"__NAME__": "ABAP_READ",
"ROLE_SCHEMA_NAME": null,
"GLOBAL_IDENTITY": null
},
...
}
Get system privileges
Retrieve system privileges from a SAP HANA Database:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/SYSTEM_PRIVILEGES?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "ADAPTER ADMIN",
"__NAME__": "ADAPTER ADMIN",
},
...
}
Get application privileges
Retrieve application privileges from a SAP HANA Database:
curl
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request GET 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphanadb/APPLICATION_PRIVILEGES/_queryFilter=true'
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "sap.hana.ide::Catalog",
"__NAME__": "sap.hana.ide::Catalog"
},
...
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the SAP HANA Database Connector
The SAP HANA Database Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
SAP HANA Database Connector Configuration
The SAP HANA Database Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Description is not available |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection username to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
SAP HANA Database login password to authenticate the user |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Page size of search |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
List of database users to be ignored by the connector |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP S/4HANA connector
The SAP S/4HANA connector lets you manage and synchronize accounts between SAP S/4HANA and IDM and Identity Cloud managed user objects. An SAP S/4HANA administrator account is required for this connector to work.
| The SAP S/4HANA connector only supports SAP HANA Cloud. To connect to HANA DB use the SAP HANA Database connector. |
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, log in to your AWS administrator account and note the following:
- Username
-
Inbound Communication user of SAP S/4HANA.
- Password
-
Inbound Communication user password of SAP S/4HANA.
- Tenant ID
-
Which tenant the SAP S/4HANA instance is hosted on.
Install the SAP S/4HANA connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/saphana-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the SAP S/4HANA connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select SAP S/4HANA Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to SAP S/4HANA Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the SAP S/4HANA connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana?_action=test"
{
"name": "saphana",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/saphana",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.saphana-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.saphana.SapHanaConnector"
},
"displayName": "SAP HANA Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the SAP S/4HANA system.
SAP S/4HANA remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the SAP S/4HANA connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the SAP S/4HANA connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the SAP S/4HANA remote connector.
Use the SAP S/4HANA connector
The following SAP S/4HANA account attributes are supported by the SAP S/4HANA connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Unique identifier for a user. |
|
The external ID of the user. This can only include uppercase letters, numbers, |
|
Auto-generated user id. |
|
Auto-generated user id. |
|
Login username for the user. This can only include uppercase letters, numbers, |
|
First name of the user. Required. |
|
Last name of the user. Required. |
|
Middle name of the user. |
|
Status of the user. Either |
|
Gender of the user. Permitted values are |
|
Salutation of the user. Permitted values are |
|
Start date for the created user, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Required. |
|
End date for the created user, in YYYY-MM-DD format. |
|
Full name of the user. |
|
Academic title of the user. Permitted values are |
|
The correspondence language for the user. For example, |
|
Additional last name of the user. |
|
Birth name of the user. |
|
Nickname of the user. |
|
Initials of the user. |
|
Academic secondary title of the user. Permitted values are |
|
Supplemental titles of the user. Permitted values are |
|
Object with the following sub-attributes:
|
|
Email address of the user. |
|
Predefined code of the company of the user. Required. |
|
Status of the work agreement for the user. Permitted values are |
|
Language code for the user. |
|
What format dates should be displayed in. For example,
|
|
What format times should be displayed in. For example,
|
|
Time zone code of the user. |
|
What decimal notation numbers should be displayed in. Available codes:
|
|
Role assignment of the user. |
|
Unique ID of the work agreement associated with the user. |
|
External ID of the work agreement associated with the user. |
|
Role of the work agreement associated with the user. Permitted values are |
|
The following attributes are mapped in the connector automatically:
|
You can use the SAP S/4HANA connector to perform the following actions on an SAP S/4HANA account:
Create an SAP S/4HANA user
The following example creates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"CompanyCode": 1010,
"GenderCode": 2
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id": "9980004320",
"TimeFormatCode": "0",
"PersonFullName": "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__": "9980004320",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"UserID": "CB9980004320",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DecimalFormatCode": "X",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"LogonLanguageCode": "EN",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"PersonUUID": "FA163EA9-3617-1EEC-B8DA-AD865EF3B625",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"TimeZoneCode": "CET",
"EndDate": "9999-12-31",
"DateFormatCode": "1"
}
|
When you create a new user, you must specify at least:
See the list of available attributes for more information. |
Update an SAP S/4HANA user
You can modify an existing user with a PUT request, including all attributes of the account in the request. The following attributes can be modified on a user:
-
__USER__ -
PersonExternalID -
FirstName -
LastName -
GenderCode -
EmailAddress -
PhoneInformation -
PersonFullName -
AcademicTitle -
CorrespondenceLanguage -
MiddleName -
AdditionalLastName -
BirthName -
NickName -
Initials -
AcademicSecondTitle -
NameSupplement -
WorkAgreementStatus -
CompanyCode -
StartDate -
EndDate -
LockedIndicator -
DateFormatCode -
DecimalFormatCode -
TimeFormatCode -
TimeZoneCode -
LogonLanguageCode -
Role
|
When updating the validity period for a user, both |
For example, to add an email address to a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"CompanyCode": 1010,
"GenderCode": 2,
"EmailAddress": "bjensen@example.com"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__/9980004320"
{
"_id": "9980004320",
"TimeFormatCode": "0",
"PersonFullName": "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__": "9980004320",
"EmailAddress": "bjensen@example.com",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"UserID": "CB9980004320",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DecimalFormatCode": "X",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"LogonLanguageCode": "EN",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"PersonUUID": "FA163EA9-3617-1EEC-B8DA-AD865EF3B625",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"TimeZoneCode": "CET",
"EndDate": "9999-12-31",
"DateFormatCode": "1"
}
Query SAP S/4HANA users
The following example queries all SAP S/4HANA users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "9980000000"
},
{
"_id": "9980000002"
},
{
"_id": "9980000004"
},
{
"_id": "9980000006"
},
[ ... ]
{
"_id": "9980004314"
},
{
"_id": "9980004316"
},
{
"_id": "9980004318"
},
{
"_id": "9980004320"
}
],
"resultCount": 2139,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
The following command queries a specific user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__/9980004320"
{
"_id": "9980004320",
"TimeFormatCode": "0",
"PersonFullName": "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__": "9980004320",
"EmailAddress": "bjensen@example.com",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"UserID": "CB9980004320",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DecimalFormatCode": "X",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"LogonLanguageCode": "EN",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"PersonUUID": "FA163EA9-3617-1EEC-B8DA-AD865EF3B625",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"TimeZoneCode": "CET",
"EndDate": "9999-12-31",
"DateFormatCode": "1"
}
Enable an SAP S/4HANA user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": true
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__/9980004320"
{
"_id": "9980004320",
"TimeFormatCode": "0",
"PersonFullName": "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__": "9980004320",
"EmailAddress": "bjensen@example.com",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"UserID": "CB9980004320",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DecimalFormatCode": "X",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"LogonLanguageCode": "EN",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"PersonUUID": "FA163EA9-3617-1EEC-B8DA-AD865EF3B625",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"TimeZoneCode": "CET",
"EndDate": "9999-12-31",
"DateFormatCode": "1"
}
Disable an SAP S/4HANA user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"__ENABLE__": false
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/saphana/__ACCOUNT__/9980004320"
{
"_id": "9980004320",
"TimeFormatCode": "0",
"PersonFullName": "Barbara Jensen",
"__UID__": "9980004320",
"EmailAddress": "bjensen@example.com",
"FirstName": "Barbara",
"UserID": "CB9980004320",
"__NAME__": "BJENSEN",
"DecimalFormatCode": "X",
"StartDate": "2022-06-02",
"LogonLanguageCode": "EN",
"LastName": "Jensen",
"PersonExternalID": "BJENSEN",
"PersonUUID": "FA163EA9-3617-1EEC-B8DA-AD865EF3B625",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"TimeZoneCode": "CET",
"EndDate": "9999-12-31",
"DateFormatCode": "1"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the SAP HANA Connector
The SAP HANA Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
SAP HANA Connector Configuration
The SAP HANA Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Username to authorize the SAP HANA APIs. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Provides the Password to authorize the SAP HANA APIs. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Provides the Tenant ID to identify your custom SAP HANA APIs. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Page Size for search operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the HTTP Proxy Password. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SCIM connector
The SCIM connector is based on the Simple Cloud Identity Management (SCIM) protocol and lets you manage user and group accounts on any SCIM-compliant resource provider, such as Slack or Facebook. The SCIM connector implements both 1.1 and 2.0 endpoints.
| ForgeRock strongly recommends that you do not use the SCIM connector to connect to Salesforce systems. Use the Salesforce connector. |
The SCIM connector uses the Apache HTTP client, which leverages the HTTP client connection pool, not the ICF connector pool.
Install the SCIM connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/scim-connector-1.5.20.20.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the SCIM connector
|
SCIM V2 supports a "path" attribute value describing the target of the operation. The attribute value is optional for patch "add" and "replace" operations. If the SCIM resource provider requires this configuration, do one of the following:
|
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select SCIM Connector - 1.5.20.20.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to SCIM Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Configure the SCIM connector using the filesystem
Alternatively, create a connector configuration file in your project’s conf directory:
-
Copy
/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-scim.jsonto your project’sconf/directory. -
Edit
conf/provisioner.openicf-scim.json, as necessary. The following changes are required:-
"enabled" : true -
To specify the connection details to the SCIM resource provider, set the
configurationProperties. The required properties vary, based on theauthenticationMethod:OAUTH-
The minimum required properties are
grantType,SCIMEndpoint,tokenEndpoint,clientId, andclientSecret. BASIC-
The minimum required properties are
userandpassword. TOKEN-
The minimum required property is
authToken.
Sample Configuration Using OAUTH
"configurationProperties" : { "SCIMEndpoint" : "https://example.com/scim", "SCIMVersion" : 1, "authenticationMethod" : "OAUTH", "user" : null, "password" : null, "tokenEndpoint" : "https://example.com/oauth2/token", "clientId" : "Kdvl...................j3fka", "clientSecret" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : true, "grantType" : "client_credentials", "disableHostNameVerifier" : true, "connectionTimeout" : 30, "maximumConnections" : 10, "httpProxyHost" : null, "httpProxyPort" : null }On startup, IDM encrypts the value of the clientSecret. -
Test the SCIM connector
After the connector is properly configured, you can test its status:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "SCIM",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/SCIM",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.scim-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.scim.ScimConnector",
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)"
},
"displayName": "Scim Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__",
"__GROUP__"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the SCIM connector can reach the configured resource provider.
SCIM remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the SCIM connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the SCIM connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the SCIM remote connector.
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The SCIM connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
Using the SCIM connector with a proxy server
If the IDM server is hosted behind a firewall and requests to the resource provider are routed through a proxy, you must specify the proxy host and port in the connector configuration.
To specify the proxy server details, set the httpProxyHost, and httpProxyPort properties in the connector configuration. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"httpProxyHost": "myproxy.home.com",
"httpProxyPort": 8080,
...
},OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Scim Connector
The Scim Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Scim Connector Configuration
The Scim Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The HTTP URL defining the root for the SCIM endpoint (https://myserver.com/service/scim). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the SCIM protocol version. Values can be either 1 or 2. Default is 1. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which method is to be used to authenticate on the remote server. Options are BASIC (username/password), OAUTH (Client id/secret) or TOKEN (static token). Defaults to OAUTH. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
In case of BASIC authentication type, this property defines the remote user. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
In case of BASIC authentication type, this property defines the remote password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When using OAuth, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be requested (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Secure client identifier for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Secure client secret for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Some service providers (Slack for instance) use static authentication tokens. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Used by the refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 grant type to use (client_credentials or refresh_token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 scope to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Content compression is enabled by default. Set this property to true to disable it. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed, set this to the certificate alias from the keystore. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed and the client certificate (private key) password is different than the keystore password, set this to the client private key password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the max size of the http connection pool used. Defaults to 10. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Hostname if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Port if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines Proxy Username if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Defines Proxy Password if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the SCIM service provider. Defaults to null. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a timeout for the underlying http connection in seconds. Defaults to 30. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The prefix to be used in the Authorization HTTP header for Token authentication. Defaults to "Bearer." |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Client Id and Client Secret are sent in the Header when this is unchecked. Defaults to true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for read operations either per seconds ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connector is using "application/json" by default. SCIM V2 Service Provider may require "application/scim+json". It can be overwritten with this property. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connector is using "application/json" by default. SCIM V2 Service Provider may require "application/scim+json". It can be overwritten with this property. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for write operations (create/update/delete) either per second ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, then "path" will always be included in Patch add or replace operations. If false, it will only be used for remove operations. Defaults to false. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the connector will read the schema from the server. If false, the connector will provide a default schema based on the object classes in the configuration. This property must be true in order to use extended object classes. Defaults to false. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Scripted REST connector
The Scripted REST connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy connector toolkit. It can interact with any REST API, using Groovy scripts for the ICF operations. This connector type lets you develop a fully functional REST-based connector for in-house applications or any cloud-based application not yet supported with the standard set of ForgeRock connectors.
To use this connector, you must write a Groovy script for each operation that you want the connector to perform (create, read, update, delete, authenticate, and so on). No sample scripts are bundled with the connector, but IDM customers have access to the Scripted REST connector source code in the connectors-customers-ga repo. This repository includes sample scripts for all the ICF operations.
You cannot configure the Scripted REST connector through the UI. Configure the connector over REST, as described in Configure Connectors Over REST.
Alternatively, a sample connector configuration and scripts are provided in the /path/to/openidm/samples/scripted-rest-with-dj/
directory and described in Connect to DS with ScriptedREST. The scripts provided with this sample demonstrate how the connector can be used, but most likely cannot be used as is in your deployment. They are a good starting point from which to base your customization. For information about writing your own scripts, refer to Scripted connectors with Groovy.
Script custom behavior
The Scripted REST connector uses the Apache HTTP client library. Unlike the Scripted SQL connector, which uses JDBC drivers and a Tomcat JDBC connection pool, the Scripted REST connector includes a special script to customize the Apache HTTP client.
This customizer script lets you customize the Apache HTTP client connection pool, proxy, default headers, timeouts, and so on.
The customizer script is referenced in the connector configuration, in the CustomizerScriptFileName property:
{
...
"configurationProperties": {
...
"customizerScriptFileName": "CustomizerScript.groovy",
...
}
}The script can implement two predefined Groovy closures — init {} and decorate {}.
init {}-
The Apache HTTP client provides an HTTPClientBuilder class, to build an instance of the HTTPClient. The Scripted REST connector injects this builder into the
initclosure when the connector is first instantiated. Theinitclosure is the ideal place to customize the HTTP client with the builder.You can customize the following elements of the client:
-
Connection pool
-
Connection timeouts
-
Proxy
-
Default HTTP headers
-
Certificate handling
Example init closure
/** * A customizer script defines the custom closures to interact with the default implementation and customize it. * Here, the {@link HttpClientBuilder} is passed to the customize closure. This is where the pooling, the headers, * the timeouts etc... should be defined. */ customize { init { HttpClientBuilder builder -> //SETUP: org.apache.http def c = delegate as ScriptedRESTConfiguration def httpHost = new HttpHost(c.serviceAddress?.host, c.serviceAddress?.port, c.serviceAddress?.scheme) PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager() // Increase max total connection to 200 cm.setMaxTotal(200) // Increase default max connection per route to 20 cm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20) // Increase max connections for httpHost to 50 cm.setMaxPerRoute(new HttpRoute(httpHost), 50) builder.setConnectionManager(cm) // configure timeout on the entire client RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()/* * . * setConnectionRequestTimeout * ( 50). * setConnectTimeout * (50) * .setSocketTimeout * (50) */.build(); builder.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig) ... } }Call the builder methods to fit your requirements. The
init{}closure does not need to return anything. -
decorate {}-
The
initclosure configures a Java instance of the HTTP client, which is injected into every CRUD script. In addition to the libraries provided by the Apache HTTP client, Groovy provides a number of libraries to deal with requests and responses.The
decorateclosure lets you inject a "decorated" instance of the HTTP client into your scripts. For example, the sample scripts use thegroovyx.net.http.RESTClientlibrary.This excerpt of a sample
deletescript shows the injection of thehttpClientandconnectionvariables into the script. Theconnectionvariable is the output of thedecorateclosure.Example decorate closure
def operation = operation as OperationType def configuration = configuration as ScriptedRESTConfiguration def httpClient = connection as HttpClient def connection = customizedConnection as RESTClient def log = log as Log def objectClass = objectClass as ObjectClass def options = options as OperationOptions def uid = uid as Uid log.info("Entering " + operation + " Script"); switch (objectClass) { case ObjectClass.ACCOUNT: connection.delete(path: '/api/users/' + uid.uidValue); break case ObjectClass.GROUP: connection.delete(path: '/api/groups/' + uid.uidValue); }
|
When you use the |
Example OAuth2 Authentication Implementation
This example shows how to use the customizer script to implement OAuth2 authentication in the Scripted REST connector.
Although grant types are largely standardized across OAuth2 authentication providers, the way in which different providers handle flows, headers, attribute names, and so on, often differs. This makes it difficult to include a single implementation of OAuth2 authentication in the Scripted REST connector. To make sure that OAuth2 authentication works in your specific use case, you use the customizer script, which can be adapted without requiring a new version of the connector itself.
The Scripted REST connector includes a simple implementation of the OAuth2 Client Credentials grant type. The connector needs to get an access token, using the Client ID and the Client Secret, cache it, and renew it when it expires or when the server revokes it. The Apache client provides interceptors for requests and responses. These interceptors can be used in the customizer script to manage the access token:
-
In the request: If the access token is absent or expired, renew the token and cache it in the Scripted REST connector property bag.
-
In the response: If the server returns a 401 error, delete the Access Token from the connector property bag. This will ensure that the next connector request gets a new access token. The HTTP POST query to get the access token is also handled by the customizer script.
This example shows a complete customizer script for the OAuth2 implementation:
init { HttpClientBuilder builder ->
switch (ScriptedRESTConfiguration.AuthMethod.valueOf(c.defaultAuthMethod)) {
// ......
case ScriptedRESTConfiguration.AuthMethod.OAUTH:
// define a request interceptor to set the Authorization header if absent or expired
HttpRequestInterceptor requestInterceptor = { HttpRequest request, HttpContext context ->
if (null == context.getAttribute("oauth-request")) {
def exp = c.propertyBag.tokenExpiration as Long
if (c.propertyBag.accessToken == null || exp < System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000) {
new NewAccessToken(c).clientCredentials()
}
request.addHeader(new BasicHeader(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION, "Bearer " + c.propertyBag.accessToken))
}
}
// define a response interceptor to catch a 401 response code and delete access token from cache
HttpResponseInterceptor responseInterceptor = { HttpResponse response, HttpContext context ->
if (HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED == response.statusLine.statusCode) {
if (c.propertyBag.accessToken != null) {
c.propertyBag.remove("accessToken")
Log.getLog(ScriptedRESTConnector.class).info("Code 401 - accessToken removed")
}
}
}
builder.addInterceptorLast(requestInterceptor)
builder.addInterceptorLast(responseInterceptor)
break
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException()
}
}
class NewAccessToken {
static final String GRANT_TYPE = "grant_type"
static final String REFRESH_TOKEN = "refresh_token"
static final String CLIENT_CREDENTIALS = "client_credentials"
static final String CLIENT_ID = "client_id"
static final String CLIENT_SECRET = "client_secret"
static final String OAUTH_REQUEST = "oauth-request"
Log logger = Log.getLog(NewAccessToken.class)
ScriptedRESTConfiguration c = null
final CloseableHttpClient client = null
final HttpPost post = null
NewAccessToken(ScriptedRESTConfiguration conf) {
this.c = conf
this.client = c.getHttpClient()
this.post = new HttpPost(c.getOAuthTokenEndpoint())
post.setHeader(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
post.setHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT, "application/json")
}
@Synchronized
void clientCredentials() {
boolean expired = (c.propertyBag.tokenExpiration as Long) < System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000
if (c.propertyBag.accessToken == null || expired ) {
if (c.propertyBag.tokenExpiration != null && expired) {
logger.info("Token expired!")
}
logger.info("Getting new access token...")
final List<NameValuePair> pairs = new ArrayList<>()
pairs.add(new BasicNameValuePair(GRANT_TYPE, CLIENT_CREDENTIALS))
pairs.add(new BasicNameValuePair(CLIENT_ID, c.getOAuthClientId()))
pairs.add(new BasicNameValuePair(CLIENT_SECRET, SecurityUtil.decrypt(c.getOAuthClientSecret())))
post.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(pairs))
CloseableHttpResponse response = null
try {
HttpClientContext ctx = HttpClientContext.create()
ctx.setAttribute(OAUTH_REQUEST, true)
response = client.execute(post, ctx)
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()
if (HttpStatus.SC_OK == statusCode) {
def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurper()
def oauthResponse = jsonSlurper.parseText(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()))
c.propertyBag.accessToken = oauthResponse.access_token
c.propertyBag.tokenExpiration = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 + oauthResponse.expires_in as Long
} else {
throw new InvalidCredentialException("Retrieve Access Token failed with code: " + statusCode)
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException ex) {
logger.info("Trace: {0}", ex.getMessage())
throw new ConnectorException(ex)
} catch (IOException ex) {
logger.info("Trace: {0}", ex.getMessage())
throw new ConnectionFailedException(ex)
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close()
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.info("Can't close HttpResponse")
}
}
}
}
}Using the Scripted REST connector with a proxy server
If the IDM server is hosted behind a firewall and requests to the resource are routed through a proxy, you must specify the proxy host and port in the connector configuration.
To specify the proxy server details, set the proxyAddress property in the connector configuration. For example:
"configurationProperties": {
...
"proxyAddress": "http://myproxy:8080",
...
}Run scripts through the connector
Groovy toolkit connectors have two operations that allow you to run arbitrary script actions: runScriptOnConnector and runScriptOnResource. runScriptOnConnector is an operation that sends the script action to the connector to be compiled and executed. runScriptOnResource is an operation that sends the script to another script to be handled.
runScriptOnConnector
The runScriptOnConnector script lets you run an arbitrary script action through the connector. This script takes the following variables as input:
configuration-
A handler to the connector’s configuration object.
options-
A handler to the Operation Options.
operation-
The operation type that corresponds to the action (
RUNSCRIPTONCONNECTORin this case). log-
A handler to the connector’s log.
To run an arbitrary script on a Groovy toolkit connector, define the script in the systemActions property of your provisioner file:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]If you want to define your script in the provisioner file itself rather than in a separate file, you can use the actionSource property instead of the actionFile one. A simple example follows:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionSource" : "2 * 2"
}
]
}
]
It is optional to prepend the last script statement in actionSource with return.
|
Running MyScript will return:
{
"actions" : [
{
"result": 4
}
]
}If your script accepts parameters, you may supply them in the request body or the query string. For example:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data-raw '{"param1":"value1"}'
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=MyScript¶m2=value2"**
You can also call it through the IDM script engine. Note that the system can accept arbitrary parameters, as demonstrated here:
openidm.action("/system/groovy", "script", {"contentParameter": "value"}, {"scriptId": "MyScript", "additionalParameter1": "value1", "additionalParameter2": "value2"})runScriptOnResource
To run an arbitrary script using runScriptOnResource, you must add some configuration details to your provisioner file. These details include a scriptOnResourceScriptFileName which references a script file located in a path contained in the scriptRoots array.
