Microsoft Intune node
Lets you integrate with Microsoft Intune using Microsoft Graph APIs. Microsoft Intune lets you control features and settings on Android, Android Enterprise, iOS/iPadOS, macOS, and Windows 10/11 devices in your organization.
The Microsoft Intune node checks the device details and determines the device’s compliance status. You can enable this node to save device information to shared state for subsequent use by other nodes in the journey.
For more information about Microsoft Intune, refer to the Microsoft Intune documentation.
Compatibility
| Product | Compatible? |
|---|---|
Advanced Identity Cloud |
Yes |
PingAM (self-managed) |
Yes |
Ping Identity Platform (self-managed) |
Yes |
Dependencies
You must set up Microsoft Intune before using this node in your Advanced Identity Cloud environment. Follow the Get started with your Microsoft Intune deployment document to set up and use a production version of Microsoft Intune.
Microsoft Intune requires a Microsoft Graph API application to be registered. Follow the register apps to use the Microsoft Graph API steps to complete the registration process.
Set the following Microsoft Intune and Graph API permissions:
| API / Permission | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Microsoft Intune |
||
|
Delegated |
Get data warehouse information from Microsoft Intune |
|
Application |
Get device state and compliance information from Microsoft Intune |
|
Application |
PFX certificate management |
|
Application |
SCEP challenge validation |
|
Application |
Exchange device telecom and Wi-Fi data usage information with Microsoft Intune |
|
Application |
Send device attributes to Microsoft Intune |
|
Application |
Send device threat information to Microsoft Intune |
Microsoft Graph API |
||
|
Delegated |
Read Microsoft Intune devices |
|
Delegated |
Sign in and read user profile |
|
The TLS handshake must be completed before the request accesses this node. During the TLS handshake, Advanced Identity Cloud obtains the device ID from the client certificate and sets it in the request header or in the shared state. You can use PingGateway to complete the TLS handshake. |
Verifying Intune setup
Use the following cURL commands to verify your Intune setup before using the node:
-
This first command retrieves the access token needed by the Intune node.
-
Sample cURL request:
curl \ --location 'https://login.microsoftonline.com/tenant ID/oauth2/v2.0/token' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode 'client_id=application client ID' \ --data-urlencode 'client_secret=client secret' \ --data-urlencode 'scope=https://graph.microsoft.com/.default' \ --data-urlencode 'grant_type=password' \ --data-urlencode 'username=Azure admin username' \ --data-urlencode 'password=Azure admin pwd'
-
Sample response:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "scope": "profile openid email https://graph.microsoft.com/DeviceManagementManagedDevices.Read.All https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read https://graph.microsoft.com/.default", "expires_in": 3971, "ext_expires_in": 3971, "access_token": "This will be the jwt token used to retrieve the device info cURL" }
