Authorize one-time access with transactional authz
Transactional authorization requires a user to authorize every access to a resource. It’s part of an Identity Cloud policy that grants single-use or one-shot access.
For example, a user might approve a financial transaction with a one-time password (OTP) sent to their device, or respond to a push notification to confirm that they have indeed signed on from an unexpected location.
Performing the extra action successfully grants access to the protected resource but only once. Later attempts to access the resource require the user to perform the configured actions again.
You implement transactional authorization as an environment condition type in an authorization policy. Transactional authorization affects the authorization decision.
|
Transactional authorization isn’t designed to work with account lockout and doesn’t increment lockout counters. As such, don’t use transactional authorization with authentication mechanisms that are susceptible to brute force attacks, such as simple username/password authentication, or OTP authentication. Configure transactional authorization if you’re using a strong authentication mechanism, such as MFA: Authenticate using push notification, which isn’t susceptible to brute force attacks. If you do use transactional authorization with a weaker authentication mechanism like OTP authentication, you must manage rate-limiting in some other way. |
Understand transactional authorization
The following diagram describes the sequence of events that occur when accessing a resource that’s protected by a REST application, and an Identity Cloud policy containing a transactional environment condition:
The sequence of events for a transaction authorization is as follows:
-
An authenticated user attempts to access a resource that’s protected by Identity Cloud.
-
The REST application, a resource server, contacts Identity Cloud to evaluate the policies that apply.
-
Because the policy has a transaction environment condition, Identity Cloud creates a transaction token in the Core Token Service (CTS) store. The initial transaction token state is set to
CREATED.The transaction token includes the following information about the policy evaluation:
-
Realm
-
Resource
-
Subject
-
Audit tracking ID
-
Authentication method
To protect against tampering, Identity Cloud verifies that these details don’t change and match those in the incoming requests for the duration of the transaction.
The transaction token has a time-to-live (default 180 seconds) defined in the Transaction Authentication Service. If the transaction isn’t completed at this time, Identity Cloud deletes the token, and the flow must be restarted. Alter the default if the transaction includes authentication actions that take more time to complete. For example, using HOTP authentication for a one-time password over email.
You can configure the time-to-live per realm. Refer to Transaction Authentication service.
-
-
In the JSON response to the policy evaluation request, Identity Cloud returns the transaction ID—the unique ID of the newly created transaction token—in the
TransactionConditionAdvicearray of theadvicesobject:{ "resource": "https://bank.example.com:443/withdraw?amount=100.00", "actions": {}, "attributes": {}, "advices": { "TransactionConditionAdvice": [ "7b8bfd4c-60fe-4271-928d-d09b94496f84" ] }, "ttl": 0 } -
The JSON response to the evaluation doesn’t grant any actions but does contain advices. Therefore, the REST application (resource server) extracts the transaction ID and returns it to the authentication service to start the authentication.
The transaction ID is included in the
TransactionConditionAdviceattribute value pair in the composite advice query parameters sent as part of the request for actions. -
Identity Cloud extracts the transaction ID from the composite advice, verifies the corresponding transaction token, and changes the state to
IN_PROGRESS.If the transaction ID isn’t in the expected state or doesn’t exist, Identity Cloud returns a
401 Unauthorizederror. For example:{ "code": 401, "reason": "Unauthorized", "message": "Unable to read transaction.", "detail": { "errorCode": "128" } } -
Identity Cloud responds with the callbacks necessary to satisfy any environment conditions.
The advices returned by transaction environment conditions have the lowest precedence when compared to the other condition advices. End users must respond to non-transactional condition advices before they respond to the transactional condition advices.
-
The REST application (resource server) renders the callbacks and presents them to the user.
-
The user completes the required actions.
For example, the user completes the journey specified in the policy, by responding to a push notification on their registered mobile device to confirm a transaction.
If the user doesn’t complete the required actions, Identity Cloud returns an HTTP 200 message, and redirects the user to the protected resource. Policy evaluation fails since the transactional authorization process failed.
-
Identity Cloud verifies the transaction token and changes the state to
COMPLETED. -
With the transaction now complete, Identity Cloud returns the original token.
Note that the authentication performed as part of an authorization flow does not behave the same as a standard authentication. The differences are:
-
The user’s original session isn’t upgraded or altered in any way.
