Session Upgrade
Sessions can be upgraded to provide access to sensitive resources.
Consider a website for a University. Some information, such as courses and degree catalogs, are free for anyone to see and therefore, do not need to be protected. The University also provides the students with a portal they can use to see their grades, which is protected with a policy that requires users to authenticate. However, to pay tuition, students are required to present additional credentials to increase their authentication level and gain access to these functions.
Allowing authenticated users to provide additional credentials to access sensitive resources is called session upgrade, which is AM's mechanism to perform step-up authentication.
An authenticated user being redirected to a URL that has the
ForceAuthparameter set totrue. For example,https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/XUI/?realm=/myRealm&ForceAuth=true#loginIn this case, the user is asked to reauthenticate to the default chain in the realm
myRealm.Important
Session upgrade using the
ForceAuthparameter is only supported for CTS-based sessions.An authenticated user trying to access a resource protected by a web or Java agent (or a custom policy enforcement point (PEP)). In this case, AM sends the agent or PEP advice that the user should perform one of the following actions:
Authenticate at an authentication level greater than the current level
Authenticate to a module
Authenticate to a service
The flow of the session upgrade during policy evaluation is as follows:
An authenticated user tries to access a resource.
The PEP, for example a web or Java agent, sends the request to AM for policy decision.
AM returns an authorization decision that denies access to the resource, and returns an advice indicating that the user needs to present additional credentials to access the resource.
The policy enforcement point sends the user back to AM for session upgrade.
The user provides additional credentials. For example, they may provide a one-time password, swipe their phone screen, or use face recognition.
AM authenticates the user.
The user can now access the sensitive resource.
Successful. One of the following will happen depending on the type of sessions configured for the realm:
If the realm is configured for CTS-based sessions, one of the following will happen depending on the mechanism used to perform session upgrade:
When using the
ForceAuthparameter, AM does one of the following:(Authentication trees only) AM issues new session tokens to users on reauthentication, even if the current session already meets the security requirements.
(Authentication chains only) AM does not issue new session tokens on reauthentication, regardless of the security level they are authenticating to. Instead, it updates the session token with the new authentication information, if required.
When using advices, AM copies the session properties to a new session and hands the client a new session token to replace the original one. The new session reflects the successful authentication to a higher level.
If the realm is configured for client-based sessions, AM hands the client a new session token to replace the original one. The new session reflects the successful authentication to a higher level.
Unsuccessful. AM leaves the user session as it was before the attempt at stronger authentication. If session upgrade failed because the login page times out, AM redirects the user's browser to the success URL from the last successful authentication.
Tip
Anonymous sessions can also be upgraded to non-anonymous sessions by using the "Anonymous Session Upgrade Node".
Configure a policy enforcement point (PEP), for example, a web or Java agent, that enforces AM policies on a website or application.
AM web and Java agents handle session upgrade without additional configuration because the agents are built to handle AM's advices. If you build your own PEPs, however, you must take advices and session upgrade into consideration.
Configure an authorization policy to protect a resource protected by the Java or web agent, or a RESTful PEP.
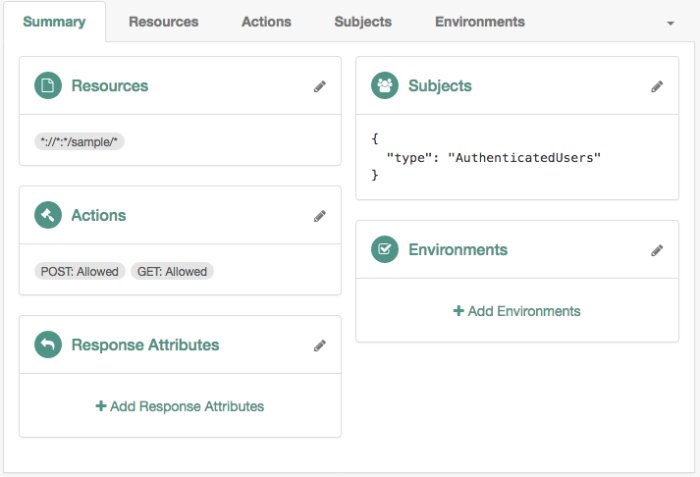
The following policy allows GET and POST access to the
*://*:*/sample/*resource to any authenticated user:
Configure an authentication tree or chain to validate users' credentials during session upgrade.
