Map a Single Source Object to Multiple Target Objects
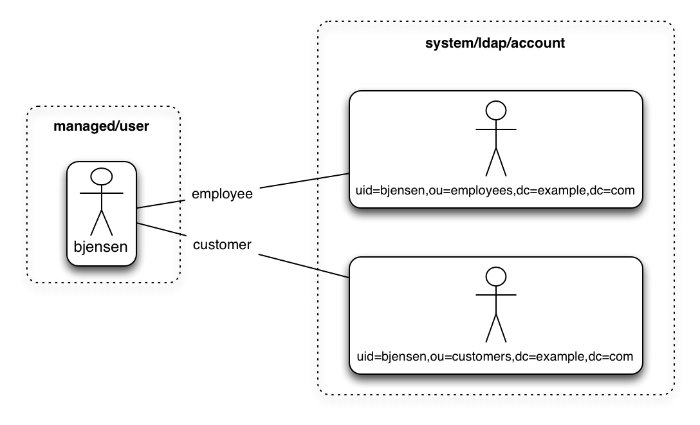
In certain cases, you might have a single object in a resource that maps to more than one object in another resource. For example, assume that managed user, bjensen, has two distinct accounts in an LDAP directory: an employee account (under uid=bjensen,ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com) and a customer account (under uid=bjensen,ou=customers,dc=example,dc=com). You want to map both of these LDAP accounts to the same managed user account.
IDM uses link qualifiers to manage this one-to-many scenario. A link qualifier is essentially a label that identifies the type of link (or relationship) between objects.
The following diagram shows two link qualifiers that let you link both of bjensen's LDAP accounts to her managed user object:
Note from this diagram that the link qualifier is a property of the link between the source and target object, and not a property of the source or target object itself.
Link qualifiers are defined as part of the mapping. Each link qualifier must be unique within the mapping. If no link qualifier is specified (when only one possible matching target object exists), IDM uses a default link qualifier with the value default.
Link qualifiers can be defined as a static list, or dynamically, using a script. The following excerpt of a sample mapping shows the two static link qualifiers, employee and customer, described in the previous example:
{
"mappings": [
{
"name": "managedUser_systemLdapAccounts",
"source": "managed/user",
"target": "system/MyLDAP/account",
"linkQualifiers" : [ "employee", "customer" ],
...The list of static link qualifiers is evaluated for every source record. That is, every reconciliation processes all synchronization operations, for each link qualifier, in turn.
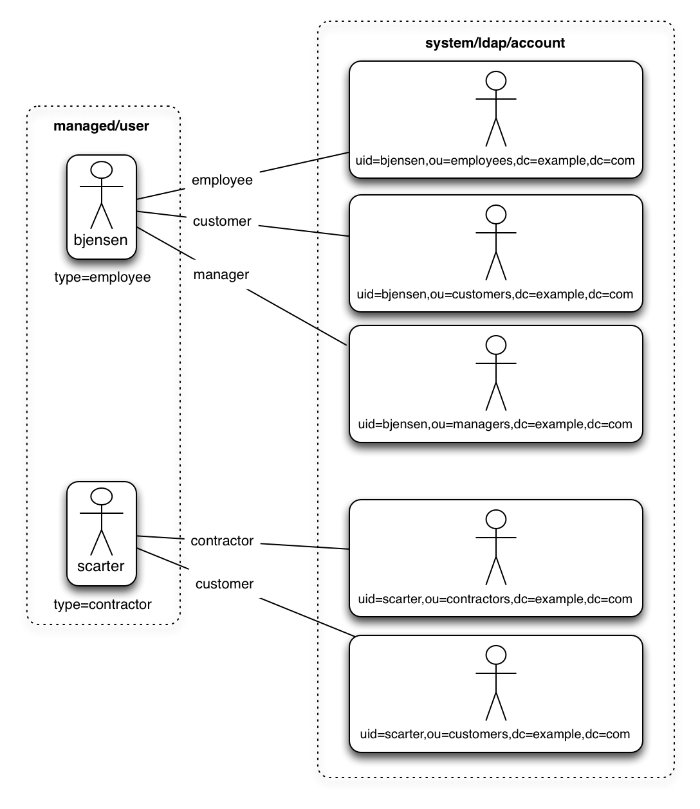
A dynamic link qualifier script returns a list of link qualifiers that can be applied to each source record. For example, suppose you have two types of managed users—employees and contractors. For employees, a single managed user (source) account can correlate with three different LDAP (target) accounts—employee, customer, and manager. For contractors, a single managed user account can correlate with only two separate LDAP accounts—contractor, and customer. The possible linking situations for this scenario are shown in the following diagram:
In this scenario, you could write a script to generate a dynamic list of link qualifiers, based on the managed user type. For employees, the script would return [employee, customer, manager] in its list of possible link qualifiers. For contractors, the script would return [contractor, customer] in its list of possible link qualifiers. A reconciliation operation would then process only the list of link qualifiers applicable to each source object.
If your source resource includes a large number of records, you should use a dynamic link qualifier script instead of a static list of link qualifiers. Generating the list of applicable link qualifiers dynamically avoids unnecessary additional processing for those qualifiers that will never apply to specific source records. Synchronization performance is therefore improved for large source data sets.
