Guide to installing and evaluating OpenIDM software. This software offers flexible services for automating management of the identity life cycle.
ForgeRock Identity Platform™ serves as the basis for our simple and comprehensive Identity and Access Management solution. We help our customers deepen their relationships with their customers, and improve the productivity and connectivity of their employees and partners. For more information about ForgeRock and about the platform, see https://www.forgerock.com.
This guide shows you how to install and get started with OpenIDM software.
This guide is written for identity management developers and administrators who build, deploy, and maintain OpenIDM services for their organizations. This guide covers the tasks you need to quickly get OpenIDM software running on your system.
As you read this guide, you will see how OpenIDM software reconciles customer identity data to ensure accurate information across disparate resources within an organization.
You will also read about what OpenIDM software can do in the areas of provisioning, self-service workflows, and password management. You will see how OpenIDM software can connect to a variety of remote data stores, with links to detailed documentation.
For example, engineers might access their systems through Active Directory accounts. Those same engineers might need to update their information in a Human Resources database, stored in a separate LDAP directory. With OpenIDM software, you can keep those user identities synchronized, so each engineer only has to update their data once.
ForgeRock publishes comprehensive documentation online:
The ForgeRock Knowledge Base offers a large and increasing number of up-to-date, practical articles that help you deploy and manage ForgeRock software.
While many articles are visible to community members, ForgeRock customers have access to much more, including advanced information for customers using ForgeRock software in a mission-critical capacity.
ForgeRock product documentation, such as this document, aims to be technically accurate and complete with respect to the software documented. It is visible to everyone and covers all product features and examples of how to use them.
The ForgeRock.org site has links to source code for ForgeRock open source software, as well as links to the ForgeRock forums and technical blogs.
If you are a ForgeRock customer, raise a support ticket instead of using the forums. ForgeRock support professionals will get in touch to help you.
Whenever you need access to important information, administrators need to know who you are. They need to know your identity, which may be distributed in multiple accounts.
As a user, you might have several accounts even within your own company, for functions such as:
Email
Human Resources
Payroll
Engineering, Support, Accounting, and other functions
Each of these accounts may be stored in different resources, such as Active Directory, OpenDJ, OpenLDAP, and more. Keeping track of user identities in each of these resources (also known as data stores) can get complex. OpenIDM simplifies the process, as it reconciles differences between resources.
With situational policies, OpenIDM can handle discrepancies such as a missing or updated address for a specific user. The server includes default but configurable policies to handle such conditions. In this way, consistency and predictability is ensured, in an otherwise chaotic resource environment.
OpenIDM can make it easier to track user identities across these resources. The server includes a highly scalable, modular, readily deployable architecture that can help you manage workflows and user information.
This software allows you to simplify the management of identity, as it can help you synchronize data across multiple resources. Each organization can maintain control of accounts within their respective domains.
OpenIDM works equally well with user, group, and device identities.
You can also configure workflows to help users manage how they sign up for accounts, as part of how OpenIDM manages the life cycle of users and their accounts.
You can manage employee identities as they move from job to job. You will make their lives easier as their user accounts can be registered on different systems automatically. Later, OpenIDM can increase productivity when it reconciles information from different accounts, saving users the hassle of entering the same information on different systems.
In this guide, you will see how OpenIDM reconciles user data between two data stores. We will look at a department that is adding a third engineer, Jane Sanchez.
Your Human Resources department has updated their data store with Jane Sanchez's information. You want to use OpenIDM to update the internal Engineering data store. But first, you have to start OpenIDM.
This section covers what you need to have on your system before running OpenIDM:
Operating System: Windows or UNIX/Linux.
Java: Java Runtime Environment (JRE) Standard Edition (Java SE) 7, update 6 or later, or Java 8. Alternatively, you can use the same version of the Java Development Kit (JDK). On Linux, you may also install the OpenJDK package native to your updated Linux distribution.
At least 250 MB of free disk space.
At least 1 GB of free RAM.
If your operating system includes a firewall, make sure that it allows traffic through (default) ports 8080 and 8443.
We provide this Getting Started document for demonstration purposes only.
With this document, we want to make it as easy as possible to set up a demonstration of OpenIDM software. To that end, we have written this document for installations on a desktop operating system, Microsoft Windows 7.
For a list of software that we support in production, see "Before You Install" in the Release Notes.
On Windows systems, after installing Java, set the
JAVA_HOME environment variable. To do so on Windows 7,
take the following steps:
Locate your JRE or JDK installation directory. For a default installation of Java 8 on Windows 7, you should find the directory here:
C:\Program Files\Java\jre-version.Select Start > Control Panel > System and Security > Advanced System Settings to open a System Properties window.