Authentication trees and chains do not require additional configuration to perform session upgrade. However, because session upgrade is a mechanism which may be used to grant users access to sensitive information, you should consider configuring a strong authentication method such as multi-factor authentication. Also, you may want to consider how long-lived sessions in your environment are. For example, if users should only have access to the protected resource to perform an operation, such as check the balance of an account, you may want to consider implementing transactional authorization instead.
For more information, see Transactional Authorization.
For more information about configuring authentication trees and chains, see the Authentication and Single Sign-On Guide.
Configure at least one of the following environment conditions in the authentication policy you created as part of the prerequisites:
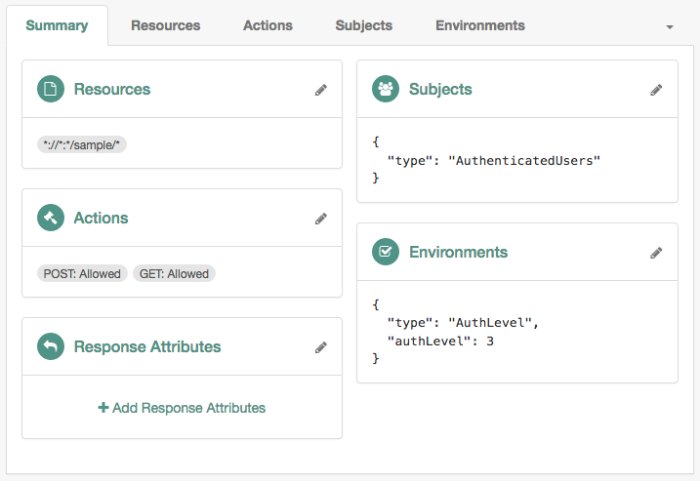
Use this condition to present a list of authentication chains that provide a greater or equal authentication level to the one specified in the condition. The user selects their service of choice if multiple chains are able to meet the criteria of the condition. For example, the following policy requires a chain that provides authentication level
3or greater:Tip
For more information about configuring the authentication level by authentication module, see "About Authentication Levels for Chains".
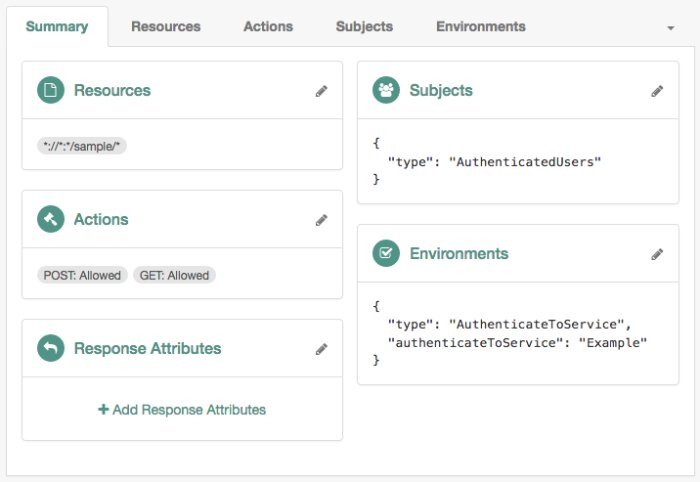
Use this condition to specify the chains or authentication trees to which the user needs to use to authenticate. For example, the following policy requires the user to log in with the
Exampletree:Note that the names of the authentication trees and chains are case-sensitive.
