Modifying the Content of Access Tokens
You can modify the key-value pairs contained within an OAuth 2.0 access token by using a script. For example, you could make a REST call to an external service, and add or change a key-value pair in the access token based on the response, before issuing the token to the resource owner.
Modification works for client-based and CTS-based access tokens, and are stored permanently in either the issued JWT or in the CTS respectively. It also works when macaroons are used in place of regular tokens, in which case, you can use scripts to both modify the key pairs in the token and/or to add caveats.
Use access token modification scripts with the OAuth 2.0 default scope validator class.
AM includes an example script that demonstrates some of the functionality available. To examine the contents of the example access token modification script, in the AM console, go to Realms > Top Level Realm > Scripts, and then select OAuth2 Access Token Modification Script.
For general information about scripting in AM, see Getting Started with Scripting.
For information about the API available for modifying access tokens with scripts, see the following:
"AccessToken" interface in the AM 7.1.4 Public API Javadoc
"AMIdentity" interface in the AM 7.1.4 Public API Javadoc
"SSOToken" interface in the AM 7.1.4 Public API Javadoc
"MacaroonToken" interface in the AM 7.1.4 Public API Javadoc
When issuing modified access tokens, consider the following important points:
Removing or changing native properties may render the access token unreadable
AM requires that certain native properties are present in the access token in order to consider it valid. Removing or modifying these properties may cause the OAuth 2.0 flows to break.
Tip
Native properties are marked in the AM 7.1.4 Public API Javadoc with a warning about loss of functionality if they are edited or removed.
Modifying access tokens affects the size of the client-based token or CTS entry
Changes made to OAuth 2.0 access tokens directly impacts the size of the CTS tokens when using CTS-based tokens, or the size of the JSON web tokens (JWT) if client-based is enabled.
You must ensure that the token size remains within your client or user-agent size limits.
For more information, see "About Token Storage Location".
Preparing AM to Modify Access Tokens
AM requires a small amount of configuration before trying the default access token modification script. The script requires that the authenticated user of the access token has an email address and telephone number in their profile. The script adds the values of these fields to the access token.
Perform the steps in the following procedures to prepare AM for testing scripted modification of OAuth 2.0 access tokens:
In this procedure, add an email address and telephone number value to the demo user's profile. The access token modification script injects the values provided into the OAuth 2.0 access token before it is issued to the resource owner.
Log in as an AM administrator. For example
amAdmin.Select Realms > Top Level Realm > Identities.
On the Identities tab, select the
demouser.In Email Address, enter a valid address. For example:
demo.user@example.comIn Telephone Number, enter a value. For example:
+44 117 496 0228
Select Save Changes.
In this procedure, uncomment functionality in the default access token modification script in order to demonstrate how to modify access tokens.
Log in as an AM administrator. For example
amAdmin.Navigate to Realms > Top Level Realm > Scripts, and then click OAuth2 Access Token Modification Script.
In the Script field:
Uncomment line 34 of the script, by surrounding the line with a pair of
*/and/*strings:*/ accessToken.setField("hello", "world") /*Uncomment lines 59 to 61 of the script, by surrounding them with a pair of
*/and/*strings:*/ def attributes = identity.getAttributes(["mail", "telephoneNumber"].toSet()) accessToken.setField("mail", attributes["mail"]) accessToken.setField("phone", attributes["telephoneNumber"]) /*
Select Save Changes.
In this procedure, create an OAuth 2.0 provider that uses the default access token modification script, as well as an OAuth 2.0 client. Obtaining an access token as the demo user can then be performed to test the script functionality.
Log in as an AM administrator. For example
amAdmin.Create an OAuth 2.0 provider by performing the following steps:
Navigate to Realms > Top Level Realm > Configure OAuth Provider, and then click Configure OAuth 2.0.
Keep the suggested settings, click Create, and then click OK.
The default setting for a new OAuth 2.0 provider is to use the default access token modification script.
For information on OAuth 2.0 provider properties, see "OAuth2 Provider".
Create an OAuth 2.0 client by performing the following steps:
Navigate to Realms > Top Level Realm > Applications > OAuth 2.0 > Clients, and then click Add Client.
Enter the following values:
Client ID:
myClientClient secret:
forgerockRedirection URIs:
https://www.example.com:443/callbackScope(s):
access|Access to your data
Click Create.
AM is now configured to issue access tokens using the default access token modification script.
Trying the Default Access Token Modification Script
This section demonstrates obtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token which has been modified by a script.
First, we will use the Authorization Code Grant flow to authenticate with AM as the resource owner, allow the client to access our profile data, and receive the authorization code.