Define these properties in your provisioner file as follows:
"configurationProperties": {
"scriptRoots": [
"path/to/scripts"
],
"scriptOnResourceScriptFileName": "ScriptOnResourceScript.groovy"
},
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "script-1",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]When you have defined the script, you can call it over REST on the system endpoint, as follows:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=scriptOnResourceScript&scriptExecuteMode=resource"
Implemented interfaces
This table lists the ICF interfaces that are implemented for the scripted REST connector:
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Scripted REST Connector
The Scripted REST Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Scripted REST Connector Configuration
The Scripted REST Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
The Remote user to authenticate with. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The Password to authenticate with. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The service URI (example: http://myservice.com/api). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The optional Proxy server URI (example: http://myproxy:8080). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The username to authenticate with the proxy server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The password to authenticate with the proxy server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Authentication method used. Can be: BASIC, BASIC_PREEMPTIVE, OAUTH or NONE. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Default HTTP request content type. Can be: JSON, TEXT, XML, HTML, URLENC, BINARY. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Placeholder for default HTTP request headers. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When using OAUTH, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be queried for (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The client identifier. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Secure client secret for OAUTH. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The refresh token used to renew the access token for the refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The optional scope. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The grant type to use. Can be: |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for read operations either per seconds ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines throttling for write operations (create/update/delete) either per second ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Scripted SQL connector
The Scripted SQL connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy connector toolkit. This connector lets you interact with any SQL database, using Groovy scripts for the ICF operations.
To use this connector, you must write a Groovy script for each operation that you want the connector to perform (create, read, update, delete, authenticate, and so on). No sample scripts are bundled with the connector, but IDM customers have access to the Scripted SQL connector source code in the connectors-customers-ga repo. This repository includes sample scripts for all the ICF operations.
Configure the Scripted SQL connector
You cannot configure the Scripted SQL connector through the UI. Configure the connector over REST, as described in Configure Connectors Over REST.
Alternatively, a sample connector configuration and scripts are provided in the /path/to/openidm/samples/scripted-sql-with-mysql/
directory and described in Connect to a MySQL database with ScriptedSQL. The scripts provided with this sample demonstrate how the connector can be used, but most likely cannot be used as is in your deployment. They are a good starting point from which to base your customization. For information about writing your own scripts, refer to Scripted connectors with Groovy.
Run scripts through the connector
Groovy toolkit connectors have two operations that allow you to run arbitrary script actions: runScriptOnConnector and runScriptOnResource. runScriptOnConnector is an operation that sends the script action to the connector to be compiled and executed. runScriptOnResource is an operation that sends the script to another script to be handled.
runScriptOnConnector
The runScriptOnConnector script lets you run an arbitrary script action through the connector. This script takes the following variables as input:
configuration-
A handler to the connector’s configuration object.
options-
A handler to the Operation Options.
operation-
The operation type that corresponds to the action (
RUNSCRIPTONCONNECTORin this case). log-
A handler to the connector’s log.
To run an arbitrary script on a Groovy toolkit connector, define the script in the systemActions property of your provisioner file:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]If you want to define your script in the provisioner file itself rather than in a separate file, you can use the actionSource property instead of the actionFile one. A simple example follows:
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "MyScript",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionSource" : "2 * 2"
}
]
}
]
It is optional to prepend the last script statement in actionSource with return.
|
Running MyScript will return:
{
"actions" : [
{
"result": 4
}
]
}If your script accepts parameters, you may supply them in the request body or the query string. For example:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data-raw '{"param1":"value1"}'
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=MyScript¶m2=value2"**
You can also call it through the IDM script engine. Note that the system can accept arbitrary parameters, as demonstrated here:
openidm.action("/system/groovy", "script", {"contentParameter": "value"}, {"scriptId": "MyScript", "additionalParameter1": "value1", "additionalParameter2": "value2"})runScriptOnResource
To run an arbitrary script using runScriptOnResource, you must add some configuration details to your provisioner file. These details include a scriptOnResourceScriptFileName which references a script file located in a path contained in the scriptRoots array.
Define these properties in your provisioner file as follows:
"configurationProperties": {
"scriptRoots": [
"path/to/scripts"
],
"scriptOnResourceScriptFileName": "ScriptOnResourceScript.groovy"
},
"systemActions" : [
{
"scriptId" : "script-1",
"actions" : [
{
"systemType" : ".*ScriptedConnector",
"actionType" : "groovy",
"actionFile" : "path/to/<script-name>.groovy"
}
]
}
]When you have defined the script, you can call it over REST on the system endpoint, as follows:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request POST \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/groovy?_action=script&scriptId=scriptOnResourceScript&scriptExecuteMode=resource"
Implemented interfaces
This table lists the ICF interfaces that are implemented for the scripted SQL connector:
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Scripted SQL Connector
The Scripted SQL Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Scripted SQL Connector Configuration
The Scripted SQL Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The connection password to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection properties that will be sent to our JDBC driver when establishing new connections. Format of the string must be [propertyName=property;]* NOTE - The "user" and "password" properties will be passed explicitly, so they do not need to be included here. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to propagate the interrupt state for a thread that has been interrupted (not clearing the interrupt state). Set the value as false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true if you wish to put a facade on your connection so that it cannot be reused after it has been closed. This prevents a thread holding on to a reference of a connection it has already called closed on, to execute queries on it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default catalog of connections created by this pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
avoid excess validation, only run validation at most at this frequency - time in milliseconds. If a connection is due for validation, but has been validated previously within this interval, it will not be validated again. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag whether ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to true if you want to ignore error of connection creation while initializing the pool. Set to false if you want to fail the initialization of the pool by throwing exception. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Register the pool with JMX or not. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can complete the transaction by calling commit on the connection as it is returned to the pool If rollbackOnReturn==true then this attribute is ignored. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to log stack traces for application code which abandoned a Connection. Logging of abandoned Connections adds overhead for every Connection borrow because a stack trace has to be generated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. Idle connections are checked periodically (if enabled) and connections that been idle for longer than minEvictableIdleTimeMillis will be released. (also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated by the idle object evictor (if any). If an object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. This property has to be set in order for the pool cleaner/test thread is to run (also see timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Flag to remove abandoned connections if they exceed the removeAbandonedTimeout. If set to true a connection is considered abandoned and eligible for removal if it has been in use longer than the removeAbandonedTimeout Setting this to true can recover db connections from applications that fail to close a connection. See also logAbandoned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Connections that have been abandoned (timed out) wont get closed and reported up unless the number of connections in use are above the percentage defined by abandonWhenPercentageFull. The value should be between 0-100. The value 0 implies that connections are eligible for closure as soon as removeAbandonedTimeout has been reached. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum number of established connections that should be kept in the pool at all times. The connection pool can shrink below this number if validation queries fail (also see testWhileIdle). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default read-only state of connections created by this pool. If not set then the setReadOnly method will not be called (Some drivers dont support read only mode, ex: Informix). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before throwing an exception. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set this to true to log errors during the validation phase to the log file. If set to true, errors will be logged as SEVERE. Set the value as false for backwards compatibility. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The fully qualified Java class name of the JDBC driver to be used. The driver has to be accessible from the same classloader as tomcat-jdbc.jar. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Returns the name of the connection pool. By default a JVM unique random name is assigned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If a statement proxy is set, wrap statements so that equals() and hashCode() methods can be called on closed statements. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A custom query to be run when a connection is first created. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The timeout in seconds before a connection validation queries fail. This works by calling java.test_sample.Statement.setQueryTimeout(seconds) on the statement that executes the validationQuery. The pool itself doesnt timeout the query, it is still up to the JDBC driver to enforce query timeouts. A value less than or equal to zero will disable this feature. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The SQL query that will be used to validate connections from this pool before returning them to the caller. If specified, this query does not have to return any data, it just cant throw a SQLException. Example values are SELECT 1(mysql), select 1 from dual(oracle), SELECT 1(MS Sql Server). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If autoCommit==false then the pool can terminate the transaction by calling rollback on the connection as it is returned to the pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
By default, the jdbc-pool will ignore the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, and simply return a previously pooled connection under the globally configured properties username and password, for performance reasons. The pool can however be configured to allow use of different credentials each time a connection is requested. To enable the functionality described in the DataSource.getConnection(username,password) call, simply set the property alternateUsernameAllowed to true. Should you request a connection with the credentials user1/password1 and the connection was previously connected using different user2/password2, the connection will be closed, and reopened with the requested credentials. This way, the pool size is still managed on a global level, and not on a per schema level. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The JNDI name for a data source to be looked up in JNDI and then used to establish connections to the database. See the dataSource attribute. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The name of a class which implements the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.Validator interface and provides a no-arg constructor (may be implicit). If specified, the class will be used to create a Validator instance which is then used instead of any validation query to validate connections. An example value is com.mycompany.project.SimpleValidator. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout value in seconds. Similar to to the removeAbandonedTimeout value but instead of treating the connection as abandoned, and potentially closing the connection, this simply logs the warning if logAbandoned is set to true. If this value is equal or less than 0, no suspect checking will be performed. Suspect checking only takes place if the timeout value is larger than 0 and the connection was not abandoned or if abandon check is disabled. If a connection is suspect a WARN message gets logged and a JMX notification gets sent once. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish the ProxyConnection class to use String.equals and set to false when you wish to use == when comparing method names. This property does not apply to added interceptors as those are configured individually. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Timeout in seconds before an abandoned(in use) connection can be removed. The value should be set to the longest running query your applications might have. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default auto-commit state of connections created by this pool. If not set, default is JDBC driver default (If not set then the setAutoCommit method will not be called). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Validate the connection when connecting to the database for the first time. Set to true if you want to use the validationQuery as an init query. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A semicolon separated list of classnames extending org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.JdbcInterceptor class. See Configuring JDBC interceptors below for more detailed description of syntaz and examples. These interceptors will be inserted as an interceptor into the chain of operations on a java.test_sample.Connection object. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The initial number of connections that are created when the pool is started. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The default TransactionIsolation state of connections created by this pool. One of the following: NONE, READ_COMMITTED, READ_UNCOMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE If not set, the method will not be called and it defaults to the JDBC driver. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used in tomcat-jdbc-pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The URL used to connect to the database. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool, and we will attempt to borrow another. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. In order to have a more efficient validation, see validationInterval. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Set to true if you wish that calls to getConnection should be treated fairly in a true FIFO fashion. This uses the org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue implementation for the list of the idle connections. This flag is required when you want to use asynchronous connection retrieval. Setting this flag ensures that threads receive connections in the order they arrive. During performance tests, there is a very large difference in how locks and lock waiting is implemented. When fairQueue=true there is a decision making process based on what operating system the system is running. If the system is running on Linux (property os.name=Linux. To disable this Linux specific behavior and still use the fair queue, simply add the property org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.FairBlockingQueue.ignoreOS=true to your system properties before the connection pool classes are loaded. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Property not used. Access can be achieved by calling unwrap on the pooled connection. see javax.test_sample.DataSource interface, or call getConnection through reflection or cast the object as javax.test_sample.PooledConnection. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Time in milliseconds to keep this connection. When a connection is returned to the pool, the pool will check to see if the now - time-when-connected > maxAge has been reached, and if so, it closes the connection rather than returning it to the pool. The value 0 implies that connections will be left open and no age check will be done upon returning the connection to the pool. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The minimum amount of time an object may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle connection validation/cleaner thread. This value should not be set under 1 second. It dictates how often we check for idle, abandoned connections, and how often we validate idle connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The indication of whether objects will be validated before being returned to the pool. NOTE - for a true value to have any effect, the validationQuery parameter must be set to a non-null string. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Use a lock when performing operations on the connection object. Set to true if you will use a separate background thread for idle and abandon checking (e.g. JMX clients). If the pool sweeper is enabled, a lock is used, regardless of this setting. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated from this pool at the same time. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The connection username to be passed to our JDBC driver to establish a connection. Note that method DataSource.getConnection(username,password) by default will not use credentials passed into the method, but will use the ones configured here. See alternateUsernameAllowed property for more details. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
ServiceNow connector
This connector lets you manage objects in the ServiceNow platform, integrating with ServiceNow’s REST API.
Before you start
The connector requires a ServiceNow instance with OAuth enabled. You might need to activate the OAuth plugin and set the OAuth activation property if OAuth is not yet enabled on your ServiceNow instance. For more information, refer to the ServiceNow documentation that corresponds to your ServiceNow version.
When Oauth is enabled, register an OAuth client application for the connection to IDM. Take note of the client_id and client_secret of the application, as you need these values when you configure the connector.