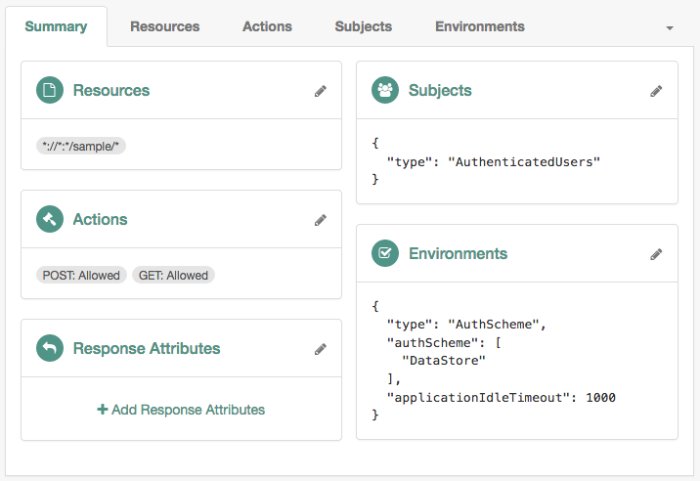
Use this condition to enforce that a user has gone through a specific authentication module. For example, the following policy requires the user to log in with the
DataStoremodule:Note
The examples feature simple policy conditions. For more information about configuring policies and environment conditions, see Configuring Policies.
Test session upgrade:
To test session upgrade with a browser, see "To Perform Session Upgrade Using a Browser".
To test session upgrade with REST, see "To Perform Session Upgrade Using REST".
To upgrade a session using a browser, perform the following steps:
Ensure you have performed the tasks in Session Upgrade Prerequisites and "To Configure the Environment for Session Upgrade".
In a browser, navigate to your protected resource. For example,
http://www.example.com:9090/sample.The agent redirects the browser to the AM login screen.
Authenticate to AM as the
demouser.AM requires additional credentials to grant access to the resource. For example, if you set the policy environment condition to
Authentication by ServiceandExample, you will be required to log in again as thedemouser.Authenticate as the
demouser. Note that providing credentials for a different user will fail.You can now access the protected resource.
To upgrade a session using REST, perform the following steps:
Ensure you have performed the tasks in Session Upgrade Prerequisites and "To Configure the Environment for Session Upgrade".
Note
This example uses composite advice with an authentication level condition, which only applies to authentication chains.
Log in with an administrative user that has permission to evaluate policies, such as
amAdmin. For example:$
curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "X-OpenAM-Username: amadmin" \ --header "X-OpenAM-Password: password" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=2.0, protocol=1.0" \ 'https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/root/authenticate'{ "tokenId":"AQIC5wM2...", "successUrl":"/openam/console", "realm":"/" }Tip
You can also assign privileges to a user to evaluate policies. For more information, see "To Allow a User to Evaluate Policies".
Log in with the user that should access the resources. For example, log in as the
demouser:$
curl \ --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "X-OpenAM-Username: demo" \ --header "X-OpenAM-Password: Ch4ng31t" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: resource=2.0, protocol=1.0" \ 'https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/root/authenticate'{ "tokenId":"AQIC5wM...TU3OQ*", "successUrl":"/openam/console", "realm":"/" }Request a policy decision from AM for a protected resource, in this case,
http://openam.example.com:9090/sample. TheiPlanetDirectoryProheader sets the SSO token for the administrative user, and thesubjectelement of the payload sets the SSO token for thedemouser:$
curl --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2..." \ --header "Accept-API-Version:protocol=1.0,resource=2.1" \ --data '{ "resources": [ "http://www.example.com:9090/sample" ], "application": "iPlanetAMWebAgentService", "subject": { "ssoToken": "AQIC5wM...TU3OQ*"} }' \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/policies?_action=evaluate"[ { "resource":"http://www.example.com:9090/sample", "actions":{ }, "attributes":{ }, "advices":{ "AuthLevelConditionAdvice":[ "3" ] }, "ttl":9223372036854775807 } ]AM returns with advice, which means the user must present additional credentials to access that resource.
For more information about requesting policy decision, see "Requesting Policy Decisions Using REST".
Format the advice as XML, without spaces or line breaks. The following example is spaced and tabulated for readability purposes only:
<Advices> <AttributeValuePair> <Attribute name="AuthLevelConditionAdvice"/> <Value>3</Value> </AttributeValuePair> </Advices>Note
The example shows the XML render of a single advice. Depending on the conditions configured in the policy, the advice may contain several lines. For more information about advices, see "Policy Decision Advice".