-
Failing the authentication during the authorization flow doesn’t increment account lockout counters.
-
-
The REST application (resource server) requests the policy decision again, including the ID of the completed transaction as a value in the
TxIdarray of theenvironmentobject:{ "resources" : ["https://bank.example.com:443/withdraw?amount=100.00"], "application" : "iPlanetAMWebAgentService", "subject" : { "ssoToken" : "AQIC5w...*AJTMQAA*" }, "environment": { "TxId": ["7b8bfd4c-60fe-4271-928d-d09b94496f84"] } } -
Identity Cloud verifies the transaction was authorized and that the transaction token is in the
COMPLETEDstate. -
If the transaction completes successfully, the authorization continues.
Identity Cloud marks the transaction token for deletion so that it can’t be used to grant more than one access.
-
As the authentication required to complete the transaction was successful, Identity Cloud returns the result of the policy reevaluation.
For example, the following response grants the
POSTandGETactions to the resourcehttps://bank.example.com:443/withdraw?amount=100.00:{ "resource": "https://bank.example.com:443/withdraw?amount=100.00", "actions": { "POST": true, "GET": true }, "attributes": {}, "advices": {}, "ttl": 0 }Successful transactional authorization responses set the time-to-live (
ttl) value to zero to ensure that the policy decision isn’t cached and can’t be used more than once.ForgeRock agents before version 5 don’t support a time-to-live value of zero and can’t be used for transactional authorization.
-
The user is able to access the protected resource once.
Additional attempts to access a resource protected by a policy containing a transactional environment condition require a new transaction to be completed.
Configure transactional authorization
To use transactional authorization, you must coordinate the configuration of:
-
An appropriate user journey for the transaction.
-
The Identity Cloud policy or policies that use the journey.
-
Support for transactional authorization in your applications.
The user journey
The journey communicates to the user what they’re authorizing when they approve the transaction, and gives them the means to approve (or reject) the operation.
For example, if the transaction involves a withdrawal from the user’s bank account, you could configure a multi-factor authentication journey that displays "Confirm $100 withdrawal from Online Bank?" with Yes and No options for a push notification to a registered device, or sends a one-time password to a registered device with a similar message.
Configure the journey in the same realm as the policy.
The policy
A transactional authorization policy specifies the conditions that trigger the required authorization. It also specifies a journey the end user must complete to authorize the transaction. In other respects, it’s a standard Identity Cloud authorization policy.