The connector configuration must include a ServiceNow user who has the following roles:
-
admin -
rest_api_explorer
If you do not want to give complete admin rights to this user, you can create a new role that provides access to the following tables:
-
sys_user_has_role -
sys_user_grmember -
sys_user_delegate -
sys_user_role -
sys_user_group -
core_company -
cmn_department -
cmn_cost_center -
cmn_location
Install the ServiceNow connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/servicenow-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the ServiceNow connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select ServiceNow Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to ServiceNow Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
The following excerpt of connector configuration shows the required configurationProperties:
"configurationProperties" : {
"instance" : "example.service-now.com/",
"username" : "admin",
"password" : {encrypted-password},
"clientID" : "4xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxee",
"clientSecret" : {encrypted-client-secret},
"readSchema" : false
}instance(string)-
The ServiceNow instance URL; for example,
example.service-now.com/. username(string)-
The name of a ServiceNow user with the
adminandrest_api_explorerroles. password(string)-
The password of the ServiceNow user.
clientID(string)-
The ID of your OAuth application.
clientSecret(string)-
The client secret of your OAuth application.
IDM encrypts the value of the password and clientSecret on startup.
Test the ServiceNow connector
When your connector is configured correctly, test its status by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "serviceNow",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/serviceNow",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.servicenow-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.servicenow.ServiceNowConnector"
},
"displayName": "ServiceNow Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"delegate",
"role",
"__ALL__",
"costCenter",
"location",
"company",
"userHasGroup",
"department",
"user",
"userHasRole",
"group"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the ServiceNow connector can reach the configured resource provider.
ServiceNow remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the ServiceNow connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the ServiceNow connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the ServiceNow remote connector.
Manage users with the ServiceNow connector
These examples show the basic CRUD operations using the ServiceNow connector.
Query all ServiceNow users
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d3f",
"__NAME__": "lucius.bagnoli@example.com"
},
{
"_id": "02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d55",
"__NAME__": "jimmie.barninger@example.com"
},
{
"_id": "02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d5e",
"__NAME__": "melinda.carleton@example.com"
},
...
],
"resultCount": 578,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Query a single ServiceNow user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user/02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d3f"
{
"_id": "02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d3f",
"internal_integration_user": false,
"department": "5d7f17f03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d43",
"sys_mod_count": "5",
"location": "0002c0a93790200044e0bfc8bcbe5df5",
"web_service_access_only": false,
"sys_updated_on": "2018-02-25 16:42:47",
"sys_domain": "global",
"notification": "2",
"sys_created_by": "admin",
"locked_out": "false",
"__NAME__": "lucius.bagnoli@example.com",
"company": "81fd65ecac1d55eb42a426568fc87a63",
"sys_domain_path": "/",
"password_needs_reset": "false",
"active": "true",
"gender": "Male",
"sys_created_on": "2012-02-18 03:04:49",
"sys_class_name": "sys_user",
"calendar_integration": "1",
"email": "lucius.bagnoli@example.com",
"sys_id": "02826bf03710200044e0bfc8bcbe5d3f",
"user_password": "md5230ls7L",
"user_name": "lucius.bagnoli",
"sys_updated_by": "developer.program@snc",
"vip": "false",
"last_name": "Bagnoli",
"first_name": "Lucius"
}
Create a ServiceNow user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"first_name": "Barbara",
"last_name": "Jensen",
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"phone": "555-123-1234"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user?_action=create"
{
"_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_mod_count": "0",
"password_needs_reset": "false",
"notification": "2",
"locked_out": "false",
"phone": "555-123-1234",
"sys_created_on": "2018-02-27 13:33:38",
"first_name": "Barbara",
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"active": "true",
"sys_domain": "global",
"calendar_integration": "1",
"web_service_access_only": false,
"vip": "false",
"sys_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_updated_on": "2018-02-27 13:33:38",
"sys_domain_path": "/",
"sys_created_by": "admin",
"sys_class_name": "sys_user",
"last_name": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"sys_updated_by": "admin",
"internal_integration_user": false
}
Update a ServiceNow user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"first_name": "Barbara",
"last_name": "Jensen",
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"phone": "555-000-0000"
}' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user/4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a"
{
"_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_mod_count": "1",
"password_needs_reset": "false",
"notification": "2",
"locked_out": "false",
"phone": "555-000-0000",
"sys_created_on": "2018-02-27 13:33:38",
"first_name": "Barbara",
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"active": "true",
"sys_domain": "global",
"calendar_integration": "1",
"web_service_access_only": false,
"vip": "false",
"sys_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_updated_on": "2018-02-27 13:35:32",
"sys_domain_path": "/",
"sys_created_by": "admin",
"sys_class_name": "sys_user",
"last_name": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"sys_updated_by": "admin",
"internal_integration_user": false
}
Delete a ServiceNow user
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request DELETE \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user/4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a"
{
"_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_mod_count": "1",
"password_needs_reset": "false",
"notification": "2",
"locked_out": "false",
"phone": "555-000-0000",
"sys_created_on": "2018-02-27 13:33:38",
"first_name": "Barbara",
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"active": "true",
"sys_domain": "global",
"calendar_integration": "1",
"web_service_access_only": false,
"vip": "false",
"sys_id": "4116e0690fa01300f6af65ba32050e7a",
"sys_updated_on": "2018-02-27 13:35:32",
"sys_domain_path": "/",
"sys_created_by": "admin",
"sys_class_name": "sys_user",
"last_name": "Jensen",
"__NAME__": "bjensen@example.com",
"sys_updated_by": "admin",
"internal_integration_user": false
}
Synchronize ServiceNow users
The ServiceNow connector supports bidirectional reconciliation and liveSync. To set up user synchronization, create a mapping between managed users and ServiceNow users.
This example assumes that you have configured a mapping. The example runs a reconciliation operation from ServiceNow to the managed user repository:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/recon?_action=recon&mapping=systemServicenowUser_managedUser"
{
"_id": "19755e51-5c3b-4362-b316-601856cb282c-13624",
"state": "ACTIVE"
}
The following example runs a liveSync operation from ServiceNow to the managed user repository:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/serviceNow/user?_action=liveSync"
{
"connectorData": {
"nativeType": "string",
"syncToken": "2018-02-275 11:29:15"
},
"_rev": "0000000031285d9b",
"_id": "SYSTEMSERVICENOWUSER"
}
|
The ServiceNow connector does not support the |
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The ServiceNow connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the ServiceNow Connector
The ServiceNow Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
ServiceNow Connector Configuration
The ServiceNow Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
URL of the ServiceNow instance, for example: dev00000.service-now.com. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
An API user in ServiceNow that can consume the REST API. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Password for the user. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Client ID of the OAuth application in ServiceNow. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Client Secret for the preceding Client ID. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Default page size. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SSH connector
The SSH connector is an implementation of the Scripted Groovy connector toolkit based on Java Secure Channel (JSch) and the Java implementation of the Expect library (Expect4j). This connector lets you interact with any SSH server, using Groovy scripts for the ICF operations.
The SSH connector is a poolable connector. This means that each connector instance is placed into a connection pool every time an action is completed. Subsequent actions can re-use connector instances from the connector pool. When a new connector instance is created, a new SSH client connection is created against the target SSH server. This SSH connection remains open as long as the connector instance is in the connection pool. Note that when a new action is performed, it finds the SSH connection in the exact state that it was left by the previous action.
The following image shows the relationship between SSH connector instances and SSH connections to the target server:
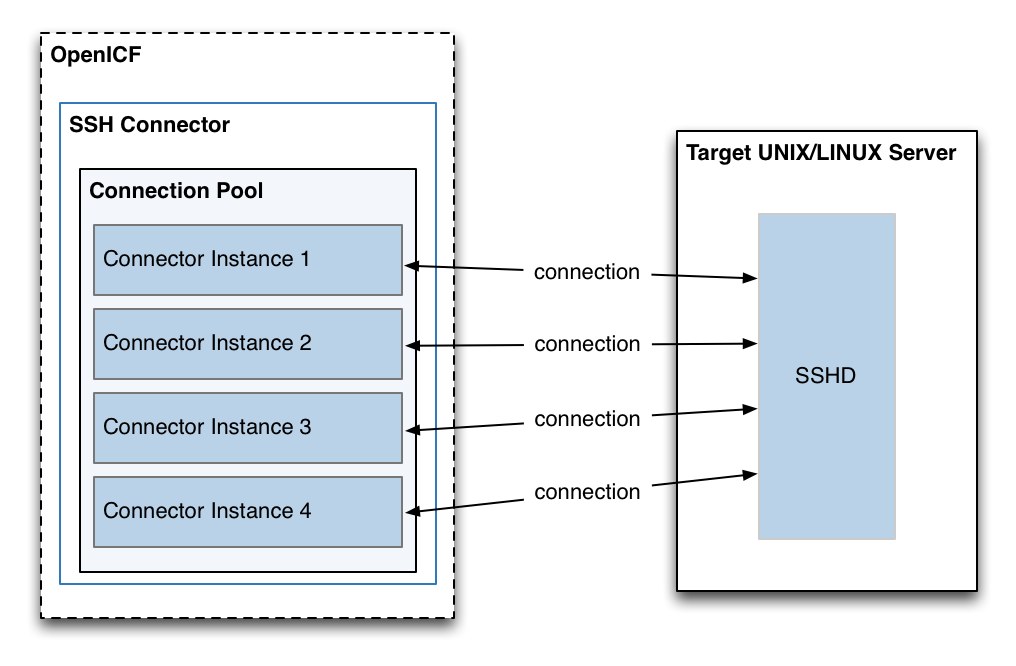
Configure authentication to the SSH server
The SSH connector authenticates to the SSH server using either a login/password or a public/private key. The authentication method is specified in the authenticationType property in the connector configuration.
- Authenticate with a login and password
-
To authenticate with a login and password, set the
authenticationTypetoPASSWORDin the connector configuration file, and set auserandpassword. For example:"configurationProperties" : { ... "authenticationType" : "PASSWORD", "user" : "<USERNAME>", "password" : "<PASSWORD>", ...The password is encrypted when IDM loads the provisioner file.
- Authenticate with a passphrase and private key
-
To authenticate with a secure certificate, generate a pair of public/private keys. Install the public key on the server side and the private key on the IDM host (where the connector is located). Set the
authenticationTypetoPUBKEYin the connector configuration file and set theuser,password,passphraseandprivateKeyproperties. For example:"configurationProperties" : { ... "authenticationType" : "PUBKEY", "user" : "<USERNAME>", "password" : "<PASSWORD>", "passphrase" : "secret", "privateKey" : ["-----BEGIN DSA PRIVATE KEY-----", "MIIBugIBAAKBgQDcB0ztVMCFptpJhqlLNZSdN/5cDL3S7aOVy52Ae7vwwCqQPCQr", "6NyUk+wtkDr07NlYd3sg7a9hbsEnlYChsuX+/WUIvbOKdMfeqcQ+jKK26YdkTCGj", "g86dBj9JYhobSHDoQ9ov31pYN/cfW5BAZwkm9TdpEjHPvMIaOxx7GPGKWwIVALbD", "CEuf1yJk9UB7v0dmJS7bKkbxAoGARcbAuDP4rB6MsgAAkVwf+1sHXEiGPShYWrVV", "qBgCZ/S45ELqUuiaN/1N/nip/Cc/0SBPKqwl7o50CUg9GH9kTAjmXiwmbkwvtUv+", "Xjn5vCHS0w18yc3rGwyr2wj+D9KtDLFJ8+T5HmsbPoDQ3mIZ9xPmRQuRFfVMd9wr", "DY0Rs7cCgYAxjGjWDSKThowsvOUCiE0ySz6tWggHH3LTrS4Mfh2t0tnbUfrXq2cw", "3CN+T6brgnpYbyX5XI17p859C+cw90MD8N6vvBxaN8QMDRFk+hHNUeSy8gXeem9x", "O0vdIxCgKvA4dh5nSVb5VGKENEGNEHRlYxEPzbqlPa/C/ZvzIvdKXQIUQMoidPFC", "n9z+mE2dAADnPf2m9vk=", "-----END DSA PRIVATE KEY-----" ], ...The default value for the
passphraseproperty isnull. If you do not set a passphrase for the private key, the passphrase value must be equal to an empty string.You must set a value for the
passwordproperty, because the connector uses sudo to perform actions on the SSH server.The private key (PEM certificate) must be defined as a JSON String array.