Select Advanced > Environment Variables.
Set the value of
JAVA_HOMEto match the JRE or JDK installation directory.
This procedure assumes that you are starting OpenIDM as a regular
(not administrative) user named user.
Download OpenIDM from ForgeRock's BackStage site.
Extract the contents of the OpenIDM binary file to your user's
Downloadsdirectory. The process should unpack the contents to theDownloads/openidmsubdirectory.Navigate to the
Downloads/openidmsubdirectory:In Microsoft Windows, use Windows Explorer to navigate to the
C:\Users\user\Downloads\openidmdirectory.Double-click the
getting-started(.bat)file. Do not select thegetting-started.shfile, as that is intended for use on UNIX/Linux systems.In Linux/UNIX, open a command-line interface and run the following commands:
$ cd /home/user/Downloads/openidm $ ./getting-started.sh
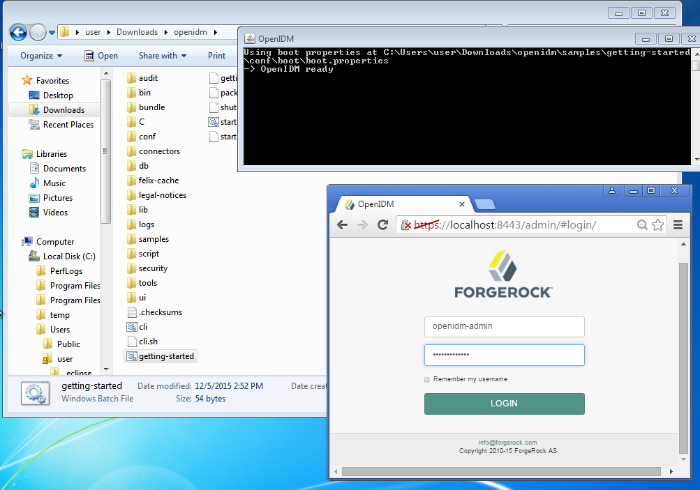
You should see the following message:
-> OpenIDM ready
When the server is ready, you can administer it from a web browser. To do so,
navigate to http://localhost:8080/admin or
https://localhost:8443/admin. If you have
installed the server on a remote system, substitute that hostname or IP
address for localhost.
Note
In production, you should connect to OpenIDM via the default secure port, 8443, and import a signed certificate into the truststore, as discussed in "Accessing the Security Management Service" in the Integrator's Guide.
Until you install that certificate, you will see a warning in your browser at least the first time you access OpenIDM over a secure port.
The default username and password for the OpenIDM Administrator is
openidm-admin and openidm-admin.
When you log into OpenIDM at a URL with the
/admin endpoint, you are logging into the Administrative
User Interface, also known as the Admin UI.
Warning
The default password for the administrative user,
openidm-admin, is openidm-admin.
To protect your deployment in production, change this password.
All users, including openidm-admin, can change their
password through the Self-Service UI, at
http://localhost:8080/ or
https://localhost:8443/. Once logged in, click
Profile > Password.
In a production deployment, you are likely to see resources like Active Directory and OpenDJ. But the setup requirements for each are extensive, and beyond the scope of this document.
For simplicity, this guide uses two static files as data stores:
hr.csvrepresents the Human Resources data store. It is in CSV format, commonly used to share data between spreadsheet applications.engineering.csvrepresents the Engineering data store. It is also in CSV format.
You can find these files in the binary package that you
downloaded earlier, in the following subdirectory:
openidm/samples/getting-started/data.
Now that you have installed OpenIDM with a "Getting Started" configuration, you will learn how OpenIDM reconciles information between two data stores.
While the reconciliation demonstrated in this guide uses two simplified data files, you can set up the same operations at an enterprise level on a variety of resources.
