Install IDM as a Service
These sections describe how to install and run IDM as a service, on Windows and Linux systems:
You can install IDM to run as a Windows service, so that it automatically starts and stops with Windows. You must be logged in as an administrator to install a Windows service.
Note
On a 64-bit Windows server, you must have a 64-bit Java version installed to start the service. If a 32-bit Java version is installed, you will be able to install IDM as a service, but starting the service will fail.
Before you launch the service.bat file, which registers the service within the Windows registry, make sure that your JAVA_HOME environment variable points to a valid 64-bit version of the JRE or JDK. If you have already installed the service with the JAVA_HOME environment variable pointing to a 32-bit JRE or JDK, delete the service first, then reinstall the service.
Unpack the IDM-7.1.6.zip file, as described previously, and navigate to the
install-directory\bindirectory:C:\>
cd openidm\binC:\openidm\bin>Run the
service.batcommand with the/installoption, specifying the name that the service should run as:C:\openidm\bin>
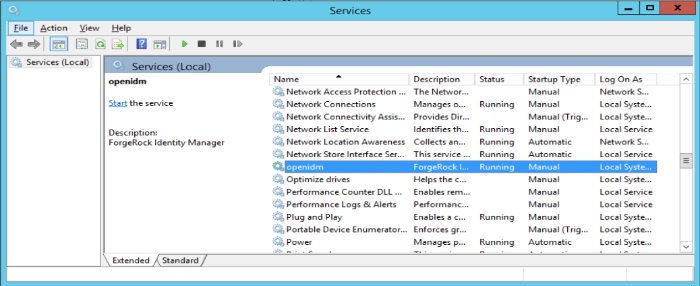
service.bat /install openidmForgeRock Identity Management Server successfully installed as "openidm" serviceUse the Windows Service manager to manage the IDM service.
By default, the IDM service is run by
Local System, which is a system-level service account built in to Windows. Before you deploy IDM in production, you should switch to an account with fewer permissions. The account running the IDM service must be able to read, write, and execute only the directories related to IDM.Use the Windows Service Manager to start, stop, or restart the service.
If you want to uninstall the IDM service, first use the Windows Service Manager to stop IDM and then run the following command:
C:\install-directory\openidm\bin>
service.bat /uninstall openidmService "openidm" removed successfullyIf desired, you can then set up IDM with a specific project directory:
C:\install-directory\openidm\bin>
service.bat /install openidm -p C:\project-directoryForgeRock Identity Management Server successfully installed as "openidm" service
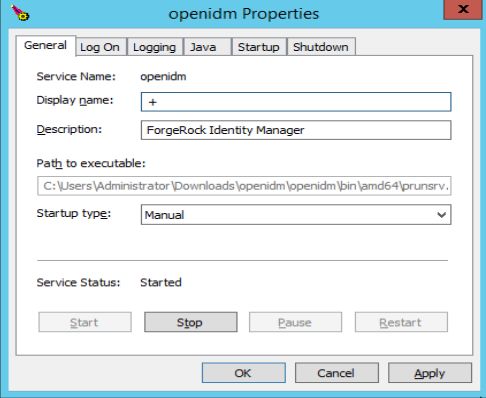
You can also manage configuration details with the Procrun monitor application. IDM includes the associated prunmgr.exe executable in the C:\install-directory\openidm\bin directory.
For example, you can open the Windows service configuration application for IDM with the following command, where ES stands for Edit Service Configuration
C:\install-directory\openidm\bin>prunmgr.exe //ES/openidm The prunmgr.exe executable also includes the monitor application functionality described in the following Apache Commons page on the: Procrun monitor Application. However, IDM does not include the Procrun service application.
For example, if you've configured IDM as a Windows service, you can start and stop it with the following commands:
C:\install-directory\openidm\bin>prunmgr.exe //MR/openidmC:\install-directory\openidm\bin>prunmgr.exe //MQ/openidm
In these commands, MR is the option to Monitor and Run IDM, and MQ stands for Monitor Quit, which stops the IDM service.
IDM provides a script that can generate SysV or Systemd service initialization scripts. You can start the script as the root user, or configure it to start during the boot process.
When IDM runs as a service, logs are written to the installation directory.