The values of the
passphrase,passwordandprivateKeyare encrypted when IDM loads the provisioner file.
Install the SSH connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/ssh-connector-1.5.20.16.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the SSH connector
You cannot configure the SSH connector through the UI. Configure the connector over REST, as described in Configure Connectors Over REST.
Alternatively, copy the sample connector configuration file (/path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-ssh.json) to your project’s conf/ directory, and edit it to match your environment.
Set the authentication properties, as described in Configure Authentication to the SSH Server. In addition, set at least the following properties:
host-
Specify the hostname or IP address of the SSH server.
port-
Set the port on which the SSH server listens.
Default:
22 user-
The username of the account that connects to the SSH server.
This account must be able to
sshinto the server, with the password provided in the next parameter. password-
The password of the account that is used to connect to the SSH server.
prompt-
A string representing the remote SSH session prompt. This must be the exact prompt string, in the format
username@target:, for exampleadmin@myserver:~$. Include any trailing spaces.
This list describes the required configuration properties of the SSH connector. Typically, you can use the default values. For a list of all the configuration properties, refer to SSH Connector Configuration
sudoCommand-
A string that shows the full path to the
sudocommand, for example/usr/bin/sudo. echoOff-
If set to
true(the default), the input command echo is disabled. If set tofalse, every character that is sent to the server is sent back to the client in theexpect()call. terminalType-
Sets the terminal type to use for the session. The list of supported types is determined by your Linux/UNIX system. For more information, refer to the
terminfomanual page (man terminfo).Default:
vt102 setLocale-
If set to
true, indicates that the default environment locale should be changed to the value of thelocaleproperty.Default:
false locale-
Sets the locale for the LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables, if
setLocaleis set totrue.Default:
en_US.utf8 connectionTimeout-
Specifies the connection timeout to the remote server, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000 expectTimeout-
Specifies the timeout used by the
expect()calls in scripts, in milliseconds.Default:
5000 authenticationType-
Sets the authentication type, either
PASSWORDorPUBKEY. For more information, refer to connector-reference:ssh.adoc#ssh-authentication.Default:
PASSWORD throwOperationTimeoutException-
If
true, the connector throws an exception when theexpectTimeoutis reached for an operation. Otherwise, the operation fails silently.Default:
true scriptRoots-
The path to the Groovy scripts that perform the ICF operations, relative to your IDM installation directory. The sample connector configuration expects the scripts in
project-dir/tools, so this parameter is set to&{idm.instance.dir}/toolsin the sample configuration. classpath-
The directory in which the compiler should look for compiled classes. The default classpath, if not is specified, is
install-dir/lib. *ScriptFileName-
The name of the Groovy script that is used for each ICF operation.
SSH remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the SSH connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the SSH connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the SSH remote connector.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the SSH Connector
The SSH Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Authenticate
-
Provides simple authentication with two parameters, presumed to be a user name and password.
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Resolve Username
-
Resolves an object by its username and returns the
uidof the object. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Script on Resource
-
Runs a script on the target resource that is managed by this connector.
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
SSH Connector Configuration
The SSH Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The hostname to connect to. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
TCP port to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The user name used to login to remote server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The password used to login to remote server. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The passphrase used to read the private key when using Public Key authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The base 64 encoded value (PEM) of the private key used for Public Key authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which authentication type should be use: PASSWORD or PUBKEY. |
||||
|
|
`root@localhost:# ` |
|
Yes |
A string representing the remote SSH session prompt. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
A string representing the sudo command. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Disable the input command echo. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the terminal type to use for the session. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Define the locale for LC_ALL, LANG and LANGUAGE environment variables to use if setLocale=true. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines if the default environment locale should be changed with the value provided for locale. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the connection timeout to the remote server in milliseconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the timeout used by the expect() calls in the scripts in milliseconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines if an OperationTimeoutException should be thrown if any call to expect times out. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines the "prompt ready" timeout for the promptReady() command in milliseconds. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Groovy Engine configuration
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The root folder to load the scripts from. If the value is null or empty the classpath value is used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Classpath for use during compilation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, debugging code should be activated. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets a list of global AST transformations which should not be loaded even if they are defined in META-INF/org.codehaus.groovy.transform.ASTTransformation files. By default, none is disabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the minimum of time after a script can be recompiled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true recompilation is enabled. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Base class name for scripts (must derive from Script). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Gets the extensions used to find groovy files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Encoding for source files. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Directory into which to write classes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The error tolerance, which is the number of non-fatal errors (per unit) that should be tolerated before compilation is aborted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the compiler should produce action information. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Warning Level of the compiler. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Custom Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Custom Sensitive Configuration script for Groovy ConfigSlurper. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Operation Script Files
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the AUTHENTICATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the CREATE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The script used to customize some function of the connector. Read the documentation for more details. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the DELETE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RESOLVE_USERNAME operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SCHEMA operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the RUNSCRIPTONRESOURCE operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SEARCH operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the SYNC operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the TEST operation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
The name of the file used to perform the UPDATE operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
SAP SuccessFactors connector
The SAP SuccessFactors connector enables you to manage and synchronize objects between SuccessFactors and the IDM managed user repository. These instructions assume you have a SuccessFactors administrator account, and you have created an OAuth2 Client Application.
Before you start
Before you configure the connector, gather the following details:
- Host
-
The SuccessFactors API hostname. For example,
apisalesdemo2.successfactors.eu. - Client ID
-
The SuccessFactors API Key or client ID. To find this:
-
Open your SuccessFactors administrator account.
-
Open Manage OAuth2 Client Applications.
-
Select your registered OAuth2 Client Application.
-
Click View.
-
Copy the API key.
-
- User ID
-
The API User ID of the SuccessFactors user who authenticates to the REST server.
- Private Key
-
A private key. To configure this, generate a key pair from the X.509 certificate and copy the value of the private key.
- Company ID
-
The API Company ID of the admin user. This is specified in the SuccessFactors login URL.
- Person Segments
-
SuccessFactors person segments; for example,
EmpJob,EmpEmployment,PerPersonal.
Install the SuccessFactors connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/successfactors-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the SuccessFactors connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select SuccessFactors Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to SuccessFactors Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Test the SuccessFactors connector
Test that the configuration is correct by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/Successfactors?_action=test"
{
"name" : "Successfactors",
"enabled" : true,
"config" : "config/provisioner.openicf/Successfactors",
"connectorRef" : {
"bundleVersion" : "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.successfactors-connector",
"connectorName" : "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.successfactors.SuccessFactorsConnector"
},
"displayName" : "SuccessFactors Connector",
"objectTypes" : [
"__GROUP__",
"__PERSON__",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok" : true
}
If the command returns "ok": true, your connector has been configured correctly and can authenticate to the SuccessFactors system.
SuccessFactors remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the SuccessFactors connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the SuccessFactors connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the SuccessFactors remote connector.
Use the SuccessFactors connector
Actions on accounts
You can perform the following actions on a SAP SuccessFactors account:
Create a SuccessFactors user
The following example creates a user with every available attribute:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"userId": "BJENSEN",
"username": "bjensen",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"email": "bjensen@example.com",
"firstName": "Barbara",
"lastName": "Jensen",
"country": "USA",
"married": false,
"timeZone": "US/Eastern",
"department": "Cloud",
"state": "New York",
"city": "New York City",
"jobLevel": "2",
"location": "40.6635°N 73.9387°W",
"__PASSWORD__": "Test@123",
"division": "Manufacturing",
"hireDate": "2021-07-26 00:00:00",
"dateOfBirth": "2012-08-22 00:00:00",
"__GROUP__": [
{"groupId": "6895"},
{"groupId": "6095"}
]
}'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/Successfactors/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"userId" : "BJENSEN",
"jobLevel" : "2",
"__GROUP__" : [
{
"groupId" : "1586",
"groupName" : "EVERYONE"
}, {
"groupId" : "6895",
"groupName" : "SAP_Managers"
}, {
"groupId" : "6095",
"groupName" : "SAP_ONB2_ErrorFlowAdmins"
}
],
"department" : "Cloud",
"dateOfBirth" : "2012-08-22 00:00:00",
"lastModifiedDateTime" : "2022-11-02 09:13:49",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"email" : "bjensen@example.com",
"country" : "USA",
"lastModified" : "2022-11-02 10:13:49",
"location" : "40.6635°N 73.9387°W",
"lastName" : "Jensen",
"lastModifiedWithTZ" : "2022-11-02 09:13:49",
"username" : "bjensen",
"timeZone" : "US/Eastern",
"city" : "New York City",
"state" : "New York",
"__NAME__" : "bjensen",
"hireDate" : "2021-07-26 00:00:00",
"married" : false,
"division" : "Manufacturing",
"firstName" : "Barbara"
}
New users must have at least the username, userId, and status properties.
|
Query all users
The following example queries all SuccessFactors users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result":[
{"_id":"1007373"},
{"_id":"1007371"},
{"_id":"1007376"},
{"_id":"1007370"},
{"_id":"1007377"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single user
The following example queries a single user by their ID:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=_id%20eq%20%22BJENSEN%22"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"userId" : "BJENSEN",
"jobLevel" : "2",
"__GROUP__" : [
{
"groupId" : "1586",
"groupName" : "EVERYONE"
}, {
"groupId" : "6895",
"groupName" : "SAP_Managers"
}, {
"groupId" : "6095",
"groupName" : "SAP_ONB2_ErrorFlowAdmins"
}
],
"department" : "Cloud",
"dateOfBirth" : "2012-08-22 00:00:00",
"lastModifiedDateTime" : "2022-11-02 09:13:49",
"__ENABLE__" : true,
"email" : "bjensen@example.com",
"country" : "USA",
"lastModified" : "2022-11-02 10:13:49",
"location" : "40.6635�N 73.9387�W",
"lastName" : "Jensen",
"lastModifiedWithTZ" : "2022-11-02 09:13:49",
"username" : "bjensen",
"timeZone" : "US/Eastern",
"city" : "New York City",
"state" : "New York",
"__NAME__" : "bjensen",
"hireDate" : "2021-07-26 00:00:00",
"married" : false,
"division" : "Manufacturing",
"firstName" : "Barbara"
}
Modify a user
You can use the SuccessFactors connector to modify the following attributes of a user entry:
-
username -
email -
status -
country -
department -
timeZone -
jobLevel -
married -
city -
state -
division -
citizenship -
location -
firstName -
lastName -
gender -
dateOfBirth -
jobCode
The following example updates the division property on a user:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "If-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"division": "Engineering"
}'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/Successfactors/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"userId" : "BJENSEN",
...
"division" : "Engineering",
"firstName" : "Barbara"
}
Reset a user’s password
The following example resets the password for a SuccessFactors user account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{
"operation": "replace",
"field": "__PASSWORD__",
"value": "__CHANGEME__"
}]'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"userId" : "BJENSEN",
...
}
| The updated password is not included in the response object; however, the value is updated in the system. |
Activate a user
The following example activates a user with the minimum required attributes:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"username": "bjensen",
"__ENABLE__": true,
"firstName": "Barbara",
"userId": "BJENSEN"
}'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id": "BJENSEN",
"userId": "BJENSEN",
...
"__ENABLE__": true
}
Deactivate a user account
The SuccessFactors connector does not support deleting accounts. To deactivate an unwanted account, set the account’s __ENABLE__ attribute value to false. A deactivated account remains in the SuccessFactors system and can still be queried by its ID, but cannot be accessed.