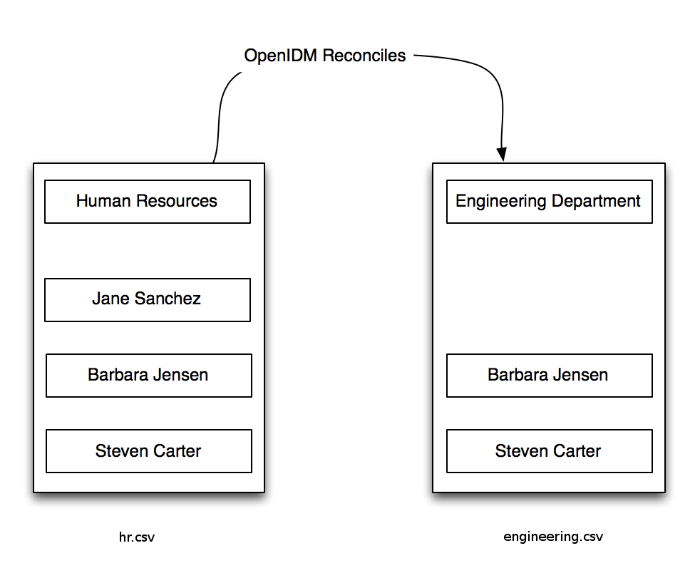
Return to the situation described earlier, where you have Jane Sanchez joining the engineering department. The following illustration depicts what OpenIDM has to do to reconcile the differences.
A central feature of OpenIDM is reconciliation - comparing the contents of two data stores and deciding what to do, depending on the differences.
This scenario is based on two data files:
hr.csv, which represents the Human Resources data storeengineering.csv, which represents the Engineering data store
Reconciliation modifies the Engineering data store by adding the newly hired Jane Sanchez. As suggested by the following illustration, it will also address detailed differences between Jane's Human Resources account and the Engineering data store.
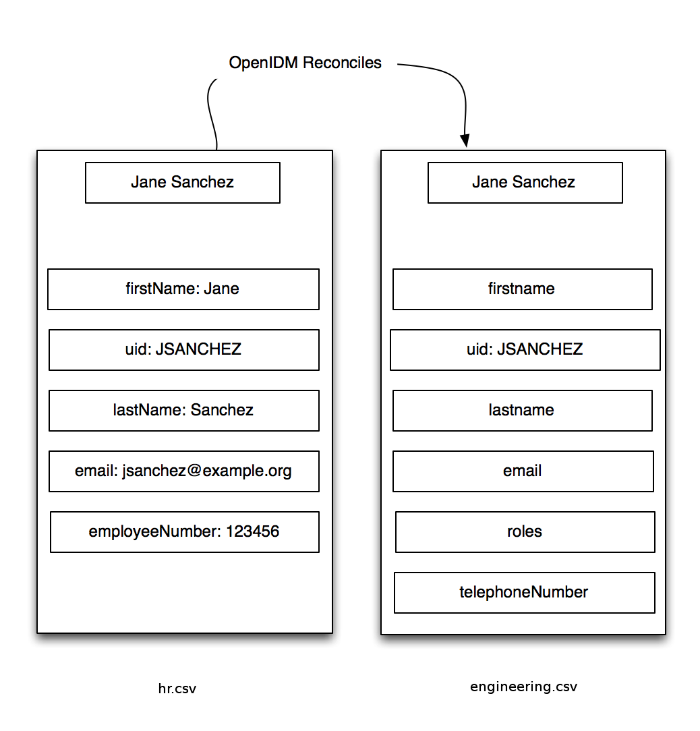
OpenIDM includes configuration files that map detailed information from
the Human Resources data store to the Engineering data store.
For example, the OpenIDM configuration maps the firstName
entry in Human Resources to the firstname entry in
Engineering.
Note
Mapping between data stores may require additional configuration. You should
find two provisioner.openicf-*.json files in the
/path/to/openidm/samples/getting-started/conf
subdirectory. The provisioner files configure connections to external
resources, such as Active Directory, OpenDJ or even the
engineering.csv and hr.csv files
used in this guide. For more information, see "Connecting to External Resources" in the Integrator's Guide.
In the Admin UI, you can see how OpenIDM reconciles the different
categories for user Jane Sanchez. Log in to the Admin UI at
https://localhost:8443/admin. The default username is
openidm-admin and default password is
openidm-admin.
Select Configure > Mappings >
HumanResources_Engineering > Properties.
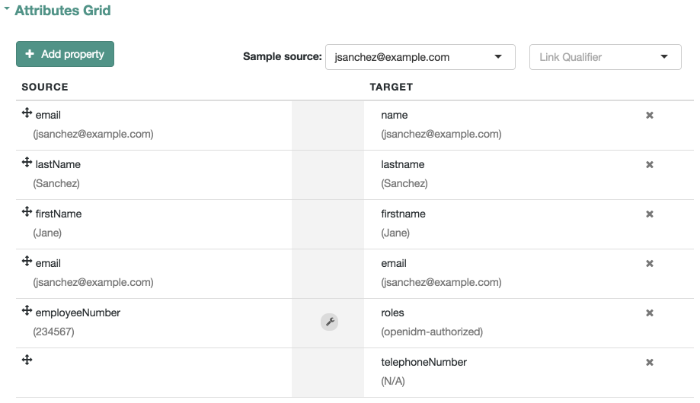
In the Sample Source text box, enter Sanchez. You
should see a drop-down entry for Jane Sanchez that you can select.