URL-encode the XML advice. For example:
%3CAdvices%3E%3CAttributeValuePair%3E%3CAttribute%20name%3D%22AuthLevelConditionAdvice%22%2F%3E%3CValue%3E3%3C%2FValue%3E%3C%2FAttributeValuePair%3E%3C%2FAdvices%3E.Ensure there are no spaces between tags when URL-encoding the advice.
Call AM's
authenticateendpoint to request information about the advice. Use the following details:Add the following URL parameters:
authIndexType=composite_adviceauthIndexValue=URL-encoded_Advice
Set the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie as the SSO token for thedemouser.
For example:
$
curl --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5wM...TU3OQ*" \ --header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=1.0,resource=2.1" \ 'https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/root/authenticate?authIndexType=composite_advice&authIndexValue=%3CAdvices%3E%3CAttributeValuePair%3E...'{ "authId":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJhdXRoSW5kZ...", "template":"", "stage":"DataStore1", "header":"Sign in", "callbacks":[ { "type":"NameCallback", "output":[ { "name":"prompt", "value":"User Name:" } ], "input":[ { "name":"IDToken1", "value":"" } ] }, { "type":"PasswordCallback", "output":[ { "name":"prompt", "value":"Password:" } ], "input":[ { "name":"IDToken2", "value":"" } ] } ] }AM returns information about how the user can authenticate in a callback; in this case, providing a username and password. For a list of possible callbacks, and more information about the
/json/authenticateendpoint, see Authenticating (REST).Call AM's
authenticateendpoint to provide the required callback information. Use the following details:Add the following URL query parameters:
authIndexType=composite_adviceauthIndexValue=URL-encoded_Advice
Set the
iPlanetDirectoryProcookie as the SSO token for thedemouser.Send as data the complete payload AM returned in the previous step, ensuring you provide the requested callback information.
In this example, provide the username and password for the
demouser in theinputobjects, as follows:$
curl --request POST \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --header "Accept-API-Version: protocol=1.0,resource=2.1" \ --cookie "iPlanetDirectoryPro=AQIC5wM...TU3OQ*" \ --data '{ "authId":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJhdXRoSW5kZ...", "template":"", "stage":"DataStore1", "header":"Sign in", "callbacks":[ { "type":"NameCallback", "output":[ { "name":"prompt", "value":"User Name:" } ], "input":[ { "name":"IDToken1", "value":"demo" } ] }, { "type":"PasswordCallback", "output":[ { "name":"prompt", "value":"Password:" } ], "input":[ { "name":"IDToken2", "value":"Ch4ng31t" } ] } ] } }' \ 'https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/realms/root/authenticate?authIndexType=composite_advice&authIndexValue=%3CAdvices%3E%3CAttributeValuePair%3E...'{ "tokenId":"wpU01SaTq4X2x...NDVFMAAlMxAAA.*", "successUrl":"/openam/console", "realm":"/" }Note that AM returns a new SSO token for the
demouser.Request a new policy decision from AM for the protected resource. The
iPlanetDirectoryProheader sets the SSO token for the administrative user, and the subject element of the payload sets the new SSO token for the demo user:$
curl --request POST \ --header "Content-Type: application/json" \ --header "iPlanetDirectoryPro: AQIC5wM2..." \ --header "Accept-API-Version:protocol=1.0,resource=2.1" \ --data '{ "resources":[ "http://www.example.com:9090/sample" ], "application":"iPlanetAMWebAgentService", "subject":{ "ssoToken":"wpU01SaTq4X2x...NDVFMAAlMxAAA.*" } }' \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/json/policies?_action=evaluate"[ { "resource":"http://www.example.com:9090/sample", "actions":{ "POST":true, "GET":true }, "attributes":{ }, "advices":{ }, "ttl":9223372036854775807 } ]AM returns that
democan performPOSTandGEToperations on the resource.