The following example deactivates a SuccessFactors account:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
--data '{
"username": "bjensen",
"__ENABLE__": false,
"firstName": "Barbara",
"userId": "BJENSEN"
}'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
_id: "BJENSEN"
}
Assign a user to a group
The following example assigns a user to a group:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"__ENABLE__": true,
"__GROUP__": [
{"groupId":1001}
]
}'
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__ACCOUNT__/BJENSEN"
{
"_id" : "BJENSEN",
"userId" : "BJENSEN",
"jobLevel" : "2",
"__GROUP__" : [
{
"groupId" : "1001",
"groupName" : "Example Working Group"
},
...
}
Actions on other objects
Query all groups
The following example queries all groups in the system:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "if-Match:*" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{"_id":"6637"},
{"_id":"2202"},
{"_id":"1588"},
{"_id":"6877"},
{"_id":"2203"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Query a single group
The following example queries a single group:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__GROUP__?/1001"
{
"_id": "1001",
"__NAME__": "1001",
"groupName": "Example Working Group",
"lastModifiedDate" : "2015-01-04 23:29:38",
"createdBy" : "v4admin",
"totalMemberCount" : "33590",
"activeMembershipCount" : "2294",
"groupID" : "1001",
"groupType" : "permission"
}
Query all persons
The following example queries all persons in the system:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__PERSON__?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result":[
{"_id":"69119"},
{"_id":"69120"},
{"_id":"69121"},
{"_id":"80279"},
{"_id":"80280"}
],
"resultCount":5,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Query a single person
The following example queries a single group:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request GET \
"https://localhost:8443/openidm/system/successfactors/__PERSON__?_queryFilter=_id%20%22scarter%22"
{
"result":[{
"_id":"scarter",
"EmpJob_payGrade":"GR-08",
"EmpEmployment_firstDateWorked":"2002-03-17 00:00:00",
"PerPersonal_maritalStatus":"10819",
"PerPersonal_nationality":"USA",
"EmpEmployment_lastDateWorked":null,
"EmpEmployment_userId":"scarter",
"PerPersonal_personIdExternal":"scarter",
"EmpEmployment_initialStockGrant":null,
"PerPerson_countryOfBirth":"USA",
"PerPersonal_endDate":"9999-12-31 00:00:00",
"PerPersonal_firstName":"Sam",
"EmpEmployment_eligibleForStock":null,
"PerPersonal_lastName":"Carter",
"EmpJob_payScaleArea":"USA/US2",
"EmpJob_jobCode":"50070968",
"PerPerson_regionOfBirth":null,
"PerPersonal_startDate":"2002-03-17 00:00:00",
"PerPerson_personIdExternal":"scarter",
"PerPerson_lastModifiedDateTime":"2015-10-30 10:05:06",
"EmpEmployment_lastModifiedDateTime":"2018-07-15 23:12:06",
"PerPersonal_lastModifiedDateTime":"2018-10-25 23:51:29",
"EmpJob_timezone":"US/Eastern",
"PerPersonal_gender":"M",
"PerPerson_dateOfBirth":"1983-02-15 00:00:00",
"PerPersonal_nativePreferredLang":"10223",
"EmpEmployment_serviceDate":null,
"EmpEmployment_assignmentIdExternal":"scarter",
"EmpJob_lastModifiedDateTime":"2020-06-23 10:50:43",
"PerPerson_createdOn":"2015-01-05 23:34:22",
"EmpJob_company":"1710",
"EmpEmployment_originalStartDate":"2002-03-17 00:00:00",
"EmpEmployment_endDate":null,
"EmpJob_position":"3000325",
"EmpJob_jobTitle":"Administrative Support",
"PerPersonal_salutation":"10810",
"EmpEmployment_seniorityDate":"2002-03-17 00:00:00",
"PerPerson_createdDateTime":"2015-01-05 22:34:22",
"EmpEmployment_professionalServiceDate":null,
"EmpJob_startDate":"2017-01-01 00:00:00",
"PerPersonal_middleName":null,
"PerPerson_createdBy":"v4admin",
"PerPersonal_preferredName":null,
"PerPerson_lastModifiedBy":"scarter",
"EmpJob_businessUnit":"CORP",
"EmpJob_seqNumber":"1",
"PerPerson_perPersonUuid":"87AF10389BCC4F29BC3F3A225B321E14",
"EmpJob_location":"1710-2001",
"EmpJob_managerId":"108743",
"EmpJob_eventReason":"PAYOTH",
"PerPerson_lastModifiedOn":"2015-10-30 11:05:06",
"EmpJob_payScaleType":"USA/US2",
"EmpJob_userId":"scarter",
"EmpEmployment_initialOptionGrant":null,
"EmpEmployment_personIdExternal":"scarter",
"PerPerson_personId":"8",
"__NAME__":"scarter"}],
"resultCount":1,
"pagedResultsCookie":null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy":"NONE",
"totalPagedResults":-1,
"remainingPagedResults":-1
}
Account attributes
The following account attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s User ID. |
|
The user’s username. |
|
The user’s status. |
|
The user’s first name. |
|
The user’s last name. |
|
The user’s middle name. |
|
The user’s email address. |
|
The user’s birthdate. |
|
The default full name for the user. |
|
The user’s password. |
|
The last modified date and time without time zone information. |
|
The user’s country of residence. |
|
The user’s country of citizenship. |
|
The user’s marital status. |
|
The state where the user lives. |
|
The city where the user lives. |
|
The division the user works in. |
|
The department the user works in. |
|
The Job code of the user. |
|
The Job level of the user. |
|
The user’s time zone. |
|
The user’s location. |
|
The user’s manager. |
|
The date the user was hired. |
|
The last modified date and time with time zone information. |
|
The last modified date. |
Group attributes
The following group attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors Connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The unique ID of the group. |
|
The name of the group. |
|
The type of the group. |
|
The number of active members. |
|
The number of total members. |
|
Users excluded from the group. |
|
Users included in the group. |
|
The user who created the group. |
|
The last modified date. |
Person attributes
PerPerson attributes
The following PerPerson attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
An ID used to represent the person externally. |
|
An ID used to represent the person internally. |
|
The person’s user ID. |
|
The person’s date of birth. |
|
The date the person was last modified. |
|
The time the person was last modified. |
|
The country the person was born in. |
|
The ID of the user who created the person. |
|
The time the person was created. |
|
The ID of the last user to modify the person. |
|
A UUID for the person. |
|
The person’s birth region. |
PerPersonal attributes
The following PerPersonal attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
An ID used to represent the employee externally. |
|
The end date of the employment. |
|
The start date of the employment. |
|
The person’s first name. |
|
The person’s last name. |
|
The person’s gender. |
|
The person’s preferred native language code. |
|
The salutation to be used for the person. |
|
The person’s marital status. |
|
The person’s nationality. |
|
The person’s middle name. |
|
The person’s preferred name. |
|
The time when the PerPersonal was last updated. |
EmpEmployment attributes
The following EmpEmployment attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
An ID used to represent the employee externally. |
|
The employee’s user ID. |
|
An assignment ID used to identify users across the suite. |
|
The first date the employee worked. |
|
The end date of the employment. |
|
The start date of the employment. |
|
Whether or not the user is eligible for stock. |
|
The initial grant value of the employment. |
|
The service date of employment. |
|
The professional service date of employment. |
|
The employment’s initial stock grant. |
|
The date of seniority. |
|
The time when the EmpEmployment object was last updated. |
|
The date of the last day the employee worked. |
EmpJob attributes
The following EmpJob attributes are supported by the SuccessFactors connector:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The sequence number associated with the job. |
|
The employee’s user ID. |
|
The reason for action. |
|
The company the job is for. |
|
The ID of the manager of the job. |
|
The time zone the job is in. |
|
The date the job begins. |
|
The date the job ends. |
|
The job’s pay grade. |
|
The job’s code. |
|
The position of the job. |
|
The job’s location. |
|
The payscale type for the job. |
|
The payscale area for the job. |
|
The business unit the job belongs to. |
|
The date the job was last modified. |
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the SuccessFactors Connector
The SuccessFactors Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
SuccessFactors Connector Configuration
The SuccessFactors Connector has the following configurable properties:
Configuration properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Hostname of the target. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The client identifier. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
User id for authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The private key which is used for signing JWT. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Company id as present in target application. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
To retrieve data based on person segments. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Page size for search operation. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connections. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the maximum connection timeout in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy host. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy port. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy username. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Provides the HTTP proxy password. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Webex Connector
The Webex connector allows you to manage users and groups between Webex Control Hub and IDM. A Webex administrator account is required for the connector to work.
Before you start
-
Create a Webex developer account.
-
Create an integration application. Add the required scopes to manage users, groups, licenses, and roles. Minimum scope required:
-
spark-admin:people_write -
spark-admin:people_read -
spark-admin:licenses_read -
spark-admin:roles_read -
identity:groups_rw -
identity:groups_read
-
-
Remember to save the client secret and client id and get a refresh token.
Install the Webex connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes[1] |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/webex-connector-1.5.20.21.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Webex connector
| The Webex connector can only be configured using REST. |
| For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Webex Connector Configuration |
Base Connector Details
-
Webex Endpoint: https://webexapis.com/v1 -
Use Basic Auth For OAuth Token Neg:true|false -
Max connections: Max size of the http connection pool used. Defaults to10. -
Connection Timeout (seconds): Defines a timeout for the underlying http connection in seconds. Defaults to30.
Authentication
-
Token Endpoint: https://webexapis.com/v1/access_token -
Client ID: Your Client ID. -
Client Secret: Your Client Secret. -
Refresh Token: Your Refresh Token.
Additional Options
-
Read rate limit: 2.5 -
Write read limi: 2.5
Object Types
If necessary, add or edit your object types to have these three objects with their properties:
__ACCOUNT__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
YES |
|
Array |
String |
YES |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
YES |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
__GROUP__
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
YES |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Array |
Object |
NO |
Roles
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
Licenses
| PROPERTY NAME | TYPE | NATIVE TYPE | REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
Integer |
Integer |
NO |
|
Integer |
Integer |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
|
String |
String |
NO |
If configuring the connector over REST or through the filesystem, specify the connection details to the Webex resource provider in the configurationProperties for the connector. If you are using OAuth for your connection, the minimum required properties are serviceUri, tokenEndpoint, refreshToken, clientId, and clientSecret.
The readRateLimit and writeRateLimit fields are for limiting the rate of requests. The recommended rate is 2.5.
Sample Configuration
{
"configurationProperties" : {
"tokenExpiration" : null,
"accessToken" : null,
"serviceUri" : "https://webexapis.com/v1",
"readRateLimit" : "2.5",
"login" : null,
"password" : null,
"writeRateLimit" : "2.5",
"authenticationMethod" : "OAUTH",
"tokenEndpoint" : "https://webexapis.com/v1/access_token",
"clientId" : "k3..........5g",
"clientSecret" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"refreshToken" : "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"authToken" : null,
"acceptSelfSignedCertificates" : false,
"disableHostNameVerifier" : false,
"disableHttpCompression" : false,
"clientCertAlias" : null,
"clientCertPassword" : null,
"maximumConnections" : "10",
"httpProxyHost" : null,
"httpProxyPort" : null,
"httpProxyUsername" : null,
"httpProxyPassword" : null,
"connectionTimeout" : "30",
"grantType" : "refresh_token",
"scope" : null,
"authorizationTokenPrefix" : "Bearer",
"useBasicAuthForOauthTokenNeg" : true
}
}
On startup, IDM encrypts the value of the clientSecret and refreshToken.
|
Mapping
From Webex users to OpenIDM Users
Attributes Grid: Where the columns represent the attribute name mapped from source to target and the necessary data transformation to synchronize successfully.
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
From OpenIDM Users to Webex Users
Attributes Grid: Where the columns represent the attribute name mapped from source to target and the necessary data transformation to synchronize successfully.
This mapping depends on the previous mapping.
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
From Webex Groups to OpenIDM Groups
Attributes Grid: Where the columns represent the attribute name mapped from source to target and the necessary data transformation to synchronize successfully.
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
From OpenIDM Groups to Webex Groups
Attributes Grid: Where the columns represent the attribute name mapped from source to target and the necessary data transformation to synchronize successfully.
