Choose your sample
This page describes the sample deployment alternatives and how the platform components interact.
|
This is not a comprehensive platform implementation guide. These sample setup instructions show a minimal integration of platform components to get you started. The ForgeRock Identity Platform offers maximum extensibility and flexibility in self-managed deployments. The platform includes many features and options these sample setup instructions do not cover. If you don’t need maximum extensibility and flexibility, there are simpler alternatives:
For help with your deployment and to validate your plans before deploying in production, contact ForgeRock. |
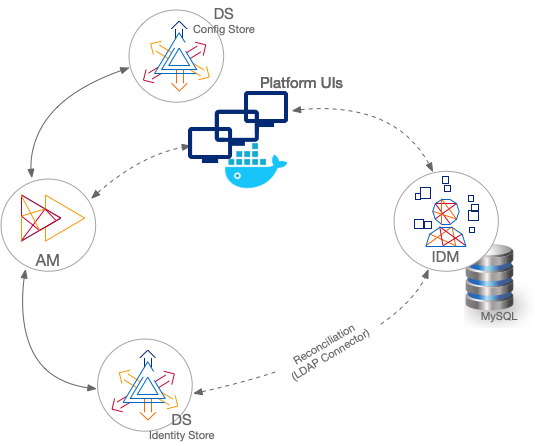
Sample: separate identity stores
This sample deployment has an external DS server configured as the AM configuration store and AM identity store (shown separately in the illustration). The IDM repository is an external JDBC database. The sample was tested with MySQL. The deployment uses an LDAP connector to synchronize the identities between IDM and AM:
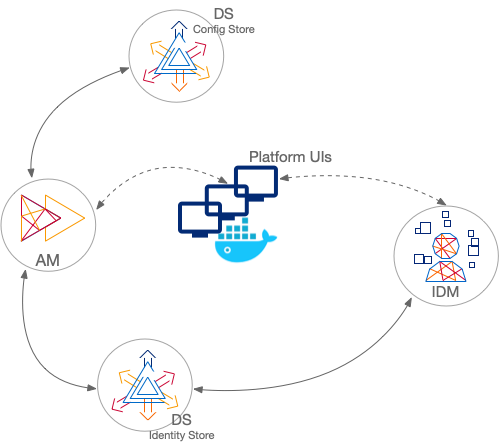
Sample: shared identity store
This sample deployment has an external DS server configured as the AM configuration store and shared by the AM and IDM servers share an external DS server as the identity store (shown separately in the illustration). No synchronization configuration is required:
|
In both sample deployments, the Platform UIs can run in separate Docker containers. If you want to run the Platform UIs in containers, get Docker before you start. |
Component interaction
A platform configuration relies on multiple components working together.
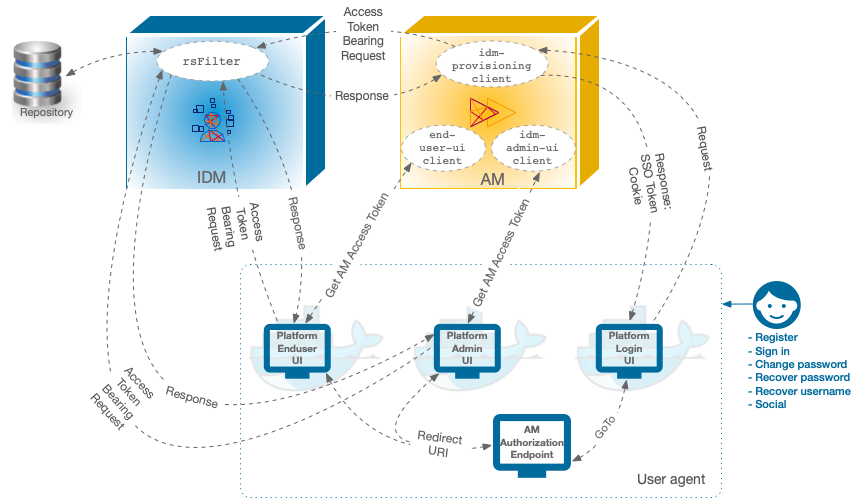
The following image shows how the AM OAuth 2 clients interact
with the IDM resource server filter (rsFilter) to grant access through the Platform UIs:
-
The Platform UIs send a request to the AM Authorization Endpoint.
-
If the end user is authenticated, the user agent is redirected back to the UI, according to the Redirection URI request parameter.
-
If the end user is not authenticated, the AM Authorization Endpoint redirects the user agent to the Platform Login UI.
-
After successful authentication, the Platform Login UI redirects the user agent back to the AM Authorization Endpoint, according to the GoTo request parameter.
|