In the second procedure, we will exchange the authorization code for an access token, which will have been altered by the default access token modification script to include:
The resource owner's telephone number and email address, taken from their profile in AM, which is acting as the authorization server.
A
hello:worldkey-value pair.
In the final procedure, we will introspect the access token to verify that it does include the modified values.
In a web browser, navigate to the /oauth2/authorize endpoint, including the parameters and values configured for the OAuth 2.0 client in the previous section.
For example:
https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/realms/root/authorize?client_id=myClient&response_type=code&scope=access&state=abc123&redirect_uri=https://www.example.com:443/callback
The AM sign in page is displayed.
Log in as the
demouser, with passwordCh4ng31t.The AM OAuth 2.0 consent page is displayed.
Review the scopes being requested, and then click Allow.
AM redirects the browser to the location specified in the
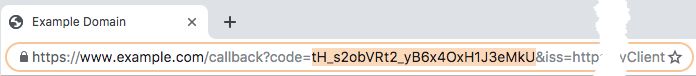
redirect_uriparameter,https://www.example.com:443/callbackin this example, and appends a number of query parameters. For example:Record the value of the
codequery parameter.This is the authorization code and is exchanged for an access token in the next procedure.
Create a POST request to the /oauth2/access_token endpoint, including the authorization code obtained in the previous procedure, and the parameters and values configured for the OAuth 2.0 client earlier.
For example:
$
curl --request POST \ --data "grant_type=authorization_code" \ --data "code=tH_s2obVRt2_yB6x4OxH1J3eMkU" \ --data "client_id=myClient" \ --data "client_secret=forgerock" \ --data "redirect_uri=https://www.example.com:443/callback" \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha/access_token"{ "access_token": "sbQZuveFumUDV5R1vVBl6QAGNB8", "scope": "access", "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 3599 }Record the value of the
access_tokenproperty.This is the access token, the properties of which have been modified by the access token modification script. Follow the steps in the next procedure to introspect the token to verify the properties have been modified.
Create a POST request to the /oauth2/introspect endpoint, including the access token obtained in the previous procedure, and the credentials of the OAuth 2.0 client earlier.
For example:
$
curl \ --request POST \ --data "client_id=myClient" \ --data "client_secret=forgerock" \ --data "token=sbQZuveFumUDV5R1vVBl6QAGNB8" \ "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha/introspect"{ "active": true, "scope": "access", "client_id": "myClient", "user_id": "demo", "token_type": "Bearer", "exp": 1556289970, "sub": "(usr!demo)", "subname": "demo", "iss": "https://openam.example.com:8443/openam/oauth2", "auth_level": 0, "auditTrackingId": "c6e22be7-6166-402b-9d72-a03134f08c22-8605", "hello": "world", "mail": [ "demo.user@example.com" ], "phone": [ "+44 117 496 0228" ] }Notice that the output includes a
hello:worldkey-value pair, as well asmailandphoneproperties, containing values taken from the user's profile data.
OAuth 2.0 Access Token Modification Scripting API
The following properties are available to scripts:
clientPropertiesA map of properties configured in the relevant client profile. Only present if the client was correctly identified.
The keys in the map are as follows:
-
clientId The URI of the client.
allowedGrantTypesThe list of the allowed grant types (
org.forgerock.oauth2.core.GrantType) for the client.allowedResponseTypesThe list of the allowed response types for the client.
allowedScopesThe list of the allowed scopes for the client.
customPropertiesA map of any custom properties added to the client.
Lists or maps are included as sub-maps.
For example, a custom property of
customMap[Key1]=Value1is returned as
customMap>Key1>Value1.To add custom properties to a client, go to OAuth 2.0 > Clients > Client ID > Advanced, and update the Custom Properties field. The custom properties can be added in the format shown in these examples:
customproperty=custom-value1 customList[0]=customList-value-0 customList[1]=customList-value-1 customMap[key1]=customMap-value-1 customMap[key2]=customMap-value-2
From within the script, you can then access the custom properties in the following way:
var customProperties = clientProperties.get("customProperties"); var property = customProperties.get(PROPERTY_KEY);
-
requestPropertiesA map of the properties present in the request. Always present.
The keys in the map are as follows:
requestUriThe URI of the request.
realmThe realm to which the request was made.
requestParamsThe request parameters, and/or posted data. Each value in this map is a list of one, or more, properties.
Important
To mitigate the risk of reflection-type attacks, use OWASP best practices when handling these properties. For example, see Unsafe use of Reflection.
scopesContains a set of the requested scopes. For example:
[ "read", "transfer", "download" ]scriptNameThe display name of the script. Always present.