If you have not yet installed IDM, follow the steps in Install IDM.
Review the options by running the following script:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.shUsage: ./create-openidm-rc.sh --[systemd|chkconfig|lsb] Outputs OpenIDM init file to stdout for the given system --systemd Generate Systemd init script. This is preferred for all modern distros. --chkconfig Generate SysV init script with chkconfig headers (RedHat/CentOS) --lsb Generate SysV init script with LSB headers (Debian/Ubuntu) ...
These examples describe how to create each of these scripts:
If you're running relatively standard versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (CentOS Linux) version 7.x, or Ubuntu 16.04 and later, you'll want to set up a systemd service script. To set up such a script, navigate to the /path/to/openidm/bin directory, and run the following command:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --systemdAs noted in the output, you can set up the IDM service on a standard systemd-based Linux distribution with the following commands:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --systemd > openidm.servicesudo cp openidm.service /etc/systemd/system/systemctl enable openidmsystemctl start openidm
To stop the IDM service, run the following command:
systemctl stop openidm You can modify the openidm.service script. The following excerpt would run IDM with a startup script in the /home/idm/project directory:
[Unit] Description=ForgeRock OpenIDM After=network.target auditd.target [Service] Type=simple SuccessExitStatus=143 Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr User=testuser ExecStart=/root/openidm/startup.sh -p /home/idm/project ExecStop=/root/openidm/shutdown.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Run the following command to reload the configuration and then start the IDM service script:
systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl start openidm
If you are running standard versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (CentOS Linux) version 6.x, set up a SysV service script with runlevels controlled through the chkconfig command. To set up such a script, run the following command:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --chkconfigYou can then set up and start the IDM service on a Linux distribution that uses SysV init scripts, with the following commands:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --chkconfig > openidmsudo cp openidm /etc/init.d/sudo chmod u+x /etc/init.d/openidmsudo chkconfig --add openidmsudo chkconfig openidm onsudo service openidm start
To stop the IDM service, run the following command:
sudo service openidm stop You can modify the /etc/init.d/openidm script. The following excerpt would run IDM with the startup.sh script in the /path/to/openidm directory:
START_CMD="PATH=$JAVA_BIN_PATH:$PATH;nohup $OPENIDM_HOME/startup.sh >$OPENIDM_HOME/logs/server.out 2>&1 &"
You can modify this line to point to some /path/to/production directory:
START_CMD="PATH=$JAVA_BIN_PATH:$PATH;nohup $OPENIDM_HOME/startup.sh -p /path/to/production >$OPENIDM_HOME/logs/server.out 2>&1 &"
Run the following command to reload the configuration and then start the IDM service script:
sudo service openidm startIf you run Linux with SELinux enabled, change the file context of the newly copied script with the following command:
sudo restorecon /etc/init.d/openidm Verify the change to SELinux contexts with the ls -Z /etc/init.d command. For consistency, change the user context to match other scripts in the same directory with the sudo chcon -u system_u /etc/init.d/openidm command.
If you're running an older version of Ubuntu Linux that supports SysV services, set up a SysV service script, with runlevels controlled through the update-rc.d command. To set up such a script, run the following command:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --lsbYou can then set up and start the IDM service on a Linux distribution that uses SysV init scripts, with the following commands:
/path/to/openidm/bin/create-openidm-rc.sh --lsb > openidmsudo cp openidm /etc/init.d/sudo chmod u+x /etc/init.d/openidmsudo update-rc.d openidm defaultssudo service openidm start
To stop the IDM service, run the following command:
sudo service openidm stop You can modify the /etc/init.d/openidm script. The following excerpt would run IDM with the startup.sh script in the /path/to/openidm directory:
START_CMD="PATH=$JAVA_BIN_PATH:$PATH;nohup $OPENIDM_HOME/startup.sh >$OPENIDM_HOME/logs/server.out 2>&1 &"
You can modify this line to point to some /path/to/production directory:
START_CMD="PATH=$JAVA_BIN_PATH:$PATH;nohup $OPENIDM_HOME/startup.sh -p /path/to/production >$OPENIDM_HOME/logs/server.out 2>&1 &"
You can then run the following command to reload the configuration and then start the IDM service script:
sudo service openidm restart