You should now see how OpenIDM would reconcile Jane Sanchez's entry
in the Human Resources data store into the Engineering data store.
Scroll back up the same page. Select Reconcile Now.
When you reconcile the two data stores, OpenIDM will make the change to the Engineering data store.
For those of you who prefer the command-line interface, you can see how
the mapping works in the sync.json file, in the
/path/to/openidm/samples/getting-started/conf directory.
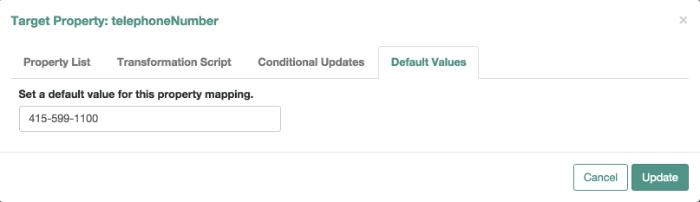
Now that you have used OpenIDM to reconcile two data stores, try something else. Assume the Engineering organization wants to overwrite all user telephone numbers in its employee data store with one central telephone number.
For this purpose, you can set up a default telephone number for the next reconciliation.
In the HumanResources_Engineering page, scroll down and select
telephoneNumber > Default Values.
When you select Update, and Save Properties, OpenIDM changes the
sync.json configuration file. The next time OpenIDM
reconciles from Human Resources to Engineering, it will include that
default telephone number for all employees in the Engineering group.
OpenIDM can do much more than reconcile data between two different sources. In this chapter, you will read about the key features of OpenIDM, with links to additional information about each feature.
A business process begins with an objective and includes a well-defined sequence of tasks to meet that objective. In OpenIDM, you can configure many of these tasks as self-service workflows, such as self-registration, new user onboarding, and account certification.
With OpenIDM, you can automate many of these tasks as a workflow.
Once you configure the right workflows, a newly hired engineer can log into OpenIDM and request access to manufacturing information.
That request is sent to the appropriate manager for approval. Once approved, the OpenIDM provisions the new engineer with access to manufacturing.
OpenIDM supports workflow-driven provisioning activities, based on the embedded Activiti Process Engine, which complies with the Business Process Model and Notation 2.0 (BPMN 2.0) standard.
Additional workflows are provided, such as new user onboarding, orphan account detection, and password change reminders. For more information, see "Workflow Samples" in the Samples Guide.
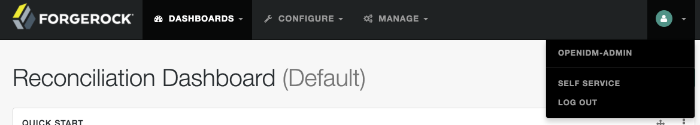
You can manage passwords from the Self-Service User Interface, also known as the Self-Service UI. From the Admin UI, click on the icon in the upper-right corner. In the menu that appears, click Self-Service:
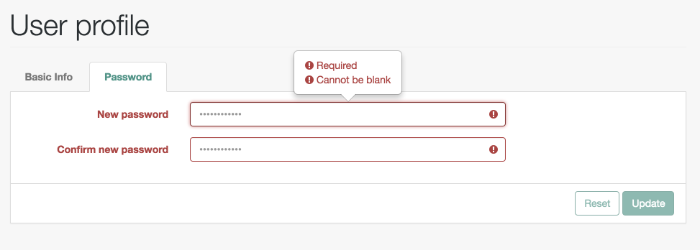
You should now be in the Self-Service UI. Click Profile > Password. You can now change your password, subject to the policy limits shown.
As you can see, OpenIDM supports a robust password policy. You can modify the rules shown, or add more rules such as the following:
Elements that should not be a part of a password, such as a family name
Password expiration dates
Password histories, to prevent password reuse
For more information, see "Managing Passwords" in the Integrator's Guide.
Some users need accounts on multiple systems. For example, insurance agents may also have insurance policies with the company that they work for. In that situation, the insurance agent is also a customer of the company.
Alternatively, a salesperson may also test customer engineering scenarios. That salesperson may also need access to engineering systems.
In OpenIDM, each of these user scenarios is known as a role. OpenIDM allows you to set up a consolidated set of attributes associated with each role. To do so, you would configure custom roles to assign to selected users. For example, you may assign both insured and agent roles to an agent, while assigning the insured role to all customers.