-
-
This second command retrieves the device info:
-
Sample cURL request:
curl \ --location 'https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/deviceManagement/manageddevices/Intune device ID' \ --header 'Authorization: Bearer This is the jwt token returned by the cURL command above'
-
Sample response:
{ "@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/$metadata#deviceManagement/managedDevices/$entity", "id": "f61dc341-c9c9-40c1-abbd-6997016f4c9e", "userId": "0f7e78ba-6e1f-485b-8b8b-fb86895f0498", "deviceName": "WINDEV2404EVAL", "managedDeviceOwnerType": "company", "enrolledDateTime": "2024-05-15T14:13:19.376941Z", "lastSyncDateTime": "2024-05-16T03:45:42.4309247Z", "operatingSystem": "Windows", "complianceState": "compliant", "jailBroken": "Unknown", "managementAgent": "mdm", "osVersion": "10.0.22621.3447", "easActivated": true, "easDeviceId": "24783A3196BAFE89291A012E4B607591", "easActivationDateTime": "2024-05-15T14:25:40.632661Z", "azureADRegistered": true, "deviceEnrollmentType": "windowsAzureADJoin", "activationLockBypassCode": null, "emailAddress": "", "azureADDeviceId": "e7f59723-3b4c-4783-89bf-9e42d492f4ac", "deviceRegistrationState": "registered", "deviceCategoryDisplayName": "", "isSupervised": false, "exchangeLastSuccessfulSyncDateTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z", "exchangeAccessState": "none", "exchangeAccessStateReason": "none", "remoteAssistanceSessionUrl": "", "remoteAssistanceSessionErrorDetails": "", "isEncrypted": false, "userPrincipalName": "", "model": "VirtualBox", "manufacturer": "innotek GmbH", "imei": null, "complianceGracePeriodExpirationDateTime": "9999-12-31T23:59:59.9999999Z", "serialNumber": "0", "phoneNumber": null, "androidSecurityPatchLevel": null, "userDisplayName": "acarter", "configurationManagerClientEnabledFeatures": null, "wiFiMacAddress": null, "deviceHealthAttestationState": null, "subscriberCarrier": "", "meid": null, "totalStorageSpaceInBytes": 133661982720, "freeStorageSpaceInBytes": 74671194112, "managedDeviceName": "acarter_Windows_5/15/2024_2:13 PM", "partnerReportedThreatState": "unknown", "requireUserEnrollmentApproval": null, "managementCertificateExpirationDate": "2025-05-15T03:56:04Z", "iccid": "", "udid": "", "notes": null, "ethernetMacAddress": "08002732B5A2", "physicalMemoryInBytes": 0, "enrollmentProfileName": "", "deviceActionResults": [] }
-
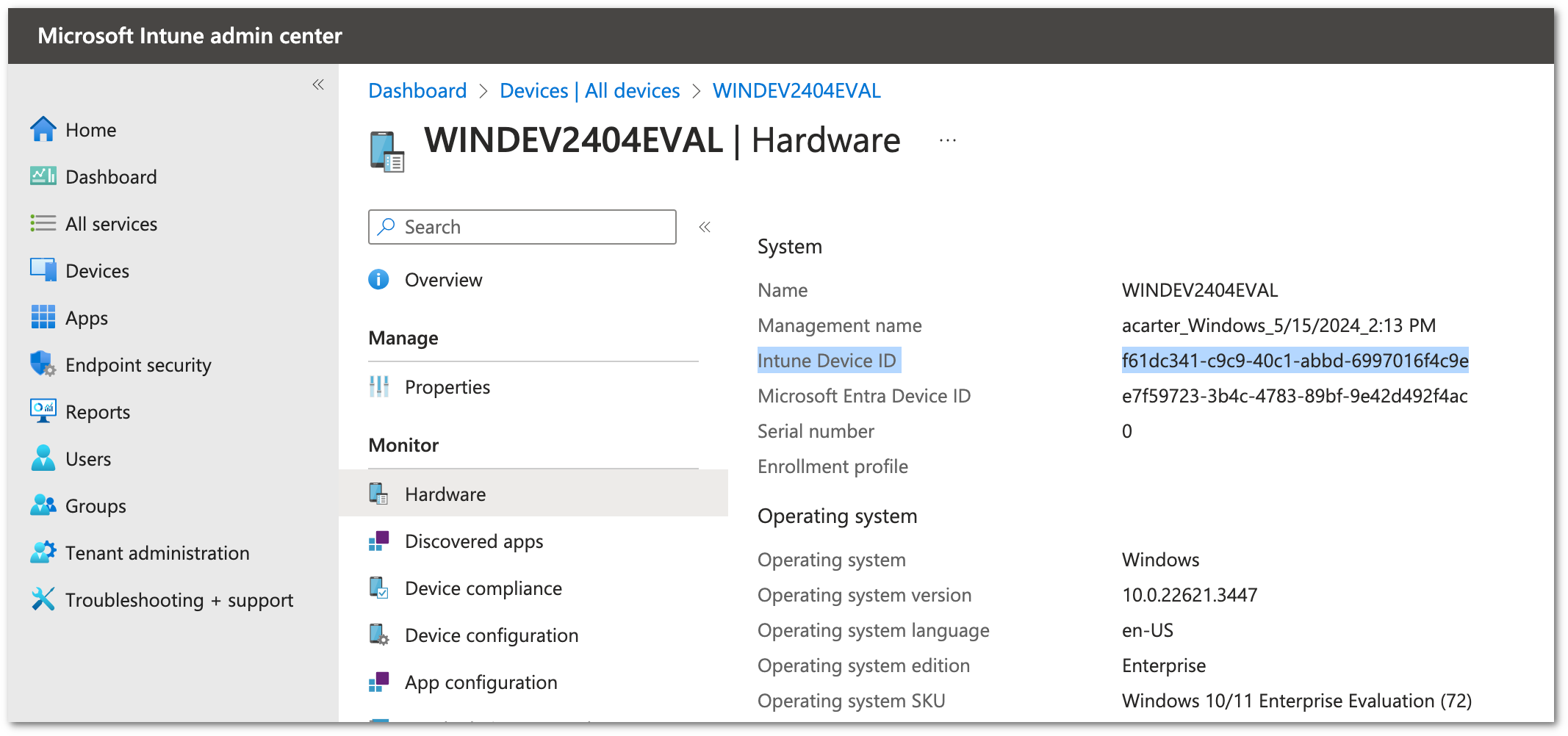
Ensure you are using the correct device ID when performing the verification tests. You can retrieve the Intune device ID from the Hardware section:
Configuration
The configurable properties for this node are:
| Property | Usage |
|---|---|
DeviceID Attribute Name |
Name of the header or shared state variable for storing the deviceID value.
The value is the |
DeviceID in SharedState |
Boolean.