You can include a dynamic link qualifier script inline (using the source property), or by referencing a JavaScript or Groovy script file (using the file property). The following link qualifier script sets up the dynamic link qualifier lists described in the previous example.
Note
In this example, the source property value has been formatted across multiple lines for clarity. In general, the script source must be formatted on a single line.
{
"mappings": [
{
"name": "managedUser_systemLdapAccounts",
"source": "managed/user",
"target": "system/MyLDAP/account",
"linkQualifiers" : {
"type" : "text/javascript",
"globals" : { },
"source" : "if (returnAll) {
['contractor', 'employee', 'customer', 'manager']
} else {
if(object.type === 'employee') {
['employee', 'customer', 'manager']
} else {
['contractor', 'customer']
}
}"
}
... To reference an external link qualifier script, provide a link to the file in the file property:
{
"mappings": [
{
"name": "managedUser_systemLdapAccounts",
"source": "managed/user",
"target": "system/MyLDAP/account",
"linkQualifiers" : {
"type" : "text/javascript",
"file" : "script/linkQualifiers.js"
}
... Dynamic link qualifier scripts must return all valid link qualifiers when the returnAll global variable is true. The returnAll variable is used during the target reconciliation phase to check whether there are any target records that are unassigned, for each known link qualifier.
If you configure dynamic link qualifiers through the UI, the complete list of dynamic link qualifiers is displayed in the Generated Link Qualifiers item below the script. This list represents the values returned by the script when the returnAll variable is passed as true. For a list of the variables available to a dynamic link qualifier script, see "Script Triggers Defined in Mappings".
Link qualifiers have no functionality on their own, but they can be referenced in reconciliation operations to manage situations where a single source object maps to multiple target objects. The following examples show how link qualifiers can be used in reconciliation operations:
Use link qualifiers during object creation, to create multiple target objects per source object.
The following mapping excerpt defines a transformation script that generates the value of the
dnattribute on an LDAP system. If the link qualifier isemployee, the value of the targetdnis set to"uid=userName,ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com". If the link qualifier iscustomer, the value of the targetdnis set to"uid=userName,ou=customers,dc=example,dc=com". The reconciliation operation iterates through the link qualifiers for each source record. In this case, two LDAP objects, with differentdns are created for each managed user object:{ "target" : "dn", "transform" : { "type" : "text/javascript", "globals" : { }, "source" : "if (linkQualifier === 'employee') { 'uid=' + source.userName + ',ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com'; } else if (linkQualifier === 'customer') { 'uid=' + source.userName + ',ou=customers,dc=example,dc=com'; }" }, "source" : "" }Use link qualifiers with correlation queries. The correlation query assigns a link qualifier based on the values of an existing target object.
During source synchronization, IDM queries the target system for every source record and link qualifier, to check if there are any matching target records. If a match is found, the sourceId, targetId, and linkQualifier are all saved as the link.
The following excerpt of a sample mapping shows the two link qualifiers described previously (
employeeandcustomer). The correlation query first searches the target system for theemployeelink qualifier. If a target object matches the query, based on the value of itsdnattribute, IDM creates a link between the source object and that target object, and assigns theemployeelink qualifier to that link. This process is repeated for all source records. Then, the correlation query searches the target system for thecustomerlink qualifier. If a target object matches that query, IDM creates a link between the source object and that target object and assigns thecustomerlink qualifier to that link:"linkQualifiers" : ["employee", "customer"], "correlationQuery" : [ { "linkQualifier" : "employee", "type" : "text/javascript", "source" : "var query = {'_queryFilter': 'dn co \"' + uid=source.userName + 'ou=employees\"'}; query;" }, { "linkQualifier" : "customer", "type" : "text/javascript", "source" : "var query = {'_queryFilter': 'dn co \"' + uid=source.userName + 'ou=customers\"'}; query;" } ] ...For more information about correlation queries, see "Writing Correlation Queries".
Use link qualifiers during policy validation to apply different policies based on the link type.
The following excerpt of a sample mapping shows two link qualifiers,
userandtest. Depending on the link qualifier, different actions are taken when the target record is ABSENT:{ "mappings" : [ { "name" : "systemLdapAccounts_managedUser", "source" : "system/ldap/account", "target" : "managed/user", "linkQualifiers" : [ "user", "test" ], "properties" : [ ... "policies" : [ { "situation" : "CONFIRMED", "action" : "IGNORE" }, { "situation" : "FOUND", "action" : "UPDATE } { "condition" : "/linkQualifier eq \"user\"", "situation" : "ABSENT", "action" : "CREATE", "postAction" : { "type" : "text/javascript", "source" : "java.lang.System.out.println('Created user: \');" } }, { "condition" : "/linkQualifier eq \"test\"", "situation" : "ABSENT", "action" : "IGNORE", "postAction" : { "type" : "text/javascript", "source" : "java.lang.System.out.println('Ignored user: ');" } }, ...With this sample mapping, the synchronization operation creates an object in the target system only if the potential match is assigned a
userlink qualifier. If the match is assigned atestqualifier, no target object is created. In this way, the process avoids creating duplicate test-related accounts in the target system.
Select Configure > Mappings.
Select a mapping, and click Properties > Link Qualifiers.
For an example that uses link qualifiers in conjunction with roles, see Link Multiple Accounts to a Single Identity.