In a similar fashion, OpenIDM allows you to assign both sales and engineering roles to the sales engineer.
You can then synchronize users with those roles into appropriate data stores.
For more information, see "Working With Managed Roles" in the Integrator's Guide. For a sample of how you can configure external roles within OpenIDM, see "Demonstrating the Roles Implementation" in the Samples Guide.
You can use OpenIDM to connect to a substantial variety of user and device data stores, on premise and in the cloud. While OpenIDM can connect to some connectors dedicated to a few data stores, OpenIDM can also connect to many more data stores using a scripted connector framework.
OpenIDM includes support for connectors to the following external resources:
Google Web Applications (see "Google Apps Connector" in the Connectors Guide).
Salesforce (see "Salesforce Connector" in the Connectors Guide).
Any LDAPv3-compliant directory, including OpenDJ and Active Directory (see "Generic LDAP Connector" in the Connectors Guide).
CSV Files (see "CSV File Connector" in the Connectors Guide).
Database Tables (see "Database Table Connector" in the Connectors Guide).
If the resource that you need is not on the list, you should be able to use one of the OpenIDM scripted connector frameworks to connect to that resource:
For connectors associated with Microsoft Windows, OpenIDM includes a PowerShell Connector Toolkit that you can use to provision a variety of Microsoft services, including but not limited to Active Directory, SQL Server, Microsoft Exchange, SharePoint, Azure Active Directory, and Office 365. For more information, see "PowerShell Connector Toolkit" in the Connectors Guide. OpenIDM includes a sample PowerShell Connector Toolkit configuration, described in "Samples That Use the PowerShell Connector Toolkit to Create Scripted Connectors" in the Samples Guide.
For other external resources, OpenIDM includes a Groovy Connector Toolkit that allows you to run Groovy scripts to interact with any external resource. For more information, see "Groovy Connector Toolkit" in the Connectors Guide. "Samples That Use the Groovy Connector Toolkit to Create Scripted Connectors" in the Samples Guide includes samples of how you might implement the scripted Groovy connector.
OpenIDM supports reconciliation between two data stores, as a source and a target.
In identity management, reconciliation compares the contents of objects in different data stores, and makes decisions based on configurable policies.
For example, if you have an application that maintains its own user store, OpenIDM can ensure your canonical directory attributes are kept up to date by reconciling their values as they are changed.
For more information, see "Synchronizing Data Between Resources" in the Integrator's Guide.
OpenIDM has access to several different authentication modules that can help you protect your systems. For more information, see "Supported Authentication and Session Modules" in the Integrator's Guide.
OpenIDM is a lightweight and highly customizable identity management product.
The OpenIDM documentation includes additional use cases. Most of them are known as Samples, and are described in "Overview of the Samples" in the Samples Guide.
These samples include step-by-step instructions on how you can connect to different data stores, customize product behavior using JavaScript and Groovy, and administer OpenIDM with ForgeRock's commons RESTful API commands.
Now that you have seen how OpenIDM can help you manage users, review the features that OpenIDM can bring to your organization:
Web-Based Administrative User Interface
Configure OpenIDM with the Web-Based Administrative User Interface. You can configure many major components of OpenIDM without ever touching a text configuration file.
Self-Service Functionality
User self-service features can streamline onboarding, account certification, new user registration, username recovery, and password reset. OpenIDM self-service features are built upon a BPMN 2.0-compliant workflow engine.
Role-Based Provisioning
Create and manage users based on attributes such as organizational need, job function, and geographic location.
Backend Flexibility
Choose the desired backend database for your deployment. OpenIDM supports MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, IBM DB2, and PostgreSQL. For the supported versions of each database, see "Before You Install" in the Release Notes.
Password Management
Set up fine-grained control of passwords to ensure consistent password policies across all applications and data stores. Supports separate passwords per external resource.
Logging, Auditing, and Reporting
OpenIDM logs all activity, internally and within connected systems. With such logs, you can track information for access, activity, authentication, configuration, reconciliation, and synchronization.
Access to External Resources
OpenIDM can access a generic scripted connector that allows you to set up communications with many external data stores.
Follow these steps to stop and remove OpenIDM.
To stop OpenIDM, return to the console window where you saw the following message:
-> OpenIDM ready
Press Return, and enter the following command:
-> shutdown
OpenIDM is self-contained. After you shut down the server, you can choose to delete the files in the
/path/to/openidmdirectory. There are no artifacts in system registries or elsewhere.
We hope that you want to continue exploring OpenIDM.
To do so, review the documentation available on ForgeRock's BackStage site.