This mapping depends on the previous mapping.
| SOURCE | TARGET | TRANSFORMATION SCRIPT |
|---|---|---|
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
Test the Webex connector
Test that the connector was configured correctly:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0' \
--request POST \
'http://localhost:8080/system/webex?_action=test'
{
"name": "Webex",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/Webex",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "1.5.20.21",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.webex-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.webex.WebexConnector"
},
"displayName": "Webex Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"__GROUP__",
"__ACCOUNT__",
"ROLES",
"__ALL__",
"LICENSES"
],
"ok": true
}
Use the Webex connector
User
Create user
To create a user, it is necessary to at least provide the email and displayName fields. Some fields,
such as extension, locationId, or siteUrls require their respective licenses. Field locationId requires the extension field,
and locationId and phoneNumbers fields are mutually exclusive.
It is possible that licenses will be added by default, so it is advisable to perform a reconciliation to be up to date.
If you create a user with a role or license (bad format) that is not allowed to be assigned or with an incorrect avatar URL, the user is still created with the exception of the fields that failed:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--data '{
"displayName" : "John Doe",
"firstName" : "John",
"LastName" : "Doe",
"groups" : [
"groupId",
"groupId"
],
"emails" : [
"john.doe@example.com"
],
"licenses" : [
"licenseId"
],
"roles" : [
"roleId"
],
"extension" : "123",
"avatar" : "urlAvatar",
"title" : "Title",
"department" : "Sales",
"manager" : "Manager Name",
"managerId" : "managerId",
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "work",
"value": "+1 010 110 1101"
}
],
"addresses": [
{
"type": "work",
"country": "US",
"locality": "Milpitas",
"region": "California",
"streetAddress": "1111 Bird Ave.",
"postalCode": "010101"
}
],
"siteUrls": [
"mysite.webex.com#attendee"
],
"orgId" : "orgId",
"locationId" : "locationId"
}'\
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__?_action=create'
{
"_id" : "userId",
"displayName" : "John Doe",
"firstName" : "John",
"LastName" : "Doe",
"groups" : [
"groupId",
"groupId"
],
"emails" : [
"john.doe@example.com"
],
"licenses" : [
"licenseId"
],
"roles" : [
"roleId"
],
"extension" : "123",
"avatar" : "urlAvatar",
"title" : "Title",
"department" : "Sales",
"manager" , "Manager Name",
"managerId" : "managerId",
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "work",
"value": "+1 010 110 1101"
}
],
"addresses": [
{
"type": "work",
"country": "US",
"locality": "Milpitas",
"region": "California",
"streetAddress": "1111 Bird Ave.",
"postalCode": "010101"
}
],
"siteUrls": [
"mysite.webex.com#attendee"
],
"orgId" : "orgId",
"locationId" : "locationId"
}
Get Users
Retrieve a list of user ids from Webex. By default, retrieves all users:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__?_queryId=query-all-ids'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "001"
},
{
"_id" : "002"
},
{
"_id" : "003"
},
],
"resultCount": 999,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Get user
Retrieve a user from Webex. The user id must be provided in the URI path.
The locationId and extension fields will only be displayed if they have their corresponding license:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__/ID'
{
"_id" : "userId",
"displayName" : "active",
"firstName" : "active",
"LastName" : "active",
"groups" : [
"groupId",
"groupId",
],
"emails" : [
"test@email.com"
],
"licenses" : [
"licenseId"
],
"roles" : [
"roleId"
],
"extension" : "gs",
"avatar" : "avatarURL",
"title" : "surname",
"department" : "Sales",
"manager" , "John Doe",
"managerId" : "managerId",
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "work",
"value": "+1 010 110 1101"
}
],
"addresses": [
{
"type": "work",
"country": "US",
"locality": "Milpitas",
"region": "California",
"streetAddress": "1099 Bird Ave.",
"postalCode": "99212"
}
],
"siteUrls": [
"mysite.webex.com#attendee"
],
"orgId" : true,
"locationId" : "locationId"
}
Get user emails
Retrieve a user in Webex filtering by the emails field:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=true&_fields=emails'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "001",
"emails": [
"email001@example.wbx.ai"
],
},
{
"_id" : "003",
"emails": [
"email003@example.wbx.ai"
],
},
{
"_id" : "003",
"emails": [
"email003@example.wbx.ai"
],
}
],
"resultCount": 999,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Get user filter by email
Retrieve a user in Webex filtering by the emails field.
The locationId and extension fields will only be displayed if they have their corresponding license:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --request GET \ 'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=emails%20eq%20"email@example.wbx.ai"' { "result": [ { "_id": "userId", "firstName": "John", "displayName": "John Doe", "lastName": "Doe", "orgId": "orgId", "emails": [ "john@example.wbx.ai" ], "roles": [ "roleId" ], "groups": [], "licenses": [ "licenseId" ], "__NAME__": "John" } ] }
Get user filter starts with
Retrieve a user in Webex filtering by the displayName field. Minimum characters to search for displayName.
The locationId and extension fields will only be displayed if they have their corresponding license:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__?_queryFilter=displayName%20sw%20"john"'
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "userId",
"firstName": "John",
"displayName": "John Doe",
"lastName": "Doe",
"orgId": "orgId",
"emails": [
"john@example.wbx.ai"
],
"roles": [
"roleId"
],
"groups": [
"groupId_1",
"groupId_2"
],
"licenses": [
"licenseId"
],
"__NAME__": "John"
}
],
"resultCount": 1,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Update user
To update a user, it is necessary to at least provide the email, displayName and licenses fields. To update the
locationId, extension, and siteUrls fields, the user must have the corresponding licenses.
locationId requires the extension field. locationId and phoneNumbers are mutually exclusive:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request PUT \
--data '{
"displayName" : "John Doe",
"firstName" : "John",
"LastName" : "Doe",
"groups" : [
"groupId",
"groupId"
],
"emails" : [
"john.doe@example.com"
],
"licenses" : [
"licenseId"
],
"roles" : [
"roleId"
],
"extension" : "123",
"avatar" : "urlAvatar",
"title" : "Title",
"department" : "Sales",
"manager" , "Manager Name",
"managerId" : "managerId",
"phoneNumbers" : [
{
"type": "work",
"value": "+1 010 110 1101"
}
],
"addresses" : [
{
"type": "work",
"country": "US",
"locality": "Milpitas",
"region": "California",
"streetAddress": "1111 Bird Ave.",
"postalCode": "010101"
}
],
"siteUrls": [
"mysite.webex.com#attendee"
],
"orgId" : "orgId",
"locationId" : "locationId"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__/USER_ID'
{
"_id" : "userId",
"displayName" : "John Doe",
"firstName" : "John",
"LastName" : "Doe",
"groups" : [
"groupId",
"groupId",
],
"emails" : [
"john.doe@example.com"
],
"licenses" : [
"licenseId"
],
"roles" : [
"roleId"
],
"extension" : "123",
"avatar" : "avatarURL",
"title" : "Title",
"department" : "Developer",
"manager" , "Manager Name",
"managerId" : "managerId",
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "work",
"value": "+1 010 110 1101"
}
],
"addresses": [
{
"type": "work",
"country": "US",
"locality": "Milpitas",
"region": "California",
"streetAddress": "1111 Bird Ave.",
"postalCode": "010101"
}
],
"siteUrls": [
"mysite.webex.com#attendee"
],
"orgId" : "orgId",
"locationId" : "locationId"
}
| To update the licenses correctly, it is necessary to deactivate the default licenses and to have the option "Preserve licenses for users joining another group" activated in Webex Control Hub in the user licenses tab. |
Delete user
Delete a user from the Webex organization. The user id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request DELETE \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__ACCOUNT__/USER_ID'
{
"_id" : "USER_ID",
"email" : "deleted.member@email.com",
...
}
GROUPS
Create group
To create a group, it is necessary to at least provided displayName field:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request POST \
--data '{
"displayName" : "Group name",
"description" : "Group Description",
"orgId" : "orgId"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__GROUP__?_action=create'
{
"_id" : "groupId",
"displayName" : "Group name",
"description" : "Group Description",
"orgId" : "orgId",
"members": []
}
Get groups
Retrieve a list of groups showing only the ids. By default returns all groups:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__GROUP__?_queryId=query-all-ids'
{
"result": [
{
"_id" : "groupid1"
},
{
"_id" : "groupId2"
},
{
"_id" : "groupId3",
},
...
],
"resultCount": 999,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Update a group
The fields that can be updated for a group are description and displayName. The group id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request PUT \
--header 'If-Match: *' \
--data '{
"displayName" : "New Group Name",
"description" : "New Description"
}' \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__GROUP__/GROUP_ID'
{
"_id" : "groupId",
"displayName" : "New Group Name",
"description" : "New Description",
"orgId" : "orgId",
"members": []
}
Delete a group
The group id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request DELETE \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/__GROUP__/GROUP_ID'
{
"_id" : "groupId",
"displayName" : "New Group Name",
"description" : "New Description",
"orgId" : "orgId",
"members": []
}
Get Roles
Retrieve a list of roles for Webex users.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/ROLES/?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result" : [
{
"_id" : "roleId",
"__NAME__" : "Role name",
},
...
],
"resultCount": 999,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Get Role
Retrieve a role from the Webex organization. The user id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/ROLES/ROLE_ID'
{
"_id": "roleId",
"__NAME__": "Role Name"
}
Get Licenses
Retrieve a list of licenses for Webex users.
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/LICENSES/?_queryFilter=true'
{
"result" : [
{
"_id" : "LicenseId",
"name" : "Role Name",
"totalUnits" : 50,
"consumedUnits": 1,
"subscriptionId": "subscriptionId",
"siteUrl": "site1-example.webex.com",
"siteType": "Control Hub managed site",
},
...
],
"resultCount": 999,
"pagedResultsCookie": null,
"totalPagedResultsPolicy": "NONE",
"totalPagedResults": -1,
"remainingPagedResults": -1
}
Get License
Retrieve a user license. The user id must be provided in the URI path:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--request GET \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/webex/LICENSES/LICENSE_ID'
{
"_id": "LicenseId",
"name": "License Name",
"totalUnits": "10",
"subscriptionId": "subscriptionId",
"siteType": "Control Hub managed site",
"__NAME__": "License Name",
"siteUrl": "sityUrl.webex.com"
}
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Webex Connector
The Webex Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Create
-
Creates an object and its
uid. - Delete
-
Deletes an object, referenced by its
uid. - Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Webex Connector Configuration
The Webex Connector has the following configurable properties:
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The service endpoint URI. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines throttling for read operations either per seconds ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The service login name. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines throttling for write operations (create/update/delete) either per second ("30/sec") or per minute ("100/min"). |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
The service user password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines which method is to be used to authenticate on the remote server. Options are BASIC (username/password), OAUTH (Client id/secret) or TOKEN (static token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
When using OAUTH as authentication method, this property defines the endpoint where a new access token should be queried for (https://myserver.com/oauth2/token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The client identifier for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Secure client secret for OAuth2. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
Static authentication token. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
To be used for debug/test purposes. To be avoided in production. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Content compression is enabled by default. Set this property to true to disable it. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed, set this to the certificate alias from the keystore. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
If TLS Mutual Auth is needed and the client certificate (private key) password is different from the keystore password, set this to the client private key password. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the max size of the HTTP connection pool used. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Hostname if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines the Port if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
Defines Proxy Username if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Defines Proxy Password if an HTTP proxy is used between the connector and the service. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Defines a timeout for the underlying HTTP connection in seconds. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Used by the refresh_token grant type. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 grant type to use (client_credentials or refresh_token). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The OAuth2 scope to use. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The prefix to be used in the Authorization HTTP header for Token authentication. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The Authentication method for refresh token (Basic Authentication or Sending the ClientId and Client Secret in the Header). |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Workday connector
Workday is a multi-tenant Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) application. The Workday connector lets you synchronize user accounts between IDM and Workday’s cloud-based HR system.
The connector supports reconciliation of users and organizations from Workday to an IDM repository, liveSync of users from Workday to IDM, and updating users in a Workday system.
To use the connector, you need a Workday instance with the required permissions and a set of credentials to access the instance, including the username, password, tenant name, and host name.