Default: The DeviceID in SharedState toggle is used to determine where to look for the device ID value. If the DeviceID in SharedState toggle is enabled, the device ID is available in the shared state, and if it’s disabled, the device ID is in the header. |
Tenant ID |
Tenant’s global unique identifier (GUID) in Azure Active Directory (AD). |
Application (client) ID |
The application ID or client ID is a value the Microsoft identity platform assigns to your application when you register it in Azure AD. |
Client Secret |
Sometimes called an application password, a client secret is a string value your application can use in place of a certificate to identify itself. |
Azure Admin User Name |
The administrative username in Azure. |
Azure Admin User Password |
The administrative password in Azure. |
Save Device Properties to SharedState |
If enabled, the device information is saved to the shared state with
Refer to the Properties table in Microsoft Intune documentation for the managed device properties. |
Save installed apps to SharedState |
If enabled, the apps installed on the Mobile Device are extracted and saved to
the Shared State with the key name - |
Outputs
-
If
Save Device Properties to SharedStateis enabled, the device property available in Microsoft Intune service is stored on the shared state. -
If
Save installed apps to ShatedStateis enabled, the details of application installed on the device are stored on the shared state.
Outcomes
Compliant-
The device is compliant.
Not Compliant-
The device does not comply with the policy.
In Grace Period-
The device is not-compliant, but it’s in the grace period defined by the administrator.
Config Manager-
The device is managed by Microsoft Intune’s Configuration Manager.
Conflict-
Multiple settings are applied to the same device and Intune can’t sort out the conflict. An administrator should review.
No Id-
No device ID is found in the header or shared state.
Status Unknown-
The device is offline or failed to communicate with Intune or Azure AD.
Error-
An error occurred within the node. Related stacktrace and message are placed in the shared state.
For more information, refer to the Microsoft Graph API documentation on Compliance State.
Errors
Review the log messages to find the reason for the error and address the issue appropriately.
Examples
An example journey using the Microsoft Intune node:
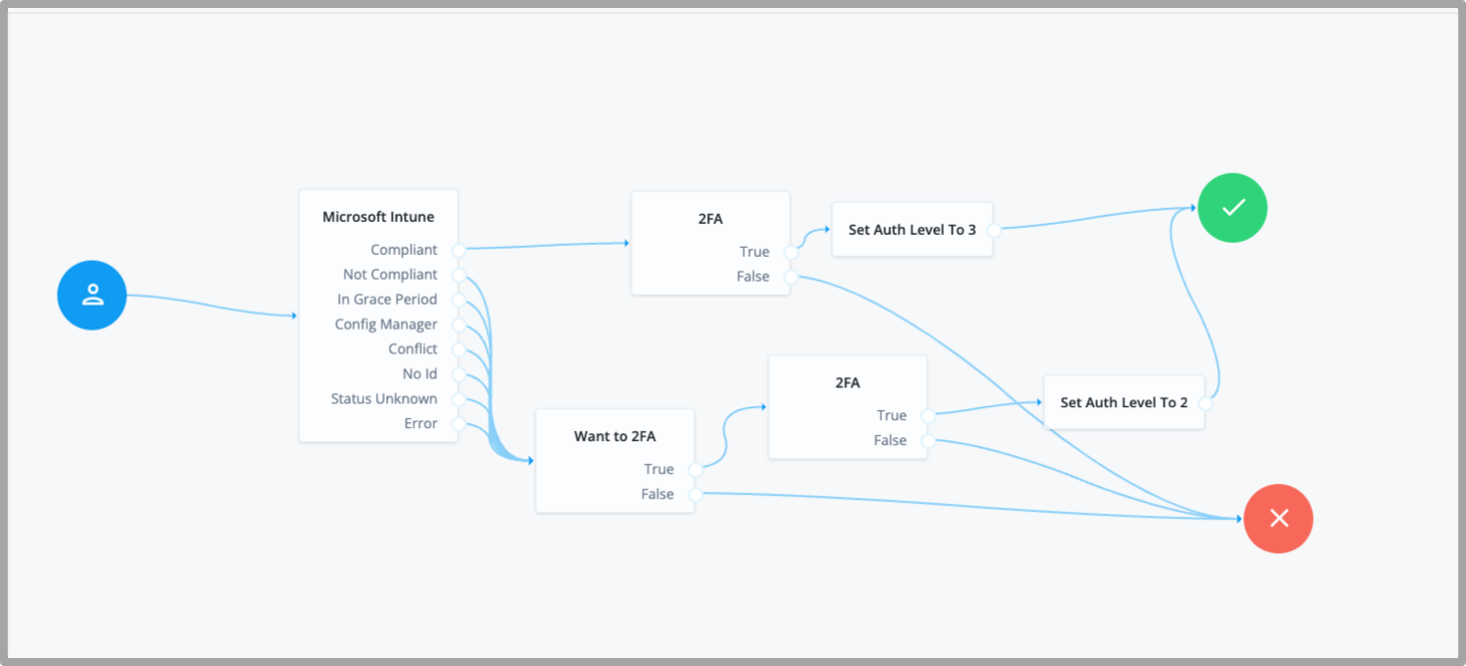
In this sample journey, the Microsoft Intune node is invoked to verify if
the client device is compliant. If the device is found compliant, a two-factor
authentication node is invoked to authenticate the user.
Upon successful authentication, the user is set to higher authentication level.
If the device is not found compliant, the user is still given an option to go
through a two-factor authentication node. In this case, the authenticated user
is set to a lower authentication level.