Custom endpoints
You can use custom endpoints to run arbitrary JavaScript code through the REST API. Custom endpoint scripts are extremely flexible and can extend Advanced Identity Cloud behavior in many ways:
-
Validate user input fields before storing them in a user profile.
-
Create utility functions, such as getting today’s date.
-
Mandate user input fields during registration to support delegated administration decisions.
-
Query identities with a particular relationship, such as being a member of an organization, and page the results.
You can consume custom endpoints within Advanced Identity Cloud or integrate them into your external UIs or system applications.
Custom endpoints scripting introduction
For an introduction to custom endpoints scripting, read the following:
To understand how to create identity object query expressions to use in the request.queryExpression property, learn more in Define and call data queries.
|
|
Scripts can potentially emit the personally identifiable information (PII) of your end users into Advanced Identity Cloud logs, and then into external services that consume Advanced Identity Cloud logs. Ping Identity recommends that you establish a review and testing process for all scripts to prevent PII leaking out of your Advanced Identity Cloud tenant environments. |
Manage custom endpoints
To manage your custom endpoints, go to Realm > Scripts > Custom Endpoints.
On the Custom Endpoints page, you can view a list of existing custom endpoints. To edit, duplicate, or delete a custom endpoint, click its More () menu.
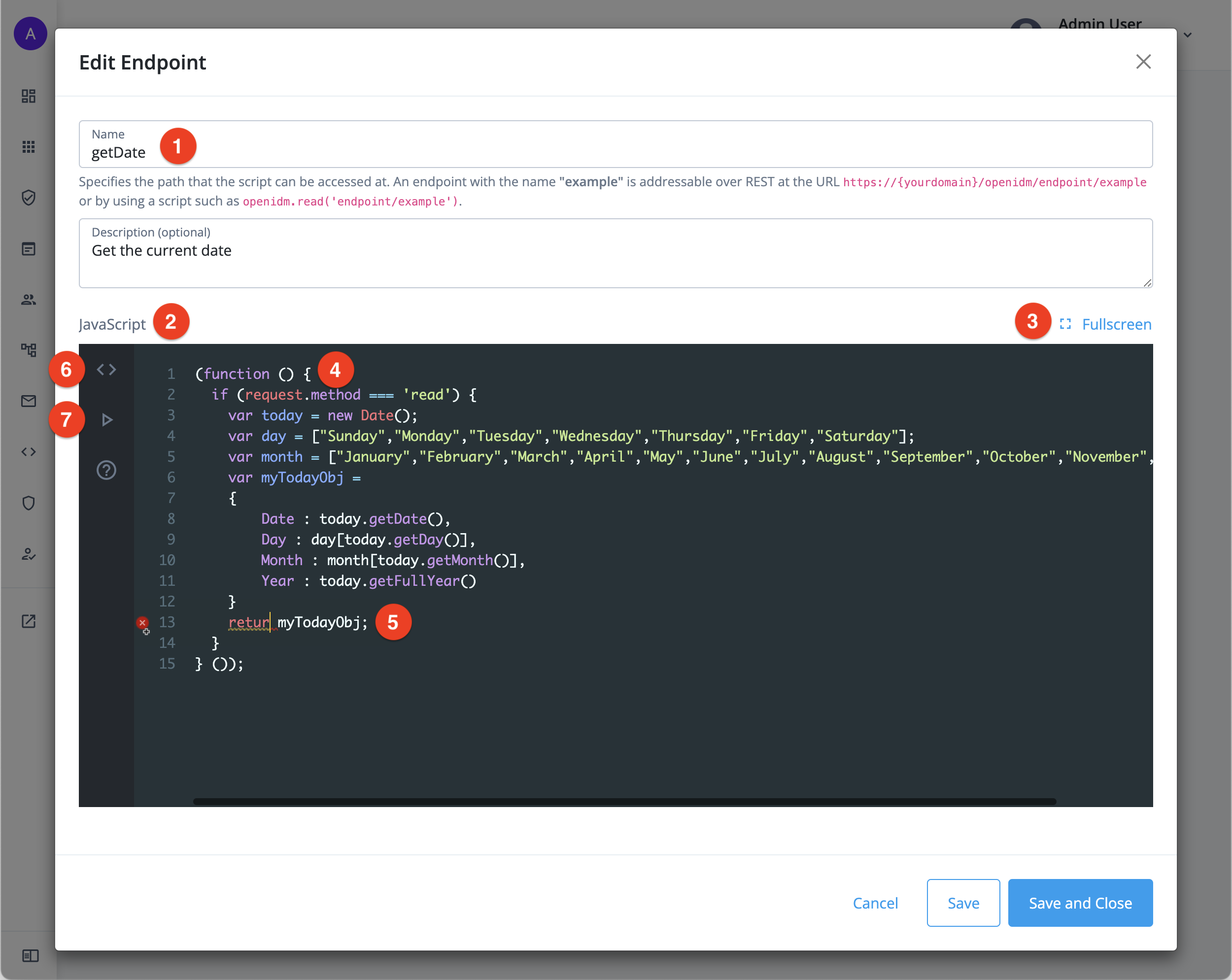
The edit option in the More menu opens the custom endpoint script in a lightweight editor. The editor features syntax highlighting and validation checking. Maximize the editor to full screen to edit larger scripts:
① Endpoint name
② JavaScript editor
③ Fullscreen option
④ Syntax highlighting
⑤ Validation checking
⑥ cURL request tab, learn more in Generate a cURL request for a custom endpoint
⑦ Test tab, learn more in Run a test request for a custom endpoint
Create a custom endpoint
-
Go to Realm > Scripts > Custom Endpoints, then click + New Script.
-
Enter a Name for your new endpoint; for example,
getDate.-
Access the new custom endpoint over HTTP at:
https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/openidm/endpoint/<name> -
Access the new custom endpoint in a script using:
openidm.read('endpoint/<name>')
-
-
(Optional) Enter a Description for your new endpoint; for example,
Get the current date. -
Next, use the editor to create your script. The editor is prepopulated with a default script, which is intended as a starting point for your custom script.
-
To test your script, click Save, then either:
-
When your testing is complete, click Save and Close.
Generate a cURL request for a custom endpoint
In the script editor:
-
Click the angled brackets icon (<>) to open the cURL Request tab.
-
In the Method field, choose an HTTP request method for the cURL request. Learn more about how HTTP request methods relate to the script
request.methodproperty values in this mapping table. -
(Optional) In the Body field, enter a JSON-formatted body for the cURL request (except when using the
GETHTTP request method). For example:{ "param1": "foo", "param2": "bar" }jsonIn the script, you can access the body using the request.contentproperty. The example above maps torequest.content.param1andrequest.content.param2. -
Click Generate to output the cURL request, which appears below your script. The cURL request is complete with an access bearer token and ready to run.
-
Click the copy icon () to copy the cURL request from the editor, then paste and run it in a terminal window.
Run a test request for a custom endpoint
In the script editor:
-
Click the triangle icon () to open the Test tab.
-
In the form field, enter a JSON-formatted configuration object for the cURL request. The form field is prepopulated with a default configuration object:
{ "request": { "method": "create" } }jsonThis default configuration object creates a request using the
POSTHTTP request method. Learn more about how HTTP request methods relate to the scriptrequest.methodvariable parameter values in this mapping table. -
(Optional) To supply a body with the request, add a
request.contentproperty:{ "request": { "method": "create", "content": { "param1": "foo", "param2": "bar" } } }jsonIn the script, you access the body using the request.contentproperty. The example above maps torequest.content.param1andrequest.content.param2. -
Click Run to run the cURL request. The result appears below the editor.