Install the Workday connector
You can download any connector from Backstage, but some come bundled with Identity Cloud, IDM, or RCS by default. When using a bundled connector, you can skip installing it and move directly to configuration.
| Connector | Identity Cloud | IDM | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
No |
No |
Download the connector .jar file from Backstage.
-
If you are running the connector locally, place it in the
/path/to/openidm/connectorsdirectory, for example:mv ~/Downloads/workday-connector-1.5.20.18.jar /path/to/openidm/connectors/
-
If you are using a remote connector server (RCS), place it in the
/path/to/openicf/connectorsdirectory on the RCS.
Configure the Workday connector
Create a connector configuration using the IDM admin UI:
-
From the navigation bar, click Configure > Connectors.
-
On the Connectors page, click New Connector.
-
On the New Connector page, type a Connector Name.
-
From the Connector Type drop-down list, select Workday Connector - 1.5.20.18.
-
Complete the Base Connector Details.
For a list of all configuration properties, refer to Workday Connector Configuration -
Click Save.
When your connector is configured correctly, the connector displays as Active in the admin UI.
Refer to this procedure to create a connector configuration over REST.
Alternatively, copy the sample configuration file /path/to/openidm/samples/example-configurations/provisioners/provisioner.openicf-workday.json to your project’s conf/ directory, and set enabled to true. Edit the configurationProperties to specify the connection to the Workday instance, for example:
"configurationProperties" : {
"hostname" : "example.workday.net",
"tenant" : "example-tenant",
"username" : "admin",
"password" : "Passw0rd",
...
}Set at least the following properties:
hostname-
The fully qualified name of the Workday instance. The connector uses the
hostnameto construct the endpoint URL. tenant-
The tenant to which you are connecting. The connector uses the
tenantname to construct the endpoint URL, and the complete username (in the formusername@tenant). username-
The
usernameused to log in to the Workday instance. Do not specify the complete username including thetenant. The connector constructs the complete username. password-
The
passwordused to log in to the Workday instance. connectionTimeout-
The timeout (in milliseconds) that the connector should wait for a request to be sent to the Workday instance. The default timeout is 60000ms or one minute. Requests that take longer than a minute throw an exception.
receiveTimeout-
The timeout (in milliseconds) that the connector waits to receive a response. The default timeout is 60000ms or one minute. Because the Workday can be slow, and the amount of information returned can be very large, you should set this parameter carefully to avoid unnecessary timeouts.
Check that the connector is retrieving the exact data that you need.
The configurationProperties also specify the data that the connector should retrieve with a number of boolean include... and exclude... properties. These properties can be divided as follows:
- Worker types
-
By default, all worker types are retrieved. Use any the following settings to exclude specific worker types:
-
excludeContingentWorkers- exclude contingent workers from query results,falseby default. -
excludeEmployees- exclude regular employees from query results,falseby default. -
excludeInactiveWorkers- exclude inactive workers from query results,falseby default.
-
- Specific worker data
-
These parameters specify the properties to return for every included worker type. For performance reasons, set all of these to false initially, and then include only the necessary properties.
Properties List
-
includeWorkerDocuments -
includeDevelopmentItems -
includeRoles -
includeQualifications -
includeTransactionLogData -
includeCareer -
includeContingentWorkerTaxAuthorityFormInformation -
includeUserAccount -
includeFeedbackReceived -
includeEmployeeContractData -
includeSkills -
includeAccountProvisioning -
includeGoals -
includeSuccessionProfile -
includeBackgroundCheckData -
includeEmployeeReview -
includeManagementChainData -
includeOrganizations -
includePhoto -
includeRelatedPersons -
includeBenefitEligibility -
includeTalentAssessment -
includeBenefitEnrollments -
includeCompensation
-
- Specific organizational data
-
Included in the data of each worker is the organization to which the user belongs. If you have set
includeOrganizationstotrue, you can specify the organizational data that should be excluded from the query response. By default, all organizational data is included. To exclude data from a response, set its corresponding property totrue. For performance reasons, set all of these totrueinitially, and then include only the necessary properties.Properties List
-
excludeCompanies -
excludeBusinessUnits -
excludeCustomOrganizations -
excludeMatrixOrganizations -
excludeGiftHierarchies -
excludeCostCenterHierarchies -
excludeGrants -
excludeProgramHierarchies -
excludeFunds -
excludeOrganizationSupportRoleData -
excludeGifts -
excludeBusinessUnitHierarchies -
excludeCostCenters -
excludePrograms -
excludeSupervisoryOrganizations -
excludeRegionHierarchies -
excludeTeams -
excludeLocationHierarchies -
excludeRegions -
excludePayGroups -
excludeFundHierarchies -
excludeGrantHierarchies
For information about all the configurable properties for this connector, refer to Workday Connector Configuration.
-
Workday remote connector
If you want to run this connector outside of Identity Cloud or IDM, you can configure the Workday connector as a remote connector. Java Connectors installed remotely on a Java Connector Server function identically to those bundled locally within Identity Cloud or installed locally on IDM.
You can download the Workday connector from here.
Refer to Remote connectors for configuring the Workday remote connector.
Test the Workday connector
When your connector is configured correctly, test its status by running the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system?_action=test"
[
{
"name": "workday",
"enabled": true,
"config": "config/provisioner.openicf/workday",
"connectorRef": {
"bundleVersion": "[1.5.0.0,1.6.0.0)",
"bundleName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.workday-connector",
"connectorName": "org.forgerock.openicf.connectors.workday.WorkdayConnector"
},
"displayName": "Workday Connector",
"objectTypes": [
"employee",
"__ALL__"
],
"ok": true
}
]
A status of "ok": true indicates that the connector can contact the Workday instance.
To retrieve the workers in the Workday system, run the following command:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request GET \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/workday/employee?_queryId=query-all-ids"
{
"result": [
{
"_id": "3aa5550b7fe348b98d7b5741afc65534",
"employeeID": "21001"
},
{
"_id": "0e44c92412d34b01ace61e80a47aaf6d",
"employeeID": "21002"
},
{
"_id": "3895af7993ff4c509cbea2e1817172e0",
"employeeID": "21003"
},
...
]
}
The first time the connector retrieves the employees from the Workday system, the following warning, which you can safely ignore, might display in the console:
WARNING: Default key managers cannot be initialized: Invalid keystore format java.io.IOException: Invalid keystore format
To retrieve a specific user, include the user’s ID in the URL. For example:
curl \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \ --header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \ --request GET \ "http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/workday/employee/3aa5550b7fe348b98d7b5741afc65534"
Reconcile users from Workday to IDM
To reconcile users from Workday to IDM, set up a mapping between Workday and IDM managed users.
When you have created a mapping, run reconciliation using the admin UI or with a REST call similar to the following:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--request POST \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/recon?_action=recon&mapping=systemWorkdayEmployee_managedUser&waitForCompletion=true"
{
"_id": "db2bc7f4-e9a8-4315-9dd1-e2cdcd85ae6e-33099",
"state": "SUCCESS"
}
Update users in the Workday system
The connector supports updates to system users only for the following properties:
-
Account credentials (
usernameandpassword) -
email -
mobile(telephone number)
The following command updates a user’s mobile number:
curl \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Username: openidm-admin" \
--header "X-OpenIDM-Password: openidm-admin" \
--header "Accept-API-Version: resource=1.0" \
--header "Content-type: application/json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[
{
"operation": "replace",
"field": "mobile",
"value": "+1 (415) 859-4366"
}
]' \
"http://localhost:8080/openidm/system/workday/employee/3aa5550b7fe348b98d7b5741afc65534"
Implementation specifics
For PATCH requests, a connector can potentially add, remove, or replace an attribute value. The Workday connector does not implement the add or remove operations, so a PATCH request always replaces the entire attribute value with the new value.
OpenICF Interfaces Implemented by the Workday Connector
The Workday Connector implements the following OpenICF interfaces. For additional details, see ICF interfaces:
- Schema
-
Describes the object types, operations, and options that the connector supports.
- Script on Connector
-
Enables an application to run a script in the context of the connector.
Any script that runs on the connector has the following characteristics:
-
The script runs in the same execution environment as the connector and has access to all the classes to which the connector has access.
-
The script has access to a
connectorvariable that is equivalent to an initialized instance of the connector. At a minimum, the script can access the connector configuration. -
The script has access to any script arguments passed in by the application.
-
- Search
-
Searches the target resource for all objects that match the specified object class and filter.
- Sync
-
Polls the target resource for synchronization events, that is, native changes to objects on the target resource.
- Test
-
Tests the connector configuration.
Testing a configuration checks all elements of the environment that are referred to by the configuration are available. For example, the connector might make a physical connection to a host that is specified in the configuration to verify that it exists and that the credentials that are specified in the configuration are valid.
This operation might need to connect to a resource, and, as such, might take some time. Do not invoke this operation too often, such as before every provisioning operation. The test operation is not intended to check that the connector is alive (that is, that its physical connection to the resource has not timed out).
You can invoke the test operation before a connector configuration has been validated.
- Update
-
Updates (modifies or replaces) objects on a target resource.
Workday Connector Configuration
The Workday Connector has the following configurable properties:
Worker Response Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Management Chain Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Organization Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Personal Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the cost centers from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the custom organizations from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Role Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the matrix organizations from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Employment Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates that Account Provisioning Data will be included in the web service response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the business unit hierarchies from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Related Person Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Photo Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the supervisory organizations from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the teams from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Transaction Log Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the company organizations from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the Business Units from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates if the Employee Contract element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates that User Account Data will be included in the web service response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes the regions from the Organization Data element response. This can only be selected when the Include Organization Data boolean is also selected. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If set to true, multiple managers in the management chain data are returned. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If true, the data for Additional Jobs and International Assignments is included in the response. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Organization Response Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether the Staffing Restrictions Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether the Supervisory Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether the Hierarchy Data element is included in the response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Indicates whether the Roles Data element is included in the response. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.
Basic Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Default | Encrypted(1) | Required(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The hostname for the Workday service. Example: https://[workday hostname]/ccx/service/[workday tenant]/. You need to configure the bracketed Workday hostname and tenant name to successfully connect to the proper instance. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The tenant in URL for the Workday service. For example: https://[workday hostname]/ccx/service/[workday tenant]/. You need to configure the bracketed Workday hostname and tenant name to successfully connect to the proper instance. |
||||
|
|
|
|
Yes |
The user name for logging into the Workday service. It will be concatenated with the tenant name (user@tenant) |
||||
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
The user password for logging into the Workday service |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes terminated employees or contingent workers whose contracts have ended from the query response (defaults to false). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes contingent workers from the query response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Excludes employees from the query response. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the amount of time, in seconds, that the client will attempt to establish a connection before it times out. The default is 30 seconds). Set to 0 for no timeout. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Specifies the amount of time, in seconds, that the client will wait for a response before it times out. The default is 60. Set to 0 for no timeout. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the page size used for search operations (defaults to 100). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
If defined, the connection to Workday goes through this HTTP proxy server. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The HTTP proxy server port number (defaults to 8080). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
The file path to the XSL File to get the custom attributes. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Optional configuration of Response_Filter/As_Of_Effective_Date element. Valid values are: Date (http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/#date-time-values http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime-order) or Duration (http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/#dt-dayTimeDuration). If set to Duration, the effective date is calculated as current date + duration. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the Get_Workers_Request/Request_Criteria/Transaction_Log_Criteria_Data/Transaction_Date_Range_Data/Effective_From for every outbound query request. Valid value could be Date (http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/#date-time-values http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime-order) or string Today representing the current time of the request. |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
Sets the Get_Workers_Request/Request_Criteria/Transaction_Log_Criteria_Data/Transaction_Date_Range_Data/Effective_Through for every outbound query request. Valid value could be Date (http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/#date-time-values http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime-order) or Duration (http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/#dt-dayTimeDuration). |
||||
|
|
|
|
No |
A list of external fields to add to the search/query criteria. |
||||
(1) Whether the property value is considered confidential, and is therefore encrypted in IDM.
(2) A list of operations in this column indicates that the property is required for those operations.