You configure the policy under Native Consoles > Access Management.
For example, this completed policy applies to the /withdraw endpoint.
Its transactional authorization environment condition specifies
that the user must complete the AuthorizeTransaction journey to authorize access to the endpoint:
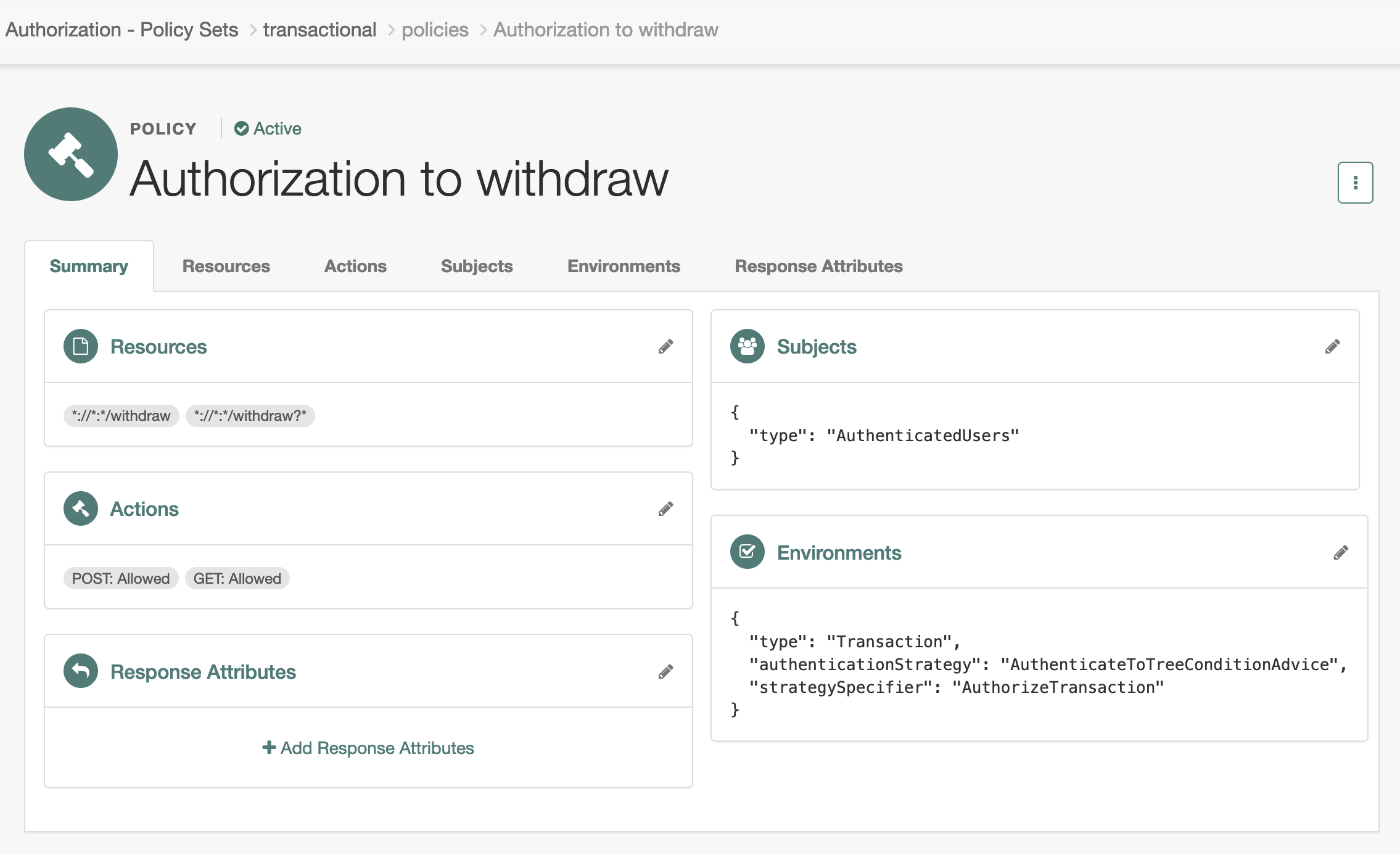
To add the environment condition, set:
- Type
-
Transaction - Authentication Strategy
-
Authenticate to Tree - Strategy Specifier
-
The name of the journey
Your application
A quick way to protect your application is to use ForgeRock software. ForgeRock Identity Gateway (IG), SDKs, and agents all support transactional authorization.
-
When using IG to protect your application, configure it for use with Identity Cloud.
Refer to the Identity Cloud pages in the IG documentation. These pages describe how to use IG as an OAuth 2.0 client of Identity Cloud and resource server. They also describe and how to use cross-domain single sign on (CDSSO) for applications that aren’t in your tenant’s domain.
Also refer to the IG documentation to configure IG as a policy enforcement point (PEP) when using CDSSO. IG as a PEP transparently manages redirection when Identity Cloud policy requires transactional authorization.
-
When using a ForgeRock SDK, refer to Perform transactional authorization in the SDKs docs.
-
When using a ForgeRock agent to protect your application, refer to the Java agent page on enforcing Identity Cloud policy decisions or the web agent page on enforcing Identity Cloud policy decisions.
Demonstrate transactional authorization
After configuring the journey, the policy, and your application, access the protected resource.
The example described here involves a bank withdrawal operation. The following steps put the end user interaction with Identity Cloud in context:
-
Barbara Jensen browses her online bank at
https://bank.example.comand signs on to access her account:
-
Barbara prepares to withdraw $100 from her account using the online bank application.
The application as PEP continues to contact Identity Cloud for policy decisions as Barbara browses through the application.
-
Barbara confirms her intention to complete the withdrawal, triggering the application to access the
/withdrawendpoint.When requesting a policy decision for this endpoint, the application gets advices indicating transactional authorization.
It redirects Barbara to the journey required for this transaction according to the policy. The important step of the journey is the decision to authorize the withdrawal:

-
Barbara receives the money and a receipt page after the application finishes processing the transaction with Identity Cloud.
The steps the application follows to perform transactional authorization are identical to those for session upgrade. For details, refer to Session upgrade with MFA.